- The Strategic Impact of Supply Chain Automation
- Key Supply Chain Automation Benefits
- Measurement and Impact Assessment of Supply Chain Automation
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Technologies Powering Modern Supply Chain Automation
- Types of Supply Chain Automation
- Real-World Use Cases of Supply Chain Automation
- Strategies for Implementing Supply Chain Automation
- Challenges in Supply Chain Automation
- How Appinventiv Empowers Enterprise Supply Chain Automation?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key takeaways:
- Supply chain automation is no longer a buzzword. It’s something companies are actually using to simplify messy, day-to-day operations.
- Many global enterprises are already noticing the difference — fewer errors, quicker turnarounds, and better coordination between teams and partners.
- Tools like AI, IoT, and RPA now do the behind-the-scenes work once handled manually, from tracking inventory to predicting shortages.
- The market for industrial automation is growing fast and could cross about $378.57 billion by 2031, which says a lot about where businesses are heading.
You’re well aware that global supply chains face enormous pressure, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic, to get smarter and faster. Automation in supply chains has shot up the priority list for enterprise leaders chasing control, visibility, and reliability in markets constantly hit by disruption. Each demand shift now means real money on the line.
This means you need to deliver faster, slash costs, and stay compliant, all while you can’t see clearly across systems. Automation has gone from being a tech upgrade to something you actually need to survive. It’s not about cutting people out. It’s about letting your teams make faster, better calls with data that’s actually connected.
Supply chain automation taps into AI, IoT, and RPA to clear out manual slowdowns, spot risks coming, and keep things accurate through the value chain. Procurement to final delivery, every choice gets backed by data you can track. The big change isn’t just the tech. It’s how companies run things with real speed and precision now.
For enterprises after more than small wins, supply chain management automation is what stands between just surviving and actually growing long-term. Let’s see how smart organizations tap into automation to rebuild their supply chains, boost how predictable things are, and build up real resilience.
It’s time to see what these numbers can mean for your business.
The Strategic Impact of Supply Chain Automation
Those days of stable demand and straightforward supply cycles? They’re gone. Now every market shock, shipping delay, or supplier hiccup tests how fast your systems can bounce back and adjust.
That’s why automation in the supply chain isn’t just another tech upgrade anymore. It’s a strategic call that decides how resilient and responsive your enterprise actually is. When you automate systems, you shift from reacting to problems to stopping them before they start. Your teams quit firefighting and get back to planning what’s next.
A recent Gartner report showed that 34% of supply chain leaders see adapting to new technology as the biggest strategic shift they need to make. This tells us priorities are changing, moving away from manual control toward digital continuity.
Automation hands you speed and the ability to see what’s coming. With connected data and predictive models, you spot delays before they mess up production. It lets you juggle costs, capacity, and what customers expect without sacrificing compliance or getting things wrong.
Here is a quick overview of the impact of automation on the supply chain:

ROI Snapshot
| Metric | Automation Impact |
|---|---|
| Operating Costs | Down 30% from less manual processing and smarter resource planning |
| Forecast Accuracy | Up 35% with predictive analytics and decisions backed by data |
| Logistics Throughput | Up 20% by automating routing, scheduling, and order tracking |
These numbers aren’t just simple predictions. They’re what global enterprises are pulling off right now through smart supply chain management automation strategies.
For leadership teams, here’s the bottom line: automation isn’t about speed alone. It’s about building supply chains that can think, adjust, and recover without constant hand-holding.
Enterprise leaders are also discovering how digital transformation in supply chain management creates end-to-end visibility and real-time decision-making capabilities that manual systems simply cannot match.
With the impact of supply chain automation in mind, let’s now learn a little about its benefits.
Key Supply Chain Automation Benefits
With global operations expanding, manual systems fall short. Supply chain automation streamlines processes, cuts costs, improves compliance, and enhances forecasting, giving businesses better control and real-time visibility to adapt quickly to market changes.
Here are some key supply chain automation benefits:
Faster Workflows
Automation wipes out tedious manual work and puts in smooth digital processes instead. Approvals go quicker, lead times get shorter, and orders get fulfilled faster. Your teams quit wasting hours on repetitive tasks and can focus on strategic problems worth solving.
Lower Costs
Automation slashes errors, rework, and delays that balloon your operating spend. AI handles planning and forecasting demand, so you balance inventory and logistics capacity way better, cutting waste throughout the value chain.
Better Visibility
Automated systems gather every data point from suppliers, right through last-mile delivery into one view. If you have technologies like computer vision in logistics and supply chain, then you can enable real-time visual tracking along with automated quality inspections. Real-time dashboards also show you bottlenecks early so you fix them before customers notice or margins take a hit.
Stronger Compliance
Automation keeps transactions, documents, and processes following internal rules and regulatory standards. Audits get easier, reporting gets more accurate, and you face way less compliance risk.
Scalable Operations
Automated workflows expand into new markets or facilities without making you rebuild everything. Flexibility like this keeps your supply chain matching business goals even when volumes and regions jump.
Sustainable Growth
Automated route planning and smarter resource use drop energy consumption and emissions. You hit sustainability targets and cut costs tied to fuel and waste at the same time.
As you just learned, there are numerous reasons to automating your supply chain; now let’s learn how you can measure the assessment of supply chain automation.
Measurement and Impact Assessment of Supply Chain Automation
When dealing with supply chain automation, jumping straight into tools and systems without a plan? Bad move. You need ways to measure whether it’s actually doing anything useful. Define performance metrics right at the start. Otherwise, you’re stuck with an expensive solution that doesn’t quite deliver what you need.
Here’s what deserves attention:
- Delivery Speed: Automation should make everything move faster. Check how much quicker you fulfill orders, ship products, and send invoices out. When automation’s working right, those numbers increase—your team shouldn’t be sitting around waiting; things should just happen.
- Agility: One of automation’s biggest advantages? Being able to pivot quickly. Real-time insights show you when a delivery gets delayed or demand suddenly jumps. It’s about acting fast without everyone scrambling around, confused.
- Cash Flow: Cash flow keeps any business alive, right? Automation helps here, whether it’s speeding up invoicing or making payments more predictable. Track whether the new system gets money flowing in and out quicker with fewer problems popping up.
- Data Management: Handling data manually is honestly a mess. AI Powered data visualization cleans up that whole situation. Once everything’s connected, analyzing data becomes way easier, and predictions get more accurate. This means making smarter decisions using reliable data instead of just guessing.
- Decision-Making: Every decision should be backed by data, not gut instinct alone. Automated systems give you real-time access to that data—sales figures, inventory levels, delivery status, whatever you need. This leads to better-informed decisions, quicker responses, and way fewer mistakes happening.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Now that you know what to track, KPIs keep everyone on the same page. These numbers tell you whether your automation strategy actually pays off or not. Don’t just guess—track these to get actionable feedback and keep refining everything.
- Operational Efficiency KPIs
- Order Fulfillment Cycle Time: This KPI indicates the total time elapsed from the placement of the order until receiving it by the customer. The shorter the cycle time, the better!
- Inventory Turnover Rate: To put it in simpler terms, it is the rate at which you are turning your inventory into sales and buying new stock. It tells whether you are keeping your stock levels under control.
- Throughput: This shows the number of units processed in a specific period, thus giving you a clear picture of your system efficiency.
- Lead Time Reduction: Speed is the main advantage of automation. This KPI measures how much your procure, produce, and delivery cycles have become faster since the installation of automation.
- Cost-Associated KPIs
- Operational Costs: One of the major reasons for automating is to cut down on labor, transport, and storage costs, so automatic processes should lead to lower operational costs.
- Cost per Order: This calculates the average cost per order for processing and delivery. The lower this cost, the better.
- Inventory Holding Costs: Inventory management is when you do not have excessive stock. The KPI reflects the cost savings that you get from more efficient inventory management.
- Accuracy & Quality KPIs
- Order Accuracy Rate: One of the most vital KPIs—one that tracks how many orders are accurately fulfilled at the first attempt. No one likes to deal with mistakes!
- Inventory Accuracy: A company needs to have a clear understanding of physical stock vs. stock that has been recorded. This particular metric is meant to address discrepancies.
- Defect Rate / Returns: The fewer defects or returns, the more advantageous the situation. Automation will contribute to keeping the rate low by implementing better quality control at the production stage.
- Customer-Facing KPIs
- On-Time Delivery Rate: Deliveries made on time are the key factor for customer satisfaction. This KPI keeps track of what percentage of your orders are delivered by the promised date.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): What is the degree of happiness of your clients after they receive their chosen products? Keeping a watch on this gives you the service quality direct feedback.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): This is a customer loyalty matter. Is it your customers that are going to spread the word about your products and services to others? The score is an indicator of how much right things you are doing in your company.
- Automation-Specific KPIs
- Robot/Automation Utilization Rate: What actual portion of the time are your automated processes doing their job? Your aim is full power running.
- Process Cycle Efficiency (PCE): This tells you how much of your process time is really worth it in terms of adding value. The more you are able to say “yes,” the better it is.
- Automated System Downtime: This one measures the time when your automated systems are not operational. Downtimes cut off consistency.
- Supply Chain Visibility KPIs
- Real-Time Inventory Visibility: Is your stock status accessible in real-time, no matter its location? This KPI is an evaluation of your inventory reporting’s precision and promptness.
- Supply Chain Event Detection: When a problem arises, how quickly can you spot it and take action? The earlier you respond, the less impact it has on your business.
- Supplier Lead Time Variance: How trustworthy are your suppliers regarding timely deliveries? It keeps track of fluctuations in supplier delivery times and helps you with scheduling.
Measuring these KPIs and focusing on real-time insights gives you a clear picture of where automation actually brings value. Continuous optimization is what keeps everything working together properly and driving better results as time goes on.
Technologies Powering Modern Supply Chain Automation
Automation really clicks when you’ve got several technologies working in sync to bring scale, clarity, and consistency to supply chain ops. Each one solves a specific headache, like nailing forecasts or controlling warehouse chaos, and when you put them all together, they create the backbone of a network that actually responds.
Here’s what’s driving the future of supply chain automation today:
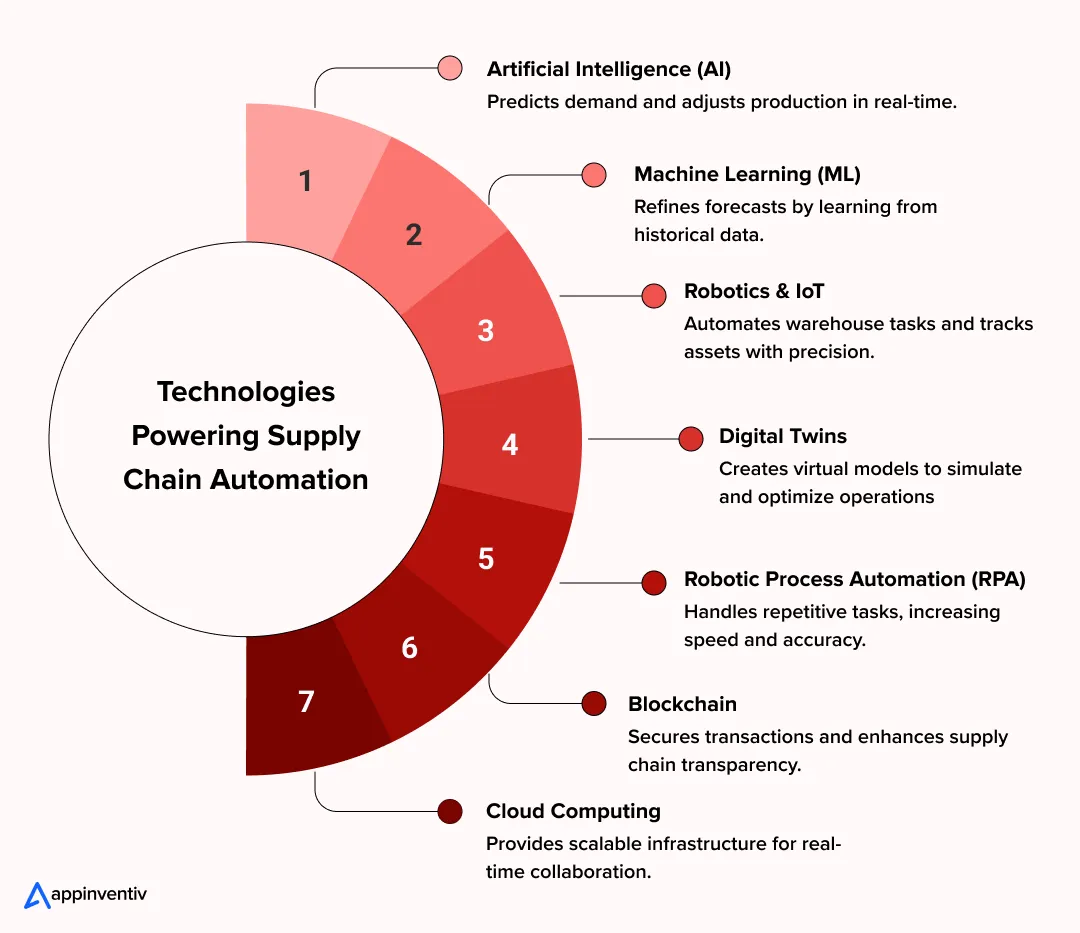
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) runs predictive analytics that let you spot demand shifts before they happen and adjust your procurement or production to match. It also tweaks pricing on the fly and flags risks by analyzing supplier and market data in real time. Leading companies are also using AI in supply chain analytics to turn raw data into actionable insights.
2. Machine Learning (ML)
Retailers and manufacturers use machine learning in retail and production environments to optimize inventory levels, personalize customer experiences, and predict demand with unprecedented accuracy. They improve forecasts, flag issues that keep popping up, and suggest what to do next without anyone having to manually figure it out.
3. Robotics & IoT
Smart warehouses today use connected robots, sensors, and scanners, which are powered by IoT in robotics. They use them to manage how goods move, checking storage conditions, and keeping tabs on assets. Human error drops while you can trace everything better across your supply chain.
4. Digital Twins
Digital twins in manufacturing or logistics make a virtual version of your supply network. You test “what-if” scenarios, predict equipment breakdowns, and make better investment choices before actually doing anything in real operations.
5. RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
RPA development enable enterprises to automate boring repetitive work like entering orders, matching invoices, and reconciling data, with accuracy going up while your people can focus on tasks needing actual thinking and oversight. Accuracy goes up while your people can focus on tasks needing actual thinking and oversight.
6. Blockchain
Blockchain in supply chain builds trust between supplier networks by keeping secure, see-through records of transactions. You can trace materials, check where stuff came from, and stop anyone messing with data when multiple parties are in the mix.
7. Cloud Computing
Cloud solutions for logistics make your infrastructure flexible and able to scale up. They link teams, partners, and vendors across regions so everyone’s got unified visibility and can collaborate faster on shared data.
8. Agentic AI
Agentic AI is intended to be an autonomous entity in intricate environments, making real-time choices and optimizing procedures without human help. Agentic AI in manufacturing or supply chain automation can cover all aspects from controlling stock to predicting customer needs, even to the point of changing supply paths and reallocating resources according to the fluctuations in the environment.
These aren’t futuristic technologies. Leading enterprises use them today. Stack them together and you’ve got systems that learn, adjust themselves, and keep performing consistently without someone always watching over them.
Types of Supply Chain Automation
Once you understand the tech, seeing how automation operates across different supply chain layers makes more sense. Each type delivers efficiency differently, whether handling repetitive work or making predictive calls.
Here is a quick overview table of automation in supply chain management:
| Type | Focus Area | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Process Automation | Swaps out repetitive, rule-based manual tasks to save time and reduce mistakes | RPA handling invoicing, creating purchase orders, and checking data |
| Physical Automation | Deploys robotics and IoT, managing physical movement and warehouse work | Automated systems for picking, packing, and moving materials around |
| Cognitive Automation | Taps AI, ML, and analytics for better decision-making | Planning demand predictively, spotting anomalies |
These three layers typically mesh together, creating a connected, intelligent automation that fixes its own problems. This is the future of supply chain automation solutions. Together, they let enterprises operate fast, accurately, and confidently, regardless of how tangled the network becomes.
Now that you are familiar with the different types of supply chain automation that exists, let’s check out a few real-world examples.
Real-World Use Cases of Supply Chain Automation
Automation is picking up at a serious rate globally. In fact, the Industrial Automation and Control Systems Market looks set to reach $378.57 billion by 2030, growing at a 10.8% CAGR from 2024. For enterprise leaders, this kind of growth says one thing: automation isn’t something you invest in for later. It’s creating operational value now.
Organizations all want proof of real outcomes, not theories about what might work. Supply chain automation’s impact gets pretty obvious once you look at how top enterprises actually apply it to sharpen precision, speed things up, and build resilience across operations.
- Warehouse Automation using Robotics
The Use Case: Warehouse automation to handle repetitive tasks like picking, packing, and inventory tracking.
The Context: Warehouse processes get manual and sluggish as the company grows— more orders, more SKUs, more chance of human mistakes.
Example: Amazon
Amazon also faced exactly that challenge. As the company grew, its fulfillment centers had to shift millions of products daily with negligible error rates.
To solve this, Amazon released thousands of Kiva robots that now patrol aisles, moving items to human packers. AI then decides the most efficient path and order for these robots.
The Outcome: The shift reduced picking errors, boosted fulfillment speed, and allowed Amazon to offer same-day or next-day delivery at scale — all while minimizing labor fatigue and congestion within warehouses.
- Predictive Analytics for Demand Forecasting
The Use Case: Using AI to predict what the customers will need even before they place an order.
The Context: Supply chains across the world are taken down by demand fluctuations. Too much inventory tied up sucks up capital; too little and shelves remain bare.
Example: Unilever
Unilever had once to deal with demand imbalances between markets — one region in shortage while the other was sitting on excess inventory.
They implemented AI-driven predictive analytics that delve deep into sales history, seasonality, promotions, and even weather patterns to predict demand.
The Result: By using predictive analytics in supply chain, Unilever’s forecast accuracy was enhanced. It eliminated excess inventory and stockouts. The business now dynamically moves inventory, acting more quickly to market changes while maintaining costs under control.
- Intelligent Logistics Optimization with Io
The Use Case: Using IoT sensors and networked devices to track shipments and control delivery routes in real-time.
The Context: Traditional route planning is not adjusted for real-world disruptions like traffic, weather, or downtime.
Example: DHL
DHL used IoT-powered fleet management to track all vehicle performance and locations in real time. The system now automatically recalculates optimal routes as conditions vary.
The Outcome: The firm reduced average delivery times, fuel usage, and on-time delivery performance. It became a success for operations and sustainability alike.
- Blockchain for Supplier Transparency
The Use Case: Building trust and visibility across supplier networks with blockchain.
The Context: Global supply chains depend on many suppliers. Without visibility, it’s hard to ensure product authenticity or spot inefficiencies early.
Example: Toyota
Toyota wrestled with rising complexity in managing hundreds of global suppliers. Counterfeit parts and delayed shipments were constant threats.
With blockchain technology adoption, Toyota set up a safe digital ledger for all components of its supply chain. Each transaction — from supplier to production floor — is recorded safely and immediately traceable.
The Result: Supplier transparency rose dramatically, counterfeit risks decreased, and Toyota strengthened compliance with global safety standards.
- Automation of Procurement through RPA
The Use Case: Automating time-consuming procurement processes like the generation of purchase orders, matching of invoices, and supplier communications.
The Context: In large organizations, procurement involves thousands of transactions on a daily basis. Inefficiencies, however minor they may be, can amount to millions of dollars in losses annually.
Example: Siemens
Siemens’ purchasing departments were bogged down by paperwork and manual data entry, which was hindering the process.
The company used Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to robotize repetitive processes — from verifying purchase orders to sending supplier reminders.
The Outcome: Manual effort was reduced, procurement cycles were shortened, and paperwork errors practically disappeared. The freed team is now dedicated to supplier strategy instead of clerical tasks.
- Digital Twin-based Manufacturing Optimization
The Use Case: Virtually replicating production lines to detect inefficiencies and predict machine breakdown before it happens.
The Context: Traditional manufacturing relies on planned maintenance — something that can prove costly if something goes awry at an unexpected time.
Example: Bosch
Bosch was the first to use digital twins — virtual replicas of its production lines that mimic all the actual processes.
With this, engineers were able to model “what-if” situations, identify performance bottlenecks, and predict when machines would likely fail.
The Outcome: Production efficiency rose, unplanned downtime fell, and Bosch was able to plan maintenance in advance instead of retrospectively.
- Automated Replenishment Systems
The Use: Automatically replenishing stock with exactly the correct quantity without needing human intervention.
The Problem: It is common for retailers to lose sales due to stockouts or spend unnecessary amounts of money overstocking. Achieving the ideal balance manually in volume is virtually unthinkable.
Example: Walmart
Walmart’s challenge was managing millions of SKUs in thousands of stores — something that could not be managed by human operators in real time.
Their automatic replenishment solution now tracks movement activity and sales in real-time. When it gets to a certain level of stock, it reorders automatically.
The Result: Stockouts fell, overstocking lessened, and overall product availability improved — resulting in happier customers and more efficient operations.
What these supply chain automation use cases show is how automation converts your data and systems into measurable performance gains. It could be tighter accuracy, faster deliveries, or just lower operating costs.
With these examples now sorted, let’s learn a bit about what you need to follow in order to implement supply chain automation.
Strategies for Implementing Supply Chain Automation
Building a connected and intelligent supply chain? You need strategy first, not technology. Don’t invest in tools yet. Create a roadmap connecting your automation goals with how operations actually work today. The right approach transforms complex, fragmented processes into one integrated system backing growth and resilience.
Here is a step-by-step guide to automating supply chain processes:
Step 1: Audit & Identify High-Impact Areas
Start by mapping what your teams do manually right now. Where do tasks repeat constantly? Which work depends heavily on timing? Where do errors keep showing up? These spots deliver the most value when automated. Check procurement first, then logistics, then how you handle inventory.
Step 2: Proof of Concept (PoC) & Pilot Runs
Scaling automation across everything without proof? That’s risky. Run a pilot first. Prove it helps your business. Track improvements you can measure: cycle times dropping, processes becoming more accurate, errors vanishing.
Step 3: Define ROI Metrics & KPIs
What does success look like for you? Decide this before you begin. Track clear wins: money saved, speed of completion, order accuracy, system reliability. Leadership won’t expand without numbers proving value.
Step 4: Build Scalable, Cloud-Native Infrastructure
Link your automation tools with AI, IoT, and ERP platforms already running. Use a secure cloud infrastructure for everything. Data flows smoothly this way. Departments collaborate with vendors as things happen rather than reacting hours behind.
Step 5: Change Management & Training
Your automation fails if people won’t use it. Bring teams in from the start. Explain what they gain without corporate speak. Invest properly in training. Employees need confidence managing new digital processes.
Step 6: Compliance & Security by Design
Build GDPR, ISO 27001, NIST CSF, and APRA CPS 234 into your planning from day one. Handle security early. You’ll avoid regulatory disasters and reputation damage later.
Step 7: Continuous Optimization
Automation isn’t a one-time project. It’s an evolving system needing regular attention. Analytics dashboards show what’s working and what’s failing. Keep adjusting configurations. Performance improves over time.
Well, now you know what steps you need to take in order to implement supply chain automation in your organization. Let’s now learn about what challenges you might run into with automation.
Challenges in Supply Chain Automation
Adopting automation across large supply networks is rarely smooth sailing. The outcomes can be significant, sure, but getting there takes serious alignment across technology, your teams, and how you govern things.
Whether automation succeeds comes down to how you handle technical and organizational constraints together. For most enterprises, ambition isn’t what’s missing. It’s execution that trips them up.
Here are the key factors affecting the adoption of AI in supply chain management:
- Integration with Legacy and Hybrid Systems
Plenty of enterprises still run on aging ERP systems, never designed for real-time data sharing. Getting them connected with modern automation tools? That usually means custom interfaces or middleware sitting between systems.
Solution:
Instead of rebuilding your system entirely, you start by implementing middleware or API adapters. These are more like a bridge, enabling your data to move seamlessly from your current systems to your new automated systems. This gives you the benefits of automation without losing the reliability of your present infrastructure.
- Interoperability Issues Across Vendors
You’re managing multiple automation solutions across procurement, logistics, and production. This creates data flows that don’t talk to each other and leaves visibility gaps everywhere.
Solution:
For there to be easy communication between systems, have a central point where data resides. This can pull information from each of the suppliers’ systems and normalize it into one platform in the center that’s accessible. All, whether procurement, logistics, or manufacturing, will all be on the same page, with the latest, real-time data available to them.
- High Initial Investment and ROI Visibility
Automation needs upfront money spent on infrastructure and training. Without clearly defined performance benchmarks, proving ROI to your leadership gets messy and difficult.
Solution:
Start small with a pilot program. Select a single area in your supply chain, like inventory management, and pilot the automation tools there. Track the impact on efficiency, cycle time, and error rates so you have a good idea of the ROI. Then, having seen those results, it will be simpler to scale, and you will have a good idea of the benefits across the whole supply chain.
- Data Privacy and Governance Concerns
Automated systems process huge volumes of sensitive data constantly. Governance models that aren’t strong enough? They increase your exposure to compliance violations and cybersecurity risks.
Solution:
Prioritize security from the very start by including data encryption and access controls to protect sensitive information. Use regular audits to keep compliance with legislation like GDPR or CCPA. Real-time monitoring software that tracks who is touching data will have everything covered and make you feel assured that your automated processes are absolutely secure.
- Cultural Resistance and Skill Gaps
Internal resistance stays one of those quiet barriers nobody talks about enough. Teams frequently see automation as threatening their jobs rather than helping them, especially when training’s inadequate and change communication falls flat.
Solution:
Instead of focusing on what automation will displace, emphasize how it will set your staff free to do more critical work. Start with engaging your people early on. Provide hands-on training workshops and allow them space to ask questions and get to know new tools. The aim is to create a culture of collaboration, where automation supports your staff, not replaces them.
These challenges might seem a bit overwhelming, but once you get to work on automating your supply chain, you will see that there are ways around everything. However, if you think that you might need expert help, then the next section will let you know how Appinventiv can help you with every automation need.
Also Read: How Technology in Supply Chain can Surpass Challenges
How Appinventiv Empowers Enterprise Supply Chain Automation?
Automation kicks off with technology, but what actually creates lasting success? Its execution. Having the right partner makes all the difference.
Appinventiv helps enterprises leave fragmented systems behind and shift toward intelligent, integrated supply chains focused on growth, compliance, and resilience. With our supply chain services and expert RPA development services, we empower businesses to streamline operations and achieve measurable results.
Why Partner with Appinventiv for Supply Chain Automation?
- 1600+ Experts, 3000+ Enterprise Solutions Delivered: Our team spans different disciplines and has taken on global-scale projects across manufacturing, logistics, and retail operations.
- Proven Expertise in AI, RPA, IoT, Cloud, and Data Analytics: We offer complete automation capabilities that tie insights, operations, and outcomes together under one cohesive strategy.
- Certified for Global Standards: Engineering follows ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR certifications, meaning every project we deliver reaches enterprise-grade security and compliance standards.
- Deep Industry Experience: Years working across supply-heavy industries mean we design automation frameworks that reflect real complexities and what your business truly requires.
- Full-Cycle Delivery: We start with Audit, work through Development and Integration, and wrap up with Optimization—managing each phase with precision and keeping things transparent throughout.
When enterprises choose Appinventiv, they’re getting way more than technology. They’re gaining a strategic ally committed to measurable business impact through supply chain automation that scales with their growth.
Ready to build a resilient, automated, and compliant supply chain? Let’s craft your enterprise automation roadmap together. Trusted by 1000+ global enterprises | ISO-Certified Partner
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is supply chain automation?
A. Supply chain automation entails the use of technology to mechanize processes that were manually performed previously, including tracking inventory, processing orders, and managing logistics.
Getting the processes mechanized releases your employees from drudgery work, and they are only left with the opportunity to work on higher-level activities like strategy, planning, and problem-solving. You are left with a leaner and more efficient supply chain.
Q. How does automation improve supply chain efficiency?
A. Automation reduces supply chain friction by vast amounts. Automation eliminates delay due to handoffs between departments or groups, where information must be passed along or checked.
Computer systems allow faster movement of information, eliminating errors and typographical mistakes, and allowing everyone to have accurate information at the moment. This allows for faster decision-making and more effective operation in general.
Q. How does automation improve warehouse and inventory management?
A. Manual monitoring is time-consuming and prone to error, especially in larger warehouses. Through automation, accuracy is obtained through sensors, scanners, and networked devices tracking stock levels in real-time.
It gives you real-time perspectives of amounts of inventory, allows you to spot issues such as slow shipments, and allows you to maximize your stock without the need for ongoing manual surveillance. Lastly, automation enhances accuracy and saves valuable time.
Q. What is the role of AI in an automated supply chain?
A. AI supports supply chain automation by translating raw data into intelligence. AI stops past trends, tracks supplier performance, and predicts demand, enabling you to make decisions based on intelligence.
With AI, your systems will make adjustments automatically as they occur, say, when a change in demand or a supply outage occurs, so you can prevent problems upfront. This boosts reliability and reduces operational risk.
Q. What are the biggest challenges in implementing supply chain automation?
A. The largest issues most commonly aren’t technology, but people and processes. Getting older systems aligned with more current tools is difficult, and there will be pushback from employees who don’t want to be replaced or who can’t adapt to newer technology.
And then there are the costs of setup and the protection of the data to deal with. The fix is to start small with a pilot program, eliminate fear with proper training, and demonstrate clear, measurable benefits from the start.
Q. What are supply chain automation tools?
A. Supply chain automation software and technologies are eliminating routine tasks such as logistics, order processing, and inventory management. These automated processes eliminate errors, enhance speed, and make better decisions.
Combine technologies like machine learning, AI, RPA (Robotic Process Automation), and IoT to automate processes, reduce costs, and achieve improved insights into your supply chain, making it easier to make better, data-informed decisions.
Q. What are the current supply chain automation trends?
Nowadays, the biggest trends in supply chain automation are AI, machine learning, and IoT. They are enabling predictive analytics, so systems can analyze data to anticipate demand and optimize processes.
Automation is also becoming increasingly focused on sustainability, with companies using it to optimize routing of vehicles, reduce energy consumption, and satisfy new compliance regulations. These trends are shaping the supply chain management future by making systems intelligent and responsive.
Q. Can you share some supply chain automation examples in action?
A. Some of the leading business companies have already seen significant returns from automating. For example, Amazon employs robots to speed up and improve order fulfillment accuracy. Unilever employs artificial intelligence to improve demand forecasting, so they are always keeping the ideal stock levels.
Bosch, however, employs digital twins to simulate production lines and maximize efficiency. These concrete results validate how automation can save costs, improve operation performance, and facilitate informed decision-making.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Yard Management System Software Development: Enhancing Logistics and Supply Chain Efficiency
When unlocking greater efficiency in logistics and supply chains, the yard is often an underestimated area for investment and innovation, with many businesses still relying on traditional pen-and-paper methods. It creates conflict that eventually puts productivity at a standstill and delays operations. In the logistics and supply chain industry, time is money, and operational delay…

Leveraging Predictive Analytics to Optimize Supply Chain Performance: Benefits and Strategies
The global market disruption and sudden turbulence in the business world have brought to light many complexities and challenges in the supply chains. For instance, Global supply chain disruptions cost large companies an average of $182 million annually. Remote work, unexpected demand surges, and logistical complexities have intensified pressure on supply chains. Around 43% of…