- Why is Integrating AI into ERP Systems a Need of the Hour?
- The Top Benefits of AI in ERP Systems You Need to Know
- Real-Time Insights for Informed Decision-Making
- Automation of Routine Tasks
- Predictive Capabilities for Proactive Strategies
- Types of AI-Powered ERP Systems: Solutions for Businesses
- Cloud-Based AI-Powered ERP Systems
- On-premises AI ERP Systems
- Hybrid AI ERP Systems
- Industry-Specific AI ERP Systems
- Real-World Use Cases of AI in ERP Systems
- Digital Transformation and App Modernization
- Demand Forecasting and Spend Management
- Order and Supply Chain Management
- Predictive Maintenance
- Enhanced CRM Management
- Human Resources Management
- Automated Invoice Processing
- Purchasing Management
- Anomaly Detection
- Process Mining
- AI ERP Integration Process: In-Depth Guide
- Define Objectives and Scope
- Assess Data Readiness
- Select AI Use Cases and Technologies
- Design the Integration Architecture
- Develop and Train AI Models
- Deploy and Integrate AI Models
- Test and Validate the Integration
- Scale and Optimize
- Understanding the Cost of AI Integration in ERP Systems
- The Future of ERP with AI
- What Makes Appinventiv a Trusted Partner to Integrate AI into an ERP System?
- Deep Technical Proficiency in Artificial Intelligence ERP Integration/Development
- Industry Recognition and Thought Leadership
- Industry Accolades
- Ethical Practices and Client-Centric Approach
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- Market Growth: The global AI in ERP market is projected to reach USD 46.5 billion by 2033, highlighting its rapid growth trajectory.
- Automation: AI automates tasks like invoice processing and inventory management, cutting costs by up to 25% using RPA and OCR.
- Use Cases: AI enhances ERP systems with capabilities such as demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, CRM, HR, and anomaly detection.
- Integration Process: Effective AI-ERP integration requires clear objectives, data readiness, the right AI tools, and continuous optimization.
- Cost Range: Integration costs range from $40,000 for smaller implementations to over $1 million for enterprise solutions, plus ongoing maintenance.
The concept of AI implementation in ERP is no longer an eventual phenomenon; it is a revolutionary process that presents no obstacles to companies modernizing their existing legacy ERP systems.
Leading such a march is Campfire, a pioneer in AI-driven ERP solutions, which recently drew immense attention by raising $ 35 million in a Series A investment. This significant investment will help accelerate product development, enhance generative AI development capabilities, and drive international growth to meet the increasing needs of global enterprises.
Why is Integrating AI into ERP Systems a Need of the Hour?
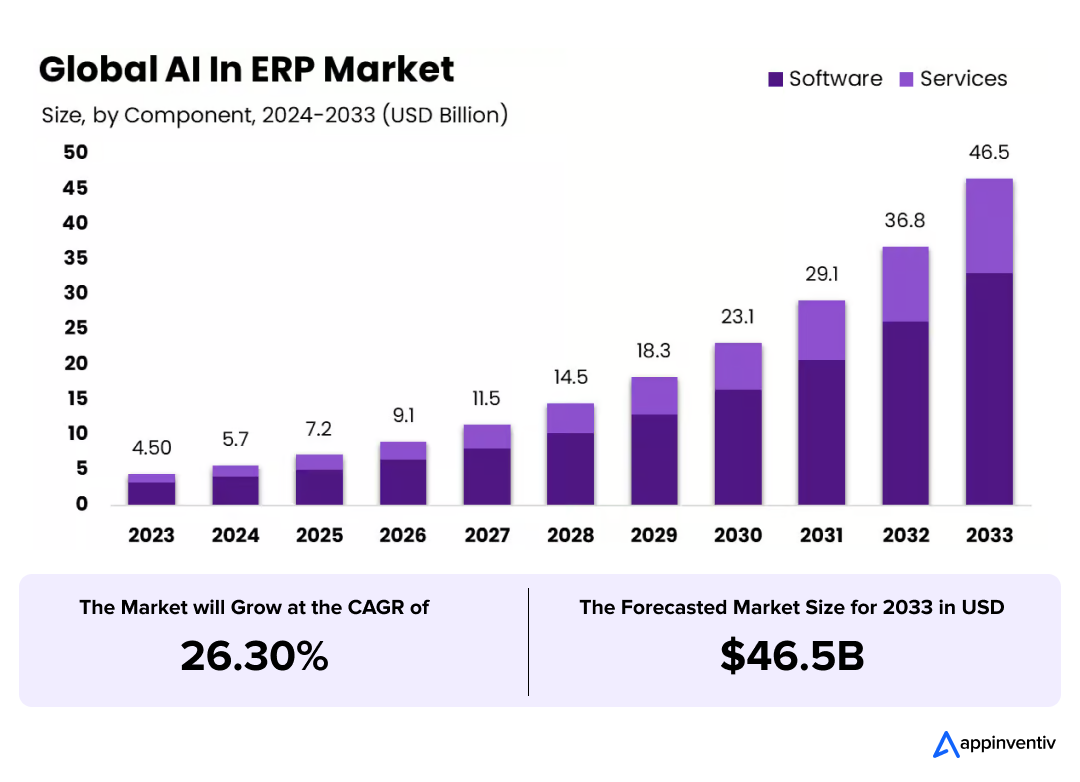
The Global AI in ERP Market is expected to be worth around USD 46.5 Billion By 2033, up from USD 4.5 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 26.30% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033. In 2023, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.4% share and holding USD 1.72 billion in revenue.
The journey ahead may be intimidating for organizations seeking to leverage the combined power of AI and ERP to automate routine processes and improve decision-making. If you’re unsure where to start or how to stage such innovations efficiently, this article will provide you with the information and knowledge to get started and navigate this revolution.
The AI in ERP market is skyrocketing to $46.5B by 2033 with a 26.3% CAGR. Automate, optimize, and dominate.
The Top Benefits of AI in ERP Systems You Need to Know
Intelligent ERP systems are the backbone of modern organizations, streamlining critical functions such as finance, supply chain, human resources, and customer relationship management. However, traditional ERP systems often face challenges like complex interfaces, siloed data, and reliance on manual processes.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into ERP systems addresses these pain points, transforming how businesses operate in the hyper-competitive global markets of 2025.

Real-Time Insights for Informed Decision-Making
AI empowers ERP systems to process massive datasets in real-time, delivering actionable insights that drive faster and more informed decisions. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical and live data from across the enterprise, identifying patterns and trends that humans might overlook.
That’s why businesses adopting AI-driven ERP solutions have experienced over a 30% increase in user satisfaction.
Mechanisms of AI in ERP Systems for Real-Time Insights
With the help of AI algorithms and data processing functions, ERP systems powered by machine intelligence transform raw enterprise data into actionable insights that can be applied to various business functions. Here’s how:
1. Data Ingestion and Processing
- Real-Time Data Stream: ERP integrates with IoT, APIs, and other external data sources, such as market, weather, or social media indicators, to capture live data in real-time. The technologies, including Apache Kafka or AWS Kinesis, enable low-latency, high-throughput data streaming.
- Data Lakes and Warehouses: AI-powered ERP systems leverage cloud-based data lakes, such as Snowflake and Databricks, to store and manage both structured and unstructured data, thereby enabling them to scale throughput and processing capabilities. It also ensures real-time cleaning, normalization, and enrichment of data through AI-optimized ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines.
- Edge Computing: This is particularly useful for time-sensitive applications in manufacturing IoT, where data is smartly processed locally to reduce latency through real-time insights provided by AI models deployed on edge devices.
Bonus Read: What is Edge Computing and Why It Matters to Enterprises?
2. Machine Learning and Analytics
- Supervised Learning: Smart machine learning algorithms, such as Random Forest or Gradient Boosting Machines like XGBoost, can be trained on archival ERP data, including sales, inventory, and financial information, and then used to make predictions for demand forecasting or identifying trends in cash flow.
- Unsupervised Learning: Clustering methods, including K-Means and DBSCAN, can help identify hidden patterns, such as customer segmentation or anomaly detection, during financial transactions.
- Deep Learning: Neural networks, particularly Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) or Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models, process time series data to predict disruptions and optimize resource allocation.
- Reinforcement Learning: Applied to dynamic decision-making problems, i.e., to optimize some production schedule or a logistics route based on feedback that arrives in real-time.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
The NLP models, such as BERT and GPT, scan the unstructured data available in an ERP system (e.g., customer feedback or contracts) and infer sentiment, intent, or compliance risks. An example: To prioritize high-risk escalations, the NLP applications for modern enterprises can potentially handle customer support ticket processing in real-time.
4. Real-Time Decision Engines
The ERP systems powered by AI leverage decision engines that integrate business rules with predictive models to provide recommendations. For example, the SAP HANA platform incorporates AI, enabling it to provide real-time recommendations for replenishing inventory based on market corrections and internal data.
Automation of Routine Tasks
AI automates repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as invoice processing, payroll management, and inventory tracking. By utilizing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in conjunction with AI, ERP systems can efficiently handle these tasks with minimal human intervention, thereby reducing errors and operational costs.
According to research by McKinsey, AI automation in ERP environments can reduce operating costs by up to 25%.
Advanced Mechanisms of AI-Driven Automation in ERP Systems
ERP with AI integration expands the role of robotic process automation (RPA) in ERP systems, enabling the anticipation of dynamically adapting intelligent task handling that is no longer based solely on rule scripting. The major mechanisms are:
- Smart Data Processing: AI utilizes optical character recognition (OCR) and natural language processing (NLP) to extract and organize data entered in unstructured applications, such as AI-powered documents, invoices, emails, or PDFs.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning (ML) models analyze past ERP data in real-time to predict what needs to be done, such as restocking inventory or adjusting payroll lines.
- Adaptive Workflow Automation: RPA bots equipped with AI learn to recognize exceptions, such as changes in data format or process, thereby minimizing the need for manual intervention. For example, with bots, no programming is required for invoice formats, as accuracy can improve by over 98%.
- Process Mining and Optimization: AI analyzes the logs of ERP processes, identifies exceptions, and optimizes them, resulting in a possible reduction in outstanding approval workflow times of 20-30%.
- Decision Automation: AI leverages rule-based and probabilistic models to facilitate the automation of decisions and reduce the need for human intervention, such as approving invoices with low value or classifying high-reward transactions with minimal input.
Predictive Capabilities for Proactive Strategies
AI’s predictive analytics enable ERP systems to forecast market trends, customer behavior, and operational risks. For instance, AI can predict demand fluctuations based on historical sales data, seasonal trends, and external factors like economic indicators. This allows businesses to optimize inventory, adjust pricing strategies, and mitigate risks before they escalate.
The McKinsey report indicates that predictive analytics in ERP systems can significantly improve demand forecasting accuracy by 30 to 50%.
Mechanisms of AI Predictive Capabilities in ERP Systems
An AI-powered ERP system leverages AI to harness the power of non-trivial algorithms, anticipating trends and enabling proactive decision-making. Key mechanisms include:
- Machine learning models: Machine learning algorithms include supervised learning (e.g., regression, time-series forecasting) and unsupervised learning (e.g., clustering), and analyze historical ERP data to predict outcomes such as demand, churn, or supply chain disruptions. For example, time-series models like ARIMA or LSTM forecast sales based on patterns in transactional data.
- Big Data Integration: AI combines both structured and unstructured data, e.g., an ERP (e.g., sales histories), with organizational-level data (e.g., social media sentiment, economic indicators) to predict more effectively. This helps with end-to-end forecasting, such as predicting changes in demand based on market sentiment.
- Real-Time Analytics: AI operates on the incoming streaming data from ERP modules (e.g., inventory or CRM) and provides runtime predictions. For example, it may compute the value of a stock using real-time sales increases.
- Anomaly Detection: AI identifies outliers in ERP data, such as unusual expense patterns or supplier delays, to minimize risks (e.g., flagging potential fraud with a 95% accuracy rate, according to industry standards).
- Scenario Modeling: AI simulates the situations to understand what is likely to occur based on several conditions (e.g., variations in pricing, disruption of supply chains), and then the business can simulate the strategies before undertaking them (in real life).
With the world’s markets becoming increasingly competitive, AI-driven ERP systems are no longer a luxury but a necessity. They enable organizations to optimize operations, reduce expenses, and remain competitive.
Bonus Read: AI Analytics for Businesses – Benefits, Use Cases, and Real Examples
Types of AI-Powered ERP Systems: Solutions for Businesses
An intelligent ERP artificial intelligence system enables the performance of business operations, the making of informed decisions, and the driving of business development. Such systems utilize machine learning, predictive analytics, and automation to streamline processes in all industries. Different types of ERP AI systems enhance capabilities and are leveraged across various business-specific applications.
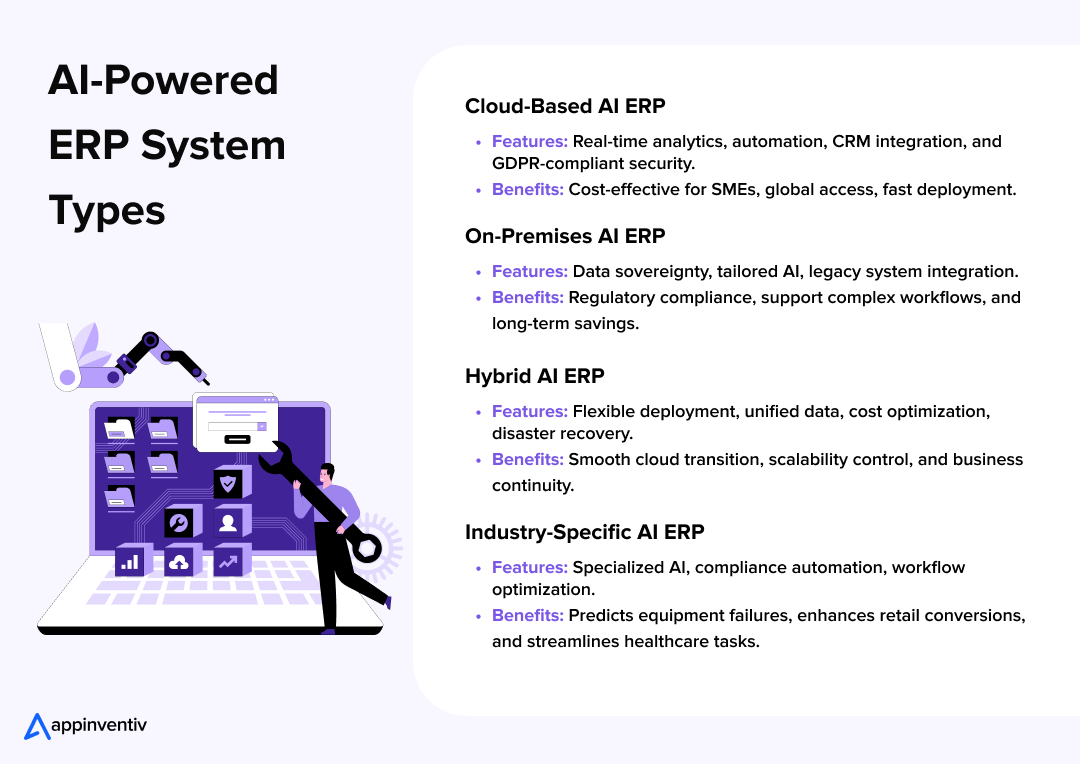
Cloud-Based AI-Powered ERP Systems
The cloud ERP AI systems are located on off-site servers, which are scalable, accessible, and provide real-time, up-to-date information. They minimize the upfront costs of infrastructure and seamlessly integrate with other cloud services, making them best suited for companies that prioritize agility and cost efficiency.
Key Features
- Real-Time Analytics: Dashboards based on AI will provide instant, real-time information on finances, supply chain, and customer trends, enabling proactive decision-making.
- Automation: Machine learning may perform basic processes such as invoice processing, demand prediction, and inventory management.
- Integration: A seamless cloud ERP integration exists between themselves and CRM, E-commerce, and IoT platforms to make up a coherent environment.
- Security: Data protection is ensured through advanced encryption and compliance with regulations, including GDPR and SOC 2.
Perks For Businesses
- Cost-Effective Approach: Small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can implement cloud ERP on a cost-effective scale.
- Global Accessibility: Multinational companies utilize live access to global information, enabling them to manage their global supply chain across international borders.
- Quick and Easy Deployment: The cloud ERP system can be set up in just a few weeks, compared to traditional systems that can take months, allowing businesses to adapt to market changes quickly.
Bonus Read: How can enterprises protect their data in cloud environments?
On-premises AI ERP Systems
On-premises ERP AI systems are deployed on company servers, providing the highest level of control over data, customization, and security. They are suitable when an organization has stringent regulatory requirements or a complex and proprietary workflow.
Key Features
- Data Sovereignty: 100% ownership of sensitive data, which is important to industries such as finance, healthcare, or the government.
- Customization: AI models can be highly customized to fit a specific business process, such as a bank, which requires an AI model to perform a personalized risk assessment.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: An easy integration with existing on-site software (avoiding the need to redeploy investments held in the legacy infrastructure).
- Machine Learning: AI is involved in enhancing on-site processes, including production scheduling and quality control.
Perks For Businesses
- Regulatory Compliance: By leveraging Dynamics 365, healthcare providers can achieve HIPAA compliance and significantly improve care delivery through the use of AI-powered data analytics.
- Multifaceted Workflows: Manufacturers with rigid production chains can customize their ERP systems to optimize machine uptime, resulting in a significant reduction in downtime.
- Long-Term Cost Control: Although initial costs are higher, on-premises systems eliminate recurring cloud subscription fees, providing predictable budgeting for large enterprises.
Hybrid AI ERP Systems
Hybrid AI-powered ERP systems are a combination of cloud and on-premises deployment types, offering flexibility to leverage the benefits of the cloud while maintaining control over critical data. They are best suited for companies transitioning to the cloud or those requiring a balance between innovation and support for legacy systems.
Key Features
- Flexibility in Deployment: Sensitive data would be kept on-premises, whereas less important features, such as CRM or HR, can utilize cloud scalability.
- Machine learning: The seamless transfer of data between cloud and on-premises modules becomes possible and helps prevent silos.
- Cost Optimization: Has the right balance between cloud subscription and investments in on-premises infrastructure.
- Disaster Recovery: Backups in the cloud will enhance resilience, whereas on-site systems will maintain operational consistency even during outages.
Perks For Businesses
- Gradual Adoption of Cloud: The gradual adoption of an AI-driven ERP cloud system has enabled a global manufacturer of heavy construction equipment to improve its supply chain visibility by 60%, reduce transportation and logistics costs by 40%, and achieve a 30% increase in operational efficiency.
- Control Scalability: For a pharmaceutical organization, a hybrid ERP can be utilized to execute AI-based R&D analytics in the cloud while retaining high-value IP locally.
- Business Continuity: The use of hybrid systems means that organizations will be spared downtime in the event of cloud outages, which is particularly important in time-sensitive sectors such as logistics.
Industry-Specific AI ERP Systems
Industry-specific AI ERP systems are tailored to the unique needs of sectors like manufacturing, retail, healthcare, or construction. They incorporate AI to address niche challenges, such as regulatory compliance, supply chain complexity, or customer engagement.
Key Features
- Specialized AI Models: Industry-specific algorithms, like predictive analytics for manufacturing or patient scheduling for healthcare.
- Compliance Automation: AI ensures adherence to sector-specific regulations, such as FDA standards for pharmaceuticals.
- Workflow Optimization: Tailored AI automates processes such as just-in-time inventory management for retail and project tracking for construction.
- Vertical Integration: Seamlessly connects with industry tools, such as CAD software for manufacturing or EHR systems for healthcare.
Perks For Businesses
- Manufacturing Efficiency: AI-powered ERP systems can predict equipment failures, reducing unplanned downtime and improving production throughput.
- Retail Personalization: AI-driven customer analytics enable targeted marketing campaigns, resulting in a significant improvement in conversion rates.
- Healthcare Optimization: AI-ERP systems for healthcare automate patient scheduling and billing, thereby reducing administrative costs.
Real-World Use Cases of AI in ERP Systems
In a world where information has become the currency and speed is the determinant of success, AI is revolutionizing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems into powerful mechanisms of innovation.
By incorporating AI into ERP, companies can access previously unimaginable levels of automation, intelligence, and responsiveness, potentially transforming their operations in a highly competitive, globalized market. Whether it is forecasting demand to the most precise detail or automating highly complex business processes, real-time understanding of anomalous behavior and AI-driven enterprise resource planning use cases are doing more than just increasing efficiency.
Below is an in-depth exploration of practical AI-driven ERP use cases, demonstrating how AI enhances ERP systems and their potential outcomes.
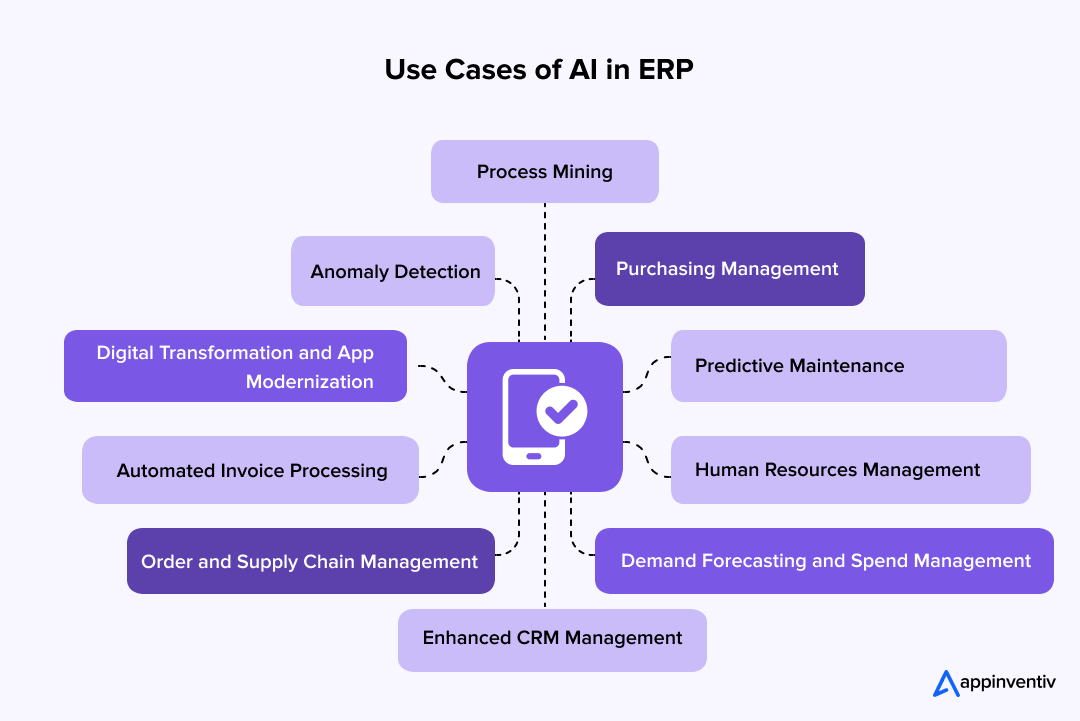
Digital Transformation and App Modernization
AI in ERP systems accelerates digital transformation by modernizing legacy systems, integrating cloud-based solutions, and enabling real-time data processing. AI-driven ERP platforms enhance agility, scalability, and user experience by automating manual processes and providing intelligent insights.
Practical Applications:
- Legacy System Integration: AI can analyze legacy ERP systems, identify inefficiencies, and suggest modernization strategies, such as migrating to cloud-based ERP platforms like SAP S/4HANA. Here, an AI-powered ERP system plays a crucial role in mapping outdated workflows to new systems, reducing migration time by up to 30%. As enterprises upgrade their legacy ERP, AI API integration in ERP modernization ensures intelligent automation without complete replatforming.
- Intelligent Process Automation: AI facilitates intelligent automation for enterprises to streamline repetitive tasks, such as data entry or report generation, enabling seamless integration with modern applications (e.g., mobile apps or IoT devices). Firms can leverage AI to integrate IoT sensor data into their ERP system, enabling smart monitoring.
- Personalized User Interfaces: AI tailors ERP dashboards to individual user roles, improving adoption rates. For example, a sales manager might view a customized dashboard with predictive sales analytics, while a warehouse manager sees insights into inventory optimization.
Implementation Considerations:
- Ensure data compatibility between old and new systems.
- Train employees to adapt to AI-enhanced interfaces.
- Utilize AI-driven change management tools to monitor adoption and effectively address any resistance.
Demand Forecasting and Spend Management
AI enhances demand forecasting by analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and external factors like economic indicators and weather patterns. In spend management, AI optimizes procurement budgets and identifies cost-saving opportunities.
Practical Applications:
- Predictive Demand Models: AI utilizes machine learning (ML) to analyze past sales, seasonal trends, and local events, accurately predicting demand based on AI analysis. Typically, a large retail entrepreneur integrates AI into their ERP systems to forecast inventory needs while reducing stockouts.
- Spend Optimization: Intelligent AI models identify patterns in purchasing data to recommend cost-effective suppliers or negotiate better contracts. AI for ERP systems automatically flags recurring purchases of raw materials at a higher price and suggests an alternative supplier, thereby saving significant costs.
Bonus Read: How to Build an Intelligent AI Model: An Enterprise Guide
Implementation Considerations:
- Integrate external data sources, such as market and social media reports, for accurate forecasting.
- Regularly update AI models to reflect changing market conditions.
- Ensure transparency in AI-driven spending recommendations to maintain trust with procurement teams.
Order and Supply Chain Management
AI can be used to optimize order processing and supply in a business, predict disruptions, automate procedures, and improve the efficiency of their logistics.
Practical Applications:
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI can analyze and compare the performance of suppliers, shipping delays, and geopolitical risks to suggest alternative suppliers or routes for managing supply chain optimization.
- Order Automation: AI can automate the order processing process by focusing on high-value orders or randomly flagging any unusual information, like fraudulent orders.
- Real-Time Visibility: AI uses IoT and ERP data collectively to track a supply chain in real-time. Logistics companies utilize AI to track the location of trucks and predict delivery delays caused by traffic or weather conditions.
Implementation Considerations:
- Invest in the IoT infrastructure to collect and analyze data in real-time.
- When connecting external supply chain partners, ensure that data security is maintained to protect sensitive information. This is to provide a safe environment.
- With the use of AI, you can track and adapt to the risks in the supply chain as they evolve.
Unlock the story behind a 60% boost in visibility for a global manufacturer using cutting-edge AI & Analytics.
Predictive Maintenance
AI-driven predictive maintenance utilizes IoT sensor data and historical equipment performance to forecast failures before they occur, thereby reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Practical Applications:
- Equipment Health Monitoring: Machines equipped with IoT sensors monitor various parameters, including pressure, vibrations, temperature, and more. These sensors continuously collect data, providing a 360-degree view of your equipment’s operation and indicating potential failures before they escalate.
- Equipment Maintenance Scheduling: AI integrates maintenance schedules into the ERP system, aligning them with production timelines to minimize disruptions and optimize maintenance efficiency.
- Cost Optimization: AI prioritizes maintenance tasks based on cost and impact. It might be recommended to repair a low-cost component before it causes a cascade failure.
Implementation Considerations:
- Install IoT sensors on critical equipment.
- Train AI models with historical maintenance data for accuracy.
- Integrate predictive maintenance alerts with ERP workflows to ensure timely action.
Enhanced CRM Management
AI enhances Customer Relationship Management (CRM) within ERP systems by personalizing customer interactions, predicting churn, and automating sales processes.
Practical Applications:
- Customer Segmentation: AI analyzes purchase history, demographics, and behavior to create targeted marketing campaigns that effectively reach the right audience.
- Churn Prediction: AI identifies at-risk customers by analyzing usage patterns and support tickets.
- Sales Automation: AI prioritizes leads based on their likelihood to convert, enabling sales teams to focus on high-value prospects. An AI-powered ERP system allows businesses to assign scores to leads based on their website interactions and past purchasing behavior.
Implementation Considerations:
- Ensure IT compliance regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) when handling customer data to maintain trust and protect sensitive information.
- Integrate CRM data with other ERP modules (e.g., inventory, finance) for a holistic view.
- Utilize AI to refine customer segmentation models continually.
Human Resources Management
AI streamlines HR processes within ERP systems by automating recruitment, talent management, and employee engagement tasks.
Practical Applications:
- Recruitment Automation: AI screens resumes, ranks candidates based on skills, and schedules interviews.
- Employee Engagement: ERP with AI integration enables businesses to analyze employee feedback through surveys and performance reviews, predicting potential turnover risks.
- Payroll Optimization: AI detects anomalies in payroll data, such as overtime spikes, and suggests cost-saving measures.
Implementation Considerations:
- Ensure AI complies with labor laws and ethical hiring practices.
- Protect employee data with robust cybersecurity measures.
- Use AI to personalize employee development plans for better engagement.
Automated Invoice Processing
AI automates invoice processing by extracting data, validating invoices, and detecting discrepancies, reducing manual errors and processing times.
Practical Applications:
- Data Extraction: AI utilizes optical character recognition (OCR) and natural language processing (NLP) to extract data from scanned invoices, regardless of the varying formats.
- Fraud Detection: AI flags suspicious invoices, such as duplicate submissions or unusual amounts, for review and investigation. A healthcare provider may use AI to detect fraudulent supplier invoices.
- Workflow Automation: AI routes invoices to the appropriate department for approval, reducing processing time from days to hours.
Bonus Read: Integrating AI in Cybersecurity: Automating Enterprise With AI-Powered SOC
Implementation Considerations:
- Train AI models to handle a wide range of invoice formats.
- Integrate with accounts payable systems for seamless payment processing.
- Monitor AI performance to ensure accuracy in high-volume environments.
Purchasing Management
AI optimizes purchasing by analyzing supplier performance, predicting price fluctuations, and automating procurement workflows to enhance efficiency.
Practical Applications:
- Supplier Evaluation: AI ranks suppliers based on delivery times, quality, and cost.
- Price Forecasting: AI predicts commodity price trends based on market data, enabling companies to optimize their purchasing strategies effectively.
- Purchase Order Automation: AI generates purchase orders based on current inventory levels and demand forecasts, minimizing the need for manual intervention.
Implementation Considerations:
- Integrate AI with supplier databases for real-time data.
- Monitor AI-driven purchasing decisions to ensure alignment with business goals.
- Use AI to track supplier compliance with contracts.
Anomaly Detection
AI effectively identifies anomalies in ERP data, such as financial transactions and inventory records, to prevent fraud, errors, and operational inefficiencies.
Practical Applications:
- Financial Anomalies: AI detects unusual transactions, such as duplicate payments or unauthorized expenses.
- Inventory Anomalies: AI identifies mismatches between physical and recorded inventory, reducing shrinkage.
- Operational Anomalies: AI monitors production data to flag inefficiencies, such as machine overuse or workflow bottlenecks.
Implementation Considerations:
- Train AI models with historical data to improve anomaly detection accuracy.
- Set clear thresholds for flagging anomalies to avoid false positives.
- Integrate anomaly alerts with ERP dashboards for quick resolution.
Also Read: Financial Fraud Detection Using Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Guide
Process Mining
AI-driven process mining analyzes ERP data to map business processes, identify inefficiencies, and suggest improvements.
Practical Applications:
- Process Visualization: AI creates visual workflows of business processes (e.g., order-to-cash, procure-to-pay), highlighting bottlenecks.
- Compliance Monitoring: AI ensures processes comply with regulations by flagging deviations. A pharmaceutical company may utilize AI to ensure its supply chain complies with FDA standards.
- Continuous Improvement: AI recommends process optimizations based on real-time data, such as automating manual steps or reassigning resources.
Implementation Considerations:
- Ensure ERP data is clean and comprehensive for accurate process mining.
- Use AI to prioritize high-impact process improvements.
- Train employees to act on AI-generated insights for continuous improvement.
AI ERP Integration Process: In-Depth Guide
This convergence of AI and ERP systems represents a significant paradigm shift in streamlining organizational structure, enhancing decision-making, and strengthening competitive advantage. Integrating AI functions into ERP systems enables businesses to predict, simplify complex processes, and facilitate resource planning across various functions, including finance, supply chain management, and customer relationship management.
Nevertheless, successful AI implementation in ERP requires a strategic plan, which includes clear objectives, effective use of data, and close technological-business alignment.
Explore a practical, step-by-step guide on how to integrate AI into ERP, drawing on solid, expert knowledge and real-life considerations to achieve the best results and measurable outcomes.
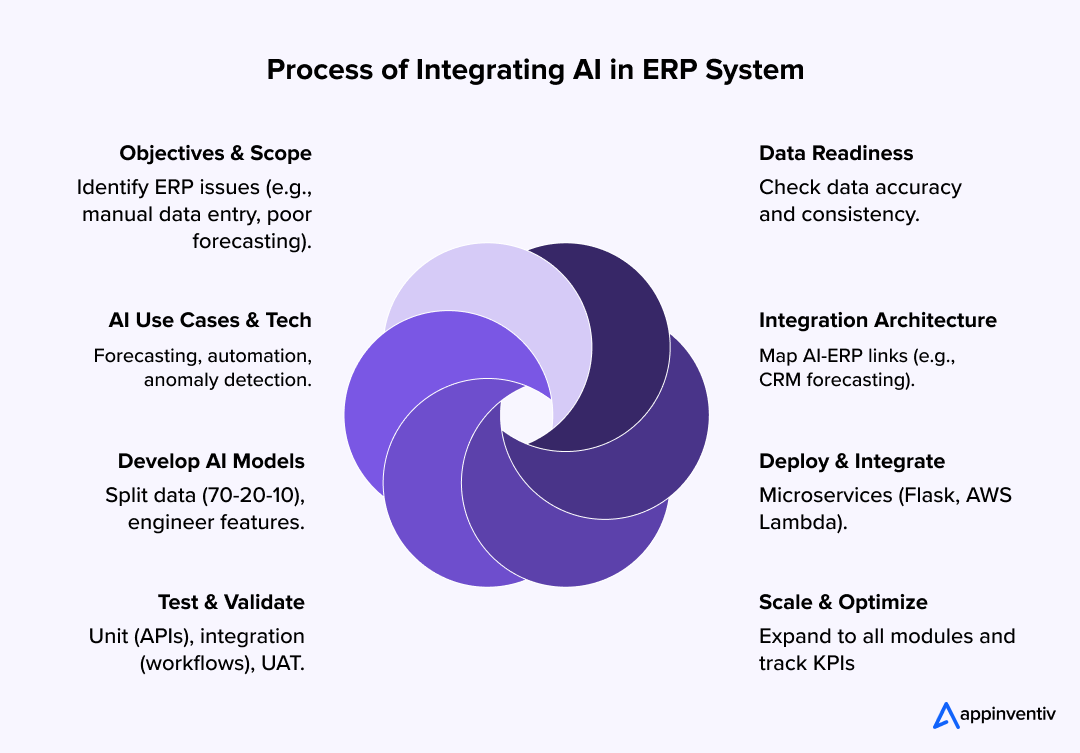
Define Objectives and Scope
Establish clear goals for integrating AI into your ERP system to align with business needs and avoid scope creep.
- Identify Pain Points: Analyze current ERP processes to pinpoint inefficiencies, such as manual data entry in supply chain management, inaccurate demand forecasting, or slow financial reporting.
- Set AI-Driven Goals: Define specific outcomes, like reducing inventory costs by 15% through AI-driven demand forecasting.
- Scope the Integration: Decide which ERP modules (e.g., finance, HR, supply chain, CRM) will integrate with AI and prioritize based on ROI. For instance, combining AI with supply chain modules might yield faster returns than HR.
Assess Data Readiness
AI thrives on quality data. Ensure your ERP system’s data is clean, accessible, and structured for AI use.
- Data Audit: Evaluate ERP data for completeness, accuracy, and consistency.
- Data Cleansing: Utilize tools like Informatica or Talend to standardize formats, eliminate duplicates, and fill data gaps. For instance, normalize data formats (e.g., MM/DD/YYYY vs. DD-MM-YY) across ERP modules.
- Data Integration: Ensure that ERP data from different modules (e.g., sales, inventory, procurement) is unified in a central data warehouse or lake (e.g., Snowflake, Azure Data Lake) for seamless access by AI models.
- Real-Time Data Needs: Determine if AI models require real-time data feeds (e.g., for predictive maintenance) and develop APIs or ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines to enable this.
- Data Governance: Establish policies for data security, compliance (e.g., GDPR, CCPA), and access control to protect sensitive ERP data used by AI.
Tools:
- Data cleansing: Informatica, Talend, OpenRefine.
- Data storage: Snowflake, Google BigQuery, AWS Redshift.
- ETL pipelines: Apache NiFi, Airflow, or native ERP connectors.
Also Read: AI in Data Governance: Reshaping Enterprise Data Strategy
Select AI Use Cases and Technologies
Choose specific AI applications and tools that align with your ERP objectives and infrastructure.
Identify AI Use Cases: Common ERP-AI integrations include:
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting demand, cash flow, or maintenance needs (e.g., using time-series models like ARIMA or LSTM).
- Process Automation: Automating invoice processing or order fulfillment with RPA (Robotic Process Automation) enhanced by AI.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying fraud in financial transactions or errors in inventory data.
Choose AI Technologies:
- Machine Learning Frameworks: TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Scikit-learn for custom models.
- Low-Code AI Platforms: For faster deployment, consider platforms like DataRobot or H2O.ai, which are designed for non-technical teams.
Evaluate Compatibility: Ensure AI tools integrate seamlessly with your ERP system via APIs, SDKs, or native connectors.
Proof of Concept (PoC): Start with a small-scale PoC (e.g., AI-based demand forecasting for one product line) to validate feasibility and ROI before full deployment.
Tools:
- AI platforms: IBM Watson, Google Cloud AI, Azure Machine Learning.
- ERP-specific AI: SAP Leonardo, Oracle Adaptive Intelligence, Dynamics 365 AI.
- RPA tools: UiPath, Automation Anywhere (for AI-enhanced automation).
Design the Integration Architecture
Create a robust technical framework to connect AI systems with your ERP environment.
- Define Integration Points: Map where AI will interact with ERP modules. For example:
1. AI models pulling sales data from ERP’s CRM module for forecasting.
2. AI pushing recommendations (e.g., reorder quantities) back to the inventory module.
- Choose Integration Method:
1. APIs: Use REST or SOAP APIs for real-time data exchange (e.g., SAP’s OData APIs).
2. Middleware: Deploy integration platforms, such as MuleSoft or Dell Boomi, to bridge ERP and AI systems.
3. Direct Database Access: For batch processing, connect AI models to ERP databases (e.g., Oracle DB, SQL Server) via JDBC/ODBC.
- Cloud vs. On-Premise: Decide whether to host AI models in the cloud (e.g., AWS, Azure) or on-premise, based on ERP deployment and compliance needs.
- Scalability and Performance: Design for scalability by utilizing microservices or containerization (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes) to handle large data volumes or high user loads efficiently.
- Security: Implement encryption (e.g., TLS for APIs), role-based access control, and audit logs to secure AI-ERP interactions.
Tools:
- Integration Platforms: MuleSoft, Dell Boomi, SAP Integration Suite.
- API Management: Postman, Apigee.
- Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud.
Also Read: On-Premise vs. Cloud: A Detailed Analysis
Develop and Train AI Models
Build or customize AI models tailored to your ERP use cases.
- Data Preparation: Split ERP data into training, validation, and test sets (e.g., 70-20-10 split). Use techniques like feature engineering to extract relevant variables (e.g., sales trends, seasonality).
- Model Selection: Choose algorithms based on the use case.
1. Regression models (e.g., XGBoost) for forecasting.
2. Clustering (e.g., K-means) for customer segmentation in CRM.
3. NLP models (e.g., BERT) for chatbot integration. - Training: Train models on historical ERP data using cloud platforms like Google Colab or AWS SageMaker. Monitor metrics like accuracy, precision, or RMSE to evaluate performance.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Optimize model performance using tools like GridSearchCV or Optuna.
- Testing: Validate models on a separate ERP dataset to ensure generalizability. For example, test a demand forecasting model on Q4 2024 data to predict Q1 2025.
- Explainability: Use tools like SHAP or LIME to make AI decisions interpretable, especially for regulated industries like finance or healthcare.
Tools:
- Model training: TensorFlow, PyTorch, SageMaker.
- Explainability: SHAP, LIME.
- Tuning: Optuna, Hyperopt.
Deploy and Integrate AI Models
Operationalize AI models by embedding them into ERP workflows.
- Model Deployment: Deploy AI models as microservices (e.g., via Flask or FastAPI) or on cloud platforms (e.g., AWS Lambda, Azure Functions).
- ERP Integration: Embed AI outputs into ERP interfaces:
1. Dashboards: Display AI-driven insights (e.g., demand forecasts) in ERP dashboards using tools like Power BI or Tableau.
2. Workflows: Automate actions (e.g., trigger purchase orders when AI predicts low inventory) using ERP’s workflow engine.
- Real-Time vs. Batch: Decide whether AI predictions run in real-time (e.g., fraud detection) or as batch processes (e.g., monthly financial forecasts).
- Monitoring: Set up monitoring for model performance (e.g., drift detection) and ERP integration health (e.g., API uptime) using tools like Prometheus or Grafana.
Tools:
- Deployment: Flask, FastAPI, AWS Lambda.
- Monitoring: Prometheus, Grafana, Splunk.
- Visualization: Power BI, Tableau, Qlik.
Bonus Read: Exploring the Power of AI in Interactive Data Visualizations
Test and Validate the Integration
Ensure the AI-ERP integration is reliable, accurate, and secure before implementing it fully.
- Unit Testing: Test individual components (e.g., APIs, AI models) for functionality. For example, verify that an AI forecasting model correctly pulls data from the ERP’s sales module.
- Integration Testing: Test end-to-end workflows, such as data flowing from ERP to AI and back to ERP (e.g., inventory updates triggered by AI predictions).
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involve end-users to validate that AI outputs meet business needs (e.g., the procurement team confirms AI-recommended purchase orders are accurate).
- Security Testing: Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability scans to secure AI-ERP data flows and protect against potential threats.
Tools:
- Testing: Postman (API testing), Selenium (UI testing), JMeter (stress testing).
- Security: OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite.
Also Read: AI in Quality Assurance: The Next Stage of Automation
Scale and Optimize
Roll out the integration across the organization and continuously improve performance.
- Full Deployment: Expand the PoC to all relevant ERP modules or business units.
- Continuous Monitoring: Track KPIs (e.g., cost savings, error rates) and model performance (e.g., prediction accuracy) post-deployment.
- Model Retraining: Periodically retrain AI models with new ERP data to address data drift or changing business conditions.
- Optimization: Fine-tune integration performance by optimizing APIs, reducing latency, or upgrading hardware (e.g., GPU clusters for AI inference).
Tools:
- Monitoring: Datadog, New Relic.
- Retraining: MLflow, Kubeflow.
Understanding the Cost of AI Integration in ERP Systems
Integrating AI in ERP systems depends on the project scope, complexity, and organizational requirements, which, therefore, have different costs. The most important cost factors of AI-ERP integration are briefly described below:
| Project Scale | Applications | Cost Range | Cost Components |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small-Scale Projects | Basic AI (e.g., chatbots, simple automation) | $40,000–$80,000 | Software, cloud hosting, basic integration |
| Mid-Sized Projects | Predictive analytics, natural language processing | $100,000–$500,000 | Data processing, model training, and infrastructure |
| Enterprise-Grade Solutions | Deep learning, autonomous systems | $1M–$10M+ | R&D, high-performance computing, compliance requirements |
Additional Costs
| Cost Category | Description | Cost Range/Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| Custom Integration | APIs, data pipeline changes, and workflow redesigns | $50,000–$200,000 |
| Infrastructure Upgrades | Modernizing legacy systems or cloud migration | Varies (project-specific) |
| Ongoing Expenses | Maintenance, model retraining, cloud storage, compliance oversight (1–3 FTEs) | $30,000 annually (or more) |
Connect with our AI experts to receive a clear, tailored cost estimate and bring your vision to life as a cutting-edge reality.
The Future of ERP with AI
The future of AI-driven ERP systems is poised for significant advancements, driven by emerging technologies and evolving business needs. Below are key trends and predictions for 2025 and beyond:
1. Greater Autonomy and Decision-Making: ERP systems will increasingly operate with greater autonomy, with AI handling complex decision-making processes such as supply chain optimization and dynamic pricing.
2. Integration with Emerging Technologies
- Blockchain: Integrating blockchain technology will enhance transparency and security in ERP systems, particularly in supply chain management.
- Edge Computing: AI-driven ERP systems will utilize edge computing to process data closer to the source, thereby reducing latency and enhancing real-time analytics.
- IoT: IoT sensors will enhance predictive maintenance and inventory management.
Bonus Read: Blockchain for Enterprise: Use Cases, Features, and Potential Challenges
3. Conversational AI and User Interfaces: Conversational AI tools will make ERP systems more accessible to non-technical users.
4. Sustainability and ESG Goals: AI-powered ERP systems will enable organizations to meet their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals by analyzing carbon emissions and optimizing resource utilization.
5. Hyper-Personalization and Industry-Specific Solutions: AI will enable ERP systems to offer hyper-personalized experiences tailored to specific industries, such as healthcare, retail, or manufacturing.
What Makes Appinventiv a Trusted Partner to Integrate AI into an ERP System?
The integration of AI in ERP systems is transforming the way businesses operate, streamlining operations and driving innovation. Finding the right technology partner is crucial to ensure ease of integration, scalability, and future prosperity.
Our bespoke ERP Software Development Services help you to tackle this complex task. With nearly 10 years of experience under our belt, a team of over 1,600 tech specialists, and a proven track record of delivering more than 3,000 digital solutions, we leverage scalable aspects to develop the most advanced and AI-inclusive ERP systems tailored to your business.
Deep Technical Proficiency in Artificial Intelligence ERP Integration/Development
At Appinventiv, we have expertise in both AI and ERP development. Our multidisciplinary team of over 1,600 technology evangelists possess proficiency in AI, machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and other emerging tech trends, enabling us to craft your enterprise software development and deliver no-code solutions meticulously.
Key Areas of Competencies:
- Custom AI Development: We leverage modern technologies, including ML models, NLP, and predictive analytics of AI, to craft our AI development services that enhance the functionality of the ERP. We have hands-on experience in creating an IoT-powered SaaS Platform for real estate ERP. The platform we’ve developed enables predictive property pricing, which has helped the client achieve a 40% increase in occupancy rates.
- Design of ERP Systems: Our decade of experience in developing and integrating ERP systems, including one for the world’s largest furniture retailer, IKEA. We designed a web and mobile-friendly ERP solution that facilitates operations, maximizes workflow processes, and enables real-time data analysis.
- Smooth System Integration: We have experience in developing APIs and system connections, as well as making AI elements easy to integrate with a company’s current IT environment, whether it’s an ERP system, CRM, or other enterprise software.
Industry Recognition and Thought Leadership
Appinventiv’s leadership in the tech industry is evident in its numerous accolades, client testimonials, and thought leadership in artificial intelligence ERP development. The company has been recognized as a top performer by reputable organizations and maintains a strong presence in the digital transformation space.
Industry Accolades
- Clutch Top 100 Fastest-Growing Companies 2025: Clutch recognized us as one of the fastest-growing companies in 2025. This highlights our progress, strong execution, and dedication to innovation.
- Clutch Global Spring Award 2024: We are honored to receive the Clutch Global Spring Award 2024. This award highlights our exceptional app development and outstanding client service.
- Deloitte Technology Fast 50 India: Appinventiv secured a spot in 2023 and topped the Digital & Cloud Tech category in 2024, achieving a remarkable 260.75% revenue growth from FY21 to FY24.
Ethical Practices and Client-Centric Approach
Trust is the cornerstone of any successful partnership, and Appinventiv builds trust through ethical practices, transparent processes, and a client-centric approach. Their commitment to delivering secure, compliant, and high-quality solutions ensures that businesses can rely on them for AI-ERP integration.
- Ethical AI and Data Integrity: We prioritize responsible and ethical AI development, ensuring that solutions are fair, transparent, and compliant with regulations in the US and EU. We also focus on data integrity, which is critical for ERP systems, where accurate data drives decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Robust Security Measures: Security is a core pillar of Appinventiv’s services. Our AI and ERP solutions adhere to strict regulatory compliance standards, protecting sensitive business data from potential threats. Whether integrating AI chatbots with ERPs or deploying ML models, we ensure robust security measures and seamless data exchange.
- Transparent and Collaborative Process: Our SAFE agile framework fosters transparency and collaboration. Clients are kept informed at every stage, from ideation to post-deployment support. This enables regular feedback and adjustments, ensuring that the final product aligns with business objectives.
- Comprehensive Support: We offer end-to-end support, encompassing initial consulting, development, deployment, and ongoing maintenance. Our post-deployment support ensures that AI-integrated ERP systems remain optimized and adaptable to evolving business needs.
By choosing Appinventiv as your technological partner for AI-ERP integration, you ally with a company that embodies professionalism, competence, authority, and reliability. Our success, extensive industry experience, and proven track record of delivering secure solutions make us the optimal choice for businesses seeking to transform their operations through AI-powered ERP systems.
Schedule a meeting today with the Appinventiv team to begin your new AI-ERP adventure and join a new era of efficiency and development.
FAQs
Q. How does AI improve ERP systems?
A. AI enhances ERP systems by automating repetitive tasks, improving data analysis, and enabling predictive capabilities. It streamlines processes like inventory management, financial forecasting, and supply chain optimization through machine learning algorithms that identify patterns and optimize workflows.
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants improve user interaction by providing real-time insights and support. Additionally, AI enables better decision-making with predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and personalized reporting, leading to increased efficiency, reduced errors, and enhanced scalability.
Q. How much does it cost to integrate AI into ERP systems?
A. The cost of integrating AI into ERP systems varies widely based on factors like the complexity of the AI solution, the ERP platform, data infrastructure, and whether custom development or off-the-shelf AI tools are used.
Basic integrations, such as adding AI-driven analytics, may range from $50,000 to $200,000. More advanced implementations, including custom machine learning models or extensive data restructuring, can cost $500,000 to $2 million or more. Ongoing costs for maintenance, cloud services, and updates should also be considered, typically 15-20% of the initial investment annually.
Q. What are some practical examples of AI in ERP systems?
A. AI in ERP systems enhances efficiency and decision-making. Examples include:
- Predictive Analytics: AI forecasts demand using historical data to optimize inventory management.
- Automated Data Entry: AI extracts data from invoices or emails, reducing manual input errors.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI analyzes supplier performance and logistics to streamline operations.
- Customer Insights: AI personalizes customer experiences by analyzing behavior within CRM modules.
Q. What are the challenges of integrating AI into ERP?
A. Challenges include:
- Data Quality and Availability: AI requires clean, structured data, but many ERP systems have siloed or inconsistent data, necessitating preprocessing.
- Compatibility: Legacy ERP systems may not support modern AI tools, necessitating costly upgrades or middleware solutions.
- Complexity and Expertise: Developing and deploying AI models demands specialized skills, which may be scarce in-house.
- Change Management: Employees may resist adopting AI-driven processes due to unfamiliarity or fear of job displacement.
- Scalability: Ensuring AI solutions scale with growing data volumes and user demands can be a technically challenging task.
- Integration Costs: High initial and ongoing costs can strain budgets, especially for smaller enterprises.
Q. How long does it take to integrate AI into ERP?
A. The timeline for AI integration into ERP systems depends on the scope and complexity. Basic integrations, like adding AI-powered analytics or chatbots, may take 3-6 months. Comprehensive projects, such as embedding machine learning for supply chain optimization or developing custom AI models, can take 12-24 months. Key phases include:
- Planning and Assessment: 1-3 months to evaluate ERP compatibility and data readiness.
- Data Preparation: 2-6 months for cleaning and structuring data.
- Development and Testing: 3-12 months for building and validating AI models.
- Deployment and Training: 2-6 months for rollout and user adoption. Delays may occur due to limitations in the legacy system or a lack of in-house expertise.
Q. What are the key AI features in ERP systems that enhance business operations?
A. AI features in ERP systems include predictive analytics for demand forecasting, intelligent process automation for streamlining workflows, natural language processing for improved user interaction, and machine learning for optimizing supply chain and financial decisions. These capabilities drive efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance decision-making.
Q. What are the risks of integrating AI into enterprise ERP?
A. Risks include:
- Data Privacy and Security: AI systems handling sensitive ERP data may be vulnerable to breaches if not properly secured.
- High Costs: Unexpected expenses from prolonged integration or maintenance can strain budgets.
- System Downtime: Integration errors may disrupt ERP functionality, impacting business operations.
- Bias in AI Models: Poorly trained models can produce inaccurate predictions or decisions, which in turn affect outcomes such as forecasting or inventory management.
- Employee Resistance: Lack of training or trust in AI can hinder adoption and reduce ROI.
- Vendor Lock-In: Dependence on specific AI or ERP vendors may limit flexibility and increase long-term costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: AI must comply with industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), which can complicate implementation.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
How to Develop an AI Chatbot for Education Platforms in UAE: Architecture, Cost, and Timeline
Key Takeaways AI chatbots are helping UAE institutions handle repetitive queries, reduce response delays, and improve the availability of student support. Bilingual capability, PDPL compliance, and integration with LMS and student systems are essential for successful deployment. Costs typically range from AED 150,000 to AED 1.47M ($40K–$400K), depending on integrations, personalization, and language support. AI-powered…
How AI in Healthcare Administration Cut Staff Workload by 40%
Key takeaways: AI automates claims, scheduling, intake, and documentation, cutting repetitive work and freeing staff to focus on oversight and patient coordination. AI validation tools flag incomplete records before submission, reduce avoidable denials by 10–20%, and improve clean-claim performance, enhancing revenue predictability. EHR and note-processing AI reclaim thousands of staff hours in large health systems,…

How AI Chatbots for eCommerce are Driving 3x More Sales in 2026
Key takeaways: AI chatbots for eCommerce have a direct impact on revenue. When aligned with buying intent, they lift conversions, increase order value, and drive repeat purchases. The strongest impact comes from personalization and guided selling, helping shoppers decide faster and buy with greater confidence. Abandoned cart recovery is a major revenue driver in 2026.…