- Evolution of OSS Architecture in Telecom - From Reactive to Real-Time
- Which Market Challenges Are Forcing OSS Systems in Telecom Adoption?
- Legacy Systems Can’t Keep Up with Modern Demands
- Network Complexity is Spiraling
- Customer Expectations Are Sky-High
- Siloed Systems Stifle Innovation
- High Operational Costs and Vendor Lock-ins
- What are the Business Cases for OSS?
- Network Management - The Control Room of Modern Telecom
- Automation of Routine Tasks - The Engine of Operational Efficiency
- Service Provisioning & Activation - Connecting Utilities, Faster
- 4. Service Assurance - The Digital Maintenance Team
- Providing Insights - Strategic Decision-Making with Real-Time Data
- OSS Architecture Models
- Microservices Architecture
- Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) / API-Centric
- Layered / Horizontal Architecture (TM Forum-Aligned)
- Federated Architecture
- Modular / Best-of-Breed Architecture
- Monolithic Architecture
- Cloud-Native / SaaS-Based OSS
- Hybrid Core + Satellite Model
- What Makes Up a Modern OSS?
- Network Inventory
- Fault Management
- Configuration & Change Management
- Performance at a Glance
- Zero-Touch Provisioning
- Service Assurance
- Workflow Automation
- Insights Layer
- API and Integration Frameworks
- Security Embedded by Design
- What are the Steps for Proper OSS Integration?
- Identify What’s Driving the Change
- Set Guiding Principles Early
- Choose the Right Reference Architecture
- Define Your Target State
- Plan for Iteration, Not Perfection
- Design for Ecosystem-Scale Integration
- Don’t Underestimate Organizational Impact
- What are Some Common Challenges in OSS Integration and Their Solutions?
- What are the Trends in Telecom OSS Architecture?
- Digital Twins, Triplets & Reality Twins
- Cloud-Native OSS/BSS
- Modern Software Development and Deployment Practices
- Rise of Open Source Frameworks
- Converged Product/Service/Resource Catalogues
- Observability Frameworks
- AIOps and Autonomous Operations
- How Appinventiv Can Accelerate Your Path to Future-Readiness in Telecom
- FAQs.
In an era where 5G rollouts, network slicing, and edge computing are redefining connectivity, telecom operators are under increasing pressure to innovate fast and operate smarter. Behind the scenes of these headline-grabbing advancements lies a less glamorous, but critical, component of the telecom engine: Operational Support Systems (OSS).
OSS architecture in telecom may not be the buzzword that gets everyone talking at tech conferences, but it’s the invisible force orchestrating everything from service assurance to network automation. It’s what keeps a multi-billion-dollar network humming smoothly while unlocking doors for innovation, scalability, and hyper-personalized customer experiences.
As telcos shift from legacy infrastructure to software-defined, AI-driven ecosystems, the telecom OSS architecture is evolving from a support role to a strategic enabler. It’s no exaggeration to say that next-gen telecom can’t happen without next-gen OSS. This article dives into why OSS in telecom is becoming the industry’s innovation engine – and what that means for the connectivity business.
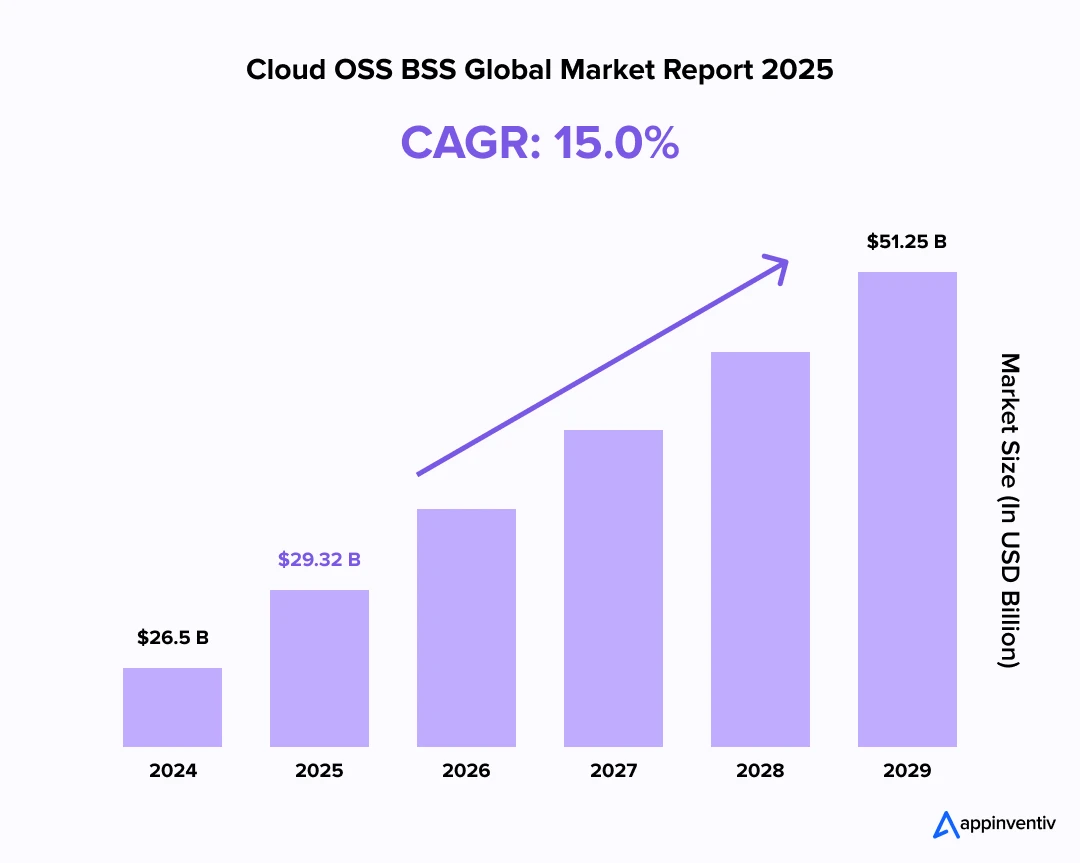
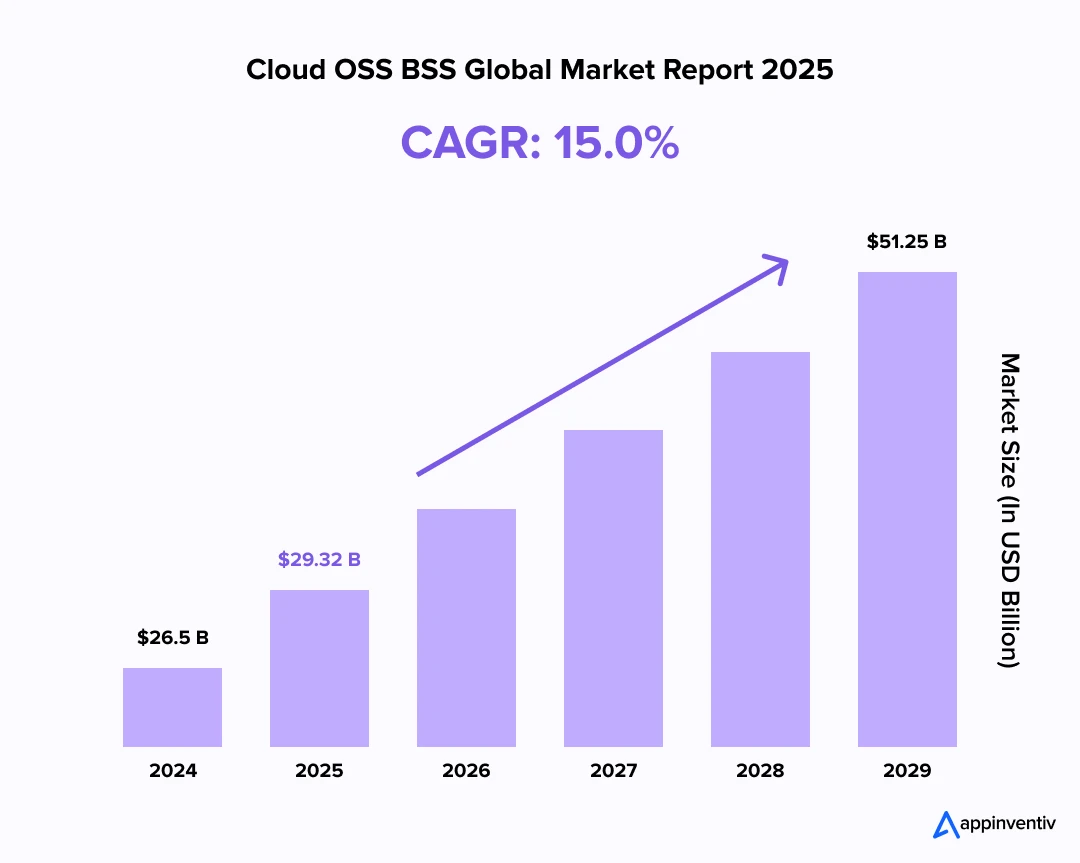
The global OSS & BSS market size was valued at USD 65.81 billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 148.26 billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.4% during 2025-2033. (Source: IMARC Group)
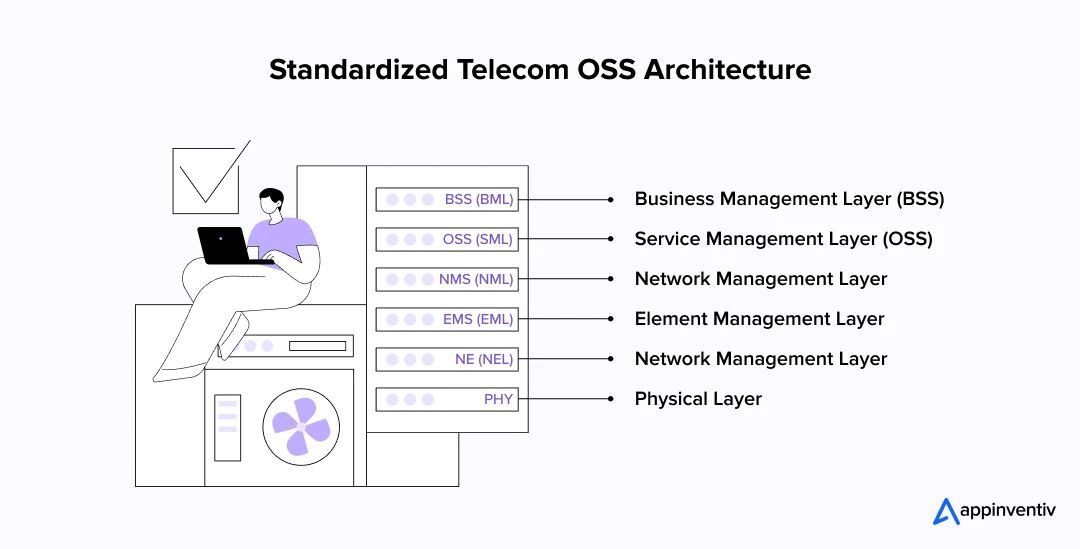
Evolution of OSS Architecture in Telecom – From Reactive to Real-Time
Before we dive into the evolution, let’s take a brief look at what is OSS in telecommunications. Operations Support Systems in telecommunications refer to the software solutions used to manage, monitor, and optimize network infrastructure, service delivery, and operational workflows. Over time, it has quietly transformed from a reactive toolkit to a proactive, intelligent backbone powering next-gen telecom. Here’s how that evolution has unfolded:
- OSS 1.0 – Hardware-Bound and Reactive: Early OSS handled basic provisioning and fault management, tightly integrated with hardware and limited in scope. It was reactive, only acting after problems occurred.
- OSS 2.0 – Siloed Automation: The rise of EMS/NMS brought some automation but created siloed domains. Every network segment had tools, data formats, and control systems, limiting end-to-end visibility.
- OSS 3.0 – Virtualization and Integration: With virtualization (NFV/SDN), OSS began integrating across domains and supporting programmable, software-defined networks. Real-time telemetry, unified views, and faster provisioning became possible.
- OSS 4.0 – Cloud-Native, AI-Driven, and Open: Today’s OSS integration in telecom is built on microservices, APIs, and real-time data pipelines. It supports AI for predictive analytics, automates operations at scale, and aligns with open standards like TM Forum’s ODA.
The evolution of OSS architecture in telecom is no longer just a support system; it’s a key enabler of innovation, speed, and customer-centric services.
Ditch siloed systems for smart, cloud-native OSS. It’s not just tech—it’s your business’s future.
Which Market Challenges Are Forcing OSS Systems in Telecom Adoption?
Telecom operators have relied on operational models weighed down by legacy systems and siloed infrastructure for years. But now, those outdated frameworks directly impact agility, cost, and customer experience, making the modernization of features of OSS architecture in telecom not a choice, but a necessity.
Legacy Systems Can’t Keep Up with Modern Demands
Traditional OSS platforms were built for hardware-centric networks with predictable loads. These rigid systems aren’t suited for today’s dynamic, cloud-native, and software-defined networks. As companies transition to 5G and AI business, they need OSS that can scale and respond in real time.
Network Complexity is Spiraling
Introducing 5G, IoT, and edge computing has exponentially increased network complexity. With millions of connected devices and the need for instant, context-aware services, managing operations manually or through siloed tools is no longer sustainable.
Customer Expectations Are Sky-High
Today’s users demand hyper-personalized experiences, zero downtime, and instant resolutions. Traditional OSS lacks the AI-driven intelligence and real-time visibility needed to meet these expectations, leading to service delays and dissatisfied customers.
Siloed Systems Stifle Innovation
Different domains often rely on disconnected OSS tools, creating barriers between provisioning, monitoring, billing, and assurance functions. This fragmentation slows innovation and creates inefficiencies when deploying cross-functional features like network slicing.
High Operational Costs and Vendor Lock-ins
Proprietary OSS stacks often lead to vendor lock-ins, expensive licenses, and complex integrations. Operators are increasingly moving to open, flexible architectures to cut costs and regain control over their innovation pace.
What are the Business Cases for OSS?
Operational Support Systems have long been the technical backbone of telecom operations. But in today’s context—marked by rising subscriber expectations, rapid service innovation, and growing network complexity—the benefits of OSS architecture for telecom operators are evolving it into a critical business enabler. It is no longer just about maintaining uptime. It’s about unlocking agility, monetizing new technologies, and future-proofing operations.
Here’s a deeper look into the key benefits of OSS architecture for telecom operators and how they directly impact business performance:
Network Management – The Control Room of Modern Telecom
OSS systems in telecom bring centralized visibility and control to sprawling telecom infrastructures. They allow operators to track assets, monitor performance metrics, detect faults, and manage configurations from a single window.
Business Value:
- Proactive fault detection reduces downtime and escalations
- Optimized resource usage leads to lower operational costs
- Greater visibility means faster root-cause analysis and better regulatory compliance
Automation of Routine Tasks – The Engine of Operational Efficiency
From repetitive tasks like configuration updates to automated incident responses, OSS systems are increasingly intelligent and policy-driven. Automation minimizes human intervention while improving consistency.
Business Value:
- Speeds up service delivery and fault resolution
- Cuts down manual errors and field workforce costs
- Frees up skilled teams to focus on innovation rather than firefighting
Service Provisioning & Activation – Connecting Utilities, Faster
Whether activating a fiber connection, launching a 5G service, or provisioning a new IoT device, OSS in telecom enables swift provisioning across multi-technology networks. It ensures that services are activated in the right order, with the right dependencies, and with minimal delay.
Business Value:
- Faster time-to-market for new offerings
- Enhanced onboarding experience for enterprise and retail customers
- Reduced revenue leakage due to failed or delayed activations
4. Service Assurance – The Digital Maintenance Team
Modern telecom OSS architecture continuously monitors service quality and ensures that networks meet performance benchmarks and SLAs. It identifies degradations before users notice and supports closed-loop remediation when paired with AI/ML.
Business Value:
- Higher customer satisfaction and lower churn
- SLA compliance with automated escalations and issue tracking
- Lower maintenance costs due to early intervention
Providing Insights – Strategic Decision-Making with Real-Time Data
OSS architecture in telecom now offers advanced analytics that go beyond operational health. From predicting network congestion to identifying underutilized infrastructure, OSS-generated insights inform CAPEX planning, service rollout decisions, and customer experience strategies.
Business Value:
- Data-driven investment decisions across regions and technologies
- Enhanced marketing through usage pattern analysis
- Agile development based on actual demand and performance metrics
For telecom operators seeking to stay competitive in a world of 5G, cloud-native networks, private mobile networks, and AI-driven operations, OSS architecture in telecom is no longer optional; it’s foundational. It empowers operators to move from reactive operations to predictive, from monolithic processes to modular agility, and from traditional services to next-gen innovation.
OSS Architecture Models
In the evolving telecom landscape, the architecture of Operational Support Systems plays a pivotal role in determining an operator’s agility, scalability, and innovation ability. Modern OSS architectures are designed to be modular, flexible, and responsive to the dynamic demands of next-generation networks. Below is an exploration of various features of OSS architecture in telecom, each offering unique advantages and considerations:
Microservices Architecture
Decomposes OSS functionalities into small, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled individually.
- Enhanced scalability and resilience
- Faster deployment cycles
- Improved fault isolation
Ideal for operators aiming for rapid innovation and scalability, especially in 5G and IoT deployments.
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) / API-Centric
Structures OSS functionalities as interoperable services, often exposed through APIs, to enable integration and reuse.
- Promotes interoperability across systems
- Facilitates integration with external partners
- Enhances flexibility in service composition
This OSS architecture in telecom is suitable for operators integrating diverse systems and services seamlessly.
Layered / Horizontal Architecture (TM Forum-Aligned)
Organizes OSS into horizontal layers (e.g., resource, service, customer) with standardized interfaces, aligned with TM Forum’s ODA.
- Reduces redundancy and complexity
- Simplifies integration and maintenance
- Enhances scalability and agility
Ideal for operators aiming for standardization and streamlined operations.
Federated Architecture
A decentralized model where multiple OSS systems operate independently but collaborate through defined interfaces.
- Supports autonomy across business units
- Scales well across regions
- Allows gradual integration of new systems
The telecom OSS architecture is best for large or multinational operators managing diverse networks.
Modular / Best-of-Breed Architecture
Combines components from various vendors, enabling operators to pick the best solutions for specific OSS functions.
- Avoids vendor lock-in
- Tailor systems to specific needs
- Encourages innovation through specialization
The OSS in telecom model is great for operators needing flexibility and customization.
Monolithic Architecture
A tightly coupled system, often from a single vendor, where all functionalities are integrated.
- Simplified deployment and operation
- Unified user experience
- Lower upfront complexity
Suitable for smaller operators or less complex networks.
Cloud-Native / SaaS-Based OSS
Uses cloud infrastructure and SaaS models to deliver OSS, emphasizing elasticity and speed.
- Rapid provisioning and updates
- Pay-as-you-grow scalability
- Reduced infrastructure costs
Ideal for telcos accelerating digital transformation.
Hybrid Core + Satellite Model
Blends a stable core OSS with flexible, modular satellite components for easy upgrades.
- Balances innovation with stability
- Ease modernization transitions
- Enables targeted improvements
OSS systems in telecom are effective for companies migrating from legacy to modern systems.
The choice of OSS architecture is not just a technical decision – it’s a strategic one. It impacts operational speed, innovation capability, and customer experience. Each model offers unique trade-offs, and selecting the right one depends on your business goals, network maturity, and transformation journey.
We’ll hook you up with the perfect architecture model to dominate.
What Makes Up a Modern OSS?
Behind every seamless call, real-time video stream, or connected device lies a set of tightly coordinated systems that telecom operators rely on daily. These are the foundational components of OSS architecture – each fulfilling a purpose, yet functioning as part of a larger, intelligent framework. Here’s a deeper look at these components and why they matter in today’s telecom environment.
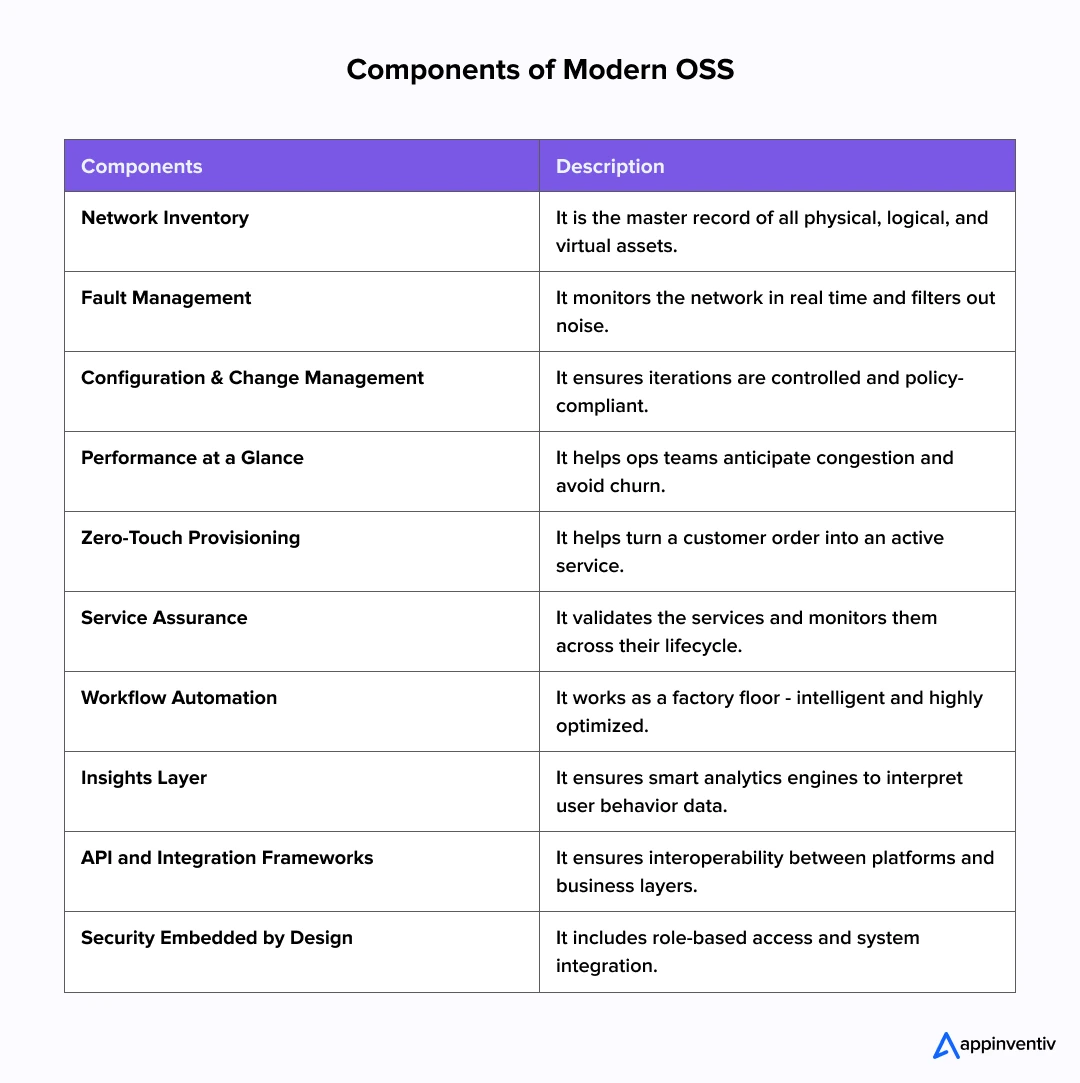
Network Inventory
Everything starts with visibility. Network Inventory is the master record of all physical, logical, and virtual assets within a telco’s ecosystem. It keeps track of routers, fiber lines, virtual functions, IP addresses – you name it. Without this, planning, troubleshooting, or provisioning services would be a shot in the dark.
Fault Management
When something breaks, fault management is the first thing to know. It monitors the network in real time, filters out noise, correlates alerts, and often pinpoints the root cause before customers even notice a glitch. With automated alarms and AI-powered insights, fault management is a key pillar of service continuity.
Configuration & Change Management
Networks evolve constantly. New devices are added, and existing ones are updated. CCM ensures these changes happen in a controlled, policy-compliant manner. Whether it’s rolling out firmware upgrades or enforcing global config templates, this layer safeguards the network’s integrity while enabling growth.
Performance at a Glance
Is your network delivering what it promised? Performance management software continuously answers that by tracking metrics like latency, throughput, and availability. It helps ops teams anticipate congestion, meet SLAs, and avoid churn. With 5G and edge deployments, this function is now more real-time and granular than ever.
Zero-Touch Provisioning
Service Provisioning and Activation turn a customer order into an active service. In modern OSS, this happens in minutes, not days, thanks to orchestration platforms that talk to BSS and network elements and coordinate provisioning across fiber, mobile, and cloud services.
Service Assurance
While provisioning activates, assurance ensures performance. It validates that services behave as expected post-activation and monitors them across their lifecycle. This includes service-level KPIs, end-to-end monitoring, and automated ticketing when something goes wrong.
Workflow Automation
Think of OSS as a factory floor – automated, intelligent, and highly optimized. Workflow engines within OSS automate repetitive tasks, reduce human touchpoints, and enforce operational processes. Some platforms now incorporate intent-based networking and AI-driven remediation.
Insights Layer
Modern OSS is increasingly data-driven. Data science & analytics for businesses interpret mountains of telemetry, user behavior, and usage data to uncover patterns, forecast demand, and guide investment. Operators who use OSS just to operate miss out; those who use it to optimize win.
API and Integration Frameworks
A siloed OSS is a legacy problem. Today’s systems are open by design and built with TM Forum Open APIs or other standards that enable interoperability between vendors, platforms, and business layers. This plug-and-play design unlocks faster innovation and ecosystem collaboration.
Bonus Read: 20 Open-Source API Management Platforms
Security Embedded by Design
With growing exposure via APIs and automation, OSS needs airtight security. This includes role-based access, audit trails, encryption, and integration with broader IAM and SIEM systems. Security isn’t a layer anymore – it’s infused into every OSS interaction.
Modern OSS systems in telecom aren’t monoliths. They’re an intelligent, distributed, real-time operating framework that connects, observes, manages, and improves every facet of a telecom operator’s business. Every single component of OSS architecture, whether it’s analyzing data or pushing a config change, is a gear in the innovation machine.
Also Read: The Growing Threat of Telecom Fraud and How to Safeguard Your Business
What are the Steps for Proper OSS Integration?
Modern OSS architecture isn’t just a plug-and-play solution, it’s a strategic transformation. And the complexity isn’t in the technology alone, but in the orchestration of people, platforms, and processes. As telcos face pressure to digitize, modernize, and monetize faster than ever, the ability to seamlessly handle OSS integration in telecom into the broader ecosystem becomes mission-critical.
Here’s how successful operators integrate telecom OSS architecture – step by step.
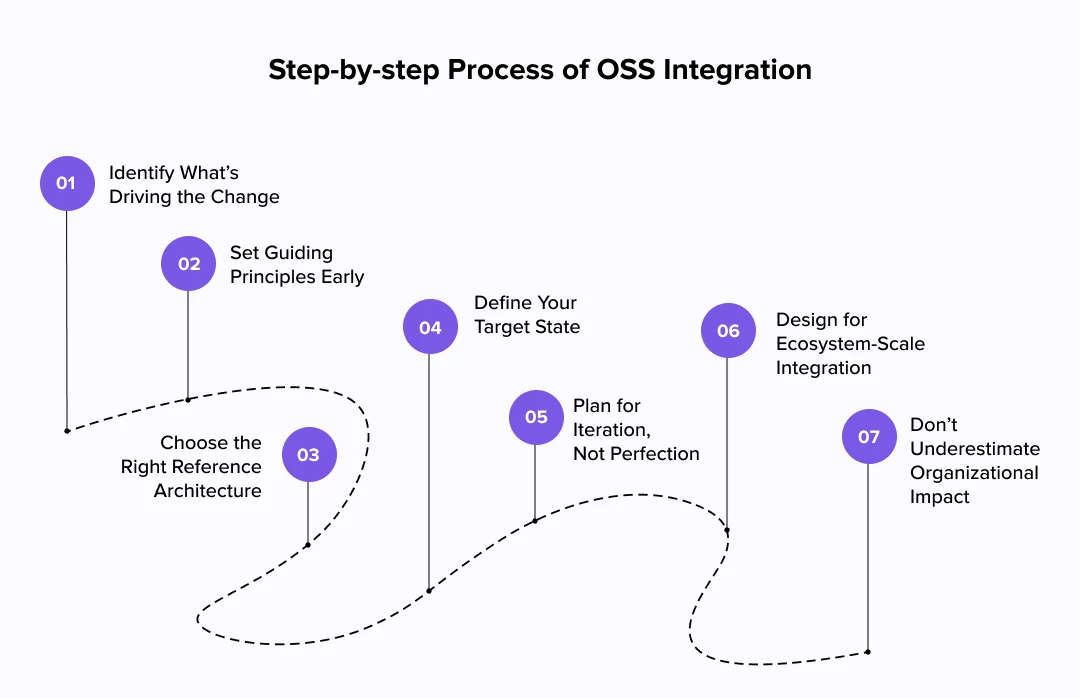
Identify What’s Driving the Change
The first step is asking “why.” Are you chasing operational cost reduction, faster time to market, or end-to-end service visibility across hybrid networks? Is it the pressure of 5G slicing, cloud-native deployments, or customer expectations for real-time self-service?
Understanding the core drivers, whether automation, agility, or analytics, anchors every decision downstream. Without this clarity, integration efforts risk becoming a tech upgrade rather than a business transformation.
Set Guiding Principles Early
Before selecting tools or vendors, organizations must define the architectural principles that will shape the OSS architecture in telecom transformation.
These include:
- Open APIs for interoperability
- Modular and microservices architecture design
- Cloud-native and containerized deployment
- Vendor-agnostic integration capability
- Real-time data availability across domains
Think of these principles as the architectural “constitution” – a consistent set of values that governs every integration move.
Choose the Right Reference Architecture
TM Forum’s Open Digital Architecture (ODA), ETSI MANO, and MEF LSO frameworks are just a few of the reference architectures gaining adoption. These blueprints help operators align with industry standards while leaving room for customization. This phase isn’t about copying a model – it’s about adopting a SAFE framework that supports both your business goals and technical constraints.
Define Your Target State
You can’t navigate a transformation without a destination. This is where target architecture modeling comes in.
It includes:
- What the end-to-end OSS stack will look like
- How it interacts with BSS, NMS, SDN, and public clouds
- Where each function – inventory, assurance, orchestration – will live
- What legacy systems will be retired, retained, or repurposed
This high-fidelity map becomes the north star for every team involved.
Plan for Iteration, Not Perfection
The move to a modern telecom OSS architecture is rarely a “big bang” deployment. Successful operators follow a phased transformation plan that prioritizes high-value integrations first – like real-time fault management or zero-touch provisioning – before tackling full-stack changes. By taking an agile approach, operators minimize risk, deliver quick wins, and build momentum across departments.
Design for Ecosystem-Scale Integration
In the 5G and IoT era, your OSS won’t just talk to your own network – it’ll interface with public clouds, enterprise IT systems, device ecosystems, hyperscaler APIs, and even customer self-care apps. Integration must extend beyond traditional boundaries.
This requires investing in:
- Open API gateways
- Data transformation layers
- Security-first communication protocols
- Workflow engines that bridge OSS and BSS
Bonus Read: API Development Guide: Build, Test, Deploy like a Pro
Don’t Underestimate Organizational Impact
OSS integration in telecom isn’t just an IT job – it changes how your entire organization works. From network ops and customer service to product design and compliance, everyone feels the shift. Leaders must ensure that change management, training, and cultural alignment go hand-in-hand with the technical rollout.
What are Some Common Challenges in OSS Integration and Their Solutions?
Transforming OSS/BSS systems is essential for telcos aiming to keep pace with evolving customer expectations and emerging technologies like 5G and IoT. But this transformation comes with its fair share of challenges. Here’s a breakdown of the most common OSS architecture in telecom challenges, along with how forward-thinking operators are solving them.
1. Legacy Systems: The Anchor of Innovation: Monolithic, outdated OSS/BSS systems make it hard to scale or integrate with new solutions.
Solution: Use a hybrid approach – modernize components in phases while wrapping legacy systems with APIs to preserve continuity and reduce disruption.
2. Vendor Fragmentation: Too Many Systems, Too Little Synergy: Managing multiple OSS/BSS platforms from different vendors leads to silos and inefficiencies.
Solution: Adopt modular or federated architecture models and use industry-standard APIs (like TM Forum Open APIs) to ensure interoperability and seamless integration.
3. Slow Digital Transformation: UI Isn’t Enough: Cosmetic upgrades don’t fix deeper operational bottlenecks.
Solution: Redesign workflows using automation, AI, and real-time orchestration to create smarter, more responsive back-end operations – not just better-looking front ends.
4. Limited Scalability in a 5G Environment: Traditional systems can’t handle the scale and speed required for 5G, network slicing, or IoT.
Solution: Move to cloud-native, microservices-based OSS architectures that allow on-demand scalability, dynamic resource allocation, and real-time analytics.
5. Poor Data Quality and Integrity: Inconsistent or inaccurate data leads to provisioning issues, billing errors, and failed automations.
Solution: Establish unified data layers, normalize records, and implement automated data validation tools powered by AI.
6. Resistance to Organizational Change: New systems often fail because people resist changing familiar tools or workflows.
Solution: Involve operational teams early, adopt agile delivery methods, and run upskilling programs to align your workforce with new systems.
7. Security and Compliance Risks with Open APIs: Exposing OSS functions via APIs can increase vulnerability and compliance risks.
Solution: Apply zero-trust security models, use API gateways with policy enforcement, and integrate automated compliance monitoring into the architecture.
8. Proving ROI and Business Value: OSS in telecom transformations is expensive, and it’s hard to show tangible benefits.
Solution: Tie transformation KPIs to business metrics like time-to-market, operational cost savings, and customer satisfaction scores – so every tech upgrade tells a business story.
What are the Trends in Telecom OSS Architecture?
As telcos pivot to software-defined, customer-centric networks, OSS/BSS is undergoing a major overhaul. Here are the most impactful future trends in telecom OSS architecture driving this transformation.

Digital Twins, Triplets & Reality Twins
Digital twins are no longer limited to physical infrastructure – they’re now extended into triplets, incorporating real-time operations and AI-driven simulations. This enables predictive maintenance, service impact analysis, and network behavior modeling. Moreover, reality twins also add spatial and geographic intelligence, giving telcos a live, interactive view of assets and service zones.
Bonus Read: How can digital twin technology help your business grow?
Cloud-Native OSS/BSS
Operators are re-architecting their OSS/BSS to be cloud-native – built on containerized microservices, running in Kubernetes environments, and leveraging CI/CD pipelines. These trends in telecom OSS architecture enables dynamic scaling, faster time-to-market, and lower operational costs. Public, private, and hybrid cloud setups are all in play, depending on regional and regulatory needs.
Modern Software Development and Deployment Practices
DevOps for business, CI/CD, GitOps, and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) are now core to OSS evolution. Telcos are investing in platform engineering, enabling cross-functional teams to deploy updates, test services, and roll back features without disruption.
Rise of Open Source Frameworks
From ONAP to OpenStack and TM Forum Open APIs, open-source is reducing vendor lock-in and accelerating innovation. Telecom software development services are increasingly co-developing and contributing to ecosystems – while ensuring compliance and code quality through governance models.
Converged Product/Service/Resource Catalogues
Modern OSS requires real-time catalogs that unify services, resources, and products across domains. This allows seamless service orchestration, faster provisioning, and cross-sell/upsell enablement. Catalogs are evolving from static repositories to rule-driven, API-first platforms.
Observability Frameworks
Telemetry, tracing, and service-level insights are vital in complex multi-cloud, multi-vendor setups. OSS architectures in telecom are adopting observability tools to ensure visibility into APIs, orchestration layers, and user journeys – moving beyond traditional monitoring to proactive performance assurance.
AIOps and Autonomous Operations
AI in telecommunication industry is being used to detect anomalies, predict failures, and even trigger self-healing workflows. AIOps platforms are becoming central to next-gen future trends in telecom OSS architecture – handling everything from alarm noise reduction to closed-loop assurance. Combined with intent-based networking, they bring us closer to autonomous network operations.
Ready to sync your OSS transformation with the latest trends? Let’s make it happen—fast.
How Appinventiv Can Accelerate Your Path to Future-Readiness in Telecom
As telecom networks grow in complexity, customer expectations evolve, and technologies like 5G, IoT, and AI reshape service delivery, OSS architecture stands at the heart of this transformation. It’s no longer just a behind-the-scenes enabler – it’s the innovation engine that empowers telcos to operate smarter, scale faster, and compete globally.
The shift toward cloud-native, modular, and AI-augmented OSS isn’t just a technical upgrade – it’s a strategic imperative. From improving service assurance and network automation to driving agility in a multi-vendor environment, OSS holds the blueprint for next-gen operational excellence.
Whether you’re modernizing legacy systems, planning a new architecture model, or navigating OSS/BSS convergence, choosing the right telecom software development services partner like Appinventiv can accelerate your path to future-readiness. Let us look at the various ways through which we, at Appinventiv can accelerate achieving future readiness.
- Custom OSS Development: We create modular and cloud-native OSS with microservice architecture. OSS design is cloud-ready and adaptable to 5G and IoT workloads because of its open APIs.
- AI and Automation Integration: Implementing AI alongside OSS is part of the strategy to perform predictive analytics, automated fault detection, as well as intelligent dynamic resource allocation. This strategy is focused towards lowering dowtime while improving service assurance as well as network performance.
- Adopting Cloud-Native Technologies: We will assist telecom companies to migrate to the cloud-native OSS architectures to support scaling on-demand, operational cost automation, and acceleration of time to market.
- Supporting Operations Remotely: We stand with customers through every step of OSS transformation providing strategic and consulting services alongside developing, testing, and maintaining the system for infrastructure and platform services, enabling us to execute agile OSS development and to propagate constant change.
Ready to transform your telecom operations? Partner with us and take the first step toward a future-ready OSS architecture today.
FAQs.
Q. What is OSS in telecommunications?
A. OSS refers to the software tools telecom providers use to manage, monitor, configure, and optimize their networks and services. It supports service provisioning, network management, fault detection, and performance assurance.
Q. What are some common challenges in OSS?
A. Some key challenges include integrating with legacy systems, managing multi-vendor environments, ensuring data accuracy, achieving real-time visibility, and aligning OSS with fast-changing customer demands and technologies like 5G or IoT.
Q. How is OSS different from BSS?
A. While OSS focuses on network operations and service management, BSS (Business Support Systems) handles customer-facing activities like billing, CRM, and order management. Together, OSS and BSS enable end-to-end service delivery and lifecycle management.
Q. Why are telecom operators modernizing their OSS?
A. Legacy OSS systems are often rigid, siloed, and costly to maintain. Modernization allows operators to gain agility, reduce manual tasks, launch services faster, and adopt AI, automation, and cloud-native technologies to stay competitive.
Q. Can OSS help improve customer experience?
A. Absolutely. A modern OSS enables faster service provisioning, quicker fault resolution, proactive performance monitoring, and personalized offerings – all of which contribute to a smoother, more responsive customer experience.
Q. What should I look for in a Telecom Software Development Services partner?
A. Look for deep telecom domain expertise, experience with cloud-native and modular architectures, open API capabilities, integration know-how, and the ability to build secure, scalable OSS solutions tailored to your business goals.
Q. How long does it take to transform an OSS environment?
A. The timeline depends on the complexity of your existing systems, desired scope (full replacement vs. phased transformation), and integration requirements. A skilled software partner can help you prioritize quick wins while planning long-term evolution.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

The Growing Threat of Telecom Fraud and How to Safeguard Your Business
Key takeaways: Telecom fraud continues to surge, with global losses now exceeding $1.03 trillion. Scams such as SIM swapping, subscription fraud, and call termination fraud are becoming increasingly sophisticated by the day. Getting ahead of fraud with solid detection and prevention systems isn't optional anymore—it's absolutely critical. Companies need to invest in AI-powered fraud detection…

Telecom Billing Software Development - Benefits, Features, Process, Costs
The world runs on connectivity. Whenever someone taps their phone to stream, pay, or simply scroll, they trigger a chain reaction across a highly complex telecom infrastructure that processes, tracks, and bills their usage in real time. Behind these seemingly instant transactions lies a sophisticated ecosystem of telecom billing software. The Telecom Billing and Revenue…

How Much Does It Cost to Develop a Telecom App Like My WE?
When it comes to the Egyptian markets, My WE is the undisputed titan, ruling the telecom sector with its unparalleled features and widespread user adoption. With its growing popularity, the app has become a benchmark for telecom applications, captivating users with its intuitive design and robust capabilities. As businesses and entrepreneurs set out to create…