- How Does Biometrics in Banking Work?
- Types of Biometric Technologies Used in Digital Banking
- Fingerprint, Facial and Retinal Recognition
- Behavioral Biometrics in Banking
- Voice Biometrics in Banking
- Palm and Iris Vein Recognition
- Multimodal AI and Continuous Authentication Models
- Strategic Advantages of Biometrics in Modern Banking
- Better Identity Protection
- Secure Banking with Biometric Device Controls
- Improved Customer Experience
- Operational Efficiency and Measurable Cost Impact
- Fraud Detection and Constant Monitoring
- Audit Readiness and Regulatory Alignment
- Use Cases of Biometrics in Banking
- Customer Onboarding and eKYC
- ATM Authentication
- Mobile Banking Access and Transaction Approval
- Call Center and Voice Verification
- Continuous Monitoring and Behavioral Analysis
- Steps for Biometric Banking Implementation
- Assess Risk and Channel Exposure
- Select Biometric Authentication Methods
- Strengthen Device and Infrastructure Security
- Align with Banking Software Development and Core Systems
- Pilot, Monitor, and Refine Governance
- Key Risks and Mitigation Strategies in Biometric Banking
- Information Privacy Risk and Governance Control
- Customer Trust and Public Perception
- Technical Integration and Infrastructure Gaps
- Machine Reliance and Hardware Restraints
- Future Trends in Biometric Authentication
- AI-Enhanced Biometric Banking
- Decentralized Biometric-based Digital Identity
- Biometric Cryptography
- Biometric Federated Learning
- Ongoing Risk-Based Identity Scoring
- Biometric Authentication in Embedded Finance Ecosystems
- Digital Signatures of Smart Contracts with Biometrics
- Biometric Security Models Resistant to Quantum Attacks
- Appinventiv’s Framework for Secure Biometric Banking Applications
- FAQ’s
Key takeaways:
- Biometrics in digital banking enhances both security and user convenience, reducing the need for weak passwords and PINs that can be easily compromised.
- Top biometric methods include fingerprint, facial, voice, and iris recognition, with each one bringing its own special benefits for secure login processes.
- Using biometrics makes customer onboarding smoother, enables easy re-authentication, and helps prevent fraud and unauthorized access.
- While biometrics make things more secure, banks still need to address risks such as data breaches and deepfake attacks by combining biometric methods with robust data protection strategies.
When Bank of America introduced biometric authentication across its mobile banking platform, it did more than streamline logins. It signaled a shift in how digital identity would be managed in financial services. For decades, banks relied on passwords, PINs, and layered security questions. Those measures worked until fraud grew more sophisticated and customers moved almost entirely to mobile channels, thus entering into the phase of biometrics in banking.
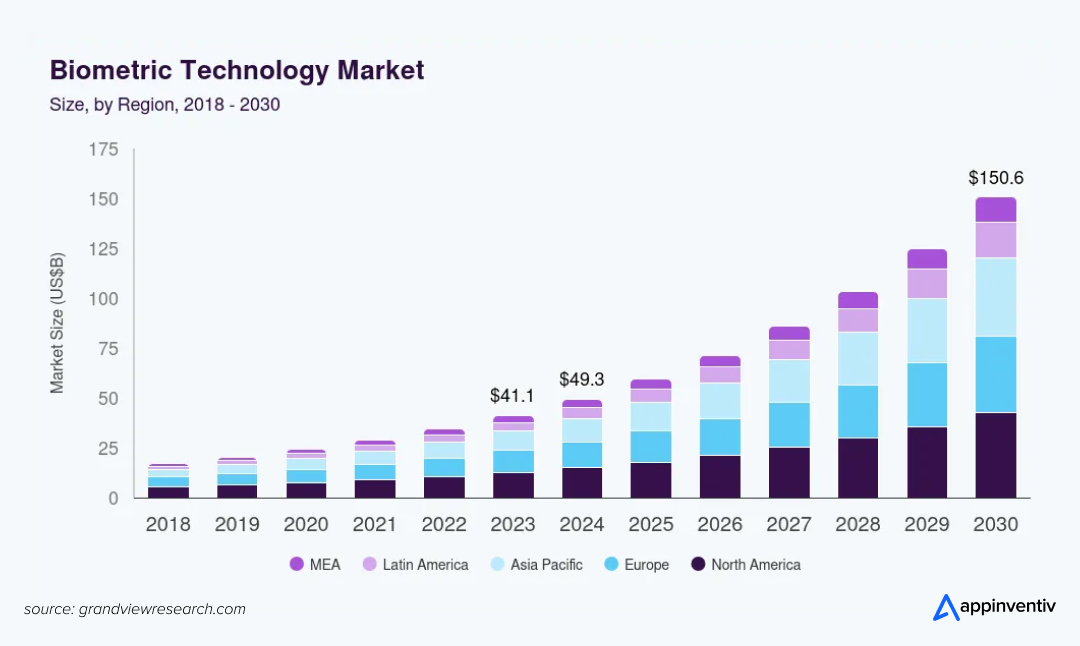
Somewhere in the middle of that transition, the numbers began to tell a clear story. The global biometrics market is projected to reach roughly $150.58 billion by 2030, with financial institutions contributing a substantial portion of that expansion. (Source: GVR)
Identity fraud continues to rise, while mobile banking adoption shows no signs of slowing. In developed markets, more than seventy percent of customers now prefer digital platforms for routine transactions. Authentication, in that setting, cannot remain static.
Bank of America responded by embedding fingerprint and facial recognition directly into its mobile experience. Access takes seconds. High-value transfers and account changes rely on the same biometric confirmation, reducing exposure to phishing and credential reuse.
This is not a single bank’s experiment. It reflects a broader recalibration of trust in digital banking. In this blog, we will examine how biometric systems are reshaping authentication standards, what technologies underpin them, and why financial institutions are treating identity as infrastructure rather than a feature.
We can guide you in integrating advanced biometric layers for safer, smarter financial services
How Does Biometrics in Banking Work?
Modern biometric security systems enable blockchain-powered digital identity verification and authorization. They are powered with special software that processes collected data and utilizes dedicated scanners, which can be small or large depending on the data type required.
To start the process, a scanner captures biometric information, converts it into a digital format, and matches it to an existing database. If the samples match, the user is granted access; otherwise, access is denied, or an appropriate message is displayed to a system operator. This makes passwords redundant by introducing certain biometric security measures instead.
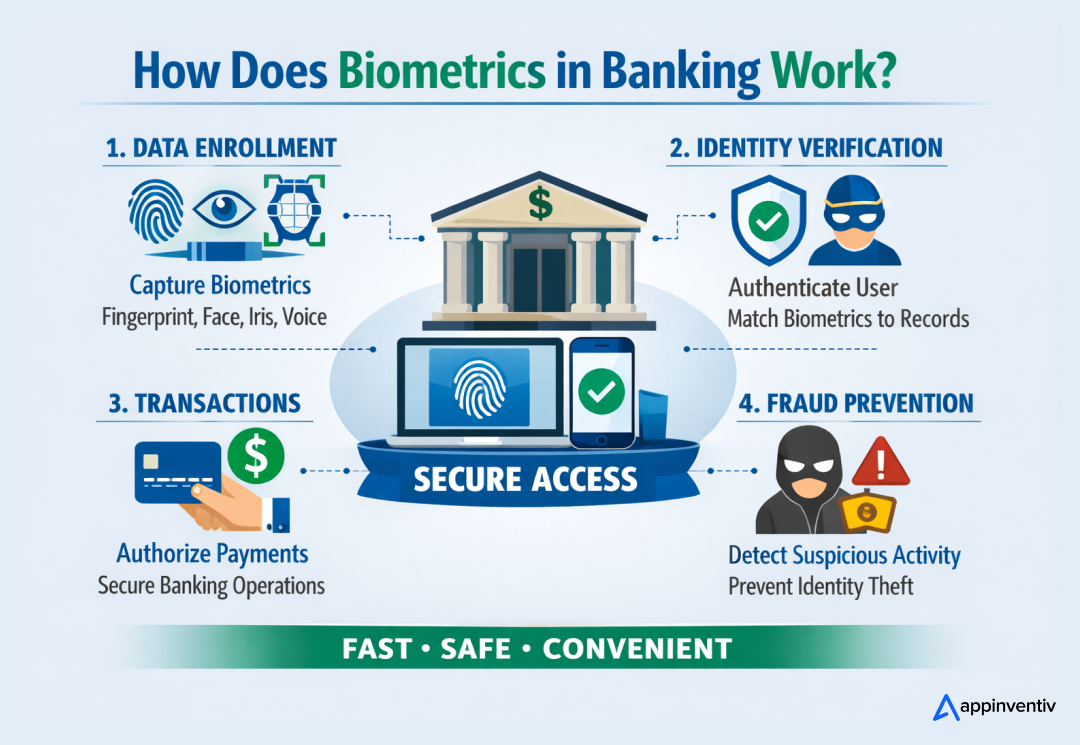
In practice, successful deployment is based on three organized phases, namely enrollment, secure storage, and comparison. Enrollment is the first identifier that is taken under controlled circumstances. Storage protects the encrypted template against fraudulent access. Comparison is used to validate identity whenever a user is authenticated.
The management of these factors ensures that biometric systems enhance security in the banking institution’s operations and also make it easier for banking consumers.
Types of Biometric Technologies Used in Digital Banking
Biometric authentication verifies user identities and authorizes specific users by leveraging unique physiological and behavioral characteristics, thereby enhancing security and the user experience in digital banking. Here are a few types of biometric technologies utilized in digital banking:
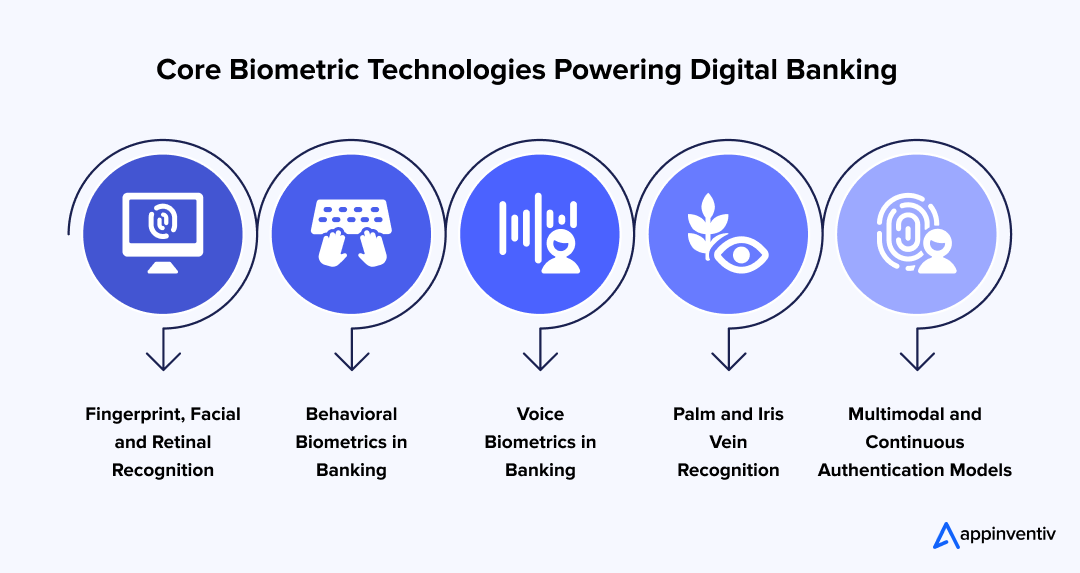
Fingerprint, Facial and Retinal Recognition
Fingerprint and facial recognition are the most noticeable biometrics in banking. The mobile apps are unlocked by scanning a device-bound fingerprint or by facial recognition, reducing the need for customer passwords.
The retina and iris scans are not prevalent in consumer banking but are used in high-security settings where tighter access controls are needed. These physical identifiers are difficult to copy and provide high verification accuracy. Consequently, banks use them in the areas of login flows, payment approvals, and controlled access to the facility.
Also Read: Benefits of Facial Recognition Software Development
Behavioral Biometrics in Banking
Another specific branch of biometric technology in banking is behavioral analytics. Rather than assessing the physical features, it assesses typing rhythm, swipe pressure, speed of navigation, and patterns of device handling.
The biometric technology runs and identifies anomalies that can be attempted to steal accounts. Since it operates in the background and makes no noise, it enhances fraud monitoring without disturbing users. Behavioral models are of particular value in remote and high-volume digital settings.
Voice Biometrics in Banking
Call centers increasingly rely on biometric authentication for banking through voice recognition systems. Customers do not have to answer several security questions, but can talk normally as the system analyzes tone, pitch, and patterns of their speech.
Voiceprints are checked against existing templates in real time, reducing average processing time and enhancing fraud protection. Voice verification is also increasing in conversational banking apps and virtual assistants as more banking businesses are now going for AI-powered voice agent development.
Palm and Iris Vein Recognition
High-tech features like palm and iris scanning are also an extension of the biometric authentication in mobile banking and branch environments. Iris recognition uses the distinctive patterns of the eye, and palm vein recognition identifies internal veins using infrared light.
They are both very resistant to spoofing and can be used in high-assurance applications, such as secure branch access and specialized financial transactions.
Multimodal AI and Continuous Authentication Models
In the new biometric banking approaches, multimodal AI is integrated into cohesive systems. Fingerprint information can be overlaid with behavioral analytics or facial recognition and contextual risk grading.
Banking biometric authentication can be enhanced by continuous surveillance, which helps evaluate user activity throughout a session rather than just at the beginning. This dynamic strategy minimizes the false acceptance while ensuring an uninterrupted customer experience over online platforms.
Strategic Advantages of Biometrics in Modern Banking
The move toward biometric identity controls is no longer at the experimental stage. It indicates the shift in structure through digital channels, fraud management structures, and customer demands. The following are the fundamental advantages of biometrics in banking, analyzed at both operational and strategic levels.
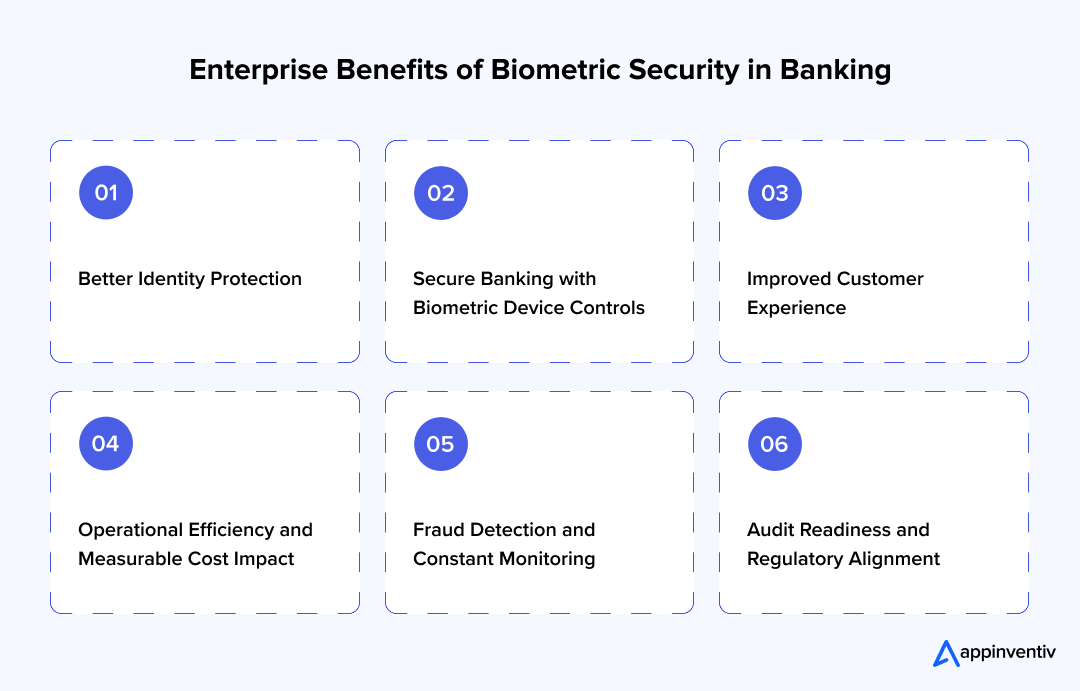
Better Identity Protection
A very common example of the use of biometrics in banking is the replacement of passwords with physical or behavioural identification parameters. Facial mapping, iris scans, voiceprints, and fingerprints are intrinsically tied to individuals and are much more difficult to duplicate than knowledge-based credentials.
This lessens exposure to phishing, credential stuffing, and account takeover attempts, especially in high-volume online settings.
Secure Banking with Biometric Device Controls
Modern smartphones and banking terminals support secure banking with biometric device authentication through encrypted hardware modules. Biometric data are not spread across the open networks, but stored in security enclaves.
A constrained architecture enabled by encryption technology reduces the attack surface and provides greater end-to-end verification without requiring additional effort from the customer.
Improved Customer Experience
Biometric authentication in banking streamlines login and transaction approval processes. Customers do not have to memorize complicated access passwords and use physical tokens.
Through a fingerprint scan or facial verification, a user can gain access within a few seconds. The decreased friction triggers the adoption of digital and decreases the rate of logging out, particularly in the mobile banking development ecology.
Operational Efficiency and Measurable Cost Impact
With more banks using biometric technology to replace manual verification and redundant security questions, the call center handling time is lower, and there are fewer password reset requests.
Implementation costs normally fall within a range of $40,000 to $300,000, depending on the scale and complexity of the integration, but the long-term benefits of reduced fraud losses and reduced operational workload tend to equalize the investment.
Fraud Detection and Constant Monitoring
Physical identifiers are now supplemented by behavioral analytics across biometrics in the financial services sphere. The systems assess typing speed, swipe patterns, and session behavior to identify anomalies in real time.
This stratified model enables institutions to step in at an early stage, where financial losses are minimized before fraudsters go too far.
Also Read: AI Agents for Fraud Detection in Financial Services
Audit Readiness and Regulatory Alignment
Biometric controls provide better identity verification than conventional password systems. Compliance reporting and audit requirements are facilitated by detailed authentication logs.
With regulators placing increased focus on digital identity, biometric verification systems offer a more robust, regulated multi-factor authentication option.
Use Cases of Biometrics in Banking
Biometric identity systems are now part of everyday financial operations rather than limited pilots. They support onboarding, transactions, and fraud monitoring across channels. The following examples show how institutions apply biometric controls in practical settings.
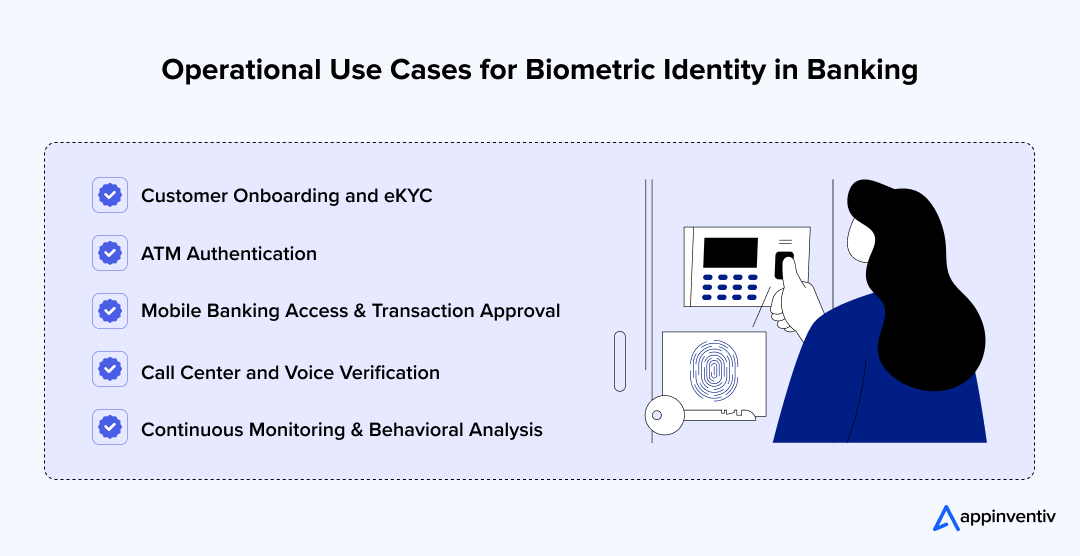
Customer Onboarding and eKYC
One of the most established examples of biometrics in banking is remote onboarding. Customers submit an identification document and complete a live facial verification through their smartphone. The system checks facial features against the document and performs liveness detection to prevent spoofing. This reduces branch dependency and accelerates Know Your Customer (KYC) automation compliance. Account activation that once required days can now occur within minutes.
ATM Authentication
Physical terminals are also evolving through biometric technology in banking. Many ATMs now combine PIN entry with fingerprint or facial recognition, while some pilot programs eliminate cards entirely. Biometric verification reduces card skimming risk and strengthens identity confirmation at the machine. Transactions become quicker and less dependent on memorized credentials.
Mobile Banking Access and Transaction Approval
The expansion of biometrics in digital banking is most visible in mobile applications. Customers log in using fingerprint or facial recognition and approve transfers through device-bound verification. For higher value payments, additional biometric confirmation may be required. This layered structure reduces password reliance while maintaining transaction integrity.
Call Center and Voice Verification
In call center environments, biometric banking often relies on voice recognition. Instead of answering multiple security questions, customers are verified through vocal characteristics such as tone and speech pattern. This shortens verification time and limits exposure to social engineering tactics.
Continuous Monitoring and Behavioral Analysis
Advanced biometric authentication methods now extend beyond login events. Behavioral systems monitor typing speed, swipe patterns, and navigation behavior during active sessions. If activity deviates from established norms, the system can trigger additional checks. This ongoing verification strengthens fraud detection without interrupting legitimate users.
Steps for Biometric Banking Implementation
Rolling out biometric capability inside a bank is rarely a straight path. It involves risk officers, compliance teams, engineers, and operations staff, all working through practical constraints. Here are the critical steps for biometric technology in banking:
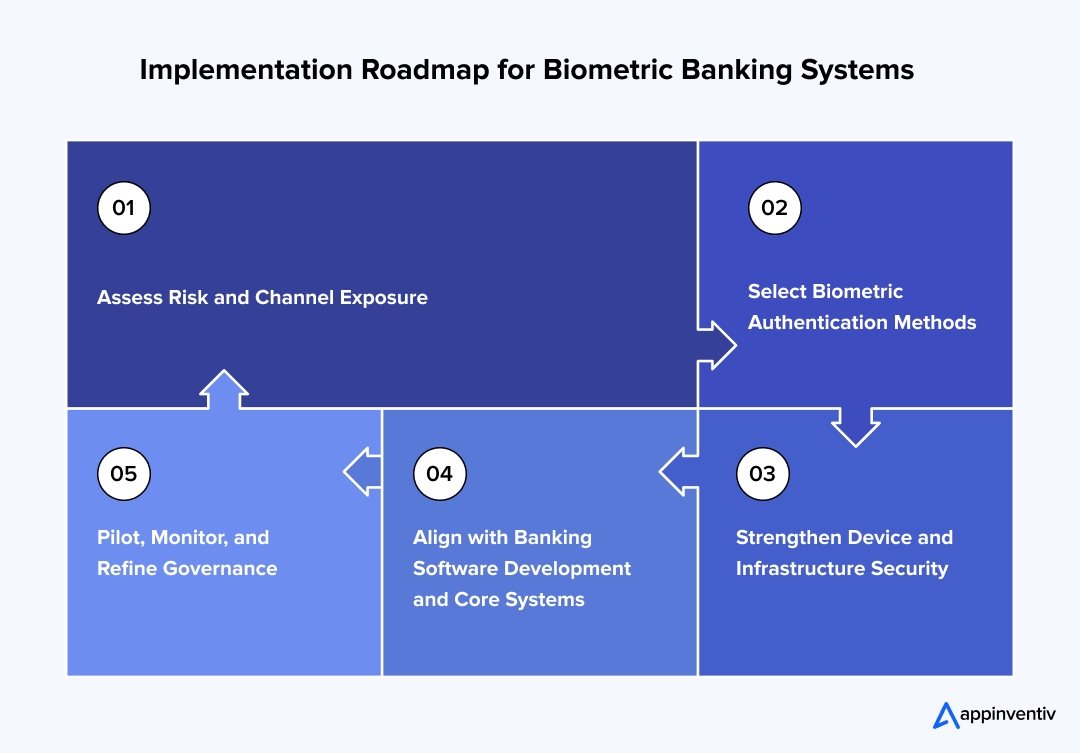
Assess Risk and Channel Exposure
Any serious move toward biometrics in digital banking starts with examining where identity controls are failing. Fraud reports, account takeover cases, login abandonment rates, and transaction disputes offer concrete evidence. Teams review this data carefully and identify which digital touchpoints require stronger verification.
The objective is not broad deployment, but targeted correction. When risk patterns are clearly understood, investment decisions become grounded in operational reality rather than industry trends.
Select Biometric Authentication Methods
Introducing biometric authentication in banking requires a thoughtful selection of appropriate methods. Fingerprint and facial verification often fit mobile ecosystems because devices already support them at the hardware level. Voice recognition aligns with call center workflows, while behavioral analysis can operate quietly across digital sessions.
Institutions compare error rates, spoof resistance, user acceptance, and regional privacy expectations. The choice is rarely technical alone. It reflects customer habits, regulatory climate, and transaction sensitivity.
Strengthen Device and Infrastructure Security
To support secure banking with biometric device environments, the infrastructure must be carefully prepared. Biometric templates should remain encrypted within hardware-backed storage areas rather than moving freely across networks.
Identity servers, API layers, and monitoring systems must align with the new verification logic. Technical teams test integration under real transaction loads. If latency rises or verification fails under scale, adjustments are made before public rollout.
Align with Banking Software Development and Core Systems
No biometric program succeeds without coordination with banking software development services teams. Authentication layers must connect smoothly with core banking systems, fraud monitoring engines, and customer data repositories.
Engineers review legacy architecture to prevent bottlenecks or security gaps. Testing cycles often reveal unexpected dependencies. These are resolved gradually, not hurriedly. Careful alignment at this stage reduces operational disruption later.
Pilot, Monitor, and Refine Governance
Before full deployment, institutions conduct structured pilots. Performance is measured through login success rates, fraud reduction trends, and customer feedback. Adjustments follow real-world results rather than theoretical benchmarks.
Governance frameworks are then formalized, covering consent management, data retention, and audit oversight. Biometric integration becomes sustainable only when technical controls and policy discipline move in step.
Key Risks and Mitigation Strategies in Biometric Banking
Biometric systems enhance identity control, but their implementation is usually beset by practical challenges. Below are some of the challenges and considerations in biometric banking.

Information Privacy Risk and Governance Control
One of the most crucial issues in biometrics in banking is sensitive identity information. It is impossible to reissue fingerprints, facial templates or voiceprints like passwords in case they are exposed. These regulatory authorities thus have stringent requirements for consent, storage, and retention.
Solution: Banks overcome this risk by encrypting biometric templates in secure hardware modules and restricting data movement across networks. Well-defined consent protocols and audit trails help enhance compliance and build customer trust.
Customer Trust and Public Perception
The wider application of biometrics in financial services has raised concerns about surveillance and abuse. Not all customers are willing to provide a facial scan or voice sample, or rather, there is no clarity in the data-handling process. Even in cases when the security benefits are apparent, low trust can slow adoption.
Solution: Open communication is helpful. Banks elaborate on how data is stored, the duration of storage, and why data storage enhances security. The resistance can be alleviated by providing opt-in models at an early stage, as confidence is built over time.
Technical Integration and Infrastructure Gaps
Weaknesses in the traditional core system are manifested by the use of biometrics in banking. Older authentication servers might not be easily compatible with current biometric engines. Latency issues, API limitations, and transaction processing conflicts may manifest during the test.
Solution: Institutions can normally implement biometric layers in small chunks, starting with mobile channels and then moving to core integrations. Strenuous pre-deployment testing and incremental rollout reduce operational strain.
Machine Reliance and Hardware Restraints
The quality of the hardware used by customers is key to ensuring secure banking with a biometric device. Advanced biometric sensors are not supported by all devices, and environmental factors, such as lighting or noise, can affect performance.
Solution: Banks implement fallback processes, e.g., step-up verification or 2nd-factor authentication. Having alternative access paths will maintain continuity and will not compromise the overall security posture.
Our team turns these challenges into secure solutions that work from day one
Future Trends in Biometric Authentication
As technology advances, businesses are adopting innovative biometric solutions to improve authentication and protect sensitive data. Let’s check out some of its key trends:
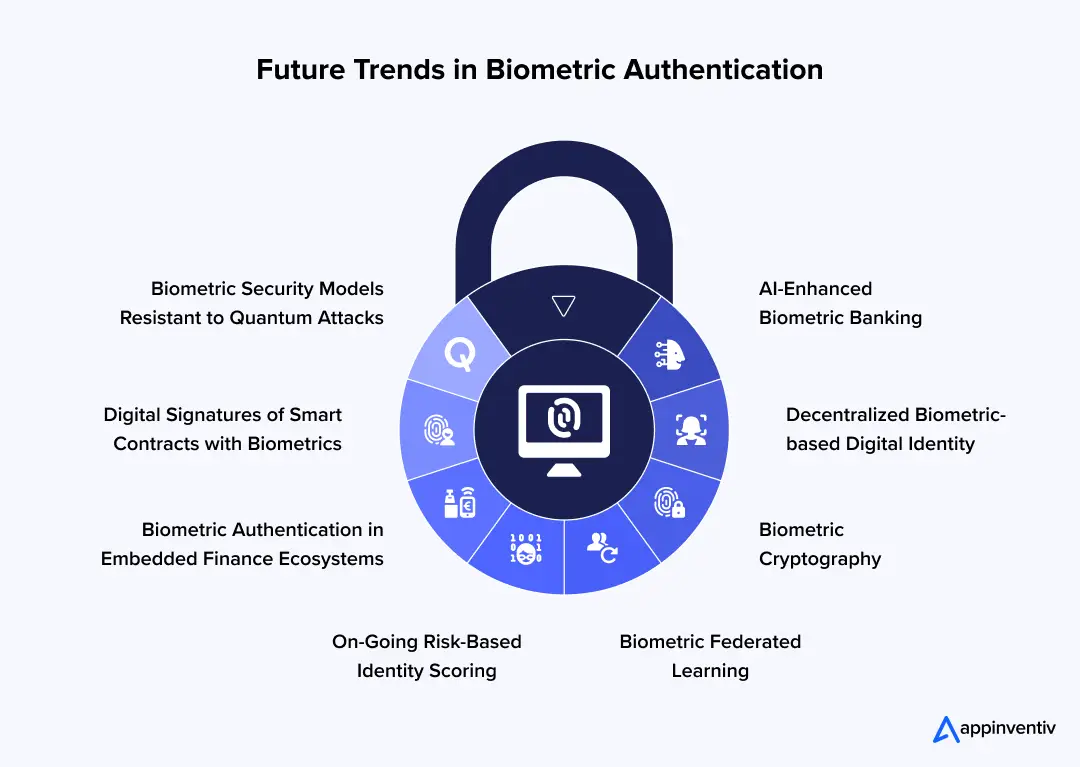
AI-Enhanced Biometric Banking
Artificial intelligence is increasingly being integrated with biometric systems in banking. AI models analyze patterns in biometric and behavioral data to detect anomalies, predict fraud, and improve authentication accuracy in real time. With increased adoption and advanced usage of AI in banking processes, financial institutions can adapt dynamically to evolving threats while providing a seamless and secure user experience.
Decentralized Biometric-based Digital Identity
Banks are considering identity structures, whereby biometric credentials exist in the form of decentralized identity or blockchain wallets as opposed to central databases. This lowers the exposure of breaches in large scale and provides customers with higher control of their digital identity between institutions.
Biometric Cryptography
The next generation will move towards tying biometric data to cryptographical keys without having the raw biometric templates stored. Homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation are among the techniques that are used to check identity without revealing sensitive biometric information.
Biometric Federated Learning
Federated learning enables biometric systems to learn directly on user devices as opposed to being trained on centralized datasets. This method enhances privacy by continually improving authentication performance.
Ongoing Risk-Based Identity Scoring
Authentication will cease to be one-time verification, but persistent identity scoring will be the order of the day. The dynamism in determining transaction risk will involve the evaluation of biometric signals, contextual data and behavioral inputs in real time.
Biometric Authentication in Embedded Finance Ecosystems
With the integration of financial services in non-banking solutions, biometric authentication will no longer be confined to the banking app but to commerce applications, mobility solutions, and IoT-based payment devices.
Digital Signatures of Smart Contracts with Biometrics
With smart contracts, biometric inputs could be utilized to activate legally binding financial systems based on blockchain. This may re-establish consent, approval and validation of high-value transactions.
Biometric Security Models Resistant to Quantum Attacks
As quantum computers continue to advance, banks are studying post-quantum cryptography combined with biometric authentication to shield long-term identity credentials against future threats to computation.
Appinventiv’s Framework for Secure Biometric Banking Applications
In the financial services industry, biometrics is gradually transforming the design and delivery of digital products by fintech companies. The patronage of identity controls is not merely about preventing fraud. They minimize operational waste, reduce onboarding time, and facilitate compliance procedures. Biometrics in digital banking is a viable and scalable option for organizations that need to verify users faster and more securely.
This change is reflected in the portfolio of Appinventiv. For the Mudra project, an AI-based budget management application, the team designed a smart financial assistant capable of processing sensitive user information within a robust, scalable framework.
Our team also created a secure environment in Edfundo, a financial literacy and prepaid card ecosystem, to enable responsible digital finance to families, in which verifiable identity and controlled access are fundamental.
For a large, European-based banking institution, we introduced advanced AI solutions for customer engagement and predictive analytics. Such undertakings require enterprise-level authentication systems, in which biometric layers can enhance the integrity of logins and transaction authentication.
Equally, in Slice, a real estate investment business where people can invest by owning a fraction, we implemented secure financial flows as the core of their product design.
As financial services further develop into smart, secure digital formats, the consideration of biometrics will be a core, not an optional, part of their offer. Those organizations that choose the right technical partner or fintech software development company during the transition will be in a better position to build trust, improve efficiency, and continue expanding in the long term.
Get in touch with our experts today to learn more about the potential benefits of implementing biometrics in banking and ways to integrate the same within your existing systems.
FAQ’s
Q. What is biometrics in banking?
A. Biometrics is an integral element of digital banking. This technology uses physical and behavioral characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, to identify customers and grant them access to their accounts through online channels. It provides an added layer of security while delivering a positive user experience. Biometric authentication in banking helps curtail fraud and improve overall banking safety.
Q. How secure is biometric authentication in digital banking?
A. Biometric authentication provides improved security compared to the traditional password-based approach in the digital banking sector. Despite this enhanced protection, biometric data might still be vulnerable to theft or manipulation, as successful attacks have occurred.
Q. Can biometric authentication replace passwords completely?
A. No. Biometrics improve security and convenience, but cannot be reset if compromised. Banks use them as part of multi-factor authentication alongside PINs or tokens.
Q. How does biometric authentication function inside banking applications?
A. Here’s how biometric authentication works inside banking applications:
- The user registers a finger, face or voice sample in the banking app
- Biometric authentication in mobile banking protocols transforms the trait into an encrypted mathematical template by the system
- The live scan is compared to the stored template during login or transaction validation
- Once the match score reaches the threshold, uncovered biometric data is not exposed, and access is granted
Q. Why are banks adopting the use of biometric authentication?
A. Biometric authentication in banking is used to enhance identity verification and provide convenience for users. Biometric traits cannot be easily guessed or shared, as is the case with passwords. This reduces account takeovers, reduces fraud-related losses, and enhances customer confidence. It is also in line with regulatory requirements for enhanced digital security controls across online and mobile channels.
Q. In what ways do biometrics reduce financial fraud?
A. Here are some of the smart ways in which biometric technology reduces the risk of financial fraud:
- Biometric technology in banking links transactions directly to a verified physical characteristic, making impersonation difficult.
- Fraudsters cannot imitate fingerprints or facial patterns on a large scale.
- Real-time identity validation will prevent phishing and credential stuffing.
- Together with behavioral analytics, biometrics develop layered protection
- It also minimizes unauthorized access and enhances the integrity of transactions on digital platforms.
Q. What can biometric authentication provide to help with AML and KYC?
A. Biometrics in financial services can aid in AML and KYC by ensuring that the identity of a customer matches the official records during the onboarding and occasional validation. Identity spoofing is prevented by facial recognition and liveness detection. This enhances audit tracks, synthetic identity fraud, and adheres to regulatory requirements without slowing down customer acquisition.
Also Read: AML Software Development
Q. What are the trends defining the future of biometrics in online banking?
A. Here are some of the top trends that define the future of biometrics in banking:
- Greater application of multimodal systems that integrate the use of fingerprints, faces and voice recognition
- Expansion of behavioral biometrics to monitor typing rhythm and the device interaction patterns
- Better encryption models that embrace privacy-first models
- Deepfake countermeasure using AI to detect liveness
- Contactless identity verification expansion was in line with the biometrics banking
Q. What are common examples of biometric security used in banking?
A. Here are some of the common biometric authentication examples:
- Fingerprint recognition for account login and payment approval in biometric banking platforms
- Digital onboarding, as well as remote verification through facial recognition
- Banking high security iris scanning
- Call center authentication by voice recognition
- Behavioral biometrics analyzes typing speed, swiping patterns, and device handling


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Open Banking in Australia: A Practical Guide for Businesses
Key takeaways: Open banking-driven “Smart Data” initiatives are projected to contribute up to $10 billion annually to the Australian economy. Enterprises that follow a phased rollout covering readiness assessment, compliance alignment, API integration, cybersecurity, and scaling achieve faster deployment and lower operational risk. Constant CDR updates, accreditation complexity, and modernising legacy banking systems continue to…

Financial Wellness App Development: Process, Features and Costs
Key Takeaways Strategic ROI: Financial wellness apps are no longer "perks"; they are critical tools for reducing financial presenteeism and improving institutional retention. Technical Integrity: Successful deployment requires seamless integration with Human Capital Management (HCM) systems and secure Open Banking APIs. Compliance-First: Enterprise-grade solutions must prioritize SOC2, GDPR, and ISO 27001 standards to protect sensitive…

Money Transfer App Development: Building Secure Payment Apps in 2026
Key Takeaways Money transfer apps in 2026 succeed when compliance, security, and scalability are designed into the platform from day one, not added later. Choosing the right app type early helps avoid costly rework as transaction volumes, regions, and regulatory demands increase. Strong internal ledgers, clear settlement states, and automation are critical to preventing reconciliation…