- First Things First: What Kind of App Is This?
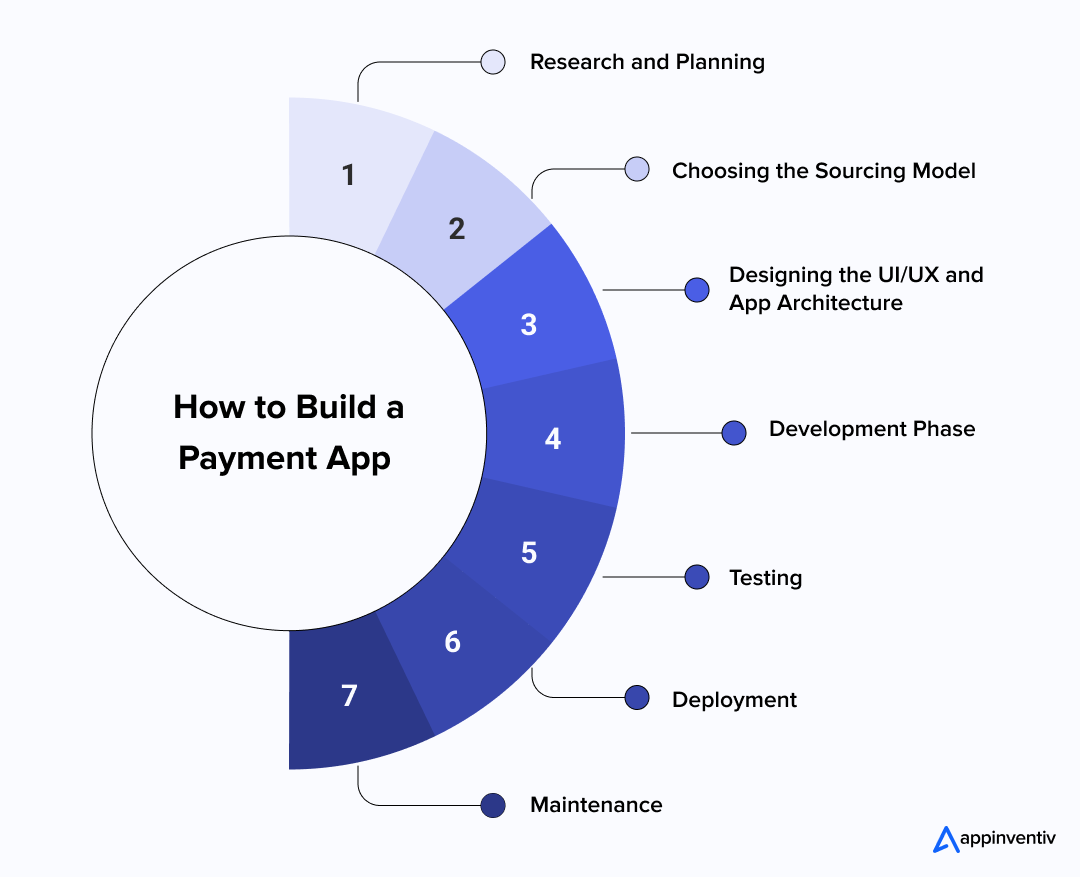
- How to Create a Payment App: A Step-by-Step Process
- Research and Planning
- Choosing the Sourcing Model
- Designing the UI/UX and App Architecture
- Development Phase
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance
- Key Features of a Payment Application: What's Essential and What's Just Noise
- The Absolute Must-Haves
- The "Advanced" Features that Make a Difference
- Choosing the Right Technology Stack for Payment App Development
- Frontend Development
- Backend Development
- Security Technologies
- APIs and Payment Gateways
- The Non-Negotiable: Security and Compliance
- PCI DSS Compliance
- Data Encryption
- Fraud Detection
- Regular Security Audits
- Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Insuring Security and Compliance in Payment Application Development
- Mobile Payment App Monetization Models
- Transaction Fees
- Interchange Fees
- Premium Features
- Interest and Investment Income
- Advertising and Partnerships
- Subscription Services
- Challenges & Solutions in Building a Payment App
- Regulatory Compliance
- Security Threats
- User Trust and Adoption
- Technical Integration Complexity
- Talent Acquisition
- How Much Does It Cost To Make a Payment App
- Ongoing Costs
- Current & Future Trends in Payment Apps
- Current Trends
- Emerging Technologies
- Future Predictions
- Why Build a Payment App with Appinventiv?
- FAQs
- The digital payment market is a massive revolution, creating a massive opportunity for businesses and entrepreneurs.
- Security is a must. PCI DSS compliance, data encryption, biometrics, advanced fraud detection, and scalable tech stack are non-negotiable.
- The cost of payment app development ranges between $40,000 and $400,000 for basic to advanced apps. For enterprise-grade apps, the cost can exceed even $600,000.
- Monetization models and user experience must be part of your plan from day one to ensure long-term success.
- The future of payments is intelligent, driven by AI, biometrics, and real-time processing.
In 2024, US consumers used proximity mobile payments totaling $670.5 billion, with projections showing this will exceed $1 trillion by 2027. Apple Pay processed over $6 trillion in transactions during 2023 alone. That’s more than the GDP of Japan, Germany, and the UK combined.
What’s remarkable is how mobile payments became the most common payment method in the US. 53% of Americans now use digital wallets more frequently than traditional payment methods.
That’s not gradual growth – it’s explosive adoption. Cash registers across America tell the same story. Walk through any major American city today and witness the transformation firsthand. From Starbucks in Manhattan to gas stations in Texas, customers reach for phones instead of wallets. Food trucks accept Venmo. Farmers’ markets take Square payments. Even street performers display QR codes for tips. Traditional payment methods are becoming the exception, not the rule.
This wasn’t always the case. Just five years ago, cash dominated most global markets. But COVID-19 changed everything. Today, the story is completely different. Two-thirds of adults worldwide now use digital payments, according to World Bank data. The market reached $114.41 billion in 2024.
The shift is accelerating rapidly. For businesses and entrepreneurs, this represents an unprecedented opportunity. But building payment apps that capture market share requires much more than basic transaction functionality. Security compliance, user trust, regulatory navigation – these factors determine success or failure.
This guide breaks down what successful mobile payment app development actually involves. We’ll examine market realities, security requirements, development costs, and monetization strategies. Whether you’re launching a fintech startup or integrating payments into existing operations, you’ll understand what it takes to build solutions that compete in today’s market.
First Things First: What Kind of App Is This?
Before you even think about building a digital payment app, you need to first evaluate, “What are your pain points?” “What problems are you solving? What type of payment app do you actually want?” The market is mushrooming with multiple types of apps, and each plays a different game, but it is full of opportunity if you find your right niche. Thus, this initial thinking is the most important part of your entire digital payment app development journey.
Here is a table outlining various types of payment applications and their specific functions to help you make an informed decision.
| Type of Payment App | Purpose | Payment Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Payment Apps | Allow users to send and receive money between individuals, often for personal transactions. | Venmo, PayPal, Cash App, Zelle |
| Mobile Wallets | Store payment methods (cards, bank accounts) for easier and faster transactions. | Apple Pay, Google Wallet, Samsung Pay |
| E-commerce Payment Systems | Enable businesses to accept payments for goods and services through an online store. | Shopify Payments, WooCommerce, Stripe |
| Cryptocurrency Payment Apps | Facilitate transactions using digital currencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. | Coinbase, Binance, BitPay |
| Buy Now, Pay Later Apps | Allow users to make purchases and pay later in installments. | Afterpay, Klarna, Affirm |
| Digital Banking Apps | Offer full banking services, including loans, investments, and payment services. | Revolut, N26, Monzo |
| Subscription Payment Apps | Manage recurring payments for subscription-based services. | Netflix, Spotify, Hulu |
| QR Code Payment Apps | Use QR codes to facilitate quick, contactless payments between buyers and sellers. | Alipay, WeChat Pay, Paytm |
| International Payment Apps | Enable cross-border transactions and currency conversions. | TransferWise, Remitly, WorldRemit |
| Charity Donation Apps | Allow users to donate money to charitable causes through their mobile phones. | GoFundMe, JustGiving, Charitable.org |
| Micro-payment Apps | Handle small payments, often for digital content like apps, music, or games. | Google Play, App Store, Steam |
| Utility Payment Apps | Facilitate payments for utilities like water, electricity, and internet bills. | Paytm, BillDesk, Biller Direct |
| UPI (Unified Payments Interface) | Facilitates real-time inter-bank payments, linking multiple bank accounts into one platform for fast, seamless transactions. | Google Pay, PhonePe, Paytm, BHIM |
| Super Apps | Offer a wide range of services beyond payments, including shopping, food delivery, social networking, and more, often with integrated payments. | WeChat, Grab, Gojek, Paytm (in India) |
Each type has totally different technical requirements, compliance needs, and user expectations. Your choice affects development complexity and how you’ll eventually make money.
Also Read: List of Top 7 Most Frequently Used Mobile Payment Apps
How to Create a Payment App: A Step-by-Step Process
Successful mobile payment app development follows a structured approach. Each phase builds on the previous one, creating a roadmap from concept to launch. Here are the key steps to create a payment app.
Research and Planning
Every successful business payment app starts with thorough research. Competition causes several startups to fall flat. Understanding your market prevents joining this statistic.
- Market Analysis identifies opportunities and gaps in existing solutions. What problems do current apps solve poorly? Where do users express frustration with existing options?
- User Research involves interviews, surveys, and behavioral analysis. Understanding how the target audience currently handles payments reveals insights shaping app design.
- Competitive Analysis examines existing solutions’ strengths and weaknesses. This research informs feature prioritization and helps identify differentiation opportunities.
- Technical Feasibility assessment evaluates whether your vision is technically achievable within budget and timeline constraints.
Choosing the Sourcing Model
Development approach significantly impacts both cost and timeline:
- In-House Development provides maximum control but requires significant investment in talent acquisition and retention. The need for engineers with blockchain, security, AI fraud detection, and compliance expertise can grow your overall payment app development cost significantly.
- Outsourcing reduces costs and provides access to specialized expertise. However, successful outsourcing requires careful vendor selection and project management, though. If you don’t know how to do it right, here is our blog for you: How to Outsource App Development in 2025
- The Hybrid Model combines in-house strategic oversight with outsourced specialized development. This approach is becoming increasingly popular for complex projects.
Designing the UI/UX and App Architecture
Great payment apps feel effortless to use. Users shouldn’t think about technology – they should focus on their task.
- User Experience Design starts with user journey mapping. How do users discover, onboard, and engage with your app? Each interaction should feel natural and necessary.
- User Interface Design translates experience into visual elements. Payment apps require clean, trustworthy designs communicating security and reliability.
- System Architecture defines how different components interact. Microservices architecture offers scalability advantages. Monolithic designs may be simpler for smaller applications.
Development Phase
Development typically follows agile methodologies with iterative releases:
- Backend Development creates server-side logic, database structures, and API endpoints. This foundation must be robust and secure from day one.
- Frontend Development builds the user interface and integrates with backend services. Careful attention to performance and security is crucial.
- Integration connects your app with payment processors, banking APIs, and third-party services. Each integration point requires thorough testing.
Testing
Payment apps require extensive testing due to security and financial implications:
- Functional Testing verifies all features work as intended across different scenarios and edge cases.
- Security Testing identifies vulnerabilities through penetration testing, code analysis, and infrastructure assessment.
- Performance Testing ensures the app performs well under expected load conditions.
- Compliance Testing verifies adherence to PCI DSS, financial regulations, and app store requirements.
Also Read: The Mobile App Testing Strategies that Appinventiv Follows
Deployment
Launching a payment app involves multiple considerations:
- App Store Submission requires compliance with platform-specific guidelines. Payment apps face additional scrutiny during the review process.
- Infrastructure Deployment involves setting up production servers, monitoring systems, and backup procedures.
- Regulatory Approval may be required depending on app functionality and target markets.
Maintenance
Payment apps require ongoing maintenance and updates:
- Security Updates address newly discovered vulnerabilities and threats.
- Feature Updates respond to user feedback and market changes.
- Compliance Monitoring ensures continued adherence to evolving regulations.
- Performance Optimization maintains app responsiveness as usage grows.
Schedule a free strategy session with our FinTech experts and get a custom roadmap for your secure payment solution.
Key Features of a Payment Application: What’s Essential and What’s Just Noise
You don’t need every feature under the sun. That just bloats the app and confuses users. What you need is lean, powerful and core features that engage users and drive real results. When we talk about key features of a payment application, we’re talking about trust.
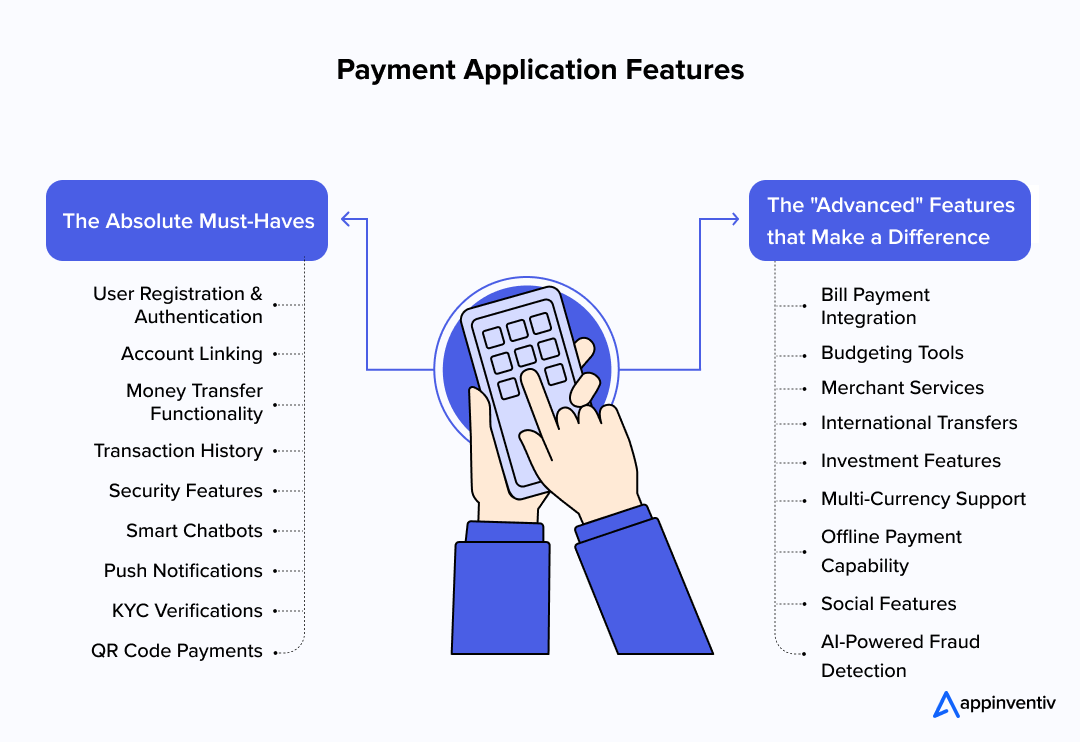
The Absolute Must-Haves
Every payment app absolutely needs these fundamental features to cater to the basic needs of targeted audiences.
- Account Linking connects bank accounts, credit cards, and debit cards securely. Involves API integration with financial institutions plus real-time verification. Users won’t trust apps that feel sketchy here.
- Money Transfer Functionality is your core value proposition. Users send, receive, and request money easily. Contact integration, payment history, and transaction confirmations all matter for adoption.
- User Registration and Authentication form your foundation. Email/phone verification, password setup, profile creation. Modern apps increasingly use biometric authentication because users expect it now.

- Security Features like PIN setup, two-factor authentication, and fraud monitoring aren’t optional anymore. Users must feel confident that their money stays safe.
- Transaction History gives users detailed records they can actually use. Search functionality, filters, and export options separate good apps from great ones.
- QR Code Payments enable contactless transactions everywhere. Users scan codes to pay at physical locations. Makes your app useful beyond peer-to-peer transfers.
- Push Notifications keep users informed about everything. This includes transactions, security alerts, and account updates. Real-time alerts build trust and engagement.
- Smart Chatbots handle basic questions instantly while human agents tackle complex issues. Users need instant help when money’s involved – make it easy to reach you.
- KYC Verification for identity confirmation meets regulatory requirements. Document upload, selfie verification, and address confirmation are standard now.
The “Advanced” Features that Make a Difference
Advanced payment apps include next-level functionality that drives users and increases their retention rates:
- Bill Payment Integration lets users pay utilities, rent, and recurring expenses directly. Drives daily engagement and keeps users coming back regularly.
- Merchant Services enable businesses to accept payments through your platform. Point-of-sale integration, inventory management, and sales analytics become revenue drivers.
- International Transfers expand utility for global users. Requires compliance with international regulations plus currency conversion capabilities.
- Investment Features allow buying stocks, bonds, and crypto directly from the payment balance. Transforms simple apps into comprehensive financial platforms.
- Offline Payment Capability works when the internet connection is spotty. Store transaction data locally and sync when the connection returns.
- Multi-Currency Support handles different currencies for international users and travelers. Real-time exchange rates and conversion fees transparency matter.
- Social Features like payment feeds, splitting bills with groups, and payment requests through social media integration. Makes payments feel more natural and social.
- AI-Powered Fraud Detection: You can’t just hope for the best. You need a system that’s smart enough to flag an unusual transaction before it goes through. This is the new standard for secure payment app development.
- Budgeting Tools help users track spending patterns and set financial goals. These features differentiate payment apps from simple money transfer utilities.
At Appinventiv, we partnered with Mudra to build a fully compliant and AI-driven budget management platform. Currently, this FinTech app is live in 12+ countries, allowing users to manage their budget efficiently.
Choosing the Right Technology Stack for Payment App Development
Tech decisions made early have a lasting impact on everything. The right tech stack ensures scalability, security, and maintainability for the long term. This isn’t just about picking popular tools; it’s about making the right decisions that can handle millions of transactions and will support your growth for years to come. Don’t know how to choose the right tech stack for payment app development? To help you choose the right one, here we have listed down the most popular and secure tech stack for mobile payment app development
Frontend Development
- Native Development offers the best performance and user experience possible. iOS uses Swift or Objective-C. Android uses Kotlin or Java. Provides full access to device features like biometric sensors and secure enclaves.
- Cross-Platform Frameworks like React Native or Flutter reduce development time and costs significantly. A single codebase works on both iOS and Android. Some platform-specific features may require native code, though.
- Progressive Web Apps work across all devices through browsers. Convenient but limited access to device-specific security features that payment apps often require.
Backend Development
- Programming Languages like Node.js, Python, and Java power server-side logic. Node.js offers excellent performance for real-time applications. Python provides extensive libraries for data processing and machine learning.
- Database Systems must handle transaction data securely and efficiently. PostgreSQL offers robust ACID compliance for financial data. MongoDB provides flexibility for user profile information.
- Cloud Infrastructure through AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure ensures scalability and reliability. These platforms offer specialized services for financial applications, including encryption and compliance tools.
Security Technologies
- Encryption protects data in transit and at rest. TLS/SSL secures data transmission. AES encryption protects stored information. End-to-end encryption ensures even service providers cannot access sensitive data.
- Tokenization replaces sensitive payment information with non-sensitive tokens. Reduces data breach risk significantly and simplifies PCI DSS compliance requirements.
- API Security includes rate limiting, authentication, and input validation. OAuth 2.0 and JWT tokens provide secure authentication mechanisms.
APIs and Payment Gateways
- Payment Processors like Stripe, Square, and PayPal handle complex credit card transaction processing. Provide APIs integrating with your app while handling PCI DSS compliance automatically.
- Banking APIs enable direct bank account integration. Open banking initiatives provide standardized APIs for account access and payment initiation.
- Third-Party Services for identity verification, fraud detection, and KYC compliance are often necessary for comprehensive payment applications.
Also Read: Payment Gateway Integration for Your App
The Non-Negotiable: Security and Compliance
Security isn’t optional in mobile payment app development. It’s the foundation everything else builds on. You are holding people’s money and their most sensitive information. This isn’t about avoiding a breach; it’s about being prepared for it. Security isn’t a feature; it is the product.
PCI DSS Compliance
Every business accepting credit card payments must comply with PCI DSS, regardless of volume, location, or integration method. This standard sets minimum requirements for protecting cardholder data.
The PCI DSS framework includes twelve key requirements in six categories:
- Build and Maintain a Secure Network. It requires firewalls and secure configurations. Change default passwords. Disable unnecessary services.
- Protect Cardholder Data mandates the encryption of stored data and protection during transmission over public networks. Merchants should only store data they need and dispose of it when no longer required.
- Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program that includes regular security updates and antivirus software on all systems handling cardholder data.
- Implement Strong Access Control that restricts cardholder data access to a need-to-know basis. Requires unique user IDs for everyone with computer access.
- Regularly Monitor and Test Networks. It involves tracking all network resource access. Regular testing of security systems and processes.
- Maintaining the Information Security Policy requires a comprehensive policy addressing information security for all personnel.
Data Encryption
Encryption protects sensitive information even if security gets compromised elsewhere. Payment apps must encrypt data both in transit and at rest.
- Data in Transit protection uses TLS 1.2 or higher for all data transmission. Includes API calls, user authentication, and payment processing communications.
- Data at Rest encryption protects stored information using AES-256 encryption. Applies to user profiles, transaction history, and any cached payment information.
Fraud Detection
Modern payment apps implement multiple fraud protection layers. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Machine Learning Algorithms analyze transaction patterns, identifying unusual behavior. These systems learn from historical data, improving detection accuracy over time.
- Real-Time Monitoring flags suspicious transactions immediately. Includes velocity checks, location verification, and behavioral analysis.
- User Verification through multiple factors helps confirm legitimate users. Might include biometrics, device fingerprinting, and SMS verification.
Regular Security Audits
Organizations are moving from annual audits to continuous monitoring and validation. This proactive approach helps stay ahead of emerging threats. Security audits should include:
- Penetration Testing by qualified security professionals identifies vulnerabilities before attackers do.
- Code Reviews identify security flaws in application logic and implementation.
- Infrastructure Assessment ensures server configurations and network security meet current standards.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Insuring Security and Compliance in Payment Application Development
Security mistakes in payment apps aren’t just embarrassing – they’re expensive and potentially business-ending. Even experienced development teams fall into predictable traps that could have been avoided with proper planning. Here are the biggest mistakes we see companies make, and how to sidestep them before they derail your project.
Ignoring Compliance Early On
Are you one of the many businesses that focus solely on building a product and leave compliance for later? This is a fatal mistake. Don’t do that. You must make regulations like KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) an inseparable part of your app’s architecture from day one.
Poor Scalability
Your app might work fine with a thousand users, but what happens when you have a million? An app built without scalability in mind will crash under pressure. This can lead to outages, transaction failures, and a massive loss of user trust. Make scalability an integral part of your payment app development process from day one.
Inadequate Testing
Don’t just test for happy paths. What happens if a user’s phone loses service in the middle of a transaction? What happens if your third-party API is down? Test your app for all the worst-case scenarios before you bring it to the end users.
Mobile Payment App Monetization Models
Building a payment app is just the beginning. Sustainable monetization strategies for a payment app ensure long-term success and continued innovation.
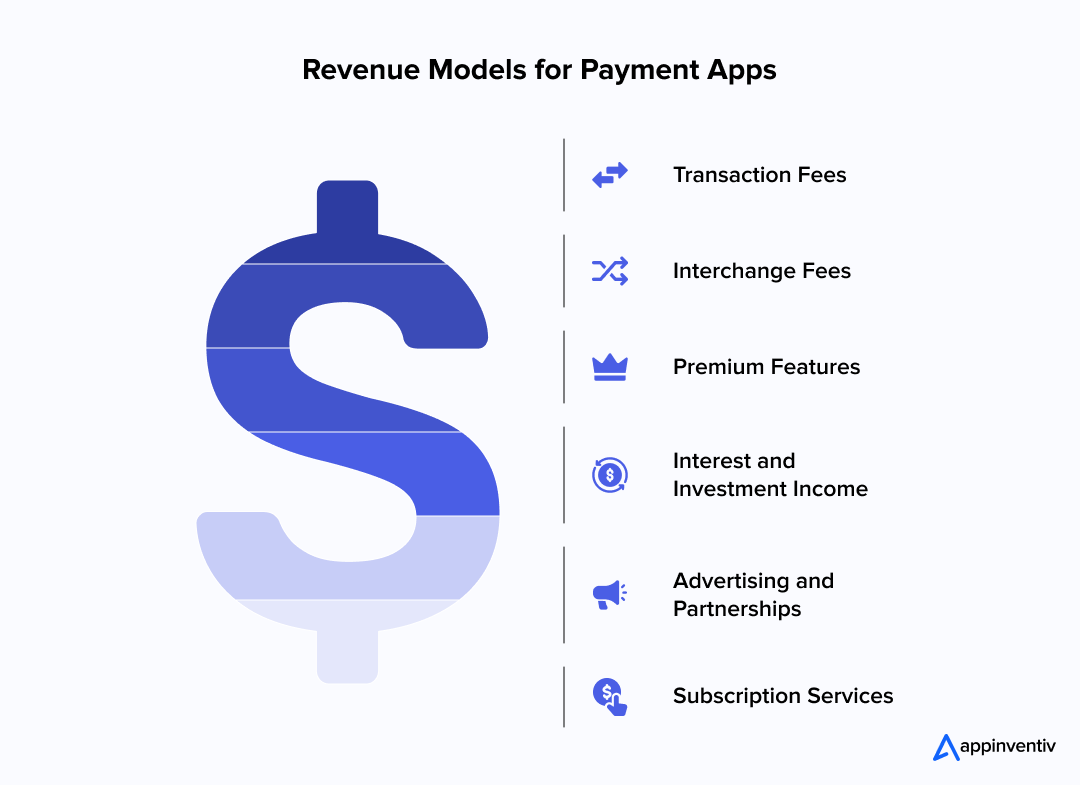
Transaction Fees
The most common approach involves charging small fees per transaction. Venmo charges 3% for instant transfers to bank accounts while keeping standard transfers free. This works because users value speed and convenience.
- Percentage-Based Fees charge a fixed percentage of each transaction. Scales revenue with transaction volume but may discourage large payments.
- Fixed Transaction Fees charge the same amount regardless of payment size. Works well for small, frequent transactions, but may be prohibitive for larger payments.
- Tiered Fee Structures combine both approaches, often with free tiers encouraging adoption and paid tiers for premium features.
Interchange Fees
When users pay with credit or debit cards through your app, you can earn a portion of the interchange fees that card networks charge merchants. It requires becoming a registered payment processor, involving significant regulatory overhead.
Premium Features
Freemium models offer basic functionality for free while charging for advanced features:
- Business Accounts provide additional features like invoicing, reporting, and integration with accounting software.
- Higher Transaction Limits allow power users to send larger amounts for a monthly or annual fee.
- Priority Support offers faster customer service response times for paying users.
- Advanced Security Features like enhanced fraud protection or additional authentication options.
Interest and Investment Income
Some payment apps generate revenue by investing user balances:
- Float Income comes from investing user funds sitting in the app between transactions. Requires careful risk management and regulatory compliance, though.
- Investment Services allow users to invest their payment app balance in stocks, bonds, and other securities. App earns revenue through trading fees or management fees.
Advertising and Partnerships
Smart partnerships can turn your user base into a revenue goldmine without charging users directly.
- Targeted Advertising based on spending patterns can generate revenue, though it must be balanced with user privacy concerns.
- Merchant Partnerships involve revenue sharing with businesses accepting payments through your app.
- Financial Product Referrals earn commissions by referring users to credit cards, loans, and other financial services.
Subscription Services
Recurring revenue is the holy grail of sustainable business models. This includes:
- Monthly or Annual Subscriptions provide predictable revenue and often include bundles of premium features.
- Business Plans offer comprehensive solutions for companies, including multiple user accounts, advanced reporting, and API access.
Challenges & Solutions in Building a Payment App
Every payment app faces predictable challenges. Understanding these obstacles and solutions can save months of development time and significant costs. Let’s uncover the potential problems and their strategic solutions:
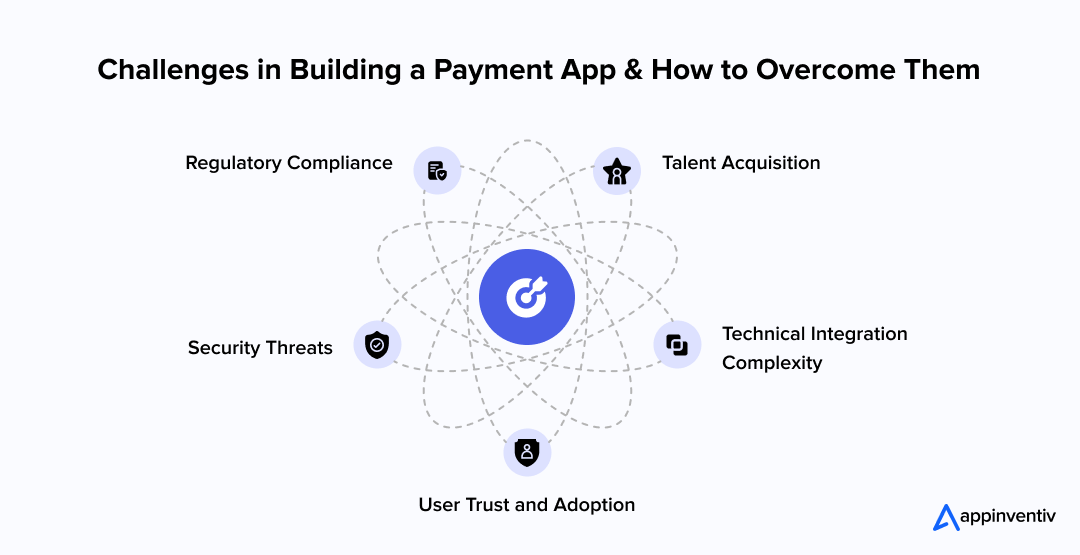
Regulatory Compliance
Challenge: Financial regulations vary significantly by country and region. What works in one market may be illegal in another. In the US, mobile payment app development must comply with the army of federal and state regulations.
Solution: Partner with regulatory experts early in the development process. Consider starting with the single market and expanding gradually as you understand compliance requirements.
Security Threats
Challenge: Payment apps are attractive targets for cybercriminals. Cumulative global payment fraud in online payments is poised to amount to $343 billion between 2023 and 2027.
Solution: Implement security as a core design principle, not an afterthought. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and staying current with threat intelligence are essential.
User Trust and Adoption
Challenge: Users must feel confident putting financial information into your app. New payment apps face significant trust barriers, especially when competing with established players.
Solution: Focus on transparency, security certifications, and gradual trust building. Start with low-risk use cases and expand as users become comfortable.
Technical Integration Complexity
Challenge: Integrating with multiple banks, payment processors, and regulatory systems creates technical complexity. Integration becomes an exercise in retrofitting old equipment with new components – usually resulting in data silos, delayed transactions, and compatibility nightmares.
Solution: Use established payment processors and banking APIs when possible. Build a modular architecture of a payment application that can adapt to different integration requirements.
Talent Acquisition
Challenge: Good fintech engineers are hard to find. Keeping them? Even harder. Specialized skills required for payment app development command high salaries and offer multiple opportunities.
Solution: Consider hybrid development models combining in-house expertise with specialized contractors. Invest in training existing team members and create compelling work environments that retain talent.
How Much Does It Cost To Make a Payment App
This is the question on every entrepreneur’s mind. Understanding payment app development cost helps plan budgets and set realistic expectations. However, the mobile payment app development cost is not a fixed number. Several factors significantly impact development costs. The initial cost variables include:
- The geographic location of the payment app development services provider affects hourly rates. For instance, hourly rates for app development in the US typically hover around $100 per hour, while in Asia the cost ranges around $40-60/hr. only
- Platform Choice impacts costs. Native development for both iOS and Android costs more than single-platform or cross-platform development.
- Integration Complexity increases costs significantly. Each additional payment method, bank integration, and third-party service adds development and testing time.
- Regulatory Requirements in different markets may require specialized compliance features, increasing development costs.
- Team Structure affects costs. In-house teams require salaries, benefits, and equipment. Outsourced teams typically charge project-based fees.
Ongoing Costs
Initial development is just the beginning. Payment apps require ongoing investment to remain functional, secure, and scalable. Maintenance and updates typically cost 15-20% of initial development annually. Here is how:
- Compliance Monitoring requires ongoing legal and technical expertise.
- Security Updates are essential and ongoing as threats evolve.
- Infrastructure Costs scale with user growth and transaction volume.
- Customer Support becomes increasingly important as the user base grows.
Here is a table outlining payment app development costs and timeline based on project complexity.
| Project Complexity | Features | Estimated Cost Range | Development Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Payment App |
| $40,000 – $100,000 | 4 – 6months |
| Intermediate Payment App |
| $100,000 – $250,000 | 6 – 9 months |
| Advanced Payment App |
| $250,000 – $400,000+ | 9 – 12 months |
| Enterprise-Level Payment App |
| $400,000 – $600,000+ | 12 – 18 months |
Current & Future Trends in Payment Apps
The fintech industry is a high-speed train, and it’s essential to keep an eye on what is dominating currently and what’s next. Understanding the current, emerging, and future trends will help you build a forward-thinking app that remains relevant.
Current Trends
- Biometric Authentication is becoming standard. Users expect fingerprint scanning, face recognition, and voice authentication for convenience and security.
- QR Code Payments are experiencing massive growth. Mobile payments through QR codes are all-time high, attracting users from all genres.
- Buy Now, Pay Later integration allows users to make purchases and pay in installments. This feature increases transaction volumes and user engagement.
- Cryptocurrency Integration is gaining traction, though it is still niche. Payment apps increasingly offer crypto buying, selling, and payments alongside traditional features.
- AI-Powered Fraud Detection improves security while reducing false positives. This is the reason that nearly all the new solutions launched in the past two years include AI-based fraud detection.
Emerging Technologies
- Voice Payments through smart speakers and mobile assistants are growing. Users can initiate payments using voice commands, though security remains a challenge.
- Wearable Payments through smartwatches and fitness trackers offer convenience for small purchases. Smart wearables have become the new norm for payments, frequently used by modern-aged customers.
- Blockchain Technology promises faster, cheaper international transfers and enhanced security. However, regulatory uncertainty and technical complexity limit current adoption.
- Internet of Things Payments enable automatic payments from connected devices. Your car could pay for fuel, or your refrigerator could order and pay for groceries.
Future Predictions
- Artificial Intelligence: AI has moved way beyond catching fraudsters. Now it’s getting personal – recommending spending insights, suggesting budget tweaks, even handling boring backend stuff automatically. Users love apps that actually understand their financial habits.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning powers those instant transaction categories, too. Buy coffee at Starbucks, and it’s automatically tagged as “Food & Dining” because the system learned from millions of similar purchases.
- Blockchain and Decentralized Finance: Yeah, it’s still pretty niche. But blockchain’s promise for app development is real – transaction records that can’t be faked, tampered with, or mysteriously disappear. Some developers are betting big on this transparency angle.
- Biometric and Contactless Payments: Your face, fingerprint, or even voice can now pay for stuff. It sounds futuristic, but it’s happening everywhere. Online payment transfer app development teams are rushing to add these features because users expect that tap-and-go convenience.

- Embedded Finance: This one’s clever. Instead of jumping between apps, financial services just live inside whatever you’re already using. Order an Uber? Payment happens invisibly. Buy concert tickets? Same thing. No app-switching, no friction.
- Invisible Payments are going to be wild. Imagine walking into your usual coffee shop and your drink’s already paid for before you even order. No tapping, no scanning – the app just knows you’re there and handles everything automatically based on your preferences.
- Global Interoperability means the app wars might finally end. You’ll send money from your Venmo to someone’s PayPal account without thinking twice about it. Different countries, different currencies, different apps – none of that will matter anymore.
Why Build a Payment App with Appinventiv?
The payment app landscape moves fast, and building something that lasts requires more than just coding skills. You need a team that understands both the technical complexities and the business realities of FinTech app development.
This is where we come in. At Appinventiv, we’ve helped over 3000 companies bring their digital vision to life. For instance, we have built a financial literacy app for Edfundo. The platform provides users with an interactive user interface, personalized learning, real-time goal tracking, and other engaging features. The results?
- $500,000 received pre-seed funding
- $3 million prepared for a seed funding round
From PCI DSS compliance to user acquisition strategies, our team of 1600+ tech experts specializes in next-gen payment platform development that processes millions of transactions safely.
What sets our custom payment apps apart isn’t fancy features – it’s rock-solid architecture that can handle growth. We’ve seen too many promising apps crash under their own success because they weren’t built to scale. Our approach focuses on creating payment systems that work seamlessly, whether you have 1,000 users or 10 million.
From choosing the right tech stack to implementing fraud detection that actually works, we handle the technical heavy lifting so you can focus on building your business. The best part? We know which shortcuts lead to security nightmares down the road.
The fintech space rewards companies that move quickly but thoughtfully. With our ISO certified excellence, regulatory compliance expertise, and deep understanding of what users actually want, we can help you build a payment solution that doesn’t just function; it thrives.
Ready to turn your payment app development idea into reality? Let’s talk about what’s possible.
FAQs
Q. Why create a payment app?
A. The payment app market offers tremendous opportunities driven by changing consumer behavior and technological advancement. These apps have the potential to increase financial inclusion, reduce friction in commerce, and enable new business models that weren’t previously possible. This represents billions of potential users who could benefit from accessible digital payment solutions.
Payment apps also provide multiple revenue streams through transaction fees, premium features, and financial services. The recurring nature of payment transactions creates predictable revenue and high user engagement.
Even if the path of building a payment platform is not easy, the rewards are significant.
Q. How long does it take to go from concept to launch for a payment app?
A. The timeline for payment app development varies depending on the project’s complexity and the expertise of the payment app development teams. For instance, a basic MVP typically takes 4-8 months, while a full-featured payment app requires 8-12 months or more. Complex enterprise apps with extensive integrations may require 12-18 months for full development.
This includes:
- Research and planning: 1-2 months
- Design and architecture: 1-2 months
- Development: 3-6 months
- Testing and compliance: 1-2 months
- Submission and launch: 1 month
Contact a payment app development company to get a more precise estimate for the timeline.
Q. What is the cost of payment app development?
A. On average, the cost of payment app development ranges between $40,000 and $600,000 or more, based on your unique project requirements and project complexity. For instance,
- Basic apps with MVP-level features cost between – $40,000 and $100,000
- Intermediate-level app development costs range from $100,000 to $250,000
- Advanced complexity app development cost is between – $250,000 and $400,000+
- Enterprise-grade payment apps with futuristic features cost – $400,000 – $600,000 or more
Discuss your payment app development idea with a reputed payment processing app development company like Appinventiv and get a detailed cost estimate tailored to your needs.
Q. How to create a mobile payment app?
A. If you are not sure how to create a payment app, here is a step-by-step process to guide you through the journey from concept to code and beyond:
- Research and Planning
- Choosing the Sourcing Model
- Designing the UI/UX and App Architecture
- Development Phase
- Testing and Quality Assurance
- Deployment and Launch
- Maintenance and Upgrade
To gain an in-depth understanding of how to create a payment app, please refer to the above blog.
Q. What measures should we take to ensure regulatory compliance in our payment app development?
A. Regulatory compliance for payment app development involves multiple requirements:
- PCI DSS Compliance
- Know Your Customer Requirements
- Anti-Money Laundering Compliance
- Data Privacy Regulations like GDPR, CCPA, etc.
These are some of the many payment compliances we adhere to while developing payment apps
Q. How do we ensure data privacy regulations?
A. Data privacy in payment apps needs solid protection measures. Here’s what works:
- Data Minimization means grabbing only what you actually need and tossing the rest when you’re done with it. Don’t hoard user info just because you can.
- Encryption keeps all sensitive stuff locked down, whether it’s moving between devices or sitting in your database. Use the good algorithms – not the bargain-basement ones.
- Access Controls make sure only the right people see user data. Everyone needs proper authentication, no exceptions.
- User Consent lets people know what you’re doing with their info and gives them real control over it. No sneaky fine print.
- Privacy by Design bakes protection into everything from day one instead of slapping it on later like a Band-Aid.
- Regular privacy check-ups and keeping up with new rules help you stay compliant as regulations change.
Q. How can we leverage AI and machine learning for personalized services?
A. AI and ML create real opportunities in payment apps such as:
- Fraud Detection spots weird transaction patterns instantly, catching actual fraud while cutting down false alarms that annoy users.
- Personalized Services studies spending habits to suggest useful financial products, budget tips, or merchant deals that actually make sense.
- Risk Assessment figures out the right transaction limits and security checks for different users without being a pain.
- Customer Support bots handle basic questions 24/7, saving money while keeping users happy.
- Predictive Analytics guesses what users want next, helping you build better features and find new revenue streams.
Implementing AI means dealing with privacy rules, bias issues, and regulatory headaches. So, ensure to use responsible AI and explainable AI practices
Q. How can we ensure payment app security?
A. End-to-end payment app development requires multiple protection layers:
- Multi-Factor Authentication mixes passwords, phones, and biometrics for bulletproof account protection.
- End-to-End Encryption locks down data from the user’s phone all the way to your servers and back.
- Regular Security Audits by real pros find weak spots before the bad guys do.
- Secure Coding Practices stop common attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting from ever happening.
- Runtime Protection catches and blocks attacks while they’re happening, not after the damage is done.
- Device Security spots jailbroken phones and prevents man-in-the-middle attacks through certificate pinning.
- Security never ends – threats keep evolving, so your defenses need constant updates and monitoring.
Q. How do we integrate biometric authentication?
A. Biometric authentication boosts both security and user experience. Here is how we implement it in the payment apps:
- Fingerprint Authentication taps into device hardware for quick, secure identity checks.
- Face Recognition works great for hands-free situations where touching the screen isn’t practical.
- Voice Recognition lets users authenticate through phone calls or voice commands.
- Behavioral Biometrics watches how people type and handle their devices for ongoing verification.
Key things to remember:
- Keep biometric data on the device, not your servers
- Always have backup authentication options
- Follow biometric data regulations religiously
- Test on different devices and real-world scenarios
Biometrics should boost other security measures, not replace them entirely.
Q. How do we add real-time notifications?
A. Real-time notifications keep users in the loop while boosting security:
- Transaction Alerts ping users the moment payments go through, fail, or get received.
- Security Notifications warn about suspicious activity, new device logins, or security changes.
- Balance Updates tell users when their money situation changes or gets low.
- Bill Reminders help people stay on top of recurring payments and due dates.
- Promotional Messages share new features, deals, or financial services that might interest them.
- The technical side involves push services (APNs for iOS, FCM for Android), webhooks for live data, and message queues for reliable delivery.
The trick is balancing helpful info with notification overload. Let users control what they get, and make sure every message actually matters.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
LLMs in finance - Benefits, Applications, and Real Examples
Key takeaways: LLMs in finance enhance data analysis by processing vast structured and unstructured datasets. Automation via LLMs reduces operational costs and frees staff for strategic tasks. Smart chatbots powered by LLMs improve customer experience with personalized advice. LLMs enable real-time fraud detection and risk assessment, enhancing security. Fine-tuning and RAG ensure LLMs deliver accurate,…

How Appinventiv Solved Scalability Challenges for FinTech Platforms with 10M+ Users
Scalability is a crucial element in the FinTech sector as it is experiencing phenomenal growth due to the global population's need for streamlined, on-demand security and instant financial services. With the rise in user bases and transaction volume, FinTech applications must manage the growing demand without compromising performance or security, while also providing a pleasant…

How Much Does it Cost to Build a Personal Finance App like Pocketsmith?
Imagine an app that knows when your rent is due, reminds you of upcoming bills, forecasts your savings 12 months ahead, and tells you if that third coffee this week is wrecking your budget. That’s the kind of experience apps like PocketSmith deliver, and it’s exactly why personal finance apps are becoming a must-have for…