- Understanding the Working Principles of a Payment App
- Start Your Digital Payment App Development Journey by Choosing the Right Types of Payment Apps
- An Essential Checklist for Payment App Features
- Must Have Payment App Features
- Advanced and Intelligence-Driven Features
- How to Create a Payment App: A Step-by-Step Process with an Estimated Timeline
- Research and Planning
- Choosing the Sourcing Model
- Choosing the Right Tech Stack
- Designing the UI/UX and App Architecture
- Development & Integration
- Testing & Quality Assurance
- Deployment
- Maintenance & Continuous Improvement
- Challenges in Building a Payment App & How to Overcome Them
- Regulatory Compliance
- Security Threats
- User Trust and Adoption
- Technical Integration Complexity
- How Long Does It Take to Build a Payment App?
- Choosing the Right Technology Stack for Payment App Development
- The Non-Negotiable: Security, Compliance, and Regulations You Must Follow
- What Are Some Lucrative Mobile Payment App Monetization Models
- What Are Some Current & Future Trends in Payment App Development
- Trends Used in Production Today
- What the Future Phase Looks Like
- Why Build a Payment App with Appinventiv?
- FAQs
Key Takeaways
- The digital payment market is a massive revolution, creating a massive opportunity for businesses and entrepreneurs.
- Security is a must. PCI DSS compliance, data encryption, biometrics, advanced fraud detection, and scalable tech stack are non-negotiable.
- The cost of payment app development ranges between $40,000 and $400,000 for basic to advanced apps. For enterprise-grade apps, the cost can exceed even $600,000.
- Monetization models and user experience must be part of your plan from day one to ensure long-term success.
A lot of businesses run into the same problem once transactions start picking up. Orders are coming in, users are ready to pay, and then something goes wrong at checkout. The payment fails. The app freezes. A user does not trust the screen asking for card details. In that moment, it is not the product that disappoints them. It is the payment experience.
We see this often with growing digital businesses. They lose customers not because prices are high or features are missing, but because paying feels slow, confusing, or unsafe. A single failed transaction can undo weeks of marketing effort.
On the other hand, a smooth payment app quietly does its job. It lets users pay the way they want, confirms transactions instantly, and builds trust without asking for it. When payments work well, users stay. Revenue flows. Support tickets drop.
What makes this more impressive is how deeply payment behavior has shifted. In 2024 alone, US consumers spent $670.5 billion through proximity mobile payments, and that number is projected to cross $1 trillion by 2027. What’s even more impressive, 53% of Americans now use digital wallets more often than traditional payment methods. Payments are no longer a backend function. They are a core part of how users judge trust and convenience.
This blog walks you through how a payment app is built and what really matters behind the scenes. We cover the core features, security and compliance requirements, technology stack choices, development costs, and monetization models, so you can clearly understand what it takes to create a reliable and scalable payment app.
Understanding the Working Principles of a Payment App
When evaluating or building a payment app, the real question is not what the user sees. It is what happens behind the screen once a transaction is initiated. Every payment relies on a short, well-defined chain of systems that must work together without delays, data exposure, or compliance gaps.
At a simplified level, this is how a payment app processes a transaction:
- User → App
The app captures the payment request and user authorization. No sensitive data is stored locally. The app’s role here is orchestration, not processing. - App → Payment Gateway
The request is encrypted and routed to the payment gateway, which handles tokenization, transaction routing, and regulatory checks. - Gateway → Bank
The gateway forwards the transaction to the issuing bank for balance validation, authentication, and risk assessment. - Bank → Confirmation
The bank responds with an approval or rejection, which is sent back through the gateway and reflected in the app in near real time.
This entire flow is designed to complete in seconds, even at scale. For enterprises, getting this sequence right is what determines transaction success rates, system reliability, and long-term trust with users and partners.
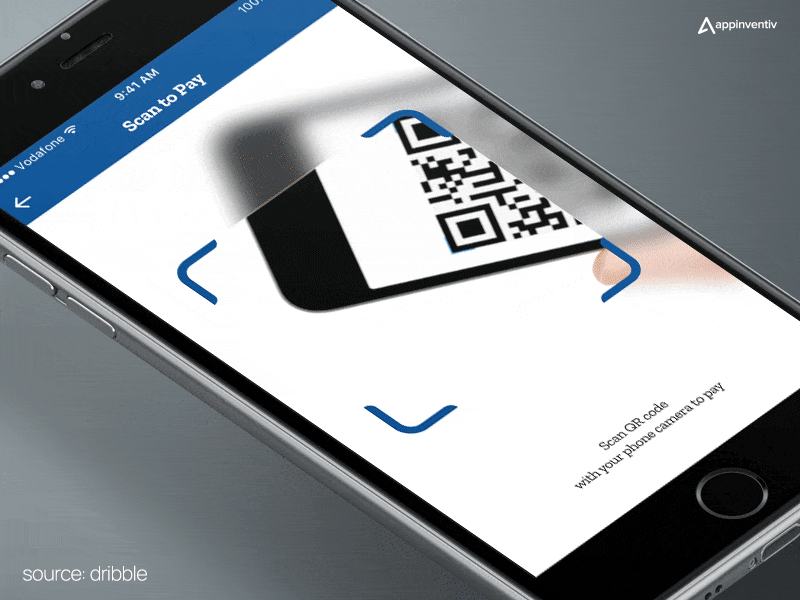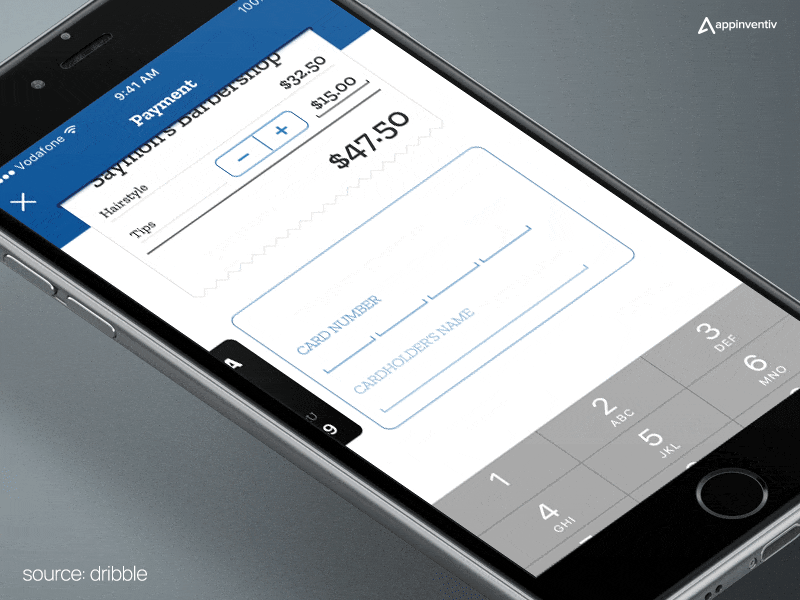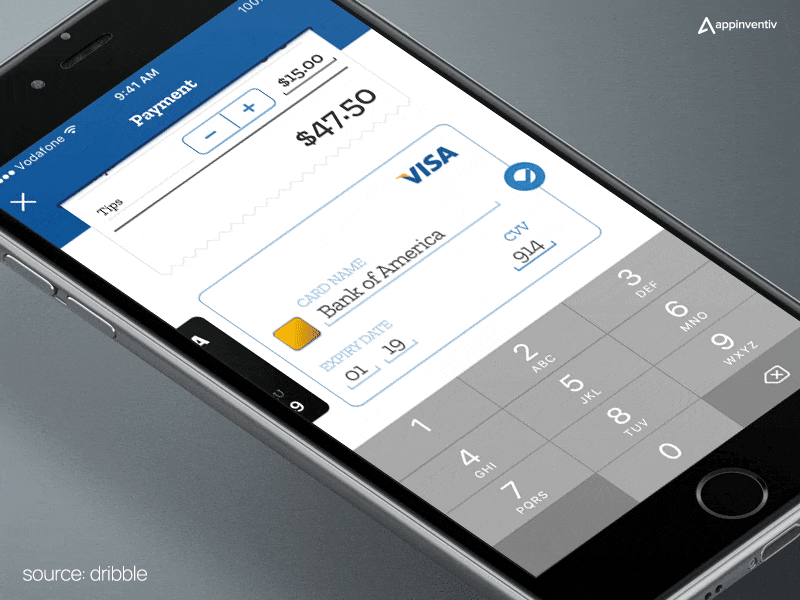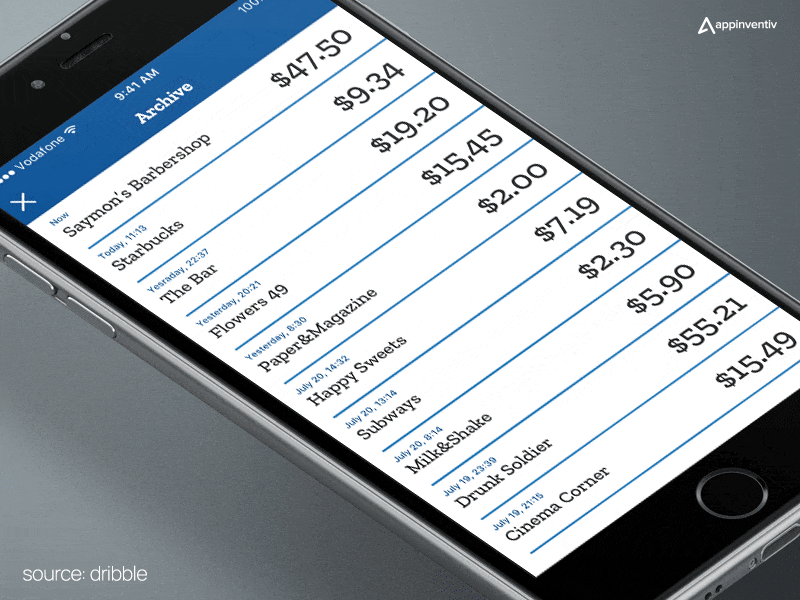
Now that you know how does a payment app work, you must understand the feasible payment app types you can build for your business.
Start Your Digital Payment App Development Journey by Choosing the Right Types of Payment Apps
Before you even think about building a digital payment app, you need to first evaluate, “What are your pain points?” “What problems are you solving? What type of payment app do you actually want?” The market is mushrooming with multiple types of apps, and each plays a different game. So, your first challenge is to figure out the right type that can align with your niche and needs.
Here is a table outlining various types of payment applications so that you can make an informed development decision:
| Types of Payment Apps | Payment Application Examples | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Payment Apps | Venmo, PayPal, Cash App, Zelle | Everyday transfers, splitting expenses, social payments |
| Mobile Wallets | Apple Pay, Google Wallet, Samsung Pay | Contactless payments and faster in-store or online checkouts |
| E-commerce Payment Systems | Shopify Payments, WooCommerce, Stripe | Online stores, D2C brands, growing marketplaces |
| Cryptocurrency Payment Apps | Coinbase, Binance, BitPay | Crypto-based commerce and blockchain-driven use cases |
| Buy Now, Pay Later Apps | Afterpay, Klarna, Affirm | Retail financing and improving checkout conversions |
| Digital Banking Apps | Revolut, N26, Monzo | Neobanks and full-service digital finance platforms |
| Subscription Payment Apps | Netflix, Spotify, Hulu | Subscription businesses and SaaS products |
| QR Code Payment Apps | Alipay, WeChat Pay, Paytm | Offline merchants and high-footfall retail environments |
| International Payment Apps | Wise, Remitly, WorldRemit | Global transfers, remittances, international payouts |
| Charity Donation Apps | GoFundMe, JustGiving, Charitable.org | Fundraising platforms and nonprofit organizations |
| Micro-payment Apps | Google Play, App Store, Steam | Games, digital content, and app-based monetization |
| Utility Payment Apps | Paytm, BillDesk, Biller Direct | Household bill management and recurring payments |
| UPI (Unified Payments Interface) | Google Pay, PhonePe, Paytm, BHIM | Real-time transfers within the Indian payments ecosystem |
| Super Apps | WeChat, Grab, Gojek, Paytm | Platform ecosystems and multi-service digital businesses |
Each type has totally different technical requirements, compliance needs, and user expectations. Your choice affects development complexity and how you’ll eventually make money.
Also Read: List of Top 7 Most Frequently Used Mobile Payment Apps
An Essential Checklist for Payment App Features
When businesses start listing features, everything can feel equally important. In reality, payment apps work best when features are layered with intent. Some capabilities are non-negotiable because they protect money and trust. Others add intelligence, speed, or operational visibility once the foundation is solid.
If you are not sure how to make a right decision, the below categorization of payment app features regarding “must-have” and “advanced” will help you gain a good understanding of how mature payment platforms are typically built in practice.
Must Have Payment App Features
These features are essential for running secure, compliant, and reliable payment operations. Without them, scaling the app becomes risky.
| Features | What It Supports in Real Use |
|---|---|
| Secure Authentication | Controls access using PINs, biometrics, or multi-factor verification |
| Payment Processing | Executes card, wallet, and bank transactions accurately |
| Fraud Detection & Risk Checks | Flags abnormal activity and reduces financial loss |
| Data Encryption & Tokenization | Protects sensitive payment information end to end |
| Transaction Records | Maintains clear logs for users, audits, and dispute handling |
| Compliance Readiness | Aligns the app with PCI DSS and regulatory requirements |
| Push Notifications | Confirms payments, failures, refunds, and account activity instantly |
Advanced and Intelligence-Driven Features
Once the core system is stable, you need to embed advanced features. These advanced functionalities help businesses improve decision-making, automate controls, and enhance user engagement.
| Features | Why You Must Consider Them |
|---|---|
| AI-Based Fraud Analysis | Learns from patterns to improve detection over time |
| Smart Payment Routing | Improves success rates by choosing optimal gateways |
| Multi-Currency Support | Enables cross-border transactions and expansion |
| Recurring & Scheduled Payments | Supports subscriptions and repeat billing models |
| Analytics & Reporting | Surfaces insights into volume, failures, and behavior |
| Role-Based Access Controls | Manages permissions across internal teams |
| System Alerts & Monitoring | Detects downtime, delays, or unusual spikes early |
How to Create a Payment App: A Step-by-Step Process with an Estimated Timeline
When considering how to create a payment app, the challenge is rarely technical alone. The harder part is deciding what the app should handle, what it should avoid, and who to count on for development. But worry not, here is a step by step process to build a secure and scalable digital payment app.

Research and Planning
Timeline: 2–3 weeks
Every successful business payment app begins long before a single line of code is written. Many of the payment app development projects fail not because the idea is weak, but because they could not align with the market they are stepping into.
This stage is about asking the right questions before committing time and budget to the next step.
- Market Analysis: What gaps exist in current payment apps, and where users face friction or trust issues?
- User Research: How do target users actually pay today, not how we assume they do?
- Competitive Analysis: What features are overdone, missing, or poorly executed?
- Technical Feasibility: Is the product realistic within cost, timeline, and compliance limits?
Choosing the Sourcing Model
Timeline: 1 week
How you build the app matters as much as what you build. It simply means that the sourcing model you choose directly affects development speed, control, and long-term payment app development cost.
The three most common and considerable sourcing models for payment app development are:
- In-House Development: It offers full control but increases hiring, infrastructure, and retention costs
- Outsourcing. It lowers cost and brings specialized skills but requires strong vendor governance
- Hybrid Model. It balances internal strategy with outsourced execution for complex payment systems
Also Read: How to Outsource App Development in 2026
Choosing the Right Tech Stack
Timeline: 1–2 weeks
Technology decisions made here are difficult to reverse later. The goal is to balance performance, security, scalability, and compliance without overengineering.
Ideal tech stack areas include:
- Backend: Node.js, Java, or .NET for high-volume transaction handling
- Databases: PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, or Cassandra for speed and traceability
- Security: Encryption, tokenization, and fraud controls using PCI-compliant tools
Designing the UI/UX and App Architecture
Timeline: 3–4 weeks
A strong payment app does not draw attention to itself. When design works, users move from action to confirmation without hesitation. It means trust, clarity, and simplicity must be built into both the interface and the system beneath it.
Key components of a successful app architecture are:
- Clear Transaction Flow: Is every step, from initiation to confirmation, logically ordered and easy to complete?
- Scalable System Structure: Can the architecture handle growing users, transactions, and integrations without rework?
- Built-in Security Layers: Are encryption, tokenization, and access controls embedded into the design from the start?
Development & Integration
Timeline: 8–14 weeks
This is where planning turns into a working product. Features discussed during planning are built and connected to real-world systems that make payments possible. Payment app development usually follows agile cycles, allowing teams to test assumptions early and refine features as the app evolves.
This phase typically focuses on:
- Backend Development: Secure transaction logic, databases, and APIs that handle scale and accuracy
- Frontend Development: Interfaces that stay responsive while meeting security expectations
- Integration: Stable connections with payment gateways, banking APIs, and third-party services
Testing & Quality Assurance
Timeline: 3–4 weeks
Because payment apps deal with real money, testing is not optional or lightweight. Each release must be examined for accuracy, security, and regulatory alignment before reaching users.
Testing efforts are usually spread across:
- Functional Testing: Validation of payment flows across normal and edge cases
- Security Testing: Identification of risks through audits and penetration testing
- Performance Testing:Stability checks under peak transaction volumes
- Compliance Testing: Alignment with PCI DSS and regional financial regulations
Also Read: The Mobile App Testing Strategies that Appinventiv Follows
Deployment
Timeline: 1–2 weeks
Launching a payment app is more than pushing code live. It involves technical readiness, regulatory checks, and careful coordination across platforms and infrastructure.
Key deployment considerations include:
- App Store Submission: Meeting platform-specific and payment-related guidelines
- Infrastructure Deployment: Production servers, monitoring, and backup systems
- Regulatory Approval: Completion of required licensing and compliance checks
Maintenance & Continuous Improvement
Timeline: Ongoing
A payment app is never truly finished. Ongoing updates are necessary to stay secure, compliant, and competitive as transaction volumes and user expectations grow.
Ongoing maintenance typically includes:
- Security Updates: Addressing new vulnerabilities as they emerge
- Feature Updates: Enhancements driven by user feedback and market shifts
- Compliance Monitoring: Tracking and adapting to regulatory changes
- Performance Optimization: Sustaining speed and stability at scale
Challenges in Building a Payment App & How to Overcome Them
Every payment app faces predictable challenges. Understanding these obstacles and solutions can save months of development time and high costs. Let’s uncover the potential problems and their strategic solutions:
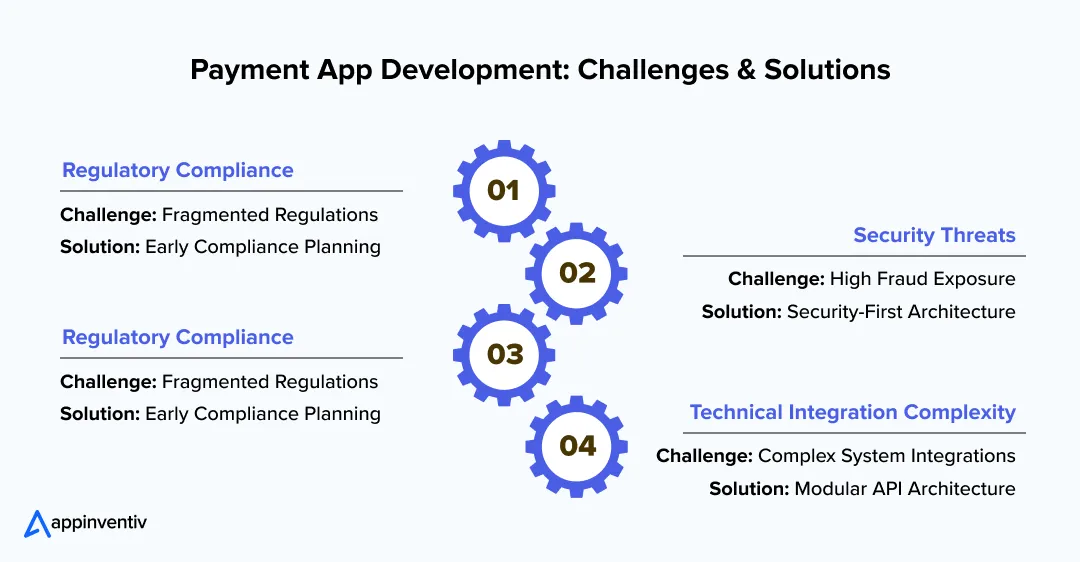
Regulatory Compliance
Challenge: Financial regulations vary significantly by country and region. What works in one market may be illegal in another. In the US, mobile payment app development must comply with the army of federal and state regulations.
Solution: Partner with regulatory experts early in the development process. Consider starting with the single market and expanding gradually as you understand compliance requirements.
Security Threats
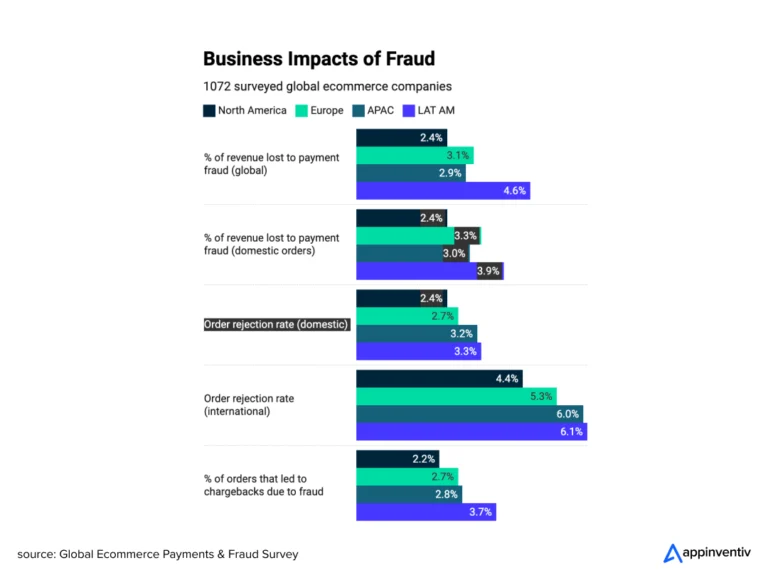
Challenge: Payment apps are attractive targets for cybercriminals. Cumulative global payment fraud in online payments is poised to amount to $343 billion between 2023 and 2027.
Solution: Implement security as a core design principle, not an afterthought. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and staying current with threat intelligence are essential.
User Trust and Adoption
Challenge: Users must feel confident putting financial information into your app. New payment apps face significant trust barriers, especially when competing with established players.
Solution: Focus on transparency, security certifications, and gradual trust building. Start with low-risk use cases and expand as users become comfortable.
Technical Integration Complexity
Challenge: Integrating with multiple banks, payment processors, and regulatory systems creates technical complexity. Integration becomes an exercise in retrofitting old equipment with new components – usually resulting in data silos, delayed transactions, and compatibility nightmares.
Solution: Use established payment processors and banking APIs when possible. Build a modular architecture of a payment application that can adapt to different integration requirements.
Now that you know how to create a payment app, the next vital questions that must be lingering in your mind are “How long does it take to build a payment app? And “How much does it cost to make a payment app?” Well, to help you plan a realistic budget and timelines, the next sections explain how much time and money you truly require to make an app.
How Long Does It Take to Build a Payment App?
Teams often ask for a fixed timeline, but payment apps rarely work that way. The time depends on how much the app needs to handle on day one. Features, security depth, integrations, and compliance checks all stretch or shrink the schedule. A lightweight app moves quickly. An enterprise platform takes patience.
Here’s how timelines usually shape up in practice:
| App Complexity | Typical Scope | Estimated Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Payment App | Simple payment flow, limited features, single market | 4–6 months |
| Moderate Complexity App | Multiple payment methods, basic integrations, added checks | 6–9 months |
| Advanced Payment App | Higher volumes, stronger security, reporting, scalability | 9–12 months |
| Enterprise-Grade Payment Platform | Custom logic, AI-driven controls, global compliance, deep integrations | 12–18+ months |
How Much Does It Cost To Make a Payment App?
On average, the cost to make a payment app ranges between $40,000 and $600,000+. But this is not a fixed number. Several factors can impact this estimated development costs. Understanding these cost driving elements helps plan budgets and set realistic expectations. With that said, the initial cost variables include:
- App scope: A basic payment flow costs far less than a feature-heavy, multi-role platform.
- Third-party integrations: Every bank, gateway, or external service adds build time, testing effort, and coordination.
- Security & compliance: Different regions bring different rules, audits, and safeguards, which raise both effort and cost.
- Payment methods: Cards, wallets, UPI, and bank transfers each come with their own logic and edge cases, which drives up the costs.
- Platforms covered: Building for iOS, Android, and web is not linear, it compounds work and costs.
- Design depth: Simple flows move fast; custom experiences take more iteration, which significantly impacts the costs.
- Ongoing upkeep: Updates, fixes, and regulatory changes continue well after launch, which adds to the overall payment app development costs.
Here is a table outlining payment app development costs based on project complexity.
For businesses looking to enter the Australian market specifically, understanding the unique regulatory requirements and cost structures is essential when developing FinTech apps in Australia.
| Project Complexity | Features | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Payment App |
| $40,000 – $100,000 |
| Intermediate Payment App |
| $100,000 – $250,000 |
| Advanced Payment App |
| $250,000 – $400,000+ |
| Enterprise-Level Payment App |
| $400,000 – $600,000+ |
Choosing the Right Technology Stack for Payment App Development
Tech decisions made early have a lasting impact on everything. The right tech stack ensures scalability, security, and maintainability for the long term. This isn’t just about picking popular tools; it’s about making the right decisions that can handle millions of transactions and will support your growth for years to come.
Don’t know how to choose the right tech stack for payment app development? To help you choose the right one, here we have listed down the most popular and secure tech stack for mobile payment app development
Frontend Development
- Native Development: Swift or Objective-C for iOS, Kotlin or Java for Android, offering high performance and full access to biometrics
- Cross-Platform Frameworks: React Native or Flutter to reduce build time with a shared codebase
- Progressive Web Apps: Browser-based access with limited device-level security support
Backend Development
- Programming Languages: Node.js, Python, and Java for handling APIs and real-time processing
- Database Systems: PostgreSQL for ACID-compliant transaction data, MongoDB for flexible user data
- Cloud Infrastructure: AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure for scalability, uptime, and compliance tooling
Security Technologies
- End-to-end encryption: TLS/SSL for data in transit and AES for stored data
- Tokenization: Replacing card and account details with secure tokens
- API Security: OAuth 2.0 and JWT for authentication and access control
APIs and Payment Gateways
- Payment Processors: Stripe, PayPal, or Square for card payments and PCI DSS handling
- Banking APIs: Open banking APIs for account access and direct transfers
- Third-Party Services: KYC, identity verification, and fraud detection tools
Also Read: Payment Gateway Integration for Your App
The Non-Negotiable: Security, Compliance, and Regulations You Must Follow
Security isn’t optional in mobile payment app development. It’s the foundation everything else builds on. You are holding people’s money and their most sensitive information. So, you must ensure the failsafe safety of their confidential information. This isn’t about avoiding a breach; it’s about protecting your customers’ rights and saving your business from financial loss and reputational damage.
In short, security and compliance shape architecture, trust, timelines, and cost from day one. If these are handled late or inefficiently, you will usually pay for it twice.
Below are the core areas you cannot afford to overlook.
- PCI DSS compliance
Mandatory for card payments. Dictates how data flows, where it is stored, and how systems are audited. - Tokenization & encryption
Card and account data should never exist in raw form. Tokenization reduces exposure. Encryption protects data in transit and at rest. - KYC & AML
Identity checks and transaction monitoring are required in most markets. They affect onboarding, risk controls, and reporting. - GDPR & regional data laws
Data location, access rights, and retention rules depend on geography. These laws influence cloud setup and data architecture.
Most teams treat this layer as risk management, not feature development. The earlier it is addressed, the better it is and the fewer barriers you will have to face later.
- Tech Company of the Year 2023, awarded by Times Business
- India’s Growth Champions in IT 2023, awarded by the Economic Times
- Consecutive Tech Fast 50 Awards in 2023 & 2024 by Deloitte
- Leader in AI Engineering & Digital Transformation 2025 by the Economic Times
What Are Some Lucrative Mobile Payment App Monetization Models
For enterprise payment platforms, monetization is usually built into usage, not pushed onto users. Money is made as transactions move through the system, merchants scale, and additional services get layered in. The strongest models grow quietly in the background.
Below are the models that tend to work in real payment ecosystems.
Transaction and Interchange Fees
This is where most payment platforms start. Revenue comes from transaction volume, either through direct transaction fees or interchange earned on card payments. The upside grows with scale, without changing user behavior.
Merchant-Based Revenue
Instead of charging users, platforms charge businesses. Merchants pay for payment acceptance, settlements, reporting, or operational tools. This model fits well in B2B, marketplace, and platform-driven products.
Subscription Services
Subscriptions usually sit on top of core payments. Here, the merchants pay for advanced dashboards, higher limits, priority support, or operational controls. It brings predictable revenue once usage stabilizes.
Value-Added Services
Here, payments become the entry point, not the product. Fraud controls, analytics, risk scoring, faster payouts, and compliance tooling are common revenue drivers. These services often carry higher margins.
Advertising and Partnerships
At scale, platforms monetize reach. Partnerships, co-branded offers, and ecosystem tie-ups generate revenue without touching the payment flow directly. This works best when user trust is already established.
Most enterprise-grade payment apps use more than one of these models. The mix depends on volume, regulation, and how deeply payments are embedded into daily business operations.
What Are Some Current & Future Trends in Payment App Development
The fintech industry is a high-speed train, and it’s essential to keep an eye on what is dominating currently and what’s next. Understanding the current, emerging, and future trends will help you build a forward-thinking app that remains relevant.
Trends Used in Production Today
These capabilities are now standard in production-grade payment systems and are often expected by users, regulators, and partners.
- AI-Based Fraud Detection
Machine learning models monitor transactions in real time to detect abnormal behavior and reduce false declines. - QR Code Payments
QR-based payments continue to grow due to low infrastructure cost and strong adoption in offline and mixed-use environments. - Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL)
BNPL is commonly embedded into checkout flows to support higher conversion and flexible payment options. - Multi-Gateway Payment Setup
Enterprises rely on multiple gateways and smart routing to improve success rates and reduce downtime risk. - Biometric and Contactless Payments
Fingerprint and facial authentication are widely used to secure transactions while keeping payment flows fast.

What the Future Phase Looks Like
These trends are influencing how new payment platforms are being designed and modernized.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI has moved way beyond catching fraudsters. Now it’s getting personal – recommending spending insights, suggesting budget tweaks, even handling boring backend stuff automatically. Users love apps that actually understand their financial habits.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning powers those instant transaction categories, too. Buy coffee at Starbucks, and it’s automatically tagged as “Food & Dining” because the system learned from millions of similar purchases.
- Blockchain for Settlement and Reconciliation
Blockchain is being adopted selectively for cross-border payments, immutable transaction records, and faster reconciliation where auditability is critical. - Embedded Payments
Payments are becoming part of larger platforms such as marketplaces, SaaS tools, and mobility apps, rather than standalone experiences. - Automation in Compliance and Risk
KYC, AML, and regulatory reporting are increasingly handled through automated systems to reduce manual overhead and error. - Global Interoperability means the app wars might finally end. You’ll send money from your Venmo to someone’s PayPal account without thinking twice about it. Different countries, different currencies, different apps – none of that will matter anymore.
For enterprises, the direction is clear. Payment apps are becoming infrastructure-first systems, built to manage risk, compliance, and scale quietly in the background rather than compete on surface-level features.
Why Build a Payment App with Appinventiv?
The payment app landscape moves fast, and building something that lasts requires more than just coding skills. You need a team that understands both the technical complexities and the business realities of FinTech app development.
This is where we come in. At Appinventiv, we’ve delivered over 3000 digital products, including 200+ Fintech solutions. Across these engagements, our payment-focused builds have consistently achieved fraud detection accuracy of up to 98%, maintained a 99.50% security SLA for transactions, and helped clients reduce operational costs by nearly 30% through smarter automation and system design.
For instance, we partnered with Mudra to build a fully compliant and AI-driven budget management platform. Currently, this FinTech app is live in 12+ countries, allowing users to manage their budget efficiently.
We have also built a financial literacy app for Edfundo. The platform provides users with an interactive user interface, personalized learning, real-time goal tracking, and other engaging features. The results?
- $500,000 received pre-seed funding
- $3 million prepared for a seed funding round
From PCI DSS compliance to user acquisition strategies, our team of 1600+ tech experts specializes in next-gen payment platform development that works seamlessly, whether you have 1,000 users or 10 million.
The fintech space rewards companies that move quickly but thoughtfully. With our ISO certified excellence, regulatory compliance expertise, and deep understanding of what users actually want, we can help you build a payment solution that doesn’t just function; it thrives.
Ready to turn your payment app development idea into reality? Let’s talk about what’s possible.

FAQs
Q. What is a payment app?
A. A payment app is a digital application that allows users or businesses to send, receive, and manage money electronically. It connects users, payment gateways, and banks to process transactions securely, whether for in-store purchases, online payments, or peer-to-peer transfers.
Q. What are the benefits of creating a payment app?
A. The payment app market offers tremendous opportunities driven by changing consumer behavior and technological advancement. These apps have the potential to increase financial inclusion, reduce friction in commerce, and enable new business models that weren’t previously possible. This represents billions of potential users who could benefit from accessible digital payment solutions.
Payment apps also provide multiple revenue streams through transaction fees, premium features, and financial services. The recurring nature of payment transactions creates predictable revenue and high user engagement.
Even if the path of building a payment platform is not easy, the rewards are significant.
Q. What is the cost of payment app development?
A. On average, the cost of payment app development ranges between $40,000 and $600,000 or more, based on your unique project requirements and project complexity. For instance,
- Basic apps with MVP-level features cost between – $40,000 and $100,000
- Intermediate-level app development costs range from $100,000 to $250,000
- Advanced complexity app development cost is between – $250,000 and $400,000+
- Enterprise-grade payment apps with futuristic features cost – $400,000 – $600,000 or more
Discuss your payment app development idea with a reputed payment processing app development company like Appinventiv and get a detailed cost estimate tailored to your needs.
Q. What is the timeline for payment app development?
A. On average, the time it takes to build a payment app ranges between 4 – 18 months:
- A simple payment app can take 4–6 months.
- Mid-level products usually need 6–12 months
- Enterprise payment platforms often run 9–18 months or more.
Q. Which payment gateway is best?
A. There is no single “best” gateway. Stripe, PayPal, and Square are popular for card payments, while the right choice depends on region, transaction volume, supported payment methods, and compliance requirements. Most enterprises support more than one gateway to reduce risk.
Q. What measures should we take to ensure regulatory compliance in our payment app development?
A. Regulatory compliance for payment app development involves multiple requirements:
- PCI DSS Compliance
- Know Your Customer Requirements
- Anti-Money Laundering Compliance
- Data Privacy Regulations like GDPR, CCPA, etc.
These are some of the many payment compliances we adhere to while developing payment apps
Q. Is PCI compliance mandatory?
A. Yes. If your app processes, stores, or transmits card data, PCI DSS compliance is mandatory. Skipping or delaying it leads to rework, failed audits, and potential penalties.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Open Banking in Australia: A Practical Guide for Businesses
Key takeaways: Open banking-driven “Smart Data” initiatives are projected to contribute up to $10 billion annually to the Australian economy. Enterprises that follow a phased rollout covering readiness assessment, compliance alignment, API integration, cybersecurity, and scaling achieve faster deployment and lower operational risk. Constant CDR updates, accreditation complexity, and modernising legacy banking systems continue to…

Financial Wellness App Development: Process, Features and Costs
Key Takeaways Strategic ROI: Financial wellness apps are no longer "perks"; they are critical tools for reducing financial presenteeism and improving institutional retention. Technical Integrity: Successful deployment requires seamless integration with Human Capital Management (HCM) systems and secure Open Banking APIs. Compliance-First: Enterprise-grade solutions must prioritize SOC2, GDPR, and ISO 27001 standards to protect sensitive…

Money Transfer App Development: Building Secure Payment Apps in 2026
Key Takeaways Money transfer apps in 2026 succeed when compliance, security, and scalability are designed into the platform from day one, not added later. Choosing the right app type early helps avoid costly rework as transaction volumes, regions, and regulatory demands increase. Strong internal ledgers, clear settlement states, and automation are critical to preventing reconciliation…