- The Market Momentum Behind Generative AI Adoption
- The Business Benefits of Generative AI
- Use Cases of Generative AI for Businesses
- 1. Knowledge and Decision Support
- 2. Customer Support and Experience
- 3. Software Development and IT Operations
- 4. Sales, Marketing, and Revenue Teams
- 5. Operations and Internal Processes
- 6. HR and Talent Functions
- Choosing the Right Generative AI Use Cases to Scale
- Real-World Examples of Generative AI in Business
- 1. Coca-Cola- AI-Driven Creative Campaigns
- 2. Zalando- Faster Marketing Content at Lower Cost
- 3. BMW- Data-Driven Insights Across Operations
- 4. Duolingo- Personalized Learning with AI
- How Different Industries Are Applying Generative AI
- 1. Financial Services
- 2. Healthcare and Life Sciences
- 3. Retail and eCommerce
- 4. Manufacturing and Supply Chain
- 5. Media, Marketing, and Creative Industries
- Framework to Implement Generative AI in Business
- Step 1: Start With the Work, Not the Technology
- Step 2: Check Data Readiness and Access
- Step 3: Design for Security and Control from Day One
- Step 4: Pilot with Purpose
- Step 5: Scale What Earns Trust
- Step 6: Measure Impact, Not Excitement
- Designing Secure, Scalable, and Trusted Generative AI Systems
- Choosing the Right Generative AI Model for Your Business Needs
- 1. Large Language Models (LLMs)
- 2. Domain-Specific or Fine-Tuned Models
- 3. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Models
- 4. Multimodal Generative Models
- Build, Buy, or Hybrid: Choosing the Right Operating Model
- Moving From Generative AI Tools to Enterprise Capability
- What the Future of Generative AI Means for Businesses
- How Appinventiv Helps Businesses Build and Scale Generative AI
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- Generative AI delivers real value only when embedded into core business workflows, not treated as a standalone tool.
- The strongest generative AI use cases focus on reducing decision friction, improving consistency, and scaling knowledge, not just automation.
- Security, governance, and data grounding determine whether generative AI can scale safely across the enterprise.
- Businesses that move beyond pilots early gain compounding advantages in learning, execution, and long-term business impact.
- Treat generative AI as infrastructure, not experimentation, to unlock sustained efficiency and growth.
Not long ago, generative AI for business was treated as an experiment. Teams tested tools, leadership watched from a distance, and results were mixed. That phase is over. Today, generative AI is being applied directly inside core workflows, shaping how real work gets done rather than sitting in isolated experiments. Customer interactions, internal reporting, software development, and operational decision-making are all starting to change for the better, driven by artificial intelligence.
McKinsey’s latest global AI survey shows this clearly: 88% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function, and generative AI business applications are steadily moving into core workflows.
What the numbers do not immediately show is how uneven progress has been. Many organisations exploring generative AI for business transformation struggle to move past pilots. Data fragmentation, unclear ownership, and late-stage security concerns slow things down. For leaders considering secure generative AI for business, the real questions are practical ones. Can it scale? Can it be governed? Can it deliver value without introducing new risks? This is where generative AI risks for business tend to surface.
In this blog, you will learn how companies are beginning to implement generative AI in business with discipline rather than urgency. We examine real business use cases for generative AI, the benefits of generative AI for business growth, and the decisions that shape long-term generative AI business impact. You will also see examples of generative AI in business that point to the future of generative AI as a dependable, enterprise-grade capability.
Beyond implementing generative AI into existing operations, exploring innovative AI business ideas can help startups and enterprises identify entirely new revenue streams and market opportunities.
McKinsey finds 88% of organizations already use AI in at least one business function. The advantage now depends on how effectively it’s scaled.
The Market Momentum Behind Generative AI Adoption
For a long time, generative AI for business felt optional. Many leadership teams parked it alongside other “watch and learn” technologies and moved on. That posture is getting harder to defend. Not because everyone suddenly loves AI, but because the questions being asked inside organizations have changed. They are no longer about curiosity. They are about relevance.
What’s driving that shift is scale. According to Grand View Research, the global generative AI market is expected to reach $324.68 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 40.8% annually.
Forecasts don’t guarantee outcomes, but they do reflect intent. Budgets move before results fully show up. Strategy follows soon after. The steady rise of generative AI in business environments suggests that companies are preparing for a future in which this capability is woven into everyday work rather than bolted on as a tool. For leaders thinking about generative AI for business growth, the real signal isn’t the size of the market. It’s the shrinking window to build experience before competitors do.
The Business Benefits of Generative AI
The real value of generative AI for business doesn’t come from novelty. It comes from removing the friction that teams have tolerated for years. Long review cycles and repetitive analysis. Decisions slowed down by scattered information. When generative AI in business is applied thoughtfully, those frictions start to ease.
What businesses notice first is not transformation. It is a relief. Work moves faster. People spend less time searching, rewriting, or rechecking. That is where generative AI business impact begins to show up.
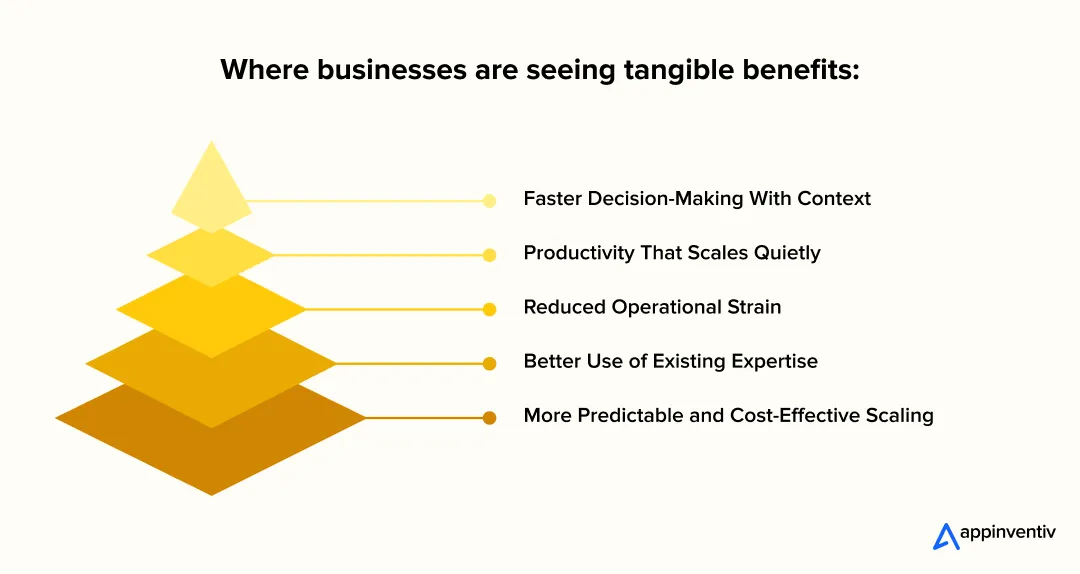
- Faster decision-making with context: Teams use generative AI business applications to pull together insights from documents, dashboards, and systems without stitching information manually. Decisions happen sooner, with better grounding.
- Productivity that scales quietly: One of the most consistent benefits of generative AI for business is the time it saves across everyday tasks. Drafting, summarization, analysis, and internal support work get lighter without forcing teams to change how they think.
- Lower operational strain: When applied to the right workflows, generative AI for business growth reduces backlogs, speeds up turnaround times, and cuts down on handoffs between teams.
- Better use of existing expertise: Instead of replacing judgment, generative AI in business often amplifies it. Years of experience and insight become easier to access, and teams avoid repeating work that has already been done.
- More predictable scaling: Over time, these gains help offset the cost of implementing generative AI in business, especially when solutions are reused across multiple teams or functions.
What matters most is intent. Businesses that see lasting results approach generative AI as a capability that needs direction, governance, and expert guidance, not as a shortcut. With the right consultation upfront, isolated wins turn into sustained generative AI for business transformation, while risks around scale, security, and compliance are addressed early rather than after the fact.
Use Cases of Generative AI for Businesses
For most businesses, the challenge is not identifying use cases for generative AI, but deciding where to apply it first. The harder question is where it actually delivers value without adding complexity. The most effective generative AI use cases tend to sit inside existing workflows, improving how decisions are made, how information moves, and how teams spend their time.
Rather than chasing isolated wins, organizations that see progress with generative AI for business focus on repeatable patterns that scale across functions.
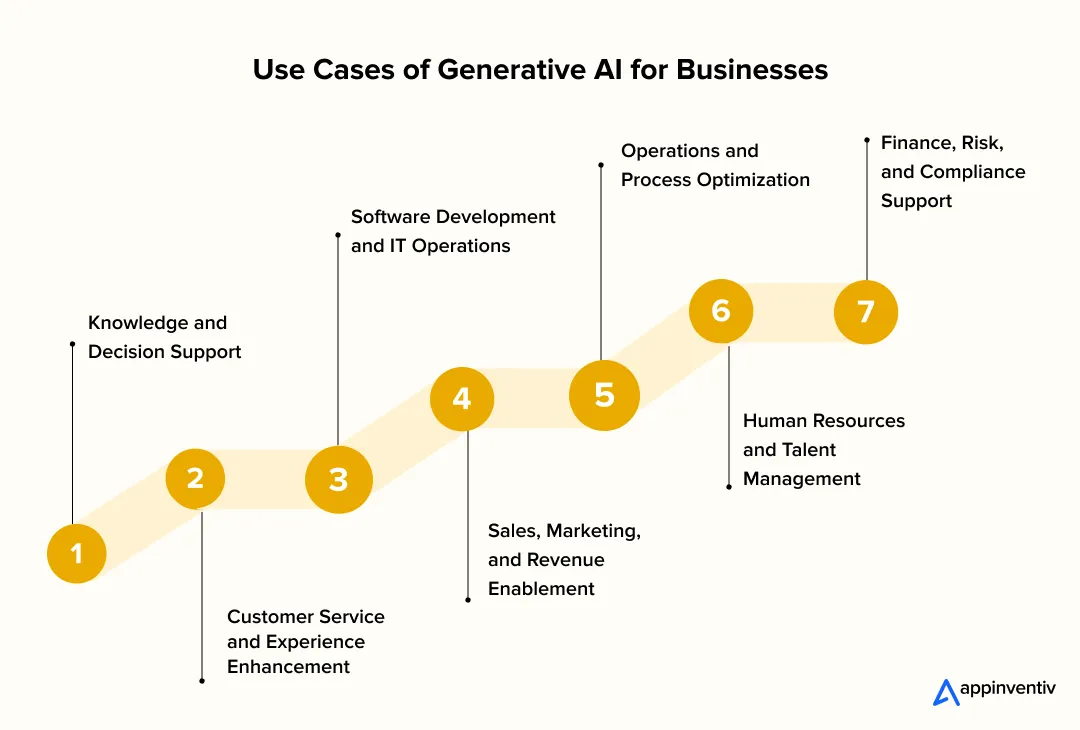
1. Knowledge and Decision Support
This is often the first place where generative AI in business creates a measurable impact.
Teams use generative AI to:
- Summarize long documents, policies, and reports
- Surface answers from internal knowledge bases
- Compare options and highlight risks using enterprise data
These generative AI business applications reduce time spent searching and synthesizing information, especially in legal, compliance, finance, and leadership roles.
2. Customer Support and Experience
Customer-facing teams rely heavily on consistency and speed. This makes them strong candidates for business use cases for generative AI.
Common applications include:
- Drafting and suggesting responses for support agents
- Summarizing customer history across systems
- Assisting with escalation handling and resolution guidance
When implemented carefully, these generative AI business use cases improve response time & quality without removing human accountability.
Also Read: AI in Customer Experience: Revolutionizing Business Growth
3. Software Development and IT Operations
Engineering teams are among the most active users of generative AI for business development.
Typical use cases include:
- Code generation and refactoring support
- Documentation and test case creation
- Explaining legacy code and system dependencies
Here, generative AI business applications reduce cognitive load rather than replacing engineering judgment, which helps adoption stick.
4. Sales, Marketing, and Revenue Teams
Revenue functions benefit from generative AI when it supports preparation rather than automation. Businesses apply generative AI to:
- Draft sales proposals and outreach content
- Personalize messaging based on customer context
- Analyze deal notes and pipeline risks
These are widely adopted examples of generative AI in marketing and other teams, especially when speed is needed without sacrificing relevance.
5. Operations and Internal Processes
Operations teams often deal with fragmented data and manual coordination. High-impact generative AI business use cases include:
- Generating operational summaries from multiple systems
- Supporting planning and forecasting discussions
- Assisting managers with performance insights
Over time, these use cases contribute directly to generative AI for business growth by reducing delays and improving execution quality.
6. HR and Talent Functions
People teams increasingly use generative AI in business applications that support scale without losing human context.
Common uses include:
- Drafting job descriptions and internal communications
- Summarizing feedback and performance reviews
- Supporting learning and onboarding content
These applications focus on efficiency rather than decision-making authority, which helps businesses manage generative AI risks.
Choosing the Right Generative AI Use Cases to Scale
Not every generative AI business use case deserves to grow. Some ideas look impressive in demos but collapse under real-world conditions. Organisations that succeed with generative AI for business are selective early and disciplined about what they scale.
Strong use cases usually share a few traits:
- They sit inside high-volume workflows
- They depend on scattered or hard-to-access information
- They benefit from consistency more than creativity
This focus helps control the cost of implementing generative AI in business and limits its risks. Over time, it also strengthens the overall generative AI adoption strategy, turning early wins into repeatable value rather than isolated experiments.
Real-World Examples of Generative AI in Business
Adoption of generative AI for business isn’t a future idea anymore- it’s happening now, with major brands experimenting across marketing, product design, customer engagement, and internal operations. These examples show how companies are using generative AI business applications to solve real problems.
1. Coca-Cola- AI-Driven Creative Campaigns
Coca-Cola has been applying generative AI business applications in its marketing efforts, including reimagining its iconic holiday advertising using AI tools that blend brand history with modern creativity. By doing so, the company explores new ways to connect with audiences at scale while preserving its signature storytelling style.
2. Zalando- Faster Marketing Content at Lower Cost
European retailer Zalando used generative AI for business to overhaul its marketing content creation. By using models to generate imagery and campaign assets, it has cut production time from weeks to days and sharply reduced costs for routine content, allowing their creative teams to focus on strategy and innovation.
3. BMW- Data-Driven Insights Across Operations
BMW isn’t just using AI in cars; it’s applying generative AI to internal business applications to analyze complex datasets and generate insights into operations and strategy. These tools help leaders make faster, better-informed decisions based on patterns that traditional reporting often misses.
4. Duolingo- Personalized Learning with AI
In education, Duolingo uses generative AI inside its language-learning platform to provide personalized practice, feedback, and language exercises tailored to each learner. This is a clear case where business use cases for generative AI directly enhance user experience and deepen engagement.
Across these brands, the common theme is not AI for its own sake. It’s generative AI in business solving real problems- making workflows faster, creative output richer, customer engagement more responsive, and decision processes smarter. These aren’t science projects; they’re early instances of generative AI for business transformation that others can learn from.
Also Read: How Much Does Duolingo like App Development Cost?
The impact you’ve seen comes from disciplined execution, not experimentation. Bring generative AI into your operations with clarity, control, and measurable outcomes.
How Different Industries Are Applying Generative AI
The way generative AI for business shows up varies widely across industries. What works in retail rarely maps cleanly to healthcare. Financial services worry about risk long before they worry about creativity. Manufacturing cares about precision, not novelty. The strongest generative AI business applications reflect those realities rather than forcing a one-size-fits-all approach.
1. Financial Services
Banks and financial institutions are applying AI in business, particularly generative AI in finance, to support research, compliance reviews, and customer interactions. Rather than replacing analysts, systems summarize documents, surface regulatory context, and assist frontline teams with faster responses. These generative AI business use cases are tightly governed, reflecting the higher tolerance for accuracy over speed.
2. Healthcare and Life Sciences
In healthcare, generative AI for business applications often focuses on documentation, clinical summarization, and knowledge support for practitioners. The goal is efficiency without disrupting clinical judgment. When AI in healthcare is applied carefully, these use cases reduce administrative load while managing generative AI risks for businesses tied to data sensitivity.
3. Retail and eCommerce
Retailers lean on generative AI in business, especially AI in eCommerce, to personalize content, speed up product descriptions, and analyze customer behavior across channels. These examples of generative AI in business directly support conversion and engagement, making them popular entry points for business growth.
4. Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Producers are applying generative AI in manufacturing through generative AI business applications that interpret operational data, summarize maintenance logs, and support production planning discussions. The value here comes from clarity rather than automation. By turning complex operational information into usable insights, these systems help teams act faster without forcing changes to existing processes or infrastructure.
5. Media, Marketing, and Creative Industries
Creative teams use generative AI in business applications to accelerate ideation and production, not replace creative direction. Content drafts, variations, and testing assets are generated faster, allowing teams to focus on strategy and storytelling.
Across industries, the pattern is consistent. Successful organizations align generative AI for business transformation with existing workflows, risk tolerance, and data maturity. The industries seeing the most impact are not chasing novelty. They are applying generative AI, which quietly improves how work gets done, day after day.
Framework to Implement Generative AI in Business
Implementing generative AI for business rarely fails because of the model. It fails because teams rush in without clarity. Too many initiatives start with tools and end with confusion. Businesses that get this right treat generative AI as a capability that grows over time, not a switch that gets flipped. A practical approach focuses less on speed and more on fit.
Step 1: Start With the Work, Not the Technology
Before choosing platforms or vendors, teams must look closely at where effort is being wasted.
Ask simple questions:
- Where do people spend time searching, rewriting, or reconciling information?
- Which workflows depend on scattered data or repeated judgment calls?
- Where would consistency matter more than creativity?
This step shapes realistic business use cases for generative AI and prevents misalignment early.
Step 2: Check Data Readiness and Access
Strong generative AI business applications depend on context. That context comes from enterprise data.
Teams typically assess:
- What data is reliable and up to date
- Who should be allowed to access what
- Where gaps or quality issues exist
This is also where early generative AI risks for business surface, especially around sensitive or regulated information.
Step 3: Design for Security and Control from Day One
Businesses that plan to scale address security and governance in generative AI environments from the outset.
This usually includes:
- Role-based access and permissions
- Human review for high-impact outputs
- Logging and traceability for accountability
Governance works best when it supports progress rather than blocking it.
Step 4: Pilot with Purpose
Pilots are not about proving the model works. They are about ensuring that the workflow improves.
Effective pilots:
- Focus on one or two generative AI business use cases
- Measure time saved, quality improved, or friction reduced
- Collect feedback from real users
This keeps the cost of implementing generative AI in business under control while building confidence.
Step 5: Scale What Earns Trust
Only a small set of pilots deserve to grow. The ones that do usually show clear value and low disruption.
Scaling generative AI in business means:
- Reusing successful patterns across teams
- Standardizing architecture and governance
- Aligning ownership and support models
Over time, this turns experimentation into a repeatable, generative AI approach for business transformation.
Step 6: Measure Impact, Not Excitement
Lasting success depends on discipline.
Businesses track:
- Adoption across teams
- Changes in cycle time or workload
- Long-term generative AI business impact
This feedback loop shapes a sustainable generative AI adoption strategy and supports steady generative AI for business growth, without chasing noise.
Also Read: Harnessing AI for Enterprise: Driving Business Innovation
Designing Secure, Scalable, and Trusted Generative AI Systems
Most problems with generative AI for business don’t show up on day one. They appear later, when more people start using the system, when real data come into play, or when an output suddenly matters more than expected. What looked fine in a demo starts to feel fragile in production.
That’s where many teams realize something important. Generative AI in business cannot be treated like another tool you roll out and forget. It behaves more like a shared capability. It touches data, workflows, and judgment simultaneously. Without clear boundaries, things get messy fast.
Teams that manage to scale usually keep a few basics in place:
- Limit what the system can see and who it can respond to
- Decide upfront where human review is non-negotiable
- Make sure outputs can be traced back and questioned
- Assign real ownership so responsibility doesn’t blur
This approach doesn’t remove risk. It makes risk visible. And that matters. When generative AI risks for businesses are understood and handled early, trust grows naturally. Over time, generative AI business applications stop feeling experimental and start feeling dependable. That’s when scale becomes possible, and the generative AI business impact actually lasts.
Choosing the Right Generative AI Model for Your Business Needs
The right generative AI business model depends more on how your organization operates than on any single technology choice.. Different models behave differently, demand different levels of control, and suit different business realities. Getting this wrong early often leads to wasted spend or stalled adoption.
At a high level, most generative AI for business initiatives fall into a few common model choices.
1. Large Language Models (LLMs)
These are the models most people think of first. They generate text, summarize information, write code, and answer questions across a wide range of topics.
Best suited for:
- Businesses looking for broad generative AI business applications
- Knowledge-heavy teams like legal, compliance, marketing, and engineering
- Organizations that need flexibility across multiple use cases
LLMs work well when paired with strong data controls, especially for secure generative AI for business environments.
Also Read: Enterprise LLM Model Development: A Complete Guide
2. Domain-Specific or Fine-Tuned Models
These models are trained or tuned on industry- or company-specific data. They trade general knowledge for precision and consistency.
Best suited for:
- Regulated industries such as finance and healthcare
- Businesses with well-structured internal data
- Use cases where accuracy matters more than creativity
For many organisations, this approach reduces generative AI risks for business and improves trust faster.
3. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Models
RAG models don’t rely only on what they were trained on. They pull answers from approved internal sources in real time and then generate responses.
Best suited for:
- Businesses are concerned about hallucinations
- Organizations with large document repositories
- Teams that need traceable, explainable outputs
RAG is often the backbone of scalable generative AI in business, especially where compliance is non-negotiable.
4. Multimodal Generative Models
These models work across text, images, audio, or video.
Best suited for:
- Media, retail, and creative industries
- Product teams working on rich customer experiences
- Businesses experimenting with design, training, or support content
They are powerful but usually require clearer guardrails to manage costs and risks.
Build, Buy, or Hybrid: Choosing the Right Operating Model
Beyond model type, businesses also choose how to deploy generative AI:
- Buy when speed and proven capability matter most
- Build when differentiation and control are critical
- Hybrid when scaling across teams with shared governance
The right mix depends on internal skills, the cost of implementing generative AI in business, and long-term ownership expectations.
Ultimately, the best generative AI business model is the one that aligns with how your organization already operates, the risk it can tolerate, and how success can be measured. When those pieces line up, generative AI for business growth becomes achievable without unnecessary complexity.
Moving From Generative AI Tools to Enterprise Capability
Using generative AI tools is easy. Turning them into something the organization can rely on is not. The difference lies in how generative AI in business is embedded into workflows, ownership models, and decision paths.
When generative AI business applications are treated as shared capabilities instead of standalone tools, adoption improves. Governance becomes clearer. Results become measurable. This shift is what enables generative AI for business transformation, where systems support real work at scale and deliver lasting generative AI business impact, not just short-term productivity gains.
What the Future of Generative AI Means for Businesses
What matters going forward is not the next big AI release, but how seamlessly generative AI supports everyday decisions and tasks.. For most companies, what happens next will feel gradual rather than disruptive.
What leaders should realistically expect:
- From tools to infrastructure: Generative AI in business will move behind the scenes, supporting workflows rather than standing out as a separate system.
- Tighter governance, fewer assumptions: As usage grows, organisations will formalize controls to manage generative AI risks for businesses without slowing adoption.
- More focus on reuse than reinvention: Successful generative AI business applications will be built once and extended across teams instead of rebuilt for every use case.
- Clearer accountability and ownership: Businesses will define who owns outcomes, not just platforms, as generative AI business impact becomes easier to measure.
- A slower, steadier path to growth: Long-term generative AI for business growth will come from disciplined scaling, not rapid rollouts.
For Businesses, the future of generative AI in business is not about racing ahead. It is about building experience early, learning deliberately, and staying ready as expectations continue to rise.
The future of generative AI belongs to enterprises that treat it as infrastructure, not experimentation. Build it once, govern it well, and scale with confidence.
How Appinventiv Helps Businesses Build and Scale Generative AI
Most enterprises don’t get stuck on ideas around generative AI. They get stuck when those ideas meet real systems, real data, and real risk. Appinventiv works with organizations at that point, providing generative AI development services built to stand up beyond pilots. As AI consultants, we stay focused on fit first. Where does generative AI belong, how much customization is necessary, and what does scale actually mean for this business?
Our work usually starts at the intersection of strategy and reality. As Generative AI consultants, we help enterprises decide where generative AI genuinely fits, which generative AI business models make sense, and how much customization is actually required. That approach has led to the launch of 80+ Gen AI applications and the training and deployment of 75+ custom generative AI models, many of them built on proprietary enterprise data rather than generic datasets.
Our work spans decision-support platforms like MyExec, scalable airline systems for Flynas, and AI-enabled healthcare engagement through YouComm.
If your organization is looking to move generative AI into real operations with confidence, Appinventiv helps turn intent into capability, without losing control along the way. Let’s Talk!
FAQs
Q. What is generative AI, and how is it used in business?
A. Generative AI refers to systems that can create content, insights, or recommendations based on patterns in data. In practice, generative AI for business is used to summarize information, assist decision-making, support customers, generate content, and help teams work faster without replacing human judgment.
Q. How can generative AI transform business processes?
A. Generative AI transforms processes by reducing manual effort in knowledge-heavy work. Instead of teams searching, rewriting, or reconciling data, generative AI in business helps surface context quickly, streamline workflows, and improve consistency. Over time, this leads to measurable generative AI for business transformation across operations.
Q. What are the top generative AI solutions for business transformation?
A. There is no single “best” solution. Most enterprises combine large language models, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and domain-specific models based on risk and use case. The strongest generative AI business applications are those grounded in internal data, governed properly, and aligned with real business outcomes.
Q. How does generative AI impact business efficiency and growth?
A. The immediate impact shows up as time saved and reduced operational friction. Over the longer term, generative AI for business growth comes from faster decision cycles, better use of internal expertise, and the ability to scale support without scaling headcount. This is where sustained generative AI business impact becomes visible.
Q. How can Appinventiv help implement generative AI for business transformation?
A. Appinventiv supports enterprises through generative AI development services and experienced Generative AI consultants who focus on fit, governance, and scalability. From identifying the right generative AI business use cases to deploying secure, production-ready systems, the goal is to turn generative AI into a dependable business capability.
Q. What challenges should businesses expect when adopting generative AI?
A. Common challenges include unclear use-case selection, data readiness issues, governance concerns, and underestimated costs. Without structure, the risks for business can grow quickly. A clear generative AI adoption strategy helps manage the cost of implementing generative AI in business while keeping risk visible and controlled.
Q. What industries benefit most from generative AI solutions?
A. Industries with complex data and knowledge workflows see the fastest value. This includes financial services, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, media, and technology. Across these sectors, examples of generative AI in business show gains in efficiency, personalization, and operational clarity when solutions are tailored to industry needs.
Q. How long does it take to implement generative AI in a business environment?
A. Timelines vary by scope and readiness. Focused pilots can take a few weeks, while enterprise-wide deployments often span several months. The key is sequencing. Organizations that implement generative AI in business gradually, with clear ownership and metrics, tend to see better long-term results.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Build AI Chatbot With RAG Integration: Appinventiv’s End-To-End Development Framework
Key takeaways: RAG chatbots improve enterprise AI accuracy by grounding responses in verified internal business knowledge. Governance, security, and explainability become critical as AI shifts from pilots to enterprise infrastructure. Investment typically ranges $50K–$500K depending on data integration, compliance, and deployment complexity. Strong data engineering and architecture discipline matter more than standalone model capability for…

The Enterprise Buyer’s Checklist Before Hiring an AI Development Partner
Key takeaways: Choosing an AI development partner is less about technical demos and more about real-world fit, governance, and operational reliability. Internal alignment on outcomes, data ownership, and integration realities is essential before engaging any enterprise AI partner. Strong partners demonstrate delivery maturity through governance controls, security discipline, and lifecycle management, not just model accuracy.…

Proving the ROI of Copilot AI Sales Enablement Software for Global Teams
Key Takeaways The ROI of Copilot AI sales enablement software shows up in revenue moments, not in generic productivity reports. Organizations that treat Copilot as an AI-powered sales enablement platform tied to sales process maturity see measurable outcomes within two quarters. Global sales teams require region-aware deployment models to avoid uneven adoption and misleading ROI…