- The Market Size Behind PCI Compliance - And Why FinTech Leaders Can’t Ignore It Now
- Understanding PCI DSS Before You Architect Your FinTech App
- What Does PCI Compliance Mean for Fintech App Business and What it Covers?
- Which FinTech Products Usually Fall Into Scope?
- Why PCI Compliance Is Critical for FinTech Apps
- It Protects Cardholder Data Across Every Interaction
- It Builds Customer Trust and Reduces Drop-Off
- It Keeps You Partner-Ready and Enterprise-Ready
- It Minimises Legal and Financial Exposure
- It Enables Smooth Scaling Without Rework
- Key PCI Compliance Requirements for Mobile FinTech Apps
- Secure Collection and Transmission of Card Data
- Limits on Storing Sensitive Information
- Tight Controls on Who Can Access What
- Visibility Into How Your Payment Systems Behave
- Regular Testing to Keep the App Safe Over Time
- A Step-by-Step Guide to PCI-Compliant Fintech App Development
- Map Your Data Flows and Define PCI Scope
- Choose PCI-Level Gateways, Vaults, and Certified SDKs
- Architect for Minimum Data Exposure
- Implement Strong Access Controls and MFA
- Build Monitoring, Logging, and Audit Trails
- Run Continuous Security Testing
- Prepare Documentation for the Assessment
- Complete the QSA Review and Fix Gaps
- Shift Into Continuous Compliance Mode
- Common PCI Compliance Challenges FinTech Apps Face
- Security Components in Payment Processing for Mobile Apps
- Encryption From Input to Processing
- Secure Coding and Input Handling
- Network Segmentation for Sensitive Payment Flows
- Strong Authentication and Multi-Factor Access Controls
- Activity Monitoring, Logging, and Real-Time Alerts
- PCI DSS Compliance Checklist for FinTech Teams
- Confirm Your PCI Scope
- Choose PCI-Compliant Gateways and Vendors
- Encrypt Data at Every Stage
- Restrict Access to Payment Systems
- Segment Your Architecture Properly
- Ensure No Card Data Is Stored Accidentally
- Implement Continuous Monitoring and Logging
- Test Security on a Regular Basis
- Keep Your Documentation Organized
- Review Your Setup Often
- Cost of Developing a PCI-Compliant FinTech App
- Types of Financial and FinTech Compliances to Consider Beyond PCI DSS
- Data Protection and Privacy Frameworks
- Security and Infrastructure Standards
- Financial Services and Banking Regulations
- Fraud, Risk, and Transaction Monitoring Compliance
- Why Appinventiv Is the Right Partner for Building a PCI-Compliant FinTech App
- FAQs
- Q. Why is it important for a fintech mobile app to be PCI DSS compliant?
- Q. What are the PCI Compliance Levels?
- Q. What are the requirements for PCI DSS compliance?
- Q. What is the relationship between PA DSS and PCI DSS?
Key Takeaways
- PCI DSS 4.0 is mandatory now, with tighter controls like MFA, continuous monitoring, and stronger cloud security.
- Designing PCI-ready architecture early saves teams from expensive rebuilds and stalled audits later.
- Breach costs now far exceed compliance costs, making PCI alignment the smarter long-term decision.
- Most fintech apps fall under PCI scope without realising it, even when card data passes through for a moment.
- PCI DSS 4.0 changes how mobile payment flows are built, requiring encryption, segmentation, and secure coding by default.
- Your development partner heavily influences audit success through proper scoping, clean flows, and accurate documentation.
If you’re leading a fintech business today, you already know the tension that sits between innovation and security. Your teams want to move fast, ship features, and get ahead of competitors. But every new payment flow, every card detail your app touches, and every integration you add quietly expands your risk surface. One data slip is all it takes for customer trust and brand value to collapse.
Most leaders feel this pressure long before a breach ever happens. It shows up in stalled releases, internal debates about encryption, or security sign-offs that drag on for weeks. And when auditors start asking tough questions, that’s when the real stress begins. Suddenly, the gap between “we are secure” and “we are compliant” becomes painfully obvious.
This is where PCI-compliant mobile app requirements come into play. Instead of reacting to risks, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) gives you a structured way to prevent them. It removes guesswork, aligns your engineering and security teams, and helps you build a payment experience customers trust. For fintech leaders, PCI is not just a checkbox but a way to give your business a security foundation that doesn’t crack under growth.
The advantage becomes even clearer when you’re building or scaling a card-handling product. Whether it’s a digital wallet, a lending platform, or a payment acceptance app, PCI-Compliant fintech app development makes sure every component-from APIs to storage to authentication-meets the bar that global financial institutions follow. It’s discipline, but the kind that pays off with fewer vulnerabilities, faster audits, and fewer sleepless nights.
In this blog, we’ll break down what PCI actually requires, the market size of apps that fall under it, the importance of PCI compliance for fintech apps, and how PCI DSS mobile app development works in the real world. You’ll learn the essential controls, the common pitfalls, the PCI compliance requirements you can’t miss, and the practical steps to build a secure, scalable, and audit-ready fintech product from day one.
If your fintech product handles card data in any form, this is the moment to build a PCI-compliant architecture that actually protects you.
The Market Size Behind PCI Compliance – And Why FinTech Leaders Can’t Ignore It Now
If you’re scaling a fintech product, you’re already operating in a space where every new wallet feature, BNPL flow, or payment integration quietly expands your PCI exposure. The market is exploding: mobile payments, card-on-file transactions, and embedded finance are becoming default behaviours for millions of users. And the more you grow, the more your app falls into the world of PCI Compliance for fintech apps, whether you planned for it or not.
This growth is happening at the same time PCI DSS has undergone its biggest shift in years. Version 4.0 brings in more than fifty strengthened expectations-tighter multi-factor authentication (MFA), continuous monitoring, clearer rules for cloud environments, and broader risk-based assessments. In simple terms, PCI compliance is no longer an annual audit; it’s the security foundation your product must run on. For anyone building a PCI-Compliant fintech mobile app, this changes how you architect every layer of the system.
And the urgency is backed by numbers. The 2025-based breach data as per IBM shows the average global incident costs around $4.44 million. In the financial sector, the impact is even heavier. A typical data breach cost around $6.08 million in 2024, which is roughly 22% higher than the global average. These aren’t theoretical risks. They represent what happens when payment apps scale without proper controls. If your product touches cardholder data-even indirectly-you’re expected to align with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard to stay secure and avoid heavy financial damage.
Fintech apps specifically made to disrupt the business environment feel this pressure more than typical digital products. You deal with mobile SDKs, partner APIs, cloud-native deployments, rapid feature cycles, and users accessing your app from every possible device. All of this creates a wider threat surface and makes PCI-compliant mobile app readiness a business necessity. At scale, the cost of developing a PCI DSS compliant fintech app becomes far cheaper than the cost of retrofitting security or recovering from a breach.
All of this leads to a clear moment for action: with PCI DSS 4.0 already shaping industry expectations, now is the right time to design or upgrade your product with compliance built into the core. It gives you a cleaner architecture, smoother audits, fewer vulnerabilities, and a competitive edge in a market where trust drives adoption. Acting early turns PCI compliance into strategy, not stress.
[Also Read: Understanding the Regulatory Compliance Implications for Cloud Businesses]
Understanding PCI DSS Before You Architect Your FinTech App
Before you commit to building a payment-driven product, you need a clear picture of what PCI DSS expects from you. It’s not something you “add later.” It quietly shapes everything, from your backend choices, partners, mobile SDKs, data flows to even timelines.
What Does PCI Compliance Mean for Fintech App Business and What it Covers?
PCI DSS defines how every touchpoint of card data must be protected inside your product ecosystem. In practical terms, this means:
- How card data enters your app, whether through input fields, tokenization flows, or partner SDKs.
- Where that data travels, including APIs, payment gateways, internal services, or third-party processors.
- How your systems store or avoid storing sensitive elements, especially anything that creates long-term risk.
- Who can access what, from engineers to automated systems that interact with payment environments.
- How you prove all this works, through ongoing monitoring, logging, and testing.
This is why PCI DSS influences architecture more than paperwork.
Which FinTech Products Usually Fall Into Scope?
Most fintech apps touch card data in ways teams don’t realise early on. You’re typically in scope if your product involves:
- Collecting or passing card details, even briefly.
- Wallets or payment apps that store cards on file or handle recurring billing.
- Lending or BNPL apps where repayments connect back to cards.
- Neobanking or issuance products interacting with card networks.
- Marketplaces that route transactions between buyers and sellers.
- Merchant-facing apps accepting payments through mobile devices.
For most scaling fintech products, scope is wider than it appears on the surface.
Why PCI Compliance Is Critical for FinTech Apps
For a fintech leader, PCI compliance isn’t just a regulatory requirement but the framework that keeps your product trustworthy, scalable, and partner-ready. The moment your app handles cardholder data, even for a split second, your business becomes responsible for protecting that information. And in a market where users jump from app to app with zero hesitation, security isn’t a feature-it’s a filter. This section breaks down why PCI compliance matters long before launch and how it directly shapes your ability to grow.
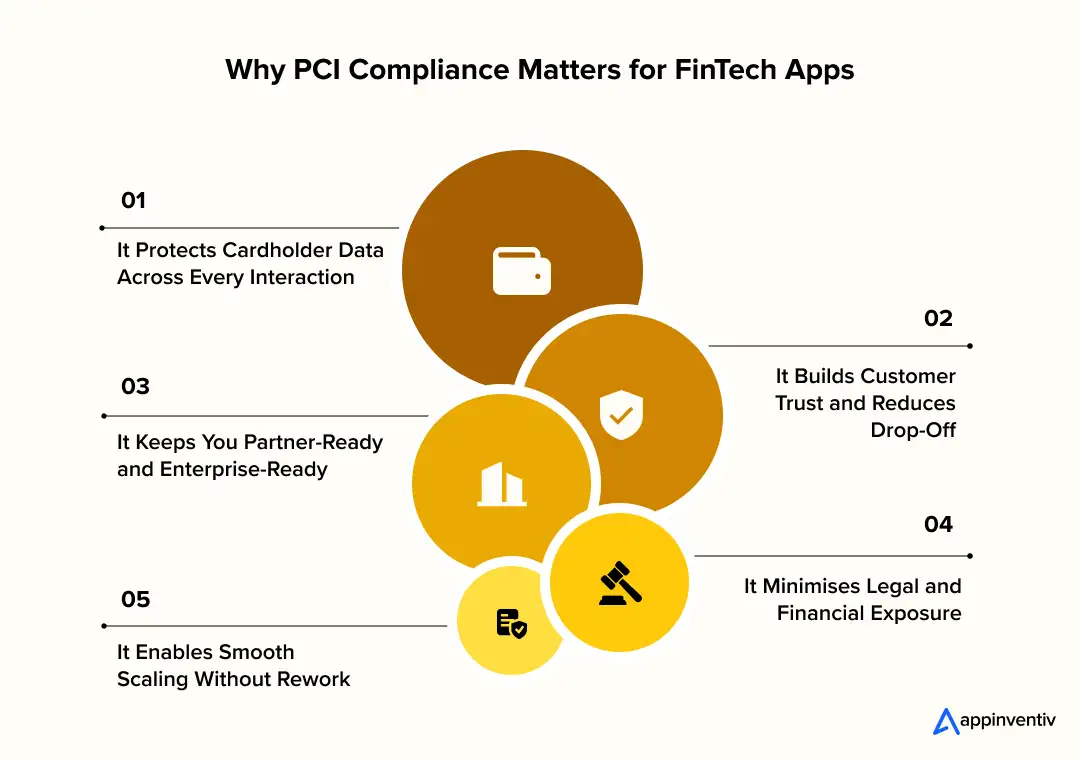
It Protects Cardholder Data Across Every Interaction
FinTech apps touch payment data in more places than most teams expect-APIs, mobile SDKs, backend systems, third-party processors, cloud environments, and analytics layers. PCI frameworks make sure each of these touchpoints is secured with the right controls so sensitive data never leaks, lingers, or gets exposed. This is where PCI DSS compliant fintech mobile app development standards become invaluable. They give your engineering team a clear blueprint for encrypting information, limiting access, and preventing weak links before they turn into security incidents.
It Builds Customer Trust and Reduces Drop-Off
Users don’t read your policies-they judge your security by how safe they feel entering their card details. When your app meets PCI Compliance for fintech apps, you’re signalling that cardholder information is handled with the same discipline followed by banks and global payment networks. That trust directly impacts everything from onboarding to conversions. A secure flow reduces checkout hesitation, boosts repeat usage, and creates long-term confidence that users won’t get burned by fraud after using your app.
It Keeps You Partner-Ready and Enterprise-Ready
Fintech apps grow by integrating with banks, processors, networks, and enterprise merchants. None of them will work with a platform that isn’t PCI compliant. Whether you’re aiming for enterprise contracts, expanding into new regions, or integrating advanced payment capabilities, PCI-Compliant fintech app development becomes a prerequisite. It speeds up partner approvals, reduces due-diligence hurdles, and positions your product as a reliable part of the payment ecosystem.
It Minimises Legal and Financial Exposure
A single card-related breach can lead to penalties, customer compensation costs, forensic audits, and massive brand damage. PCI DSS gives you a structured way to prevent the vulnerabilities that usually trigger these incidents. When your architecture follows PCI DSS compliant fintech mobile app development guidelines, you’re reducing the odds-and cost-of security failures that could set your product back years. Compliance isn’t an overhead; it’s insurance against unnecessary risk.
It Enables Smooth Scaling Without Rework
The earlier you align with PCI DSS, the easier it becomes to scale. Teams that ignore compliance in the early stages eventually face costly rebuilds, blocked features, and delayed rollouts because the foundation wasn’t designed for secure payment handling. When PCI is built into your app from day one, growth becomes frictionless. You avoid compliance debt, maintain clean audit trails, and make future product expansions-like tokenization, international payments, or multi-processor routing-much faster.
Key PCI Compliance Requirements for Mobile FinTech Apps
Once you decide to build a payment-focused app, there are a few PCI rules you simply can’t ignore. These requirements shape how your data flows work, how your backend is designed, and even which partners you’re allowed to integrate with. Getting the basics right early makes development smoother and keeps you out of trouble later.
Secure Collection and Transmission of Card Data
Card details must be handled with care from the second a user types them in. This means your app screens, payment fields, and SDKs need to collect that information through protected pathways. The data should move only through encrypted channels when it travels between your app, servers, and processors. These safeguards form the backbone of a PCI-compliant mobile app and prevent leaks at the most vulnerable points.
Limits on Storing Sensitive Information
PCI rules are strict about what you can store-and in most cases, the answer is “as little as possible.” Card numbers, CVV codes, and track data should never sit in your database. If you must retain anything, it needs to be tokenized or encrypted. This plays a major role in PCI DSS compliant fintech mobile app development because it forces teams to design systems that avoid unnecessary exposure.
Tight Controls on Who Can Access What
Not everyone on your team should have their hands anywhere near payment environments. PCI DSS 4.0 pushes for strong access controls, including multi-factor authentication, so only the right people and systems can reach sensitive areas. This avoids accidental misuse, internal mistakes, or credential-based attacks-three common issues in PCI compliance for fintech app teams.
Visibility Into How Your Payment Systems Behave
You can’t protect what you can’t see. PCI requires detailed logs, clear audit trails, and ongoing monitoring of the systems handling card data. This helps you catch unusual activity early and gives auditors the proof they need. For teams working on PCI DSS mobile app development, good monitoring is what keeps small issues from becoming major incidents.
Regular Testing to Keep the App Safe Over Time
Even a well-built app becomes risky if it isn’t tested often. PCI expects routine security checks-penetration tests, vulnerability scans, and code reviews-to ensure new features or integrations don’t create gaps. This reduces PCI compliance challenges later and keeps your app aligned with payment industry expectations as it grows.
A Step-by-Step Guide to PCI-Compliant Fintech App Development
Building a PCI-Compliant FinTech app is not a last-minute compliance exercise. It’s a development approach where you design your product so cardholder data never becomes a liability. When you build this foundation early, your app scales faster, integrates with payment partners easily, and avoids the expensive rewrites that crush timelines during PCI audits. Here’s what the process looks like when teams follow a real-world PCI engineering and compliance mindset from day one.

Map Your Data Flows and Define PCI Scope
Everything starts with understanding how card data moves through your system. You map the screens where data is entered, the SDKs that handle encryption, the APIs that pass payment details, and the backend services that respond to payment events. A tighter scope reduces effort, cost, and friction across your PCI compliance for FinTech app journey.
Choose PCI-Level Gateways, Vaults, and Certified SDKs
Half of PCI DSS compliant FinTech mobile app development depends on picking the right partners. PCI Level 1 gateways, tokenization services, and certified SDKs ensure your app never touches raw card data. This step alone removes months of engineering and audit pressure.
Architect for Minimum Data Exposure
A PCI-ready app is designed so sensitive card information never reaches your backend. Tokenization, direct-post flows, isolated payment microservices, and segmented VPCs help shrink your PCI footprint. These practices form the technical base of PCI DSS mobile app development.
Implement Strong Access Controls and MFA
PCI DSS 4.0 is far stricter about identity and access rules. Multi-Factor authentication, job-based permissions, no shared credentials, and logged privileged actions keep internal risks low and help your PCI-compliant mobile app hold up during audits. The PCI DSS implementation steps also require strict role separation, real-time access reviews, and continuous enforcement of least-privilege policies to ensure only the right people touch the right systems at the right time.
Build Monitoring, Logging, and Audit Trails
PCI isn’t only about preventing issues. It’s about proving you can detect them. Centralized logs, audit-safe storage, alerts for suspicious behaviour, and retained event histories ensure your FinTech app stays transparent and audit-ready at all times.
Run Continuous Security Testing
Security testing runs alongside development-not after. Pen tests, SAST, DAST, dependency checks, and CI/CD-based scans keep your PCI DSS mobile app aligned with PCI DSS 4.0 even as features evolve. Continuous testing prevents last-minute surprises.
[Also Read: Cybersecurity in FinTech Industry – How to Build a Financial App with Proactive Security Measures?]
Prepare Documentation for the Assessment
PCI requires evidence: updated diagrams, access logs, test results, vendor certificates, configuration details, and incident response plans. Teams that document early pass faster. Teams that don’t, will scramble later.
Complete the QSA Review and Fix Gaps
A Qualified Security Assessor reviews your controls, highlights gaps, and validates your readiness. Fixing these early ensures that your PCI DSS compliant FinTech app can meet enterprise requirements and integrate into the broader payments ecosystem without friction.
Shift Into Continuous Compliance Mode
PCI isn’t a one-time certification. Quarterly scans, annual assessments, access reviews, and architectural updates keep your product aligned with PCI DSS 4.0. Staying compliant prevents costly rebuilds and supports long-term scale.
PCI success depends heavily on who builds your product. A team experienced in PCI-Compliant FinTech app development already knows how to shrink scope, design tokenization flows, handle MFA edge cases, and prepare audit-friendly documentation. The wrong team forces rewrites and delays. The right team builds compliance into your code, your cloud, and your workflow- quietly and correctly.
As a firm experienced in payment processing & gateway development services, we can guide you through architecture, implementation, and audit readiness so your product stays compliant from the first release to every future update.
Common PCI Compliance Challenges FinTech Apps Face
Even well-funded fintech teams hit roadblocks when they start working toward PCI compliance. Most of these issues don’t show up in the early development stages – they appear during integration, scaling, or audits. Understanding these challenges upfront helps you avoid expensive rework and gives you a clearer path to a clean, PCI-ready product. Below is a practical table that breaks down the most common problems, what they actually mean in day-to-day development, and how to fix them with the least friction.
| Challenge | What It Actually Means | How to Resolve It (Practical Fixes) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope Creep (Unnecessary Systems Falling Into PCI Scope) | Card data touches more systems than intended-logs, proxies, microservices, analytics tools, or message queues accidentally end up handling sensitive data. | Redesign flows to ensure only the gateway sees raw card data. Use tokenization + direct-post integrations. Segment VPCs and isolate all payment logic. Keep analytics and logs outside card data paths. |
| Storing Card Data Without Realizing It | Debug logs, crash reports, SDK behaviour, or temporary payloads might retain PAN or partial card information. This creates unexpected storage violations. | Disable verbose logging for payment flows. Use redaction rules. Implement strict data retention policies. Ensure SDKs tokenize before data reaches your backend. Validate all logs before production. |
| Weak Access Controls and Shared Credentials | Developers, QA, DevOps engineers, and automation tools sometimes share access to payment environments, violating PCI DSS 4.0 requirements. | Enforce MFA everywhere. Adopt role-based access control. Use secret managers. Remove shared logins. Implement just-in-time access for sensitive systems. Audit access regularly. |
| Non-Compliant Third-Party SDKs or Gateways | A payment SDK, fraud tool, or analytics library may not follow PCI rules, putting your entire app at risk even if your code is clean. | Use PCI Level 1 service providers. Validate SDK documentation. Avoid tools that intercept, modify, or store cardholder data. Request Attestation of Compliance (AOC) from all vendors. |
| Poorly Segmented Infrastructure | Payment traffic and general app traffic share the same networks, microservices, or subnets – expanding audit scope dramatically. | Create isolated VPCs/subnets for payment components. Restrict internal routes. Use separate security groups and IAM roles. Keep payment proxies minimal and isolated. |
| Incomplete Logging and Monitoring | Events involving card data aren’t logged properly, or logs are missing fields auditors need. This leads to audit failures and undetected threats. | Implement centralized logging. Capture payment API events, access logs, WAF logs, and admin actions. Enable immutability. Add alerts for suspicious behaviour like repeated failed transactions. |
| Lack of Continuous Testing and Security Automation | Teams run pen tests once a year or only before audits, leaving months of untested code and new vulnerabilities. | Automate SAST, DAST, dependency scans, container scans, and configuration checks. Run pen tests quarterly. Integrate security checks into CI/CD pipelines. |
| Using Storage, Caches, or Queues That Leak Card Data | Message queues, caches (Redis), or object storage inadvertently catch sensitive payloads during processing. | Tokenize before queueing. Block raw card data from ever entering storage or distributed systems. Validate payloads in staging before deploying to production. |
| Misconfigured Cloud Services | Open ports, weak network ACLs, incorrect IAM roles, or unencrypted storage violate PCI expectations. | Enforce encryption at rest and in transit. Close non-essential ports. Use private endpoints. Restrict IAM roles with least-privilege principles. Add continuous misconfiguration scanning. |
| Documentation Gaps During Audit Time | Systems may be secure, but missing evidence, inconsistent diagrams, or incomplete policies lead to failed assessments. | Maintain architecture diagrams, data-flow charts, change logs, access reviews, and configuration evidence from day one. Keep a compliance runbook updated every sprint. |
From tokenization flows to low-scope architectures, we build fintech apps that stay compliant without slowing you down.
Security Components in Payment Processing for Mobile Apps
When you’re undertaking PCI-Compliant fintech app development, security isn’t one feature – it’s the foundation every other feature sits on. Users might see a simple card input screen, but behind that screen is an entire chain of protections that keep their data safe. These components work together to prevent leaks, block attackers, and ensure your app can handle payments at scale without breaking compliance rules. Here are the core pieces every mobile payment flow must have.
Encryption From Input to Processing
Encryption protects card data at every stage of its journey. The moment a user enters their details, the information should be encrypted on the device, safeguarded in transit, and unreadable to any system that isn’t supposed to see it. This includes:
- Client-side encryption through the gateway’s SDK
- TLS 1.2+ for all communication between app, server, and processor
- Strong key management using tools such as AWS KMS or HashiCorp Vault
If attackers intercept the data, they get nothing but encrypted noise.
Secure Coding and Input Handling
Many breaches start with insecure coding practices, not infrastructure issues. Your app must treat payment inputs with extra caution. This includes:
- Sanitizing and validating all payment-related input
- Avoiding client-side logic that exposes sensitive operations
- Preventing card data from touching logs, debugging tools, or analytics SDKs
- Using secure frameworks that reduce the chance of injection attacks
Clean, defensive code removes entire categories of vulnerabilities before they ever reach production.
Network Segmentation for Sensitive Payment Flows
Not every service in your app should be near payment data. Segmentation creates a smaller, safer zone where payment operations happen in isolation. This involves:
- Isolating payment microservices into dedicated VPCs or subnets
- Creating strict firewall rules that limit lateral movement
- Restricting internal traffic so non-payment components can’t reach payment systems
Segmentation keeps attackers from using one weak link to access your entire environment.
Strong Authentication and Multi-Factor Access Controls
Attackers often target internal access rather than user accounts. PCI DSS 4.0 expects multi-factor authentication (MFA) for anyone accessing environments involved in payment handling. A strong setup includes:
- MFA at the cloud console, CI/CD, and admin panel level
- Clear role-based access controls
- No shared credentials or admin accounts
- Regular review of who has access and why
If someone doesn’t absolutely need access to payment systems, they shouldn’t have it.
Activity Monitoring, Logging, and Real-Time Alerts
You can’t protect a payment system you can’t observe. Proper monitoring ensures that suspicious activity is caught early. Essential components include:
- Immutable logs for all payment-related events
- Alerts for failed payment attempts, privilege escalation, or unusual behaviour
- Centralized log storage using ELK, Datadog, CloudWatch, or similar
- Regular log reviews tied to your compliance process
Monitoring turns raw events into actionable security insight.
PCI DSS Compliance Checklist for FinTech Teams
This checklist gives your product, engineering, and security teams a clear view of what needs to be in place before calling your app PCI-ready. Each point is written as something you can actually act on during development of a PCI DSS compliant fintech mobile app.
Confirm Your PCI Scope
The first step is understanding exactly where card data flows in your system. Map the points where card details enter, move, and exit your app. Check whether any backend service, log, or third-party tool accidentally touches raw card data. The goal is to keep your PCI scope as small as possible, ideally by relying on tokenization early.
Choose PCI-Compliant Gateways and Vendors
Your entire compliance effort depends on the partners you integrate with. Before writing code, confirm that your payment gateway, fraud tools, and mobile SDKs hold valid PCI certifications. If a partner can’t provide an Attestation of Compliance, they shouldn’t be anywhere near your payment flow.
Encrypt Data at Every Stage
Encryption shouldn’t be limited to one part of the system. Card data must be encrypted on the device, during transmission, and anywhere it temporarily exists. Using TLS 1.2+ and secure key management ensures your PCI-compliant mobile app doesn’t leave sensitive details exposed at any step.
Restrict Access to Payment Systems
Only a very small group of people should ever access payment-related environments. PCI DSS 4.0 expects multi-factor authentication, role-based permissions, and full visibility into privileged actions. If someone doesn’t need access to card-related systems to do their job, they shouldn’t have it.
Segment Your Architecture Properly
A well-segmented system ensures payment components stay isolated from the rest of your infrastructure. Separate VPCs, strict routing rules, and clear boundaries between microservices minimize the impact of a failure and simplify audits for a PCI DSS compliant fintech mobile app.
Ensure No Card Data Is Stored Accidentally
A common compliance failure happens when logs, error traces, or SDK behaviour store sensitive details without the team noticing. Run checks regularly to confirm no raw card numbers or CVV codes are appearing anywhere. Tokenization should replace all sensitive data before it reaches your servers.
Implement Continuous Monitoring and Logging
PCI compliance requires full visibility. Make sure every payment event, API call, and admin action is captured in tamper-proof logs. Alerts should notify your team whenever suspicious activity occurs. This helps detect issues early and makes PCI reviews smoother.
Test Security on a Regular Basis
Compliance isn’t a once-a-year event. Schedule ongoing penetration tests, vulnerability scans, dependency checks, and secure code reviews. Integrate automated testing into your DevOps pipeline so issues are caught long before release.
Keep Your Documentation Organized
A secure system still fails audits if the documentation isn’t ready. Maintain updated architecture diagrams, data-flow charts, access reviews, and vendor certificates. Having everything organised upfront saves weeks of back-and-forth during PCI assessments.
Review Your Setup Often
Your app will evolve, and your PCI controls need to evolve with it. Review your SDKs, integrations, policies, and architecture whenever new features ship. This keeps your system aligned with PCI DSS 4.0 and reduces last-minute surprises.
Cost of Developing a PCI-Compliant FinTech App
The cost of PCI-compliant fintech app development depends on how much card data your system touches, the complexity of your payment flows, and how early your team starts designing for compliance. What most leaders don’t realise is that PCI doesn’t “add cost” – poor planning does. The more card data your backend handles, the more expensive your build, audit, and ongoing maintenance become.
A simple mobile app that uses tokenization and keeps card data out of the backend will naturally cost less. A complex app that handles recurring billing, card lifecycle management, or multi-processor routing will cost more because the architecture is heavier and the PCI scope is larger. In general, here’s what the range looks like:
- Basic PCI-ready fintech app: $30,000 – $80,000
Apps with direct-post payment flows, simple card storage via vault providers, and minimal backend exposure. - Mid-complexity PCI development: $80,000 – $150,000
Apps with lending flows, wallets, EMI setups, subscription billing, fraud checks, and multi-environment support. - Advanced PCI DSS compliant fintech app development: $150,000 – $300,000+
Products with tokenization engines, issuer processing, multi-tenant routing, orchestration layers, and deep cloud segmentation.
What really drives cost is not development hours – it’s the size of your PCI scope. Smaller scope means less infrastructure to secure, fewer audits, fewer compensating controls, and far lower operational overhead. That’s why choosing PCI Level 1 partners and designing for “zero raw card storage” can reduce long-term cost dramatically. A clean architecture always pays for itself.
[Also Read: Cost to Build a FinTech App: What You Need to Know]
Types of Financial and FinTech Compliances to Consider Beyond PCI DSS
PCI DSS might be the most urgent compliance requirement for payment-driven apps, but it’s not the only one fintech founders need to think about. As your product grows, you’ll run into different regulatory expectations based on how you handle data, who your customers are, and which markets you operate in. These compliances work alongside PCI DSS to keep your app safe, trustworthy, and partner-ready.
Data Protection and Privacy Frameworks
These govern how customer data is collected, processed, shared, and stored.
- GDPR (Europe) for user rights, consent, and data residency
- CCPA/CPRA (California) for privacy controls and opt-outs
- India DPDP Act, UK GDPR, APAC privacy laws, depending on your market
If your app stores personal data alongside card data, privacy compliance becomes unavoidable.
Security and Infrastructure Standards
These guide how your systems, cloud environments, and internal processes should be secured.
- SOC 2 for security, availability, and operational integrity
- ISO 27001 for information security management
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework for risk and control maturity
Enterprise clients often require these before integration.
Financial Services and Banking Regulations
If your product moves money, offers lending, or partners with banks, you may fall under industry-specific rules.
- FFIEC (US banking)
- PSD2 and Open Banking (EU, UK)
- RBI regulations (India)
- AUSTRAC and ASIC (Australia)
- FinCEN and AML/KYC requirements
Any app handling identity verification or cross-border payments will eventually deal with some of these.
Fraud, Risk, and Transaction Monitoring Compliance
Products with lending or money movement features often face additional obligations:
- AML/KYC frameworks
- Transaction monitoring requirements
- Model governance for AI-driven fintech compliance automation
- Audit trails for credit and underwriting decisions
These controls build the foundation for trust with regulators, banks, and partners.
Why Appinventiv Is the Right Partner for Building a PCI-Compliant FinTech App
We hope this guide has given you clarity on PCI-compliant fintech app development. Most teams underestimate PCI until they’re deep into development or stuck in an audit review. By now, you’ve seen how much the architecture, data flows, access controls, cloud setup, and partner choices matter long before a single feature goes live.
If this blog helped you understand the difference between “secure enough” and “PCI DSS ready,” then you already know why most fintech founders treat PCI as a strategic priority. The earlier you design for it, the cleaner your architecture, the smoother your audits, and the faster your product scales. Compliance isn’t friction – it’s what keeps your users confident and your business credible as you grow.
And that brings us to the most important part: choosing a team that actually knows how to build payment systems the right way. PCI is a specialised discipline. It needs engineers who understand tokenization workflows, architects who can design low-scope infrastructure, DevSecOps teams who can secure CI/CD pipelines, and compliance specialists who can guide your audit readiness.
This is exactly where Appinventiv stands out.
With years of experience building compliant fintech software – wallets, issuer systems, lending platforms, orchestration engines, merchant apps, BNPL flows, and fully PCI-aligned architectures – we know what a compliant system looks like in the real world.
As a leading fintech app development services provider, our team design zero-exposure data flows, implement secure SDKs, build isolated cloud environments, integrate multi-factor authentication, and ensure your entire payment chain stays audit-ready from day one. We’ve worked with global banks, enterprise processors, and fast-scaling fintech startups, giving us the technical depth and regulatory understanding most vendors simply don’t have.
More importantly, we don’t just “build the app”; we build the compliance framework around it. That means clear documentation for assessors, clean logs for audits, secure CI/CD pipelines, continuous testing, and a long-term compliance roadmap that keeps your product aligned as PCI DSS evolves.
If you want a partner who reduces your PCI scope, protects your architecture, and accelerates your go-to-market – not one who leaves you fixing issues at the end – Appinventiv is the team you want beside you. Get in touch with our experts now!
FAQs
Q. Why is it important for a fintech mobile app to be PCI DSS compliant?
A. Because the moment your app touches card details, even for a second, you’re responsible for keeping that information out of the wrong hands. PCI DSS gives you a clear rulebook for doing that. It keeps you out of trouble with partners, protects your users from fraud, and stops one security slip from turning into a nightmare. In fintech, trust disappears fast – PCI compliance is what keeps that trust steady.
Q. What are the PCI Compliance Levels?
A. PCI has four levels, and they’re based on how many card transactions your business handles in a year.
Level 1 is the highest – that’s for companies processing millions of payments.
Level 4 is the lowest – smaller merchants and early-stage apps usually start here.
Most fintech products eventually move into Level 1 or Level 2 as they grow, which means deeper checks, more documentation, and a cleaner architecture. A PCI DSS compliant fintech mobile app is easier to manage as you climb those levels.
Q. What are the requirements for PCI DSS compliance?
A. In simple terms, PCI lays out how you collect, move, store, and protect card data. It covers encryption, secure coding, tokenization, access controls, network design, logging, and regular testing. If your app follows these basics, you’re already halfway toward a PCI-compliant mobile app that can pass an audit without drama.
For businesses looking to undertake PCI-compliant fintech app development, we can guide you through every requirement, from architecture and controls to audits and documentation, so nothing gets missed.
Q. What is the relationship between PA DSS and PCI DSS?
A. PA DSS used to be the standard for payment application vendors, while PCI DSS focuses on protecting card data across the whole system. Over time, PA DSS got merged into the broader PCI framework. For a fintech leader, PCI DSS is the main thing to follow, but PA DSS principles still help when you’re choosing payment SDKs or designing modules that sit close to card data.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Financial Wellness App Development: Process, Features and Costs
Key Takeaways Strategic ROI: Financial wellness apps are no longer "perks"; they are critical tools for reducing financial presenteeism and improving institutional retention. Technical Integrity: Successful deployment requires seamless integration with Human Capital Management (HCM) systems and secure Open Banking APIs. Compliance-First: Enterprise-grade solutions must prioritize SOC2, GDPR, and ISO 27001 standards to protect sensitive…

Money Transfer App Development: Building Secure Payment Apps in 2026
Key Takeaways Money transfer apps in 2026 succeed when compliance, security, and scalability are designed into the platform from day one, not added later. Choosing the right app type early helps avoid costly rework as transaction volumes, regions, and regulatory demands increase. Strong internal ledgers, clear settlement states, and automation are critical to preventing reconciliation…

Building a Custom ACH Payment Software - Benefits, Features, Process, Costs
Key takeaways: A custom ACH payment system helps enterprises cut payment fees, reduce delays, and gain full control of payouts and collections. Modern ACH payment software development supports high-volume transactions, real-time tracking, and faster handling of errors. Strong compliance with NACHA rules, bank-grade security, and role-based access remain core parts of an enterprise ACH setup.…