- Key Factors That Affect Dating App Development Cost
- Product Scope and Feature Depth
- Trust, Safety, and Moderation Systems
- Compliance, Security, and Data Governance
- Scalability and Infrastructure Readiness
- Platform Choice and Its Impact on Dating App Development Cost
- Revenue Generation Strategies That Influence Platform Cost
- Where the Dating App Development Budget Goes
- How Development Timelines Influence Dating App Cost
- Enterprise Cost Modeling for Dating App Platforms
- Dating App Development Cost Breakdown Snapshot
- Types of Dating Apps Ranked by Cost Impact
- How Geography Influences Dating App Development Cost
- Middle East
- Australia
- Europe
- United States
- Other Regions and Distributed Teams
- Build vs Customize, Cost Implications for Enterprises
- Hidden and Ongoing Costs Enterprises Often Overlook
- Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- How Enterprises Optimize Dating App Development Costs Without Increasing Risk
- How Does Appinventiv Deliver Secure Dating Platforms at Scale?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Dating app investment ranges $40K–$400K, driven by scale, compliance, and trust infrastructure.
- Long-term ownership costs often exceed build-to-suit costs due to moderation, security, and scaling.
- Platform, geography, and rollout strategy act as multi-year cost multipliers.
- Enterprises that plan governance and architecture early avoid expensive re-engineering later.
Most enterprise product teams reach a point where launching another transactional app no longer moves the needle. Engagement, retention, and owned digital communities start becoming the real growth lever. That is where social discovery platforms, including dating-led ecosystems, enter the conversation.
You might already be seeing it in your portfolio. Loyalty apps are evolving into community layers. Media platforms are experimenting with interaction-driven experiences. Consumer brands exploring private social networks that deepen lifetime value. Dating and social discovery technology now sits inside broader digital ecosystems, not as standalone products.
At the same time, building one of these platforms is no longer a design-led exercise. Cost decisions today revolve around governance models, safety enforcement, compliance readiness, and the ability to scale without rewriting your architecture every six months. UI polish matters. Still, it is rarely what drives enterprise investment risk.
For reference, the cost to build a dating app in 2026 typically ranges from $40K to $400K, depending on scale, trust systems, and compliance depth.
This guide is not a development walkthrough. It is a cost decision framework to help your team understand where budgets go, where risks hide, and how to plan investment with long-term control in mind.
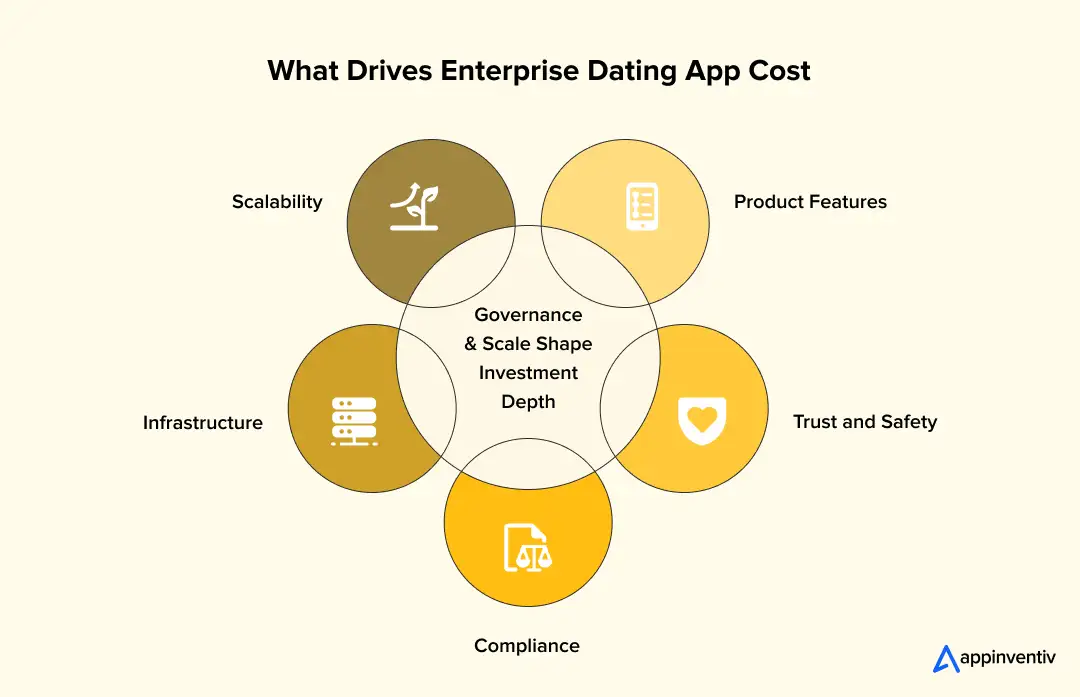
Key Factors That Affect Dating App Development Cost
Once your team starts scoping a social discovery platform, cost planning shifts from feature lists to system behavior. This shift is happening in a market expected to reach $3.24 billion by the end of 2026 and $3.51 billion globally by 2030.
The real question becomes simple. How much infrastructure, governance, and resilience does your platform need to handle real user behavior at scale?
Below are the core cost drivers that shape the cost to build a dating app at enterprise scale.
Product Scope and Feature Depth
Every dating platform looks simple on the surface. Profiles, matches, chats. Still, costs increase when systems must adapt in real time to user behavior, preferences, and monetization logic.
Feature scope is usually where cost variance starts, with dating app building cost per feature increasing as complexity grows. Core features are expected. Advanced features raise infrastructure, moderation, and compliance load.
Essential experience layers
- User profile creation and profile verification
- Easy messaging system with real-time chat
- Swipe features and matching algorithms
- Search filters and discovery controls
- Push notifications for engagement
Advanced experience layers
- AI-based matching and personalized recommendations
- Gamification mechanics and icebreakers
- Video calls and voice chats
- Social media integration
- Embedded safety features and reporting tools
As feature depth increases, so do backend orchestration, moderation coverage, and ongoing maintenance demands.
The more dynamic your product experience becomes, the more backend orchestration, data storage, and compute layers you need to maintain.
Cost Impact Overview
| Factor | Technical Cost Driver | Cost Impact Range |
|---|---|---|
| Matching Sophistication | Ranking models, behavioral data pipelines | Medium to High |
| Real-Time Interactions | WebSocket servers, event queues, push infra | Medium to High |
| Monetization Engines | Billing APIs, fraud checks, analytics loops | Medium |
| AI Discovery Systems | Model training, data governance, tuning cycles | High |
Trust, Safety, and Moderation Systems
Once real people interact in real time, safety becomes a system, not a feature. This is where enterprise-grade cost profiles begin to take shape.
Typical trust architecture includes:
- Automated content scanning using NLP and computer vision models
- Moderation queues with human review dashboards
- Identity and age verification integration
- Case management systems for abuse escalation
- Audit logs for regulator and legal review
At a low scale, moderation can be manual. At enterprise scale, it becomes a parallel platform with its own workflows, staffing, tooling, and analytics.
Cost Impact Overview
| Factor | Technical Cost Driver | Cost Impact Range |
|---|---|---|
| AI Moderation Pipelines | ML inference, content scanning services | High |
| Human Review Systems | Internal tools, reviewer queues, SLAs | Medium to High |
| Identity Verification | Third-party APIs, fallback flows | Medium |
| Abuse Escalation | Case management and audit tooling | Medium |
Compliance, Security, and Data Governance
Once your platform stores identity data, location history, and private conversations, compliance becomes continuous work.
This typically involves:
- Consent and preference management engines
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Role-based access control for internal teams
- Automated data retention and deletion workflows
- Regional data residency enforcement
Enterprises also need audit-ready governance. That means traceable logs, security testing cycles, and incident response playbooks.
Cost Impact Overview
| Factor | Technical Cost Driver | Cost Impact Range |
|---|---|---|
| Privacy Compliance | Consent tracking, retention automation | Medium |
| Security Hardening | Encryption, access control, and pen testing | Medium to High |
| Audit Readiness | Logging, traceability systems | Medium |
| Regional Data Governance | Multi-region hosting, data routing | High |
Scalability and Infrastructure Readiness
Social discovery platforms behave like communication networks. Systems must respond instantly, even during unpredictable demand spikes.
Scalable architecture usually includes:
- Load-balanced microservices
- Real-time messaging clusters
- Notification delivery pipelines
- Auto-scaling compute and database layers
- Redundancy and failover systems
These foundations define how your platform behaves under real user load. The next decision is choosing technology layers that can support this architecture without frequent re-platforming later.
In 2026, enterprises lean on mature, scale-tested technology layers. The focus is stability, observability, and readiness for long-term growth.
Typical platform stack choices include:
- React Native or Flutter for cross-platform experience consistency
- Swift and Kotlin for performance-critical native interactions
- Node.js and Golang microservices for matching and messaging workloads
- PostgreSQL, Redis, and Elasticsearch for data, sessions, and discovery
- Kafka or RabbitMQ for event-driven processing
- Python ML pipelines for AI-based matching
- WebRTC and cloud media servers for video and voice
- Kubernetes on AWS, Azure, or GCP for automated scaling and monitoring
These stack decisions reduce re-platforming risk and long-term maintenance costs.
Video and live interaction introduce further infrastructure, significantly increasing the cost to build a dating app with chat and video capabilities. Streaming servers, bandwidth management, and live content moderation add ongoing operational costs.
Some teams build for scale upfront. Others rebuild after growth. Re-architecture later usually costs more and carries platform risk.
Cost Impact Overview
| Factor | Technical Cost Driver | Cost Impact Range |
|---|---|---|
| Messaging Throughput | Real-time servers, queue systems | Medium to High |
| Notification Systems | Push gateways, event schedulers | Medium |
| Video Interactions | Streaming infra, bandwidth, moderation | High |
| High Availability | Redundancy, failover, and monitoring | Medium to High |
Platform Choice and Its Impact on Dating App Development Cost
The platform path you choose, whether native or evaluating cross-platform dating app building cost, quietly locks in cost behavior for years. Understanding the native vs. cross-platform dating app cost matters because some options reduce launch spend, while others reduce scaling and optimization risk later.
| Platform Approach | Typical Price Signal |
|---|---|
| iOS Native | $60K–$150K |
| Android Native | $60K–$150K |
| Flutter (Cross-Platform) | $45K–$110K |
| React Native (Cross-Platform) | $50K–$120K |
| Progressive Web App (PWA) | $35K–$90K |
| Wearable Companion Apps | $30K–$100K |
| Web App (Responsive) | $30K–$90K |
Native builds, including iOS dating app building cost considerations, raise upfront investment but ease long-term performance tuning at scale. Cross-platform speeds up launch and lowers early Android dating app building cost, though complex real-time and video features may later need native optimization.
Revenue Generation Strategies That Influence Platform Cost
Your dating app monetization model does more than drive profit. They shape system design, data flows, and compliance requirements. How your platform earns revenue directly affects development and long-term operating costs.
Common dating app monetization approaches include:
- Paid subscription tiers offering premium access and an ad-free experience
- In-app purchases such as profile boosts and virtual gifts
- Sponsored profiles and native advertising placements
- Affiliate marketing and referral fee partnerships
- Commission models tied to third-party services
- Payment orchestration for recurring billing and global currencies
Each dating app monetization model introduces different requirements. Subscription engines need billing reliability. Advertising demands targeting and consent controls. Third-party services require secure integrations. These choices influence backend complexity, compliance exposure, and maintenance cost.
Where the Dating App Development Budget Goes
Once planning moves beyond prototypes, budget allocation becomes a leadership decision. Understanding dating app building cost per feature matters because you are not only funding features. You are investing in systems that must stay stable, compliant, and resilient as use grows.
Below is how enterprise-grade dating platform budgets typically distribute.
| Cost Area | % of Budget | Enterprise Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Core Engineering | 35–40% | Maintainability and extensibility |
| Trust and Safety Systems | 15–20% | Brand and legal protection |
| Compliance and Security | 10–15% | Regulatory risk mitigation |
| Infrastructure and DevOps | 10–15% | Scalability and uptime |
| QA and Risk Testing | 8–10% | Failure prevention |
Core engineering funds backend services and system architecture that keep the platform adaptable. Trust and safety investments protect user confidence and reduce legal exposure. Compliance and security ensure audit readiness. Infrastructure keeps experiencing reliability at scale. QA prevents costly post-launch failures.
How Development Timelines Influence Dating App Cost
Most enterprise teams underestimate how much timelines shape cost. Speed is not only a delivery preference. It changes how many people, systems, and approvals must run in parallel.
A few patterns show up across large platform builds:
- Parallel engineering teams accelerate launch but increase short-term spend
- Phased releases reduce early cost but extend the time to full capability
- Compliance and security reviews add fixed checkpoints to every release cycle
- Late governance planning often leads to rework and budget overruns
Timeline Impact Overview
| Delivery Approach | Typical Outcome | Cost Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| MVP-First Rollout | Faster entry with a limited scope | Lower early cost, higher expansion spend later |
| Scale-Ready Build | Architecture designed for growth from day one | Higher initial cost, lower re-architecture risk |
| Multi-Region Enterprise Launch | Compliance and infrastructure are ready across markets | Highest upfront investment, controlled long-term scaling |
For leadership teams, the message is direct. Timelines decide when costs appear, not whether they appear.
Enterprise Cost Modeling for Dating App Platforms
Once leadership approves an investment range, whether evaluating dating app building cost for startups or an enterprise scale, finance teams ask the next question. How does that number form in real project terms? A simple model helps anchor planning.
Enterprise dating app cost formula
Total Cost = App Complexity × Hourly Charges × Key Development Phases + Infrastructure + Governance
Each variable scales based on platform ambition and risk posture.
Dating App Development Cost Breakdown Snapshot
Budget planning becomes easier when cost components are visible in one place. This snapshot reflects typical enterprise-scale investment distribution for a modern dating platform.
| Cost Component | What It Covers | Typical Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Product Design and UX | User flows, interaction logic, safety UX | $15K–$40K |
| Core Backend Development | Matching algorithms, messaging, APIs | $40K–$120K |
| Mobile and Web Development | Swipe experience, chat, notifications | $30K–$100K |
| Trust and Safety Systems | Profile verification, moderation tools | $20K–$60K |
| Compliance and Security | Privacy controls, audits, encryption | $15K–$50K |
| Infrastructure Setup | Hosting, scaling, monitoring | $15K–$50K |
| Analytics and Optimization | User insights, engagement tracking | $10K–$30K |
Mainstream platforms like Tinder, Grindr, Bumble, and Hinge operate at high levels of app complexity. Their cost structures reflect continuous backend development, API scaling for communication, analytics pipelines, and in-app purchase optimization.
This is why enterprise-grade platforms treat development as a multi-year investment cycle rather than focusing solely on the dating app MVP building cost as a one-time build.
Align cost, scale, and compliance before committing enterprise budgets.
Types of Dating Apps Ranked by Cost Impact
Not all dating platforms carry the same cost profile, and understanding the dating app building cost for startups versus enterprise builds matters. What matters is how much intelligence, interaction, and governance your experience demands once real users arrive at scale.
In the US, nearly 30% of adults already use online dating platforms, making scale a starting assumption rather than a future goal.
Here is how common dating app models rank by enterprise cost impact.
| Rank | App Type | Primary Cost Drivers | Price Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AI-Driven Matchmaking Platforms |
| $200K–$400K |
| 2 | Video-First and Live Dating Apps |
| $150K–$300K |
| 3 | Niche Dating Platforms |
| $100K–$250K |
| 4 | Swipe-Based Mainstream Apps |
| $80K–$200K |
| 5 | Event-Based Dating Apps |
| $60K–$150K |
AI-led dating or matchmaking platforms carry the highest cost to build an AI-powered dating app because they rely on continuous model training and data governance. Video-first experiences add streaming and moderation overhead.
Niche platforms invest more in compliance and tailored flows. Swipe-based apps focus on scale and real-time reliability. Event-based models remain lighter but still require location and scheduling systems. Your product model sets the baseline cost before development begins.
How Geography Influences Dating App Development Cost
Once rollout planning begins, geography becomes a direct cost lever. The same platform can demand very different investment levels depending on where it is built, hosted, and governed. Regulation, talent markets, infrastructure pricing, and moderation expectations all reshape the budget.
Below is an enterprise view, starting from the lowest regional cost base and moving upward.
Middle East
Typical cost range: $100K–$300K
The dating app building cost in the UAE and the broader Middle East offers a strong balance between capability and cost for many enterprises. Engineering talent is increasingly mature, while regulatory frameworks for social platforms are still developing compared to Western markets. This creates a favorable environment for building scale-ready platforms without immediate heavy compliance overhead.
Key cost drivers:
- Local data residency requirements in select markets
- Cultural sensitivity in content moderation and review policies
- Regional payment gateway and telecom integrations
- Arabic language processing for discovery and safety systems
Australia
Typical cost range: roughly double the Middle East investment
Australia typically requires close to twice the Middle East baseline due to higher engineering wages and tighter privacy controls. Platforms operating here must meet strict data protection and age-verification requirements from day one, which increases early compliance and infrastructure spending.
Key cost drivers:
- Privacy Act compliance and consent management systems
- Mandatory age verification and identity validation workflows
- Higher cloud hosting and infrastructure operating costs
- Local app store compliance and review requirements
Europe
Typical cost range: higher than Australia, driven by GDPR depth
The dating app building cost in the UK and European deployments tends to exceed Australian cost levels because GDPR influences nearly every data-handling and governance decision. Enterprises often invest heavily in consent automation, audit readiness, and region-specific hosting to avoid regulatory exposure.
Key cost drivers:
- GDPR compliance cost for dating apps includes consent, retention, and deletion automation
- Regional data residency and cross-border data routing controls
- Audit-ready governance documentation and traceability
- Multi-language localization and regional support structures
- Strong consumer protection enforcement
United States
Typical cost range: highest global investment tier
The dating app building cost in the USA represents the most expensive environment for corporate dating and social discovery platforms. Premium engineering talent, active litigation risk, and evolving state-level privacy laws drive continuous investment in trust, safety, and security systems.
Key cost drivers:
- State-level privacy regulations and CCPA compliance
- COPPA enforcement and rigorous age-gating systems
- Advanced trust and safety tooling and escalation workflows
- High-availability and disaster recovery infrastructure
- Intensive security, penetration testing, and legal review cycles
Other Regions and Distributed Teams
Some enterprises offset development spend through distributed delivery models. This lowers the base engineering cost. At the same time, governance coordination, cross-region compliance management, and communication overhead become new cost factors.
Geography-Based Cost Summary Table
| Region | Cost Impact | Typical Price Signal |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Highest | $150K–$400K |
| Europe | High | $130K–$350K |
| Australia | Medium–High | $120K–$300K |
| Middle East | Medium | $100K–$300K |
| Other and Distributed Teams | Variable | Depends on the governance model |
Geography changes more than development rates. It reshapes compliance exposure, infrastructure planning, and long-term operating costs.
Global platforms demand enterprise-grade delivery and governance
Build vs Customize, Cost Implications for Enterprises
When timelines feel tight, buying or customizing an existing solution can look attractive. Building from scratch feels slower and more expensive. Still, the long-term cost story usually flips once scale and governance come into play.
Most enterprises face two realistic paths.
| Approach | Upfront Cost | Long-Term Cost | Cost Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Build (Custom) | Higher | Controlled | Predictable at scale |
| Customize (Hybrid) | Medium | Variable | Integration constraints |
Custom builds cost more upfront but keep architecture, compliance, and scaling under your control. Hybrid or white-label dating app cost options reduce early spend but often introduce integration limits and rising costs as the platform grows.
Key takeaway: Short-term savings often increase long-term cost exposure.
Hidden and Ongoing Costs Enterprises Often Overlook
Most enterprise teams budget for launch. Few budgets have equal precision for what happens after real users, real data, and real risk enter the system. This is where ongoing costs quietly accumulate and often reshape total investment.
| Hidden Cost Area | Why It Adds Cost Over Time |
|---|---|
| Moderation Scaling Post-Launch | Review volumes grow with users, requiring more tools, staff, and automation |
| Security Audits and Penetration Testing | Regular testing cycles become mandatory as data and risk exposure increase |
| App Store Compliance Updates | Policy changes force ongoing updates and resubmissions |
| Infrastructure Spikes During Rapid Growth | Traffic surges demand higher hosting and monitoring capacity |
| Feature Refactoring and Depreciation | Early design choices need rebuilding as usage patterns evolve |
These costs rarely show up in initial estimates. Still, they shape long-term budget reality.
Also Read: What Does It Cost to Maintain an App in 2026? A Complete Enterprise Budget Guide
Appinventiv built a high-engagement social and community platform, Vyrb, for an enterprise client, featuring real-time interaction and scalable messaging. Within the first year, moderation demand grew faster than projected. By implementing automated review pipelines and analytics-driven monitoring, manual moderation costs dropped by more than 35% while maintaining safety and compliance standards.
Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Most cost conversations end once the platform ships. Enterprise cost reality starts after launch. Users generate data. Moderation queues grow. Compliance checks repeat. Infrastructure scales. This is where ownership cost takes shape. Especially when user adoption already operates at mass-market levels.
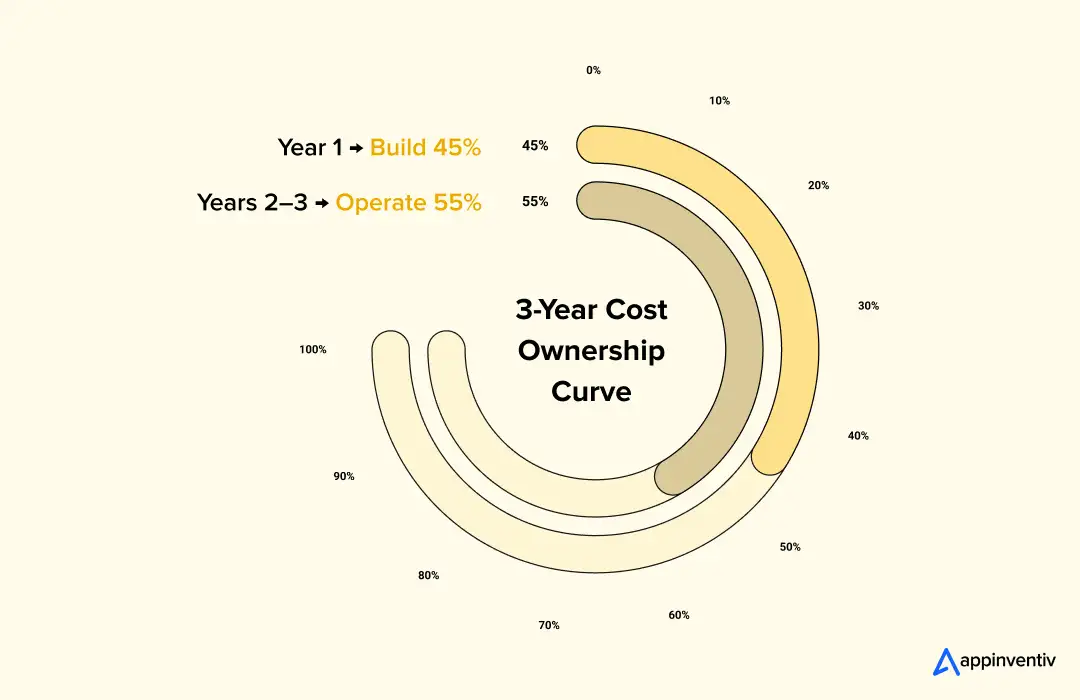
A practical TCO view separates early build spend from long-term operating commitment.
- Build cost covers engineering, architecture, and initial compliance setup
- Operational cost includes hosting, moderation, security, and optimization cycles
- Year-1 spend is product-heavy, Year-3 spend is stability and scale-heavy
- Enterprises plan controlled cost expansion to avoid reactive re-architecture
Typical TCO behavior at enterprise scale
| TCO Phase | Cost Behavior Range |
|---|---|
| Year-1 (Build and Launch) | ~40–50% of the total 3-year investment |
| Year-2 to Year-3 (Operate and Scale) | ~50–60% of the total 3-year investment |
The shift is predictable. Build cost gets you to market. Operational cost keeps you safe, compliant, and scalable once growth arrives.
Appinventiv partnered with a large media and entertainment enterprise to deliver an avatar-based social networking platform, AVATUS, across multiple regions. By designing GDPR-ready data governance and scalable backend architecture from the start, the platform avoided costly re-platforming later. Over three years, controlled compliance planning and automated infrastructure scaling reduced unexpected expansion costs by nearly 30%.
Model long-term costs before committing enterprise investment
How Enterprises Optimize Dating App Development Costs Without Increasing Risk
Enterprise cost optimization is rarely about spending less. It is about paying at the right time and in the right layers of the platform. The goal is simple. Avoid costly rework while maintaining compliance, safety, and scalability.
Certain strategies consistently help teams control costs without increasing risk.
- Modular architecture separates core systems from feature layers, allowing updates without touching critical infrastructure.
- Phased regional rollout delays heavy compliance and hosting investments until market demand is validated.
- Feature gating controls dating app MVP building cost by preventing overbuilding complex capabilities before users actually need them.
- Automation in moderation workflows reduces long-term staffing pressure while maintaining safety standards.
These practices shift the cost from reactive fixes to planned growth. That is where enterprise platforms stay profitable and resilient.
How Does Appinventiv Deliver Secure Dating Platforms at Scale?
Most enterprises evaluating the cost to build a dating app do not struggle with ideas. They battle with execution at scale. Turning a social discovery concept into a platform that stays compliant, stable, and trusted under real user load requires partnering with an experienced dating app development company that brings engineering maturity and governance discipline.
If you are evaluating a social networking app-building company for a large-scale dating or community platform, Appinventiv brings proven experience where scale, governance, and speed intersect.
With 150+ social platforms launched, 10+ years of delivery experience, and 2000+ applications shipped, enterprise teams gain a partner that understands scale from day one. Our clients have achieved 100M+ global app downloads, supported by an average MVP delivery cycle of three weeks and an uptime SLA of 99.90%.
Our delivery approach stays compliance-first and trust-driven. Safety systems, data governance, and scalability planning are embedded in the architecture from the start, not added later. Enterprises also benefit from faster deployment cycles, often reaching market readiness twice as quickly without compromising stability. Let’s connect and plan your feasibility call.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is the average cost of developing a dating app?
A. The cost to build a dating app at enterprise-grade typically falls between $40K and $400K. The wide range comes from differences in scale, compliance depth, safety systems, and real-time infrastructure needs. A simple launch version costs less. A platform built for long-term growth and governance costs more.
Q. Is moderation a recurring operational cost in dating app development?
A. Yes, moderation is an ongoing cost. As users grow, content reviews, abuse reports, and safety checks increase. Your team will need a mix of automation, human reviewers, and case management tools. These systems require continuous staffing, tooling upgrades, and policy updates.
Q. How much should enterprises budget post-launch of their daiting app?
A. Post-launch spending on a daiting app often matches or exceeds initial build cost over time. Hosting, monitoring, moderation, security audits, compliance updates, and feature improvements all continue after release. Many enterprises plan operational budgets at 50-60% of their three-year total investment.
Q. Can costs be optimized without compromising safety?
A. Yes, but only with smart planning. Modular architecture, phased rollouts, and automated moderation reduce waste without lowering safety standards. The key is building trust systems early, so they scale efficiently rather than retrofitting them later at much higher cost.
Q. How do enterprises evaluate ROI for dating app investments?
A. Enterprises measure ROI through user acquisition cost, retention rates, subscription conversion, and lifetime value growth. Cost efficiency in moderation, infrastructure scaling, and compliance also factor in. A positive ROI usually emerges when platforms achieve stable engagement and recurring revenue without increasing operational risk.
Q. How can Appinventiv help enterprises manage ongoing maintenance and support costs?
A. Appinventiv supports enterprises beyond launch with structured app maintenance, regular updates, and continuous UI/UX design improvements based on user behavior. Our teams handle bug fixes, security updates, performance monitoring, and server hosting to keep platforms stable. We also manage payment gateways, third-party integration, and customer support and moderation workflows, helping enterprises control annual maintenance costs while ensuring reliability and scalability.
Q. What development process should enterprises follow when building a dating app?
A. Enterprises typically start with market research and business model definition to validate demand. Teams then create an MVP through UI UX design, prototyping, and user profile structuring. Backend development, frontend development, and tech stack selection follow, including geolocation-based matching features. A dedicated project manager oversees quality assurance testing, launch readiness, and post-launch maintenance to ensure smooth scaling and long-term performance.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

How Much Does It Cost to Build a Dating App Like Grindr?
Key takeaways: The cost to build a dating app like Grindr ranges between $40,000 and $200,000+, depending on features and scale. Privacy, security, and compliance with global data laws are major cost drivers in LGBTQ+ dating app development. Advanced features like AI matchmaking, video calls, and community tools increase overall development costs. The global dating…

Dating App Development in Australia: Features, Process and Costs
Key takeaways: In Australia, the adoption of dating apps shows no signs of slowing, and the market is expected to reach a value of $58.4 million by 2029. Features like geolocation, profile management, real-time messaging, video calls, and privacy settings are crucial to ensure a seamless user experience and user engagement. It's important to consider…

How to Build AI-Powered Dating Apps: A Step-by-Step Guide
Key takeaways: By tracking preferences and behavior of users, AI is used to match them together more effectively than an algorithm does, resulting in greater satisfaction and engagement of the users. The dating application market is projected to experience tremendous growth, and this is where AI-powered dating applications can be innovative and seize a portion…