- Positioning 5G at the Core of Healthcare Evolution
- From Raw Speed to Real Strategy: Making 5G Work for Healthcare
- The 15 Strategic Applications: How 5G is Reshaping the Industry
- 1. Real-Time Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
- 2. High-Fidelity Telemedicine and Virtual Consultations
- 3. Connected Ambulances and Next-Gen Emergency Services
- 4. Instantaneous Access to Electronic Health Records (EHR)
- 5. The Rise of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 6. Democratizing Expertise with Remote and Robotic Surgery
- 7. Advanced Predictive Analytics for Patient Care
- 8. Immersive Medical Training with AR and VR
- 9. Automated Hospital Kiosks and Self-Serve Stations
- 10. Digital Twins for Personalized Treatment Planning
- 11. Resilient Supply Chain and Smart Inventory Management
- 12. Enhanced Medical Imaging and Faster Diagnostics
- 13. Seamless Collaboration Between Healthcare Professionals
- 14. Improved Patient Data Security and Privacy
- 15. Supporting Rural and Underserved Communities
- Navigating the Hurdles: Challenges and Solutions for 5G Adoption
- Challenge 1: Prohibitive Infrastructure Costs & Complex Deployment
- Challenge 2: Heightened Cybersecurity & Data Privacy Risks
- Challenge 3: Interoperability with Legacy Systems
- Leading the Charge or Playing Catch-Up?
- Transform Your Healthcare Vision with Appinventiv's Award-Winning Excellence
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Key takeaways:
- Revolutionizing Healthcare: 5G makes it possible to conduct surgeries from far away, use smart computers to help diagnose patients, and have smooth video doctor visits
- Instant Data, Smarter Decisions: Super-fast speeds with almost no delay make sure information moves correctly.
- IoMT Integration: 5G connects millions of medical devices together, creating one big connected healthcare system.
- Improved Access to Care: 5G brings telemedicine and specialist doctor visits to country areas and remote places.
Healthcare technologies like telemedicine, remote diagnostics, and patient monitoring have existed for years, but they’ve always been limited by slow networks, connectivity issues, and bandwidth constraints that prevented them from reaching their full potential.
5G in healthcare is changing the entire equation. 5G transforms basic video calls into ultra-high-definition consultations where specialists can examine patients with unprecedented clarity. AI-powered remote monitoring was possible, but now thousands of devices can transmit data simultaneously without network strain.
We’re talking about real transformation here, not just small improvements to existing systems. Technologies like IoT and AI in healthcare have helped plenty, but slow networks have always held them back. Unlocking the full potential of these technologies requires different connectivity—not just faster internet, but 5G networks that actually work reliably when lives depend on them most.
Organizations that treat 5G mobile technology in healthcare as just another tech upgrade will miss the bigger picture, while those building their entire digital health strategy around ultra-reliable connectivity will set the standard for what modern healthcare looks like.
Must Read: Innovative Technologies That Are Changing the Healthcare Sector
Positioning 5G at the Core of Healthcare Evolution
In today’s healthcare environment, technology adoption is no longer about closing operational gaps; it’s about creating entirely new capabilities that transform how care is delivered, accessed, and monetized. Forward-looking organizations aren’t merely asking for faster networks; they’re rethinking how connectivity itself can become a driver of competitive advantage.
This is where the 5G impact on the healthcare industry takes center stage; not as a supporting tool, but as the backbone of a new generation of medical innovation.
Why leaders are placing 5G at the heart of their growth strategy:
- Moving beyond “fixing what’s broken” to building services, experiences, and revenue streams that were previously out of reach.
- Turning network infrastructure into a business enabler that fuels predictive, personalized, and data-rich care models.
- Creating operational resilience and scalability to thrive in a digitally connected, patient-centric healthcare ecosystem.
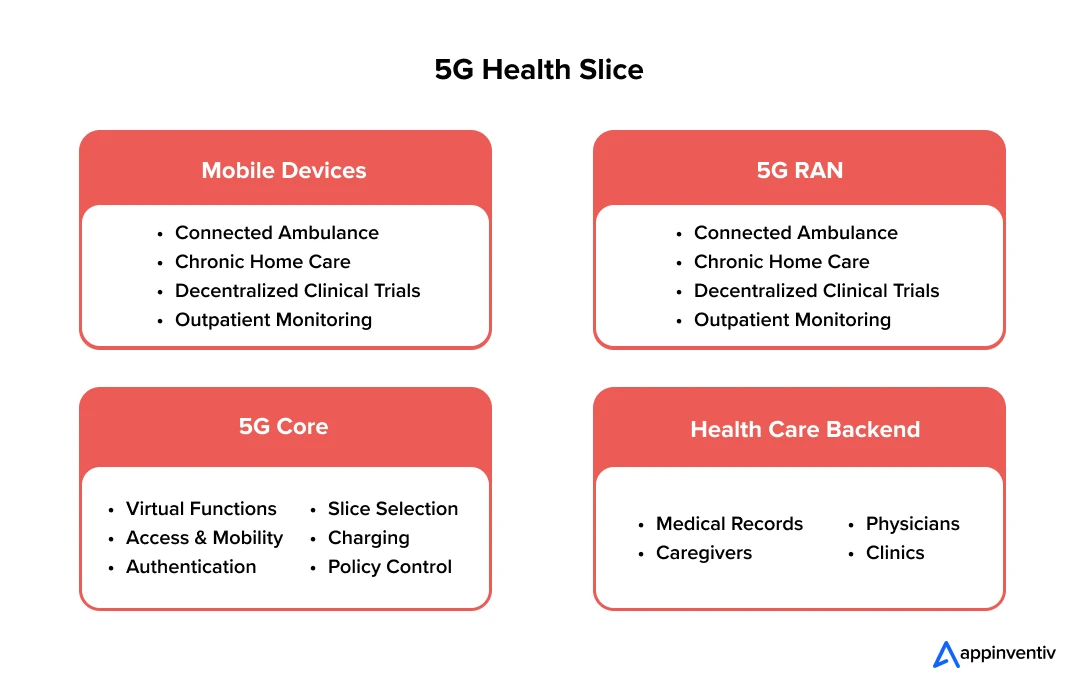
Those embracing 5G in healthcare early are already reaping strategic gains: unlocking new care delivery models, optimizing resources, and strengthening their position in an increasingly competitive market. For decision-makers, 5G isn’t a side project—it’s the framework shaping their next decade of relevance, resilience, and growth.
Bonus Read: 5G and IoT
From Raw Speed to Real Strategy: Making 5G Work for Healthcare
Unlike previous network upgrades, 5G technology in healthcare isn’t defined solely by faster downloads—it’s engineered to remove the very constraints that have historically slowed innovation. The real opportunity lies in how these capabilities translate into measurable business and clinical gains.
| Area | Challenges | Strategic Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Network Infrastructure | High upfront costs, legacy system integration | Phased deployment, network-as-a-service, backup systems |
| Data Security & Compliance | IoMT security risks, regulatory compliance | Zero Trust, end-to-end encryption, regulatory compliance |
| Telemedicine Integration | Bandwidth for HD video, remote accessibility | eMBB for high-quality streaming, mobile health solutions |
| Real-Time Analytics | Delays in data processing for critical care | URLLC for instant data transfer, AI-powered diagnostics |
| IoMT Integration | Managing millions of devices, reliable communication | mMTC for scalable IoMT, centralized control systems |
| Operational Efficiency | Siloed operations, resource allocation inefficiencies | 5G-powered collaboration, real-time resource tracking |
| Scalability of Services | Scaling telehealth during high demand | Flexible, scalable solutions with 5G-enabled cloud integration |
Three pillars that turn speed into strategy:
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Move massive data files—such as 4K MRI or PET scans—in seconds. This accelerates diagnostics, enables high-definition telemedicine, and brings the “hospital without walls” concept to life.
- Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC): Near-instant responsiveness allows for real-time applications like remote robotic surgery or IoT-based time-critical patient monitoring, where reliability is as essential as precision.
- Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC): Support for up to a million connected devices per square kilometer enables a truly smart hospital ecosystem with seamless IoMT integration.
Why this matters for leaders:
- The benefits of 5G in healthcare extend beyond patient care into operational efficiency, resource allocation, and long-term market positioning.
- Healthcare 5G networks make advanced AI diagnostics, predictive analytics, and virtual collaboration scalable, not just experimental.
- The technology provides a foundation for data-driven strategies that reduce treatment delays, improve outcomes, and open new revenue channels.
In short, 5G’s value isn’t just in how fast it moves data—it’s in how it transforms that speed into strategic capabilities, setting the stage for the next era of healthcare innovation.
The 15 Strategic Applications: How 5G is Reshaping the Industry
Let’s move from the theoretical to the practical. The benefits of 5G in healthcare are best understood through its applications. Here are 15 concrete ways this technology is driving tangible results, with each demonstrating a clear return on investment.

1. Real-Time Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
5G’s ability to connect thousands of devices makes remote patient monitoring normal healthcare instead of a specialty service. Medical wearables can continuously send health data to hospital AI systems that watch for problems. This catches health issues early and prevents patients from returning to the hospital—exactly what modern 5G healthcare should accomplish.
Real World Implementation: Medtronic’s CareLink network lets heart patients send device readings from home straight to their doctors. Adding 5G makes these data transfers more reliable, so critical health information reaches medical teams almost immediately. Doctors can make treatment decisions faster, and clinics operate more efficiently—that’s advanced healthcare 5G working effectively.
Must Read: Remote Patient Monitoring Software Development Cost
2. High-Fidelity Telemedicine and Virtual Consultations
5G makes virtual doctor visits much more realistic. The faster networks support ultra-clear 4K video calls, helping remote medical exams work better. A skin doctor examining moles or rashes can see everything in sharp detail without connection delays. This builds doctors’ confidence in remote diagnoses and helps patients trust virtual appointments more, proving why 5G technology in healthcare matters strategically.
Real World Implementation: Teladoc Health, which leads global virtual healthcare, uses fast internet connections to improve its services. 5G lets their system handle better video quality and connect advanced medical devices during virtual visits. This makes online appointments more clinically useful, especially for medical specialties where seeing fine details matters most, demonstrating effective 5G for healthcare implementation.
Related Read: 7 Telemedicine Trends Shaping the Future of Healthcare
3. Connected Ambulances and Next-Gen Emergency Services
A 5G-enabled ambulance transforms into a mobile emergency room, transmitting HD video and patient vitals to the hospital in real-time. This “pre-hospital” care saves critical time, drastically improving outcomes for stroke and cardiac arrest patients. This is one of the most compelling 5G healthcare use cases.
Real World Implementation: University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust partnered with BT to demonstrate the UK’s first remote diagnostic procedure using a 5G connected ambulance in November 2019. The trial enabled clinicians over two miles away to guide paramedics through real-time ultrasound examinations using VR headsets and haptic gloves, allowing remote diagnosis without hospital transport.
4. Instantaneous Access to Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Massive EHR files can be slow to access on mobile networks. With 5G, a physician can pull up a patient’s complete history, including high-resolution imaging files, on a tablet at the bedside in seconds. This seamless access to information at the point of care is a core pillar of effective 5G healthcare.
Real World Implementation: Rush University Medical Center in Chicago utilizes EHR systems from Epic. By deploying a private 5G network, the hospital ensures that clinicians can access these dense Epic records on mobile devices anywhere on campus without latency. This untethers doctors from workstations and puts critical data at their fingertips, a key benefit of dedicated healthcare 5G networks.
Related Read: Guide to EHR Software Development
5. The Rise of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
From smart inhalers to connected infusion pumps, IoMT in healthcare is creating a web of intelligent devices. 5G is the network that can handle this massive influx of data reliably. For hospital administrators, this means a real-time digital twin of the hospital’s operational status, a key component in optimizing patient flow. The growth of 5G in the healthcare market is directly fueling this IoMT explosion.
Real World Implementation: Philips, through its HealthSuite platform, showcases the power of IoMT. The platform securely analyzes data from millions of connected medical devices. Deploying this in a 5G-enabled hospital, data from thousands of devices can be aggregated in real-time without network strain, providing a comprehensive, live dashboard of hospital operations. This is a prime example of 5G in healthcare.
6. Democratizing Expertise with Remote and Robotic Surgery
Remote surgery is now a reality thanks to 5G’s ultra-low latency. A specialist can operate on a patient miles away, controlling a robotic arm with near-zero delay. This doesn’t just centralize expertise; it democratizes it, bringing world-class surgical care to underserved populations. The technical feasibility of this relies entirely on a robust healthcare 5G network.
Real World Implementation: Shanghai Minimally Invasive Surgical Robot Center performed the world’s first 5G remote robotic-assisted thyroidectomy in August 2024, with surgeons in Shanghai successfully operating on a patient in Shenzhen using the Chinese Tumai MT-1000 robotic system. The 170-minute procedure achieved minimal latency and uninterrupted 5G connectivity throughout the surgery, demonstrating how advanced 5G networks enable precise remote surgical control across significant distances and establishing new possibilities for 5G for healthcare.
Must Read: Use of Mixed Reality in Operating Modern Surgery
7. Advanced Predictive Analytics for Patient Care
By aggregating real-time data from thousands of monitors and sensors, AI algorithms running on 5G networks can identify patterns invisible to the human eye. Patient analytics can predict which patients are at high risk for sepsis or forecast admission surges for better staff scheduling. This is where the true 5G impact on the healthcare industry begins to compound.
Real World Implementation: The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has partnered with Verizon to establish a 5G-enabled “living lab” at the VA Palo Alto Health Care System. A key goal is to use the network to power predictive models for patient care, allowing for proactive rather than reactive clinical interventions. The entire 5G in healthcare market is watching such initiatives closely.
8. Immersive Medical Training with AR and VR
Medical augmented reality is transforming medical education. With 5G, medical students can participate in a complex virtual surgery with haptic feedback, all streamed to their headsets without lag. Surgeons can overlay a patient’s MRI scans onto their body during a live operation. This technology, powered by the immense bandwidth of 5G mobile technology in healthcare, reduces costs and improves precision.
Real World Implementation: GE HealthCare partnered with MediView XR to launch the OmnifyXR Interventional Suite at North Star Vascular and Interventional in June 2024. This augmented reality system enables remote collaboration and immersive medical training through Microsoft HoloLens 2 headsets, allowing multiple healthcare professionals to participate simultaneously in virtual learning sessions powered by advanced connectivity, demonstrating the growing potential of the 5G in healthcare market.
Bonus Read: Metaverse in Healthcare
9. Automated Hospital Kiosks and Self-Serve Stations
To improve patient flow and reduce administrative burden, hospitals are deploying smart kiosks for check-in, co-payment, and wayfinding. 5G ensures these devices are always connected and responsive, even during peak hours. This simple application frees up administrative staff to focus on more complex patient needs, directly impacting operational efficiency and showcasing clear benefits of 5G in healthcare.
Real World Implementation: Boston Children’s Hospital partnered with T-Mobile to deploy the first hybrid 5G network in healthcare in 2024, enabling seamless connectivity for smart kiosks and patient intake systems throughout the facility. The 5G infrastructure ensures instant data synchronization between kiosks and the hospital’s Epic EHR system, allowing patients to complete registration and payments without delays while maintaining real-time connectivity whether inside or outside the hospital. This demonstrates a practical example of 5G in healthcare at work.
10. Digital Twins for Personalized Treatment Planning
Imagine creating a virtual replica of a patient’s heart before a complex procedure. Surgeons can use this “digital twin” to simulate different surgical approaches and identify the optimal one, de-risking the actual operation. This requires immense computational power and data throughput, making it a prime application for 5G infrastructure in healthcare.
Real World Implementation: Dassault Systèmes’ “Living Heart Project” is a pioneering example of a digital twin. It creates a validated 3D simulation model of a human heart. The immense datasets required to create a patient-specific model are perfectly suited for a 5G network, which can transfer the necessary imaging files and computational data rapidly to and from a high-performance computing cloud, a significant advance for the 5G in healthcare market.
11. Resilient Supply Chain and Smart Inventory Management
By placing 5G-enabled sensors on everything from vaccine vials to surgical toolkits, hospitals gain an unprecedented, real-time view of their entire supply chain. Automated alerts are triggered when supplies run low. This proactive approach prevents costly stockouts and waste, a crucial advantage in a post-pandemic world and a driver of the 5G impact on the healthcare industry.
Real World Implementation: The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University deployed 5G-enabled IoT sensors for comprehensive medical device tracking and asset management in 2024. The hospital’s smart healthcare system uses 5G connectivity to monitor equipment location, status, and maintenance needs in real-time, significantly reducing time spent searching for critical medical devices and enabling predictive maintenance schedules. This demonstrates clear efficiency gains from 5G technology in healthcare.
12. Enhanced Medical Imaging and Faster Diagnostics
A single MRI study can be hundreds of megabytes. Transferring these files over a traditional network can create a diagnostic backlog. With 5G, these files can be transferred to a radiologist’s workstation almost instantly. This accelerates the time-to-diagnosis, which is critical in oncology and neurology, and is one of the key features of 5G in connected health.
Real World Implementation: Siemens Healthineers has partnered with network providers to explore the power of 5G for medical imaging. Their Syngo Carbon platform creates a unified data environment. With 5G, a large imaging file can be sent directly to this cloud platform for processing by an AI algorithm and simultaneously shared with a specialist, a workflow that demonstrates a key advantage of 5G for healthcare.
13. Seamless Collaboration Between Healthcare Professionals
Effective care is a team sport. 5G facilitates seamless communication, allowing a primary care physician, a specialist, and a surgeon to collaborate on a complex case in real-time, sharing high-definition video, images, and patient data simultaneously. This level of collaboration ensures a more holistic and effective treatment plan, enabled by robust 5G mobile technology in healthcare.
Real World Implementation: Mayo Clinic, in January 2025, developed foundation AI models that integrate multimodal radiology images and data. Their collaborative platform enables large imaging files from CT scans and MRIs to be processed directly through cloud-based AI algorithms with real-time sharing to specialists via advanced connectivity. This multimodal approach demonstrates a key advantage of 5G for healthcare by streamlining radiology workflows and improving diagnostic accuracy.
14. Improved Patient Data Security and Privacy
While connecting more devices increases the attack surface on healthcare data security, 5G offers advanced, built-in security features like network slicing. This allows a hospital to create a dedicated, isolated “network slice” purely for mission-critical medical data, separating it from less secure traffic. Unlike traditional VLANs that use software-based segmentation, 5G network slicing provides hardware-level isolation with dedicated radio resources and separate encryption keys for each slice, ensuring that compromising one slice cannot provide access to critical medical systems. This provides superior end-to-end security governance, addressing a key concern about 5G impact on healthcare.
Real World Implementation: The 6G Health Institute in Markkleeberg, Germany, partnered with Telefonica Germany to implement Germany’s first mobile 5G campus network with advanced network slicing in 2024. Their system creates four dedicated slices for different healthcare applications, with resources prioritized based on medical needs. Each slice operates with hardware-level isolation, ensuring medical IoT, emergency services, and patient monitoring systems remain completely separate. This segmentation prevents security breaches on one slice from compromising critical medical operations on others, demonstrating enterprise-grade security for healthcare.
Must Read: Key Strategies for Ensuring Cybersecurity in Healthcare
15. Supporting Rural and Underserved Communities
Perhaps the greatest societal benefit is the potential to bridge the urban-rural health gap. 5G-powered Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) can bring high-speed internet to remote clinics that lack fiber infrastructure. This enables these clinics to offer advanced telemedicine and access specialist consultations, fundamentally changing the quality of care available to millions. This powerful application of 5G for healthcare is a tool for health equity.
Real World Implementation: T-Mobile’s Project 10Million is a broad initiative to provide internet access to underserved communities. By leveraging its 5G network for FWA, T-Mobile can provide a rural health clinic with the high-speed connectivity it needs to join a larger telehealth network. This allows patients in remote areas to have virtual appointments with specialists who would otherwise be geographically inaccessible.
Navigating the Hurdles: Challenges and Solutions for 5G Adoption
5G could change everything, but rolling it out isn’t easy. Healthcare executives who understand these problems early can build better plans that actually work. We’re not talking about simple tech hiccups—these are complicated business issues that need smart thinking ahead of time. The organizations that figure out how to handle challenges with 5G for the healthcare industry will get way ahead of everyone else who struggles.
| Challenge | Business Impact | Strategic Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Prohibitive Infrastructure Costs | High capital investment; Complex system and network setup; High operational costs | Phased Deployment & Financial Models; Step-by-step rollout; Start with pilot projects; Use Network-as-a-Service models |
| Cybersecurity & Data Privacy Risks | New IoMT devices create attack vectors; Risk of ransomware and HIPAA fines | Zero Trust & Network Slicing; Identity verification; Isolate critical data networks |
| Interoperability with Legacy Systems | Complex legacy systems; Broken workflows; Disruption to patient care | Open Standards & API Integration; Use HL7 FHIR standards; Gradual system updates with middleware solutions |
Challenge 1: Prohibitive Infrastructure Costs & Complex Deployment
The biggest hurdle remains the substantial capital investment required upfront. Building a comprehensive private 5G network involves much more than installing antennas. Hospitals need a complete 5G core system, sophisticated radio access networks, extensive fiber infrastructure connecting all sites, and numerous small cells distributed throughout large medical facilities to ensure coverage everywhere.
Land acquisition costs, construction expenses, network hardware, and specialized spectrum licensing easily reach millions of dollars—significant expenditure even for major healthcare systems managing multiple budget priorities.
Installing everything requires complex engineering expertise. Teams must carefully plan radio frequency mapping to eliminate coverage gaps and prevent interference with critical medical equipment that hospitals rely on for patient care.
Strategic Solution: Phased Deployment & Innovative Financial Models
Rather than trying to implement everything at once, healthcare executives should use a step-by-step rollout that matches specific business goals. These stages in 5G healthcare enable controlled spending while proving return on investment. Start with a test project in one high-value area—maybe the emergency room for connected ambulances, or operating rooms for augmented reality surgical tools. Success stories and money saved from this first phase help justify expanding the network to other hospital areas.
At the same time, look into new payment options like Network-as-a-Service from major telecom companies and technology providers. This changes the financial structure from huge upfront equipment purchases to manageable monthly operating costs. The telecom partner owns and runs the network infrastructure while the hospital pays subscription fees for service, making 5G much more affordable to start and providing ongoing technical support plus automatic upgrades.
Challenge 2: Heightened Cybersecurity & Data Privacy Risks
Adding thousands of new medical devices, infusion pumps, patient monitors, and wearables creates many more ways for hackers to break into hospital networks. Every connected device becomes a possible gateway for cybercriminals.
The dangers are serious: coordinated attacks could shut down entire hospital computer systems, malicious software could lock up patient records, and data breaches could expose private health information, resulting in massive HIPAA fines and destroyed patient confidence. The enormous amount of data flowing through 5G healthcare networks, combined with data moving between multiple endpoints and cloud services, makes old-style security approaches that just protect the network perimeter completely inadequate for modern threats.
Strategic Solution: Zero Trust Architecture & Network Slicing
The answer involves implementing modern, data-focused security strategies. Zero Trust Architecture becomes essential here. This approach follows “never trust, always verify” principles, requiring every device, user, and application to prove identity and get permission before accessing any network resources, no matter where they connect from.
5G’s built-in features help solve this problem effectively. Network slicing lets IT teams build multiple separate virtual networks using the same physical equipment. Hospitals can establish a highly secure, isolated section for critical patient data, keeping it completely separate from networks handling administrative work or public guest internet access.
This separation contains security breaches and ensures that even when hackers compromise one network area, the most sensitive medical information stays protected, reducing the potential 5G impact on the healthcare industry.
Challenge 3: Interoperability with Legacy Systems
Most hospitals run on complicated mixtures of older computer systems. Electronic health records from companies like Epic and Cerner, medical imaging systems, and various department software weren’t built for the always-connected, instant-data world that 5G creates.
The real challenge involves making sure information from new 5G medical devices gets properly absorbed and used by these existing, essential systems. Without genuine compatibility between old and new technology, 5G just creates more isolated data pockets, breaking workflows into fragments instead of bringing everything together smoothly.
Strategic Solution: Embrace Open Standards & API-First Integration
Solving this problem requires focusing on open technology standards. Choose new vendors in the 5G healthcare market that design their systems around modern compatibility standards like HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources). FHIR uses current web-based connection technology to help different hospital systems share medical information using the same format.
For older systems that can’t work with FHIR, hospitals need an API-focused integration approach. This means using integration software or connection gateways that work like universal translators, changing data from new 5G devices into formats that older systems can read, and doing the reverse when needed. This middle-layer solution enables gradual technology updates without completely replacing core hospital systems that medical staff depend on for daily patient care operations.
Leading the Charge or Playing Catch-Up?
We are at the beginning of a transformative decade for medicine. The integration of 5G mobile technology in healthcare is not just an incremental improvement; it is a foundational enabler that unlocks the full potential of AI, IoT, and big data analytics. The journey from a reactive, hospital-centric model to a proactive, patient-centric ecosystem is being paved by this ultra-reliable connectivity. The various 5G applications in healthcare demonstrate a clear path toward a more efficient, accessible, and intelligent system.
For today’s leaders, the imperative is clear. The time for waiting is over. The organizations that thrive will be those that view 5G healthcare not as an IT project, but as a core business strategy. They will be the ones who ask the hard questions now and begin building the infrastructure to capitalize on this shift.
The future of healthcare 5G will be defined by the bold decisions made today, creating a legacy of innovation that will redefine the standards of care for generations to come. The fundamental components of 5G technology in healthcare, such as network slicing and URLLC, provide the tools; leadership provides the vision.
Transform Your Healthcare Vision with Appinventiv’s Award-Winning Excellence
As a leading healthcare software development company, Appinventiv stands at the forefront of healthcare digital transformation, delivering cutting-edge solutions that revolutionize patient care and streamline medical operations. With over a decade of experience and a team of 1,600+ skilled technical experts, we have established ourselves as the trusted partner for healthcare organizations worldwide.
Our expertise spans HIPAA-compliant applications, AI-powered diagnostics, telemedicine platforms, and comprehensive health management systems. The top expertise of our healthcare software developers is behind our renowned healthcare clients, including Soniphi, YouComm, Health-e-People, DiabeticU, and ShifaCare, creating innovative solutions that have transformed millions of lives globally. These partnerships demonstrate our commitment to addressing complex healthcare challenges through technology-driven innovation.
Proven Excellence Meets Healthcare Innovation:
- Certified & Recognized Leadership Entrepreneur.com “App Development Company of the Year” + ISO 9001:2008 Certification + Leader in AI Product Engineering & Digital Transformation (Economic Times)
Your Benefit: Medical-grade quality standards applied to every 5G healthcare solution
- Consecutive Growth Recognition Deloitte Technology Fast 50 India (2023-2024) + Clutch Global Spring Award 2024
Your Impact: Rapid deployment of 5G-ready healthcare platforms that scale with your growth
- Security-First Approach NIST CSF-Based Security Framework + 3,000+ secure digital solutions
Your Peace of Mind: Zero-breach record across 50+ live 5G healthcare implementations
Our deep understanding of healthcare workflows, combined with expertise in emerging technologies, enables us to build solutions that seamlessly integrate into existing medical ecosystems. From startups to Fortune 500 healthcare giants, our clients trust us to navigate complex regulatory landscapes while delivering user-centric applications that drive measurable outcomes. This comprehensive approach has positioned us as the go-to partner for healthcare innovation across 35+ countries worldwide.
Partner with us to harness cutting-edge technologies, including AI, ML, IoT, and blockchain, creating offerings that not only meet your current healthcare demands but also future-proof your organization for tomorrow’s challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. How Is the 5G Revolution Transforming Healthcare?
A. Healthcare’s getting a massive upgrade thanks to 5G. Surgeons can operate on people halfway around the world now because there’s basically no delay in the connection. Rural patients who never had access to specialists can video chat with top doctors whenever they need to. Plus, all those huge medical files that used to take forever to send – MRI scans and stuff – now transfer instantly. AI diagnosis tools work better, health trackers stay connected, and basically everyone gets better healthcare, no matter where they live.
Q. What Are 5G Wearable Devices in Healthcare?
A. Healthcare wearables with 5G are basically fitness trackers, smartwatches, and medical devices that connect to super-fast networks so they can monitor your health constantly. They track heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, and how you sleep – then immediately send everything to your doctor. What is the difference from regular wearables? No waiting around for data to sync later. If something goes wrong, like your heart starts acting up, doctors know right away. This lets them jump in fast when there’s trouble, which makes preventing problems way easier and helps patients worry less about their health.
Q. Why Does 5G Matter for Healthcare?
A. Why does 5G in healthcare matter so much? It gets rid of those annoying delays that have held back medical tech forever. We’re talking speeds 100 times faster than 4G with basically zero lag, so doctors can actually trust that data arrives instantly when making life-or-death calls. Remote surgeries work just as well as if the surgeon was in the same room. Ambulance crews can livestream everything to the hospital on their way there. Doctors from different countries can work together like they’re sitting next to each other. Patients get diagnosed quicker, chronic diseases get monitored better, and everyone can access top medical experts no matter where they live. Healthcare finally works the way it should.
Q. How Will 5G Transform Hospital Operations?
A. 5G turns hospitals into “smart” buildings where patient beds talk to medical machines and everything stays connected all the time. Hospital workers can find equipment instantly, check patient stats without walking around constantly, and use AR glasses to coordinate with other teams. The network handles thousands of gadgets at once, so inventory tracks itself, machines predict when they’ll break down, and patients move through the hospital smoothly. Fewer mistakes happen, paperwork disappears, and nurses actually get to spend time with patients instead of filling out forms.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
How to Build a Custom Pediatric EMR and EHR System?
Key takeaways: Clinical Precision: Custom systems accommodate pediatric-specific data points like percentile curves and weight-based longitudinal dosing. Interoperability: Seamless data exchange via HL7 FHIR ensures your practice stays connected to pharmacies, labs, and state registries. Regulatory Resilience: Built-in compliance with HIPAA, HITECH, and MACRA/MIPS reduces legal friction. Enhanced Engagement: Parent portals reduce administrative overhead by…

Change Management in Healthcare: Principles, Processes, and Models
Key Takeaways Change in healthcare fails quietly when ownership, workflow alignment, and follow-through are missing. Successful change management in healthcare focuses on adoption, not just system implementation. Clinical workflows and workforce capacity determine whether transformation sticks or stalls. Governance, clear accountability, and post-go-live support matter more than the model used. Sustainable healthcare transformation depends on…

A Practical Guide to Building Your Mental Health Chatbot - Use Cases, Cost, & ROI
Key takeaways: Mental health chatbots work when they know their limits. They’re most useful as a gentle first step, not as a stand-in for real care. Good chatbot design is more about judgment than AI. Clear boundaries, calm responses, and safety matter more than smart language models. Enterprises invest in chatbots to make support easier…