- RPA in Automotive: Market Insights and Adoption Drivers
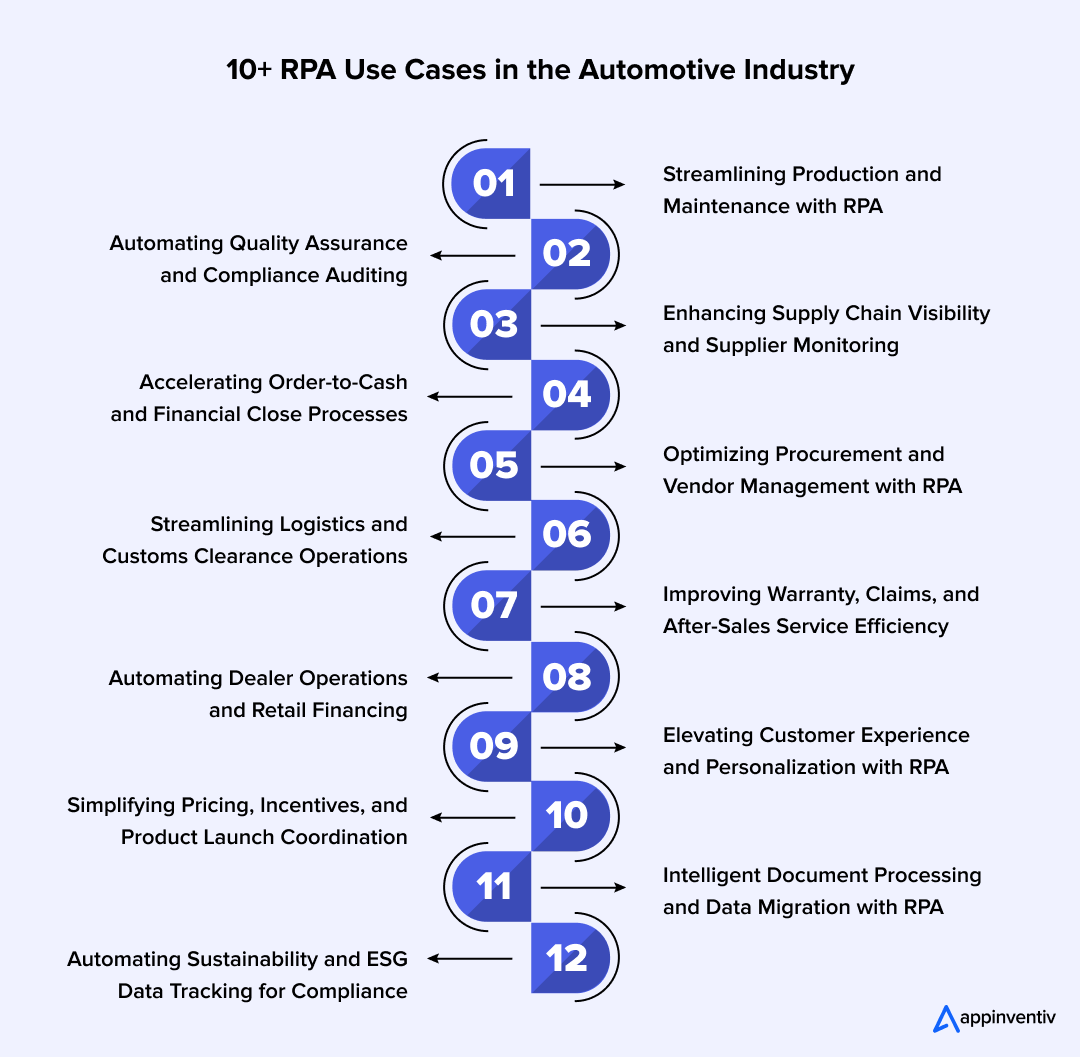
- 10+ RPA Use Cases in the Automotive Industry
- 1. Predictive Maintenance and Equipment Monitoring
- 2. Quality Assurance and Compliance Auditing
- 3. Supply Chain Visibility and Supplier Performance Monitoring
- 4. Order-to-Cash and Financial Close Acceleration
- 5. Procurement and Vendor Management
- 6. Logistics and Customs Clearance
- 7. Warranty, Claims, and After-Sales Service
- 8. Dealer Operations and Retail Financing
- 9. Customer Experience and Personalization
- 10. Pricing, Incentives, and Product Launch Coordination
- 11. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) for Supplier Documents
- 12. Sustainability and ESG Data Tracking
- Key Benefits of RPA in Automotive Enterprises
- 1. Operational Efficiency
- 2. Enhanced Productivity
- 3. Cost Reduction
- 4. Regulatory Compliance
- 5. Faster Time-to-Market
- Technical Depth: Engineering for the “Success Disaster”
- What “engineering for success” really means
- Why this matters in real operations
- How to Implement RPA in the Automotive Industry
- 1. Start with Processes that Deliver Measurable ROI
- 2. Build RPA on Clean, Connected Data
- 3. Focus on Human-Bot Collaboration, Not Replacement
- 4. Adopt a Scalable, Modular RPA Architecture
- 5. Measure, Iterate, and Scale
- 6. Ensure Compliance and Cybersecurity from Day One
- 8. Partner with Experienced RPA Experts
- RPA Implementation Challenges and Solutions in the Automotive Industry
- 1. Legacy System Compatibility
- 2. Change Management and Workforce Adoption
- 3. Balancing Cost and ROI
- 4. Security and Compliance Risks
- Future Trends of RPA in Automotive Industry
- How Appinventiv Enables Automotive Leaders to Scale with RPA
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- Streamlined Operations and Efficiency Gains: RPA automates repetitive tasks like invoice processing and data entry, improving overall efficiency and freeing up teams to focus on more strategic activities.
- Proactive Maintenance and Cost Reduction: By integrating RPA with IoT, automotive companies can predict and prevent equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Optimized Supply Chain and Financial Processes: RPA enhances supplier management, order processing, and financial reconciliation, reducing backlogs and improving accuracy across the supply chain and finance teams.
- Future-Ready Automation with AI Integration: The combination of RPA and AI, along with machine learning, enables smarter, adaptive systems that optimize processes and drive innovation in the automotive industry.
Step into any modern automotive facility, and you’ll immediately sense the pressure. Supply chains stretch across continents, electric vehicle adoption is rapidly gaining momentum, and customers demand faster delivery with flawless execution. Amidst this complexity, automakers face a significant challenge: manual processes simply can’t keep up.
That’s where Robotic Process Automation (RPA) steps in. RPA in automotive handles repetitive, rule-based digital tasks that slow everything down, such as supplier onboarding, order processing, warranty claims, and inventory updates. It doesn’t replace people. It removes the work, preventing them from focusing on what actually drives value.
This shift is happening now, not coming later. Grand View Research projects the global RPA in the automotive market will hit USD 30.85 billion by 2030, growing roughly 44% annually.
What these numbers actually mean: automation moved beyond factory floors. It’s now tackling back-office operations, compliance work, logistics coordination, and customer service, areas that traditionally depended on manual effort and created bottlenecks.
In the sections ahead, we’ll look at real use cases of RPA in the automotive industry. How leading manufacturers are using automation to accelerate workflows, reduce costs, and build operational intelligence that they couldn’t access before.
Accelerate your automotive operations, cut costs, and scale seamlessly.
RPA in Automotive: Market Insights and Adoption Drivers
The automotive industry has always embraced automation, but the current wave isn’t on factory floors. It’s digital. Supplier coordination, quality checks, compliance processes, and the backend infrastructure of automaking are being rebuilt through Robotic Process Automation in the automotive industry.
Several factors are pushing this rapid adoption:
- Operational complexity: Automakers coordinate thousands of suppliers and millions of components. One mistake shuts down production lines across multiple continents simultaneously. The interconnectedness that enables global manufacturing also makes it incredibly fragile.
- Cost pressure: Global competition and shrinking margins require OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers to do more with fewer resources. The phrase “Do more with less” has moved beyond a motivational slogan—it’s now a fundamental operational necessity.
- Disconnected systems: ERP, MES, and CRM platforms don’t communicate properly. Information gets trapped in silos. Critical decisions get delayed because data lives in three different systems that weren’t built to communicate with each other.
- Customer expectations: Real-time order tracking. Expedited deliveries. Proactive service support before problems occur. These aren’t premium features anymore; they’re baseline requirements. Customers are comparing you to Amazon’s delivery experience, whether that’s fair or not.
RPA in automotive tackles these challenges directly. Automating repetitive, rule-based digital tasks, such as invoice matching, warranty claim processing, and data transfers, enables human teams to focus on activities that require human judgment: innovation, design refinement, and customer relationship building.
10+ RPA Use Cases in the Automotive Industry
RPA has quietly become the hidden engine behind digital transformation in automotive enterprises. From managing supplier invoices to improving customer service turnaround, the technology is removing friction from nearly every process that once depended on manual intervention.
1. Predictive Maintenance and Equipment Monitoring
In automotive manufacturing, acting too early or too late on maintenance can be equally costly.
RPA helps coordinate predictive maintenance by linking IoT insights with operational planning. When sensors detect early signs of failure, RPA workflows are triggered to evaluate the impact before any action is taken.
Instead of immediately scheduling maintenance, RPA can first trigger a maintenance event in a Digital Twin environment to assess the impact on downtime, line dependencies, and resource availability. Once validated, RPA creates work orders, schedules technicians, and reserves parts. This ensures maintenance actions reduce downtime without disrupting live production.
For Example, Bosch runs AI-driven predictive maintenance using machine learning for real-time equipment monitoring. They put IoT sensors on critical machinery, capturing temperature, vibration, pressure, and performance metrics nonstop. AI models crunch this data, catch patterns and anomalies, and flag potential failures before they actually happen.
Here’s what changed: instead of fixing machines after they break, you’re preventing breakdowns before they occur. Maintenance happens when you decide, not when equipment decides for you.
That control matters when downtime costs tens of thousands per hour
2. Quality Assurance and Compliance Auditing
Quality checks and emissions reports used to require hours of data compilation. RPA gathers inspection results from MES and QMS systems, validates documentation, and formats compliance reports automatically. RPA in the automotive industry now handles this by automating data collection, quality checks, and compliance documentation.
For Example, Mercedes-Benz AG has adopted RPA in its quality management processes, resulting in faster and more accurate business operations. The implementation saved 5.075 full-time equivalents (FTEs) and increased product quality. This case study serves as a starting point for RPA in automotive quality management, with potential for further improvements through process mining and AI integration.
3. Supply Chain Visibility and Supplier Performance Monitoring
Automotive supply chains get messy fast, with thousands of SKUs and hundreds of vendors. RPA pulls supplier data from portals, tracks shipment updates, validates invoices, and flags discrepancies as they happen.
Example: Stant, a Tier-1 automotive supplier, implemented RPA to automate its invoicing system. This initiative reduced invoice matching backlogs from three weeks to just four days, achieving 80% straight-through processing and eliminating data entry errors.
This is a great example of RPA automation ideas that improve supplier performance and operational efficiency across the automotive supply chain.
4. Order-to-Cash and Financial Close Acceleration
Finance teams in automotive juggle complex regional regulations, multiple currencies, and massive transaction volumes daily. RPA automotive bots handle ledger reconciliation, invoice processing, and payment updates, substantially cutting manual work while catching errors humans miss.
Finance teams spend more time analyzing strategic decisions and less time entering data into systems.
Example: BMW Group is rebuilding production logistics and financial processes with modern SAP architecture. The goal is to boost efficiency and enable AI usage as part of their Group-wide cloud-based IT rollout.
5. Procurement and Vendor Management
From supplier onboarding to purchase order verification, RPA bots validate vendor credentials, update procurement records, and perform 3-way PO matching.
This ensures that payments and inventory align without constant human follow-ups.
Example: Volkswagen Financial Services has implemented RPA to shorten processing times in IT service management. By automating routine tasks, the company has improved efficiency and reduced the workload on its IT support teams.
6. Logistics and Customs Clearance
Automotive logistics generates mountains of paperwork, shipment manifests, customs declarations, and tracking reports. Handling this manually eats time and creates errors constantly. RPA bots automate customs filings, generate shipping labels, and coordinate with carriers. The entire logistics process moves faster.
Example: DHL has integrated robotic process automation to automate time-consuming tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value work and improving customer service. Additionally, DHL has signed a memorandum of understanding with Boston Dynamics to deploy over 1,000 robotic units across its operations, accelerating its cross-business automation strategy.
7. Warranty, Claims, and After-Sales Service
Warranty management is a huge cost center for automakers. RPA bots analyze claim data, verify warranty eligibility, cross-check service histories, and process approvals automatically.
Example: Toyota Material Handling Norway, which is part of the Toyota group, describes how RPA improved its sales order process and freed up the team for more customer-facing work.
RPA also powers smarter scheduling by checking technician availability, parts inventory, and service slots, then updating customers automatically.
8. Dealer Operations and Retail Financing
Dealerships often handle thousands of financing documents daily. RPA bots verify documents, process loan details, and integrate updates with CRM and DMS systems.
Example: Bridgestone Thailand leveraged RPA for retail operations, automating credit approvals and improving turnaround time.
Why it matters: Better dealer efficiency translates to improved customer experience and faster car delivery.
9. Customer Experience and Personalization
Customers now expect seamless interactions across online and offline channels. Not a preference—a baseline requirement. RPA delivers real-time updates from test drive scheduling through loan processing by connecting CRM, ERP, and service systems that weren’t designed to communicate.
Example: BMW Group runs RPA combined with chatbots for personalized service reminders and post-purchase engagement.
Why it matters: This isn’t automation for cost savings. It’s fixing a customer experience problem. Someone browses cars online, walks into a showroom, and the salesperson has no idea what they looked at. RPA connects those dots. Customers notice when their online activity doesn’t follow them into the store—and they see when it does.
10. Pricing, Incentives, and Product Launch Coordination
Automotive pricing changes constantly. Regional taxes shift. Inventory levels fluctuate. Incentives get updated weekly, sometimes daily. RPA pushes price updates across ERP, CRM, and dealer systems automatically, keeping every location aligned.
Example: Porsche New Zealand’s dealer network (Giltrap Group) deployed Kofax RPA to sync incentive data across showrooms. Customers see identical offers at every location now.
Why it matters: Inconsistent pricing destroys trust instantly. Customer calls Showroom A, hears one number. Visits Showroom B, gets quoted something different. That customer’s gone. RPA prevents this scenario by updating pricing across the system simultaneously.
One source of truth. No discrepancies. No awkward conversations about why prices don’t match.
11. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) for Supplier Documents
Automotive supply chains rely on large volumes of unstructured supplier documents that vary by format and quality.
RPA-enabled IDP combines OCR and AI-based classification to extract and understand document content. OCR captures text from scanned or handwritten files, while AI models identify document types and key compliance details.
RPA then routes documents, updates enterprise systems, flags exceptions, and maintains audit trails. Human review is applied only where needed, improving speed without increasing compliance risk.
Example: Stellantis Group used RPA-IDP integration for compliance documents during mergers, processing hundreds of document types 5× faster than before.
12. Sustainability and ESG Data Tracking
Sustainability reporting isn’t optional anymore in Europe and the GCC; it’s a regulatory requirement. Automotive companies now track ESG metrics constantly. RPA automates the collection and consolidation of data like energy consumption, emissions, and supplier certifications. Everything feeds into centralized dashboards for compliance and audits.
Also Read: RPA in Finance: A Guide to Implementation and Benefits
Leverage RPA to enhance production, improve customer experience, and streamline supply chain coordination.
Key Benefits of RPA in Automotive Enterprises
When production lines and supply chains operate on razor-thin margins, Robotic Process Automation has shifted from an efficiency tool to a competitive necessity. Companies either implement it effectively or fall behind competitors who have already done so.
Here’s what’s actually happening in automotive operations right now:
1. Operational Efficiency
RPA handles the repetitive work nobody enjoys but everyone needs done. Invoice processing, ERP updates, and compliance reports are handled faster and more accurately by bots than manual processing ever managed.
Cycle times drop noticeably. Operations teams stop spending entire days firefighting and start focusing on throughput improvements and quality gains instead.
2. Enhanced Productivity
Automation removes the tedious work from people’s plates. Engineers optimize workflows rather than entering data manually. Finance teams analyze patterns instead of copying numbers between systems. Managers access current insights rather than waiting three days for someone to compile a report.
People handle strategy, problem-solving, and innovation. RPA executes the repetitive tasks that honestly should have been automated years ago.
3. Cost Reduction
Process inefficiencies cost real money. Rework from data entry mistakes. Human errors that cascade through systems. Approval bottlenecks are delaying critical decisions. Most organizations underestimate how quickly these costs accumulate.
Standardizing repetitive processes through RPA reduces administrative overhead substantially.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Automotive companies are drowning in documentation requirements. Quality checks for every component. Supplier audits across dozens of partners. Emissions data is tracked constantly. Warranty claims are documented meticulously. Everything needs records that withstand regulatory scrutiny.
RPA logs every action with precise timestamps and complete traceability. Compliance audits shift from stressful ordeals into routine reviews. This automated documentation helps companies manage increasingly complex global regulations without proportionally expanding their compliance teams.
5. Faster Time-to-Market
From prototype approval through supplier coordination, automation compresses product development timelines.
Bots process change requests immediately rather than sitting in approval queues. Documentation updates happen in real-time. Logistics coordination occurs instantly. Manufacturers launch new products or features weeks faster while maintaining supply chain flexibility that manual processes couldn’t match.
Technical Depth: Engineering for the “Success Disaster”
Automation rarely fails at the pilot stage. It fails after it succeeds. Enterprise leaders are less concerned about whether an RPA bot can run and more focused on what happens when that bot becomes embedded in live production operations. At scale, a small automation error can cascade into delayed production schedules, supplier disruptions, or compliance gaps.
That is why RPA in automotive environments must be engineered for controlled failure, not just speed or efficiency.
What “engineering for success” really means
At scale, automation must assume systems will change, data will be incomplete, and exceptions will occur. Enterprise-grade RPA is designed with safeguards that prevent silent failures and operational blind spots:
- Validation before execution to avoid triggering actions that disrupt active production lines
- Human-in-the-loop checkpoints for high-impact decisions
- Clear exception ownership across operations, IT, and compliance teams
- End-to-end audit visibility for traceability and regulatory reviews
Why this matters in real operations
When automation is treated as a set of scripts, failures remain invisible until damage is done. When it is treated as an operating layer, failures are:
- Visible in real time
- Contained in defined workflows
- Recoverable without halting core operations
This difference determines whether RPA remains a pilot initiative or becomes a production-critical system that leadership can trust.
How to Implement RPA in the Automotive Industry
Implementing RPA in the automotive industry comes with its own set of challenges, but with the right steps, automakers can successfully scale automation. Here are the steps to strategically implementing RPA:
1. Start with Processes that Deliver Measurable ROI
Don’t automate just because everyone else is. Pick repetitive, rule-based tasks where you’ll see results fast: invoice reconciliation, warranty claims, parts inventory checks.
Those early wins matter. They get you internal buy-in and funding for what comes next. Focus on areas where RPA automation ideas can yield quick ROI.
2. Build RPA on Clean, Connected Data
Bots work only as well as the data feeding them. Inconsistent product codes, duplicate vendor records, and siloed ERP data kill scalability faster than anything else.
Fix your data pipelines first. Make sure systems can actually talk to each other.
3. Focus on Human-Bot Collaboration, Not Replacement
RPA’s job isn’t replacing people. It’s eliminating the tedious tasks, so your team can focus on work that requires actual human judgment.
RPA handles repetitive tasks like invoice validation. People oversee exception handling and negotiate with suppliers. Cycles got faster. Relationships improved.
When your employees view automation as something that helps them rather than threatens them, adoption happens much faster across the organization.
4. Adopt a Scalable, Modular RPA Architecture
Legacy systems are everywhere in automotive plants. Trying to automate everything at once? That usually fails.
Smart companies take a modular approach with cloud-based RPA platforms that integrate with ERP, MES, and CRM systems, one process at a time.
This minimizes disruption. You can roll things out in phases across procurement, production, logistics, and HR.
5. Measure, Iterate, and Scale
Automation isn’t something you set up once and forget about. Keep measuring performance, accuracy, processing time, cost savings, and employee satisfaction.
BMW Group runs quarterly RPA audits. They identify redundant processes and find optimization opportunities. That continuous improvement approach keeps automation useful even when business needs change.
6. Ensure Compliance and Cybersecurity from Day One
Automotive companies handle tons of sensitive data. Vendor contracts. Customer payment information. All of it.
RPA bots that interact with these systems must comply with global security standards, including ISO 27001, GDPR, and APRA CPS 234. Regular audits. Encrypted data transfers. Secure credential storage. None of this is optional.
A secure foundation protects your systems. More importantly, it protects your reputation.
8. Partner with Experienced RPA Experts
Implementing RPA across a large, multi-system ecosystem isn’t simple. You need experience in both process engineering and automotive operations.
That’s why leading OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers work with enterprise RPA development firms like Appinventiv. They combine domain knowledge with scalable automation frameworks.
From building proofs of concept to deploying AI-assisted bots for supply chain orchestration, experienced partners help you avoid costly mistakes and deliver value faster.
Also Read: RPA in Banking – How Robotic Process Automation
RPA Implementation Challenges and Solutions in the Automotive Industry
RPA in the automotive industry sounds great on paper. Reality? Scaling automation across automotive operations hits obstacles most vendors won’t mention upfront. Here’s what actually goes wrong—and how companies are dealing with it.
1. Legacy System Compatibility
Walk into most plants and you’ll find ERP and MES platforms from the early 2000s, maybe earlier. Nobody designed these systems with bots in mind. Connecting RPA without breaking production becomes a genuine headache.
What actually works: API connectors or middleware that sit between old and new systems. Handle this hybrid mess better now than they did three years ago, though integration still takes longer than sales teams claim.
2. Change Management and Workforce Adoption
Roll out automation and watch the rumor mill start. “They’re replacing us with robots” spreads through the plant floor faster than any official communication.
What actually works: Be honest upfront. RPA handles repetitive tasks so people can do more valuable work—but only if you say that from day one and back it up with reskilling programs. Deloitte’s 2025 Future of Work Report found that companies that invested in training and communicated early saw adoption rates double compared to those that didn’t.
Silence breeds resistance. Transparency speeds adoption.
3. Balancing Cost and ROI
Early RPA spending feels risky when payback isn’t immediate. Finance sees invoices for licenses, implementation, consulting. They don’t see savings yet. CFOs get skeptical quickly.
What actually works: Pick one high-volume, straightforward process first. Invoice processing. Data entry. This is something that shows clear time savings within weeks, not quarters.
Prove the concept works. Show finance the numbers. Then ask for a budget to scale. Trying to automate everything simultaneously just burns money and credibility.
4. Security and Compliance Risks
RPA bots touch everything: customer data, supplier contracts, financial records, and quality documentation. One misconfigured bot can expose sensitive information or create compliance gaps nobody notices until an audit happens.
What actually works: Lock down access from the start. Encryption, strict permissions, and detailed audit logs showing exactly which bot accessed what data when.
Work with automation providers certified under ISO 27001 or SOC 2. Compliance can’t be retrofitted easily; build it into the architecture initially, or you’ll rebuild it later at three times the cost.
Future Trends of RPA in Automotive Industry
Automotive automation’s next phase isn’t just bots executing tasks; it’s systems that actually learn from what happens on the floor and adjust accordingly. RPA is merging with AI and Machine Learning now, which means manufacturers can move toward operations that optimize themselves rather than following fixed rules.
AI-powered RPA automotive analyzes sensor data from equipment, spots patterns indicating machinery might fail soon, and kicks off maintenance workflows automatically. No human needs to review the data first. A connected factory could have RPA bots scheduling repairs, ordering replacement parts, and updating inventory, allowing production to keep running the whole time.
Customer-facing operations are seeing similar changes. Bots process vehicle data in real-time, send service reminders automatically, and suggest upgrades matching how someone actually drives their car. Every interaction after the sale becomes a chance to keep that customer engaged.
Here’s one example already happening: AI visual inspection on assembly lines. Cameras with computer vision spot tiny defects in components. RPA flags the problem immediately, logs it in the quality system, and alerts supervisors. Inspection time drops significantly. Precision improves because you’re catching defects that human eyes miss.
Where this goes: automotive automation becomes deeply interconnected. Robotics, AI vision, and process automation all work together as a continuous digital infrastructure rather than separate systems. Less downtime for manufacturers. Faster product launches. Operations that recover from disruptions better because systems adapt instead of breaking.
AI-driven RPA automation ideas will improve processes beyond the factory floor, extending to areas like customer service and predictive analytics, revolutionizing the way the automotive industry functions.
That’s the shift happening now, not five years from now.
Unlock the future of automotive automation with Appinventiv’s AI-driven RPA services. Streamline operations and boost productivity today.
How Appinventiv Enables Automotive Leaders to Scale with RPA
Appinventiv works with automakers and suppliers transitioning away from manual processes. We build RPA development services and automotive software development services that streamline operations, improve quality, and deliver measurable returns. Here’s how we’ve helped the leaders:
We worked with Mudra, a budgeting management app, where AI was implemented to automate financial processes, making budgeting more efficient. For Sonny’s Enterprises, we designed an intelligent app for Alfred Car Wash that uses AI to optimize service delivery. Similarly, our AI in Banking solution helped improve customer service by integrating AI-driven solutions for real-time financial advice.
We design modular automation that works across multiple plants, geographies, and departments. Built to expand as operations grow.
RPA in automotive is not just a trend—it’s becoming the foundation for modernizing the industry. From production lines to customer service, robotic process automation in the automotive industry is helping companies reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer experiences. By leveraging RPA automation ideas, automakers can accelerate their transformation and scale their operations like never before.
If you’re ready to embrace the future of automotive automation, contact us today and discover how our RPA solutions can transform your business.
FAQs
Q. What is RPA Automation?
A. RPA (Robotic Process Automation) uses software bots to automate repetitive tasks that were once done manually. These tasks can include data entry, invoice processing, customer service, and more. The benefit of RPA automation is that it boosts efficiency, reduces errors, and frees up employees to focus on more strategic tasks. In the automotive industry, RPA is transforming supply chain management, customer service, and other operations by enabling faster, more accurate processes that scale with demand.
Q. How much does it cost to implement RPA in automotive processes?
A. The cost of introducing RPA in automotive processes really depends on what you’re automating and how complex the systems are. On average, you’re looking at $1,000 to $5,000 per bot, but if you’re dealing with more intricate tasks or needing custom solutions, it can run anywhere from $50,000 to $500,000. Think of it as an investment in efficiency that can eventually pay for itself. So, while the initial setup might seem like a big leap, the long-term savings and improvements are totally worth it.
Q. How does robotic process automation benefit automotive companies?
A. RPA is a game-changer for automotive companies, and here’s why:
- Cost Savings: By automating repetitive tasks, you can cut down on labor costs and avoid human errors.
- Efficiency Boost: Think faster order processing, smoother supplier communication, and quicker compliance reporting.
- Accuracy: Bots are meticulous – they don’t forget details or make mistakes.
- Scalability: Want to grow without increasing your workforce? RPA handles it without breaking a sweat.
- Happier Employees: With the boring tasks out of the way, your team can focus on more impactful work.
Q. Can RPA improve efficiency in car production?
A. Absolutely! RPA can streamline a lot of the behind-the-scenes work in car production, like managing inventory, checking supplier details, and keeping track of compliance. For example, Constellation Automotive Group used RPA to save an impressive 126,000 hours annually – that’s a lot of time freed up to focus on the important stuff!
Q. Do automotive companies have to replace their legacy software to implement RPA bots?
A. Not at all! One of the great things about RPA is that it can work alongside your existing systems. You don’t need to scrap everything and start from scratch. RPA bots simply interact with your current software, automating tasks without needing to make big changes to the core systems. It’s a much smoother way to modernize without the hefty cost of overhauling everything.
Q. Can RPA bots work 100% automatically without requiring human supervision and decision-making?
A. RPA bots are pretty smart, but they do have their limits. For tasks that are clear-cut and rule-based (like processing invoices), they can work totally independently, which is great for efficiency. But for more complex scenarios where human judgment is needed, they might need a little help. You have a few options:
- Unattended Bots: These work completely on their own, great for repetitive tasks.
- Attended Bots: These need a human to kick things off or guide them when exceptions pop up.
- Hybrid Bots: A mix of both, offering flexibility when needed.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

How AI Chatbots for eCommerce are Driving 3x More Sales in 2026
Key takeaways: AI chatbots for eCommerce have a direct impact on revenue. When aligned with buying intent, they lift conversions, increase order value, and drive repeat purchases. The strongest impact comes from personalization and guided selling, helping shoppers decide faster and buy with greater confidence. Abandoned cart recovery is a major revenue driver in 2026.…

AI-Powered Booking Optimization for Beauty Salons in Dubai: Costs, ROI & App Development
Key Highlights AI booking optimization improves utilization, reduces no-shows, and stabilizes predictable salon revenue streams. Enterprise salon platforms enable centralized scheduling, customer insights, and scalable multi-location operational control. AI-enabled booking platforms can be designed to align with UAE data protection regulations and secure payment standards. Predictive scheduling and personalization increase customer retention while significantly reducing…

Data Mesh vs Data Fabric: Which Architecture Actually Scales With Business Growth?
Key takeaways: Data Mesh supports decentralized scaling, while Data Fabric improves integration efficiency across growing business environments. Hybrid architectures often deliver flexibility, governance, and scalability without forcing premature enterprise-level complexity decisions. Early architecture choices directly influence reporting accuracy, experimentation speed, and future AI readiness across teams. Phased adoption reduces risk, controls costs, and allows architecture…