- Understanding the Role of Master Data Management in Healthcare MDM and Its Business Relevance
- The Interoperability Gap: What’s Broken in Healthcare Data Today
- Key Components of a Unified MDM For Healthcare
- Real Impact and Practical Use Cases of Healthcare MDM
- Before and After MDM Implementation
- Real-World Examples: How Leading Healthcare Systems Improved Operations with Data Management
- Intermountain Health: Reducing Duplicate Records to Improve Care Coordination
- Appinventiv’s Middle East Example: Unifying Health Data at Scale
- Yale New Haven Hospital: Turning Data Consistency into Faster Patient Flow
- Michigan Health Information Network (MiHIN): Building Statewide Interoperability at Scale
- Utah Health Information Network (UHIN): Improving Match Accuracy in a Multisystem Environment
- Payer–Provider–Patient Interoperability: The Missing Piece
- Why This Connection Matters
- Compliance, Security, and Ethical Data Governance
- 1. Keeping Data Safe, No Matter Where It Lives
- 2. Meeting Compliance Requirements Without Stress
- 3. Ethical Data Use Goes Beyond Legal Requirements
- 4. Data Governance That Works in the Real World
- 5. Why This Matters for Enterprise Healthcare Systems
- Emerging Technologies Shaping the Future of Healthcare MDM
- 1. AI for Smarter Identity Matching and Data Cleanup
- 2. Blockchain for Secure and Transparent Data Sharing
- 3. Cloud-Native MDM Platforms
- 4. Graph Databases for Understanding Relationships
- 5. Real-Time Integration of IoT and Wearable Data
- Why These Technologies Matter for Enterprises
- Development Roadmap for Building Healthcare Master Data Management Systems
- Step 1: Technical Discovery and Data Architecture Audit
- Step 2: Designing the Master Data Model and Governance Engine
- Step 3: Building API Gateways and Data Pipelines (HL7, FHIR, Custom Integrations)
- Step 4: Implementing the MDM Engine (Matching, Merging, Deduplication)
- Step 5: Security, Privacy and Compliance Engineering (HIPAA, GDPR, PDPL)
- Step 6: Unified Analytics, AI Models and Data Services Layer
- Performance Checklist for CIOs and CTOs
- How to Choose the Right MDM Partner (What Enterprises Should Look For)
- 1. Real Healthcare Experience, Not Just IT Skills
- 2. Strong Interoperability Capabilities
- 3. Advanced Identity Matching and Deduplication
- 4. Clear Governance and Compliance Expertise
- 5. Flexible, Scalable Architecture
- 6. Proven Track Record With Enterprise Deployments
- 7. Ability to Support Custom Development
- How Appinventiv Enables a Unified Data Strategy
- FAQ
Key Takeaways
- Unified MDM gives one trusted view of patient, provider, and payer data, which unlocks true interoperability.
- Clean, connected data cuts duplicates, speeds claims, improves clinical decisions, and lowers IT and admin costs.
- A solid framework includes integration via HL7/FHIR, identity matching, governance, golden records, and analytics.
- Follow a clear roadmap with KPIs like duplicate reduction, claims turnaround, interoperability score, and governance maturity.
- Real results show up in daily workflows and use cases, from single patient records to provider directories and audit readiness.
Walk into any hospital today and you’ll find data everywhere, on screens, in systems, and across departments that barely talk to each other. McKinsey’s report says healthcare data is growing nearly 36% every year, yet most of it remains scattered in silos. Doctors still chase missing lab results, insurance teams spend hours verifying claims, and patients get frustrated repeating the same information. All because the systems holding this data were never built to work together.
Even with advanced EHRs and billing platforms, real interoperability still feels out of reach.Most healthcare leaders are still trying to close the technology gap between these tools. Hospitals may have modern software, but their data doesn’t move freely.
That’s where healthcare master data management (MDM) changes the picture. It creates one trusted, accurate view of every patient, provider, and payer. When data is clean and connected, decisions become faster, errors drop, and everyone works with confidence.
For forward-looking organizations, now is the time to build custom healthcare master data management software that finally brings all systems together. Beyond compliance with HIPAA and FHIR, it’s about giving healthcare what it truly needs, data that actually helps people, not holds them back.
Ready to modernize your healthcare data management?
Understanding the Role of Master Data Management in Healthcare MDM and Its Business Relevance
In healthcare, Master Data Management (MDM) software development for healthcare is more than a tool for cleaning records. It’s the backbone of how modern care systems function. Deloitte’s Global Healthcare Outlook shows that over 70 percent of healthcare executives consider improving operational efficiency and interoperability their top goals this year.
They know the issue isn’t the lack of data, but the lack of connection between systems. Master data management in healthcare bridges that gap by setting clear rules on how information should be gathered, verified, and shared while keeping everything secure and compliant with HIPAA and FHIR standards.
A good healthcare master data management framework ties together three essential pillars:
- Patient Data: From test results to wearables, every bit of information matters. When this data sits in one trusted system, doctors can make quicker, safer decisions without chasing missing details.
- Provider Data: Credentials, affiliations, and schedules, keeping this information accurate means fewer billing issues and smoother coordination between teams.
- Payer Data: Plan details, claims, and payment history. When MDM software development in healthcare connects payers and providers, claims move faster and errors drop.
When these three streams flow into one connected framework, data finally starts doing what it should, which is to support care instead of slowing it down. That’s the real value of healthcare data management software development. For any organization aiming to modernize, the next step is to build custom healthcare master data management software that unites every system, protects every record, and gives every decision a foundation of truth.
The Interoperability Gap: What’s Broken in Healthcare Data Today
Most hospitals today have gone digital, but their systems still act like strangers. Data sits in silos like EHRs, billing software, lab databases, and insurance platforms, and each one of them running separately. The result is a constant struggle to find, match, and trust the right information.
Here’s where the gaps usually appear:
- Disconnected systems: Hospitals use multiple tools that don’t communicate well with each other. Data exchange is either slow or nonexistent.
- Duplicate and mismatched records: One patient might appear as John Smith in the EHR and Jonathan Smith in billing. These inconsistencies cause errors in diagnosis, claims, and reporting.
- Misaligned payer-provider data: When provider information doesn’t sync with payer databases, claims get delayed or rejected, frustrating both staff and patients.
- Manual data fixes: Teams often spend hours reconciling records that should have matched automatically. This slows operations and drains productivity.
- Compliance pressure: Regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, HL7/FHIR, and PDPL add layers of complexity. Every region and system has its own standards for how data can be shared or stored.
- Financial drain: The lack of interoperability leads to repeated tests, denied claims, and wasted administrative hours, which costs healthcare systems an estimated $300 billion every year.
In short, healthcare isn’t suffering from a lack of data, but it’s suffering from too much data trapped in disconnected systems. Until organizations build a unified data backbone, every digital upgrade will stay surface-level. The future of healthcare depends on fixing the foundation first.
Key Components of a Unified MDM For Healthcare
Solving healthcare’s data challenges starts with structure. A strong healthcare master data management framework doesn’t just hold information, it connects it with every system. It ensures that data coming from hospitals, insurers, and labs moves smoothly, stays accurate, and follows every compliance rule along the way.
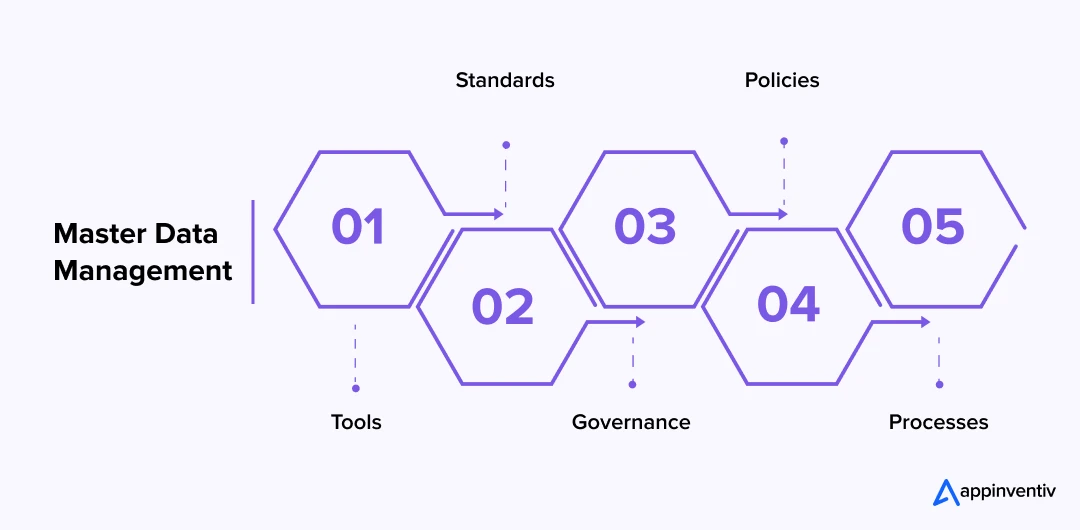
- Data Integration Layer: Every system from EHR to billing software, CRM, and insurance portal, must communicate in real time. Through mdm healthcare solutions integration, modern APIs (like REST/SOAP), event-driven architecture, and healthcare standards like HL7 and FHIR let data flow securely between platforms. This layer lays the groundwork for true interoperability.
- Identity Resolution and Matching: Duplicates are one of the biggest challenges of health data management. This component uses intelligent matching algorithms (using both probabilistic and deterministic matching) to recognize when John Smith and Jonathan Smith are the same person. It’s how master data management in healthcare turns scattered records into a single, verified profile.
- Data Quality and Governance: Data quality defines trust. A MDM software development for healthcare systems applies governance rules to check accuracy, validate entries, and standardize formats. It also limits access through role-based permissions to keep information compliant with HIPAA, GDPR, and PDPL requirements.
- Master Indexing and Golden Records: The heart of master data management for healthcare providers lies here. It creates a “golden record,” one clean, consistent version of truth for every patient, provider, and payer. Whether it’s updating a treatment plan or verifying insurance eligibility, everyone works from the same data source.
- Analytics and Reporting Hub: Once information is unified, organizations can make smarter decisions. Hospitals can track outcomes, identify inefficiencies, and predict future needs. For enterprises investing in healthcare data management software development, this layer turns raw data into insights that improve care and efficiency.
With these components working together, hospitals no longer have to patch data gaps manually. Instead, they can focus on what matters, which is to offer improved care, speeding up operations, and building systems that actually work together. The right approach to build custom healthcare master data management software turns disconnected systems into one connected ecosystem.
Real Impact and Practical Use Cases of Healthcare MDM
When data finally connects, the change is visible. Operations speed up. Claims stop getting stuck. Clinicians make decisions with confidence. A well-built healthcare master data management program makes every choice faster, clearer, and safer. Here are the core benefits of health data management and where they show up in daily work.
Business and Clinical Impact
- Operational efficiency: With MDM in healthcare, one clean record replaces manual checks across EHR, billing, labs, and payer systems.
- Faster claims processing: Shared, accurate payer-provider data cuts rework and shortens approvals.
- Clinical accuracy: With strong healthcare data management software development, clinicians see complete histories, which reduces errors.
- Cost optimization: Master data management in the healthcare industry eliminates duplicate systems and repeated tests.
- Compliance and audit readiness: Audit trails and role-based access simplify HIPAA, GDPR, and PDPL reporting.
High-Value Use Cases
- Creating a single, reliable patient record: MDM links duplicates and incomplete profiles so teams work from one source of truth.
- Smoother claims and fewer rejections: When payer and provider data match, claims move faster and denials drop.
- Keeping provider data consistent: MDM standardizes credentials, specialties, affiliations, and schedules for referrals, billing, and credentialing.
- Better coordination across sites: As patients move between hospitals, urgent care, or labs, their history follows them. That reduces repeat tests and speeds decisions.
- Making compliance easier: Clear ownership, standards, and audit trails keep organizations ready for HIPAA, GDPR, and PDPL.
- Clean inputs for analytics and AI: Accurate master records power forecasting, risk analytics, and population health insights without conflicting data.
Bottom line: Strong Master data management strategies turn scattered records into a single, trusted foundation. With the right healthcare master data management design and healthcare data management software development, enterprises get faster operations, fewer denials, safer care, and measurable savings.
Before and After MDM Implementation
| Metric | Before MDM | After MDM |
|---|---|---|
| Duplicate Patient Records | Multiple versions of the same patient across systems. | Up to 66% reduction in duplicates with verified records. |
| Claims Processing Time | 15–30 days on average due to mismatched data. | Resulting in an 80% reduction in claim denials and a faster payment cycle |
| Operational Efficiency | Manual data checks and disconnected systems. | Automated workflows, fewer errors, and smoother coordination. |
| Data Accuracy Rate | Inconsistent and unreliable data across departments. | Improves data accuracy and consistent reporting. |
| Audit Preparation | Manual compilation that takes weeks. | Real-time audit trails and quick compliance checks. |
Real-World Examples: How Leading Healthcare Systems Improved Operations with Data Management
Real change is best understood when you see it in action. Across the world, some of the most respected healthcare systems have already shown how strong master data management can reshape patient safety, operational efficiency, and payer coordination. These real examples show what happens when data finally starts working the way it should, clean, connected, and consistent.
Intermountain Health: Reducing Duplicate Records to Improve Care Coordination
Intermountain Health has long been recognized as a leader in data-driven healthcare. But even they struggled with high duplicate record rates, especially when patients moved between clinics, emergency departments, and specialist centers.
To fix this, Intermountain implemented an enterprise-grade identity management framework that used probabilistic matching, enriched data points, and continuous stewardship. The results were dramatic. Duplicate record creation dropped, cross-facility coordination improved, and clinicians gained a clearer view of each patient’s history — no more chasing missing files or re-running tests simply because records didn’t line up.
Appinventiv’s Middle East Example: Unifying Health Data at Scale
In the UAE region, Appinventiv demonstrated similar capability through the Health-e-People project. The challenge was to consolidate health data coming from more than 200 different devices and wellness apps, all using different data formats and structures. Users needed a single space to track health, caregivers needed visibility, and researchers needed accurate models across populations. Fragmented data made all three difficult.
Appinventiv designed a unified data layer that pulled everything together into one structured ecosystem. This created a seamless experience for users and an actionable platform for health partners. The solution shows how effective data management and identity alignment can transform care delivery, just as it did for major global healthcare systems.
Yale New Haven Hospital: Turning Data Consistency into Faster Patient Flow
Yale New Haven, one of the largest academic medical centers in the US, learned firsthand that any delay in data movement creates real delays for patients. Their emergency departments and inpatient units were struggling with congestion because information wasn’t flowing cleanly between systems.
After adopting an integrated data management and command-center model (aligned with MDM principles), they achieved faster patient throughput, fewer bottlenecks, and consistent reporting across departments. Nurses and physicians no longer had to compare conflicting records or wait for departments to update their systems. For patients, this meant shorter wait times and smoother transitions between care units.
Michigan Health Information Network (MiHIN): Building Statewide Interoperability at Scale
MiHIN is one of the most successful examples of interoperability in the United States. Their mission was simple: make sure data follows patients — not the other way around.
By building a statewide data management-aligned framework and creating a unified structure for patient identity, provider updates, and real-time event notifications, MiHIN enabled hospitals, payers, public health agencies, and labs to all operate from synchronized information. The impact showed up in fewer repeated tests, drastically improved care transitions, and better reporting for population health programs.
Utah Health Information Network (UHIN): Improving Match Accuracy in a Multisystem Environment
Once COVID data began flowing from dozens of sources, UHIN discovered that traditional matching systems weren’t enough. Their EMPI required tuning to handle name variations, unstructured data, and incomplete demographic entries.
Through a combination of MDM-aligned identity resolution and ongoing data stewardship, UHIN increased match accuracy and reduced manual reconciliation. More importantly, they achieved a level of consistency that supported Utah’s pandemic response, accurate case reporting, fewer duplicates, and faster data exchange between hospitals and public health authorities.
Payer–Provider–Patient Interoperability: The Missing Piece
Most healthcare organizations work hard to connect their internal systems, but the real challenge begins when data needs to move outside the walls of a hospital. Providers, payers, and patients are all part of the same care journey, yet their information often lives in three completely different worlds. That’s where interoperability usually breaks down — not because the data doesn’t exist, but because no one is seeing the same version of it at the same time.
When healthcare master data management steps in, these gaps start to close. Here’s how each connection improves when the three pillars finally sync up:
1. Patient to Provider
Patients expect their doctors to have all the information they need, but that rarely happens without unified data. When MDM ties patient histories, lab results, prescriptions, and insurance details together, providers get a complete view. Care becomes safer, faster, and more personal because doctors aren’t guessing or searching through scattered files.
2. Provider to Payer
This relationship is where many delays happen. If a provider’s records don’t match what the payer has, claims stall or get rejected. With MDM in healthcare, both sides share one verified source of truth. Eligibility checks are quicker, claims get approved faster, and disputes drop because the data lines up the first time.
3. Payer to Patient
Patients often find insurance information confusing or outdated. Unified payer data makes coverage details clear, accurate, and easier to understand. It also reduces unnecessary back-and-forth calls about authorizations or claim statuses, giving patients more transparency and confidence.
Why This Connection Matters
- Care teams stop working in isolation.
- Claims no longer bounce between payer and provider due to mismatched entries.
- Patients get clearer, more consistent information and smoother experiences.
- Data becomes a shared asset, not a siloed problem.
- Organizations finally build the foundation needed for real interoperability — not just internal integration.
When enterprises choose to build patient data management systems, they’re not just fixing internal systems, they’re unlocking a three-way connection that improves every part of the healthcare journey. Once these three pillars move in sync, hospitals deliver better care, insurers move faster, and patients feel supported instead of lost in the process.
Compliance, Security, and Ethical Data Governance
In healthcare, data isn’t just information, it’s someone’s life story. That’s why security and governance matter as much as technology. As organizations move toward unified healthcare master data management solutions, the responsibility grows: protecting every record, honoring patient consent, and making sure data never travels where it shouldn’t.
This section focuses on the part that often feels invisible but decides whether an MDM program succeeds or falls apart.
1. Keeping Data Safe, No Matter Where It Lives
Healthcare data moves across EHRs, claims systems, apps, and partner networks. Each of these touchpoints is a potential risk. Strong MDM brings all of this under one consistent security framework.
This usually includes:
- Encryption for every data transfer
- Role-based access so people see only what they need
- Regular audits to find gaps before someone else does
- Monitoring tools that flag unusual behavior
Security becomes easier when data isn’t scattered everywhere.
2. Meeting Compliance Requirements Without Stress
Regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, PDPL, and country-specific privacy laws aren’t just boxes to tick. They define how patient data should be handled, stored, and shared.
MDM helps because it:
- Creates clean audit trails automatically
- Tracks who accessed what and when
- Centralizes consent and preference management
- Simplifies reporting during audits
Instead of scrambling before an audit, organizations already have everything organized.
3. Ethical Data Use Goes Beyond Legal Requirements
Even when laws are followed, there’s a bigger question: Are we using patient data in a way that respects the patient?
Ethical governance ensures:
- Patients know how their data is being used
- AI models don’t introduce bias
- Sharing rules respect patient choices
- Data is used to improve care, not complicate it
Ethics isn’t paperwork, it’s about building trust.
4. Data Governance That Works in the Real World
Good governance isn’t a policy stored in a folder. It’s a living practice that guides how people work every day.
Effective governance includes:
- Clear ownership of data domains
- Defined rules for updating and validating records
- Change-control processes for new integrations
- Regular reviews to keep rules relevant
When done right, teams know who to ask, what to follow, and how to keep data clean.
5. Why This Matters for Enterprise Healthcare Systems
As organizations scale, new facilities, new partners, new digital apps are making the volume of data grow even faster. Without a strong compliance and governance backbone, even the best MDM setup can become risky.
Enterprise teams use MDM to:
- Reduce exposure to breaches and penalties
- Make cross-system data sharing safer
- Strengthen patient confidence
- Support AI and analytics without compromising privacy
It’s the part of MDM that doesn’t show up on dashboards, yet it’s what keeps everything running smoothly and legally.
Emerging Technologies Shaping the Future of Healthcare MDM
Healthcare is moving into a world where data needs to be fast, accurate, and available the moment someone needs it. Older systems weren’t built for this pace. That’s why new technologies are stepping in, they are not to replace MDM, but to make it stronger, smarter, and ready for the future.
These technologies help healthcare organizations move beyond basic record-keeping and toward true interoperability, where every update flows smoothly across hospitals, insurers, and patient-facing systems. Here’s how each one is making a real difference.
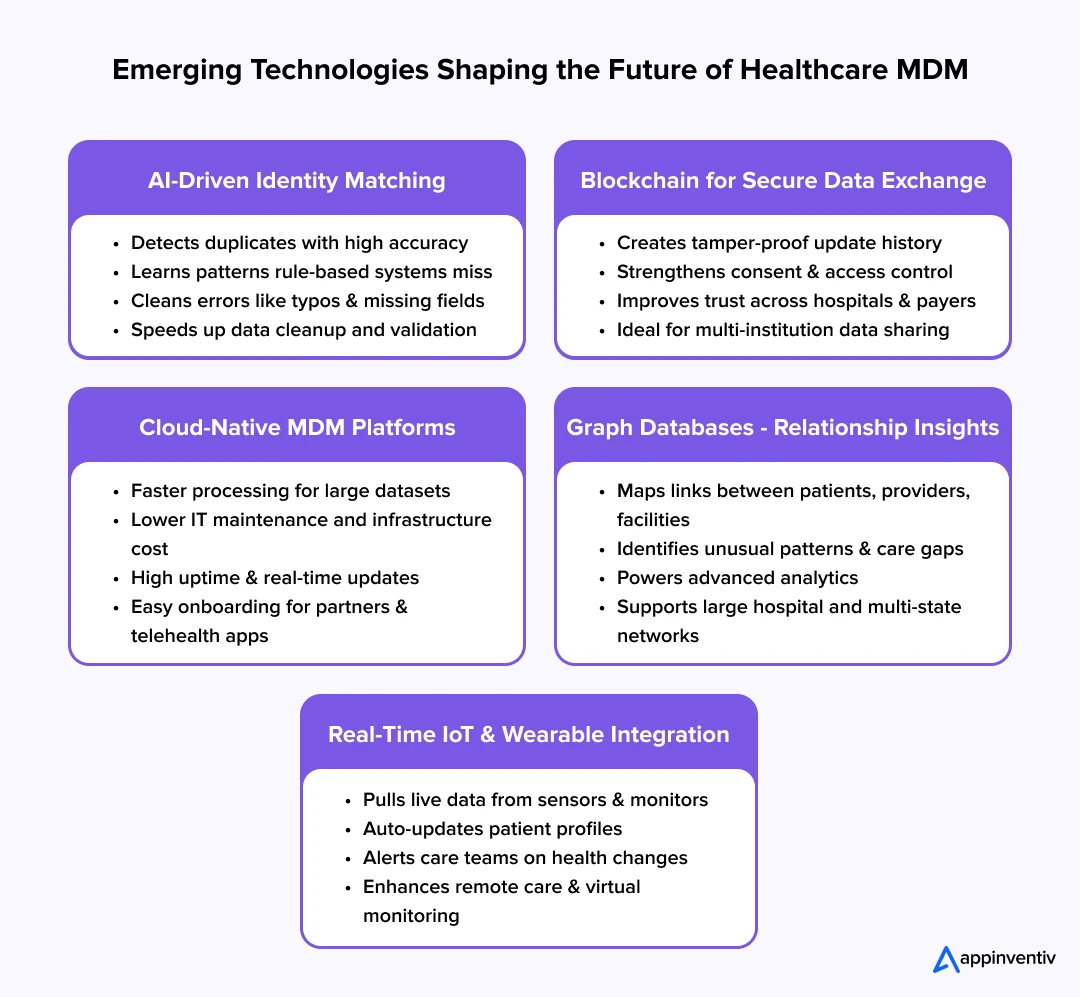
1. AI for Smarter Identity Matching and Data Cleanup
One of the biggest challenges in MDM is figuring out whether two slightly different records belong to the same person. AI is making this dramatically easier.
- It spots duplicates with far more accuracy than manual matching.
- It picks up patterns that traditional rule-based systems miss.
- It improves over time, learning from every correction.
AI reduces the burden on staff and brings clarity to messy data that used to take days to untangle. It also helps fix simple mistakes that can cause huge delays in care or claims such as misspellings, swapped digits, or incomplete entries.
2. Blockchain for Secure and Transparent Data Sharing
Blockchain is still new in healthcare, but its promise is huge. It creates a “chain” of updates that no one can alter without being noticed.
- Every record has a traceable history.
- Sensitive data becomes harder to tamper with.
- Patients gain more control over who can access their information.
For healthcare organizations struggling to meet compliance requirements or manage consent, blockchain adds an extra layer of trust. It’s especially helpful when multiple institutions need to share data without compromising security.
3. Cloud-Native MDM Platforms
Cloud technology is removing the limitations of old, slow, on-premise systems. Modern MDM in healthcare platforms built on the cloud offer:
- Faster processing even with large datasets
- Lower IT costs and easier maintenance
- Better uptime and availability
- Real-time updates across departments and partner networks
Cloud MDM also makes it easier to onboard new partners like pharmacies, telehealth platforms, or insurance networks that too without heavy integration work.
4. Graph Databases for Understanding Relationships
Healthcare is full of relationships:
- A patient connects to multiple providers.
- Providers connect to different facilities.
- Claims connect to plans, diagnoses, and services.
Graph databases help visualize and understand these relationships instead of treating each record as an isolated piece of information.
- They make it easier to detect unusual patterns.
- They support advanced analytics.
- They help identify gaps in care or communication.
For large hospital networks or multi-state health systems, graph technology brings a much clearer view of how everything links together.
5. Real-Time Integration of IoT and Wearable Data
More patients now rely on devices/wearables outside the hospital, tech instruments such as fitness trackers, glucose monitors, heart-rate sensors, home ECG tools, and more. This data offers valuable insight, but only if it becomes part of the patient’s master record.
MDM systems are evolving to:
- Pull in live data from wearables
- Update patient profiles automatically
- Alert care teams when important changes happen
- Support remote monitoring and virtual care programs
This creates a fuller, more accurate picture of patient health, not just what appears during hospital visits.
Why These Technologies Matter for Enterprises
For healthcare organizations looking to modernize, these technologies aren’t add-ons — they’re essential building blocks. They help enterprises:
- Reduce the time spent fixing or validating data
- Scale interoperability across partners and locations
- Improve decision-making with real-time insights
- Strengthen compliance and security without slowing operations
- Build a future-ready foundation for digital health initiatives
Whether you’re planning to upgrade your systems or build custom healthcare master data management software, these technologies help your MDM strategy grow with your organization. They ensure your data stays trusted, secure, and useful — no matter how fast the healthcare landscape evolves.
Development Roadmap for Building Healthcare Master Data Management Systems
When healthcare enterprises decide to unify patient, provider and payer data, the real work happens inside the development cycle. A strong MDM solution is not deployed like an IT tool. It is engineered layer by layer. Below are the steps that show how experienced teams typically build custom healthcare data management software and advanced mdm healthcare solutions from the ground up.
Step 1: Technical Discovery and Data Architecture Audit
Engineers begin by auditing every data source and system that will connect to the MDM platform. This includes EHRs, claims engines, lab systems, imaging repositories, scheduling platforms and CRM modules.
Developers map data schemas, identify mismatches, understand how records are created, and document all transformation rules. This step sets the technical foundation for building a unified healthcare master data management model with accurate entity relationships.
Step 2: Designing the Master Data Model and Governance Engine
Instead of generic governance policies, developers create an AI governance engine within the platform.
This includes:
- entity definitions for patient, provider and payer
- survivorship rules
- attribute-level quality rules
- referential integrity constraints
- lineage tracking
- update propagation logic
This is where engineers define how the “golden record” behaves and how conflicts are resolved programmatically.
Step 3: Building API Gateways and Data Pipelines (HL7, FHIR, Custom Integrations)
After the model is defined, developers build secure API gateways, ETL pipelines and event-driven data flows.
This usually includes:
- HL7 v2 listeners
- FHIR-compliant resources
- ETL flows for legacy EHRs
- Kafka or RabbitMQ streams for real-time data movement
- API connectors for claims and insurance systems
This is the most critical engineering stage because it determines how cleanly systems exchange data and how well the MDM adapts to future additions.
Step 4: Implementing the MDM Engine (Matching, Merging, Deduplication)
Developers now deploy the actual MDM engine.
This includes building:
- deterministic matching logic
- probabilistic matching algorithms
- ML-based record matching (for high-volume records)
- deduplication modules
- merge/unmerge workflows
- survivorship scoring
This is where fragmented datasets turn into a single, trusted “golden record” for patient, provider and payer entities.
For teams investing in healthcare data management software development, this step delivers the first visible transformation.
Step 5: Security, Privacy and Compliance Engineering (HIPAA, GDPR, PDPL)
Engineers implement compliance directly into the product architecture.
This includes:
- encryption at rest and in transit
- RBAC and ABAC access models
- tokenization or masking of sensitive fields
- audit logging and version history
- isolated biometric vaults
- PDPL-aligned data residency rules
This is where the platform becomes compliant by design and audit-ready for healthcare regulators.
Step 6: Unified Analytics, AI Models and Data Services Layer
After mastering data correctness, developers build advanced capabilities on top of it.
This includes:
- analytics cubes
- quality dashboards
- anomaly detection
- patient-risk prediction with AI
- claim-fraud patterns
- provider network optimization models
This stage proves the real value of MDM in healthcare, where data transitions from being “clean and consistent” to becoming “predictive and insightful.”
Performance Checklist for CIOs and CTOs
| KPI | What to Track | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Duplicate Reduction | How much cleaner your records become. | Aim for a 90% drop in duplicate entries. |
| Claims Turnaround | Time taken to process claims. | Shorten by 40–60%. |
| Interoperability Score | How well your systems communicate. | Target at least 80% seamless data flow. |
| Governance Maturity | How consistent your data policies are. | Work toward fully standardized, proactive governance. |
Final Outcome
Following this development roadmap helps engineering teams build custom healthcare master data management software that is stable, scalable, secure and analytics-ready. Once the MDM engine is live, healthcare organisations spend far less time reconciling records and far more time improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
How to Choose the Right MDM Partner (What Enterprises Should Look For)
Choosing an MDM partner isn’t just a tech decision, it’s a long-term relationship. The right partner helps you fix today’s data problems and prepares you for the next five to ten years of growth. The wrong one leaves you with another expensive system that looks promising on paper but never delivers in real life.
Here’s what enterprises should actually look for when selecting a healthcare master data management solution.
1. Real Healthcare Experience, Not Just IT Skills
Healthcare isn’t like other industries. The data is sensitive, the workflows are complex, and compliance isn’t optional. Your MDM partner must understand:
- Provider-payer workflows
- Clinical terminology and coding standards
- EHR limitations and integration challenges
- Regional privacy laws
If a partner can’t speak the language of healthcare, they won’t build a system that works for it.
2. Strong Interoperability Capabilities
MDM for healthcare is pointless if the partner can’t make systems talk to each other. Look for expertise in:
- HL7 and FHIR integration
- API development
- Connecting EHRs, claims platforms, CRMs, and lab systems
- Synchronizing data across large networks
Your partner should be able to connect old systems with new ones without forcing a full technology overhaul.
3. Advanced Identity Matching and Deduplication
Every hospital struggles with duplicates. A strong partner needs proven capabilities in:
- Identity resolution
- Golden record creation
- AI-assisted matching
- Handling mismatched, incomplete, or legacy data
This is the core of MDM in healthcare, and it’s where many projects fail if the partner is inexperienced.
4. Clear Governance and Compliance Expertise
Technology alone can’t solve governance issues. Your partner should help you:
- Define ownership rules
- Build validation workflows
- Set access controls
- Meet HIPAA, GDPR, and PDPL requirements
A good partner creates policies that are usable, not theoretical. If you need more information read our – complete guide on healthcare compliances.
5. Flexible, Scalable Architecture
Healthcare organizations are growing rapidly with new clinics, new apps, new departments. Your MDM partner must build a system that scales without breaking.
Look for:
- Cloud-native architecture
- Ability to integrate new data sources
- Modular design for easy upgrades
- Support for IoT, remote care, and analytics tools
You shouldn’t have to rebuild your MDM every time your organization expands.
6. Proven Track Record With Enterprise Deployments
Ask for real stories, not generic claims. The right partner should show:
- Past projects involving large hospital networks
- Demonstrated improvements in data accuracy
- Faster claims cycles
- Reduced operational overhead
- Long-term support and maintenance success
If a partner can’t prove they’ve done it before, they shouldn’t do it for you.
7. Ability to Support Custom Development
Every healthcare organization is unique. A strong partner must be able to build custom healthcare master data management software when off-the-shelf tools fall short.
This includes:
- Custom connectors
- Tailored governance workflows
- AI-driven modules
- Analytics dashboards
- Role-based user interfaces
Your MDM shouldn’t force you to change how you operate, it should fit into how you work.
How Appinventiv Enables a Unified Data Strategy
Choosing a partner is about trusting their technical-level experience. With 10+ years in HealthTech and 500+ digital health platforms delivered, Appinventiv brings the engineering capability needed to support serious healthcare data management software development. Our focus is on solving the core data problems that slow down care delivery, claims, and analytics.
While many vendors push a fixed MDM product, our strength lies in building the high-throughput data pipelines, integration layers, and API frameworks that power a unified data ecosystem. We do not stop at developing applications.
We design the scalable infrastructure that keeps them accurate, secure, and always in sync. This comes from years of hands-on work in healthcare custom software development, where every system must be designed to support real clinical workflows and mission-critical operations.
Our expertise is in the foundational work this article describes:
- Complex Integrations: We have a proven track record of unifying disparate data sources—from legacy EHRs (like Epic and Cerner) to LIS, RIS, and modern cloud-based claims platforms.
- Interoperability Standards: Our teams are not just developers; they are HealthTech specialists fluent in HL7, FHIR, and x12/EDI standards, ensuring data flows securely and accurately.
- Data Governance & Security: We build with a “compliance-first” architecture, architecting every solution to meet the rigorous demands of HIPAA, GDPR, and PDPL.
For organizations ready to move from siloed data to a unified strategy, our experts provide the deep data engineering and HealthTech-specific experience required to build a data ecosystem that is secure, scalable, and delivers a single source of truth.
FAQ
Q. What is MDM in healthcare?
A. MDM in healthcare is the practice of creating a single, accurate, and trusted version of core data such as patients, providers, and payers. Instead of storing multiple, conflicting records across EHRs, billing tools, lab systems, or insurance platforms, an MDM system brings everything together into one unified source of truth. This helps hospitals reduce errors, improve coordination, and support safer decision-making across the care journey.
Q. Why is health data management increasingly important?
A. Healthcare data is growing at a pace most organizations can’t keep up with. Every appointment, test result, wearable device, or insurance interaction adds more information to the system. Without proper health data management, this data becomes scattered and unreliable. Strong management ensures accuracy, minimizes duplicate records, speeds up claims, strengthens compliance, and gives clinicians dependable information when they need it the most.
Q. What role does metadata management play in healthcare MDM, and how can it be effectively implemented?
A. Metadata management ensures every data element in the healthcare ecosystem has clear meaning, ownership, and context. For example, two departments may record “admission date” differently unless there’s a shared definition. By standardizing terms and tracking how each field is used, metadata management prevents inconsistencies that create errors in reports, analytics, and clinical decisions.
Effective implementation involves setting definitions, building governance rules, maintaining a centralized metadata catalog, and regularly updating it as new systems are added.
Q. How can a healthcare MDM system support data analytics and reporting for healthcare organizations?
A. Analytics only works when the data feeding it is clean and consistent. A healthcare MDM system improves reporting by merging duplicates, correcting mismatches, and standardizing patient and provider information. Once the organization has one reliable record per patient and provider, analytics teams can build accurate dashboards, uncover performance trends, predict risks, and support operational planning. Unified data also strengthens AI models and population health insights because the inputs are no longer fragmented.
Q. What is the role of data standards like HL7 in healthcare MDM?
A. Data standards such as HL7 and FHIR ensure that different systems can share information in a structured, predictable way. In master data management healthcare environments, these standards make it possible for EHRs, claims platforms, labs, pharmacies, and digital apps to exchange data without losing accuracy. They also make healthcare master data management software implementation smoother by reducing custom integration work.
When organizations invest in healthcare data management software development, using HL7 ensures interoperability stays strong as new systems and partners are added over time.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Change Management in Healthcare: Principles, Processes, and Models
Key Takeaways Change in healthcare fails quietly when ownership, workflow alignment, and follow-through are missing. Successful change management in healthcare focuses on adoption, not just system implementation. Clinical workflows and workforce capacity determine whether transformation sticks or stalls. Governance, clear accountability, and post-go-live support matter more than the model used. Sustainable healthcare transformation depends on…

A Practical Guide to Building Your Mental Health Chatbot - Use Cases, Cost, & ROI
Key takeaways: Mental health chatbots work when they know their limits. They’re most useful as a gentle first step, not as a stand-in for real care. Good chatbot design is more about judgment than AI. Clear boundaries, calm responses, and safety matter more than smart language models. Enterprises invest in chatbots to make support easier…

How To Hire the Right Healthcare Developers As Per Your Business Needs?
Key Takeaways The guide to the step-by-step approach to recruiting the right healthcare software developers to meet your business requirements. In-depth dissection of the major technical skills, certifications and healthcare-specific expertise required in developers. Guidelines for carrying out the evaluation of candidates using portfolios, technical interviews, and trial projects. Industry-specific ERM approaches help address regulatory,…