- Market Growth and Global Trends Shaping Hyperlocal Delivery
- Types of Hyperlocal Delivery Platforms
- Benefits of Hyperlocal Delivery App Development for Businesses
- 1. Faster Delivery and Customer Convenience
- 2. Better Inventory Planning
- 3. Real-time Order Tracking
- 4. Higher Customer Retention
- 5. Competitive Advantage in Urban Markets
- 6. Increased Revenue Through Local Reach
- 7. Stronger Vendor Partnerships
- 8. Scalable Logistics Backbone
- Core Features To Have In Your Hyperlocal Delivery App
- Customer App Features
- Delivery Agent App Features
- Store or Merchant App Features
- Admin Panel Features
- Advanced Features That Improve the Experience
- White Label or Custom Build: Which One Fits Your Hyperlocal Strategy?
- White Label Hyperlocal Platforms
- Custom Built Hyperlocal Platforms
- Step-by-Step Hyperlocal Delivery App Development Process
- Step 1: Product Discovery and Market Analysis
- Step 2: Technical Architecture Planning
- Step 3: UX and UI Design
- Step 4: Backend, Frontend, and API Development
- Step 5: Integration with Third Party Tools
- Step 6: Real-Time Tracking and Mapping Setup
- Step 7: Quality Assurance and Performance Testing
- Step 8: Pilot Launch in Limited Zones
- Step 9: Rollout, Iterations, and Continuous Optimization
- Technology Stack for Hyperlocal Delivery App Development
- Cost of Hyperlocal Delivery App Development
- Cost Breakdown by Complexity
- Cost Breakdown by Region
- Long Term Ownership and Maintenance Cost
- Cost Add ons for Advanced Features
- Challenges and Solutions in Hyperlocal Delivery App Development
- Real-Time Tracking Accuracy
- Inventory Syncing Issues
- Last-Mile Cost Optimization
- Managing Multi Vendor Workflows
- Route Planning for Peak Hours
- Ensuring Compliance With Data Laws
- Compliance and Data Security Requirements
- Future of Hyperlocal Delivery App Development
- How Appinventiv Helps You Build a High Performance Hyperlocal Delivery App
- FAQs
- Hyperlocal delivery is really about keeping things close. Customers order from nearby stores and get their items in a short window without the usual wait.
- The cost to build one of these apps can vary a lot, but most projects fall somewhere between $40K to $400K.
- What makes the whole model work is simple. Clean tracking, good routing, and stock that updates when it should.
- AI now plays a quiet but important role, helping predict demand and match the right delivery partner at the right moment.
- The future looks even faster, with early experiments in automation, smarter logistics, and tech that moves decisions closer to where the order happens.
Urban shoppers now expect things to arrive quickly, not as a premium service but as the new normal. In most big cities, people want groceries, medicines, and everyday essentials delivered within an hour, and they want the experience to feel smooth every time. This shift has quietly changed how businesses think about inventory, local partners, and the way their delivery networks operate.
The momentum behind this change is clear in the numbers. Fortune Business Insights estimates the global hyperlocal services market at USD 4,025.05 billion in 2025, projected to reach USD 9,974.09 billion by 2032. A major part of this rise is coming from the hyperlocal grocery delivery market, which continues to grow rapidly across the United States.
Hyperlocal delivery app development brings all the moving parts together. It links customers, nearby stores, and last mile delivery partners inside small service zones where speed and accuracy matter. These platforms manage the entire journey from ordering and inventory visibility to assignment, routing, and real time tracking. In this blog, we look at the benefits, the development process, the core features, the cost breakdown, and the trends shaping hyperlocal delivery for global and US businesses.
Market Growth and Global Trends Shaping Hyperlocal Delivery
The rise of on-demand hyperlocal delivery continues as customers expect shorter and predictable fulfilment windows. The tables below highlight the major trends shaping the market of quick commerce apps.
| Key Trends in Hyperlocal Delivery | |
|---|---|
| Trend | What It Means |
| One hour and ten minute deliveries | Faster fulfillment driven by dense urban networks and optimized routing. |
| Dark stores and micro warehousing | Small, local storage hubs that reduce delivery time. |
| AI-based demand forecasting | Predicts order spikes and helps manage inventory. |
| Route optimization | Improves delivery speed and reduces last-mile cost. |
| Ultra fast logistics integrations | Connects payment, tracking, and warehouse systems seamlessly. |
| Autonomous systems | Early use of drones, bots, and automated sorting. |
| Customer experience personalization | Tailored recommendations and real-time updates. |
Types of Hyperlocal Delivery Platforms
Hyperlocal delivery platforms follow a few core models, each built around how a business manages orders and last-mile fulfilment. Below is a simple overview of hyperlocal grocery delivery app development.
- Marketplace Led Platforms: These platforms connect many nearby stores in one app and handle ordering, routing, and delivery assignments. Popular examples of hyperlocal on-demand delivery apps follow this model because it offers variety and fast discovery.
- Store Led Delivery Platforms: A single brand manages its own stock, pricing, and fulfillment within defined zones. This model is common in hyperlocal grocery delivery app development, where real-time inventory and predictable delivery windows matter.
- Dark Store and Micro Fulfillment Platforms: These rely on small storage hubs placed inside busy neighbourhoods. They help brands deliver groceries, essentials, and everyday goods faster by shortening travel distance.
- Hyperlocal Food Delivery Platforms: Built for restaurants and cloud kitchens, these platforms coordinate preparation time, batching, and quick routing. They suit fast food chains and high-volume local operators.
- Courier and Parcel Delivery Platforms: This model handles short distance parcel movement. Users schedule pickups, and delivery partners transport items directly to the destination.
Benefits of Hyperlocal Delivery App Development for Businesses
Different types of hyperlocal delivery platforms support unique business needs across food, grocery, and everyday essentials.
These platforms combine demand forecasting, local inventory placement, and real-time routing to support faster fulfillment. For enterprises, this model improves customer experience while strengthening last-mile operations across dense service zones.
1. Faster Delivery and Customer Convenience
One of the biggest benefits of hyperlocal food delivery app adoption is predictable delivery time for customers. Shorter distances and automated store selection allow businesses to complete orders quickly. When combined with optimized routing and live location visibility, delivery times stay consistent even during peak hours.
Key advantages:
- Nearest store or micro hub automatically selected
- Shorter fulfillment windows across urban areas
- Map based tracking improves customer satisfaction
2. Better Inventory Planning
Hyperlocal systems collect data at the neighborhood level, and for enterprises exploring hyperlocal grocery delivery app development, this insight helps reduce stockouts and cancelled orders.
Key advantages:
- Demand forecasting based on real buying patterns
- Fewer stockouts due to better planning
- Integration with POS or warehouse systems for live updates
3. Real-time Order Tracking
Customers, merchants, and delivery partners all see transparent status updates. This reduces support queries and keeps operations predictable.
Key advantages:
- Live GPS movement of delivery partners
- Step-by-step status notifications
- Admin view for fleet and route performance
4. Higher Customer Retention
Reliable and fast deliveries encourage repeat orders, especially for customers using a hyperlocal grocery delivery service where speed directly impacts basket size. Apart from that personalized recommendations and loyalty benefits inside the app also help strengthen long term engagement.
Key advantages:
- Better repeat order rate
- App driven promotional programs
- Predictable delivery experience
5. Competitive Advantage in Urban Markets
Hyperlocal models outperform traditional fulfillment in busy city centers. Businesses can respond faster to demand spikes and offer delivery windows that match consumer expectations.
Key advantages:
- Zone based delivery optimization
- Dynamic pricing for peak hours
- Faster response to market fluctuations
6. Increased Revenue Through Local Reach
Serving smaller geographic clusters lowers operational cost and increases order density, one of the key benefits of hyperlocal food delivery app adoption for multi-outlet brands.
Key advantages:
- Higher orders per delivery partner
- Possibility of subscriptions, surge pricing, and add ons
- Strong conversion rates due to quick fulfilment
7. Stronger Vendor Partnerships
Merchants gain clear visibility into orders, settlements, and customer feedback. This strengthens trust and helps expand the seller network.
Key advantages:
- Real-time store level dashboards
- Transparent payouts and order logs
- Better coordination with partner stores
8. Scalable Logistics Backbone
A hyperlocal platform scales through modular components like automated dispatching, zone expansion, and multi store management. Cloud infrastructure keeps performance stable as order volume increases.
Key advantages:
- Easy rollout to new neighborhoods and cities
- Automated load balancing for peak times
- Stable performance through cloud and DevOps support
Core Features To Have In Your Hyperlocal Delivery App
A hyperlocal platform works only when every part of the system communicates well. Customers need a clean way to place an order. While stores need a simple dashboard to prepare it, similarly delivery partners need clear routes, and the admin team needs a full view of what is happening on the ground. Below mentioned features of a hyperlocal delivery app for businesses capture what a practical, day to day setup usually includes.
Customer App Features
The customer app is where the experience begins. It needs to be simple enough for someone rushing through their day and accurate enough to avoid confusion.
Core features:
- Search and location-based browsing: Customers can look up nearby stores or products based on where they are.
- Real-time order tracking: A live map that actually tells them where the delivery partner is.
- Payment gateway integrations: Card, wallet, UPI, or whatever is common in that region.
- Delivery instructions and chat support: A short note for the rider or a quick message when needed.
- Ratings and reviews: Helps keep the quality in check for both stores and delivery partners.
Delivery Agent App Features
Delivery partners rely on an app that removes guesswork. If the flow is smooth, they complete more orders in less time.
Core features:
- Order acceptance: Clear pickup and drop details so they can decide quickly.
- Optimized routes: Navigation that accounts for traffic and saves a few extra minutes.
- Live status updates: Simple taps to update every stage without slowing them down.
- Earnings dashboard: A place to check what they made that day or week.
- In-app calling and messaging: For quick coordination with stores and customers.
Store or Merchant App Features
Stores often juggle walk-ins and online orders at the same time. Their app needs to fit into that workflow without creating extra steps.
Core features:
- Inventory updates: Keep stock levels current, especially for fast-moving items.
- Product listing management: Change titles, photos, or descriptions whenever required.
- Order alerts: Immediate notifications so nothing sits unprepared.
- Price updates: Useful during promotions or sudden stock changes.
- Promotions and coupons: Simple tools to push offers to nearby customers.
Admin Panel Features
The admin panel is the operations center. A well-structured hyperlocal delivery management system gives teams full visibility into demand, capacity, and zone performance.
Core features:
- Fleet management: Know exactly how many delivery partners are active and how busy they are.
- Zone management: Set up service areas and adjust them as the business expands.
- Delivery radius configuration: Control how far each store can deliver.
- Analytics: Trends, order volume, delays, peak hours, and everything that needs attention.
- Multi store controls: One place to manage several store partners.
- Payment settlements: Automated payouts with a clear record for each store and agent.
Advanced Features That Improve the Experience
These features help the platform feel more responsive and intelligent as volume grows.
Advanced features:
- AI-based ETAs: Smarter delivery time predictions that factor in patterns and traffic.
- Dynamic delivery pricing: Adjusts fees when demand spikes or distances vary.
- Gamification for agents: Small incentives that improve speed and reliability.
- Automated refund workflows: Faster handling when an order goes wrong.
- Smart stock prediction: Helps stores prepare for high-demand items.
- Loyalty program integration: Points and rewards that keep customers coming back.
Together, these capabilities shape the core features of hyperlocal delivery apps for businesses that want predictable fulfilment and better operational control.
White Label or Custom Build: Which One Fits Your Hyperlocal Strategy?
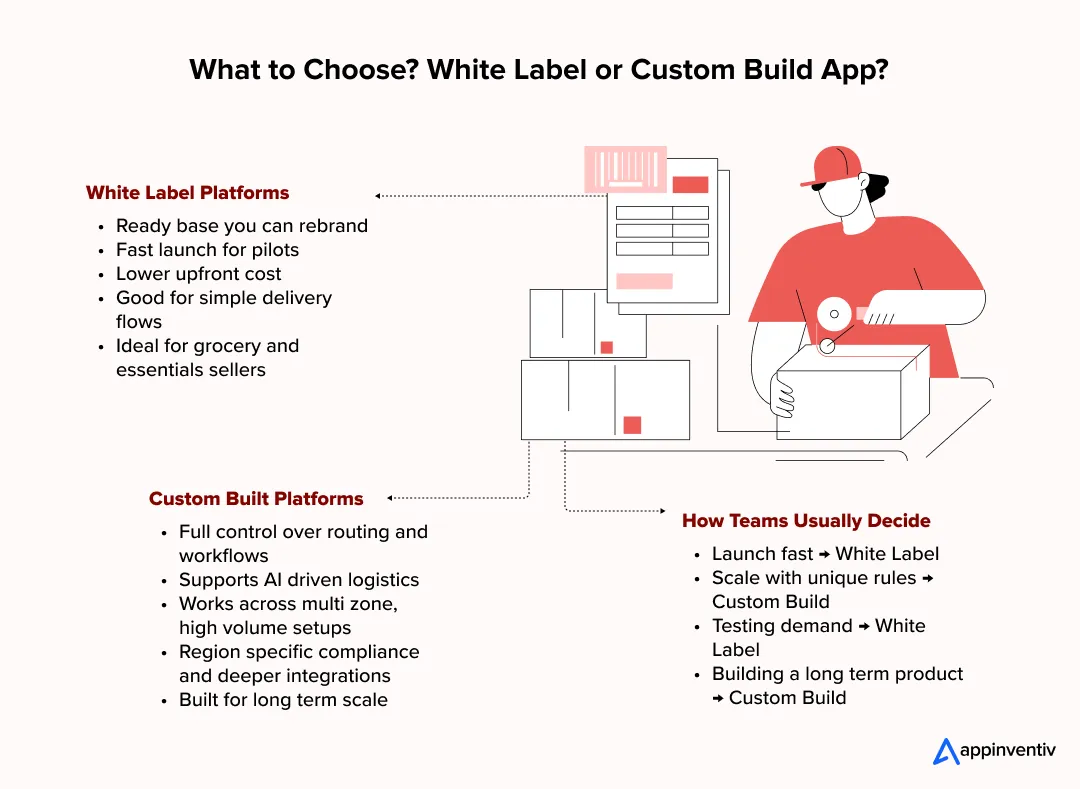
Teams entering the hyperlocal space usually choose between a white label platform and a custom build. Both options work. The decision mostly comes down to how fast you want to launch and how much control you need over the experience.
White Label Hyperlocal Platforms
A white label setup gives you a ready base to work with. You change the branding, configure the features, and go live without waiting months for development. It is a practical choice for pilots, early market testing, and grocery or essentials sellers who want to understand demand before committing to a bigger build.
It keeps things simple. You get predictable timelines, lower initial cost, and a structure that works well for straightforward delivery flows.
Custom Built Hyperlocal Platforms
A custom build lets you shape everything from the route logic to merchant workflows. This path suits businesses that operate in multiple zones, handle high order volumes, or want deeper personalization across customer, merchant, and agent journeys.
It takes more time, but the payoff is control. You can add AI in logistics to optimize dispatching, micro warehousing logic, region specific compliance, and integrations that match your actual operations.
How do teams usually decide which to choose?
If the goal is to validate the market quickly, a white label platform is often enough. If the plan is to operate at scale with unique delivery rules and long term growth in mind, a custom build becomes the smarter investment.
Step-by-Step Hyperlocal Delivery App Development Process
Building a hyperlocal delivery app involves more than creating a customer interface. It requires aligning business operations, logistics workflows, and a scalable technical foundation that can handle real-time movement across multiple zones. The steps to build a hyperlocal delivery app mentioned below outline how teams usually move from initial planning to a live, functioning, and optimized hyperlocal ecosystem.
A structured development approach helps reduce risks, especially for businesses aiming to scale on-demand hyperlocal delivery models across multiple neighborhoods. Each phase contributes to product stability and prepares the platform for continuous updates once orders start flowing in.
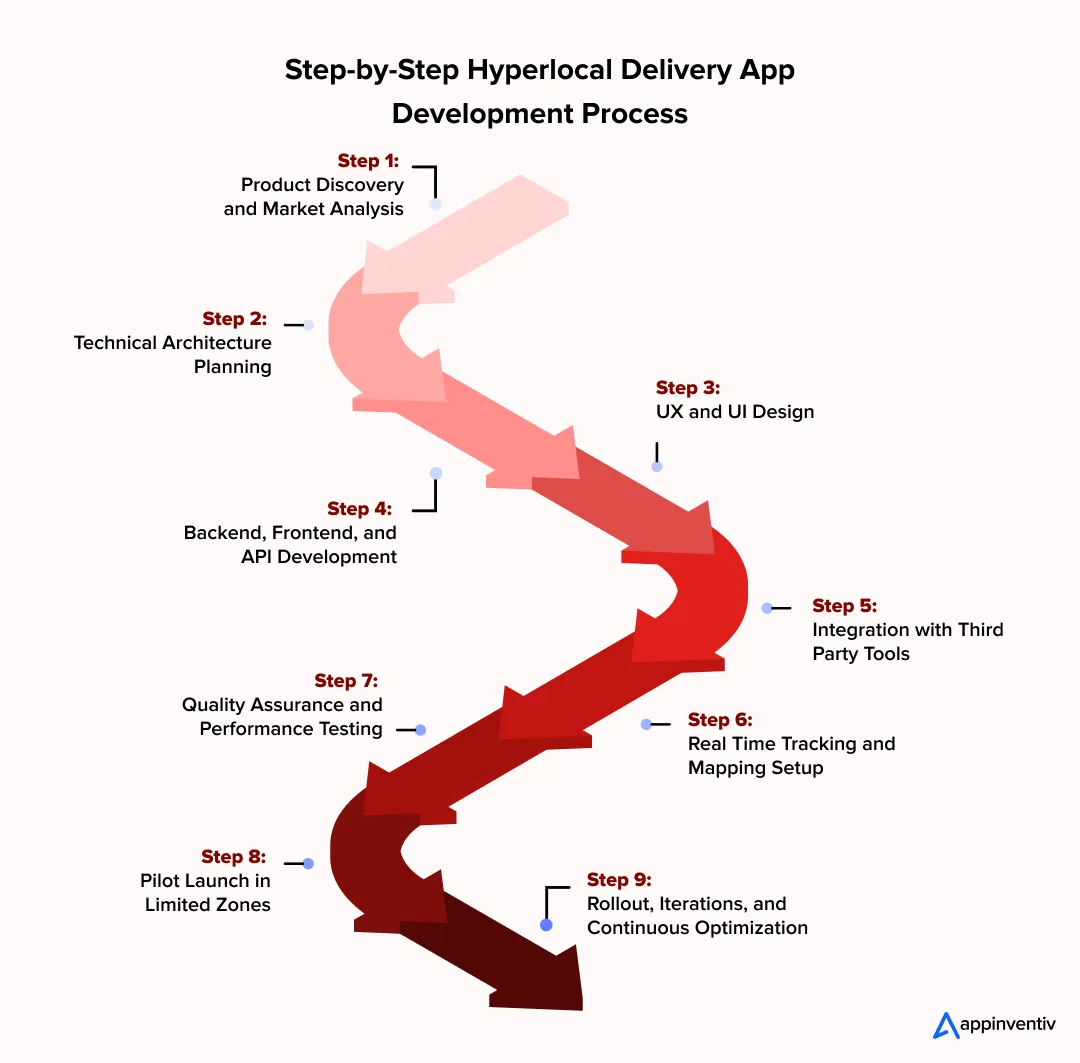
Step 1: Product Discovery and Market Analysis
The discovery phase helps teams understand demand patterns, competition, and operational constraints within selected zones. This includes identifying the service categories, customer personas, and the type of stores best suited for a hyperlocal model. Workshops convert these insights into clear functional requirements.
The team also defines delivery windows, pricing strategy, revenue models, and expansion pathways. By the end of this stage, stakeholders have a validated roadmap with priorities, KPIs, and user journeys that reflect actual business needs.
Step 2: Technical Architecture Planning
This is the stage where the structure of the entire platform starts taking shape. Architects look at how the mobile apps, backend services, API development, and databases will talk to each other. They decide things like how the data should move, where caching helps, how users will be authenticated, and which cloud setup makes sense for long term growth. The idea is simple. The system should stay steady even when activity peaks without warning.
They also map out scaling needs, recovery plans, security, and compliance rules. Once these pieces fit together, the platform can support large order volumes, new cities, and future upgrades without forcing big redesigns later.
Step 3: UX and UI Design
Design work begins with understanding how each user will move through the platform. Customers, store teams, delivery partners, and admins all have different jobs to complete, so their flows are drawn out separately. Wireframes show how each action will look and feel. The goal is to keep every step easy and reduce the small irritations that slow people down.
After the flows feel right, UI elements are created with a consistent style across all apps. Early prototypes help in spotting friction points quickly when tested with internal teams or a small set of merchants or riders.
Step 4: Backend, Frontend, and API Development
This is where the platform starts coming to life. Backend teams build the engines that power authentication, ordering, tracking, inventory, notifications, and data insights. In parallel, mobile and web teams create the screens and actions users interact with.
APIs connect all these layers so every update shows up everywhere in real-time. If a store accepts an order or a rider updates their task, the system reflects it instantly across all apps without any lag.
Step 5: Integration with Third Party Tools
A hyperlocal platform cannot function well without external tools. Integrating secure payment gateways, SMS alerts, OTP checks, email updates, maps, and navigation are all stitched into the workflow. These integrations complete the order journey from start to finish.
Larger businesses may also plug in POS systems, inventory platforms, or accounting tools. Teams usually rely on modular patterns so any tool can be replaced or upgraded later without breaking the system.
Step 6: Real-Time Tracking and Mapping Setup
Real-time tracking is one of the strongest pillars of a hyperlocal app. Engineers set up GPS updates, background location services, and map rendering across every interface. The logic handles traffic issues, route changes, and patchy network conditions so users always see accurate movement.
This step also introduces dispatch logic that assigns tasks to the right delivery partner based on distance, availability, and workload. Admin panels show active agents, pending tasks, and route performance in real-time.
Step 7: Quality Assurance and Performance Testing
QA teams test everything from ordering flows to payments, cancellations, and refunds. They also run edge cases like unstable networks or sudden location dropouts.
Performance tests simulate real-world pressure, especially in high-density areas. This helps confirm the platform will stay responsive even when orders spike or when many stores update their activity at the same time.
Step 8: Pilot Launch in Limited Zones
A controlled pilot is rolled out in a few neighborhoods or cities to observe real-user behavior. Store partners, delivery agents, and customers interact with the platform while operations teams track issues that testing may not reveal.
Feedback from this phase helps refine ETAs, routing, store workflows, and app usability. The goal is to capture real challenges early and validate that the system performs well under operational pressure.
Step 9: Rollout, Iterations, and Continuous Optimization
After a stable pilot, the platform expands to additional zones and cities in phases. Teams monitor data to fine tune routing accuracy, delivery partner incentives, and store onboarding processes.
Continuous improvements are added through regular releases, completing the core steps to build a hyperlocal delivery app that can scale across diverse service zones. Later, new features like AI-based forecasting, loyalty modules, or new payment methods are introduced based on business goals and customer feedback.
Technology Stack for Hyperlocal Delivery App Development
Selecting the right tech stack for hyperlocal app development determines how well the platform handles growth.
As a hyperlocal delivery platform relies on well engineered hyperlocal delivery software to support real-time tracking and routing. So, the stack usually combines mobile frameworks, backend services, databases, cloud infrastructure, and third party tools for maps, payments, and communication.
| Layer | Technologies |
|---|---|
| Mobile apps (Customer and Delivery Partner) | Swift, Kotlin, React Native, Flutter |
| Merchant and Admin Interfaces | React, Angular, Vue.js, Next.js |
| Backend Services | Node.js, Java, Kotlin, Python, Go |
| APIs and Integration Layer | REST APIs, GraphQL, API Gateway (Kong, AWS API Gateway, Apigee) |
| Databases | PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, Redis |
| Real-time Communication | WebSockets, MQTT, Socket.io |
| Maps and Location Services | Google Maps Platform, Mapbox, OpenStreetMap with routing libraries |
| Payment Processing | Stripe, Braintree, Adyen, Razorpay (for India), regional gateways |
| Notifications and Communication | Firebase Cloud Messaging, Apple Push Notification service, Twilio, SendGrid |
| Cloud Infrastructure | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform |
| DevOps and Deployment | Docker, Kubernetes, CI CD tools (Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI) |
| Analytics and Monitoring | Google Analytics, Mixpanel, Datadog, Prometheus, Grafana |
| Security and Compliance | OAuth 2.0, JWT, TLS, WAF, IAM |
Selecting the right tech stack for hyperlocal app development ensures that user analytics, routing performance, and real-time tracking remain consistent as the platform expands.
Cost of Hyperlocal Delivery App Development
The cost to develop a hyperlocal delivery app depends heavily on how many roles the platform needs to support and how real-time the operations are. Most enterprise builds fall somewhere in the $40,000 to $400,000 range, covering everything from the customer and delivery partner apps to merchant dashboards, admin controls, and the backend required to keep fulfillment running smoothly.
Beyond development, teams should factor in long term costs like API usage, cloud hosting, map services, and analytics. These ongoing pieces often shape the real ownership cost more than people expect, which is why budgets usually shift based on complexity and geography.
Cost Breakdown by Complexity
Different product scopes lead to different investment levels. A simple single category delivery app costs significantly less than a multi city platform with automated routing, advanced AI analytics, and microservices. The table below outlines how cost aligns with capability.
| Build Type | What It Includes | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Hyperlocal App | Single category, basic ordering, simple tracking | 40,000 to 80,000 |
| Mid Level App | Multi store, real-time tracking, payments, merchant tools | 80,000 to 200,000 |
| Advanced Platform | Multi category, complex routing, microservices, analytics | 200,000 to 400,000+ |
A basic build works well for early pilots or local operations. Mid-level platforms suit businesses planning multi store operations. Advanced builds are designed for scale and require stronger architecture planning, which increases cost.
Cost Breakdown by Region
Development cost also varies based on geography. Teams in the United States and Europe often fall on the higher end of the range. India and Southeast Asia provide cost effective development without compromising on capability. The table below shows a high-level comparison.
| Region | Typical Development Cost |
|---|---|
| United States | Highest cost range due to engineering and design standards |
| Europe | Comparable to US for enterprise driven builds |
| UAE and Middle East | Mid to high range depending on integrations and compliance |
| India | Cost effective development with enterprise capabilities |
| United Kingdom | Mid to high range similar to Western Europe |
| Australia | Moderate to high depending on complexity |
Costs shift depending on team size, experience, and whether the platform requires region specific compliance. Once the scope for each zone is defined, the development budget becomes more predictable.
Long Term Ownership and Maintenance Cost
Building the app is only the first part of the investment. Enterprises also budget for ongoing support, new feature releases, cloud hosting, map APIs, building effective DevOps pipelines, and partner onboarding.
Typical annual costs include:
- Cloud hosting and DevOps
- Map and routing APIs
- Security updates
- Performance optimization
- Feature enhancements
- Support for peak seasons or new zones
Average annual operational cost ranges from 15 to 25 percent of total development spend.
Cost Add ons for Advanced Features
Some capabilities significantly increase development time and infrastructure needs.
Additional cost drivers:
- AI-based demand forecasting
- Predictive ETAs
- Multi warehouse inventory sync
- Multi tenant merchant ecosystem
- Advanced analytics and reporting
- Communication workflows with automation
- Real-time fraud and risk detection
These add ons typically push the budget higher, which influences the overall cost to develop a hyperlocal delivery app for enterprises planning multi-city expansion.
Challenges and Solutions in Hyperlocal Delivery App Development
Running a hyperlocal delivery management system involves real-time decision making across stores, delivery partners, and customers. As order volume grows, even small operational gaps can affect fulfillment speed, cost, and customer satisfaction. The challenges below are common across most hyperlocal models, along with the solutions enterprises typically use to manage them.
Real-Time Tracking Accuracy
Accurate tracking depends on reliable GPS updates, stable device signals, and optimized location services. Fluctuations in network strength or device settings often lead to delays or inconsistencies.
Solution: Teams improve accuracy through background location services, frequent but optimized GPS pings, fallback mechanisms, and map matching algorithms. A strong dispatch engine helps correct small location errors and maintain consistent ETAs.
Inventory Syncing Issues
Fast-moving items sell out quickly, and many stores still rely on manual updates. When inventory is not synced in real-time, orders get cancelled, which affects both customers and store partners.
Solution: Integrating POS systems or lightweight inventory APIs keeps stock levels current. Automated alerts, batch syncing, and buffer quantities help reduce mismatches, especially during rush hours.
Last-Mile Cost Optimization
Last-mile delivery is the most expensive part of the fulfillment chain. Inefficient routing, low order density, or long-distance runs drive up cost per delivery.
Solution: Dynamic batching, optimized zoning, and AI-based route planning reduce unnecessary mileage. Incentive models for delivery partners and integration with micro warehouses also improve cost efficiency.
Managing Multi Vendor Workflows
When multiple vendors operate in the same zone, each with different preparation times and stock conditions, coordinating fulfillment becomes complex.
Solution: A unified merchant dashboard allows stores to manage orders, pricing, and preparation times more consistently. Automated order routing and real-time communication tools help align store operations with delivery timelines.
Route Planning for Peak Hours
Traffic, weather, and demand spikes can slow down deliveries and disrupt planned ETAs. Without proper routing logic, delays compound quickly.
Solution: Peak hour routing models use traffic data, historical delivery patterns, and agent availability to suggest faster paths. Load balancing across delivery partners and temporary zone adjustments help keep the flow stable during high-demand periods.
Ensuring Compliance With Data Laws
Hyperlocal platforms handle user data, location data, and payment details. Regulations vary by region and require strict control of how information is stored and processed.
Solution: Teams follow frameworks like CCPA for the United States, GDPR for Europe, and PDPL for the Middle East. Encryption, secure API gateways, consent workflows, and access controls ensure the platform remains compliant across markets.
Compliance and Data Security Requirements
A hyperlocal delivery platform handles a steady flow of personal information throughout the day. Every order carries customer details, live GPS movement, store data, and payment information. As the platform expands into new regions, the responsibility around privacy grows with it. This makes compliance and security part of daily operations rather than a technical checklist.
- CCPA for US customers:
Serving customers in the United States means following CCPA rules. Users should know what data is collected and why, and they should be able to access or remove their information without complications. It also pushes businesses to be more careful with how personal data is stored and shared across internal systems. - GDPR for Europe:
GDPR is stricter. Data must have a clear purpose, be stored only when necessary, and stay protected through encryption and controlled access. Hyperlocal platforms running in Europe must also support user rights, including requests to correct or limit how their data is used. - UAE PDPL for Middle East companies:
For companies operating in the Middle East, UAE PDPL puts strong emphasis on consent, secure processing, and keeping data within approved environments. This becomes even more important when the platform relies on live location updates and real time tracking. - PCI DSS for payments:
Any app accepting or processing card payments must meet PCI DSS guidelines. This includes using secure gateways, encrypting transactions, and running regular audits to ensure sensitive information never leaks into the wrong place. - Secure authentication and encrypted communication:
Access control forms the first line of defense. OAuth, JWT tokens, and multi factor checks help keep user accounts protected. Encryption and secure API paths ensure data stays safe as it moves between apps, dashboards, and backend services.
Future of Hyperlocal Delivery App Development
Hyperlocal delivery is moving into a phase where speed alone will not define the experience. The focus is shifting toward smarter systems that can make decisions on their own, reduce wasted effort, and support fulfillment even during unpredictable conditions. The ideas below reflect where the industry is heading over the next few years.
- AI Driven Logistics: AI is starting to handle tasks that teams once managed manually, and this shift will define the future of hyperlocal food delivery app automation in dense urban zones. It learns how certain neighborhoods behave, predicts when orders will spike, and assigns delivery partners with better accuracy. The goal is to keep the system running smoothly without constant intervention.
- Predictive Delivery Models: Predictive analytics tools look a little further ahead, which is becoming important as the hyperlocal grocery delivery market grows across major US and global regions. By studying past data, traffic patterns, and seasonal changes so the platform can prepare before demand rises. This helps stores keep the right items in stock and reduces last-minute rushes.
- Autonomous Delivery Systems: Autonomous food delivery robots are slowly making their way into short distance deliveries. They are not mainstream yet, but early pilots show promise for late night runs and repetitive routes that do not always need a human rider.
- Drone Delivery Experiments: AI in drones is shaping the future of hyperlocal food delivery app capabilities across select regions. They can skip traffic completely and move lightweight items across short distances much faster. For certain zones, this could become a practical alternative.
- Multi Cloud and Edge Computing Influence: More platforms are shifting to multi cloud setups to avoid downtime and handle sudden spikes in orders. Edge computing is also becoming important because it brings processing closer to the end user, which improves tracking accuracy and reduces delays in map updates.
How Appinventiv Helps You Build a High Performance Hyperlocal Delivery App
Appinventiv approaches hyperlocal delivery app development the same way we handle any large scale digital product. It starts with discovery, where teams map the service zones, workflows, merchant requirements, and delivery patterns needed for a reliable hyperlocal model. From there, architects outline the technical foundation across mobile apps, backend services, APIs, and cloud infrastructure, ensuring the system can handle real-time movement at scale. Design teams shape the customer, merchant, agent, and admin experiences so each group has a clear, intuitive path through the platform.
Once the blueprint is set, engineering teams move into development with a focus on performance and stability. This includes real-time tracking, optimized dispatch logic, secure payments, and merchant workflows that match day-to-day operations. For brands seeking deeper capabilities, such as loyalty programs or advanced routing, Appinventiv integrates custom modules or supports add ons common in projects handled by a food delivery application development company. The goal is to deliver a system that feels fast, reduces operational friction, and is ready for expansion across new neighborhoods or cities.
Appinventiv has worked with some of the largest food and delivery brands, building platforms that handle high order volumes with predictable performance. Our work on the KFC food delivery app and the Pizza Hut food delivery app shows how strong engineering, clear workflows, and reliable real-time features come together in enterprise grade delivery ecosystems. These projects demonstrate what businesses can achieve when the right strategy and technology are aligned.
If you want to explore how enterprise grade hyperlocal delivery software can support your growth across new cities, we can help you plan the next steps.
FAQs
Q. What is a hyperlocal delivery app and how does it work?
A. A hyperlocal delivery app connects customers, nearby merchants, and delivery partners operating within a limited geographic radius. Users browse products, place an order, and track the delivery in real-time. Merchants receive the order through their dashboard, prepare it, and hand it to a delivery partner assigned by the system.
In hyperlocal delivery app development, the focus is on fast routing, accurate inventory visibility, and smooth coordination across stores and riders. These elements help businesses manage different hyperlocal delivery business models, including marketplace, store led, or dark store driven operations.
Q. How much does it cost to build a hyperlocal delivery app?
A. The cost of building a hyperlocal delivery app typically ranges from $40,000 to $400,000, depending on features, user roles, real-time tracking needs, and backend complexity. Elements like integrations, zone expansion, and micro warehousing support can increase the budget.
When teams plan hyperlocal delivery app development at scale, they also consider cloud hosting, API usage, and automation tools, which play a major role in long term cost.
Q. How do hyperlocal delivery systems support ultra fast deliveries?
A. Hyperlocal systems achieve fast fulfillment by focusing on shorter delivery distances, smart store selection, and optimized routing. Automated dispatch engines assign the nearest rider, while AI predictions help estimate accurate delivery windows.
These capabilities are a core part of modern hyperlocal delivery business models and shape how enterprises approach hyperlocal delivery app development for dense urban regions.
Q. What challenges occur during hyperlocal delivery app development?
A. Common challenges include achieving consistent tracking accuracy, syncing inventory across multiple merchants, managing peak hour routing, and controlling last-mile cost. Compliance with regional data laws also requires careful planning.
A well-structured approach to hyperlocal delivery app development addresses these issues through strong architecture, real-time communication, and modular integrations.
Q. How much time does it take to build a hyperlocal grocery delivery app?
A. It generally requires 4-9 months to develop a hyperlocal grocery delivery application based on the number of applications, real-time functions, integrations, and the complexity of the backend.
The timeline of building these apps may vary depending on the extent of development and the performance needs of the grocery business segment which tends to require robust inventory matching.
Q. How to build a hyperlocal grocery delivery app?
A. The process of developing a hyperlocal grocery delivery application includes discovery, architecture planning, UX design, back and frontend development, integrations, real-time tracking implementation, testing, and gradual rollout.
The approach depends on the hyperlocal delivery business models that you wish to serve including marketplace grocery delivery and store led delivery. The development process of a structured hyperlocal delivery app would guarantee that the platform will be scalable and maintainable at fulfillment times.
Q. What is the role of AI and automation in hyperlocal delivery solutions?
A. AI improves demand forecasting, delivery partner assignment, route planning, and ETA predictions. Automation handles tasks like order grouping, inventory syncing, and promotions.
Together, they help enterprises scale different hyperlocal delivery business models, especially those that rely on micro fulfilment or high order density.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

What’s To Come For Food Tech and F&B Sector After COVID-19
The outbreak of COVID-19 has placed the whole world at a standstill. Epidemiologists, biologists, doctors and other healthcare workers are working tirelessly towards a cure for the coronavirus. However, we cannot predict the exact date and time as to when we will be free from this global pandemic, but what we can do is make…