- Key Types of Healthcare Software Products
- Software Products for Providers & Hospitals
- Software Products for Patients & Communities
- Features of Healthcare Software Product Development
- Must-Have Features: The Foundation Every Product Needs
- Advanced Features: Enhancing Value and Differentiation
- Step-by-Step Breakdown of Custom Healthcare Software Development Process
- 1. Problem Identification & Requirements Gathering
- 2. Market & Technical Research
- 3. Defining End Users & Use Cases
- 4. Planning & Architecture
- 5. Prototyping & Design
- 6. Compliance & Security Planning
- 7. Development & Integration
- 8. Testing
- 9. Deployment & Launch
- 10. Post-launch Support & Maintenance
- 11. Continuous Improvement
- Navigating Healthcare Compliance: More Than a Checklist
- Overcoming the Hurdles: Key Challenges in Building a Healthcare Software Product
- The Challenge of Regulatory Complexity
- The Interoperability Impasse
- The Escalating Threat of Cybersecurity
- The Battle for User Adoption
- The Demand for Scalability and Performance
- Emerging Trends and Technologies in Healthcare Software Product Development
- Artificial Intelligence
- Machine Learning
- Generative AI
- Cloud-Native Platforms
- AR/VR for Training, Guidance, and Rehabilitation
- Big Data & Predictive Analytics
- Cost of Healthcare Software Product Development
- Estimated Cost & Timeline by Complexity Level
- Measuring Success & ROI of Healthcare Software
- KPIs That Matter
- ROI Framework for Healthcare IT Projects
- Balancing Dollars and Care Quality
- Long-term View
- In-house vs. Freelancers vs. Outsourced Development: Which is the Right Choice for Healthcare Product Development
- Guiding Principles: Best Practices for the Success of Healthcare Software Development
- From Concept to Reality: How Appinventiv Builds Healthcare Products that Last
- DiabeticU
- Health-e-People
- Soniphi
- Why Appinventiv is the Right Partner for Healthcare Product Development
- Compliance and Security at the Core
- Architectures Built to Last
- A Proven Record in HealthTech
- Full-Spectrum Healthcare Services
- Recognized by Industry Leaders
- Scale That Drives Innovation
- FAQs
Key Takeaways
- Healthcare software is both a major growth driver and a major risk; security and compliance can’t be optional.
- Features such as data encryption, interoperability, audit trails, configurable workflows, and patient self-service drive adoption and ROI.
- A disciplined, iterative process reduces cost overruns and compliance failures.
- Healthcare software product development costs scale with complexity; MVPs start at nearly $40,000 while enterprise-grade software requires $600,000 investment or more.
- Outsourcing to a specialized healthcare software partner strikes a balance between speed, compliance, cost and expertise.
Healthcare now stands at a crossroads. On one side lies extraordinary promise, such as AI-assisted diagnostics, connected ecosystems, and personalized patient care at scale. On the other lies growing complexities: cybersecurity threats, regulatory scrutiny, and legacy systems struggling to keep pace.
We saw what this looks like in practice in 2024, when Change Healthcare was hit by the largest data breach in US history, exposing the records of nearly 190 million Americans. It became a wake-up call for every healthcare organization. The message was simple: software can be a game-changer, but it also carries immense risk.
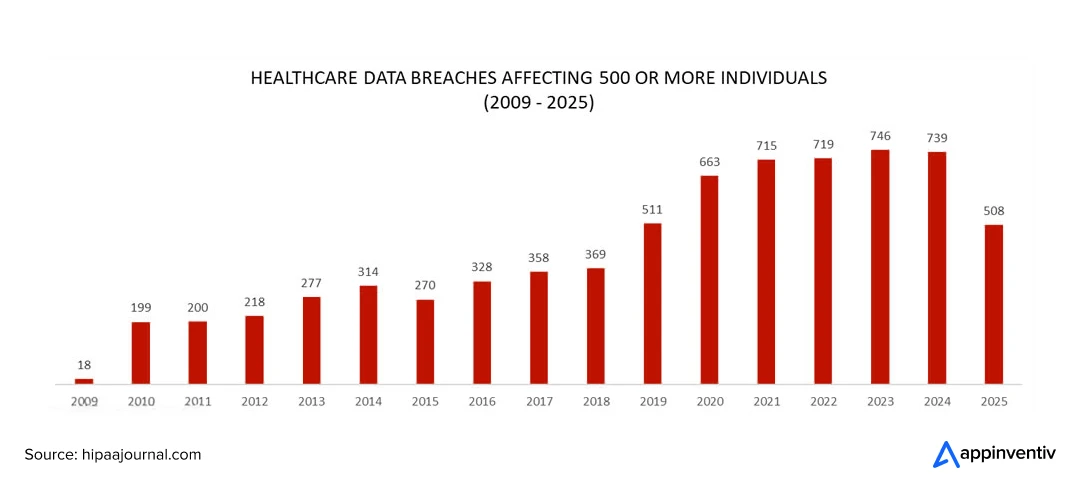
At the same time, investment in healthcare technology has never been higher. From EHR modernization to generative AI pilots, executives are betting big on digital platforms to transform care delivery. Recent McKinsey research reveals that 85% of healthcare leaders are already testing Generative AI to improve efficiency and decision-making.
This dual reality between risk and opportunity is not just reshaping the healthcare software market; it’s redefining how leaders must think about digital transformation. This gives a clear sign that healthcare transformation is underway, and for C-Suite leaders, the adoption of healthcare software product development is no longer optional, but essential. The real question is not if to build, but how to do it securely, strategically, and at scale.
That’s why this guide exists: to help C-suite executives cut through the noise, understand the risks, and chalk out the right path for building healthcare software products that are secure, compliant, and built to last. Whether you’re leading a provider network, health plan, medical device company, or technology firm serving the healthcare industry, this guide is for you.
This guide offers a practical lens for executives, walking through:
- What healthcare product development really entails.
- The main categories of solutions and their business impact.
- Step-by-step development processes that align with compliance.
- Key challenges and how to navigate them.
- Cost and ROI of custom healthcare software product development
- The emerging technologies that define the next generation of digital health platforms.
The intent is not to offer a technical manual, but to equip decision-makers with a strategic framework so that when your organization considers building a healthcare software product, you lead with clarity, compliance, and confidence.
Key Types of Healthcare Software Products
Healthcare runs on a wide mix of digital tools. Each addresses a unique challenge like clinical care, administration, finance, or patient engagement. For executives, knowing the major categories helps in deciding where to invest.
Software Products for Providers & Hospitals
Running a hospital or clinic today means managing a web of systems from patient data and diagnostics to staffing and compliance. The right software can turn that complexity into coordination, helping teams deliver safer, faster, and more efficient care. Here are the main types of software solutions built to support healthcare providers and hospital operations.
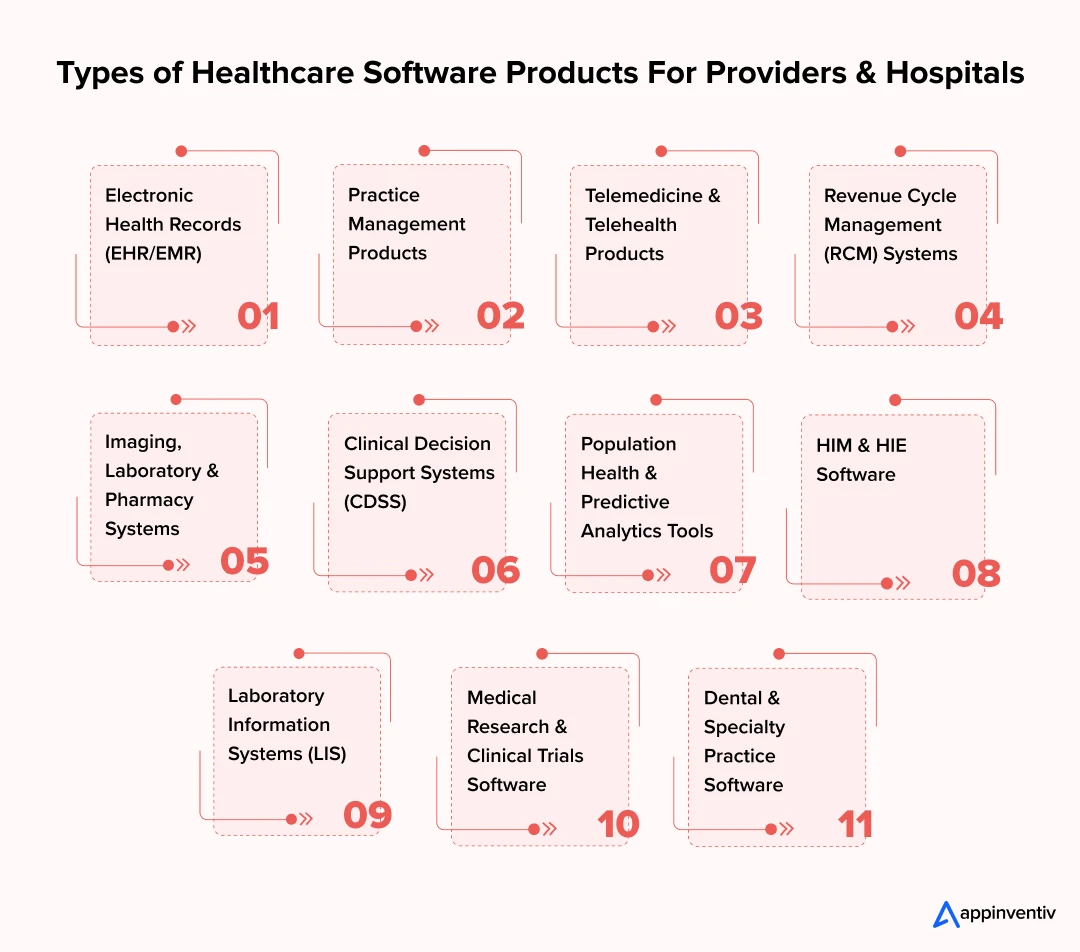
Electronic Health Records (EHR/EMR)
EHRs and EMRs are the backbone of hospital IT. They pull together patient histories, test results, and treatment notes in one record. The payoff shows when data moves cleanly across departments instead of getting stuck in silos; it gives clinicians a full picture of the patient and reduces errors in diagnosis or treatment.
Also Read: EHR Software Development: A Complete Guide for 2025
Practice Management Products
Hospitals run on logistics as much as medicine. Scheduling, billing, and staff allocation take enormous effort. Practice management products handle much of this routine work, cutting admin costs and giving executives a clearer financial picture.
Telemedicine & Telehealth Products
Telehealth is no longer about just video calls. Today’s telehealth trend often includes AI-driven triage, secure prescriptions, and links to remote monitoring devices. For providers, this means more access points without stretching on-site capacity.
Also Read: AI in Telemedicine: Use Cases, Challenges & Future Trends
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) Systems
Cash flow in hospitals depends on clean claims and fast reimbursement. Revenue cycle management (RCM) systems streamline coding, reduce denials, and keep revenue predictable. A poorly designed one usually shows up in mounting delays and shrinking margins.
Imaging, Laboratory & Pharmacy Systems
From PACS in radiology to lab automation and pharmacy software, these systems cut turnaround times. Faster diagnostics almost always translate into earlier and better-informed treatment.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
CDSS tools deliver recommendations, alerts, and predictive insights directly inside the EHR. When implemented well, they help clinicians avoid errors and back decisions with evidence.
Population Health & Predictive Analytics Tools
Large health systems now rely on analytics to forecast patient demand, spot high-risk cohorts, and plan resources. Without these tools, planning is guesswork at scale.
HIM & HIE Software
HIM solutions manage records lifecycle, coding, and compliance, while HIE systems enable secure data exchange between institutions, ensuring continuity of care.
Laboratory Information Systems (LIS)
LIS is the dedicated platform for labs that manages test ordering, processing, and reporting with accuracy and compliance at scale.
Medical Research & Clinical Trials Software
These tools support research workflows, patient recruitment, trial data management, and regulatory submissions. These are the critical functionalities for pharma and academic centers.
Dental & Specialty Practice Software
Specialized solutions tailored to dentistry, ophthalmology, physiotherapy, and other focused care domains improve efficiency and outcomes in niche practices.
| Type of Product | Primary Use Case | Key Users | Estimated Development Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| EHR/EMR Systems | Unified patient records | Clinicians | $200,000 – $400,000 |
| Practice Management Products | Scheduling, billing | Admin Staff | $80,000 – $180,000 |
| Telehealth Platforms | Virtual care & monitoring | Providers, Patients | $120,000 – $300,000 |
| RCM Systems | Claims, reimbursements | Finance Teams | $80,000 – $200,000 |
| Imaging/Lab/Pharmacy Systems | Diagnostics & automation | Specialists | $150,000 – $350,000 |
| CDSS | Clinical decision support | Clinicians | $150,000 – $350,000 |
| Population Health & Analytics Tools | Risk forecasting | Executives | $180,000 – $400,000 |
| HIM & HIE Software | Record lifecycle & exchange | IT, Admin Leaders | $120,000 – $250,000 |
| Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) | Test order, processing, report | Lab Specialists | $100,000 – $250,000 |
| Research & Clinical Trials Software | Trial mgmt & compliance | Researchers, Pharma | $150,000 – $350,000 |
| Dental & Specialty Practice Software | Specialty workflows | Dentists, Specialists | $60,000 – $150,000 |
Software Products for Patients & Communities
For patients, healthcare doesn’t end at the hospital door. Digital tools now help them stay connected, informed, and engaged in their own care. From wellness software to remote monitoring platforms, these systems create a bridge between clinics and communities. Below are the core types of patient-focused software shaping this new connected care era.

Patient Portals & Engagement Platforms
These portals give patients direct access to their health records, appointment scheduling, and secure communication with providers. Transparency builds loyalty over time.
Mobile Health (mHealth) & IoT Products
Wearables and IoT platforms extend monitoring into homes. Using mHealth products, conditions like hypertension or diabetes can be tracked continuously, not just during clinic visits.
Mental Health Platforms
Mental health platforms bring therapy and behavioral tracking online. AI-driven support tools add another layer, helping scale access to mental health services.
Also Read: Mental Health Technology – Trends & Innovations
Senior Care Products
Senior care technology focuses on fall detection, medication reminders, and dashboards for caregivers. Families get real-time updates, while providers reduce emergency events.
Pregnancy & Maternity Products
Maternity solutions support prenatal care, flag risks early, and continue into postnatal monitoring. Many are built to integrate with provider systems for a full care continuum.
Pediatric Health Products
Pediatric tools cover vaccinations, growth tracking, and ongoing consultations. Interfaces are designed for parents, making it easier to manage care consistently.
Personal Health Record (PHR) Platforms
Unlike provider-owned EHRs, PHR platforms let patients collect and manage their own health data across providers, improving portability.
Wellness & Fitness Products
These are the broader lifestyle tools that track fitness, diet, and overall well-being. While consumer-focused, wellness and fitness products are increasingly integrated into care pathways for preventive health.
| Type of Product | Primary Use Case | Key Users | Estimated Development Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Portals | Access & communication | Patients | $80,000 – $180,000 |
| mHealth & IoT Products | Remote monitoring | Care Teams, Patients | $60,000 – $150,000 |
| Mental Health Platforms | Therapy & behavioral support | Patients, Therapists | $80,000 – $200,000 |
| Senior Care Products | Elderly monitoring & caregiver aid | Patients, Families | $100,000 – $250,000 |
| Pregnancy & Maternity Products | Maternal health management | Mothers, Providers | $60,000 – $150,000 |
| Pediatric Health Products | Child health & care | Parents, Doctors | $80,000 – $180,000 |
| Personal Health Record (PHR) Software | Patient-owned health data | Patients | $60,000 – $120,000 |
| Wellness & Fitness Products | Lifestyle & preventive health | Consumers, Patients | $40,000 – $100,000 |
Figures include compliance and integration costs; long-term maintenance is additional.
Features of Healthcare Software Product Development
In healthcare, features are not just functionality; they’re the shields against risk, levers for ROI, and enablers of future growth. For executives, the question is less about what we can build and more about what we must include to stay compliant and competitive.
Must-Have Features: The Foundation Every Product Needs
Before innovation comes reliability; every healthcare software product must first meet the baseline expectations of security, compliance, and usability. Without these fundamentals, even the most advanced platform risks falling short of regulatory or operational standards.
Role-Based Access and Authentication
Not every staff member should see every piece of information. Access must be tiered and secured with multi-factor checks. This reduces breach risks and ensures compliance with privacy laws.
Comprehensive Audit Logging
Every action inside the product should be traceable. Audit logs support internal governance and simplify compliance audits, reducing surprises during regulatory reviews.
User-Centered Interface
In a high-pressure environment, clunky software is abandoned quickly. Interfaces designed with clinicians in mind cut training costs, prevent frustration, and improve adoption rates.
Automated Alerts and Reminders
Critical lab results, medication schedules, or missed appointments require timely prompts. Automated push notifications reduce risks and keep patients engaged in their care plans.
Data Encryption and Secure Storage
Protecting sensitive health records in transit and at rest is no longer optional. Encrypted storage demonstrates that patient data is handled with the same rigor as financial information, which strengthens both compliance and public trust.
Interoperability with EHR and Legacy Systems
Hospitals rarely start fresh. Products must integrate with EHRs, labs, and billing systems via standards like HL7 and FHIR. Without this, a new platform risks becoming a disconnected silo.
Also Read: How to Achieve Interoperability in Healthcare IT
Advanced Features: Enhancing Value and Differentiation
Once the essentials are in place, the next layer is innovation. Advanced features set your product apart in a crowded market and create measurable value for both providers and patients.
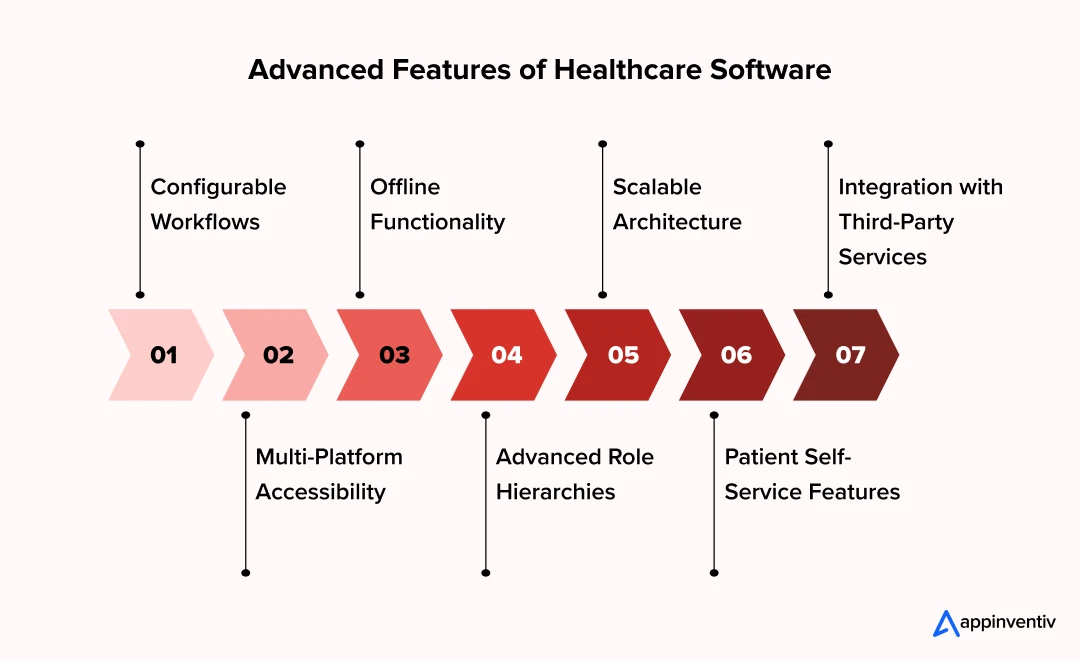
Configurable Workflows
Every provider works differently. Software that allows hospitals or clinics to tailor workflows, without deep technical rework, fits more naturally into existing operations and sees higher adoption.
Multi-Platform Accessibility
Modern care teams and patients expect access across desktops, tablets, and mobile devices. Products that maintain consistency across platforms improve usage and reduce friction.
Offline Functionality
In many care settings, internet connectivity is not guaranteed. Integrating the features of offline accessibility in healthcare products ensures continuity in rural hospitals, mobile clinics, or during emergencies.
Advanced Role Hierarchies
Beyond basic access control, sophisticated role hierarchies allow finer distinctions, for example, separating attending physician privileges from trainee doctors or support staff. This precision reduces errors and strengthens accountability.
Scalable Architecture
A product that supports a single clinic must also be able to scale to an entire health network if needed. Scalability in design protects investments and avoids costly rebuilds later.
Patient Self-Service Features
Features like appointment scheduling, digital intake forms, and billing portals shift routine tasks away from staff and empower patients directly, improving efficiency and satisfaction.
Integration with Third-Party Services
From insurance verification to pharmacy networks, advanced integration points extend product value. Leaders gain flexibility to plug into evolving ecosystems without major rebuilds.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of Custom Healthcare Software Development Process
Building a healthcare software product is rarely a straight line. It’s an iterative journey; shaped by compliance rules, user needs, and constant feedback. For executives, understanding the process provides both visibility and control over how resources are used.
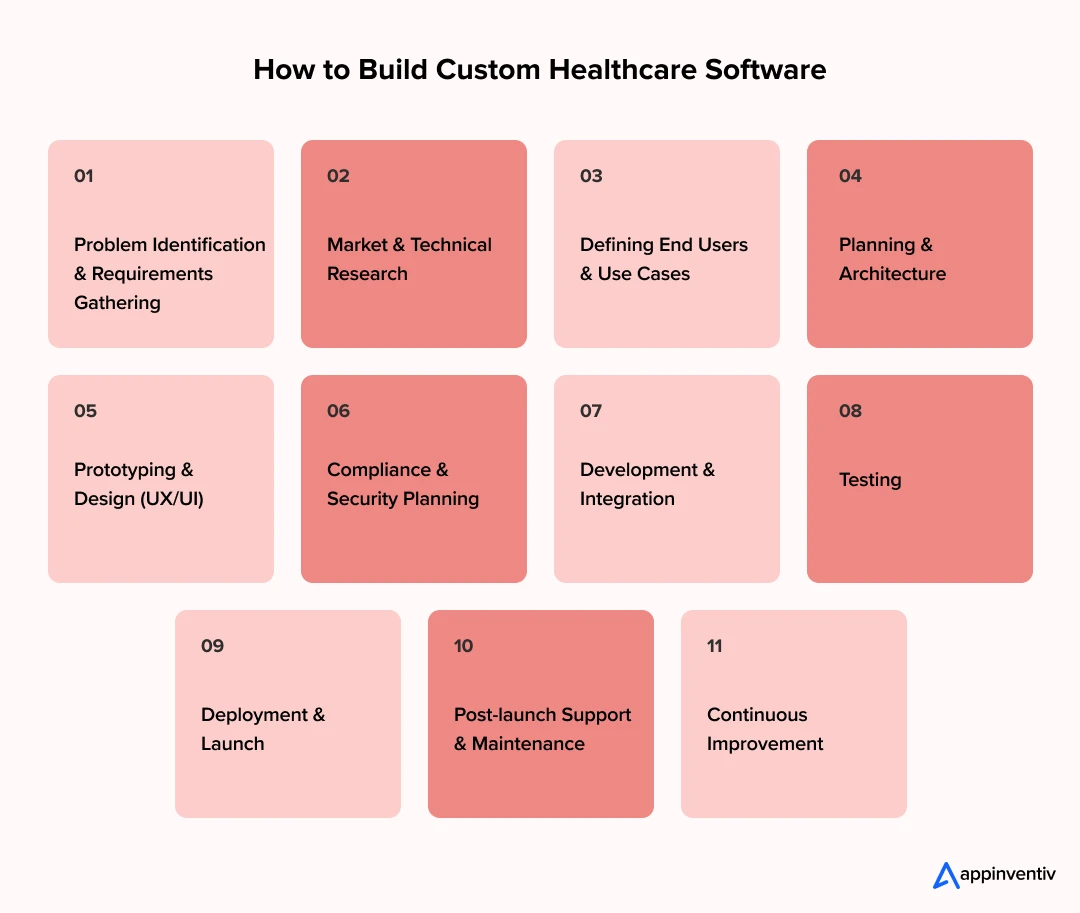
1. Problem Identification & Requirements Gathering
Every strong product begins with a clear problem. Are we trying to reduce paperwork? Improve patient engagement? Streamline claims? The answer shapes everything that follows. It’s also why clinicians, administrators, and IT leaders must be at the table early.
2. Market & Technical Research
Good ideas still need proof. Market research shows where adoption gaps exist and what competitors are moving toward. Technical studies reveal what’s realistic to build. Together, they prevent wasted budgets and make sure the idea aligns with both demand and feasibility.
3. Defining End Users & Use Cases
Healthcare software doesn’t serve one audience. Patients, nurses, doctors, billing staff; all interact differently. Mapping use cases avoids mismatched workflows. A feature that delights patients but slows clinicians down will fail in practice.
4. Planning & Architecture
This stage is the blueprint. Executives need assurance that the healthcare software product architecture is secure, scalable, and interoperable. Weak foundations turn into costly compliance gaps and scaling challenges later.
Healthcare demands agility, with emerging healthcare trends requiring systems that can absorb growth, adapt to new regulations, and integrate technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain.
5. Prototyping & Design
Prototypes and wireframes allow early testing with real users instead of waiting for a finished product. In healthcare, this is critical. Design that feels intuitive reduces clinical errors and speeds adoption among busy practitioners.
6. Compliance & Security Planning
Regulation cannot come after development. HIPAA, GDPR, and regional laws shape how data is stored and shared. Thus, encryption, audit logs, and role-based access must be embedded before coding starts. Patching compliance later is costly and risky.
7. Development & Integration
Once guardrails are in place, development begins. Agile methods support smaller, testable releases. The real hurdle is integration; new tools must connect with existing EHRs, lab systems, or pharmacies. That requires both technical depth and strong vendor coordination.
8. Testing
Testing in healthcare is about more than bugs. Teams validate security, compliance, and performance in real clinical workflows. Failures here don’t just break software; they can harm patients. Key phases of healthcare software testing include:
- Usability Testing: Real users identify workflow bottlenecks.
- Compliance Testing: Independent audits confirm regulatory alignment.
- Performance Testing: Stress scenarios test system capacity.
- Security Testing: Penetration tests and scans close vulnerabilities.
9. Deployment & Launch
Rollout strategies for healthcare software vary. A phased launch minimizes disruption and gathers feedback, while a full launch may be the only option if legacy systems need immediate replacement. Whatever the case, deploy your healthcare software cautiously in the intended environments.
10. Post-launch Support & Maintenance
Go-live is not the finish line. Continuous monitoring, compliance updates, and responsive support build trust with users and protect patient data. Hospitals should evaluate vendors as much by their post-launch support as by the quality of the software itself.
11. Continuous Improvement
Healthcare changes rapidly. Therefore, your software products must evolve through analytics, feedback, and regulatory updates. The strongest solutions adapt with their users instead of being replaced in a few years.
Navigating Healthcare Compliance: More Than a Checklist
Healthcare technology does not run on code alone. It is bound by regulation, and ignoring that fact can cost far more than money. A single gap in compliance may trigger lawsuits, fines, or worse, a collapse of patient confidence. This is why compliance is not a final audit step. It belongs in the earliest design discussions.
HIPAA
In the US, HIPAA sets the ground rules. Encryption, staff access, data transfer; it covers all of it. Miss one safeguard and the financial penalties will hurt. However, the real damage comes when patients stop trusting you.
Also read: HIPAA Compliance Software Testing – A Complete Guide
HITECH
HITECH expanded HIPAA, bringing electronic health records forward and tightening breach reporting. The takeaway is simple: hiding a problem is not an option. Systems must reveal issues quickly and allow leaders to respond openly.
GDPR
Operate in Europe, and the focus shifts again. GDPR compliance is about data rights: consent, erasure, and control over borders. If those elements are not designed into your product, it will not pass scrutiny.
FDA Oversight
Any tool tied to diagnosis or treatment often falls under FDA review. Approval is proof of safety. Skip it; and launches stall, sometimes for years.
Standards and Certification
HL7, FHIR, ISO 13485, SOC 2: these are not acronyms to skim. They are the signals that systems can connect and that an organization takes compliance seriously.
The Ongoing Task
Rules change, threats evolve. Compliance never ends. Regular audits, updates, and discipline keep companies ahead instead of scrambling to catch up.
Overcoming the Hurdles: Key Challenges in Building a Healthcare Software Product
The path to a successful digital health product is lined with unique challenges. Anticipating and planning for them is the difference between a stalled project and a market-leading solution.
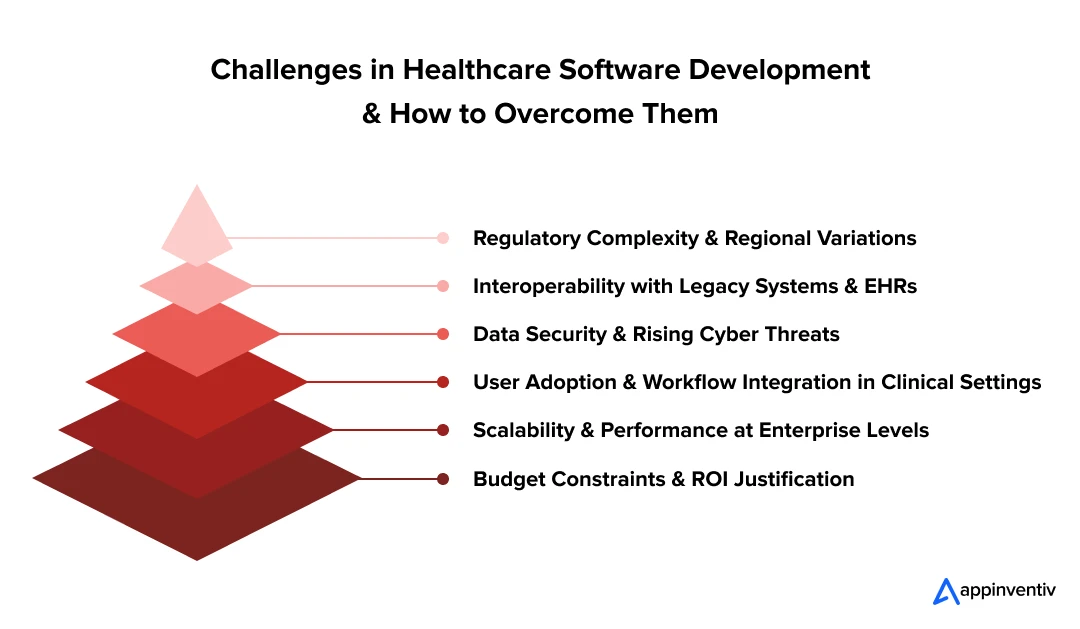
The Challenge of Regulatory Complexity
Challenge: Healthcare regulation is a moving target. What passes HIPAA checks in the US might fail GDPR standards in Europe. A product that looks compliant in one market can stumble badly in another.
How to Address It: Bring regulatory experts in at the beginning, not the end. Map out requirements for every region you plan to operate in. Many teams now lean on cloud providers like AWS or Google Cloud, which offer HIPAA-ready environments, but that doesn’t replace having your own roadmap.
The Interoperability Impasse
Challenge: Hospitals still struggle with data locked inside older EHRs. Too often, new software products become isolated islands because they can’t exchange information with Epic, Cerner, or Allscripts.
How to Address It: Start by designing for interoperability. Use standards like FHIR and modern APIs, but don’t stop there. Budget dedicated resources for integration work. Without it, your system may look good in demos but deliver little value in the field.
The Escalating Threat of Cybersecurity
Challenge: Hackers target healthcare more than any other sector. Patient data sells at a premium, and breaches are devastating. In 2024, the average cost of a healthcare breach reached $10 million, with each record averaging $408.
How to Address It: Security has to be baked in. Multi-factor authentication, end-to-end encryption, real-time monitoring, penetration testing, and even staff training; all of these reduce risk. Skipping one creates an easy entry point.
The Battle for User Adoption
Challenge: Doctors and nurses already feel stretched thin. If new software slows them down, it won’t be used, no matter how innovative it is. That’s the reality.
How to Address It: Involve end-users from the start. Watch how they work, then design around their routines. A tool should feel like a helping hand, not another screen standing in the way.
The Demand for Scalability and Performance
Challenge: A system that handles 50 users in a pilot may crumble when 5,000 log in. Healthcare doesn’t forgive downtime; system failure can delay care.
How to Address It: Build cloud-native software. Microservices and serverless computing give flexibility to scale up or down quickly. And don’t skip load testing. Real stress tests expose bottlenecks long before they put lives at risk.
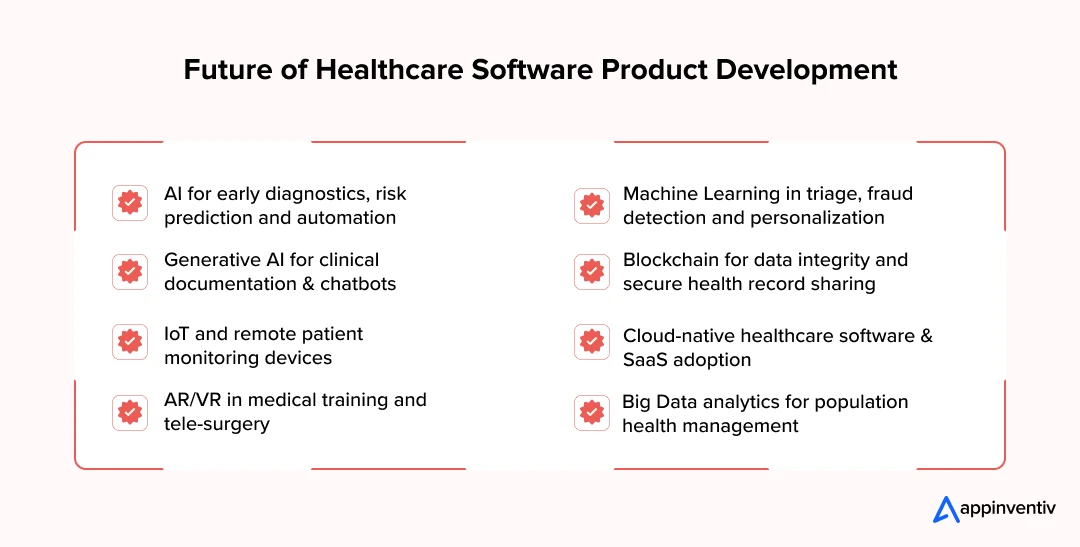
Emerging Trends and Technologies in Healthcare Software Product Development
Innovation is reshaping how care is delivered, documented, and paid for. What matters to the C-Suite isn’t the novelty of a tool but whether it reliably moves clinical, operational, or financial needles without creating new risk. Below are the shifts we see defining the trends for healthcare software development in 2026.
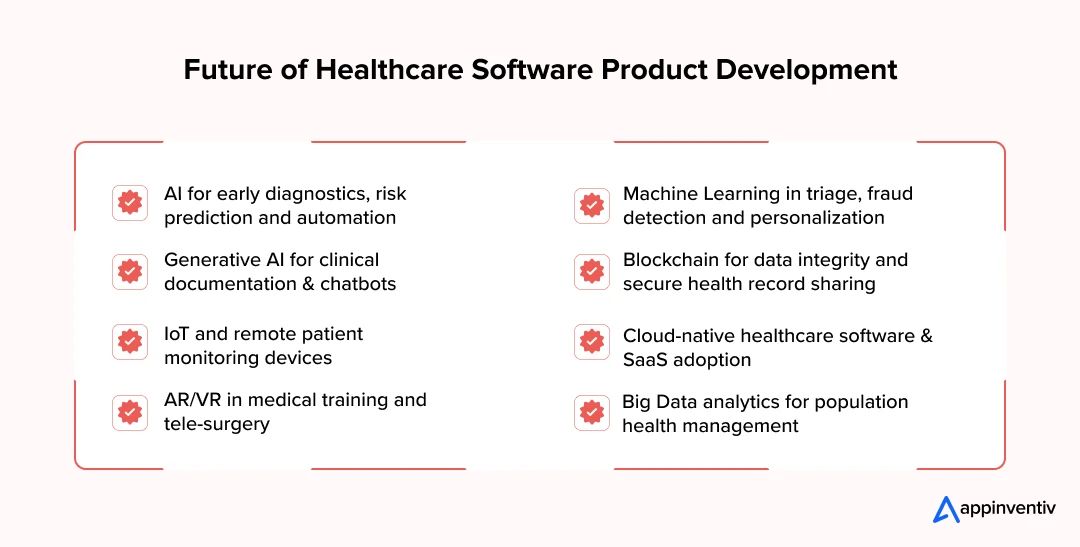
Artificial Intelligence
AI is already powering diagnostics, risk prediction, and workflow automation. Its real strength lies in helping clinicians work faster without sacrificing accuracy. Unlike traditional rule-based systems, AI models in healthcare adapt as they process more data. This makes them indispensable in complex, data-heavy clinical tasks.
According to MarketsandMarkets, the global AI in healthcare market is projected to grow from $14.92 billion in 2024 to $110.61 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 40.2%.
Machine Learning
Classical ML in healthcare already sits inside many clinical and operational pipelines like risk scores, imaging triage, readmission prediction, fraud detection. The advantage is pragmatic: models trained on well-governed data improve decisions without rewriting the entire tech stack.
The winning pattern pairs explainability with guardrails, so clinicians and auditors can see why a model suggested a path, not just what it suggested.
Generative AI
Generative AI in healthcare is moving from pilot projects to real deployment. A McKinsey survey of 150 US healthcare leaders found 85% are already exploring or using gen AI, with most focusing on clinical productivity and administrative efficiency. Notably, 64% of those implementing use cases report positive ROI; a sign that this is more than hype.
Internet of Things & Remote Patient Monitoring
Connected devices now stream vitals from the home to the EMR and care team dashboards. The upside is continuous context: trends matter more than single readings. To avoid alert fatigue, mature RPM programs blend edge processing, clinically tuned thresholds, and escalation rules tied to service-level commitments. The business case strengthens when RPM slots into care pathways and reimbursement models, not as a standalone product.
Cloud-Native Platforms
Cloud-first architectures let teams ship faster, scale on demand, and automate compliance tasks (logging, encryption, key management). Multi-cloud with a clear data residency stance reduces lock-in and eases cross-border privacy obligations. For regulated workloads, treat identity, secrets, and network segmentation as product features, not afterthoughts, and align early with HITRUST/SOC 2 evidence requirements.
AR/VR for Training, Guidance, and Rehabilitation
Immersive tech is maturing where repetition and precision matter, such as surgical rehearsal, complex device training, exposure therapy, and stroke rehab. The ROI leans on fewer errors, shorter learning curves, and more consistent protocols.
Big Data & Predictive Analytics
Modern data platforms unify claims, EMR, device streams, and SDOH into governed models that executives can actually use. Health systems are moving from retrospective dashboards to forward-looking allocations, including staffing, bed management, supply chain, and outreach for high-risk cohorts.
Blockchain & Verifiable Records (integrity and provenance)
Select use cases benefit from tamper-evident logs and portable credentials like consent proofs, clinical trial chains of custody, and device/service provenance. Adoption remains targeted, but where auditability and cross-enterprise trust dominate, ledgers and verifiable credentials can simplify due diligence without adding manual overhead.
Cost of Healthcare Software Product Development
The cost of developing a healthcare software product is rarely one-size-fits-all. It is shaped by the scale of ambition, the regulatory footprint, and how well the system must integrate with existing infrastructure. For executives, the best way to define software development costs for healthcare is by complexity level rather than product category.
Key Cost Drivers
- Scope & Features: Adding AI-driven analytics, IoT monitoring, or multi-role portals multiplies effort compared to a simple scheduling tool.
- Compliance Requirements: HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, and SOC 2 certifications demand rigorous documentation and validation, often adding months to delivery.
- Systems Integration: Linking with legacy EHRs, labs, and billing platforms can consume as much budget as building new features.
- Talent Mix: Engaging experienced healthcare software product developers, architects, and compliance consultants increases upfront cost but lowers risk long term.
Estimated Cost & Timeline by Complexity Level
| Complexity Level | Scope / Examples | Estimated Cost | Typical Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| MVP (Minimum Viable Product) | Core features only; used to validate concept and user demand | $40,000 $100,000 | 3 – 6+ months |
| Low Complexity | Simple software or portals with limited functionality | $100,000 – $150,000 | 6 – 8+ months |
| Medium Complexity | Telehealth platforms, analytics dashboards, practice management systems | $150,000 – $250,000 | 8 – 10+ months |
| High Complexity | EHR/EMR modules, AI-supported tools, multi-integration solutions | $250,000 – $400,000 | 10 – 12+ months |
| Enterprise Grade Software | Large-scale, cloud-native systems spanning multiple hospitals, full compliance, advanced AI & IoT integration | $1400,000 – $600,000+ | 12 – 14+ months |
These ranges cover development, compliance validation, and launch support. Maintenance, upgrades, and user training add recurring costs beyond these figures.
ROI Perspective
Budget discussions should never stop at price tags. An MVP costing $100,000 may validate a market opportunity worth millions. An enterprise build costing several million may repay itself by lowering readmissions, improving billing efficiency, or expanding into new revenue models.
The cost of healthcare product development is best justified when mapped directly to patient outcomes, compliance assurance, and competitive advantage. Let’s map the ROI of healthcare software development in detail:
Measuring Success & ROI of Healthcare Software
Writing the check for a healthcare software product is only the beginning. The real question for executives is whether the investment creates measurable value, financially, operationally, and clinically. ROI in this space cannot be reduced to balance sheets alone; it has to reflect patient outcomes and long-term resilience. Here are some of the key areas where healthcare businesses can witness improved ROI:
KPIs That Matter
Executives should look beyond usage statistics. Metrics such as reduced readmission rates, faster claim processing, shorter appointment wait times, or improved patient satisfaction provide a truer picture of value. For enterprise systems, even a 2–3% improvement in efficiency can translate into millions saved annually.
ROI Framework for Healthcare IT Projects
A structured approach helps leaders defend technology investments. The framework often includes four layers:
- Clinical Impact – measurable improvements in diagnosis accuracy, treatment adherence, or patient outcomes.
- Operational Efficiency – reductions in administrative overhead, duplication of tests, or IT maintenance costs.
- Financial Return – net effect on revenue, margins, or reimbursement rates.
- User Satisfaction – Higher adoption rates, positive feedback and satisfaction scores from both patients and providers.
Among organizations already investing in digital priorities, 72% report satisfaction; for robotics and advanced analytics, satisfaction rises to 82% and 81% respectively (Source: McKinsey), evidence that well-targeted bets pay back.
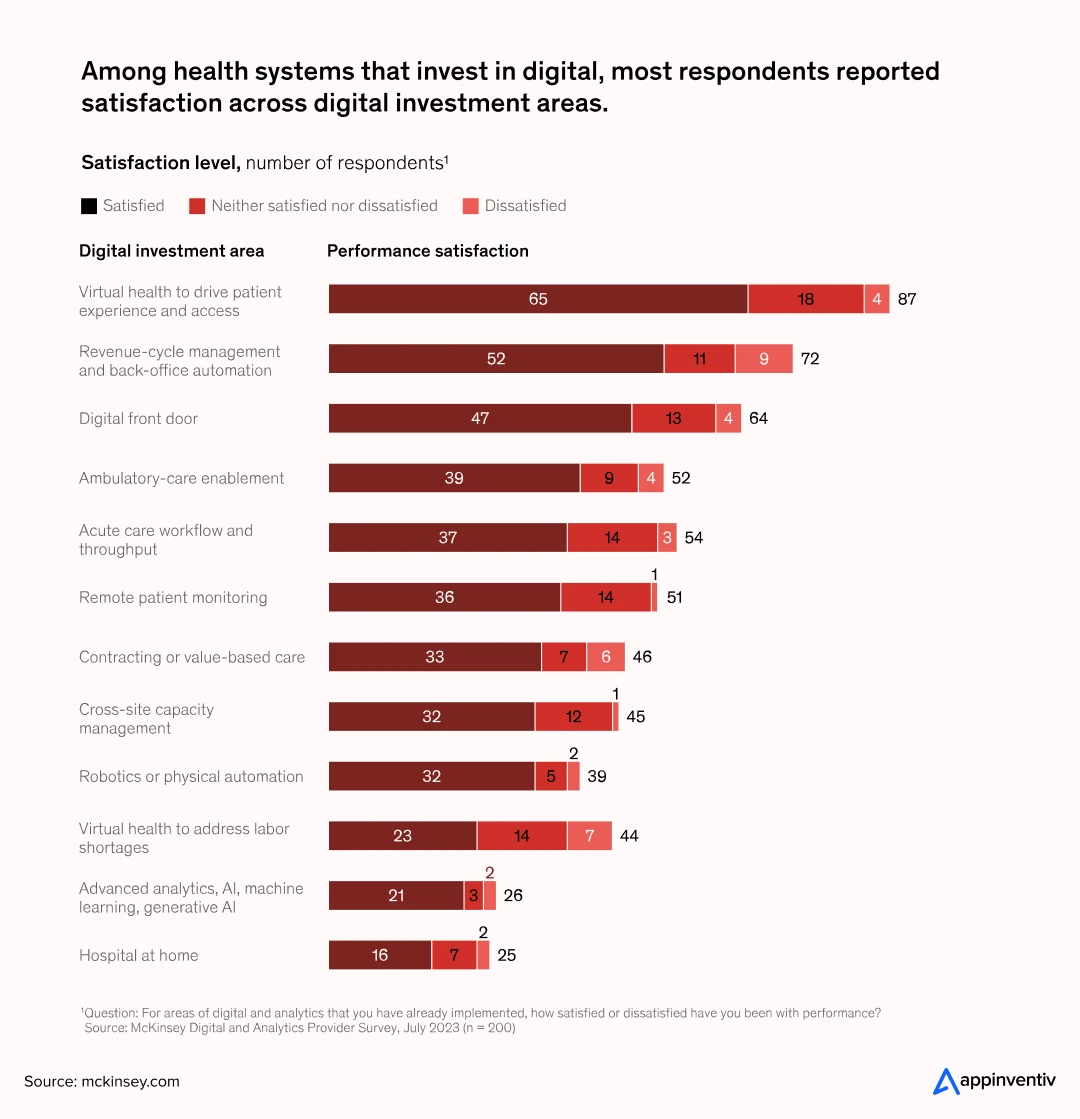
This mix ensures that the custom healthcare software product development steps align not only with financial returns but also with mission-driven goals.
Balancing Dollars and Care Quality
A common pitfall is chasing ROI purely in cost savings. Healthcare executives should consider “dual value”: financial lift and better patient outcomes. A telehealth platform that reduces hospital visits by 15% does not just lower costs; it improves access for patients who might otherwise delay care.
Long-term View
ROI in healthcare often unfolds over years. Compliance upgrades may look like additional costs in the short term, yet they protect organizations from multi-million-dollar penalties. Similarly, analytics platforms may take time to mature but eventually drive better planning, staffing, and risk management.
In-house vs. Freelancers vs. Outsourced Development: Which is the Right Choice for Healthcare Product Development
Once you know how to build and how much it will cost, the next critical question is who will build it. You typically have three choices here: in-house teams, freelancers, and outsourcing partners. The right choice of your development team profoundly impacts outcomes, timelines, costs, and risks. Each model offers distinct advantages and disadvantages.
| Model | Strengths | Limitations | Best Fit For |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house | Full control, cultural alignment, long-term IP ownership | High cost, slow to scale, harder to attract niche talent | Large organizations with steady pipelines |
| Freelancers | Flexible, lower upfront cost, quick for small tasks | Limited compliance knowledge, low accountability, inconsistent quality | Short-term, low-risk add-ons or MVP experiments |
| Outsourced Partner | Domain expertise, compliance readiness, scalability, predictable delivery | Less direct control, dependency on vendor relationship | Enterprise systems, regulated products, multi-integration projects |

When choosing to outsource, look for a tech partner who demonstrates:
- Proven healthcare domain expertise with relevant case studies
- HIPAA compliance and security certifications (SOC 2, ISO 27001)
- Established quality management systems (ISO 13485 if applicable)
- Strong references from healthcare clients
- Transparent communication practices and cultural compatibility
- Appropriate insurance coverage and contractual protections
- Intellectual property safeguards ensuring your ownership
Guiding Principles: Best Practices for the Success of Healthcare Software Development
Healthcare software projects carry real risk. One wrong choice can cost millions or stall adoption. The teams that get it right usually keep a few guiding habits in mind.
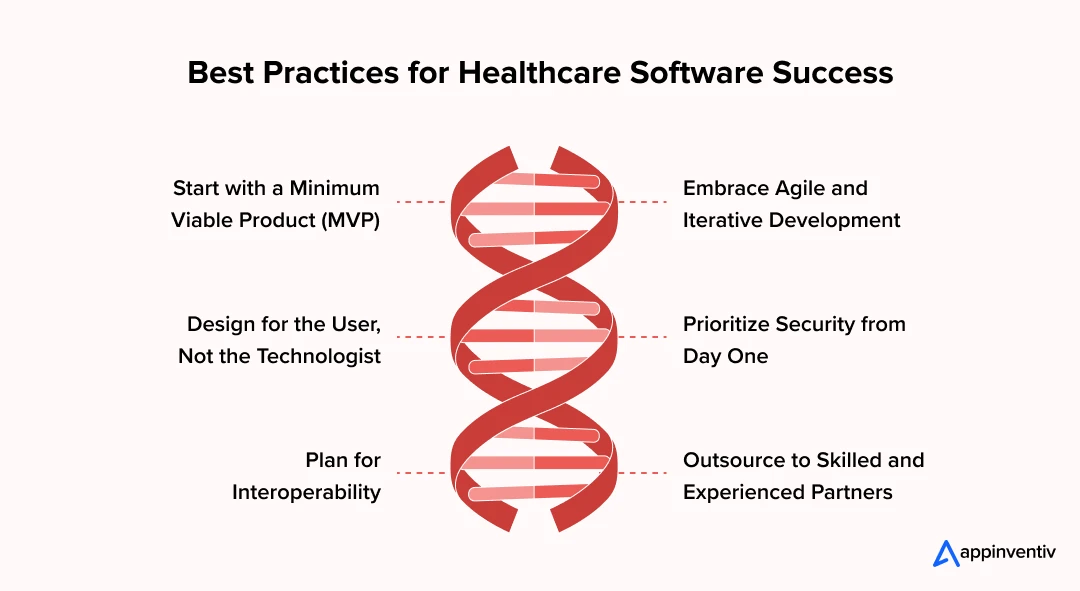
Start with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Don’t build everything at first. Start with a lean version to solve one critical issue, then listen to users. It’s cheaper, faster, and more accurate than guessing in a boardroom.
Embrace Agile and Iterative Development
Change is constant in terms of regulations, workflows, and even tech stacks. Agile methods let you shift without starting over. Think of it as steering, not rebuilding.
Design for the User, Not the Technologist
Here’s where many fail. A system might impress engineers, but if clinicians find it clunky, they won’t use it. Bring them in early, test with them often. Adoption depends on ease, nothing else.
Prioritize Security from Day One
Security late is security lost. Encryption, access controls, audit logs; these belong at the design table. Skip them, and one breach can undo years of trust.
Plan for Interoperability
Healthcare is full of silos already. New tools must connect with EHRs, labs, and pharmacy systems. HL7 and FHIR standards aren’t optional; they’re the price of entry.
Outsource to Skilled and Experienced Partners
Sometimes the in-house team can’t cover it all. A healthcare software development company with domain expertise closes the gap. This isn’t about cost or time; it’s about the global talent pool you can access.
Best practices aren’t theory. They are survival rules. Ignore them, and adoption, compliance, and ROI all will suffer.
From Concept to Reality: How Appinventiv Builds Healthcare Products that Last
The best way to measure a partner’s ability is to see what they’ve already delivered. At Appinventiv, we’ve worked with healthcare clients who wanted more than just a platform; they wanted products that can solve problems at scale. Here are three examples that show how vision, technology, and execution came together.
DiabeticU
The client’s goal was not another blood sugar tracker; they wanted a tool that could become part of a patient’s daily routine. Our team designed DiabeticU, a platform where users log blood sugar, activity, and medication while interacting with a conversational assistant that offers real-time tips and reminders.
The result was a 24/7 support system, described by early adopters as the first-of-its-kind diabetes care platform. It replaced generic trackers with personalized daily guidance and has become a practical ally for patients managing Type 2 diabetes.

Health-e-People
For Health-e-People, the problem was fragmentation; patients were juggling multiple devices, each with its own app. We built a scalable platform for Health-e-People that connects with over 200 devices and applications, consolidating health data into a single dashboard.
Users can track daily metrics more easily, and researchers or caregivers can receive live updates in real time. By simplifying the experience, the platform has given thousands of people a clearer picture of their health and a seamless way to share it with those who matter.
Soniphi
Soniphi’s vision was ambitious: analyze subtle shifts in vocal tone and breathing to generate wellness insights. The challenge was making advanced bio-acoustic analysis accessible to everyday users.
We built a voice-based wellness platform for Soniphi that translates recordings into health assessments in seconds. With 94% of vocal input analyzed in real time, Soniphi reached 10,000+ early users, proving that preventive health can be delivered through something as natural as the human voice.
Why Appinventiv is the Right Partner for Healthcare Product Development
In healthcare, credibility doesn’t come from promises; it comes from results. Systems must run without fail, protect sensitive data, and improve both efficiency and patient outcomes. At Appinventiv, we’ve built our reputation on delivering exactly that: secure platforms, reliable performance, and measurable impact backed by scale and industry recognition. Here are some of the key reasons why global healthcare enterprises and startups alike count on us for their healthcare software development projects:
Compliance and Security at the Core
Every healthcare solution we deliver is designed with regulatory frameworks in mind. HIPAA, GDPR, HITECH, HL7, and FHIR are not afterthoughts but part of the foundation. By embedding compliance into architecture and workflows from day one, we help organizations lower regulatory exposure and strengthen patient trust.
Architectures Built to Last
Healthcare demands agility. Our approach to healthcare software product architecture ensures systems can absorb growth, adapt to new regulations, and integrate emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain. Scalability and interoperability are treated as business essentials, not optional add-ons.
A Proven Record in HealthTech
As a leading provider of medical device software development services, we’ve delivered more than 500 digital health platforms for 450+ clients, integrating with 300+ connected medical devices along the way. Our portfolio includes projects such as Soniphi, Health-e-people, YouComm, and Diabeticu, each demonstrating how technical complexity can coexist with patient-first design.
The outcome is not just working software, but solutions that win adoption, deliver efficiency, and earn patient satisfaction.
Let’s map our healthcare expertise via numbers:
- 99.90% uptime achieved across critical systems
- 45% efficiency gains reported by hospital clients
- 90%+ clinical data accuracy maintained in production
- 95% patient satisfaction in deployed healthcare platforms
Full-Spectrum Healthcare Services
We support the entire digital health journey, from modernizing legacy systems and enabling interoperability with HL7 and FHIR, to building patient engagement platforms, remote monitoring solutions, and AI-powered analytics for better decision-making.
Recognized by Industry Leaders
Our commitment has been validated with multiple recognitions:
- The Economic Times’ Leader in AI Product Engineering & Digital Transformation (2025)
- Deloitte Technology Fast 50 India Winner (2024 & 2023)
- Statista High Growth Companies APAC (2025 & 2024)
- Clutch Spring Award for Elite Chatbot and Android Apps (2025)
- Clutch Top 100 Fastest-Growing Companies (2025)
- Times Group Tech Company of the Year (2023)
- Statista India’s Growth Champions (2023)
- Fastest-Growing AI Development Company (2024) by MobileAppDaily
- CIO Klub Preferred Partner Award (2024)
Scale That Drives Innovation
Beyond healthcare, Appinventiv has delivered 3000+ digital solutions across industries, powered by a team of 1600+ experts worldwide. This depth allows us to transfer proven innovations from other industries into healthcare while tailoring every solution to its unique regulatory and clinical context.
With Appinventiv, organizations don’t just get software developers; they gain a partner trusted by global healthcare leaders, recognized by industry analysts, and proven in the field. The result: platforms that are secure, compliant, and built to deliver measurable outcomes.
Ready to build the future of healthcare? Let’s connect and discuss your vision of healthcare software product development.
FAQs
Q. What Are the Standards and Regulations for Healthcare Software Product Development?
A. Healthcare software is governed by some of the strictest frameworks anywhere. A few of the key ones:
- HIPAA (U.S.) – Rules on how patient data is stored and shared.
- HITECH Act – Reinforces HIPAA and adds breach-notification requirements.
- GDPR (EU) – Consent and privacy regulations for organizations handling European data.
- FDA Guidance – Applies when software touches diagnosis, treatment, or medical devices.
- HL7 and FHIR – Interoperability standards so systems actually talk to each other.
These are not optional. Without alignment, a product often can’t even reach the market.
Q. What Are the Costs of Healthcare Software Product Development?
A. There is no universal figure. Costs vary depending on scope, integrations, and compliance needs. Rough benchmarks:
- MVPs and Mid-range platforms: $40,000–$300,000
- Complex and advanced platforms (telehealth, analytics): $300,000–$400,000
- Enterprise-grade with AI, IoT, and multi-system integration: $400,000–$600,000+
Q. How to Choose the Right Healthcare Software Product Development Partner?
A. When choosing the right healthcare software developers, three things matter the most:
- Domain Expertise – Experience in healthcare, not just generic products.
- Compliance Knowledge – HIPAA, GDPR, HL7, FDA should be baked into their process.
- Reliability at Scale – The ability to deliver and support post-launch.
Q. How long does it take to develop a healthcare software product?
A. Timelines depend heavily on complexity. A basic software may launch in 3–6 months. An enterprise platform, like an IoT-driven EHR extension, often takes 12–14 months or more.
The biggest delays usually come from compliance checks, integration with legacy systems, and clinical testing. Many organizations choose phased rollouts to balance safety with speed.
Q. How can healthcare software product development help in changing the modern healthcare era?
A. Healthcare software product development helps change the modern healthcare delivery through the following ways:
- Reduce administrative burdens by automating repetitive workflows.
- Enable continuous care through telehealth and remote monitoring.
- Improve accuracy with AI-driven clinical decision support.
- Create transparency and trust with blockchain-based record sharing.
- Empower patients with portals that put data and decisions in their hands.
In short, developing a healthcare software product isn’t just about digitization; it’s about creating entirely new care models that are more connected, accessible, and patient-centered.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
How to Build a Custom Pediatric EMR and EHR System?
Key takeaways: Clinical Precision: Custom systems accommodate pediatric-specific data points like percentile curves and weight-based longitudinal dosing. Interoperability: Seamless data exchange via HL7 FHIR ensures your practice stays connected to pharmacies, labs, and state registries. Regulatory Resilience: Built-in compliance with HIPAA, HITECH, and MACRA/MIPS reduces legal friction. Enhanced Engagement: Parent portals reduce administrative overhead by…

Change Management in Healthcare: Principles, Processes, and Models
Key Takeaways Change in healthcare fails quietly when ownership, workflow alignment, and follow-through are missing. Successful change management in healthcare focuses on adoption, not just system implementation. Clinical workflows and workforce capacity determine whether transformation sticks or stalls. Governance, clear accountability, and post-go-live support matter more than the model used. Sustainable healthcare transformation depends on…

A Practical Guide to Building Your Mental Health Chatbot - Use Cases, Cost, & ROI
Key takeaways: Mental health chatbots work when they know their limits. They’re most useful as a gentle first step, not as a stand-in for real care. Good chatbot design is more about judgment than AI. Clear boundaries, calm responses, and safety matter more than smart language models. Enterprises invest in chatbots to make support easier…





































