- Why Healthcare Data Security is a Critical Necessity
- The Journey of Patient Data: Identifying Vulnerability Points
- Common Healthcare Data Security Challenges and Proven Best Practices: A Detailed Breakdown
- Risk Factors and Causes of Data Breaches in Healthcare
- How to Protect Healthcare Data: 6 Integral Steps
- The Future of Healthcare Data Security: Innovation and Adaptation
- Stay Ahead in Healthcare Data Privacy with Appinventiv
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- Healthcare data breaches can cost around $9.77 million per incident in 2024, making it the costliest industry for 14 consecutive years
- Implementing comprehensive security measures can reduce breach incidents by up to 75% and save millions in potential costs
- AI-powered security solutions detect threats more accurately and quickly than traditional methods, significantly reducing response times
- Businesses need to embrace a multi-layered security approach to address vulnerabilities across the entire patient data lifecycle.
The modern era has delivered remarkable benefits and breakthroughs to healthcare, spanning from remote medical appointments to artificial intelligence-driven diagnosis tools. However, these technological leaps forward create a significant obligation. What exactly is this obligation? It involves protecting the confidential patient data that serves as the foundation for these innovations.
The critical nature of this issue becomes clear when we consider a startling statistic: “During January 2025, 66 healthcare data security breaches impacted 500 or more individuals, which equals one breach occurring every 11 hours (Source: The HIPAA Journal).”
This troubling rate of cyber incidents targeting healthcare facilities demonstrates the serious dangers confronting this field. Such attacks threaten to undermine patient confidence, damage financial health, and disrupt daily operations, potentially leading to devastating consequences. Implementing decision intelligence via Causal AI can help healthcare providers make data-driven decisions to strengthen security protocols.
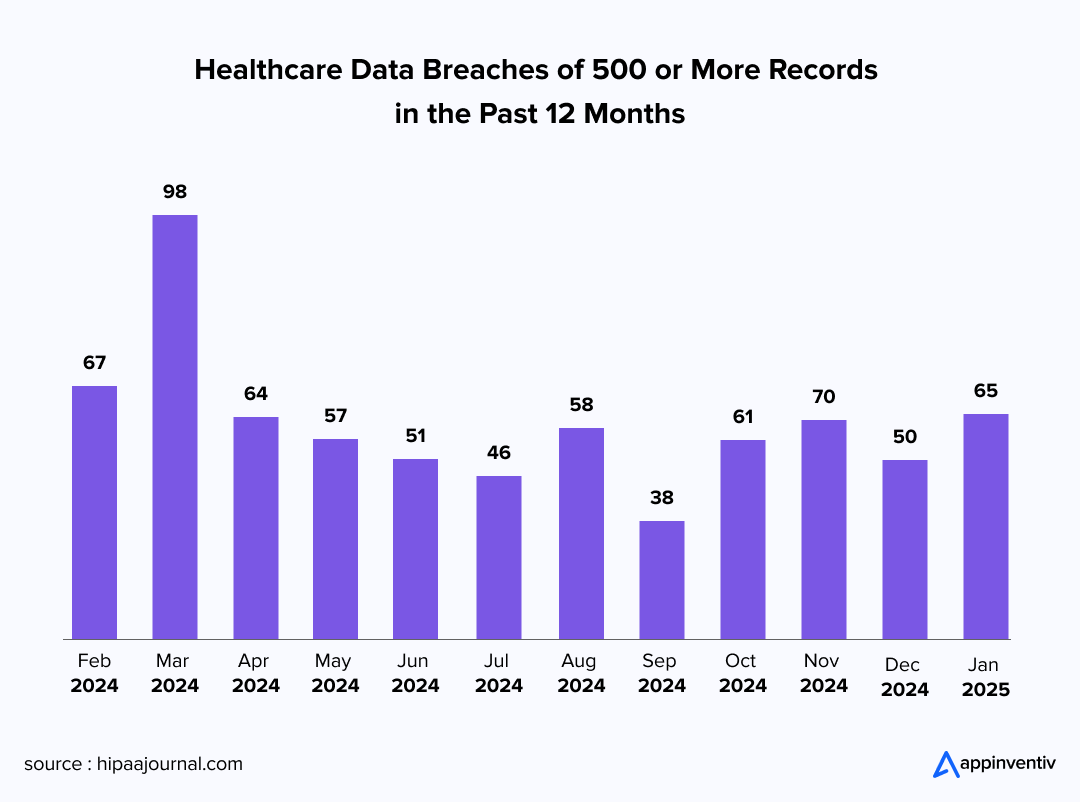
This worrying pattern reveals the increasing financial motivation driving cybercriminals to focus on healthcare organizations. With cyber threats becoming more frequent and dangerous, especially the surge in ransomware incidents, medical institutions must act quickly to bolster their data protection strategies.
Throughout this blog, we’ll examine typical healthcare data security obstacles and provide practical recommendations for protecting patient information during every phase of its existence. Starting with secure information gathering through to appropriate destruction, we’ll investigate methods for safeguarding sensitive details while maintaining adherence to important regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
Start securing your healthcare data today to avoid the rising costs of breaches.
Why Healthcare Data Security is a Critical Necessity
The financial impact of healthcare data breaches is massive, with each breach costing healthcare providers an average of $9.77 million (Source: Statista). That’s a hefty price tag, especially when compared to breaches in other industries.
Healthcare data protection is a goldmine for cybercriminals, fetching a premium on the dark web. In fact, 276.78 million patient records were compromised in 2024, a staggering 26% increase over the prior year. On average, that is 758,288 records per day!
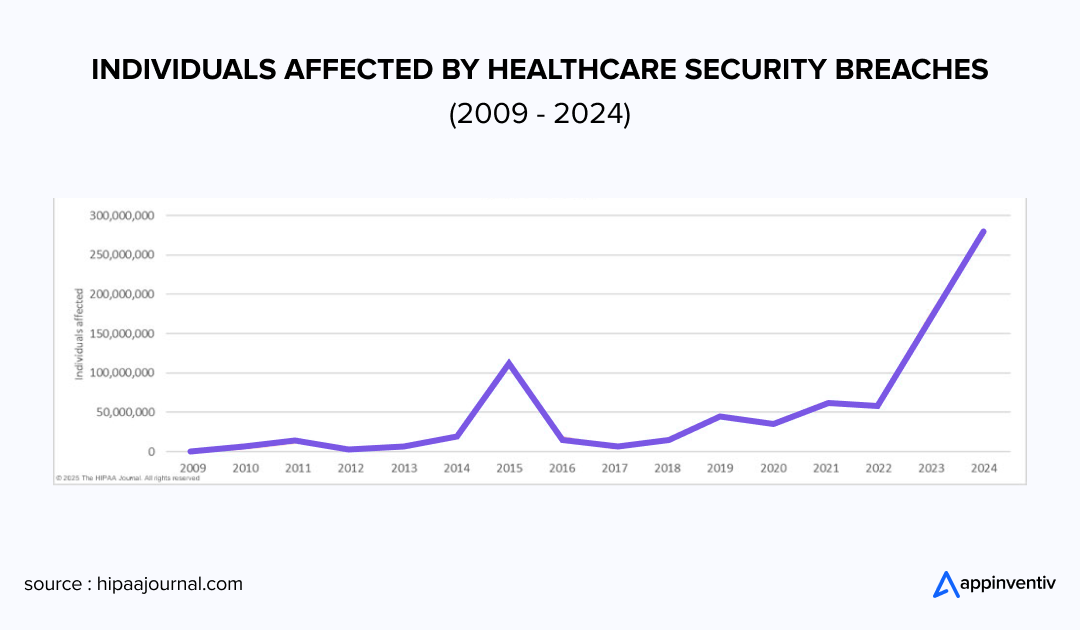
This enormous financial burden goes far beyond regulatory penalties. It includes investigation expenses, notification requirements, damaged reputation, attorney fees, and the devastating operational shutdowns of essential systems. When ransomware paralyzes a hospital’s infrastructure, the consequences reach well past accounting books to create immediate barriers to patient treatment, sometimes resulting in life-threatening situations.
These breaches cause serious financial hits as well as erode patient trust and harm the reputation of the organization, making data security in healthcare more important than ever.
Also Read: Key Strategies for Ensuring Cybersecurity in Healthcare
The Journey of Patient Data: Identifying Vulnerability Points
Healthcare data security in the cloud begins the moment patient data is created, flowing through numerous systems and touchpoints within the healthcare data security standards. Understanding this journey is the first step in identifying where vulnerabilities lie and how to implement robust security measures at every stage. From diagnosis to discharge and beyond, every interaction with patient data security presents both an opportunity for enhanced care and a potential point of compromise.
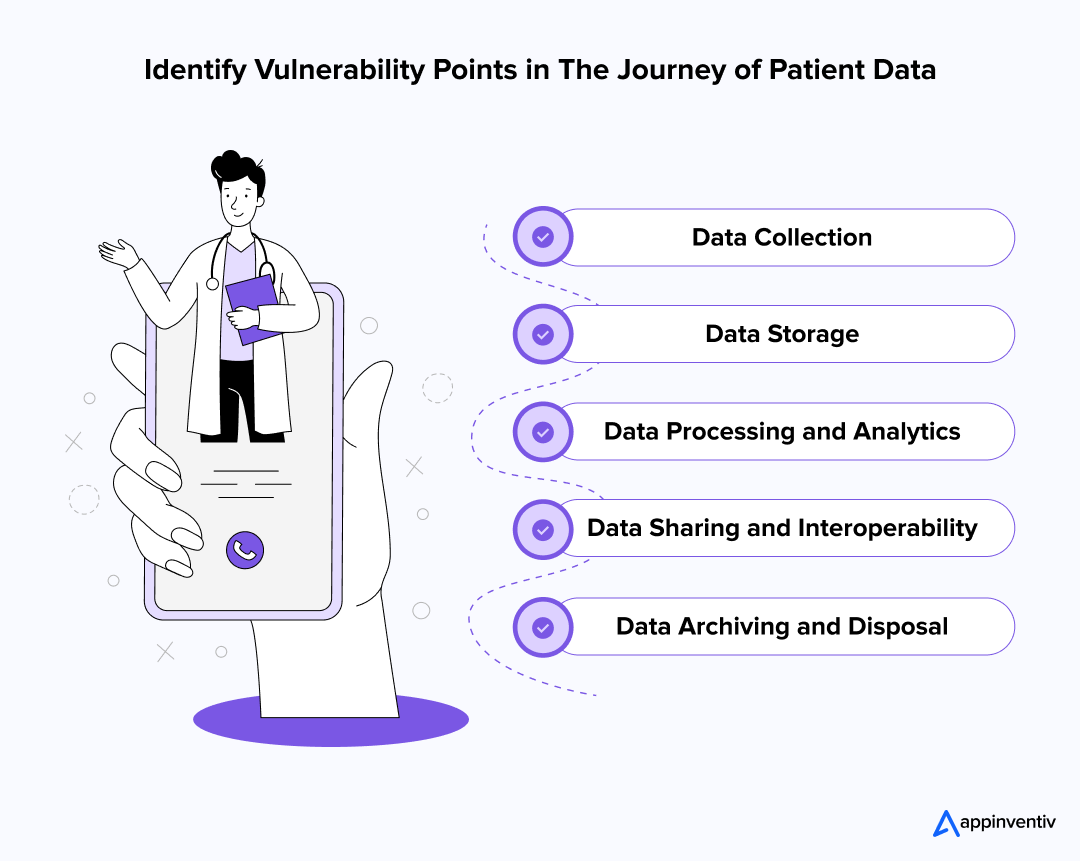
Data Collection
Patient information gathering spans from intake paperwork to wearable technology and IoMT (Internet of Medical Things) devices in healthcare, representing the initial crucial phase. Security weaknesses appear when information comes from unprotected channels, including unencrypted enrollment documents or vulnerable IoMT devices broadcasting confidential details.
Data Storage
After gathering, patient information requires secure housing. Numerous healthcare facilities continue using local servers, while cloud environments (public, private, and hybrid) grow increasingly common. Every storage approach brings distinct dangers, from setup errors to possible data breaches.
Data Processing and Analytic
Implementing AI in healthcare data security, machine learning, and big data in healthcare has transformed diagnostic capabilities and individualized treatment. Yet analyzing massive amounts of confidential information heightens exposure risks during data analysis in healthcare. Strong encryption and strict access management remain essential for maintaining protection throughout processing phases.
Data Sharing and Interoperability
Medical information moves regularly between healthcare facilities, pharmacies, testing centers, and external partners. When proper encryption and secure transmission protocols aren’t established, patient data security faces threats, leaving data exposed to capture during transfers.
Data Archiving and Disposal
When patient records reach the end of their retention period, healthcare organizations face the challenge of secure elimination. Proper data wiping techniques, along with physically destroying hard drives and storage media, stop anyone from recovering old patient files. These careful disposal practices help medical facilities meet their obligations under healthcare data protection laws and industry standards.
Now that we know the data lifecycle perspective, let’s explore the most common healthcare data security challenges and proven best practices to safeguard patient data security throughout its lifecycle.
Common Healthcare Data Security Challenges and Proven Best Practices: A Detailed Breakdown
Securing patient data security across its entire lifecycle is a complex undertaking fraught with unique challenges. This section delves into the most prevalent data security challenges in healthcare, coupled with proven best practices and technological approaches to overcome them.

Challenge 1: Insecure Data Collection and Ingestion
Data vulnerabilities often begin at the point of entry—unsecured forms or IoMT devices transmitting sensitive data can be prime targets for attackers.
Best Practice: Secure Data Ingestion & Encryption at the Edge
- Use TLS/SSL encryption for online forms and implement device-level encryption for IoMT devices.
- Leverage secure APIs to facilitate safe data transfer from wearables and other devices.
Challenge 2: Vulnerable Data Transmission Between Healthcare Entities
Data transfers between healthcare systems, such as from hospitals to pharmacies, are vulnerable to interception and unauthorized access.
Best Practice: Enforcing Secure Interoperability & Communication Protocols
- Use end-to-end encryption and secure messaging protocols like FHIR and HL7 to ensure that data is protected during transfer.
- Use protected APIs to guarantee safe information transfer from wearables and similar devices.
Challenge 2: Exposed Data Movement Between Medical Organizations
Transferring data between different healthcare systems, such as hospitals, pharmacies, etc. can be vulnerable to interception and unauthorized access.
Best Practice: Implementing Secure Interoperability & Communication Protocols
- Apply complete encryption and protected messaging standards such as FHIR and HL7 to keep information safe during transfers.
Challenge 3: Securing Electronic Health Records (EHRs) During Storage and Active Use
EHRs represent attractive targets for digital criminals looking to exploit patient information for profit, frequently through ransomware incidents or internal security threats.
Best Practice: Complete EHR Security
- Encrypt EHR databases both at rest and in transit. Enforce role-based access control (RBAC) and regularly audit access logs to monitor unauthorized attempts.
Also Read: How to Build an EHR System: Key Steps & Insights
Challenge 4: Securing Data in Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) and Medical IoT Devices
IoMT devices with limited built-in security features can expose patient data to attackers, making them easy targets for exploitation.
Best Practice: Device-Centric Security & Secure Data Pipelines
Implement authentication for devices, encrypt data at the source, and ensure secure communication channels between devices and central systems.
Also Read: We can add Iot in RPM blog after it gets live
Challenge 5: Insufficient Access Control and User Identity Management in Healthcare Apps
Managing diverse access for multiple stakeholders, from patients to clinicians, can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive patient data.
One of the most critical steps toward securing patient data is implementing identity and access management in healthcare that covers users, devices and systems.
Best Practice: Identity & Access Management (IAM) with MFA
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users accessing sensitive patient data and enforce context-aware policies to ensure that only personnel with authority can view specific records.
Challenge 6: Cloud Security Risks in Healthcare
With the ever growing adoption of cloud computing in healthcare, businesses encounter serious challenges related to misconfigurations, data loss, and breaches. This all occurs due to the shared responsibility model in the cloud. The hybrid and multi-cloud environments can lead to security gaps if not managed properly.
Best Practice: Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Implement cloud encryption for both data at rest and in transit.
- Utilize CSPM tools to detect misconfigurations in cloud environments and ensure compliance with healthcare data security standards.
- Employ DLP solutions to prevent sensitive data from leaving authorized environments.
Also Read: Everything you need to know about cloud application security
Challenge 7: Inadequate Secure Data Disposal Procedures
As healthcare organizations retire or decommission old systems and hardware, there is a risk of sensitive patient data remaining on devices that have not been properly sanitized. This can lead to data exposure and unauthorized access.
Best Practice: Comprehensive Data Sanitization and Certified Disposal
- Implement certified data wiping methods to ensure all sensitive patient data is securely erased from devices.
- Use physical destruction (e.g., shredding or degaussing) for hard drives and other storage devices containing PHI (Protected Health Information).
- Maintain detailed audit trails of data disposal to ensure full accountability and compliance.
Challenge 8: Mobile Healthcare App Vulnerabilities
With the growing development of mobile healthcare applications for telemedicine, patient portals, and EHR access, security vulnerabilities are emerging in app development. If not properly secured, AI-driven telemedicine apps can become a vector for data breaches in healthcare, exposing sensitive patient data.
Best Practice: Security-by-Design in Mobile Healthcare App Development
- Implement encryption for data stored within the app and during data transmission.
- Follow secure coding practices and conduct regular security audits to detect feasible vulnerabilities in the app.
- Protect against common mobile threats, such as insecure data storage and broken cryptography.
Challenge 9: Overcoming Threats from AI/ML in Healthcare
While AI and machine learning are revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing predictive analytics, improving diagnostic accuracy, and personalizing treatments, they also introduce new risks. These include threats like data re-identification from anonymized datasets, model manipulation, and adversarial attacks on AI systems.
Best Practice: Privacy-Preserving AI & Robust Model Security
- Implement federated learning to train AI models without exposing sensitive patient data directly.
- Utilize differential privacy techniques and homomorphic encryption to protect patient data while enabling AI-driven analysis.
- Regularly audit and secure AI/ML pipelines to prevent adversarial attacks that can compromise model integrity.
Challenge 10: Third-Party Vendor Risk and Data Sharing Complexity
As healthcare organizations increasingly rely on third-party vendors (e.g., cloud providers, data analysts, SaaS solutions), this creates a larger attack surface. Ensuring data security for healthcare when shared with external vendors becomes increasingly complex, especially when these third parties are less secure.
Best Practice: Robust Vendor Risk Management & Data Privacy Agreements
- Conduct thorough security assessments for all third-party vendors before sharing patient data.
- Establish strong Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) and Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) that explicitly outline security requirements.
- Mandate encryption for all data exchanged with vendors, ensuring that data remains protected even if a third-party vendor is compromised.
Also Read: From Theory to Practice- 10- Real-World Applications of Synthetic Data in Healthcare
Risk Factors and Causes of Data Breaches in Healthcare
Healthcare data security breaches are often caused by a combination of technological vulnerabilities and human errors. Here are some key causes of healthcare data breaches:
- Weak Passwords and Lack of Authentication: Poor password practices and lack of multi-factor authentication make it easier for hackers to access sensitive patient data.
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals tend to send phishing emails to trick receivers into revealing login credentials. This leads to unauthorized access.
- Insider Threats: Disgruntled or careless employees with access to patient data can intentionally or unintentionally compromise security.
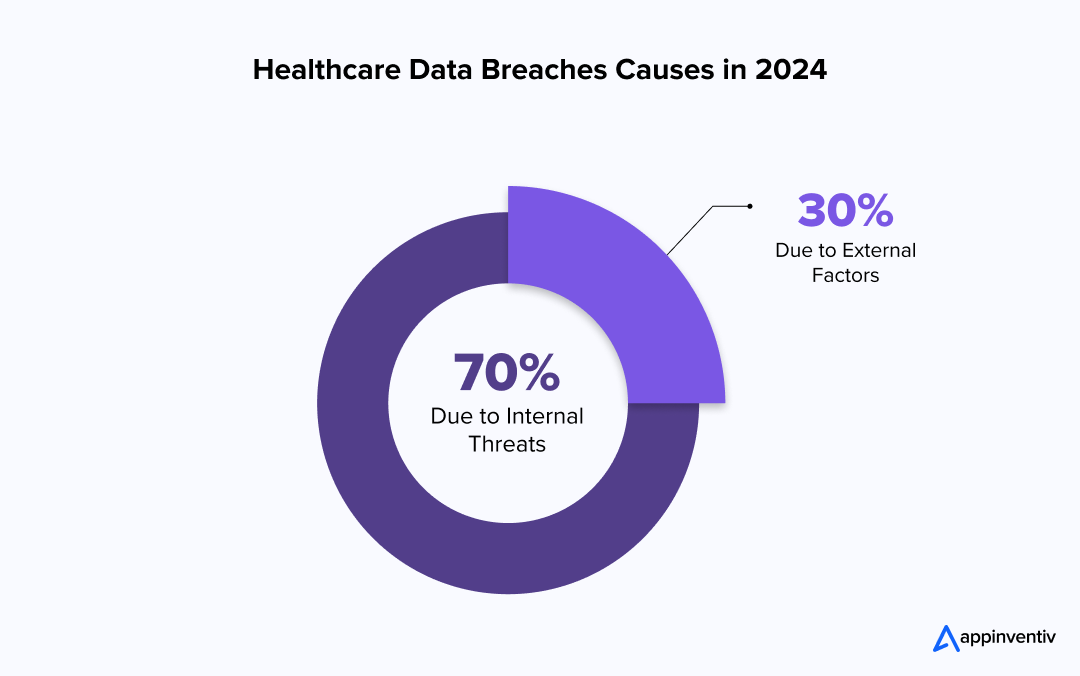
- Insecure Mobile Devices and IoT: Unsecured mobile and IoMT devices can be exploited to access sensitive patient information.
- Lack of Staff Training: Employees unaware of cyber threats may accidentally fall victim to scams, mishandle sensitive data, or ignore security protocols.
- Legacy Software and Systems: Healthcare organizations with outdated software or unpatched systems are more susceptible to cyberattacks exploiting known vulnerabilities.
Also Read: A Guide to Modernizing Legacy Systems in Healthcare
By finding out these risk factors and following the proven practices, businesses can easily reduce the likelihood of a data breach.
How to Protect Healthcare Data: 6 Integral Steps
Securing healthcare data is essential to maintain patient privacy, prevent data breaches, and comply with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. and the good news is that there are effective ways to do so. Healthcare organizations can can some strategic steps to protect their data and minimize risks. Here are six key steps to protect healthcare data:
Leverage Data Encryption Technique
Data encryption ensures that sensitive patient data remains protected during transmission. When data is encrypted, it is turned into unreadable code that can’t be accessed without a secret decryption key. This makes it nearly impossible for cyber thefts to intercept or read the data while it’s being transferred between systems, whether it’s within the organization or externally to other providers, patients, or vendors. By encrypting data at rest and in transit, healthcare companies can significantly minimize the risk of data theft.
Use of Anti-Virus Apps
Antivirus applications are crucial for detecting and stopping malware before it can infiltrate a healthcare organization’s network. These apps continuously scan for viruses, worms, trojans, and other types of malicious software. With the increasing frequency of cyberattacks in healthcare data security, antivirus software acts as an essential layer of defense, blocking threats and preventing them from compromising the network.
System Monitoring Apps
System monitoring applications allow healthcare IT teams to actively monitor the network and endpoints for any signs of suspicious activity. These tools track all devices and systems connected to the network, providing visibility into potential vulnerabilities or unauthorized access attempts.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is another great way to add an extra layer of security. This technique requires users to provide a combination of integral information such as a password, an authentication token), and biometric data, like a fingerprint or facial scan).
Ransomware Protection
Ransomware attacks are a growing threat to healthcare data security. These attacks involve malware that locks up critical systems, demanding a ransom for release. To protect against this type of attack, healthcare organizations should use specialized anti-ransomware software that identifies and blocks ransomware before it can cause harm.
Employee Training
Even the most advanced technical defenses are ineffective if employees aren’t properly trained to recognize and respond to cyber threats. Employee training programs should cover the importance of safeguarding login credentials, recognizing phishing attempts, and using strong, unique passwords. Additionally, training should educate staff on how to protect their devices and understand the risks associated with cyber threats.
Partner with Appinventiv to implement comprehensive security solutions that protect your patients, your data, and your organization’s reputation.
The Future of Healthcare Data Security: Innovation and Adaptation
As digital transformation continues to shape the healthcare industry, the need for innovative and adaptive data security solutions is more crucial than ever. Technologies like blockchain, machine learning, and AI in healthcare data security offer new opportunities to enhance healthcare data protection and streamline security protocols.
Key technologies shaping healthcare data security include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Automates real-time threat detection and enhances data protection in healthcare by identifying vulnerabilities faster.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain in healthcare secures patient data with a decentralized approach, ensuring data integrity and enhancing data privacy and security in healthcare.
- Cloud Security: Scalable, flexible storage with end-to-end encryption ensures data security for healthcare across cloud environments.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Zero Trust approach significantly reduces the attack surface and minimizes the impact of potential breaches, making it a robust framework for healthcare data security standards.
- Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: The future of protecting patient data will involve transitioning to quantum-resistant cryptography (PQC) to ensure long-term confidentiality and integrity of patient data security against future computational power.
- Behavioral Analytics: By creating baselines of normal behavior, it can flag deviations that might indicate a cyber threat or an insider risk, adding another layer to data security measures in healthcare.
The future of healthcare security will focus on automation, continuous monitoring, and resilient infrastructures that provide a proactive approach to data security measures in healthcare.
Also Read: Top Healthcare Trends to Leverage in 2025
Stay Ahead in Healthcare Data Privacy with Appinventiv
At Appinventiv, we are at the forefront of ensuring robust healthcare data privacy and security for our clients. Our solutions are designed to meet the evolving needs of the healthcare data security industry, from encryption strategies to compliance with regulatory standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
We’ve successfully worked with Soniphi, DiabeticU, and Health-e-People, helping them secure their patient data and build innovative solutions that adhere to the strictest privacy standards. Our expertise in custom healthcare software development allows businesses to focus on their growth while we ensure that their sensitive data remains safe.
With a track record of delivering over 3000 successful projects in a decade of industry experience, our expertise translates into resilient security frameworks for your healthcare initiatives. Our team of 1600+ tech experts is committed to providing solutions that protect data and optimize operations, ensuring that your healthcare business can thrive in a digitally connected world.
Contact us now to know how Appinventiv can help you safeguard your healthcare data.
FAQs
Q. What is data security in healthcare?
A. Data security in healthcare refers to the comprehensive set of measures and practices designed to protect sensitive patient information and other critical health data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
It encompasses technological safeguards like encryption and access controls, alongside administrative policies, physical security, and ongoing employee training. The goal is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all medical data security throughout its entire lifecycle, from collection to disposal, adhering to strict healthcare data security standards.
Q. Why is data security important in healthcare?
A. The importance of data security in healthcare cannot be overstated.
- Firstly, it’s fundamental to patient data security and maintaining patient trust; individuals must feel confident that their highly personal health information is protected.
- Secondly, healthcare data breaches carry severe financial consequences, including substantial fines from regulatory bodies like HIPAA and GDPR, legal fees, and reputational damage.
- Thirdly, compromised health data security can disrupt critical healthcare operations, potentially leading to delays in care, compromised diagnoses, and even direct harm to patients.
- Ultimately, robust data security for healthcare is essential for ethical practice, legal compliance, and operational continuity.
Q. How Do Data Breaches Impact the Healthcare Industry?
A. Data breaches impact the healthcare industry in a multitude of devastating ways.
- Financially, they result in significant costs, covering everything from investigation and remediation to notification expenses and legal battles.
- Reputationally, breaches erode patient trust, which can lead to patient attrition and a damaged brand image.
- Operationally, data security breaches in healthcare can cause system downtime, disrupting patient care, scheduling, and billing, sometimes for extended periods, as seen with the recent rise in ransomware attacks.
- Furthermore, they can lead to loss of intellectual property, compromised research data, and strict regulatory penalties, underscoring the critical need for advanced healthcare data security solutions.
Q. What are the key regulations governing healthcare data security?
A. The key regulations governing healthcare data security are designed to enforce stringent protection measures for sensitive patient information.
- In the United States, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets the national standard for data privacy and security in healthcare, particularly concerning Protected Health Information (PHI).
- In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict rules on how personal data, including health data, must be handled.
- Other significant regulations include India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP Act), the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and various industry-specific healthcare data security standards that dictate how patient data must be collected, stored, processed, and transmitted.
Adherence to these regulations is non-negotiable for any organization handling medical data security.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
How to Build a Custom Pediatric EMR and EHR System?
Key takeaways: Clinical Precision: Custom systems accommodate pediatric-specific data points like percentile curves and weight-based longitudinal dosing. Interoperability: Seamless data exchange via HL7 FHIR ensures your practice stays connected to pharmacies, labs, and state registries. Regulatory Resilience: Built-in compliance with HIPAA, HITECH, and MACRA/MIPS reduces legal friction. Enhanced Engagement: Parent portals reduce administrative overhead by…

Change Management in Healthcare: Principles, Processes, and Models
Key Takeaways Change in healthcare fails quietly when ownership, workflow alignment, and follow-through are missing. Successful change management in healthcare focuses on adoption, not just system implementation. Clinical workflows and workforce capacity determine whether transformation sticks or stalls. Governance, clear accountability, and post-go-live support matter more than the model used. Sustainable healthcare transformation depends on…

A Practical Guide to Building Your Mental Health Chatbot - Use Cases, Cost, & ROI
Key takeaways: Mental health chatbots work when they know their limits. They’re most useful as a gentle first step, not as a stand-in for real care. Good chatbot design is more about judgment than AI. Clear boundaries, calm responses, and safety matter more than smart language models. Enterprises invest in chatbots to make support easier…