- Enterprise Risk Management Frameworks, Models, Strategy
- What Enterprise Risk Management Means Today
- Common Enterprise Risk Management Framework Alignment in the U.S.
- Enterprise Risk Management and Compliance Integration
- Enterprise Security Risk Management Snapshot
- Enterprise Risk Management Strategy Considerations
- AI-Native ERM Architecture and Technology Stack
- Where Legacy ERM Platforms Start Struggling
- Core Architecture of an AI-Native Enterprise Risk Management System
- Model Governance and Explainable AI Controls
- Integration Across Enterprise Systems
- Enterprise Risk Management Process, Assessment, and Mitigation Lifecycle
- Risk Identification
- AI-Driven Risk Scoring
- Prioritization and Enterprise Risk Mitigation
- Monitoring and Reporting
- Continuous Optimization and AI Risk Oversight
- Integrated Risk Management vs Enterprise Risk Management
- Industry-Specific Enterprise Risk Management Implementations
- Enterprise Risk Management for Financial Institutions and Banking
- Enterprise Risk Management in Healthcare
- Enterprise Risk Management for Insurance Companies
- Enterprise Risk Management in Manufacturing
- Third-Party AI and Vendor Risk
- Real Life Enterprise Risk Management Examples
- ExxonMobil Enterprise Risk Governance
- Toyota Supply Chain and Operational Risk Management
- JPMorgan Cyber Risk Response
- Benefits of Enterprise Risk Management
- KPIs That Signal ERM Effectiveness
- Implementation Roadmap and Governance
- Phase 1: Risk Maturity Assessment
- Phase 2: Architecture and Framework Selection
- Phase 3: Deployment and Integration
- Phase 4: Continuous Optimization
- Governance Elements That Cut Across All Phases
- Role Evolution: The Modern Enterprise Risk Manager
- From Compliance Oversight to Resilience Thinking
- AI Awareness Is Becoming Practical
- Cross-Team Coordination Is Now Routine
- Governance Still Matters, Just Broader
- Future Outlook: ERM as Enterprise Resilience Infrastructure
- Why Appinventiv for Enterprise Risk Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Takeaways
- Enterprise risk management is shifting from periodic reporting toward continuous operational risk visibility.
- Integrated risk data improves decision speed, readiness for compliance, and overall business resilience.
- Governance alignment and data integration strengthen the effectiveness of enterprise risk management in complex environments.
- Industry-specific ERM approaches help address regulatory, operational, and technology-driven risk exposure.
- Structured ERM strategy supports resilience, compliance, stability, and more confident enterprise decision-making.
If you work around enterprise risk long enough, you start noticing when the usual processes stop keeping up. A new AI vendor gets approved, security requests updated controls, and compliance reviews often reveal risk data scattered across multiple systems. Risk is no longer limited to finance or operations. AI adoption, cyber threats, third-party dependencies, and tighter regulations have expanded the scope, while traditional ERM approaches built for slower cycles still rely heavily on static reporting.
That is where enterprise risk management is evolving. The focus is shifting from documenting risks after the fact to spotting signals early through continuous monitoring, shared data layers, and AI-assisted analytics. Risk dashboards now influence investment timing, compliance insights shape product decisions, and automated alerts highlight emerging exposure, making ERM part of business planning rather than just a reporting function.
Market projected to reach $7.76 billion by 2030 at 8.6% CAGR
Enterprise Risk Management Frameworks, Models, Strategy
When risk conversations start scaling across teams, definitions suddenly matter. Finance, IT security, compliance, and governance teams often use similar terms but mean different things. That clarity is becoming more important as enterprise risk management adoption grows.
In fact, the global ERM market is expected to reach about $7.76 billion by 2030, expanding at roughly an 8.6 percent CAGR. Clearing up terminology early keeps your enterprise risk management efforts practical instead of theoretical.
What Enterprise Risk Management Means Today
Enterprise risk management is less about static documentation and more about ongoing visibility. Most U.S. enterprises now treat ERM as a decision support capability.
You are typically managing risks across:
- Cybersecurity and AI adoption challenges
- Regulatory compliance and reporting
- Third-party vendor exposure
- Operational resilience and business continuity
- Data governance and privacy
This broader scope explains the growing importance of enterprise risk management at the executive level.
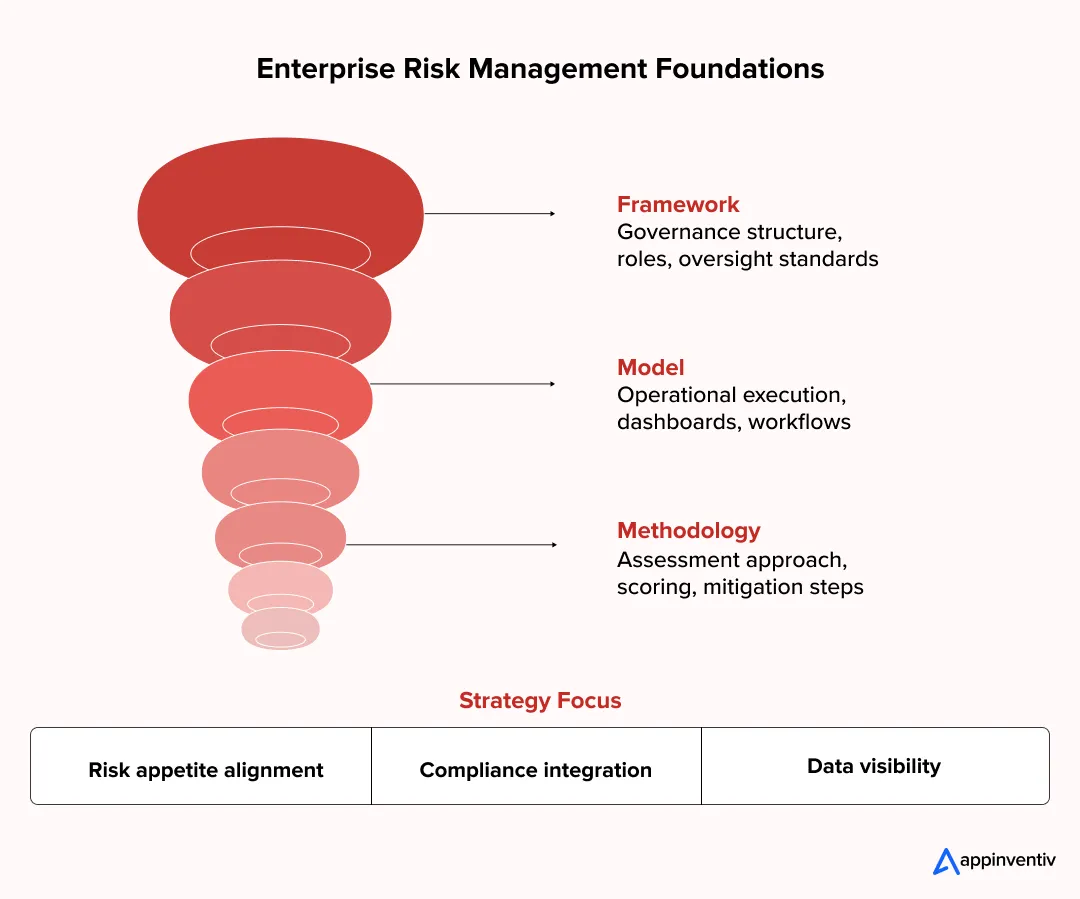
Framework vs Model vs Methodology (Quick Clarity)
| Term | What It Covers | Practical Example |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Risk Management Framework | Governance structure and oversight principles | COSO structure defining risk ownership and reporting |
| Enterprise Risk Management Model | How the framework runs operationally | Risk dashboards, scoring systems, workflows |
| Enterprise Risk Management Methodology | Day-to-day execution approach | Assessment frequency, scoring logic, mitigation steps |
You rarely choose just one. Mature programs align all three.
Common Enterprise Risk Management Framework Alignment in the U.S.
Most enterprises combine multiple standards:
- COSO for governance and enterprise reporting alignment
- ISO 31000 for international consistency
- NIST AI RMF for AI and technology risk governance
This layered approach keeps ERM relevant as risks evolve.
Enterprise Risk Management and Compliance Integration
Compliance used to run separately. That separation is fading.
Integration usually means:
- Shared risk data pipelines
- Automated regulatory reporting
- Unified audit visibility
- Continuous monitoring instead of periodic checks
It reduces duplication and strengthens accountability.
Enterprise Security Risk Management Snapshot
Security risk now sits inside the broader ERM strategy.
Key focus areas include:
- Cloud identity and access risks
- AI model security exposure
- Vendor and supply chain risks
- Data protection governance
When enterprise security risk management connects properly with ERM, leadership gets a clearer, real-time risk picture instead of fragmented reports.
Also Read: Why Enterprise Application Security is Mission Critical and How to Get it Right
Enterprise Risk Management Strategy Considerations
When organizations talk about enterprise risk management strategy, the focus usually shifts from reporting risks to shaping how the business responds to uncertainty. The goal is alignment. Risk visibility should support decisions, not slow them down.
Common strategic considerations include:
- Defining risk appetite so leadership knows acceptable exposure levels
- Aligning governance with regulatory expectations and business priorities
- Integrating risk data with operational and technology platforms through AI in data governance practices
- Building resilience into digital transformation initiatives
- Establishing clear accountability across business, security, and compliance teams
When these elements stay connected, enterprise risk management becomes a planning tool rather than just a compliance exercise.
AI-Native ERM Architecture and Technology Stack
Most enterprises do not rethink risk architecture until something exposes a gap. Sometimes it is a compliance review. Other times, an AI rollout moves faster than governance. One financial services team I worked with discovered during a SOX prep cycle that risk data was split across security logs, vendor spreadsheets, and a GRC tool.
Nothing failed outright, yet leadership lacked a reliable picture. That scenario is pushing many organizations toward AI-native enterprise risk management technology.
Where Legacy ERM Platforms Start Struggling
Older ERM setups still support governance, but they often show strain when risk becomes continuous:
- Batch reporting instead of real-time visibility
- Siloed operational, cyber, and compliance data across legacy systems without modern data warehouse capabilities
- Limited predictive analytics capability
- Manual compliance evidence gathering
- Weak integration with modern AI and cloud ecosystems
That is why newer enterprise risk management solutions emphasize data flow and automation first.
Core Architecture of an AI-Native Enterprise Risk Management System
Defines how risk data, analytics, compliance workflows, and reporting systems connect for continuous enterprise architecture visibility.
1. Risk Telemetry Data Pipelines
Modern ERM relies on steady risk data movement.
Typical elements include:
- Event-driven ingestion from cloud logs, security tools, ERP systems
- API-first integration with vendor and operational platforms
- Streaming pipelines such as Kafka or cloud-native equivalents
- Data lineage tracking to preserve auditability
This creates a unified risk data strategy fabric rather than isolated reports.
2. AI and ML Risk Analytics Engines
This layer turns raw signals into foresight.
Common capabilities:
- Predictive risk scoring models
- Scenario simulations for operational and financial exposure
- Drift detection for AI models impacting business workflows
- MLOps pipelines for validation, retraining, and monitoring
These engines move enterprise risk management systems from reactive reporting toward early warning intelligence.
3. Compliance Automation Layer
Compliance now intersects directly with ERM.
Typical automation includes:
- Continuous control monitoring aligned with SOX, HIPAA, FFIEC, or NIST guidance
- Automated regulatory mapping across jurisdictions
- Evidence collection workflows for audits through content management systems
- Policy enforcement integrated with IT systems
This tightens enterprise risk management and compliance alignment while reducing manual overhead.
4. Executive Intelligence Dashboards
Leadership rarely needs raw risk data.
Effective dashboards focus on:
- Real-time enterprise risk posture
- Cross-domain risk correlation
- Risk appetite threshold alerts
- Decision-ready summaries for executives
This is often where IT enterprise risk management becomes visible at the board level through business intelligence dashboards.
Model Governance and Explainable AI Controls
Ensures transparency, accountability, and audit-readiness when AI models influence enterprise risk monitoring and decision-making.
Model governance typically covers:
- Central model registries tracking ownership and lifecycle status, especially for private AI deployments
- Model cards documenting datasets, assumptions, and validation history
- Version control with audit trails
- Human review checkpoints for high-impact decisions
Explainability practices often include:
- Feature attribution reporting
- Data provenance tracking
- Transparent scoring documentation
These controls support regulatory readiness and internal trust.
Also Read: How Explainable AI can Unlock Accountable and Ethical Development of Artificial Intelligence
Integration Across Enterprise Systems
An AI-native enterprise risk management system rarely stands alone. It connects ERM with operational, security, compliance, and business platforms to maintain consistent risk visibility.
Integration usually spans:
- ERP platforms for the financial risk context
- GRC tools for governance workflows
- Cybersecurity platforms aligned with zero trust principles
- Identity governance systems monitor access risk
- Cloud infrastructure telemetry feeds
When these connections work well through emerging technologies integration, enterprise risk management technology stops acting like a reporting tool and starts functioning as a decision infrastructure
Enterprise Risk Management Process, Assessment, and Mitigation Lifecycle
Risk management rarely follows a neat calendar anymore. A vendor update, a new AI deployment, or even a regulatory notice can shift priorities quickly. That is why the modern enterprise risk management process works best as a continuous lifecycle instead of a scheduled exercise.
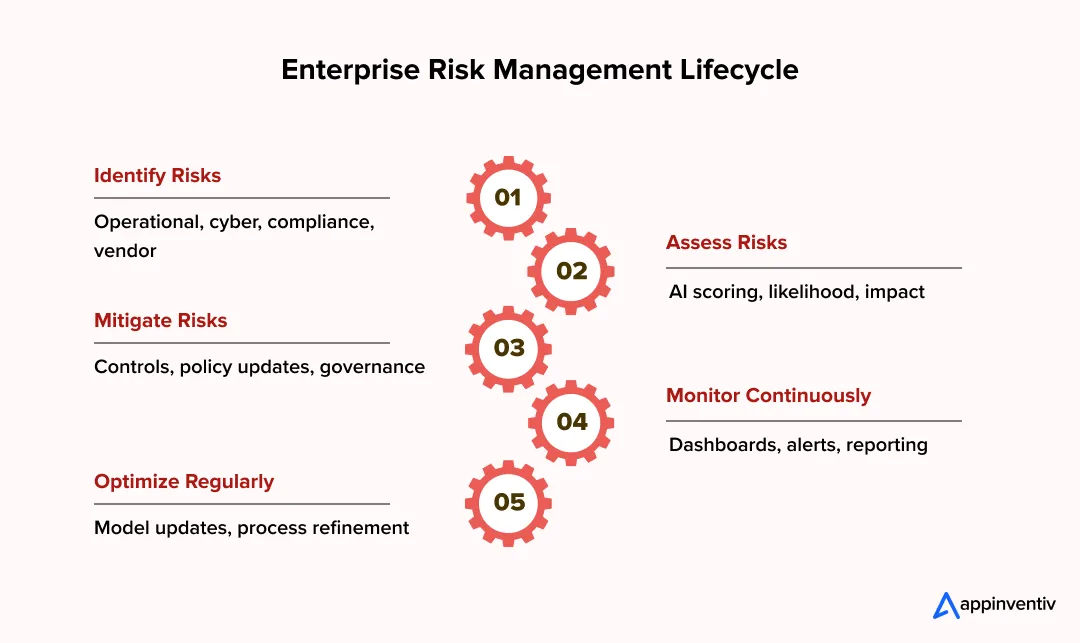
Risk Identification
Continuous enterprise risk assessment gathers signals across systems so emerging risks surface early rather than after impact.
Typical inputs include:
- Security telemetry and cloud infrastructure logs
- AI model performance data and usage patterns
- Vendor and third-party risk signals
- Compliance and regulatory updates
- Operational system alerts
Many enterprises automate ingestion pipelines so risk visibility stays current.
AI-Driven Risk Scoring
AI-driven scoring evaluates likelihood and impact quickly, helping leadership prioritize risks using real-time predictive intelligence as part of their overall AI strategy.
AI-driven scoring usually involves:
- Predictive analytics estimating risk probability
- Behavioral anomaly detection
- Scenario simulations for operational exposure
- Automated classification aligned with risk appetite
This step prevents teams from reacting equally to every risk signal.
Prioritization and Enterprise Risk Mitigation
Enterprise risk mitigation focuses on reducing exposure through controls, policies, and operational adjustments without slowing business progress.
Common mitigation approaches include:
- Control implementation and policy refinement
- Vendor access restrictions or contract adjustments
- Infrastructure hardening and identity governance updates
- AI model guardrails and usage governance
Clear ownership keeps mitigation practical and accountable.
Monitoring and Reporting
Continuous monitoring ensures risk visibility remains operational, supporting timely decisions rather than delayed retrospective reporting.
Monitoring typically includes:
- Real-time risk posture dashboards
- Automated compliance reporting workflows
- Exception alerts tied to governance thresholds
- Executive summaries for leadership oversight
- Software audit documentation
This keeps risk insight actionable across departments.
Continuous Optimization and AI Risk Oversight
Continuous optimization strengthens the enterprise risk management process by adapting controls, analytics, and governance as risks evolve.
Key technical practices include:
MLOps Risk Monitoring
- Model drift detection affecting predictions or decisions
- Data quality validation across ingestion pipelines
- Continuous retraining pipelines maintain accuracy
Also Read: Unleashing the power of custom MLOps platforms – Why and how must enterprises build one
Adversarial Testing and Incident Response
- AI stress testing for bias or manipulation risks
- Incident response playbooks aligned with cybersecurity protocols
- Audit documentation supporting regulatory readiness
These practices help organizations shift from reactive risk response to proactive risk intelligence.
Continuous monitoring helps align governance, analytics, and operational risk visibility
Integrated Risk Management vs Enterprise Risk Management
This question comes up once organizations start layering AI, cloud platforms, and multiple compliance requirements on top of existing risk programs. What worked when risks were mostly operational or financial can feel fragmented today. That is usually when the conversation shifts toward integrated enterprise risk management.
Both approaches aim to improve visibility. The difference mostly shows up in how connected the data, tools, and governance processes become.
| Area | Enterprise Risk Management | Integrated Risk Management |
|---|---|---|
| Main Goal | Enterprise-level risk oversight | Connected, cross-domain risk visibility |
| Data Flow | Often departmental or periodic | Continuous, shared across systems |
| Tech Role | Reporting and governance support | Centralized analytics and automation |
| When It Fits | Stable governance environments | AI-heavy, multi-platform enterprises |
| Governance Impact | Executive reporting focus | Ongoing operational coordination |
In practice, integrated risk management rarely replaces enterprise risk management. It usually grows out of it once technology, compliance, and operational risks start overlapping more closely.
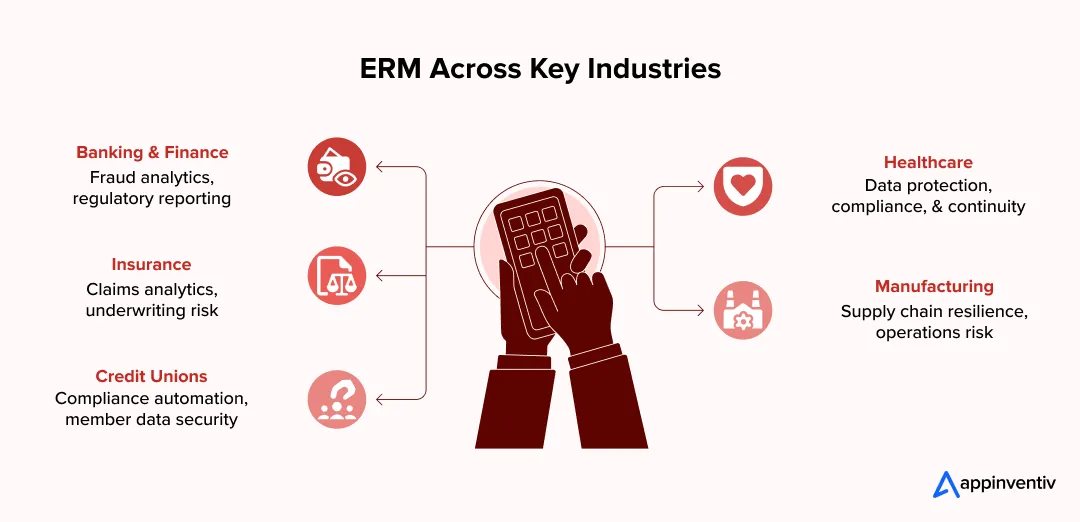
Industry-Specific Enterprise Risk Management Implementations
If you sit in enough risk review meetings, one thing becomes obvious quickly. The concerns change depending on the industry. A banking team might spend an hour reviewing transaction anomalies.
Meanwhile, a hospital risk lead worries about patient data access logs, and a manufacturer tracks supplier delays that could stop production next week. Same enterprise risk management goal, very different priorities.
Enterprise Risk Management for Financial Institutions and Banking
Banking risk programs usually revolve around regulation and fraud exposure. Reporting requirements are strict, and even small anomalies get attention.
You will often see:
- Transaction monitoring tied to fraud analytics, financial analytics for risk modeling
- Automated regulatory reporting workflows
- Credit exposure modeling
- Vendor and fintech partnership oversight
That is why enterprise risk management in banking and finance tends to invest early in predictive analytics.
Enterprise Risk Management in Healthcare
Healthcare teams often talk about reliability and privacy in the same sentence. Clinical systems need uptime, and patient data protection is non-negotiable.
Common priorities:
- HIPAA-aligned data risk monitoring
- Cybersecurity visibility across clinical platforms
- Vendor technology risk checks
- AI governance for clinical support tools
Enterprise risk management in healthcare usually blends compliance with operational continuity, supported by robust healthcare software development practices.
Enterprise Risk Management for Insurance Companies
Insurance risk conversations often circle back to underwriting accuracy and claims integrity. Small data shifts can ripple financially over time.
Typical focus areas:
- Claims fraud analytics
- Underwriting risk modeling
- Regulatory reporting automation
- Third-party data provider evaluation
Enterprise risk management for insurance companies increasingly relies on analytics maturity and emerging solutions like smart contracts in insurance.
Enterprise Risk Management in Manufacturing
Manufacturing risk tends to surface when supply chains tighten or manufacturing ERP systems slow down. One delayed component can impact production schedules.
Common priorities:
- Supplier continuity monitoring
- Operational cybersecurity oversight
- Production disruption forecasting
- Regulatory and sustainability tracking
That makes enterprise risk management manufacturing programs heavily resilience-focused.
Enterprise Risk Management for Credit Unions
Credit unions face many banking-style regulations, but often operate with leaner teams.
Typical areas of focus:
- Compliance reporting automation
- Member data security monitoring
- Fraud analytics
- Vendor partnership risk evaluation
Enterprise risk management for credit unions usually aims for efficiency without sacrificing oversight.
Third-Party AI and Vendor Risk
AI adoption has added another consideration. Many enterprises now depend on external AI vendors or data providers.
Risk teams increasingly check:
- Training data transparency
- Data lineage clarity
- Contract accountability for AI outputs
- Ongoing vendor performance signals
Across industries, enterprise risk management is slowly expanding beyond internal operations toward ecosystem risk visibility.
Real Life Enterprise Risk Management Examples
Sometimes enterprise risk management feels abstract until you see how companies actually use it. Large organizations rarely implement ERM all at once. It usually evolves after a disruption, a regulatory shift, or a major operational challenge. These real examples help show how ERM plays out in practice.
ExxonMobil Enterprise Risk Governance
ExxonMobil applies enterprise risk management across different business units with a focus on structured risk identification, prioritization, and governance coordination. The aim is consistency. Operational, financial, and regulatory risks are tracked systematically so leadership gets a clearer picture when making decisions.
Toyota Supply Chain and Operational Risk Management
Toyota strengthened its risk oversight after recalls and natural disasters disrupted production. The company increased supplier monitoring, improved operational controls, and invested in stronger planning processes to stabilize operations and reduce future disruption risk.
JPMorgan Cyber Risk Response
After a large data breach affecting millions of customers, JPMorgan tightened authentication controls, improved monitoring, and strengthened coordination across risk and security teams. The focus shifted toward earlier detection and stronger governance alignment.
These enterprise risk management examples show how organizations often move from reactive fixes toward more structured and continuous risk visibility over time.
Benefits of Enterprise Risk Management
You usually notice the value of enterprise risk management when something changes fast. A new AI tool gets introduced, a compliance review tightens expectations, or a vendor issue suddenly affects operations. Teams with mature ERM rarely panic in those moments. They already have visibility, ownership, and response plans in place.
Organizations getting consistent results usually focus on a few fundamentals. These enterprise risk management best practices often turn ERM from a reporting function into a planning tool.
- Predictive risk intelligence: AI-assisted analytics help surface risk patterns early instead of after exposure grows.
- Faster compliance readiness: Automated reporting and control monitoring reduce last-minute audit preparation.
- Improved operational resilience: Early warning signals allow teams to adjust before disruptions escalate.
- Stronger decision velocity: Leadership makes decisions faster when risk data is reliable and current, similar to the benefits seen in enterprise CRM use cases.
- Governance-first architecture: Clear ownership, escalation paths, and reporting structure prevent confusion later.
- Explainable AI adoption: Transparent models support compliance, internal trust, and audit readiness.
- Shadow AI risk control: Visibility into unsanctioned AI tool usage helps prevent data exposure.
- Enterprise AI security alignment: Risk teams coordinate closely with cybersecurity and identity governance groups.
Consistency here matters more than complexity.
KPIs That Signal ERM Effectiveness
Measuring outcomes keeps ERM grounded. Some commonly tracked indicators include:
| KPI | What It Indicates |
|---|---|
| Time to detect risk | How quickly new exposures are identified |
| Incident response latency | Speed of mitigation actions |
| Compliance automation gains | Reduction in manual audit preparation |
| Risk reporting cycle time | Operational visibility maturity |
These metrics help leadership see whether enterprise risk management is improving resilience or just generating reports.
Implementation Roadmap and Governance
Rolling out enterprise risk management rarely starts with a grand transformation plan. It often begins when teams notice risk data living in too many places. Someone pulls numbers from a security dashboard, another from a compliance tool, and leadership still lacks a clear view. That disconnect usually pushes organizations toward a more deliberate enterprise risk management strategy.
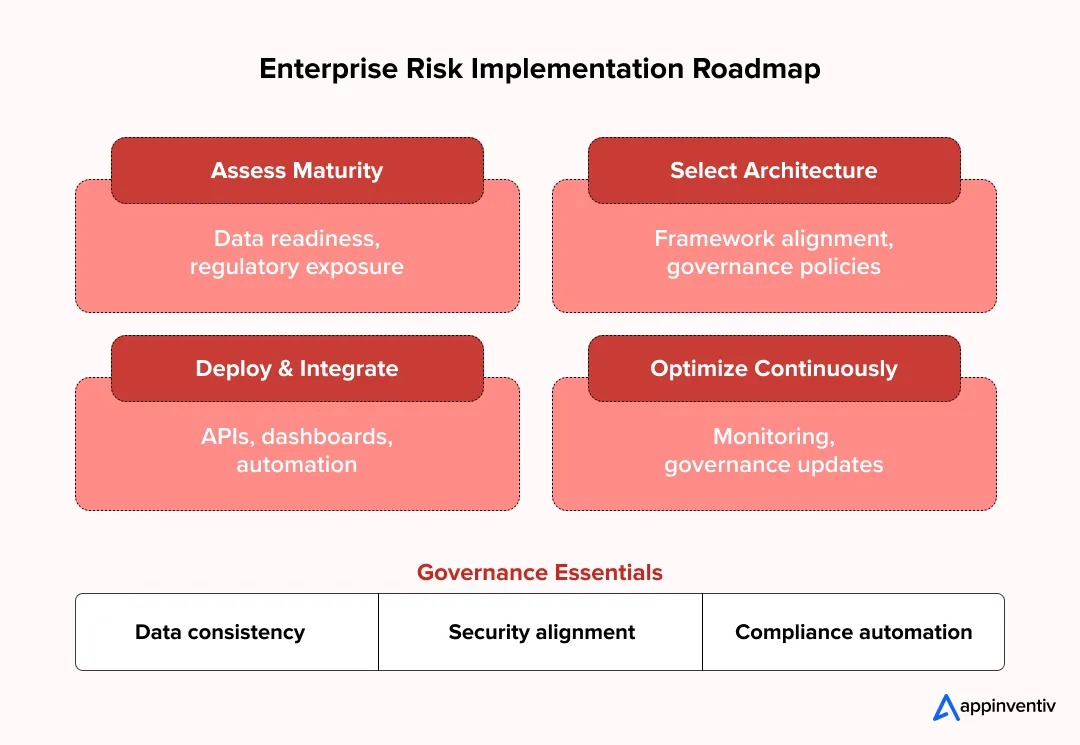
Phase 1: Risk Maturity Assessment
Before introducing new platforms, most teams take stock of what already exists. This tends to reveal both strengths and hidden gaps.
Typical focus areas:
- Where risk data currently sits, ERP systems, security logs, and GRC tools
- Data quality and lineage visibility
- Existing regulatory obligations, such as SOX or HIPAA
- Integration readiness across business systems
- Current analytics or AI usage in risk monitoring
This stage prevents unnecessary tool expansion.
Phase 2: Architecture and Framework Selection
Once visibility improves, architecture choices become clearer. Enterprise risk management framework selection also matters here because governance expectations differ across industries.
Common considerations:
- Whether a cloud-native or a hybrid deployment fits better
- Alignment with COSO, NIST, or internal governance standards
- Identity access governance and security alignment
- AI oversight policies, including model accountability
- Integration feasibility with operational platforms
These decisions shape long-term scalability.
Phase 3: Deployment and Integration
Deployment works best when it stays incremental. Many organizations start with a pilot, often in a high-risk business function.
You will typically see:
- API integrations with ERP, GRC, and cybersecurity systems
- Automated compliance reporting workflows
- Real-time telemetry ingestion from operational platforms
- Executive dashboards are gradually replacing static reports
Adoption tends to improve when business teams see immediate visibility benefits.
Phase 4: Continuous Optimization
Risk environments rarely stay stable. AI models change, vendors shift, and regulations evolve. Continuous adjustment becomes part of normal operations.
Teams often focus on:
- Monitoring analytics accuracy and model drift
- Improving data consistency across pipelines
- Updating governance policies as regulations shift
- Expanding automation where manual effort remains high
Over time, this steady refinement is what makes enterprise risk management solutions sustainable.
Governance Elements That Cut Across All Phases
Some fundamentals remain constant regardless of the maturity stage:
- Clear ownership and escalation paths
- Consistent risk data governance practices
- Security alignment across identity, infrastructure, and cloud
- Continuous compliance monitoring instead of periodic audits
When these basics stay intact, enterprise risk management usually shifts from reactive reporting toward proactive decision support.
Organizations exploring enterprise risk maturity often look for proof that governance and technology alignment work in practice. In one automotive transformation engagement, Appinventiv partnered with a global manufacturer to unify fragmented data systems, establish centralized governance, and modernize analytics infrastructure, enabling more consistent visibility, faster deployment cycles, and improved operational coordination across regions.
Role Evolution: The Modern Enterprise Risk Manager
Talk to someone who has been in enterprise risk for ten years, and they will tell you the job feels different now. It used to revolve around audit prep, policy reviews, and quarterly reports. Those tasks still exist. But the conversation increasingly shifts toward how risk affects day-to-day business decisions, especially with AI systems, cloud platforms, and automated workflows becoming normal.
From Compliance Oversight to Resilience Thinking
Many enterprise risk managers now spend time interpreting signals rather than just documenting them.
That can mean:
- Looking at security alerts alongside operational metrics
- Understanding how predictive risk scores are generated
- Joining discussions about system reliability or vendor exposure
- Translating technical findings for leadership
The emphasis moves toward anticipation rather than documentation.
AI Awareness Is Becoming Practical
You do not need to build machine learning models. Still, knowing how they behave helps.
Typical touchpoints include:
- Reviewing model performance dashboards
- Asking where the training data came from
- Checking whether automated decisions remain traceable
- Evaluating external AI vendors before adoption
It is less about deep data science, more about informed oversight.
Cross-Team Coordination Is Now Routine
Risk rarely sits neatly in one function anymore.
Enterprise risk managers often interact with:
- Cybersecurity teams reviewing infrastructure risks
- Data teams maintaining reporting pipelines
- Legal and compliance groups handling regulation
- Vendor management teams tracking external exposure
That coordination usually improves visibility.
Governance Still Matters, Just Broader
Reporting standards, regulatory alignment, escalation paths, those fundamentals remain. What changed is the context. Risk managers now interpret technical signals, support resilience planning, and help ensure governance keeps pace with how modern enterprises actually operate.
Align architecture, governance, and compliance before scaling enterprise risk initiatives
Future Outlook: ERM as Enterprise Resilience Infrastructure
Risk management is slowly becoming part of everyday operations instead of something teams review once a quarter. As AI systems, cloud platforms, and compliance expectations expand, ERM is starting to look more like operational infrastructure than a reporting function.
Trends you will likely see shaping enterprise risk management:
- More organizations are using continuous monitoring instead of periodic risk assessments
- AI governance requirements are getting clearer across U.S. regulatory bodies
- Risk data flowing directly into operational dashboards, not separate reports
- Greater attention on third-party AI vendors and data provenance
- Predictive analytics helps teams spot operational disruptions earlier
- Closer coordination between cybersecurity, compliance, and business operations
- Risk visibility is increasingly tied to resilience planning rather than audit preparation
For many enterprises, ERM is gradually shifting from documentation toward anticipation.
Also Read: Why Appinventiv is an Ideal Choice for Enterprise Software Development
Why Appinventiv for Enterprise Risk Management
Choosing the right consulting partner often comes down to one question. Can they translate complex risk signals into practical business outcomes? That balance between technical depth and execution is where many enterprises look for outside support.
Appinventiv has worked across regulated industries where risk, compliance, and technology intersect closely. The focus typically stays on building scalable enterprise risk management solutions while keeping governance, security, and operational continuity aligned.
Many organizations also engage their broader IT consulting services when aligning risk architecture with enterprise technology ecosystems.
Consulting scale and expertise at a glance:
- 2000+ strategy and transformation projects delivered
- 24/7 advisory support across global engagements
- 8+ global consulting partnerships
- 1600+ tech evangelists across engineering and advisory roles
- 15+ global recognitions and industry awards
- Experience spanning 35+ industries
Typical business impact clients report:
- Around 30% average revenue growth supported through consulting initiatives
- Up to 2x faster go-to-market for technology-driven programs
- Approximately 98% ROI reported from consulting engagements
Enterprises working on AI-native ERM initiatives often look for structured governance, technical integration support, and measurable outcomes. The approach usually combines risk strategy alignment, architecture design, and ongoing advisory support so risk management evolves alongside business priorities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is the role of an enterprise risk manager?
A. An enterprise risk manager helps your organization spot, assess, and respond to risks before they disrupt operations. The role now goes beyond compliance reporting. It often includes interpreting data signals, coordinating across departments, supporting governance decisions, and ensuring risk insights inform strategy, security posture, and operational resilience planning.
Q. What is the difference between an ERM framework and an ERM model?
A. An ERM framework defines governance structure, roles, and risk oversight principles. An ERM model focuses on how that framework works in practice, including scoring methods, reporting workflows, and analytics tools. Simply put, the framework sets direction, while the model reflects day-to-day execution within your enterprise.
Q. How often should enterprise risk assessments be performed?
A. Most organizations still conduct formal assessments annually or quarterly. Still, many are moving toward continuous monitoring using automated dashboards and analytics. If your environment involves AI, cloud platforms, or strict regulations, ongoing assessment usually provides better visibility than periodic reviews alone.
Q. How does ERM help organizations meet regulatory requirements?
A. ERM centralizes risk data, compliance reporting, and control monitoring so audits become more manageable. It helps track regulatory obligations, automate documentation, and identify gaps early. When risk governance stays consistent, organizations usually respond faster to changing regulations and reduce last-minute compliance pressure.
Q. What strategic approaches help risk leaders strengthen ERM?
A. Risk leaders, including chief risk officers, often focus on continuous monitoring, alignment with leading standards, and enterprise resilience management practices. Priorities usually include managing AI risks, strengthening cyber resilience strategies, refining incident response plans, supporting internal audit coordination, and using executive dashboards, resilience reporting, and risk and resilience indicators to reinforce strategic resiliency.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Turning Legacy Data into Business Intelligence: A Food Chain’s Success Story
When you walk into a food outlet and place an order, it looks simple: swipe your card, grab your meal, and go. But behind every order lies a stream of valuable data. Now, imagine this happening across hundreds of stores spread across multiple countries, with each outlet running several POS (Point of Sale) systems. That’s…

Building a Robust Enterprise Data Strategy - Benefits, Use Cases, Process, Costs & Best Practices
Key takeaways: A solid enterprise data strategy removes silos, reduces costs, and restores confidence in decisions. AI initiatives only succeed when built on reliable, well-governed enterprise data foundations. Executives, employees, and customers gain through faster insights and personalized experiences. The roadmap starts with goal alignment, audits, future vision, and phased execution. Industries see measurable ROI:…

Why Enterprise Application Security is Mission Critical and How to Get it Right
Key takeaways: Enterprise applications are increasingly complex, spanning cloud-native architectures, APIs, and third-party integrations, which broadens the attack surface. Adopting DevSecOps and embedding security early in the development lifecycle reduces breach impacts by up to 30%, proving proactive security integration is vital. Regulatory compliance, business continuity, and customer trust hinge on effective application security strategies…