- What Digital Transformation in Banking Really Means
- Difference between basic digitization and true transformation
- What Are the Core Pillars Driving Banking Transformation?
- What Is Driving Digital Transformation in Banking Today?
- Demand for Faster, Frictionless Business Transactions
- Regulatory Pressure and the Push to Digitize Compliance
- Competition From Fintech and Digital-First Banks
- The Need for Cost Efficiency and Scalable Operations
- What Technologies Are Actually Powering Digital Banking Today?
- Cloud-Based Banking Infrastructure
- API-Driven Ecosystems and Open Banking
- AI and Data Analytics in Decision Making
- Automation and Workflow Digitization
- Digital KYC and Identity Verification
- Cybersecurity and Identity Management
- 5G Connectivity and Real-Time Banking Experiences
- How Does Digital Banking Impact Businesses From Day One?
- Faster Onboarding and Account Management
- Improved Access to Credit and Financing
- Real Time Payments and Cash Flow Visibility
- Better Treasury, Reporting, and Reconciliation
- Reduced Dependency on Physical Branches
- How Can Banks Drive Effective Digital Change in the Banking Sector?
- Anchor Digital Initiatives to Clear Business Outcomes
- Modernize in Phases, Not Through Big-Bang Replacements
- Build Ownership Beyond the IT Function
- Embed Risk and Compliance Into the Change Process
- Invest in Skills, Not Just Systems
- Measure Progress Through Operational Impact
- What Are the Long Term Benefits of Digital Transformation in Banking?
- Improved Operational Efficiency
- Better Financial Control and Forecasting
- Enhanced Customer and Vendor Experiences
- Lower Transaction and Processing Costs
- Scalable Banking Support for Growing Enterprises
- What Are the Real Challenges of Digital Transformation in Banking, and How Do Banks Get Past Them?
- Legacy Systems That Slow Everything Down
- Data That Does Not Agree With Itself
- Security and Regulatory Pressure That Never Eases
- People Struggling to Keep Up With Change
- Costs That Rise Before Value Is Obvious
- Getting Too Tied to One Vendor
- Top Examples of Digital Transformation Solutions in Modern Banking
- Mobile Banking Apps
- Data Analytics Solutions
- AI-Powered Chatbots
- Neobanks and Digital-Only Banking
- Robo-Advisors
- Biometric Authentication
- How Does Digital Banking Impact Businesses From Startups to Enterprises?
- SMEs and Startups
- Mid-Market Enterprises
- Large Enterprises and Global Corporations
- Why Business Size Changes the Impact
- What Does the Future of Digital Transformation in Banking Look Like?
- How Appinventiv Can Support Your Digital Transformation in Banking
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- Digital transformation in banking now defines how fast and reliably businesses operate.
- Modern banking is built on real-time systems, automation, and deep integration, not just digital channels.
- Businesses benefit through faster onboarding, better cash visibility, and fewer manual processes.
- Successful banking transformation is phased, outcome-driven, and designed to scale under regulation.
Digital transformation in banking no longer sits on a roadmap for the future. It is already shaping how businesses move money, manage risk, and plan growth. Today, banks that have modernized their platforms are not just faster. They operate differently. Decisions happen in real time. Services plug directly into business systems. Financial operations feel less like a bottleneck and more like an enabler.
McKinsey’s latest banking research highlights how quickly this shift is accelerating. Banks that are scaling digital and AI-driven models are seeing materially lower operating costs and stronger returns, while those holding on to legacy systems continue to lose ground. McKinsey also notes that digital capabilities are now a core driver of competitiveness in banking, not a support function.
This shift highlights the growing importance of digital transformation in banking as financial systems become core infrastructure for modern business operations.
For businesses, this matters in very practical ways. Digital transformation in banking changes how quickly companies can onboard, access credit, reconcile transactions, and integrate financial data into their wider technology stack. Digital banking transformation is no longer about better apps. It is about building financial infrastructure that can keep up with how modern businesses operate.
What Digital Transformation in Banking Really Means
Definition from a business and operational perspective
Digital transformation in banking is not simply about moving services online. From a business and operational standpoint, it refers to redesigning how banks operate, make decisions, and deliver value by embedding digital technologies across core functions. This includes payments, lending, risk management, compliance, customer servicing, and partner integrations.
For businesses, digital transformation in banking changes the role banks play. Banks shift from being transactional service providers to becoming integrated financial platforms that support real time operations, data driven decisions, and scalable growth. In the digital transformation in the banking industry, technology becomes part of the operating model, not a supporting layer.
Difference between basic digitization and true transformation
Many banks confuse digitization with transformation. The difference is structural, not cosmetic.
| Aspect | Traditional Banking | Digitally Transformed Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Core systems | Legacy, monolithic platforms | Cloud native, modular architectures |
| Processes | Manual or semi automated | End to end automated workflows |
| Decision making | Periodic, report driven | Real time, data led |
| Customer and business access | Branch and form based | API and platform based |
| Innovation speed | Slow, release driven | Continuous, scalable updates |
| Integration with business systems | Limited or custom | Native API integrations |
What Are the Core Pillars Driving Banking Transformation?
If you strip away the buzzwords, banking transformation comes down to a few hard choices. What systems get replaced, what stays. And where banks are willing to rethink how work actually gets done. These pillars are where that intent shows up.
- Modern core infrastructure: Legacy systems are slowly being phased out. Cloud ready, modular cores make change easier and outages less frequent.
- API driven ecosystems: Banking services connect directly with ERP systems and finance tools. This is central to digital transformation in corporate banking and transaction banking.
- Data and intelligence at scale: Real time data analytics in banking and AI support faster risk checks, fraud detection, and credit decisions.
- Process automation: Automation reduces delays in onboarding, compliance, payments, and reconciliation.
- Security and compliance by design: Identity controls and regulatory checks are built into workflows, not added later.
Put together, these pillars explain why digital transformation in banking is no longer treated as an IT upgrade. It changes how banks operate at a structural level and how reliably they can support businesses that expect speed, clarity, and consistency.
What Is Driving Digital Transformation in Banking Today?
Banking did not change overnight. Pressure built up slowly, then all at once. What we see now is not a trend cycle, but a response to how businesses operate, how regulation is enforced, and how competition has shifted the baseline.
This shift is not limited to banks alone. Digital transformation in BFSI is accelerating as financial institutions respond to similar pressures around speed, compliance, and operational efficiency.
Below are the factors driving digital transformation in banking:
Demand for Faster, Frictionless Business Transactions
Expectations shaped by retail banking digital transformation have carried over into business banking, where speed and ease are now baseline requirements.
- Near real time payments are becoming standard
- Cash flow visibility is expected, not optional
- Banking steps need to fit business workflows, not interrupt them
This expectation is one of the strongest forces behind digital banking transformation, especially for businesses managing high transaction volumes.
Regulatory Pressure and the Push to Digitize Compliance
Regulation is no longer periodic or static. Requirements change more often and scrutiny is continuous. Manual compliance processes struggle to keep up and increase exposure rather than reduce it.
- Regulators expect traceable, auditable data at all times
- Reporting cycles are tightening across regions
- Manual checks increase both delay and risk
This is why digital transformation in banking and financial services increasingly focuses on automating compliance rather than layering controls on top of outdated systems.
Competition From Fintech and Digital-First Banks
Fintechs did not win by offering more features. They won by removing friction. Digital transformation in FinTech showed that onboarding could be quick, integrations could be simple, and releases did not need long lead times.
- Faster setup has reset customer expectations
- API first models simplify business integrations
- Feature updates happen continuously, not annually
This shift has forced traditional players to rethink long held assumptions, accelerating digital transformation in the banking industry.
The Need for Cost Efficiency and Scalable Operations
Growth used to mean more systems, more people, and more overhead. That model does not scale well. Legacy platforms are expensive to maintain and even more expensive to expand.
- Manual work drives up operating costs
- Scaling legacy infrastructure adds complexity
- Growth without automation increases failure points
Digital transformation in the banking sector addresses this by replacing rigid systems with platforms designed to scale without matching cost increases.
Taken together, these drivers explain why digital transformation in banking is no longer framed as innovation. It is a response to reality. Banks that adapt can support modern businesses more reliably. Those that do not fall behind, quietly at first, then very quickly.
What Technologies Are Actually Powering Digital Banking Today?
When people ask how digital banking really works, they are usually not looking for a list of tools. They want to understand what sits underneath the experience. The answer comes down to a few core technologies that banks have been forced to rethink, often after years of patching old systems.
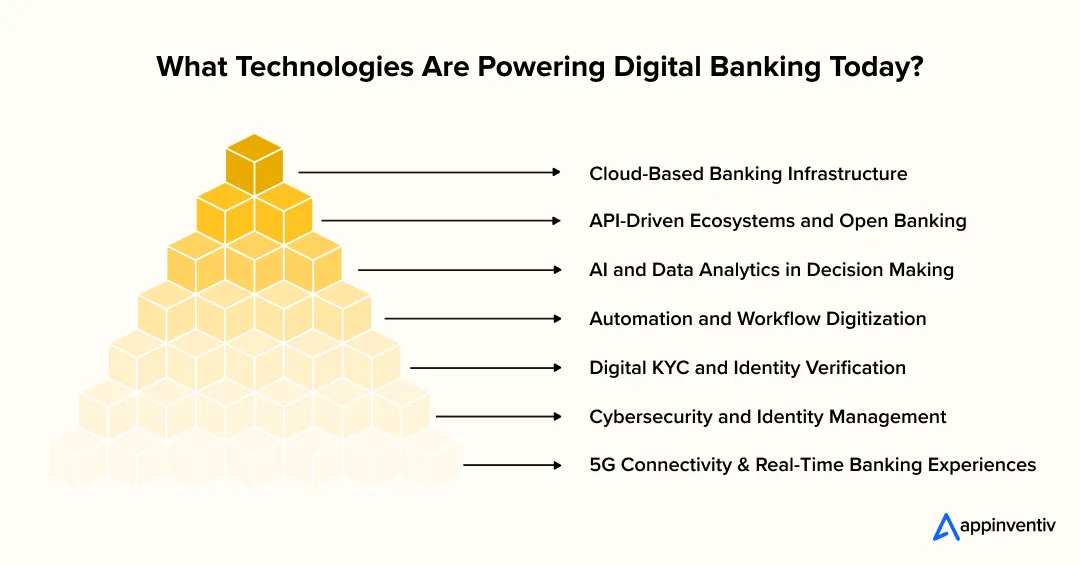
Cloud-Based Banking Infrastructure
For a long time, core banking systems were difficult to touch. Any change carried risk. Cloud infrastructure has started to change that equation. With the integration of the cloud, banks are now more open to using FinTech APIs to promote data sharing and enhance the overall experience.
- New services can be rolled out faster
- Capacity can scale during peak usage without disruption
- Maintenance becomes less dependent on large, scheduled upgrades
From a business perspective, this usually shows up as more stable platforms and fewer unexpected slowdowns.
API-Driven Ecosystems and Open Banking
Banking services connect directly with ERP systems and finance tools. This is central to digital transformation in corporate banking and digital transformation in transaction banking.
- Banking connects directly with ERP and accounting tools
- Third-party platforms can be added without heavy customization
- Data moves automatically instead of through manual exports
This shift is central to digital transformation in banking and financial services, especially where speed and integration matter more than standalone features.
AI and Data Analytics in Decision Making
Banks have always collected data. What has changed is how quickly it can be used. AI in banking now helps banks respond while situations are still unfolding, not weeks later.
- Credit decisions can be made faster and with more context
- Fraud can be flagged earlier, often before damage escalates
- Liquidity and cash positions become easier to monitor in real time
The focus moves from reporting what happened to acting on what is happening.
Automation and Workflow Digitization
Many of the delays businesses experience come from manual steps buried inside banking processes. Automation removes some of that friction.
- Onboarding and verification move faster
- Payments and reconciliation require fewer handoffs
- Errors caused by repetition and rekeying are reduced
Automation does not remove oversight. It reduces unnecessary waiting.
Digital KYC and Identity Verification
Customer verification has traditionally been one of the slowest parts of banking. Digital KYC changes that by replacing paper-heavy, manual checks with automated and data-driven verification.
- Identity checks run digitally instead of through physical documentation
- Onboarding timelines shorten without lowering compliance standards
- Ongoing verification reduces the need for repeated reviews
For businesses, this often means faster account setup and fewer interruptions once relationships are established.
Cybersecurity and Identity Management
As systems become more connected, security becomes harder to manage if it is treated as an add-on. Digitally mature banks build it into the workflow itself.
- Access is controlled through strong identity checks
- Activity is monitored continuously, not periodically
- Compliance requirements are enforced quietly in the background
Modern banks are turning to biometric authentication, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and zero-trust security models to protect sensitive financial data. Advanced threat intelligence platforms and AI agents in fraud detection are also becoming industry standards.
5G Connectivity and Real-Time Banking Experiences
Network speed is becoming an invisible but important enabler of digital banking. With 5G, real-time interactions become more reliable, especially in high-volume or mobile-heavy environments.
- Faster data transmission supports real-time payments and updates
- Mobile banking experiences become more responsive
- Latency-sensitive processes like fraud checks run more smoothly
While often overlooked, connectivity plays a growing role in making digital banking feel immediate rather than delayed.
Taken together, these technologies explain why digital banking transformation is not about a single upgrade. It is about building systems that can change, integrate, and scale without breaking under pressure.
How Does Digital Banking Impact Businesses From Day One?
The impact of digital transformation in banking is most visible in everyday business operations, where speed, visibility, and reliability matter more than abstract strategy. The changes are practical. Things move faster. Visibility improves. Dependence on manual steps reduces. Over time, these shifts compound into real operational advantages.
Faster Onboarding and Account Management
Opening or modifying a business account used to take weeks, sometimes longer if documents moved across teams. Digital banking has shortened that cycle significantly.
- Digital onboarding reduces paperwork and back and forth
- Verification happens in parallel instead of in sequence
- Account updates can be handled without branch visits
For growing companies, this speed matters. Delays at the banking layer often slow down hiring, vendor onboarding, and market expansion.
Improved Access to Credit and Financing
Access to capital is no longer based only on static financial statements. Digital banking transformation allows banks to evaluate businesses using richer, more current data.
- Faster credit decisions using real time financial signals
- More flexible financing options tied to actual cash flow
- Reduced dependency on lengthy manual reviews
This shift is especially visible in digital transformation in corporate banking, where financing needs are dynamic and time sensitive.
Real Time Payments and Cash Flow Visibility
One of the most immediate benefits businesses notice is visibility. Knowing where money is, when it will arrive, and where it is going changes how teams plan.
- Real time payment tracking replaces delayed confirmations
- Cash positions update continuously, not at day end
- Fewer surprises during reconciliation cycles
This level of transparency supports better decision making and tighter financial control.
Better Treasury, Reporting, and Reconciliation
Digital banking integrates more easily with internal finance systems, reducing manual reconciliation and fragmented reporting.
- Automated data flows into treasury and accounting tools
- Fewer manual adjustments and rekeying errors
- Faster month end and quarter end close cycles
For finance teams, this means less time spent fixing mismatches and more time spent analyzing trends.
Reduced Dependency on Physical Branches
Branch based banking still has a role, but it is no longer the default. Digital channels now handle most routine and many complex interactions.
- Services are accessible regardless of location
- Approvals and support move online instead of in person
- Banking aligns better with distributed teams and remote operations
As digital transformation in banking and financial services matures, physical presence becomes optional rather than essential.
In practice, these improvements change how finance teams work day to day. Less time is spent chasing updates or fixing mismatches, and more time goes into planning, forecasting, and supporting business decisions. Digital banking becomes part of the operating rhythm of the business, not a separate layer to work around.
Also Read: How Sustainable Banking Is Shaping the Future of FinTech
How Can Banks Drive Effective Digital Change in the Banking Sector?
Digital transformation in banking does not fail because the technology is wrong. It usually slows down because the change is treated like a project instead of a shift in how the organization operates. Banks that make real progress tend to approach digital change as an ongoing way of working, not something with a fixed end date.
Across the digital transformation in the banking sector, the banks that move forward consistently follow a few practical habits.
Anchor Digital Initiatives to Clear Business Outcomes
Many transformation efforts lose momentum when teams cannot clearly explain what is supposed to improve. Platforms get delivered, but the day-to-day impact is vague.
Banks that handle this well start with simple, concrete targets:
- Shortening onboarding time for business customers
- Improving visibility into cash positions for corporate clients
- Reducing manual effort in transaction processing
When digital transformation in banking is tied to outcomes people can see and measure, decisions become easier and priorities stay aligned.
Modernize in Phases, Not Through Big-Bang Replacements
Large-scale replacements sound efficient on paper, but they rarely work that way in practice. The risk is high, and the blast radius is wide.
Most banks that succeed take a slower, more controlled path:
- Legacy systems are opened up through APIs first
- High-friction workflows are modernized before low-impact ones
- Core components are replaced gradually, not all at once
This approach has become common in digital transformation in banking and financial services because it allows progress without putting critical operations at risk.
Build Ownership Beyond the IT Function
When digital change sits only with IT teams, it tends to stall at the handoff point. Adoption drops once systems meet real operational constraints.
Banks that move faster spread ownership wider:
- Business teams help define what “good” looks like
- Risk and compliance teams are involved early, not after build
- Operations teams validate whether workflows actually work
This shared ownership is especially important in digital transformation in corporate banking, where processes cut across many functions.
Embed Risk and Compliance Into the Change Process
Treating compliance as a final checkpoint almost always creates rework. It also slows down future releases.
Banks that avoid this bake controls into the process itself:
- Risk checks are designed into workflows
- Audit trails are generated automatically
- Compliance teams review patterns, not individual cases
Risk management strategies, including AI-driven cybersecurity, help protect the bank’s reputation and prevent regulatory issues. This approach strengthens digital transformation in banking sector programs by reducing friction between innovation and governance.
Invest in Skills, Not Just Systems
New platforms do not change much if people are unsure how to use them. Hesitation often looks like resistance, but it is usually uncertainty.
Banks that manage this invest beyond tools:
- Training focuses on real scenarios, not feature lists
- Roles and responsibilities are updated alongside systems
- Teams are encouraged to test and adjust within clear limits
As digital banking transformation deepens, these skills matter just as much as the technology.
Measure Progress Through Operational Impact
Delivery milestones look good in reports, but they do not always reflect reality on the ground.
Banks that stay on track measure things that affect daily work:
- How much faster processes run
- How often exceptions occur
- Whether automation is reducing costs and rework
These signals give a more honest view of whether digital transformation in banking industry initiatives are actually working.
Driving effective digital change in the banking sector is rarely fast, and it is never linear. The banks that make it stick focus less on perfect plans and more on steady improvement, adjusting as they go while keeping outcomes in sight.
What Are the Long Term Benefits of Digital Transformation in Banking?
The real benefits of digital transformation in banking are rarely dramatic on day one. They show up gradually, in fewer delays, cleaner processes, and decisions that feel less reactive. Over time, these small improvements start changing how businesses run their financial operations.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Most finance teams spend more time managing processes than they want to admit. Digital banking removes some of that drag by reducing manual work across everyday tasks.
- Routine actions move faster with fewer handoffs
- Less time is spent chasing approvals or updates
- Teams deal with fewer exceptions and follow ups
Efficiency here is not about working harder. It is about removing steps that never needed to exist.
Better Financial Control and Forecasting
When financial data updates slowly, planning becomes guesswork. Digital banking shortens that gap and gives teams a clearer picture of where things stand.
- Cash positions are easier to track as they change
- Forecasts rely on current signals, not old reports
- Potential issues surface earlier, not at the last minute
This helps leaders plan with more confidence, especially during periods of uncertainty or growth.
Enhanced Customer and Vendor Experiences
Banking processes sit quietly in the background, until something goes wrong. Late payments, unclear confirmations, or reconciliation issues often spill over into customer and vendor relationships.
- Vendors get paid on time, more consistently
- Customers face fewer billing or settlement delays
- Disputes reduce as records become clearer
When financial operations run smoothly, external relationships tend to follow.
Lower Transaction and Processing Costs
Costs tied to banking operations are often hidden inside manual effort. Digital workflows reduce the need for rework and repeated checks.
- Automation cuts processing overhead
- Errors and corrections become less frequent
- Volume grows without the same cost increase
Savings here are incremental, but they add up over time.
Scalable Banking Support for Growing Enterprises
As businesses grow, complexity increases. More accounts, more users, more transactions. Digital banking platforms are built to handle that change without constant restructuring.
- New markets and teams can be added with less friction
- Higher transaction volumes are easier to manage
- Banking systems keep pace with expansion
Instead of slowing growth, banking becomes something businesses can rely on to scale quietly in the background.
Rather than transforming everything at once, these benefits change how financial work feels day to day. Fewer interruptions. Clearer information. And systems that support the business without demanding constant attention.
What Are the Real Challenges of Digital Transformation in Banking, and How Do Banks Get Past Them?
The challenges of digital transformation in banking usually do not show up in the proposal phase. They appear later, when systems start interacting, timelines stretch, and teams feel the impact of change in their daily work. Most banks face the same issues. What differs is how they respond once those issues surface.
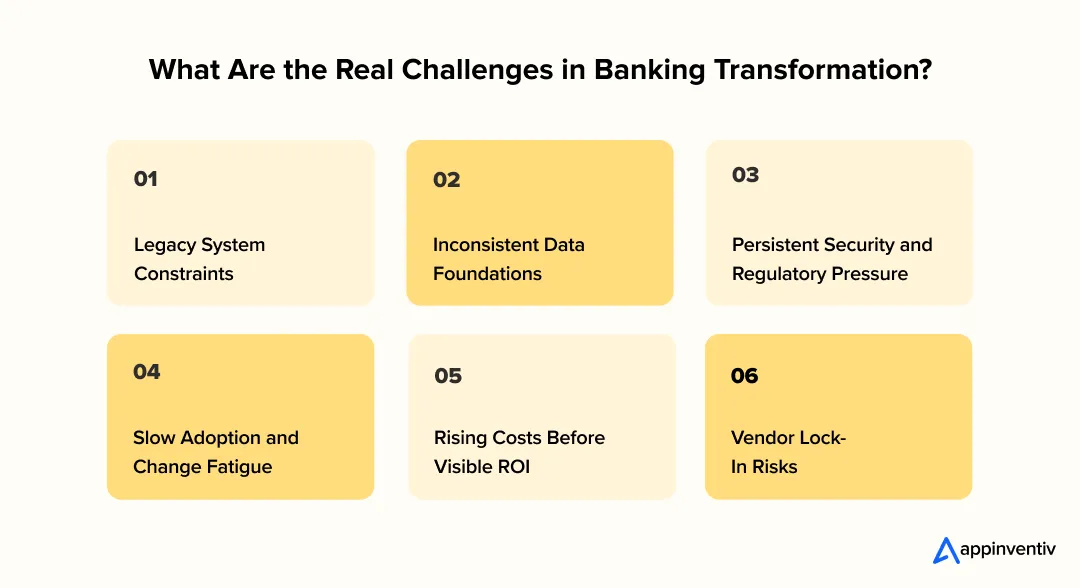
Legacy Systems That Slow Everything Down
One of the biggest challenges of digital transformation in banking is dealing with legacy cores that were never designed to change quickly. These systems still run critical operations, which makes replacing them risky.
Most banks do not try to fix this in one move. They work around it. Existing systems are opened up through APIs. Specific workflows are modernized first. Core replacements happen in stages, often over several years.
This is how digital transformation in the banking sector moves forward without putting day-to-day operations at risk.
Data That Does Not Agree With Itself
Data problems rarely announce themselves early. They show up when reports do not match, numbers differ across teams, or dashboards stop being trusted.
Banks that move past this focus on basics before sophistication. They clean up definitions. They decide which data source is the reference point. They reduce reliance on delayed reports and move closer to real-time feeds.
Once data becomes consistent, digital transformation in banking stops feeling fragile.
Security and Regulatory Pressure That Never Eases
As systems connect more tightly, risk increases. At the same time, regulatory expectations continue to shift. In digital transformation in banking and financial services, compliance is no longer something handled at set intervals.
Banks that manage this well build controls into everyday processes. Identity checks run quietly in the background. Audit trails are generated automatically. Monitoring happens continuously, not just during reviews.
When security is embedded, it stops blocking progress.
People Struggling to Keep Up With Change
Even strong technology programs fail when adoption lags. Most resistance is not about refusal. It comes from uncertainty. Teams worry about breaking things or not understanding new processes.
Banks that handle this better move slower with people than with technology. Changes are introduced in phases. Training focuses on real scenarios, not feature walkthroughs. Users are involved before systems are finalized.
Confidence usually follows clarity.
Costs That Rise Before Value Is Obvious
Another challenge of digital transformation in banking is cost perception. Spending often comes early. Benefits take time to show.
Banks avoid losing momentum by defining what success looks like upfront. They track improvements in turnaround time, error reduction, and operational load. They avoid heavy customization that makes systems expensive to maintain later.
Clear expectations help keep transformation grounded.
Getting Too Tied to One Vendor
Locking into a single platform can feel efficient at first. Over time, it limits options.
To avoid this, many banks choose modular architectures and open standards. Systems are designed to be portable. Dependencies are reviewed before they become hard to unwind.
This keeps digital transformation in the banking sector flexible as needs change.
None of these challenges mean transformation is failing. They are part of the process. Banks that accept digital transformation in banking as a long-term shift, rather than a one-time program, tend to move forward steadily, even when progress feels slow.
Top Examples of Digital Transformation Solutions in Modern Banking
When banks talk about digital transformation, the conversation often starts with technology. In practice, it usually starts with frustration. Too many steps. Too many handoffs. Systems that technically work, but slow everything down.
Digital transformation solutions matter when they remove that friction. Not because they look modern, but because they change how work actually gets done. The examples below are not exhaustive, but they reflect the kinds of solutions banks rely on today to simplify operations and respond faster.
Mobile Banking Apps
Mobile apps are no longer an add-on. For many customers and businesses, they are the bank.
What used to require branch visits or long email chains can now be handled in minutes. Transfers, balance checks, loan applications, even document submissions happen through a phone. For businesses, this often means fewer delays and less dependency on physical processes. For banks, it reduces pressure on support teams while keeping services accessible.
Data Analytics Solutions
Banks are not short on data. They are short on time.
Analytics tools help teams move beyond static reports and delayed insights. Instead of looking backward, banks can monitor trends as they form. Credit risk, fraud signals, liquidity positions, and performance metrics become easier to track and adjust.
The shift is subtle but important. Decisions stop waiting for reports and start happening closer to real events.
AI-Powered Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots did not start out very impressive. But today they are offered by almost all the banks.
Their capability to handle the repetitive questions that slow teams down. Such as offering assistance in balance inquiries, status checks, basic requests allows human agents to focus on issues that actually need judgment.
For customers, the benefit is simple. Faster answers. No waiting for business hours.
Neobanks and Digital-Only Banking
Neobanks showed what happens when banking is built without legacy constraints. No branches. Fewer layers. Cleaner experiences.
Platforms like Chime, Monzo, and Revolut gained traction by making onboarding easier and fees more transparent. Their impact goes beyond their own growth. Many features now expected in traditional banking were first normalized by digital-only models.
In that sense, neobanks reshaped expectations even for banks that do not plan to go fully digital-only.
Also Read: Understanding the Neobank App Development Cost
Robo-Advisors
Robo-advisors sit in an interesting middle ground. They are not trying to replace human advisors entirely, but they change who gets access to investment guidance.
By using algorithms to suggest portfolios based on goals and risk tolerance, these platforms lower the barrier to entry. Costs drop. Decisions become less intimidating. For many customers, robo-advisors are a first step rather than a final solution.
Biometric Authentication
Passwords are inconvenient and easy to compromise. Biometrics solve part of that problem.
By integrating biometric authentication (fingerprint scans, facial recognition, and voice identification) make access quicker while improving security. From a user’s point of view, logging in becomes easier. From a bank’s point of view, the risk tied to stolen credentials drops.
It is one of those changes that feels small, but adds up over time.
How Does Digital Banking Impact Businesses From Startups to Enterprises?
Digital banking does not affect every business in the same way. The difference usually comes down to scale. A startup worries about speed and access. A mid-market firm worries about control and integration. A large enterprise worries about reliability, reach, and visibility across markets.
Looking at how different businesses actually use digital banking makes this clearer. The following examples reflect how digital transformation in banking case study scenarios play out differently based on business size and operating complexity.
SMEs and Startups
For small businesses and startups, banking friction shows up early. Opening accounts takes time. Tracking cash is manual. Getting short-term credit often depends on paperwork rather than real performance.
Digital banking has started to ease some of these pain points.
Many startups use Stripe not just for payments, but for embedded financial services. With Stripe Financial Accounts (formerly Stripe Treasury), businesses can hold balances, manage payouts, and track funds directly inside their product or platform. There is no separate banking portal to manage every day.
Another practical example of how digital financial tools support businesses can be seen in platforms like Mudra, a budget and expense management app built by Appinventiv. Designed for small and growing businesses, Mudra helps teams track expenses, manage budgets, and gain real-time visibility into spending patterns. By bringing financial data into a single digital view, tools like this reduce reliance on manual tracking and improve everyday financial decision-making.
For SMEs, digital transformation in banking is mostly about removing delays. Less waiting. Less paperwork. More visibility into what cash is available right now.
Mid-Market Enterprises
Mid-market companies usually hit a different set of problems. Volumes increase. Reporting becomes harder. Finance teams spend more time reconciling than analyzing.
This is where digital banking starts to focus on integration and control.
HSBC offers Treasury APIs and digital liquidity tools that give businesses real-time data flows and automation instead of manual reporting. These features help mid-sized companies automate reconciliations and cash management tasks more efficiently.
Citi takes a similar approach with API-based banking services. Mid-market firms can connect payments, account data, and reconciliation directly into their ERP systems. This reduces manual work and improves accuracy as transaction volumes grow.
https://www.citigroup.com/global/treasury-and-trade-solutions/apis
At this stage, digital banking is less about convenience and more about keeping complexity under control.
Large Enterprises and Global Corporations
For large enterprises, banking operates at a very different scale. Transactions run across countries. Compliance requirements vary by region. Small delays can have large downstream effects.
This is where digital transformation in banking becomes deeply strategic.
JPMorgan Chase has invested billions in cloud platforms, data infrastructure, and AI to support corporate clients with global operations. These capabilities also support digital transformation in investment banking, where transaction volumes, risk exposure, and speed of execution are tightly linked.
In Europe, BNP Paribas has expanded its open banking and API capabilities to help multinational clients automate payments, reporting, and reconciliation while staying compliant with local regulations. This allows large organizations to centralize financial operations without losing regional oversight.
For global corporations, digital banking is not about faster transactions alone. It is about visibility, predictability, and governance at scale.
Why Business Size Changes the Impact
The same digital banking capability can solve very different problems depending on where a business sits.
- Startups benefit from speed and access.
- Mid-market firms benefit from integration and control.
- Large enterprises benefit from scale and real-time insight.
Together, these digital transformation examples in banking illustrate why scale changes both priorities and outcomes. Understanding this difference helps businesses choose banking partners that support not just current needs, but the next stage of growth as well.
What Does the Future of Digital Transformation in Banking Look Like?
The future of digital transformation trends in banking is not going to arrive as a single moment or a big shift everyone agrees on. It is already happening in small ways, inside operations most customers never see. Banks are spending less time adding new layers and more time trying to make existing systems react faster and with better judgment.
One noticeable change is how AI agents and virtual assistants are being used internally. They are not replacing people. They are sitting alongside teams, helping sort through alerts, flagging unusual activity, or guiding routine reviews. When these tools are backed by machine learning and advanced data analytics, they help teams focus on what actually needs attention instead of working through long queues.
A few patterns keep showing up across the industry:
- Fintech startups and challenger banks keep forcing the issue. They move quickly, release often, and make inefficiencies visible simply by not carrying them.
- Neobanks and digital wallets have reset expectations around access and speed. Once people get used to real-time updates, going back feels frustrating.
- Fraud detection systems and transaction monitoring systems are becoming less rigid. Instead of fixed rules, they adapt as behavior changes, which matters in a world where patterns shift constantly.
- Identity verification is no longer a single step at the start of a relationship. It is becoming something that runs quietly in the background, checking signals over time.
- Ethical AI is becoming unavoidable. As decisions become more automated, banks are being pushed to explain outcomes, reduce bias, and show restraint, not just efficiency.
What this points to is not louder innovation, but quieter systems. Digital transformation in banking starts to feel less like a project and more like an environment. When it works well, nothing dramatic happens. Fewer false alarms. Faster responses. Fewer surprises. And systems that help people do their jobs without constantly getting in the way.
How Appinventiv Can Support Your Digital Transformation in Banking
Digital transformation in banking works best when strategy and execution stay closely aligned. Over the years, Appinventiv has supported banks and financial institutions at different stages of maturity, from modernizing legacy platforms to building new digital banking capabilities designed for scale and regulatory resilience.
That experience reflects in measurable outcomes.
- 300+ banking transformation projects delivered across payments, onboarding, lending, and core modernization
- 30+ countries served with banking platforms, spanning varied regulatory and operational environments
- 10+ years of banking domain expertise, built through sustained work in complex financial ecosystems
These engagements shape how Appinventiv approaches digital transformation services today. The focus remains on building reliable, adaptable systems through structured banking software development services that fit real operating conditions rather than ideal scenarios.
If your institution is assessing its next phase of digital transformation in banking, connecting with our experts can help clarify technical readiness, constraints, and realistic paths forward. A focused discussion with the team is often the most effective first step toward building systems that last.
FAQs
Q. What Is Digital Transformation in Banking?
A. Digital transformation in banking refers to reworking how banks operate at a structural level using digital technologies. It goes beyond launching mobile apps or online portals. It includes modernizing core systems, automating workflows, integrating data across platforms, and embedding intelligence into decision-making. For businesses, this means faster onboarding, better cash visibility, and banking services that integrate directly into their operating systems.
Q. How Do Banks Measure ROI From Digital Transformation?
A. Banks usually measure ROI through operational and risk-related outcomes rather than direct revenue alone. Common indicators include reduced processing time, lower operating costs, fewer manual errors, faster customer onboarding, and improved compliance efficiency. Over time, banks also look at scalability, system stability, and the ability to launch new services without major reinvestment.
Q. What Are Common Mistakes Banks Make During Digital Transformation?
A. One common mistake is treating transformation as a one-time project instead of a long-term capability. Others include modernizing technology without changing processes, involving compliance teams too late, or trying to replace all legacy systems at once. Banks that struggle often focus on delivery milestones rather than whether day-to-day operations actually improve.
Q. What Are the Biggest Compliance and Cybersecurity Challenges in Digital Banking Transformation?
A. As systems become more connected, managing risk becomes more complex. Key challenges include protecting sensitive data across integrated platforms, maintaining audit trails in automated workflows, and adapting to evolving regulatory requirements across regions. Cybersecurity risks also increase when controls are added after systems are built rather than designed into them from the start.
Q. How Does KYC and AML Automation Support Digital Transformation in Banks?
A. KYC and AML automation replaces slow, manual verification with continuous, data-driven checks. Digital KYC shortens onboarding timelines while maintaining compliance, and automated AML systems monitor transactions in real time instead of relying on periodic reviews. Together, they reduce friction for customers and lower operational risk for banks.
Q. What Role Does Blockchain Play in Banking Transformation?
A. Blockchain is mainly used where transparency, traceability, and shared records matter. In banking, it supports use cases such as cross-border payments, trade finance, settlement reconciliation, and identity verification. While it is not a replacement for core banking systems, blockchain can reduce reconciliation effort and improve trust between multiple parties in complex transactions.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Banking Technology Consulting: A Strategic Roadmap for Core Modernization and Guaranteed ROI
Key takeaways: Banking modernization is now a strategic necessity, not a technology upgrade. Most banks lose value due to legacy complexity, fragmented data, and slow compliance response. Structured banking technology consulting delivers measurable gains in cost, stability, and governance. Core modernization succeeds when roadmaps, risk, and regulatory alignment are clearly defined. ROI comes from reduced…

How Gamification in Banking Helps Enterprises Build Lasting Customer Loyalty
Key takeaways: A winning banking gamification strategy isn't about badges; it’s about using behavioral psychology to form daily financial habits. Industry leaders like DBS Bank and Revolut prove the concept works, driving higher savings and millions in user acquisition. The cost to implement gamification in banking and financial services ranges between $40,000 and $400,000 or…

KYC Automation - Benefits, Use Cases, Steps, Tools and Best Practices
Key takeaways: KYC automation cuts verification from days to minutes and keeps checks consistent across teams. AI and ML reduce manual errors, catch risk earlier, and make compliance far easier to scale. Manual KYC drains time, increases cost, and slows onboarding — automation fixes all three. Automated workflows handle spikes in customer volume without compromising…