- The Trust Problem: Why Accuracy is a Commercial Issue
- Hallucinations: Plausible But False
- Stale Knowledge: Data That Ages Badly
- Opaque Outputs: No Provenance, No Trust
- Business Metrics That Make The Problem Real
- RAG 101: How Retrieval Makes Generative AI Accountable
- The Basic Idea
- Core Components
- RAG vs Fine-tuning: Comparing Approaches
- RAG 2.0: Evolution and Emerging Patterns
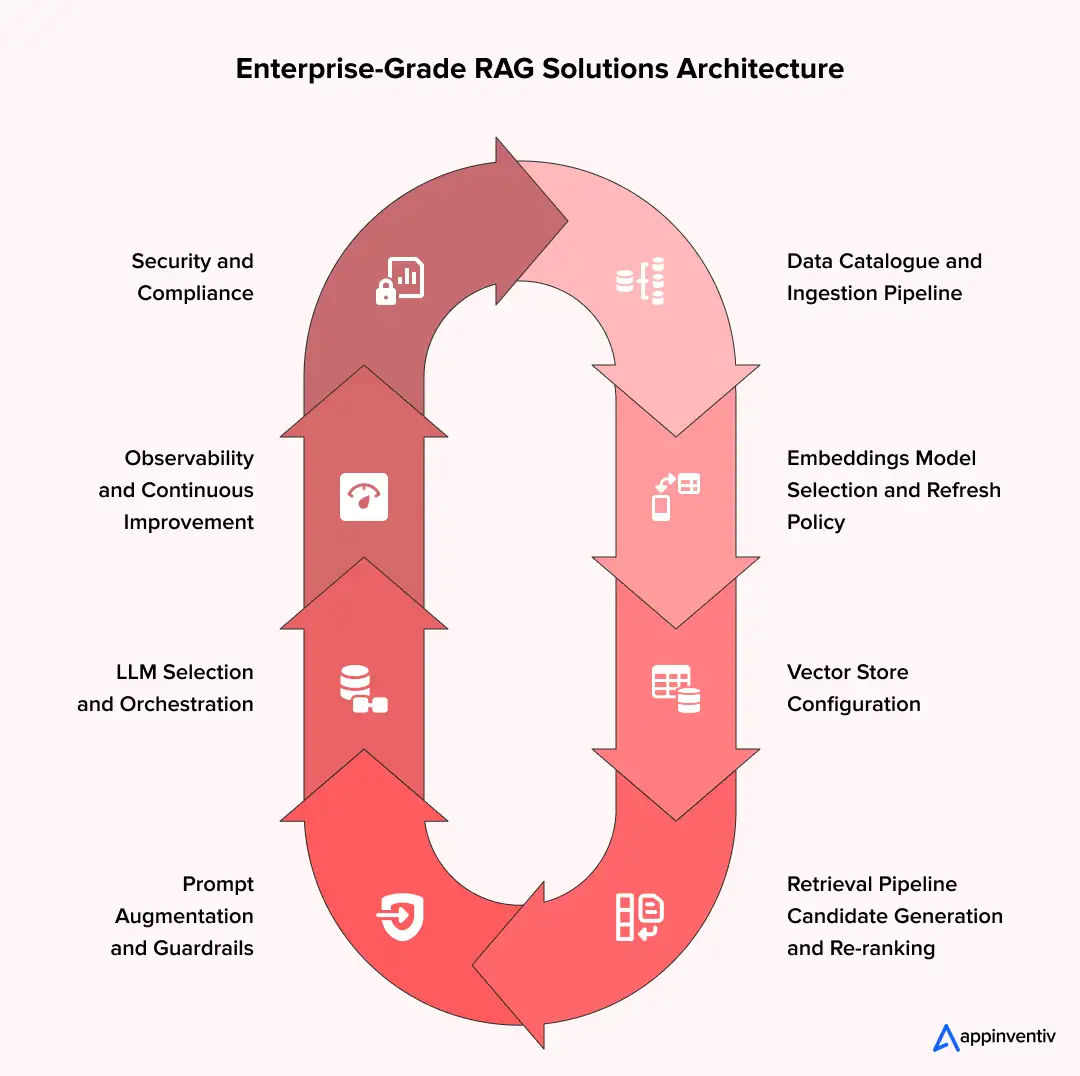
- Building an Enterprise-Grade RAG Solutions Architecture
- 1. Data Catalogue and Ingestion Pipeline
- 2. Embeddings: Model Selection and Refresh Policy
- 3. Vector Store Configuration
- 4. Retrieval Pipeline: Candidate Generation and Re-ranking
- 5. Prompt Augmentation and Guardrails
- 6. LLM Selection and Orchestration
- 7. Observability and Continuous Improvement
- 8. Security and Compliance
- Measuring ROI: Metrics, Benchmarks and An Example Model
- What to Measure (Technical + Business)
- Case Study Simulation: Financial Services Knowledge Base
- RAG Implementation for Business Use Cases and Patterns: Where RAG Delivers First
- Customer Support and Knowledge Assistants
- Sales Enablement and Quoting
- Legal and Compliance
- Clinical Decision Support (Healthcare)
- Research and R&D Documentation
- Governance, Security and Explainability: Essentials for Trust
- Data-level Controls
- Provenance and Audit Trails
- Explainability
- Redaction and Policy Enforcement
- SOC2/HIPAA / Privacy Language
- Deployment Models: On-prem, Private Cloud, Managed
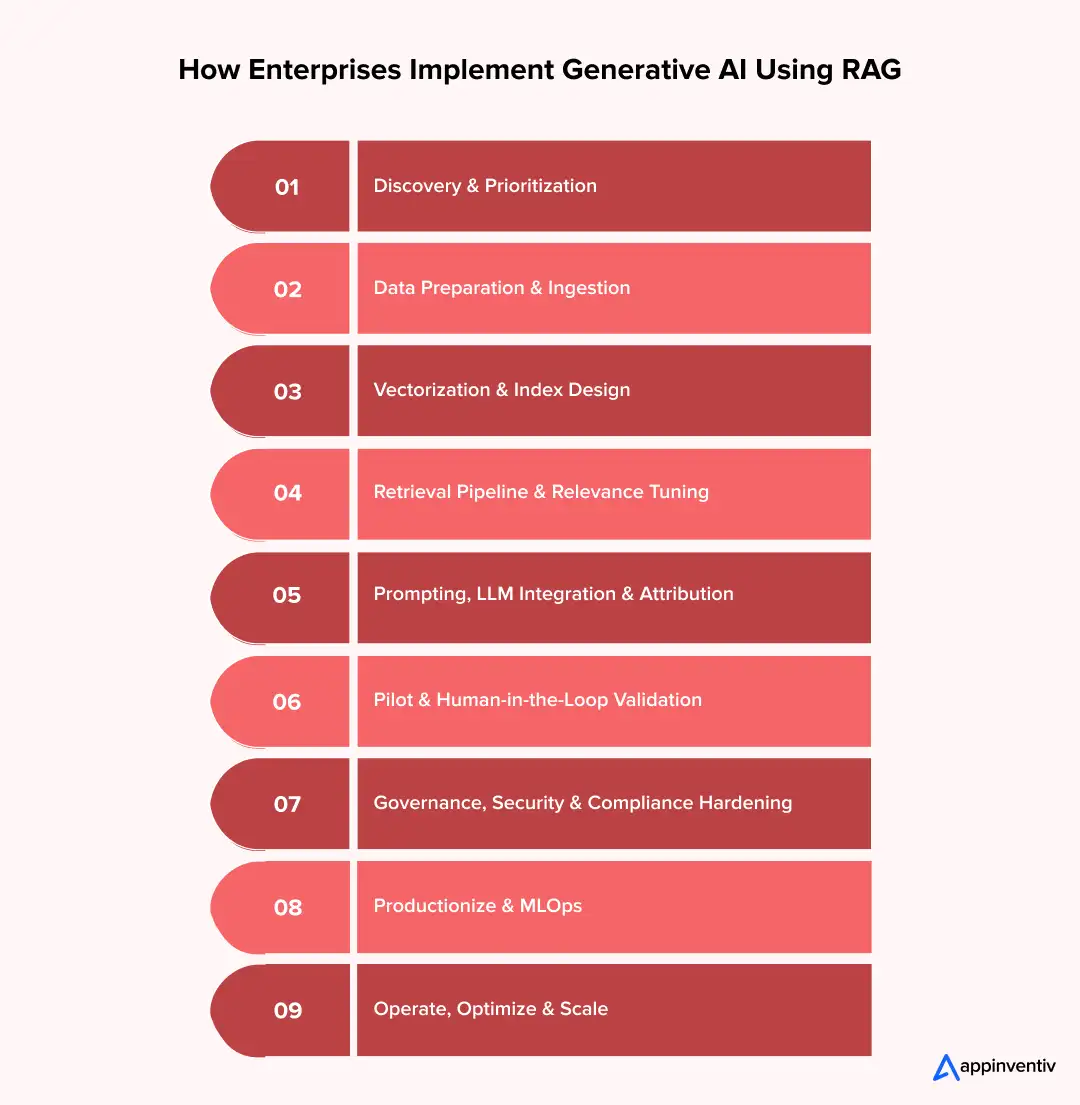
- How Enterprises Implement Generative AI Using RAG (Step-by-Step)
- Step 1: Discovery & Prioritization (2–4 Weeks)
- Step 2: Data Preparation & Ingestion (2–6 Weeks)
- Step 3: Vectorization & Index Design (1–3 Weeks)
- Step 4: Retrieval Pipeline & Relevance Tuning (2–4 Weeks)
- Step 5: Prompting, LLM Integration & Attribution (1–3 Weeks)
- Step 6: Pilot & Human-in-the-Loop Validation (4–8 Weeks)
- Step 7: Governance, Security & Compliance Hardening (2–6 Weeks, Overlap With Pilot)
- Step 8: Productionize & MLOps (4–12+ weeks)
- Step 9: Operate, Optimize & Scale (Ongoing)
- Where Generative AI with RAG Fails, and How to Prevent It
- 1. Ingesting Uncurated or Noisy Data
- 2. Over-indexing Irrelevant Content
- 3. Over-reliance on Vector-only Retrieval
- 4. No Provenance or Source Attribution
- 5. Missing Monitoring and Human Feedback Loops
- 6. Neglecting Security and Compliance Requirements
- 7. Hardwiring Vendor-specific Architecture
- 8. Scaling Prematurely Without Business Validation
- 9. Ignoring Model Selection Tradeoffs
- 10. Skipping Change Management and User Onboarding
- The Future: RAG for Enterprise Generative AI and Operational Models
- RAG as a Standard for Enterprise-grade Generative AI
- RAG 2.0 and The Next Architectural Leap
- Operationalization Through Managed Services and Platforms
- Maturing Standards and Implementation Playbooks
- Agentic RAG: Autonomous, Goal-driven Retrieval and Action
- GraphRAG: Relationship-aware Retrieval for 360° Reasoning
- Why Now is the Time to Invest in RAG Readiness
- Practical Checklist to Start a Pilot
- How Appinventiv Helps Turn RAG Into Reliable Business Value
- What We Do Well:
- Why Clients Choose Us:
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- RAG models in generative AI attach real, verifiable sources to model outputs, which sharply cuts hallucinations and raises user confidence.
- Accuracy directly impacts ROI, driving fewer escalations, faster decision cycles, and lower support costs.
- RAG vs fine-tuning: RAG allows real-time updates without retraining, offering faster deployment and lower maintenance.
- Vector databases for RAG and hybrid retrieval pipelines enhance precision, scalability, and governance readiness.
- RAG implementation consulting or managed RAG services help businesses deploy secure, explainable AI systems faster.
Generative models, large language models and their kin are now core tools across product, support, research and compliance teams. They write, summarise, and answer questions in ways that save work and shorten cycles. Yet their language fluency hides a persistent problem: plausible-sounding errors. Those errors are commonly called hallucinations that turn pilots into liabilities when left unchecked.
Studies show RAG can reduce hallucination rates by 40-71% across benchmarks like Vectara’s HHEM Leaderboard for top models in 2025.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) provides a practical remedy. Instead of relying solely on a model’s frozen training, RAG systems fetch relevant, curated information at query time and feed that context to the model. The result is an answer that can be traced back to a source. That traceability is what turns an experimental assistant into a trusted tool.
This article explains how RAG models in Generative AI are used for accurate work, how to measure the business value (the ROI of RAG models), and how to implement systems that meet rigorous security and compliance needs. It also outlines practical steps for rolling a pilot into production and highlights common failure modes.
Throughout, emphasis is on technical clarity and business outcomes. If your objective is to reduce risk and raise adoption, the content that follows shows the path.
Appinventiv shortens time-to-value.
The Trust Problem: Why Accuracy is a Commercial Issue
Language models are probabilistic predictors. They are brilliant at pattern completion but not inherently tied to truth. This creates three related failure modes that matter in business settings.
Hallucinations: Plausible But False
A model will sometimes show fact-agnostic outputs to fill gaps. A support bot might claim a product has a feature that was retired. A knowledge assistant might cite a non-existent clause in a regulation. These are not minor inconveniences. Each mistaken answer can trigger rework, escalations, or worse. Reducing AI hallucinations using RAG is, therefore, a business priority.
Stale Knowledge: Data That Ages Badly
AI models trained on a dataset frozen at a past date cannot reflect real-time changes. Product catalogs, regulatory updates, pricing tables—these all move. Relying only on a static model requires constant fine-tuning or manual checks. That slows workflows and erodes trust.
Opaque Outputs: No Provenance, No Trust
If a model provides an answer without a source, users must validate it themselves. That extra step defeats the productivity promise of automation. Provenance, who said what, and where that assertion came from, changes behaviour. People trust cited answers more and use them with less manual verification.
Business Metrics That Make The Problem Real
Executives need numbers. Frame the trust problem into metrics you can act on:
- Hallucination rate: percentage of sampled answers that are factually wrong on human review.
- Time-to-answer and time-to-resolution: how long it takes to resolve a query, with and without the assistant.
- Support ticket volume and escalation rate: frequency of issues caused by wrong answers.
- Cost per interaction: human cost plus overhead spent on verifying or fixing AI outputs.
- Adoption and retention: percentage of users who rely on the assistant over time.
When you translate trust into these metrics, accuracy becomes something you can budget and measure.
RAG 101: How Retrieval Makes Generative AI Accountable
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances language models by feeding them factual, query-specific data at runtime, ensuring outputs are grounded, current, and verifiable.
The Basic Idea
In a RAG system, an incoming query triggers a retrieval from a curated knowledge store. The best-matching documents or document passages are appended to the model’s prompt. The model then composes its answer with that evidence visible. Put bluntly: instead of guessing, the model consults.
This simple addition changes the properties of the output:
- Answers cite sources.
- The model is constrained by facts pulled from trusted content.
- Updates to knowledge are a function of the index, not the base model.
Core Components
A functional RAG pipeline typically includes:
- Ingestion and canonicalisation of documents.
- Embeddings that convert text to vectors.
- A vector database to store and search embeddings. (Hereafter, vector databases for RAG.)
- A retrieval layer (semantic, keyword, or hybrid).
- Prompt augmentation and an LLM for generation.
- Logging, monitoring, and governance.
Each component needs operational discipline. Messy source content, stale embeddings, or a brittle re-ranking model will undermine the system.
Also Read: RAG Application Development: Process & Cost
Embeddings and Vector Search
Embeddings map semantic meaning into a numeric space. Good embeddings make retrieval precise. The vector store must support approximate nearest neighbour (ANN) search, scale to the size of your knowledge base, and provide replication and snapshots. Choices here affect latency, cost, and retrieval precision.
Choose an embedding model and design indexing with context window management and a semantic ranker, tuning cosine similarity thresholds to optimise precision and token cost efficiency.
Retrieval Modes: Semantic, Keyword, Hybrid
- Semantic AI search (vector-only) surfaces conceptually similar passages and is good for paraphrased queries.
- Keyword search excels with precise identifiers: part numbers, statute citations, and contract IDs.
- Hybrid approaches combine both and often deliver the best practical performance for business cases.
Attribution and Provenance
When a response includes source excerpts and clear links to the originating documents, user trust goes up. Provenance also provides an audit trail, a critical requirement for many regulated sectors.
RAG vs Fine-tuning: Comparing Approaches
Fine-tuning adjusts model weights so the model internalises domain knowledge or style. Benefits include consistent style and sometimes faster inference (no retrieval latency). Yet fine-tuning is a heavier operationally:
- Retraining is costly and slow when your knowledge changes.
- Fine-tuned models can still hallucinate and may bake in unwanted biases.
- RAG allows you to update content in near real time by reindexing, without retraining.
| Dimensions | RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) | Fine-Tuning |
|---|---|---|
| Update cadence | Instant index updates — reindex to reflect new knowledge | Retraining / re-fine-tuning required; slower |
| Cost profile | Lower recurring model training cost; compute on retrieval + inference | Higher retraining cost; long-term model maintenance |
| Freshness | Near real-time (index refresh) | Stale until retrained |
| Governance & provenance | Strong: source snippets, audit trails | Weak: facts embedded in weights; harder to attribute |
| Best fit | Knowledge-centric Q&A, policy, support, regulated responses | Proprietary reasoning, consistent stylistic constraints |
Thus, for knowledge-centred use cases: policy Q&A, product info, legal references, the benefits of RAG over fine-tuning usually favour RAG. Fine-tuning remains appropriate where you must embed proprietary reasoning or a hard-to-encode style.
RAG 2.0: Evolution and Emerging Patterns
RAG architecture is evolving rapidly. Expect these capabilities to become common in near-term deployments:
- Multi-modal retrieval: combine text, tables, images, and audio. A patent image plus its technical brief? RAG 2.0 can retrieve both.
- Dynamic context windows: systems that select only the most relevant passages within a token budget.
- Retrieval feedback loops: the system learns which retrieved passages led to correct answers and re-ranks accordingly.
- Runtime governance: automated redaction, sensitivity scoring, and policy-based filters applied at query time.
- Explainable AI and RAG integration: confidence scores, citation snippets, and change logs, built into every response.
This next stage, RAG 2.0, will push RAG from a defensive tool (fixed knowledge grounding) to a proactive RAG for knowledge-grounded AI that can reason across heterogeneous data while preserving traceability.
Building an Enterprise-Grade RAG Solutions Architecture
A production-ready architecture is more than a prototype. Below are practical design choices and trade-offs.
1. Data Catalogue and Ingestion Pipeline
Identify canonical sources. Prioritise the things users consult most often: manuals, policy documents, product sheets, release notes, and approved FAQs. Canonicalise formats (PDF → text, remove OCR errors) and tag documents with metadata: author, version, sensitivity level.
If you skip this step, retrieval will surface low-quality passages that confuse the model and users.
2. Embeddings: Model Selection and Refresh Policy
Choose embeddings that reflect your domain. Off-the-shelf encoders often perform adequately, but for specialised vocabularies, a domain-tuned encoder helps. Decide how often to refresh embeddings, weekly, nightly, or on-change, based on content churn.
3. Vector Store Configuration
Select a vector database and design for scale. Consider:
- Sharding and replication for availability.
- Snapshot policies so you can revert indexes.
- Cost vs. latency trade-offs: some stores are cheaper but slower; others are engineered for low latency at scale.
When you produce a design, also include an export path: you should be able to move the index between providers if needed.
4. Retrieval Pipeline: Candidate Generation and Re-ranking
Use a two-stage approach:
- Candidate generation (semantic vector or keyword).
- Re-ranking with a light-weight model or BM25.
Re-ranking optimises precision before the model sees the context. It reduces prompt bloat and often increases answer quality.
5. Prompt Augmentation and Guardrails
Append passages with the source title, snippet, and link. Limit the number of passages to control token consumption. Implement AI guardrails, filters that suppress content flagged as sensitive unless the user has permission to view it.
6. LLM Selection and Orchestration
You can pair the retrieval layer with many models. Factors to weigh:
- Latency and cost: some models are faster but pricier.
- Compliance: Is a private endpoint required?
- Quality: test multiple models on the same prompt and context to compare hallucination rates and fluency.
Consider multi-LLM orchestration in which a primary model handles most queries and a fallback model handles edge cases or peak loads.
7. Observability and Continuous Improvement
Log queries, retrieved passages, and final outputs. Sample responses for human review to maintain an ongoing labelled dataset. Track metrics such as hallucination rate, provenance coverage, and user satisfaction. Those logs also support audits.
8. Security and Compliance
Implement role-based access controls (RBAC), encryption at rest/in-transit, and document-level sensitivity tags. For regulated industries, consider on-premises or private-cloud deployments and data residency guarantees.
Also Read: How to Avoid Compliance Violations While Developing AI Products
Today’s RAG deployments typically pair retrieval with large models such as Llama 3.2, GPT-4o / GPT-4 family or Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Sonnet, depending on latency, cost and compliance needs. Llama 3.2 and Claude 3.5 families provide strong multimodal and domain performance for on-prem or private-cloud options, while GPT-class APIs often lead in generalist benchmarks.
Model selection should weigh context window management, token cost, and measured hallucination rate on a project test set.
Measuring ROI: Metrics, Benchmarks and An Example Model
You need a credible measurement plan. Look at practical KPIs and a simple financial model.
What to Measure (Technical + Business)
Tracking both system performance and business impact is essential to validate RAG’s effectiveness and guide scale-up decisions.
Technical:
- Hallucination rate: percentage of sampled outputs judged incorrect.
- Precision@k: relevance of top-k retrieved passages.
- Provenance coverage: portion of answers that include at least one citation.
- Average latency: total response time.
Business:
- Time saved per interaction: minutes of human time avoided.
- Ticket reduction: percentage drop in support tickets caused by incorrect information.
- Cost per interaction: compute + support effort per query before and after.
- Adoption and retention: active users over time and repeat usage.
- Compliance incidents avoided: count and estimated financial exposure prevented.
These metrics map technical gains to financial value.
Case Study Simulation: Financial Services Knowledge Base
Mid-sized financial services firm; 200,000 annual knowledge queries across support, compliance and sales channels. Baseline human handling cost = $8.00 per interaction. Existing AI pilots use a frozen LLM with frequent verification overhead.
Assumptions (Year 1):
- Annual queries: 200,000
- Pre-RAG avg cost per interaction (human + verification): $8.00 → $1,600,000 baseline
- Post-RAG avg cost per interaction (reduced verification): $4.00 → $800,000
- Implementation + first-year ops: $600,000 (indexing, engineering, governance, MLOps)
Token cost efficiency: RAG reduces average prompt size by 40% (because retrieval supplies compact evidence rather than long context), lowering model token spend by $0.10 per query on average → annual token savings ≈ $20,000
Model drift & maintenance cost: Without RAG, periodic retraining & remediation cost estimated at $120,000 annually; with RAG, drift remediation focused on index curation estimated at $30,000 annually.
Results (Year 1):
- Direct annual savings (staff + token): $800,000 saved vs baseline = $800,000.
- Add avoided model drift cost differential: $90,000.
- Net annual benefit: $890,000.
- Payback: $600,000 / $890,000 ≈ 0.67 years (~8 months).
Why this matters: The case shows RAG’s combined impact on operational costs, token cost efficiency, and model drift mitigation. Token reductions and targeted index curation materially lower the total cost of ownership versus heavy retraining cycles.
Scale with architecture, governance, and KPIs that align with your business.
RAG Implementation for Business Use Cases and Patterns: Where RAG Delivers First
RAG is not a one-size-fits-all silver bullet, but it is highly effective for knowledge-centred workflows.
Customer Support and Knowledge Assistants
Index product docs, policy pages, and release notes. When the assistant cites a specific clause, customer service agents and customers act on the answer without extra validation. Result: fewer escalations and faster resolutions.
Sales Enablement and Quoting
Hook into CRM and pricing tables. Provide sales reps with sourced responses that reference the price schedule or contractual limits. That reduces quoting errors and shortens sales cycles.
Legal and Compliance
Use curated legal texts, internal policies, and precedent decisions. Large language models in RAG implementation can summarise relevant language while linking to the authoritative source. That produces a defensible audit trail.
Clinical Decision Support (Healthcare)
Restrict retrieval to curated guidelines, peer-reviewed literature, and institutional SOPs. Add a human-in-the-loop for high-risk outputs. The outcome: faster literature synthesis and better support for clinical teams.
Also Read: AI in Clinical Decision Making: Empowering Smarter Healthcare
Research and R&D Documentation
Aggregate internal design notes, public standards, and external papers. Provide engineers with explainable summaries and direct links to the source material.
Governance, Security and Explainability: Essentials for Trust
To build the ‘Trust’ in generative AI systems, no RAG system is complete without governance.
Data-level Controls
Tag documents with sensitivity levels and enforce RBAC. Sensitive content should be excluded from public indexes and only accessible to authorised users. Use encryption and secure key management.
Provenance and Audit Trails
Record which document passages were retrieved for each query. Preserve the prompt and the model’s output. These artifacts support audits and compliance reviews.
Explainability
Integrate explainable AI and RAG integration by returning citations and confidence markers. Where necessary, surface the raw passages so human reviewers can judge the strength of the evidence.
Redaction and Policy Enforcement
Automate redaction rules at ingestion and at query time. For example, PII fields can be masked or removed from retrieval results. Implement policy engines to prevent disallowed outputs.
SOC2/HIPAA / Privacy Language
Enterprises must align RAG deployments with established compliance frameworks. For many regulated organizations, controls include SOC2 Type II processes for operational security, HIPAA safeguards for clinical data, and strict data privacy in LLMs (PII redaction, purpose-limited indexing, data residency).
Practically, that means RBAC with document-level sensitivity labels, encryption at rest and in transit, auditable retrieval logs, and a documented incident and remediation plan that aligns with SOC2/HIPAA evidence requirements. When selecting managed providers, require SOC 2 Type II certification and contractual assurances regarding data processing and residency.
Deployment Models: On-prem, Private Cloud, Managed
Some organisations require on-prem deployments to meet strict data residency constraints. Others prefer a hosted approach with tight API controls. Managed RAG as a service can be the right balance for teams that want enterprise-grade features without building the entire stack internally.
Also Read: On-Premise vs. Cloud: A Detailed Analysis
How Enterprises Implement Generative AI Using RAG (Step-by-Step)
This playbook converts the roadmap phases into concrete actions, owners, deliverables and acceptance criteria. Use it as the operational appendix to a vendor brief or internal project plan.
Step 1: Discovery & Prioritization (2–4 Weeks)
Objective: select a single, high-value, low-risk use case and define success metrics.
Key activities:
- Stakeholder interviews (business, legal, IT, security).
- Inventory and quick audit of candidate sources (docs, CRM, product sheets).
- Define KPIs and SLAs (hallucination rate target, time-to-answer, adoption).
Deliverables: use-case brief, data inventory, KPI baseline, success criteria.
Owner: Product lead + Data owner.
Acceptance: sponsor sign-off on use case and KPIs.
Step 2: Data Preparation & Ingestion (2–6 Weeks)
Objective: assemble a clean, canonical knowledge base.
Key activities:
- Extract and canonicalize documents (OCR cleanup for PDFs).
- Tag metadata (source, version, sensitivity).
- Remove duplicates and low-value content.
- Create an ingestion pipeline (ETL) with automated checks.
Deliverables: canonical document set, ingestion scripts, sensitivity tags.
Owner: Data engineering + domain SMEs.
Acceptance: ≥95% document readability; sample retrieval returns authoritative passages.
Step 3: Vectorization & Index Design (1–3 Weeks)
Objective: convert content into embeddings and build a resilient index.
Key activities:
- Select embedding encoder (off-the-shelf or domain-tuned).
- Configure vector database (shards, replication, snapshot policy).
- Decide to refresh cadence (on change, nightly, weekly).
Deliverables: initial vector index, embedding config, export path for portability.
Owner: ML engineer/infra.
Acceptance: precision@10 above the defined threshold on a test query set.
Decision Point: RAG vs Fine-tuning
- If the use case requires rapidly changing facts or frequent legal/policy updates → choose RAG.
- If you must embed proprietary inference patterns or a unique reasoning workflow that cannot be expressed via retrieval → consider fine-tuning (or hybrid: small fine-tune + retrieval).
Document this choice and include cost/time implications in the project plan.
Step 4: Retrieval Pipeline & Relevance Tuning (2–4 Weeks)
Objective: implement candidate generation and re-ranking to maximise precision.
Key activities:
- Implement hybrid retrieval (vector + keyword) and chunking logic.
- Build a re-ranking component (BM25 or small neural re-ranker).
- Create a relevance test suite from real user queries.
Deliverables: retrieval API, re-ranker, relevance metrics dashboard.
Owner: Search engineer + ML engineer.
Acceptance: re-ranked top-3 contain correct sources ≥ target rate.
Step 5: Prompting, LLM Integration & Attribution (1–3 Weeks)
Objective: assemble prompt templates and connect to the chosen LLM(s).
Key activities:
- Design prompt augmentation format: source title, snippet, link, and instruction for citation.
- Test multiple LLMs (compare hallucination rate, latency, cost).
- Implement provenance injection and explicit citation formatting.
Deliverables: prompt templates, LLM selection report, and sample responses with citations.
Owner: AI engineer + prompt engineer.
Acceptance: sampled responses include correct citations and meet the quality bar.
Step 6: Pilot & Human-in-the-Loop Validation (4–8 Weeks)
Objective: validate behaviour with real users and measure KPIs.
Key activities:
- Run a controlled pilot with the target user cohort.
- Apply HITL review: label false positives and edge cases.
- Collect UX feedback and CSAT.
Deliverables: labelled dataset, pilot KPI report, prioritized fixes backlog.
Owner: Product manager + domain SMEs.
Acceptance: hallucination rate below target; user acceptance score above threshold.
Step 7: Governance, Security & Compliance Hardening (2–6 Weeks, Overlap With Pilot)
Objective: ensure the system is defensible and enterprise-ready.
Key activities:
- Implement RBAC, encryption, redaction and retention policies.
- Build audit logging for retrieval and generation.
- Apply data residency and legal checks.
Deliverables: policy docs, access controls, audit trail samples.
Owner: Security/compliance + platform team.
Acceptance: audit passes internal security checklist; legal sign-off.
Step 8: Productionize & MLOps (4–12+ weeks)
Objective: automate operations, monitoring and scaling.
Key activities:
- Automate embedding refresh, reindexing and CI for prompts.
- Add observability: hallucination tracking, provenance coverage, latency, cost.
- Implement failover or multi-LLM orchestration if needed.
- Put FinOps controls for cost per inference.
Deliverables: runbook, monitoring dashboards, autoscaling config.
Owner: Platform/MLOps team.
Acceptance: SLA for latency and availability met; automated reindexing validated.
Step 9: Operate, Optimize & Scale (Ongoing)
Objective: continuously improve relevance and business impact.
Key activities:
- Periodic data audits and content pruning.
- Use retrieval feedback to re-rank candidates (RAG 2.0 pattern).
- Track business KPIs and extend use cases.
Deliverables: quarterly ROI report, updated index, training plan for new cohorts.
Owner: Product + MLOps + domain teams.
Acceptance: progressive improvement on adoption and cost metrics.
When to Consider Managed Services or External Consulting
If you lack in-house vector DB experience, embedding ops, or compliance controls, evaluate managed RAG-as-a-service or external RAG implementation consulting for the MVP and early production phases. These options shorten time-to-value and transfer operational risk.
Quick Acceptance Checklist (To Gate Production)
- Hallucination rate <= agreed threshold on 1,000 sampled queries.
- Provenance present in ≥ X% of responses (X = project target).
- Security & legal sign-offs complete.
- Performance SLA (p95 latency) met.
- Monitoring and incident playbooks are in place.
Where Generative AI with RAG Fails, and How to Prevent It
While Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) offers a practical way to bring control and accuracy to generative AI, many implementations stall or fail due to avoidable mistakes. These breakdowns often occur not because of model limitations, but due to architectural oversights, rushed execution, or inadequate AI data governance.
Below are the most common failure points observed in enterprise deployments, along with proven strategies to resolve or prevent them.
1. Ingesting Uncurated or Noisy Data
Problem: Poor-quality source material leads to low-relevance retrieval and degraded model performance. If internal documents are outdated, inconsistent, or lack metadata, the model retrieves irrelevant or conflicting information, resulting in inaccurate responses even when hallucinations are technically absent.
Why it happens: Teams rush to integrate as many sources as possible without curating for quality, consistency, or business relevance.
Mitigation:
- Start with a lean, high-value corpus of verified documents.
- Apply document version control, deduplication, and tagging before ingestion.
- Assign ownership for content quality and create refresh policies.
2. Over-indexing Irrelevant Content
Problem: Indexes that contain too much “noise” reduce retrieval precision and increase prompt bloat. This lowers answer quality and raises token usage costs.
Why it happens: Engineering teams treat all enterprise content as equal, indexing slide decks, email logs, and unstructured notes alongside product documentation or SOPs.
Mitigation:
- Define inclusion criteria during the data audit phase.
- Exclude non-canonical or unstructured sources unless business-critical.
- Monitor retrieval relevance metrics to surface underperforming documents.
3. Over-reliance on Vector-only Retrieval
Problem: While semantic retrieval is powerful, it sometimes misses exact matches, especially for short queries, proper nouns, or numeric references.
Why it happens: Teams implement vector search pipelines without adding a keyword or a hybrid retrieval fallback, assuming embeddings will cover all edge cases.
Mitigation:
- Use hybrid retrieval (semantic + keyword) for better recall.
- Incorporate re-ranking logic to fine-tune top-k selections.
- Include a fallback path (e.g., hardcoded queries for known edge cases) where needed.
4. No Provenance or Source Attribution
Problem: If model responses don’t include citations or origin traces, users can’t verify them. This limits adoption and undermines regulatory defensibility.
Why it happens: Prompt design omits source formatting, or models are allowed to respond freely without constraints to cite.
Mitigation:
- Inject source snippets with titles and links directly into the prompt.
- Prompt the model to include inline references or numbered citations.
- Implement output filters that reject answers lacking provenance.
5. Missing Monitoring and Human Feedback Loops
Problem: Drift in model performance, degradation in retrieval relevance, and unnoticed hallucinations persist without feedback mechanisms.
Why it happens: Pilots often go live without structured human-in-the-loop review or metric instrumentation.
Mitigation:
- Set up hallucination sampling with regular manual review.
- Track metrics like provenance coverage, latency, precision@k, and user satisfaction.
- Use review feedback to update re-ranking rules and curate training data for improvements.
6. Neglecting Security and Compliance Requirements
Problem: Sensitive or restricted documents get indexed or exposed to unauthorised users, creating legal and operational risk.
Why it happens: Indexes are built quickly, often before RBAC, encryption, or data sensitivity tagging is enforced.
Mitigation:
- Enforce access controls at both the data and retrieval layer.
- Tag documents with sensitivity labels and apply runtime filters.
- Use redaction and content-scoping mechanisms before ingestion.
7. Hardwiring Vendor-specific Architecture
Problem: Lock-in to a single vector database, embedding provider, or LLM API limits future flexibility and increases switching costs.
Why it happens: Teams optimize for speed and adopt tightly coupled vendor solutions with no abstraction layers.
Mitigation:
- Choose vector databases that allow export/import of embeddings.
- Wrap LLM calls behind internal APIs or orchestration layers.
- Maintain versioned prompts and model performance logs to support migrations.
8. Scaling Prematurely Without Business Validation
Problem: Expanding to more RAG implementation for business use cases or larger data volumes without confirming initial ROI leads to unnecessary spend and stakeholder fatigue.
Why it happens: Excitement around generative AI pushes teams to “scale fast” before early pilots deliver measurable value.
Mitigation:
- Don’t move beyond pilot until key KPIs (e.g., hallucination rate, cost per interaction, user retention) are met.
- Run structured ROI analysis before adding more use cases.
- Reuse RAG architecture templates for enterprises and retrieval patterns where possible, but validate fit.
9. Ignoring Model Selection Tradeoffs
Problem: Teams lock into a single LLM based on initial benchmarks without considering latency, cost per query, or deployment model needs (e.g., private LLM vs API).
Why it happens: Early experiments favour convenience over operational requirements.
Mitigation:
- Test multiple LLMs with the same context + query pair.
- Log cost, latency, and hallucination metrics per model.
- Consider multi-LLM orchestration where different use cases need different capabilities.
10. Skipping Change Management and User Onboarding
Problem: End users underuse the assistant or rely on old workflows because they don’t trust the new tool or don’t understand its capabilities.
Why it happens: Teams focus on tech deployment and forget that enterprise AI tools require education and behaviour change.
Mitigation:
- Run structured onboarding sessions and demos with example use cases.
- Offer in-tool feedback mechanisms and citation explanations.
- Track user drop-off and feedback to surface friction points.
Most RAG failures are not technical; they are operational. They stem from rushed execution, unclear governance, or misaligned incentives.
With proper planning, disciplined data handling, and ongoing oversight, RAG systems can become core business tools rather than ungoverned experiments. Treat governance and feedback as core architecture, not just add-ons and your generative AI deployment for business will scale with both confidence and control.
The Future: RAG for Enterprise Generative AI and Operational Models
Retrieval-Augmented Generation is no longer an emerging concept; it’s becoming foundational to enterprise-grade generative AI strategies. But its architecture, tooling, and adoption of RAG AI models are rapidly evolving. What began as a workaround for hallucinations is maturing into a structured, systemised approach for deploying controlled and explainable AI applications across industries.
RAG as a Standard for Enterprise-grade Generative AI
We are approaching a point where RAG for enterprise generative AI becomes the baseline architecture for internal-facing AI tools, policy advisors, knowledge agents, and customer support bots.
The key driver: business leaders want systems that are accurate, transparent, and governed. As compliance requirements tighten and reliance on AI increases, enterprises will prioritise RAG-powered systems that can explain outputs and trace decisions back to source material.
RAG 2.0 and The Next Architectural Leap
The next wave, RAG 2.0, brings sophistication in both retrieval and reasoning. Expect:
- Multi-modal retrieval: Systems will pull from text, PDFs, tables, diagrams, and even structured datasets in parallel.
- Retrieval-feedback loops: AI agents for enterprises will learn which retrieved documents led to verified correct answers and improve selection over time.
- Context shaping: RAG AI models will dynamically adjust which evidence is included in a prompt based on question type, answer length, or metadata relevance.
- Retrieval chaining: For complex workflows (e.g., legal reviews or medical histories), systems will retrieve in stages, feeding results from one query into the next.
These changes don’t require entirely new infrastructure, but they do require smarter pipelines, deeper data modelling, and more emphasis on retrieval quality engineering.
Operationalization Through Managed Services and Platforms
As demand for generative AI outpaces internal AI/ML team capacity, managed RAG-as-a-service offerings are on the rise. Vendors now offer full-stack services, including ingestion, indexing, vector store management, LLM orchestration, and SLA-backed support, for teams that need reliability without building everything in-house. This trend is especially relevant for sectors with compliance complexity or limited ML bandwidth (e.g., healthcare, finance, manufacturing).
These services also enable modular integration with existing tools, such as RAG-enhanced search in CRMs, embedded assistants in ticketing systems, or private documentation copilots.
Maturing Standards and Implementation Playbooks
To support faster and more reliable adoption, large language models RAG implementation frameworks are being formalised. Expect:
- Reference architectures for different industries and use cases.
- Tooling interoperability guides (e.g., how to use LangChain, LlamaIndex, or vector DBs like Weaviate or Pinecone in governed pipelines).
- Certification and auditing toolkits to evaluate retrieval quality, output risk, and compliance coverage.
These frameworks will shorten time-to-value and reduce implementation errors, especially for teams deploying RAG in regulated environments.
Agentic RAG: Autonomous, Goal-driven Retrieval and Action
Agentic RAG describes systems that do more than answer: they plan and execute multi-step tasks using retrieval, tools, and workflow automation. For example, a compliance agent may retrieve regulations, fill a remediation ticket, and notify stakeholders, all while recording provenance for each action.
Agentic patterns require tighter orchestration: a semantic ranker, tool-use policies, action validation, and an auditable decision log. Gartner projects rising adoption of agentic systems for operational automation, making Agentic RAG a key enterprise pattern for 2026 and beyond.
GraphRAG: Relationship-aware Retrieval for 360° Reasoning
While vector-based RAG excels at similarity search, GraphRAG augments retrieval with structured relationships (entities and edges). This lets the system reason about how a regulation maps to a product line or how a contract clause affects downstream SLAs.
GraphRAG improves cross-document reasoning and supports causal queries that plain vectors struggle with, making it valuable for legal, finance and product-risk workflows. (See GraphRAG surveys and recent papers for technical reference.)
Why Now is the Time to Invest in RAG Readiness
The differentiators in the next wave of AI adoption won’t just be the model used; it will be data discipline, retrieval architecture, and governance. Companies that invest early in document quality, retrieval infrastructure, and prompt design will deploy faster, comply more easily, and extract clearer ROI from generative systems.
If your current AI assistants still rely on frozen LLM knowledge and offer no citations, now is the time to evaluate RAG-readiness, before internal stakeholders lose trust or before legal teams block production scaling.
Practical Checklist to Start a Pilot
Before expanding RAG across departments or functions, it’s essential to validate the architecture, knowledge base quality, and business impact through a focused pilot. Below is a concise checklist to guide that first implementation.
- Choose a single, high-value use case.
- Audit and tag canonical documents.
- Select an embedding model and vector store.
- Define KPIs (hallucination rate, time saved, ticket reduction).
- Implement provenance injection and logging.
- Run a controlled pilot with human-in-the-loop review.
- Measure and refine before scaling.
Appinventiv can help run this checklist end-to-end and supply a pilot with clear ROI targets.
Most enterprises have the data but lack the retrieval hygiene to make it actionable. Appinventiv doesn’t just build bots; we build sovereign intelligence systems.
How Appinventiv Helps Turn RAG Into Reliable Business Value
Appinventiv combines engineering depth, product design and program-level delivery to put RAG architectures into regular use, not just pilot projects. Our RAG development services focus on the three things that matter most to business leaders: measurable accuracy, repeatable operations, and defensible governance.
What We Do Well:
- RAG implementation consulting: We assess knowledge assets, design retrieval pipelines, and run pilots that prove the ROI of RAG models in generative AI for a specific use case.
- Production engineering & custom MLOps: Index automation, embedding refresh, vector DB operations, and multi-LLM orchestration so systems remain accurate and cost-efficient as scale grows.
- Managed RAG as a service: Fully managed index and model operations for teams that prefer outcome ownership without building the stack in-house.
- Security, compliance, and explainability: RBAC, encryption, provenance logging, and reportable audit trails to meet regulatory and internal controls requirements.
- Integration and change adoption: Connectors to CRMs, knowledge bases and enterprise systems, plus targeted onboarding to accelerate user trust and adoption.
Why Clients Choose Us:
- Cross-industry experience: Work spanning 35+ industries means we apply proven patterns and avoid common pitfalls when mapping RAG to domain needs.
- Delivery scale: More than 3,000 solutions designed and delivered, and 150+ AI models deployed, demonstrating our ability as a leading generative AI development company to move from experiments to production.
- Skilled teams: Access to 1600+ technologists and product specialists who pair domain context with engineering rigour, shortening time-to-value.
- Transformation track record: We’ve modernised 500+ legacy processes, which is why our RAG projects emphasise integration and operational durability, not just functionality.
If your priority is reducing AI hallucinations using RAG, building confidence in AI outputs, and demonstrating a clear cost/benefit case, we can help with a short assessment that maps your data, a pilot scope with target KPIs, and an estimated payback period.
For a practical next step, request a RAG readiness review or a pilot proposal, and we’ll return a concise plan with expected outcomes and timelines.
FAQs
Q. How does RAG improve AI accuracy?
A. RAG improves accuracy by retrieving contextually relevant, source-verified information at query time, guiding the model to respond based on facts rather than predictions alone.
Q. How do RAG models improve trust in generative AI?
A. By attaching citations and sourcing content from curated knowledge bases, RAG enables verifiable outputs, helping users trust the response without manual cross-checking.
Q. Why are enterprises adopting RAG over pure LLMs?
A. RAG enables faster updates, lower hallucination rates, and better control without the cost or complexity of constant fine-tuning, making it more suitable for business-critical use cases.
Q. What ROI benefits do RAG models deliver for businesses?
A. RAG reduces time spent verifying answers, lowers error-related costs, improves support efficiency, and speeds up decision cycles, directly impacting productivity and bottom-line savings.
Q. How can enterprises reduce hallucinations in generative AI?
A. By combining LLMs with retrieval pipelines that supply vetted content, enterprises can ground responses in factual data, cutting hallucinations by up to 70–90% in practice.
Q. Is RAG necessary for production-grade enterprise AI?
A. For AI systems requiring reliability, explainability, and up-to-date knowledge, RAG is essential; it provides the control, traceability, and governance that pure LLMs lack.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
Real Estate Chatbot Development: Adoption and Use Cases for Modern Property Management
Key takeaways: Generative AI could contribute $110 billion to $180 billion in value across real estate processes, including marketing, leasing, and asset management. AI chatbots can improve lead generation outcomes by responding instantly and qualifying prospects. Early adopters report faster response times and improved customer engagement across digital channels. Conversational automation is emerging as a…

AI Fraud Detection in Australia: Use Cases, Compliance Considerations, and Implementation Roadmap
Key takeaways: AI Fraud Detection in Australia is moving from static rule engines to real-time behavioural risk intelligence embedded directly into payment and identity flows. AI for financial fraud detection helps reduce false positives, accelerate response time, and protecting revenue without increasing customer friction. Australian institutions must align AI deployments with APRA CPS 234, ASIC…

Agentic RAG Implementation in Enterprises - Use Cases, Challenges, ROI
Key Highlights Agentic RAG improves decision accuracy while maintaining compliance, governance visibility, and enterprise data traceability. Enterprises deploying AI agents report strong ROI as operational efficiency and knowledge accessibility steadily improve. Hybrid retrieval plus agent reasoning enables scalable AI workflows across complex enterprise systems and datasets. Governance, observability, and security architecture determine whether enterprise AI…

























![Google Material Design’s Impact on Mobile App Design [Complete Guide]](https://appinventiv.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/Mobile-App-Designer’s-Guide-On-Material-Design.jpg)