- Understanding Non-Fungible Tokens: What They Are and How They Work
- Step 1: Defining the Asset and Minting the NFT
- Step 2: Assigning Ownership on the Blockchain
- Step 3: Listing and Selling the NFT
- Step 4: Smart Contracts and Royalties
- Step 5: Uniqueness and Rarity Driving Value
- Step 6: Transfer and Resale
- Step 7: Exploring Real-World Uses
- Exploring the Different Types of NFTs
- Digital Art
- Music and Video NFTs
- Virtual Real Estate and Gaming
- Collectibles
- Domain Names and Intellectual Property NFTs
- Fashion and Wearable NFTs
- Event Tickets and Experiences
- NFT Marketplaces: Where Digital Assets Are Traded
- How to Pick the Right NFT Marketplace
- Identify Your Goal
- Know the Blockchains in Play
- Study the Crowd
- Weigh the Fees
- Test the Experience
- The Key Benefits of NFTs: How They’re Shaping the Digital Economy
- Verifiable Ownership
- Direct Creator-Consumer Interaction
- Royalties on Resales
- Scarcity and Exclusivity
- New Revenue Streams
- Improved Transparency and Security
- Access to a Global Marketplace
- How to Get Started with NFTs: A Step-by-Step Guide to NFT Development
- Setting Up and Funding a Wallet
- Choosing the Right Blockchain and Marketplace
- Minting or Creating an NFT
- Creating High-Quality Content and Metadata
- Storing and Managing Your NFTs
- Risks Associated With NFTs and Solutions to Tackle Those
- Valuations
- Storage
- Regulation
- Hot Potato Effect
- What’s the Future of NFT Technology
- Integration with Web3 and the Metaverse
- Mass Adoption on the Horizon
- Legal Frameworks and Regulation
- Cross-Industry Innovation
- Get Started With Your NFT Journey With Appinventiv
- FAQ’s
- NFTs are evolving into high-value digital assets, influencing sectors like art, gaming, and real estate.
- Blockchain technology secures NFT ownership with transparency and immutable proof of authenticity.
- NFTs empower creators to earn royalties on resales, offering more control than traditional markets.
- These tokens are transforming industries such as gaming, fashion, and healthcare, fueling new digital economies.
NFTs have evolved way beyond simple digital collectibles; they’re now a legitimate digital asset class that’s completely changing how we think about ownership in the online world. From virtual real estate and gaming items to exclusive digital content, NFTs are creating genuine value in spaces that didn’t exist a few years ago.
What was once seen as a speculative trend is now being embraced by artists, brands, gamers, and even real estate developers. We’re witnessing the birth of a new kind of economy; one where digital assets hold real-world value, exclusivity is verifiable, and creators are finally in control of their monetization.
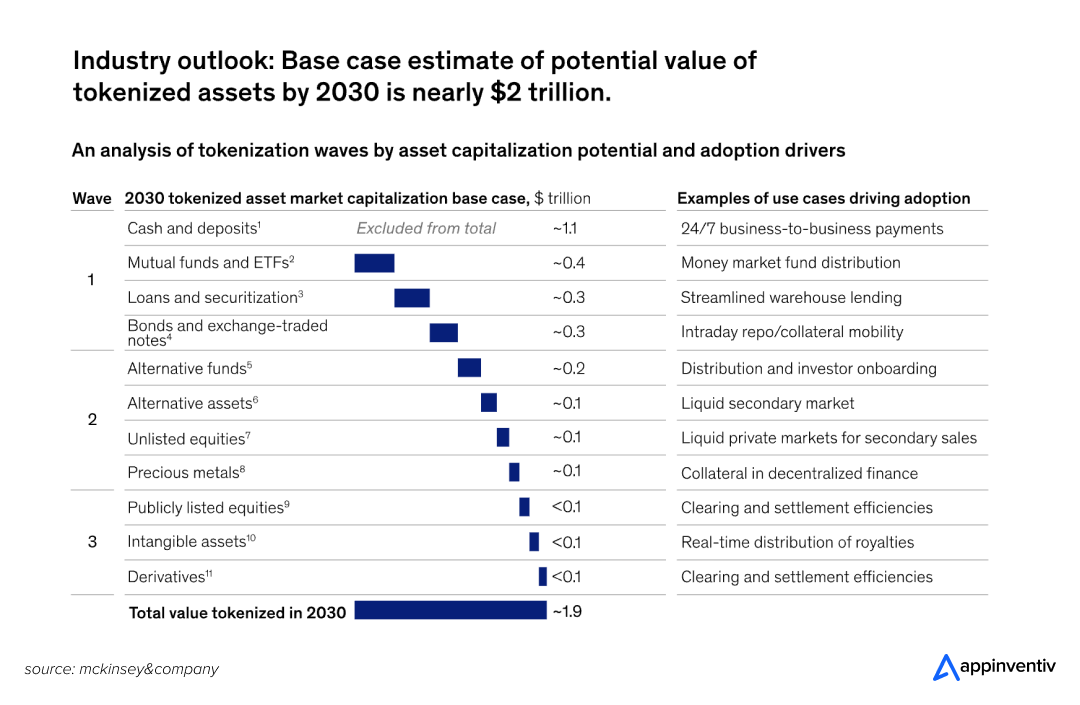
A recent McKinsey report indicates that the tokenized asset market is projected to reach over $2 trillion by 2030. This isn’t just hype anymore; NFTs are actually reshaping entire industries.
So what exactly is an NFT, and how does the whole thing work?
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about NFTs, how they’re created and traded, how they hold value on the blockchain, and what makes them “non-fungible” in the first place. We’ll cover the platforms that support them and explain why everyone from big corporations to independent creators and even government agencies are jumping on board.
Whether you’re looking to invest into gaming, creating digital art, or simply curious about what all the fuss is about, this guide will provide you with the solid foundation you need to understand and navigate the NFT world with confidence.
Let’s delve into this comprehensive guide to NFT development and explore how NFTs function, their applications, and the direction this space is heading.
Position your brand at the forefront of NFT innovation
Understanding Non-Fungible Tokens: What They Are and How They Work
To understand NFTs, it’s important to first distinguish between fungible and non-fungible assets. Fungible assets, like traditional money, can be exchanged for identical items of equal value. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs), on the other hand, are unique digital assets. Their ownership and authenticity are verified on blockchain networks like Ethereum. In this guide to NFT development, you will also learn how these unique digital assets are created, traded, and the impact they are making across various industries.
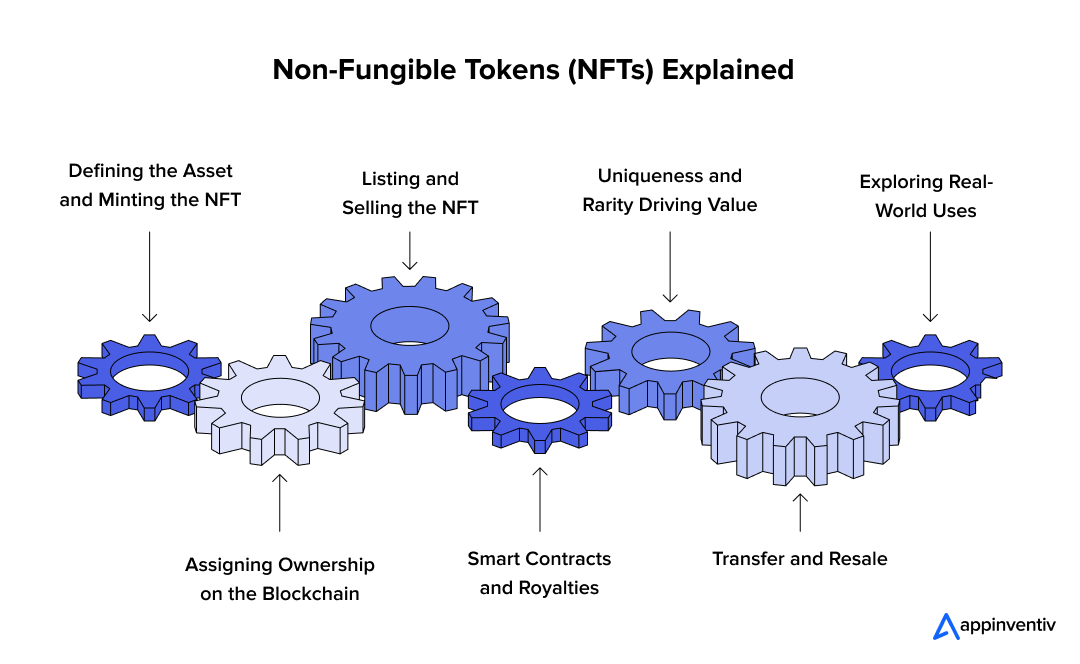
Step 1: Defining the Asset and Minting the NFT
The journey of an NFT begins with selecting a digital asset—whether it’s artwork, music, videos, in-game items, or even virtual real estate. Once the asset is chosen, it must be minted into an NFT. Minting refers to the process of creating a unique token on the blockchain that is tied to that specific asset.
This process involves uploading the digital file to an NFT platform, where it is linked to a blockchain network, most commonly Ethereum, though other blockchains like Solana and Tezos are gaining traction.
This NFT is essentially a digital certificate of ownership for the asset, and this process makes it unique, immutable, and traceable on the blockchain. The metadata, such as the creator’s information, ownership history, and even the file’s authenticity, is embedded within the NFT during minting, ensuring its singularity.
Step 2: Assigning Ownership on the Blockchain
Once an NFT is minted, ownership is recorded on a blockchain, which serves as an immutable, decentralized ledger. This means that each time the NFT is transferred or resold, the blockchain updates to reflect the new ownership.
Unlike traditional art or collectibles that could be forged or duplicated, NFTs rely on the blockchain to provide security, transparency, and irrefutable proof of ownership. This creates a trust-based environment where anyone can verify the asset’s authenticity and provenance.
Step 3: Listing and Selling the NFT
Once minted and ownership is recorded on the blockchain, the NFT can be listed for sale on various NFT marketplaces like OpenSea, Rarible, or Foundation. These platforms act as virtual galleries or marketplaces where users can buy, sell, or trade NFTs. To list an NFT, the creator or owner simply uploads the asset to the platform, sets a price, and decides whether they want to sell via auction or fixed price.
NFT marketplaces operate as intermediaries, providing the interface where creators and buyers can meet. The buyer then purchases the NFT using cryptocurrency, usually Ethereum or another supported token, which is transferred to the seller’s wallet. After the transaction, the blockchain updates to reflect the new ownership, marking the completion of the exchange.
Also Read: How much does it cost to develop a NFT marketplace?
Step 4: Smart Contracts and Royalties
One of the defining features of NFTs is the use of smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into the code. Smart contracts automate the entire transaction process, from the sale of the NFT to royalty payments.
In terms of royalties, NFTs can be programmed so that creators earn a percentage each time their NFT is resold on the secondary market. For example, a digital artist could set a royalty fee of 10%, ensuring they continue to earn every time their artwork is resold. This ongoing revenue stream provides creators with a level of financial security and fair compensation that traditional art markets often lack.
Step 5: Uniqueness and Rarity Driving Value
The non-fungible nature of NFTs is what gives them value. Each NFT is unique, which means it can’t be replaced or exchanged for something of equal value, much like a rare collectible item. Factors such as rarity, uniqueness, and the creator’s reputation can all influence the market price of an NFT.
For example, a digital artwork by a famous artist may carry a much higher price tag than a piece by an unknown creator. Similarly, the rarity of a certain NFT, such as a limited-edition item or one tied to a notable event, can drive its price higher in the marketplace. These elements of scarcity and exclusivity are what attract collectors and investors, driving the value of NFTs.
Step 6: Transfer and Resale
After a purchase has been made, the NFT can be held in the buyer’s wallet, which functions as their digital vault for assets. The buyer can choose to keep the NFT, show it off in virtual galleries, or sell it on the secondary market. When an NFT is resold, the smart contract ensures that royalties are paid to the original creator. This system ensures that creators are rewarded not only for the initial sale but also for the future success of their work.
When reselling NFTs, buyers and sellers must be aware of market trends and the factors that impact the NFT’s value. With the increasing interest in NFTs across various sectors, the resale market has grown substantially, providing ample opportunities for both creators and collectors to generate profits.
Step 7: Exploring Real-World Uses
NFTs are used for much more than just digital art. They can represent ownership of digital goods, virtual land in metaverse platforms, in-game assets, and even physical items, such as luxury goods or collectibles. The versatility of NFTs is evident across various industries, including gaming, entertainment, music, and fashion, and their applications continue to expand.
For example, in the gaming world, players can buy, sell, or trade in-game items like skins, characters, or virtual real estate using NFTs. In the art world, NFTs offer a new means for artists to monetize their work and retain control over how their creations are utilized. The impact of NFTs on various sectors is substantial, and as more industries adopt them, we can expect to see new, innovative uses emerge.
Exploring the Different Types of NFTs
NFTs have emerged as a transformative force in the digital world, revolutionizing various industries. From art and music to virtual real estate and collectibles, NFTs offer unique opportunities for creators and investors alike. In this section, we’ll dive into the various types of NFTs, each with its own distinct characteristics and impact.
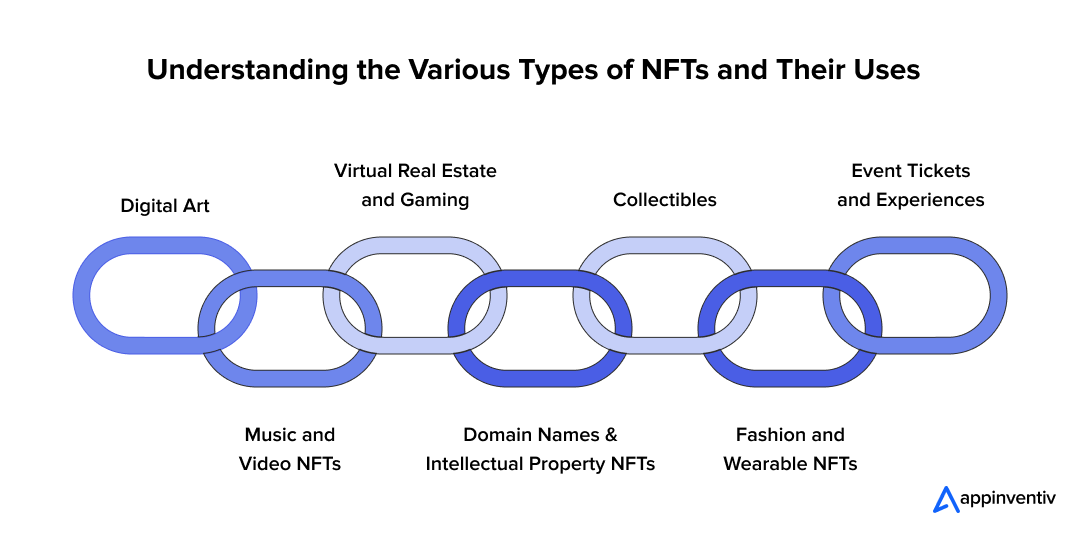
Digital Art
Digital art NFTs have revolutionized the art world. Artists can now turn their work into unique, verifiable digital assets and sell them directly to collectors. This eliminates middlemen, giving artists greater control over the authenticity and ownership history of their work. It has become one of the most prominent types of NFTs, showcasing the significant impact NFTs are having on the creative fields.
Music and Video NFTs
Musicians and content creators are using NFTs to sell exclusive tracks, albums, or video content—often with special perks like backstage passes or limited collector’s editions thrown in. This creates entirely new ways for artists to make money while building stronger connections with their fans through scarcity that wasn’t possible with traditional streaming. For anyone wondering what does NFT mean for the music business, it’s opening doors to opportunities that didn’t exist before.
Virtual Real Estate and Gaming
In virtual worlds, NFTs represent actual ownership of digital property and game items. Players buy, sell, and trade these assets just like real estate, creating economies where virtual stuff has genuine value. Platforms like Decentraland and The Sandbox have made virtual real estate one of the fastest-growing types of NFTs, fundamentally changing how digital economies work. This shift has sparked a surge in Metaverse NFT marketplace development, enabling seamless trading of virtual assets and powering the next generation of immersive digital economies.
Collectibles
NFTs have breathed new life into digital collecting by allowing people to own and trade rare, limited-edition items, such as digital trading cards, memorabilia, and virtual goods. These collectibles can appreciate over time, attracting both casual fans and serious investors. The impact of NFTs on collecting has been huge, creating markets that didn’t exist before.
Domain Names and Intellectual Property NFTs
People are using NFTs for digital assets like domain names, trademarks, and intellectual property rights. This creates transparent, blockchain-verified ownership that’s easy to track and transfer. It’s expanding the types of NFTs beyond just art and collectibles into serious business applications.
Fashion and Wearable NFTs
Fashion brands are creating NFTs for digital clothing and accessories that avatars can wear in virtual worlds. These digital wearables are becoming increasingly popular and sometimes integrate with real-world fashion pieces, creating exclusive online fashion experiences. The impact of NFTs on fashion is transforming our perspective on ownership in both digital and physical realms.
Event Tickets and Experiences
NFTs work perfectly as digital event tickets because they’re fraud-proof and can’t be counterfeited. They also unlock VIP experiences and become collectible souvenirs after the event. This shows how types of NFTs are expanding into entertainment and events, creating new ways for organizers to engage with their audiences.
NFT Marketplaces: Where Digital Assets Are Traded
NFT marketplaces are digital platforms that enable the buying, selling, minting, and showcasing of NFTs. These decentralized exchanges form the backbone of the NFT economy, connecting creators with collectors and providing tools to manage digital assets securely. These are some of the most widely used platforms in the NFT space, each catering to different types of users and content formats.
OpenSea: OpenSea is the largest and most versatile NFT marketplace. It supports Ethereum, Polygon, and Base, making it ideal for creators and collectors across categories like art, collectibles, gaming, and domain names.
Rarible: Rarible is a multi-chain, community-driven platform with its own governance token, RARI. It provides a streamlined, no-code minting experience and supports Ethereum, Tezos, and Polygon.
Foundation: Foundation offers a curated, invite-only platform for digital artists. Known for high-end art sales and a sleek user interface, it targets serious collectors looking for premium content.
SuperRare: SuperRare is an exclusive marketplace focused on single-edition, museum-quality digital art. Artists are vetted before listing, making it a go-to platform for fine digital art connoisseurs.
How to Pick the Right NFT Marketplace
While analyzing the guide to NFT development, it’s also crucial to be aware of the ways to pick the right marketplace for your NFTs. Choosing the right platform is a significant decision that impacts your visibility, earnings, and overall experience in the digital space. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you find the platform that best aligns with your goals and technical needs.

Identify Your Goal
Before you dive into a marketplace, take a moment to clarify your objectives. Are you an artist looking to sell limited-edition digital art? Perhaps you’re a collector hunting for rare, one-of-a-kind NFTs? Or maybe you’re a gamer interested in trading in-game assets or skins?
Your goals will help you narrow down platforms that specialize in your area of interest. Understanding what you want to achieve will ensure you focus on the platforms that cater to your niche.
Know the Blockchains in Play
NFT marketplaces operate on different blockchains, and not all blockchains are created equal. For example, OpenSea and Rarible run on Ethereum, while Magic Eden uses Solana, and Objkt is built on Tezos. Each blockchain has its own advantages in terms of speed, gas fees, and environmental impact.
You should choose a marketplace that supports the blockchain you’re most comfortable with. Consider the transaction costs, the speed of transactions, and the sustainability of the blockchain when making your decision.
Study the Crowd
The audience of each NFT platform can vary significantly, and knowing your community is key. For instance, OpenSea attracts a broad mix of collectors, creators, and enthusiasts, whereas SuperRare is a platform focused on high-quality digital art, appealing to a more refined crowd.
Foundation, on the other hand, is known for its exclusive, creator-driven content. Each platform has its own community with specific tastes and preferences, so it’s crucial to pick one where your work or interests will resonate the most.
Weigh the Fees
When it comes to choosing a platform, understanding the fee structure is vital. Most marketplaces charge minting fees and transaction fees when you buy or sell NFTs.
Additionally, many platforms offer royalty support, meaning you can earn a percentage each time your NFT is resold. The fees can vary widely between platforms, so take time to compare them and choose a marketplace that offers a transparent, fair fee structure based on your needs. You don’t want unexpected costs eating into your profits.
Test the Experience
Once you’ve narrowed down your choices, it’s time to evaluate the user experience. Try signing up, connecting your wallet (like MetaMask or Coinbase Wallet), and exploring the platform. Is the interface user-friendly and intuitive? Can you navigate smoothly without feeling lost? A well-designed marketplace that is easy to use makes a world of difference, especially for beginners.
Look for platforms that offer seamless onboarding, straightforward navigation, and reliable customer support. A platform that’s easy to use will save you time and frustration in the long run.
The Key Benefits of NFTs: How They’re Shaping the Digital Economy
While analyzing the guide to NFT development, it is essential to understand the unique advantages NFTs bring to various industries. From providing verifiable ownership to creating new revenue streams for creators, NFTs offer a range of benefits that are reshaping digital economies. Let’s dive into the key advantages they offer.
Verifiable Ownership
One of the most significant benefits of NFTs is that they provide rock-solid proof of ownership for digital assets. Each NFT resides on a blockchain, making it incredibly easy to track ownership and verify authenticity.
This eliminates concerns about fakes or copies, creating a transparent system where buyers can be assured they’re getting authentic assets. The ability to verify ownership gives both creators and collectors real confidence and legitimacy in the digital marketplace.
Direct Creator-Consumer Interaction
NFTs eliminate the middlemen, such as galleries and auction houses, allowing creators to sell directly to their audience. This fosters stronger, more personal relationships between artists and fans while giving creators complete control over pricing, distribution, and exclusivity.
By removing intermediaries, artists retain a significantly higher percentage of their profits, making NFTs an incredibly attractive way to monetize digital work. These advantages of NFT technology are transforming the way creative industries operate.
Royalties on Resales
One of the most notable features is that creators can earn money every time their NFT is resold. Unlike traditional art, where artists typically only profit from the initial sale, NFTs enable creators to set royalty percentages that automatically apply with each resale through smart contracts.
This creates ongoing income streams that can last for years, adding serious long-term value for both creators and collectors.
Scarcity and Exclusivity
NFTs bring the concept of rarity to the digital world by allowing creators to produce limited editions or exclusive items for specific buyers. This scarcity drives value because collectors naturally gravitate toward unique or hard-to-find pieces.
Whether it’s digital art, collectibles, or virtual fashion, NFTs recreate the exclusivity traditionally found in physical assets. This attracts collectors and investors seeking items that may appreciate in value over time.
New Revenue Streams
The advantages of NFT adoption extend far beyond art and collectibles, opening entirely new revenue opportunities across gaming, music, and virtual real estate. They provide fresh ways to monetize digital assets—selling in-game items, virtual property, or exclusive experiences that were previously impossible.
As more industries embrace NFTs, they’re creating innovative business models and building new digital economies from the ground up.
Improved Transparency and Security
NFTs use blockchain technology to ensure every transaction is completely transparent. Each transfer gets publicly recorded, making it simple to trace an NFT’s complete history and verify its authenticity.
This transparency dramatically reduces fraud and gives buyers confidence in the marketplace. The decentralized nature of blockchain also provides enhanced security, minimizing the risks of hacking and tampering that plague traditional digital platforms.
Access to a Global Marketplace
The benefits of NFTs include creating a global marketplace where creators and buyers can connect seamlessly across borders. Unlike physical art, which is limited by geography, NFTs can be bought and sold anywhere in the world.
This global reach expands the potential audience for creators while giving buyers access to exclusive items from around the world. The international accessibility of NFTs fosters a truly unified digital economy, bringing diverse creators and collectors together.
How to Get Started with NFTs: A Step-by-Step Guide to NFT Development
Entering the NFT space can be both exciting and complex. Whether you’re a digital artist, collector, or brand innovator, knowing how to create an NFT is your gateway into the world of blockchain-based digital ownership. This step-by-step guide simplifies the process so you can confidently start your journey.
Setting Up and Funding a Wallet
The first step is to create a digital wallet that supports NFTs. Options like MetaMask, Coinbase Wallet, or Trust Wallet allow you to store digital assets and connect with NFT marketplaces. Fund your wallet with cryptocurrency (typically ETH), which will be needed for minting, buying, and paying gas fees. Always store your recovery phrase securely offline.
Choosing the Right Blockchain and Marketplace
Next, select a blockchain platform—Ethereum remains the most widely used, but alternatives like Polygon, Solana, and Flow offer lower transaction fees. Choose a marketplace compatible with your blockchain, such as OpenSea, Rarible, or Magic Eden. Look for platforms that align with your goals, whether that’s selling art, launching collections, or collecting rare items.
Minting or Creating an NFT
Minting involves converting your digital file into a blockchain-based NFT. If you’re wondering how to mint or make an NFT, most marketplaces offer no-code tools to upload your asset, set royalties, and add metadata. Alternatively, you can browse existing NFTs and purchase them directly using your connected wallet.
Creating High-Quality Content and Metadata
Before minting, invest in crafting original, high-quality digital content. Whether it’s artwork, music, or video, strong visuals and storytelling increase market appeal. Add relevant metadata, including title, description, traits, and unlockable content, to enhance value and discoverability.
Storing and Managing Your NFTs
Once acquired or minted, your NFTs appear in your wallet’s collectibles tab. For high-value assets, consider cold storage using hardware wallets like Ledger or Trezor. Keep track of ownership history, royalties earned, and asset performance for future resale or portfolio management.
Build your NFT solution today with a team that delivers scalable success
Risks Associated With NFTs and Solutions to Tackle Those
While NFTs offer exciting opportunities, they also come with risks like market volatility, intellectual property issues, and security vulnerabilities. As we come to the end of this guide to NFT development, understanding the associated challenges is crucial. Once paired with the right strategies, you can build secure, sustainable NFT solutions that stand the test of time.
Valuations
NFTs, much like collectibles, are a risky investment with uncertain valuations. Since the NFT market is still emerging, there’s no guarantee of sustained demand. Buying an NFT without a clear understanding of its market value could result in overpaying for an asset that may decrease in value or become unsellable. Likewise, if you create an NFT, there’s no assurance of a buyer, which could lead to wasted time and money.
Solution: To mitigate these risks, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research on the NFT’s potential demand, its creator’s reputation, and historical trends within similar markets. Understanding market sentiment and choosing well-established platforms can also increase the chances of success. For creators, promoting NFTs effectively and engaging with the community can help generate interest and attract potential buyers.
Storage
NFTs are stored on platforms like OpenSea and Rarible, and are recorded through blockchain technology to prove ownership. However, if these platforms were to shut down, there would be no guarantee of access to your NFT, making it less secure than physical assets like art or trading cards that can’t simply vanish.
Solution: To address this, always ensure your NFT is stored on a reputable, secure platform with a proven track record. Additionally, consider diversifying storage by using decentralized solutions or creating backups to preserve your digital assets. Blockchain-based storage solutions can offer a higher level of security and ensure long-term access.
Regulation
The NFT space is currently unregulated, relying heavily on trust between buyers and sellers. There’s a risk that an NFT could be a replica, leading to potential copyright issues. Furthermore, if regulatory bodies begin to impose restrictions, it could significantly affect the value of NFT tokens and limit market participation.
Solution: To combat this, it’s essential to purchase NFTs from verified creators and established platforms that adhere to intellectual property rights. As the market evolves, it’s crucial to stay informed about potential regulatory changes and adapt by working with legal professionals who can help navigate copyright and trademark concerns.
Hot Potato Effect
NFTs, particularly in gaming, can experience a “hot potato” effect. Players may buy assets with the hope of selling them for a profit, but if the market collapses or there are no buyers, they can suffer significant losses. This creates a volatile market where the value of an NFT is largely dependent on finding the next buyer.
Solution: To mitigate this risk, players should approach NFTs with caution, understanding that the market can be unpredictable. It’s important to focus on the intrinsic value of the NFT rather than speculative pricing. Diversifying investments and participating in established and stable NFT markets can also help avoid the “hot potato” effect. For creators, ensuring the asset has genuine utility and value can encourage long-term interest and reduce market volatility.
As we near the conclusion of this ‘Step-by-Step Beginner’s Guide to NFT Development’, we’ve explored the diverse types of NFTs, understood how they differ from cryptocurrencies, and unpacked their core benefits, potential risks, and existing challenges. Now, let’s look ahead and explore what the future holds for NFTs in an increasingly decentralized and digital-first world.
What’s the Future of NFT Technology
The future of NFTs is intrinsically tied to the evolution of Web3, blockchain interoperability, and metaverse ecosystems. As digital ownership gains traction, NFTs are expected to transition from speculative assets to functional digital tools with real-world utility.
Integration with Web3 and the Metaverse
NFTs are foundational to the decentralized Web3 vision, where users own their data, assets, and identities. In metaverse environments like Decentraland, The Sandbox, and Meta’s Horizon Worlds, NFTs serve as proof of ownership for virtual land, avatars, and wearables.
Web3 and Metaverse, as cross-platform interoperability becomes more seamless, users will be able to carry their NFT-based identities and assets across multiple metaverse experiences, creating a persistent digital presence.
Mass Adoption on the Horizon
While early NFT adoption was driven by art and collectibles, the next wave is being shaped by utility-driven NFTs. These include NFTs for memberships, event access, loyalty programs, and even tokenized real estate. With major brands like Nike, Starbucks, and Gucci entering the space, mainstream adoption is accelerating. Simplified onboarding, wallet-free access, and improved user interfaces will be critical in bridging the gap for non-crypto-native users.
Legal Frameworks and Regulation
As the NFT ecosystem matures, regulatory clarity will play a key role in building trust. Issues like intellectual property rights, royalties enforcement, securities classification, and anti-money laundering (AML) compliance are gaining attention from global regulators.
Jurisdictions in the EU, Singapore, and the U.S. are actively exploring how NFTs fit into existing financial and consumer protection laws. A robust legal infrastructure will be essential to support institutional adoption and investor confidence.
Cross-Industry Innovation
NFTs are poised to disrupt a wide range of industries beyond entertainment. In education, NFTs can represent verifiable digital diplomas and skill certifications. In healthcare, they could be used to secure and tokenize personal health records on a blockchain.
Enterprises can leverage NFTs for supply chain transparency, digital twin creation, and IP protection. These emerging use cases highlight the potential of NFTs to become foundational digital assets across sectors.
Get Started With Your NFT Journey With Appinventiv
The future of NFTs is incredibly bright, with endless possibilities for innovation across industries such as gaming, entertainment, art, and even real estate. As more businesses and creators embrace this technology, NFTs will continue to disrupt traditional models of ownership, unlocking new revenue streams and creative opportunities. The integration of NFTs into virtual worlds, metaverses, and decentralized platforms is likely to evolve further, making them even more impactful in the coming years.
At Appinventiv, we are at the forefront of this transformation, offering cutting-edge NFT solutions for businesses and creators. Our team has successfully developed projects like AVATUS, an avatar-based social networking platform that integrates NFTs to provide users with unique virtual identities.
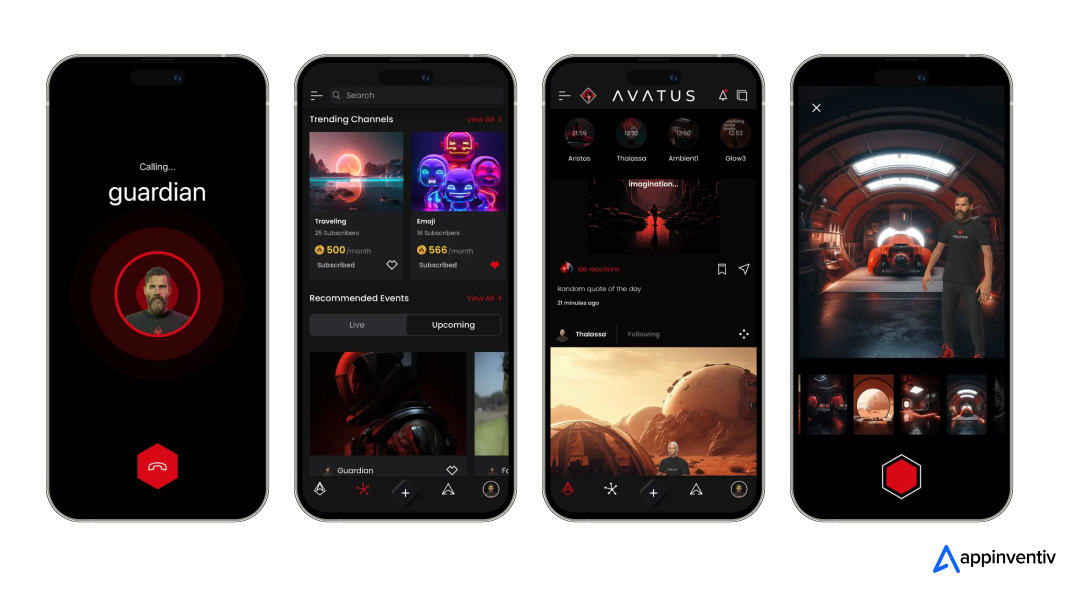
This project exemplifies how NFTs can be used to enhance social interaction and digital ownership in virtual spaces. The results were exceptional. AVATUS’s digital infrastructure was transformed into a highly secure, scalable, and efficient ecosystem. With seamless cloud and blockchain integration, the platform achieved faster operations, reduced overheads, and delivered a significantly enhanced and trustworthy user experience.
Suppose you’re ready to start your NFT journey. In that case, we, as your trusted blockchain app development partner, can help you through every step, providing expertise and innovative solutions to help you thrive in the ever-evolving NFT landscape.
FAQ’s
Q. How to create an NFT?
A. Creating an NFT is a simple process with a few essential steps:
- Select Your Digital Asset: Choose the digital item you want to turn into an NFT, like artwork, music, or in-game items.
- Pick a Blockchain: Choose a blockchain to mint your NFT, such as Ethereum, Solana, or Tezos, depending on fees and speed.
- Set Up a Digital Wallet: Set up a wallet (MetaMask, Coinbase, etc.) to store your NFTs and connect it to the blockchain network.
- Choose an NFT Marketplace: Pick a marketplace (e.g., OpenSea, Rarible, Mintable) to mint and list your NFT.
- Mint the NFT: Upload your digital asset to the marketplace, fill in the details, and mint your NFT by paying a gas fee.
- List for Sale (Optional): After minting, you can list your NFT for sale at a fixed price or auction, and set royalties for future resales.
For a more detailed walkthrough, refer to our complete guide to NFT development above to ensure you’re following best practices at every step.
Q. How do NFTs work?
A. NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) work by using blockchain technology to prove the ownership and authenticity of a unique digital asset, whether it’s artwork, music, a video clip, or even virtual real estate. Each NFT is recorded on a decentralized blockchain ledger, making it tamper-proof and easily verifiable.
When someone buys or sells an NFT, the transaction is logged on the blockchain, transferring ownership in real time. Unlike cryptocurrencies, NFTs are unique and non-interchangeable, deriving their value from rarity, utility, and demand.
Q. Which tools do I need to create an NFT?
A. To create an NFT, you’ll need a few essential tools. First, digital asset creation tools like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, or Procreate for artwork, and GarageBand or Audacity for music. You’ll also need a cryptocurrency wallet, such as MetaMask or Trust Wallet, to manage your assets.
Choose an NFT marketplace like OpenSea or Rarible to mint and sell your NFT, and select a blockchain network like Ethereum or Solana. Lastly, smart contract tools like OpenZeppelin may be used to handle transactions.
Q. What are some of the top use cases of NFTs beyond digital art?
A. While digital art is the most well-known use case for NFTs, their potential extends far beyond that. Here are some other exciting applications of NFTs:
- Gaming and Virtual Real Estate
- Music and Media
- Collectibles and Memorabilia
- Tokenizing Physical Assets
- Domain Names and Intellectual Property
Q. What are the risks of investing in NFTs?
A. While NFTs have opened up new opportunities, there are also several risks involved in investing in them. Here are some of the key risks to be aware of:
- Market Volatility
- Lack of Liquidity
- Environmental Impact
- Legal and Copyright Issues
- Scams and Fraud


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Step-by-Step Guide to Crypto Trading Bot Development in 2026
Key takeaways: Crypto trading bot development in 2026 functions as full-scale trading systems, not experimental scripts. They require the same engineering discipline as any financial platform. Execution quality drives results more than strategy logic. Latency control, order handling, and risk limits shape real-world performance. AI-based strategies work only when supported by reliable data flows, controlled…

Decentralized Exchange (DEX) Development: Features, Implementation Cost, and Enterprise ROI
Key Takeaways The development of a decentralized exchange will enable businesses to provide secure and user-controlled trading, improve transparency, and minimize the use of intermediaries. The cost of DEX development can vary depending on the platform's features, the chosen network, and regulatory requirements, and the approximate cost is about $50,000, with higher costs for customization,…

Key takeaways: Dubai's VARA framework mandates strict compliance protocols for blockchain enterprises. To comply with VARA in Dubai, enterprise blockchain systems should use private networks that only approved members can join. Choosing between Hyperledger Fabric, private Ethereum, Corda platforms, etc., significantly impacts long-term scalability, compliance automation, and maintenance costs. Enterprises implementing VARA enterprise blockchain development…




































