- Decoding Cyberattacks: Types and Their Impact on Security
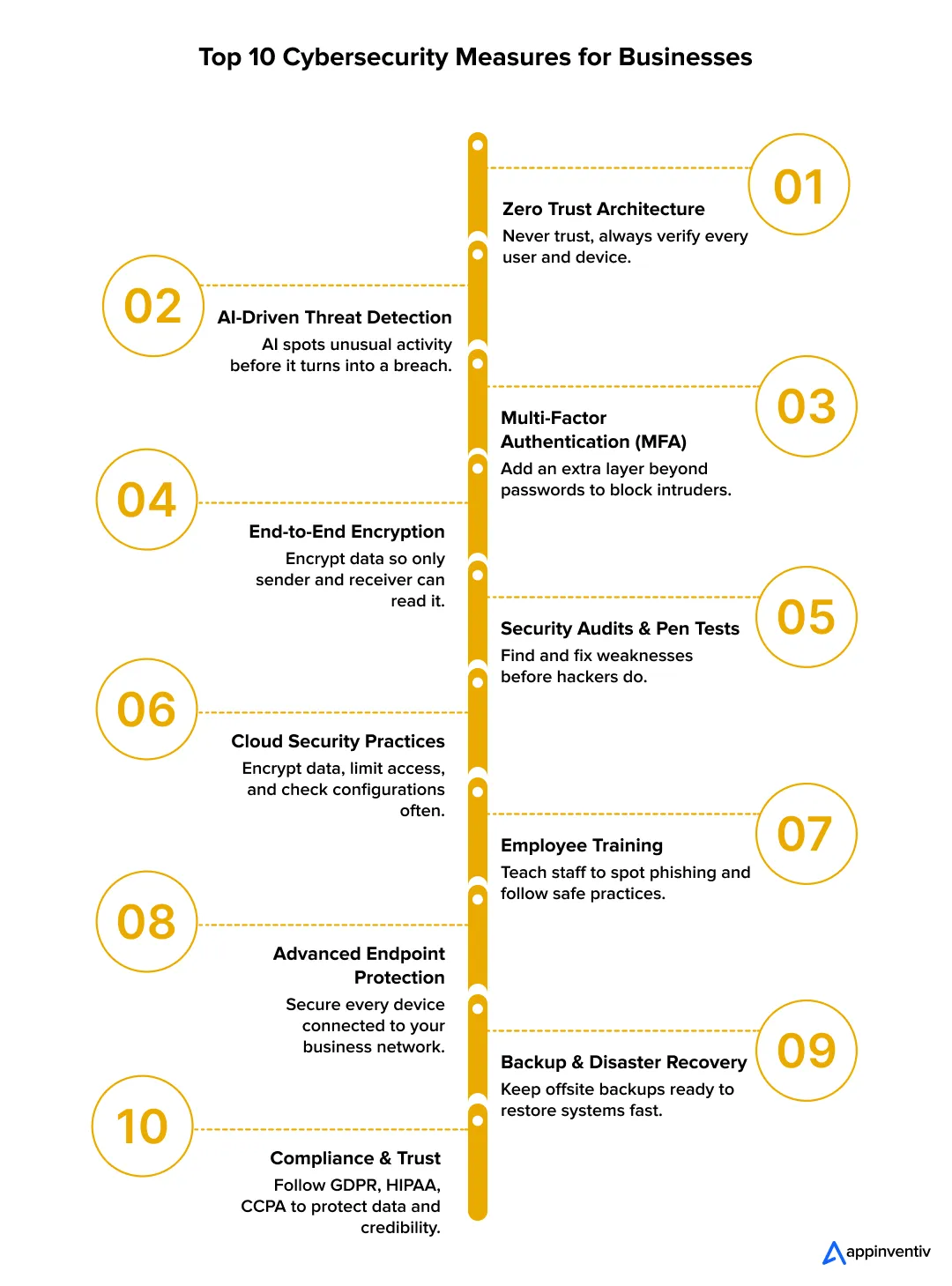
- Top 10 Cybersecurity Measures For Businesses To Look For In 2026
- 1. Zero Trust Architecture
- 2. AI-Driven Threat Detection
- 3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- 4. End-to-End Encryption
- 5. Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
- 6. Cloud Security Best Practices
- 7. Employee Cybersecurity Training
- 8. Advanced Endpoint Protection
- 9. Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
- 10. Compliance and Regulation Readiness
- The Bigger Picture
- Unlocking the Benefits of Cybersecurity for Business
- 1. Proactive Threat Hunting
- 2. Better Customer Confidence
- 3. Building a Security-First Culture
- 4. Stronger Supply Chain Security
- 5. Faster Recovery and Less Downtime
- 6. Smarter Use of Data
- 7. Real Competitive Advantage
- Strengthening Business Resilience: Cybersecurity Solutions Across Industries
- Finance
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Retail
- Energy and Utilities
- Real-World Use Cases of Cybersecurity in Business
- 1. Uber – Credential Theft and Insider Access
- 2. Anthem Inc. – Massive Patient Data Exposure
- 3. The Clorox Company – Ransomware via Service-Provider Error
- Cutting-Edge Cybersecurity Tools & Technologies
- Process of Implementing Cybersecurity in Business
- Step 1: Start With What You Have
- Step 2: Build a Plan That Actually Fits
- Step 3: Get the Basics Right
- Step 4: Teach Your Team
- Step 5: Prepare for the Worst
- Step 6: Keep an Eye on Things
- Step 7: Update Everything
- Step 8: Ask for Help
- Emerging Trends Shaping the Future of Cybersecurity for Business
- 1. Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
- 2. Security Automation
- 3. Privacy-Enhancing Computation
- 4. Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture
- 5. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
- 6. Quantum Cryptography
- 7. Biometric and Passwordless Authentication
- 8. Deception Technology
- 9. Cyber Insurance and Risk Modeling
- 10. Behavioral Analytics
- How Appinventiv Can Strengthen Your Cybersecurity Strategy
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- Cyberattacks aren’t “if,” they’re “when.” Staying safe today is more about habits and awareness than fancy software.
- Tools like Zero Trust systems, AI monitoring, and strong encryption are now the basics, not upgrades, for any business that wants to stay secure.
- People are your biggest defense. Regular training and small checks often stop the problems that firewalls can’t.
- Real stories from Uber, Anthem, and Clorox remind us that one weak password or careless click can shut things down fast.
- Spending on security isn’t a luxury anymore. Good cybersecurity measures for businesses protect your data, your reputation, and your peace of mind.
The networks we build today carry our businesses—our ideas, transactions and relationships—yet they also expose us in ways we never imagined. Every unlocked phone, remote-login session and cloud database gives both opportunity and opening for cyber-threats. What once felt like an IT concern now demands boardroom attention.
According to McKinsey, cyber-attacks may inflict as much as US $10.5 trillion annually, and the market opportunity for cybersecurity technology and services could swing toward US $1.5 trillion to US $2 trillion, far beyond current levels.
That gap between risk and readiness is where real business value lies. When you recognise that cybersecurity isn’t just a cost, but a strategic asset, the question shifts from “Should we protect ourselves?” to “How effectively are we doing it?” This article will map the evolving threats and show the major cybersecurity measures for businesses you should adopt now—so you’re not simply reacting, but staying ahead of the curve.
Secure your business now before it becomes part of that number.
Decoding Cyberattacks: Types and Their Impact on Security
Most businesses don’t get hacked because they’re careless, they get hacked because someone got lucky on the other side. Maybe an employee clicked a link too quickly. Maybe an old password never got changed. That’s all it takes.
The truth is, cyber security threats to business have become part of daily life, not rare events. Every app or device connected online adds another layer of risk. You don’t notice it until something breaks. Then you realize how fragile everything really is.
Here are some of the common types of security risks that businesses face today and what actually happens when they hit.
Phishing: A fake email lands in an inbox. It looks real, even the logo, the tone, even the signature. Someone clicks a link, logs in, and just like that, an attacker has the keys to the system.
Impact: Access to private data, stolen identity, and hours of confusion trying to figure out how it happened.
Malware: Sometimes, the danger comes from a download that looks harmless. It could be a PDF or a software update. Once opened, the malware quietly spreads.
Impact: Files get locked, systems slow down, and sometimes, the whole network goes dark. Recovery can take days.
Denial-of-Service (DoS): Imagine thousands of people trying to walk through a single door at once. That’s a DoS attack — your website or app gets flooded until it stops responding.
Impact: Your business looks offline, customers can’t reach you, and revenue takes a hit.
Man-in-the-Middle: Hackers position themselves between two people exchanging data — a customer and your payment gateway, for example. You never see them.
Impact: Sensitive details like card information or passwords get intercepted and sold or used elsewhere.
Ransomware: This one feels personal. A screen pops up, your files are encrypted, and there’s a note demanding money to get them back.
Impact: Even if you pay, there’s no guarantee the attacker will restore anything. The business stops. People panic. Work piles up.
SQL Injection: Hackers exploit weak website code to access backend databases. It’s a quiet but devastating breach.
Impact: Confidential records, customer data, even financial information — all at risk in a few seconds.
Credential Stuffing: One password gets leaked in a breach, and hackers try it everywhere else. Sometimes, it works.
Impact: One careless password can unlock several systems, making cybersecurity measures for businesses like strong authentication and identity management more critical than ever.
Understanding the link between cybersecurity threats and measures helps organizations see that prevention is not just a technical task but a shared business responsibility.
Top 10 Cybersecurity Measures For Businesses To Look For In 2026
Most cyberattacks don’t start with something dramatic. They usually start with something small. A missed software update. A reused password. A random link someone clicked without thinking. That’s all it takes.
When you look closely, cybersecurity is not just about defense tools. It’s about habits, structure, and discipline. Here are ten things that help form a reliable cybersecurity defense for businesses, helping them protect operations without slowing down innovation.
These cybersecurity for businesses practices are not just about prevention but about keeping every layer of your operation responsive and secure.
1. Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust means exactly what it sounds like. You don’t trust anyone or anything until it proves it’s safe. Every user, device, and app must verify itself before accessing data.
It’s not about paranoia. It’s about being realistic. Hackers don’t always come from outside. Sometimes the problem starts inside the network.
In simple terms, Zero Trust breaks large networks into smaller segments. So, if someone breaks in, they can’t move freely. It limits the damage. Many modern companies combine Zero Trust with multi-cloud systems and access control tools that check identities continuously. It’s one of the strongest cybersecurity measures for businesses right now.
2. AI-Driven Threat Detection
The old way of finding attacks was to look for known patterns. That doesn’t work anymore. Attackers change their methods constantly. AI tools in cybersecurity look for behavior instead.
They learn what normal traffic looks like, who logs in when, how data usually flows. When something odd happens, for example a file download at 3 a.m. or a sudden data spike, the system will react automatically.
AI doesn’t get tired. It monitors every connection, every login, every packet of data. The goal isn’t to stop every attack instantly, but to catch problems before they explode. For large organizations, this kind of AI monitoring is now a must, not an option.
As these AI tools are among the most innovative cybersecurity measures available today, helping businesses predict, identify, and respond to attacks long before they cause harm.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Most breaches still happen because of stolen passwords. Implementing MFA in your organization fixes that. It asks for something more, maybe a one-time code, a fingerprint, or a trusted device approval.
It sounds simple, but it stops more attacks than any other security layer. Even if someone steals a password, they can’t log in without the second key.
Good MFA systems also use what’s called adaptive access. That means the system knows when to ask for extra verification based on location or device. It’s a small habit that saves huge headaches.
4. End-to-End Encryption
Every piece of information your business sends out can be intercepted somewhere along the way. Encryption makes that useless to anyone who tries.
With the advantage of end-to-end encryption, only the sender and the receiver can read the data. Even the service provider in between can’t see it. Businesses usually rely on strong standards like AES or RSA encryption for this.
If you’re handling customer data, payments, or private communication, encryption is not optional anymore. It’s the digital version of locking your front door every night.
5. Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
No system is perfectly secure. That’s why testing it matters. A regular audit shows you where your weak points are.
Penetration testing goes further. It’s when ethical hackers try to break in, just like real ones would. They test your networks, applications, and devices to find blind spots.
What comes next is even more important, fixing what they find. Together, regular audits and ethical hacking form effective solutions to cyber security threats, giving teams time to fix issues before they escalate.
6. Cloud Security Best Practices
The cloud has changed how we work, but it’s also changed how we get attacked. Most breaches in cloud systems happen because of poor setup, not bad luck.
Use identity management tools to limit access. Encrypt all your stored and moving data. Scan configurations regularly to make sure nothing is left open. And review who can access what.
It’s also smart to understand the best practices of cloud security that most people don’t, and that’s where problems begin.
7. Employee Cybersecurity Training
You can have the best firewalls and software in the world, but one careless email click can undo it all. Employees need to understand what threats look like and how to handle them.
Simple cybersecurity tips for businesses like verifying sender addresses, avoiding unknown downloads, and using password managers can prevent most everyday breaches
Make the training simple and regular. Show real examples of phishing emails. Teach them how to use password managers, how to spot fake login pages, and how to report anything suspicious.
When people get used to spotting danger, security becomes second nature. A trained team is your most reliable defense.
8. Advanced Endpoint Protection
Every laptop, tablet, or phone that connects to your system is a door. You can’t guard the building if you leave the doors open.
Advanced endpoint tools keep an eye on those devices. They detect unusual behavior, block harmful files, and automatically isolate a device if it gets infected.
With remote work and personal devices becoming common, this level of control has turned from optional to essential.
9. Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
Ransomware is one of the ugliest problems out there. It locks your files and demands payment to get them back. Paying doesn’t guarantee recovery. A solid ransomware response plan does.
The right way to do this is through automated backups stored in secure, offsite systems. Test them regularly. Don’t assume they work, ensure they do.
If an attack happens, your backup should let you restore everything in hours, not days. That’s the difference between a bad day and a full-blown crisis.
10. Compliance and Regulation Readiness
Data privacy laws are strict for a reason. They protect people from misuse of their information. Following them isn’t just about avoiding fines, it’s about showing customers you care about their trust.
Whether it’s GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, make sure your business understands what applies to you. Automate compliance reports where you can, keep logs of who accessed what, and have clear data policies in writing.
A company that treats compliance as a habit, not a task, builds credibility that marketing money can’t buy.
The Bigger Picture
There’s no single tool that fixes everything. Security is like health — it’s a daily practice. You don’t stay safe by reacting. You stay safe by preparing.
Businesses that treat cybersecurity as part of their culture, not as an IT department’s job, will always be a step ahead.
Unlocking the Benefits of Cybersecurity for Business
Cybersecurity isn’t just about building walls around your data or following compliances anymore. It’s about keeping your business alive when something goes wrong. As digital threats evolve, investing in cybersecurity for businesses has turned from optional spending into essential risk management.
The reality is, no system is ever 100% safe. But companies that invest in security don’t just prevent attacks, but also recover faster, lose less, and win more trust from customers. The role of cyber security in business has evolved from simple protection to building trust and ensuring smooth, uninterrupted operations across every department.
Here’s what cybersecurity practice looks like.
1. Proactive Threat Hunting
Most businesses react to attacks only after damage is done. The smart ones hunt for trouble before it starts. They test their own systems, watch network patterns, and patch the weak spots before someone else finds them. This habit alone can save millions and build lasting cybersecurity for businesses that truly work in the background, quietly protecting everything that matters.
2. Better Customer Confidence
Customers today don’t just care about what you sell — they care about how safe it is to deal with you. A secure checkout, encrypted chats, and verified logins show that you value their privacy.
That sense of safety is what keeps people coming back. It’s not just a tech win, it’s a business one.
3. Building a Security-First Culture
Cybersecurity doesn’t start with firewalls. It starts with people. One careless click can undo a million-dollar security setup. When employees are trained to spot threats, use stronger passwords, and question suspicious messages, your defenses get stronger automatically.
Over time, this habit of awareness is what defines strong cybersecurity for business today as people remain the best line of defense.
That’s why strong cyber security for company operations begins with awareness. When people treat data as an asset, not an afterthought, risks drop across every department.
4. Stronger Supply Chain Security
Your vendors, partners, and software providers are part of your system whether you like it or not. If one of them gets breached, you’re affected too.
That’s why modern cybersecurity measures for businesses extend to third-party networks. Checking their protocols, limiting shared access, and encrypting data transfers go a long way in preventing chain reactions.
5. Faster Recovery and Less Downtime
When something bad happens — and it will, eventually — the difference between a crisis and a comeback lies in how prepared you are.
A clear response plan helps teams act fast, limit damage, and get systems running again. Every hour of downtime hurts revenue, but good planning turns panic into action.
6. Smarter Use of Data
Security and data analytics now go hand in hand. By analyzing user behavior, login patterns, and system logs, companies can spot unusual activity long before it turns into a full-scale breach.
It’s like having a digital early warning system built into your business.
7. Real Competitive Advantage
Cybersecurity doesn’t slow growth — it fuels it. Companies that show they can protect customer data attract better clients and stronger partnerships. In industries where trust is everything, being secure becomes your edge.
Strengthening Business Resilience: Cybersecurity Solutions Across Industries
Whether it’s finance, healthcare, or manufacturing, cybersecurity for businesses in each sector has its own priorities but the same mission, keep the system running, keep people’s trust, and keep the bad guys out. It’s not about who spends the most on tools. It’s about who pays attention.
Finance
The finance world never really sleeps. Transactions happen by the second, and that’s enough reason for attackers to stay active all the time. Banks know this. Fintech startups learn it fast.
Most use heavy encryption and multiple layers of authentication. They track unusual spending patterns, even the small ones. If a customer suddenly withdraws from a new country or logs in from two places at once, systems flag it. AI is getting better at spotting this kind of behavior early.
For banks, cybersecurity isn’t a line item in the budget. It’s survival.
Healthcare
Hospitals have a different problem. They aren’t just protecting data — they’re protecting lives. A system that goes down can delay treatment or expose medical history that’s meant to stay private.
That’s why hospitals have started moving to systems where every person, even staff, has to verify access every single time. Patient files are encrypted. Devices that store or transmit data are monitored constantly. Some hospitals now run practice drills for cyber incidents the same way they do for power failures.
In healthcare, security isn’t about rules. It’s about keeping people safe.
Manufacturing
Factories are a hacker’s dream. Old machines. New software. And thousands of connected devices that all talk to each other. If one gets infected, the rest follow.
The smart factories now keep their production networks separate from the main office systems. Even if someone breaks into an email account, they can’t touch the robots. Some plants track every piece of connected hardware and cut off anything that behaves oddly.
For them, a few hours of downtime can cost millions. Staying secure means staying in business.
Retail
In retail, attacks usually hit where money moves, payment gateways, online carts, customer data. Most breaches happen quietly. A small leak in a point-of-sale system or a fake email asking for credentials.
Stores now rely on tokenization, secure servers, and constant monitoring to catch these things fast. Many also train their staff as not everyone in a store knows what a phishing email looks like, so that’s where it starts.
Customers might forget a discount, but they never forget a data leak.
Energy and Utilities
The energy sector is in a league of its own. One breach here doesn’t just affect a company, but it affects cities, hospitals, entire grids.
That’s why they build layered defenses. They isolate systems, track every sensor, and run 24/7 control centers that can shut things down before damage spreads. Even backup systems have backups.
They don’t get to take chances. When the lights go out, people remember who was responsible.
Each of these examples shows one simple truth — cybersecurity isn’t about luck. It’s about paying attention before someone forces you to. You can buy tools, but you can’t buy vigilance.
And that’s what separates companies that recover from those that don’t.
Real-World Use Cases of Cybersecurity in Business
Learning from others mistakes and recoveries helps companies strengthen their own systems. Here are a few real-world use cases of cybersecurity in business that show what happens when prevention meets reality.
1. Uber – Credential Theft and Insider Access
In 2016, Uber faced a major security incident when attackers used stolen credentials to gain access to its internal systems.
Lesson:
The attack showed that human error is often the weakest link. Uber’s response reinforced how cybersecurity measures for businesses must include stronger identity management, multi-factor authentication, and tighter endpoint controls. It’s one of the most recognizable examples of cybersecurity for businesses that learned from exposure and came back stronger.
2. Anthem Inc. – Massive Patient Data Exposure
Anthem Inc. (now Elevance Health) experienced one of the largest healthcare breaches in U.S. history, exposing the personal information of nearly 79 million individuals, including names, Social Security numbers, and medical IDs.
Lesson:
The incident showed just how valuable healthcare data is — not only to patients but also to cybercriminals. It emphasized the need for stronger encryption, consistent employee training, and proactive network monitoring. Anthem’s case remains a defining example of cybersecurity for businesses that failed to scale with its data exposure and later became a key compliance benchmark for healthcare providers.
3. The Clorox Company – Ransomware via Service-Provider Error
The Clorox Company accused its IT provider of accidentally handing over credentials to hackers, resulting in a ransomware attack that cost around US $380 million.
Lesson: This is a clear reminder that supply-chain oversight is as important as internal defense.
Third-party access must be logged, verified, and limited. The Clorox case stands as proof that good vendor control forms the foundation of cybersecurity measures for businesses operating across multiple partners and networks.
Each of these stories demonstrates that examples of cybersecurity for business don’t always come from success — often, they come from recovery. The smartest organisations use these use cases of cybersecurity in business as a mirror, shaping policies that prevent history from repeating itself.
Cutting-Edge Cybersecurity Tools & Technologies
The future of cybersecurity for business will rely heavily on automation, AI-driven monitoring, and faster, more adaptive security tools. With the rise in sophisticated attacks, organizations increasingly prioritize robust cybersecurity measures for businesses to protect their valuable information and maintain operational integrity.
As a result, many are leveraging cutting-edge tools and technologies to strengthen their defenses and mitigate risks. Let’s take a closer look at these essential cybersecurity tools and technology that can help businesses safeguard against emerging threats.
Let’s comprehend it through a chart:
| Cybersecurity Tools & Technology | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Collects and analyzes security data for threat detection and compliance. | Splunk, IBM QRadar, LogRhythm |
| Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) | Monitors network traffic for suspicious activities and blocks/reports potential threats. | Snort, Cisco IDS/IPS, Suricata |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Protects sensitive data from unauthorized access and exfiltration through policy enforcement. | Symantec DLP, McAfee Total Protection for DLP, Digital Guardian |
| Web Application Firewalls (WAF) | Monitors and filters HTTP traffic to protect web applications from attacks. | Imperva, AWS WAF, F5 BIG-IP Application Security Manager |
| Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Manages user identities and access to resources for security and compliance. | Okta, Microsoft Azure AD, Ping Identity |
| Vulnerability Management Tools | Identifies, assesses, and prioritizes vulnerabilities in software and systems. | Qualys, Nessus, Rapid7 |
| Secure Web Gateways (SWG) | Protects users from web-based threats by enforcing security policies. | Zscaler, Symantec Web Security Service, Cisco Umbrella |
| Network Access Control (NAC) | Ensures only authorized devices can access the network. | Cisco Identity Services Engine, Aruba ClearPass, ForeScout |
| Threat Hunting Platforms | Actively seeks out threats that may have bypassed traditional security defenses. | CrowdStrike Falcon, Cybereason, Huntress |
| Mobile Device Management (MDM) | Manages and secures mobile devices used in an organization. | VMware Workspace ONE, MobileIron, Microsoft Intune |
| Email Security Solutions | Protects against email-based threats such as phishing and malware. | Mimecast, Proofpoint, Barracuda Email Security |
| Forensic Analysis Tools | Investigates security incidents by analyzing digital evidence and recovering data. | EnCase, FTK Imager, X1 Social Discovery |
| Behavioral Analytics Tools | Analyzes user behavior to detect anomalies indicating potential threats. | Exabeam, Sumo Logic, Balbix |
| Secure Access Solutions | Provides secure access to applications and data without a VPN. | Cloudflare Access, Zscaler Private Access, Google BeyondCorp |
| Risk Management Solutions | Helps organizations identify, assess, and prioritize risks related to cybersecurity threats. | RSA Archer, LogicManager, RiskWatch |
Process of Implementing Cybersecurity in Business
You don’t build cybersecurity overnight. It’s not a tool you install and walk away from. It’s more like maintaining a house, you start with checking the locks, fix what’s weak, and keep an eye on things before they fall apart.
Strong cybersecurity for business begins long before an attack. It starts with the systems, culture, and accountability you build day to day.
Every business that takes security seriously goes through the same few steps. Not all at once, but one layer at a time.
Step 1: Start With What You Have
You can’t protect what you don’t know exists.
Take a slow walk through your systems. What devices are connected? Where’s your data stored? Who has access and still needs it?
Most companies find surprises here as old user accounts, forgotten drives, free tools someone downloaded years ago are still in your system. These small things cause big problems later.
Make a list. Clean it up. That’s your starting point.
Step 2: Build a Plan That Actually Fits
There’s no universal security plan. What works for a hospital doesn’t fit an e-commerce store.
Start with your core, what would hurt the most if it was lost or leaked? That’s what you protect first.
Keep your plan short and clear.
- List your top risks
- Note who handles what
- Decide who gets access to sensitive data
- Add a simple response checklist in case something breaks
The goal isn’t to make it fancy. The goal is to make it doable.
Step 3: Get the Basics Right
Before you buy expensive security tools, cover the basics properly.
Here’s what that looks like:
- Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication
- Updated firewalls and antivirus
- Regular data backups stored somewhere safe
- Encryption for any file that leaves your network
- Limited admin permissions
At its core, cyber security for company systems is about consistent habits as mentioned above. If you can get these right, you’ve already fixed most of the risks small businesses face.
Step 4: Teach Your Team
You can’t fix human error with software. People need to know what danger looks like.
Run small training sessions. Training doesn’t have to be complicated. A few practical cybersecurity tips for businesses go a long way when teams know what phishing looks like and how to handle suspicious files.
Also, make it normal to ask questions. If someone’s unsure about a link or a file, they should feel safe reporting it. That one message can save you from a mess later.
Step 5: Prepare for the Worst
Even with good protection, something will slip through. That’s why you plan for bad days before they happen.
Write down what to do during a breach:
- Who leads the response
- Who handles communication
- Which systems to shut down first
- How to restore backups
Run drills once in a while. Not for compliance, but to build muscle memory. When panic hits, you’ll be glad you practiced.
Step 6: Keep an Eye on Things
Set up alerts for logins, file transfers, and network activity. You don’t need a massive setup, even basic monitoring helps.
The goal is simple: spot trouble before it grows.
Cybersecurity isn’t about being perfect. It’s about noticing change fast enough to act.
Step 7: Update Everything
The biggest risk isn’t hackers, it’s laziness.
People forget to update software or ignore those “restart to install” pop-ups. That’s how old vulnerabilities stay open.
Schedule regular reviews. Update what’s outdated. Replace what’s broken. It’s the unglamorous part of security, but it’s what keeps you safe.
Step 8: Ask for Help
Even the best teams miss things. There’s no shame in bringing experts to test your systems once or twice a year.
Ethical hackers can show you where someone could sneak in. Auditors can check if you’re compliant with the latest laws.
Sometimes an outside eye catches what’s invisible to you.
Good cybersecurity isn’t built from fear. It’s built from habit. Small routines done right keeps a business safer than any expensive software ever could.
Emerging Trends Shaping the Future of Cybersecurity for Business
Cybersecurity never stands still. The tools we use today will look outdated in a year or two. Attackers move fast, and businesses are learning to move faster. What’s interesting now is how technology is shifting from “defense” to “prediction.” Security is no longer about reacting, it’s about knowing what’s coming next.
Here’s what’s shaping the future right now.
1. Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
Companies used to monitor every system separately, one tool for emails, another for endpoints, another for servers. It worked, but only until an attacker slipped between the cracks. XDR changes that.
It connects all your data sources into one view: endpoints, cloud logs, network traffic, even user behavior. When something looks suspicious, it connects the dots across systems and tells your team exactly where the breach started.
It’s more than a dashboard, it’s a detective.
2. Security Automation
Security teams spend too much time on repetitive work: closing tickets, blocking IP addresses, running scans. Automation tools handle those tasks instantly.
Here’s how it helps:
- Automatically quarantines infected devices
- Resets passwords if credentials leak
- Flags repeated login failures
- Sends alerts only when something truly needs human review
This doesn’t replace people. It frees them to focus on serious threats instead of clicking “resolve” all day.
3. Privacy-Enhancing Computation
This one’s gaining traction fast. Imagine running analytics on customer data without ever seeing the raw data itself. That’s what privacy-enhancing computation allows.
Techniques like homomorphic encryption and federated learning make it possible to process information securely, even when it’s shared between multiple organizations. It’s a big deal for industries like healthcare and finance, where data privacy is everything.
It’s basically the future of collaboration without exposure.
4. Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture
Most companies have multiple systems across departments and cloud providers. The old model of having one big security perimeter doesn’t fit anymore.
Cybersecurity Mesh breaks the big wall into smaller zones. Each asset, such as a database, an app, a device should have its own security perimeter. It’s modular, flexible, and fits well in hybrid environments.
If one part is attacked, the rest stay safe. It’s like having separate locks on every door instead of one giant gate.
5. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
SASE combines networking and security into a single cloud-based service. It’s designed for businesses with remote teams, distributed offices, or people working from anywhere.
It merges VPN, firewall-as-a-service, Zero Trust access, and cloud monitoring into one platform.
That means no more jumping between five different tools just to secure connections. Everything runs through one consistent security layer, no matter where the user logs in from.
6. Quantum Cryptography
Quantum computing sounds like science fiction until you realize it can break most of today’s encryption methods in seconds. That’s why quantum-safe cryptography is being built right now.
Instead of relying on mathematical complexity, quantum encryption uses the principles of quantum mechanics and photon states to make interception nearly impossible.
This is still early-stage, but the race to make data “quantum-proof” has already started. Big banks and governments are testing it first.
7. Biometric and Passwordless Authentication
Passwords have outlived their usefulness. They’re hard to remember, easy to steal, and often reused.
Now, authentication is moving toward fingerprints, facial scans, and security tokens. These methods are faster and harder to fake.
Passwordless logins backed by FIDO2 standards are already being used by major companies. It’s the kind of change that makes security invisible, as it just works in the background.
8. Deception Technology
This one’s clever. Instead of just blocking attackers, deception systems lay traps like fake databases, decoy credentials, or test servers that mimic real ones.
When an intruder interacts with these, the system flags it instantly and starts tracking their behavior.
It turns the game around. The attacker thinks they’re winning, but the system’s already watching.
9. Cyber Insurance and Risk Modeling
As threats grow, more companies are turning to cyber insurance. But policies are getting stricter. Insurers now require proof of basic security hygiene for things like MFA, encryption, and incident response plans.
What’s new is risk quantification with the help of data models to predict the financial impact of cyber incidents. It helps companies understand not just “if” they’re at risk but how much that risk could cost.
10. Behavioral Analytics
Instead of focusing on the system, behavioral analytics focuses on the people. It learns how employees normally use devices and flags odd activity — like copying hundreds of files or logging in from unusual locations.
Paired with AI, it becomes a continuous learning loop. The system adapts as people’s patterns change. It’s especially useful for catching insider threats that firewalls can’t see.
These trends aren’t just buzzwords. They show where security is heading — toward systems that think, adapt, and respond before you even know something’s wrong.
In the next few years, cybersecurity won’t be a background function. It’ll be woven into every part of how businesses run, as natural as locking your front door when you leave the house.
How Appinventiv Can Strengthen Your Cybersecurity Strategy
Most companies today understand that cybersecurity matters, but many don’t know where to begin. It’s not really about chasing the latest tools. It’s about knowing what fits your business and what keeps it steady when things go wrong. That’s the kind of work Appinventiv does every day.
We help businesses build security that runs quietly in the background — systems that protect people, data, and operations without making things complicated. Before touching anything, we take time to understand how your teams work and what’s most important to protect. Then we design a plan that fits naturally into your setup.
Here’s what we focus on:
- Assess and Protect: We look closely at your network, find the cracks, and build reliable defenses around them.
- Detect and Respond: Our monitoring tools watch for strange behavior and alert you before problems grow.
- Train and Prepare: People make or break security, so we teach teams what real threats look like and how to react fast.
- Stay Compliant: We help you meet global data privacy laws like GDPR and HIPAA without slowing your business down.
We also refine the cybersecurity measures for business you already have. Sometimes that means tightening access controls, other times rebuilding outdated systems. Whatever it takes, we make sure your protection keeps pace with how fast your business moves.
If you’re looking for a cybersecurity service provider who can help your business become resilient against cyber threats, we can help you get there, step by step, without overcomplicating the process.
Our solutions are built to scale, making cybersecurity for enterprises more adaptive, compliant, and resilient in the face of evolving global threats.
Let’s make your business stronger, safer, and ready for what’s next.
FAQs
Q. How can businesses improve their cybersecurity?
A. Improving cybersecurity starts with awareness. Most breaches happen because someone missed a small detail like an outdated system, a reused password, or a missed update. Businesses can improve protection by keeping all software current, enforcing multi-factor authentication, backing up data regularly, and running quarterly security audits. It also helps to train teams to recognize scams and suspicious behavior. True security comes from habits, not just hardware.
Q. How do you prevent cyber attacks on businesses?
A. Preventing attacks means reducing every possible weak point. Start by limiting access, only share permissions with people who truly need them. Encrypt sensitive data, monitor network traffic, and use real-time alerting systems. Partnering with trusted IT or cybersecurity experts also helps identify hidden risks. The best protection is layered: people, processes, and technology all working together.
Q. Why is cybersecurity so important for businesses?
A. Because every modern business runs on data (customer information, financial records, or internal communications) and losing that data can halt everything. A single breach can cost money, reputation, and customer trust. Cybersecurity isn’t just an IT issue anymore; it’s a survival issue. It protects the brand, keeps operations stable, and ensures compliance with laws that guard customer privacy.
Q. What are the best practices for preventing cyberattacks?
A. Some best practices include:
- Protecting every endpoint like laptops, mobiles, and personal devices.
- Using Zero Trust Architecture to verify every access attempt.
- Encrypting data both in storage and during transfer.
- Running regular penetration tests and risk assessments.
- Training employees to identify phishing and social engineering attempts.
- Keeping backups offsite and testing recovery plans.
These steps make sure the business is never caught off guard by a threat that could have been prevented.
Q. What are the best cybersecurity practices for small to medium businesses?
A. For small and mid-sized teams, start simple but consistent. Focus on cybersecurity measures for businesses that are practical and affordable: strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, automatic updates, and secure cloud storage. Limit administrative access and review who can see what. Small teams also benefit from partnering with a managed security provider that can monitor networks 24/7 without adding overhead. Even basic measures, when followed properly, make a huge difference.
Q. Why is cyber security so important for businesses?
A. Cyber security for business is vital as it safeguards sensitive data and ensures regulatory compliance while maintaining customer trust. With the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, protecting proprietary and personal information from breaches is essential. A data breach can lead to substantial financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory fines, making proactive and innovative cybersecurity measures critical. Businesses must also be aware of common vulnerabilities that can expose them to risk. Weak passwords, phishing attacks, unpatched software, and insider threats can compromise security. By identifying and addressing these vulnerabilities, organizations can create a more robust cybersecurity framework to protect their operations and maintain their reputation.
Q. What are the common vulnerabilities that businesses need to be aware of?
A. Here are some common vulnerabilities businesses must be aware of:
- Weak Passwords: Many employees use easily guessable passwords or reuse passwords across multiple sites, making them susceptible to breaches.
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals often use phishing emails to trick employees into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware.
- Unpatched Software: Failing to apply security patches and updates can leave systems vulnerable to exploitation.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with malicious intent or who inadvertently expose sensitive data can pose significant risks.
- Insecure Networks: Using unsecured Wi-Fi networks or outdated hardware can increase cyberattack vulnerability.
- Lack of Security Awareness Training: Employees untrained in cybersecurity best practices can unknowingly compromise security through negligence.
Q. What role do third-party vendors play in a company’s cybersecurity strategy?
A. Third-party vendors are critical in a company’s cybersecurity strategy, as their access to sensitive information can introduce risks. Regular vendor assessments and compliance checks are necessary to mitigate these vulnerabilities.
To evaluate their cybersecurity posture, businesses can conduct security audits and risk assessments, utilizing penetration testing by ethical hackers to uncover weaknesses. Combining these strategies helps organizations enhance their innovative cybersecurity measures for businesses and reduce the risk of breaches.
Q. How often should businesses conduct cybersecurity audits or assessments?
A. The frequency of cybersecurity audits should depend on the industry’s specific risks and compliance requirements. Generally, an annual audit is a good baseline.
Still, organizations should also consider conducting assessments after significant changes in their IT environment, such as system upgrades, mergers, or data breaches.
This approach ensures that security measures remain robust and relevant to the organization’s current threat landscape.
Q. How can businesses assess their current cybersecurity posture?
A. To assess their current cybersecurity posture, businesses should start with a thorough risk assessment that identifies potential vulnerabilities within their systems and networks.
This process involves reviewing existing security policies, conducting vulnerability scans, and evaluating employee training on cybersecurity best practices. By gaining insights into their security strengths and weaknesses, businesses can prioritize areas for improvement.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Cybersecurity Risk Management - Strategy, Framework, Implementation Plan
Key takeaways: Digital transformation is rapidly increasing attack surfaces, rendering annual risk assessments obsolete in as little as 90 days. Effective cybersecurity risk management has to be treated just as any other business risk: with executive-level accountability and ongoing monitoring. Breaches involving third-party vendors exceed 60%, underscoring the need for end-to-end supply chain risk management.…

How to Build a Robust Cybersecurity Strategy in Australia for Your Business?
Key takeaways: For most Australian businesses today, cybersecurity has become as crucial as finance or operations; there is no separating it from the bigger picture. The national 2023–2030 strategy is a great backdrop, but real protection depends on how each company applies it to their own systems. Proactive businesses are focusing on fundamentals - risk…

Healthcare Cybersecurity - Key Strategies and Best Practices to Protect Patient Data
Isn't it incredible how technology is revolutionizing patient care? It’s exciting and a bit daunting! The connection between healthcare and cybersecurity cannot be ignored in this digital age. As hospitals connect their systems, the risks amplify. Cyber threats in healthcare can put patient data at risk and disrupt life-saving treatments. We must tackle these challenges…