- High-Impact Use Cases Powered by AI Agents for Insurance (Across the Value Chain)
- AI Agents for Insurance Claims Processing
- AI Agents for Underwriting Automation
- AI Agents for Fraud Detection in Insurance
- AI Agents for Policy Servicing and Customer Operations
- AI-Driven Insurance Process Orchestration
- Types and Key Features of AI Agents for Insurance
- Common Types Including Top AI Voice Agents for Insurance Industry
- Key Features Enterprises Look For
- Framework for Building AI Agents for Insurance (From Pilot to Production)
- Stage 1: Business Objectives and Risk Alignment
- Stage 2: Data Foundation and Governance
- Stage 3: AI Agent Architecture Design
- Stage 4: Model and Tooling Layer
- Stage 5: Enterprise Integration
- Stage 6: Regulatory-Compliant AI in Insurance - Security and Continuous Monitoring
- Technology Stack for Insurance AI Agent Development
- ML Models and LLM Layer
- Agent Orchestration and Workflow Layer
- Integration and API Layer
- Security, Compliance, and Monitoring Layer
- ROI of AI Agents in Insurance: What Enterprises Actually Measure
- Operational Cost Reduction Across Claims and Servicing
- Claims Cycle Time and Backlog Reduction
- Fraud Loss Prevention and Recovery Improvement
- Underwriting Throughput and Decision Consistency
- Customer Experience Impact
- Indicative Enterprise Benchmarks
- Cost of Insurance AI Agent Development
- Typical Cost Range for Insurance AI Agent Development
- Challenges in Scaling AI Agents Across Insurance Enterprises (And How to Address Them)
- Legacy System Complexity
- Data Quality and Fragmentation
- Explainability and Regulatory Scrutiny
- Managing Risk Without Slowing Everything Down
- Organizational Adoption and Change Management
- Maintaining Performance Over Time
- Future Trends and Innovations in AI for Insurance
- How Appinventiv Helps Insurance Enterprises Build Production-Grade AI Agents
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- AI agents are moving insurance operations beyond pilots into scalable, regulatory-compliant AI in insurance production-grade systems.
- Enterprise-ready AI agents require governance-first frameworks, hybrid architectures, and deep integration with core systems.
- ROI compounds through reduced cycle times, improved decision consistency, and non-linear operational scalability.
- Insurers succeeding with AI agents treat them as operational infrastructure, not isolated automation tools.
- Most insurance teams do not wake up one day and decide to “adopt AI agents.” It usually starts with pressure building in familiar places.
Claims volumes keep rising. Underwriting teams spend more time chasing data than assessing risk. Fraud patterns become harder to spot, even with mature analytics in place. At the same time, cost ratios tighten, and regulators expect clearer explanations for every automated decision.
If you are leading technology or operations in an insurance enterprise, you have likely already invested in AI-powered insurance automation. RPA, workflow tools, chatbots, predictive models. They helped, to a point. Still, many processes remain fragmented. Decisions bounce between systems. Human teams step in more often than planned.
That gap is where AI agents for insurance are starting to matter.
Instead of automating one step at a time, AI agents for insurance operate across workflows. They pull information from multiple systems, apply business logic and models, trigger actions, and loop humans in when risk or complexity increases. Claims move faster because the agent handles intake, validation, routing, and early assessment in a single step. Underwriting improves because risk signals are evaluated in context, not in isolation.
This shift is already underway across U.S. insurance enterprises, not as experiments, but as production systems tied to claims turnaround, fraud losses, underwriting capacity, and customer experience.
This guide focuses on building AI agents for insurance responsibly and at scale. We will walk through high-impact use cases, a practical implementation framework, technology considerations, and how enterprises measure real ROI. The goal is simple. Help your team develop an insurance AI transformation strategy moving from isolated automation to intelligent, compliant operations that hold up in the real world.
51% researching AI agents, only 12% deploying at scale today
High-Impact Use Cases Powered by AI Agents for Insurance (Across the Value Chain)
Most insurance leaders already know where friction exists across the value chain. Claims backlogs form after peak events. Underwriting queues grow during renewal cycles. Fraud teams chase signals that arrive too late.
What has changed is momentum. 51% of companies worldwide are actively researching AI agents for insurance, while 37% are already experimenting with them in real-world processes.
This momentum reflects broader AI agent business opportunities across industries, with insurance being among the most promising sectors.
What usually helps is understanding how AI-driven insurance workflows fit without forcing a full systems overhaul
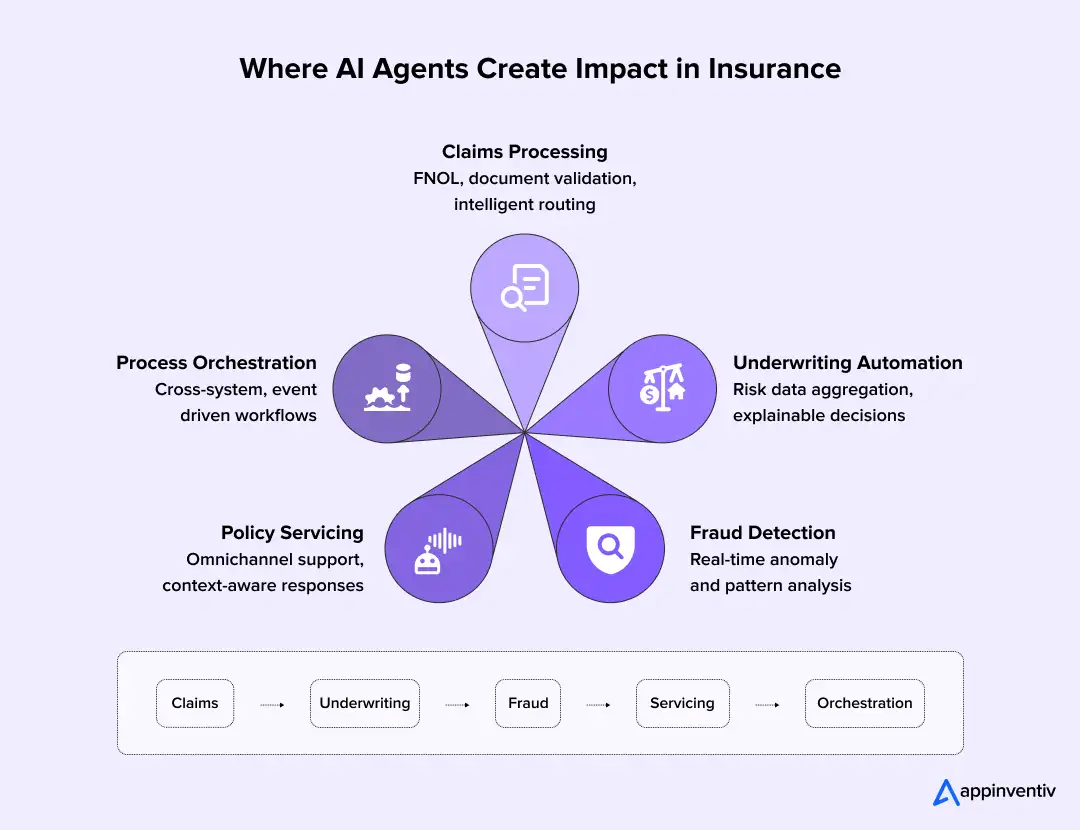
Below are the insurance AI use cases enterprises are deploying today, function by function. Insurance exemplifies how vertical AI agents transform complex, regulated industries through specialized domain expertise.
AI Agents for Insurance Claims Processing
Claims are often where insurance AI use cases demonstrate value first, as operational stress becomes visible. Intake may be digital, but everything after that still depends on fragmented systems, partial data, and manual coordination.
Only about 12% of enterprises have deployed AI agents for insurance claims processing at scale so far, which is why many operations still feel the strain despite early pilots. AI agents stay involved from the first notice through resolution.
Where agents are used
- Ingestion and validation of photos, invoices, medical reports, and police records. Health insurance claims leverage document processing capabilities similar to agentic AI in healthcare for medical record analysis.
- Coverage checks against policy terms and exclusions
- Claims triage based on severity, policy limits, and early risk signals
- Fraud indicators surfaced during active claims handling
- FNOL intake using the best AI voice agents for insurance across chat and voice, adapting questions based on claim type. For organizations interested in building AI voice agents from scratch, the technical requirements include natural language understanding, context management, and secure integration.
What changes in practice
- Straightforward claims move forward without repeated manual reviews
- Adjusters receive structured case summaries instead of raw documents
- Exceptions are identified early, reducing rework and leakage
AI Agents for Underwriting Automation
Among insurance AI use cases, Underwriting teams with insurance risk assessment using AI are rarely short on expertise. The bottleneck usually sits upstream, gathering data, validating sources, and documenting decisions.
AI agents for underwriting automation help compress that cycle.
Where agents are used
- Aggregating risk data from internal systems and third-party providers
- Normalizing inputs before scoring and assessment
- Supporting straight-through underwriting for low-risk submissions
- Escalating complex or borderline cases to human underwriters
- Running automated risk evaluations with underwriting decision intelligence and explainability built in. Risk assessment techniques used in agentic AI in finance translate well to insurance underwriting, particularly for commercial lines.
What changes in practice
- Turnaround times drop without lowering underwriting standards
- Underwriting decision intelligence remains traceable for audit and compliance reviews
- Senior underwriters spend less time on routine submissions
AI Agents for Fraud Detection in Insurance
Fraud detection represents one of the most critical insurance AI use cases, most effective when it happens continuously, not at isolated checkpoints. AI agents for fraud detection in insurance operate alongside live workflows, monitoring patterns as activity unfolds.
Where agents are used
- Claims and application fraud detection
- Behavioral analysis across customer interactions
- Network-based pattern recognition across related entities
- Post-claim investigation and recovery analysis
- Real-time anomaly detection during claims or policy changes. Insurance fraud detection shares many techniques with AI financial fraud prevention in banking, including behavioral analysis and network pattern recognition.
What changes in practice
- Fraud signals surface earlier in the process
- Investigation teams focus on high-probability cases
- False positives decline as context improves
AI Agents for Policy Servicing and Customer Operations
Policy servicing remains one of the high-volume insurance AI use cases that often appears automated externally. Internally, it still requires coordination across policy administration, billing, and customer support systems.
At the same time, customer expectations are shifting, with nearly 70% of consumers saying they would use AI agents for complex purchases, and 50–60% open to using them across everyday product decisions. This shift mirrors adoption patterns in AI agents in retail, where customers increasingly prefer automated interactions for routine transactions.
AI agents reduce that internal complexity.
Where agents are used
- Policy changes, endorsements, and renewals
- Call deflection backed by real backend execution
- Agent assistance for service representatives during live interactions
- Omnichannel servicing across chat, voice, and contact centers. Leading insurers deploy AI customer service agents that maintain context across all channels, improving both efficiency and customer satisfaction.
What changes in practice
- Customers move between channels without restarting conversations
- AI for insurance agents and service teams reduces time navigating multiple systems
- After-call work decreases as context and actions are pre-filled
AI-Driven Insurance Process Orchestration
The most advanced insurance AI use cases emerge when agents work across functions instead of inside silos. Here, intelligent insurance automation acts as a coordinator through agents.
Where agents are used
- Orchestrating workflows across claims, underwriting, finance, and compliance. Autonomous business agents coordinate these cross-functional workflows without constant human intervention.
- Triggering downstream actions based on policy, claim, or customer events. Claims settlements increasingly leverage agentic payment systems that execute transactions automatically when approval criteria are met.
- Maintaining state across long-running insurance processes
What changes in practice
- Fewer manual handoffs between departments
- Faster end-to-end processing without sacrificing controls
- Better alignment between operational teams and compliance requirements
While use cases show what AI agents can do, enterprise teams often ask what this looks like in production. Appinventiv answered this by building MyExec, an AI-powered business consultant that analyzes enterprise documents, synthesizes insights, and delivers decision-ready recommendations through a conversational interface.
The platform demonstrates how AI agents can move beyond automation into continuous business advisory, operating reliably across real-world data and workflows.
Types and Key Features of AI Agents for Insurance
By the time insurers start designing AI agents for insurance programs, the focus shifts from experimentation to fit. Different insurance workflows demand the best AI for insurance agents with varying capabilities in AI-powered insurance automation, and successful deployments reflect that distinction clearly.
Common Types Including Top AI Voice Agents for Insurance Industry
These agents are typically deployed based on their roles in claims, underwriting, fraud detection, and customer-facing insurance workflows.
Conversational AI agents for insurance
Used for claims processing, policy inquiries, and customer service operations. These agents rely on strong conversational AI and natural language understanding to guide customers through FNOL, coverage questions, and servicing requests.
Virtual assistants and virtual receptionists
Designed as AI for insurance agents in front-office and contact center support. The best AI voice agents for insurance manage call routing, basic servicing tasks, and customer intake while maintaining conversation context across channels.
Pre-trained task agents
Applied to repeatable workflows such as document classification, policy lookups, and basic validation. These agents accelerate deployment while handling high-volume, low-variance tasks.
Specialized decision agents
Built for fraud detection and insurance risk assessment using AI with underwriting risk signals. They combine machine learning models with business rules to support explainable insurance decisions.
Key Features Enterprises Look For
Insurance enterprises evaluate AI agents based on how well they perform in real workflows, not in isolated demos. The focus is on reliability, integration depth, and decision support across regulated processes.
Core functional capabilities
- API integration with claims platforms, policy administration systems, and customer-facing applications
- Document and policy intelligence to extract, validate, and interpret unstructured data such as forms, images, and contracts
- Machine learning models tuned for insurance-specific tasks, including classification and prediction
Operational intelligence
- Support for end-to-end claims processing, from intake to routing and resolution
- Built-in fraud detection using behavioral patterns and anomaly signals
- Risk assessment engines that surface clear, explainable underwriting risk signals
Customer-facing intelligence
- Conversational AI agents for insurance handling policy inquiries, FNOL, and service requests across channels
- The best AI voice agents for insurance include virtual assistant capabilities, including a virtual receptionist, to support customer service operations and contact centers
- Context awareness that enables personalizing recommendations during renewals, endorsements, and servicing interactions
When these features work together, AI agents move beyond task automation. They support insurance teams with accurate decisions, faster resolution, and consistent customer experiences, all while operating within enterprise governance and compliance expectations.
Framework for Building AI Agents for Insurance (From Pilot to Production)
Most insurance enterprises do not struggle to launch pilots. The real friction in building AI agents for insurance shows up when pilots need to pass compliance reviews, integrate with core systems, and keep delivering value quarter after quarter.
Insurance AI agent development that survives that transition requires a deliberate framework. One that balances speed with control, and innovation with accountability. Below is the insurance AI implementation framework mature teams use to structure the journey from early experimentation to production-grade deployment.
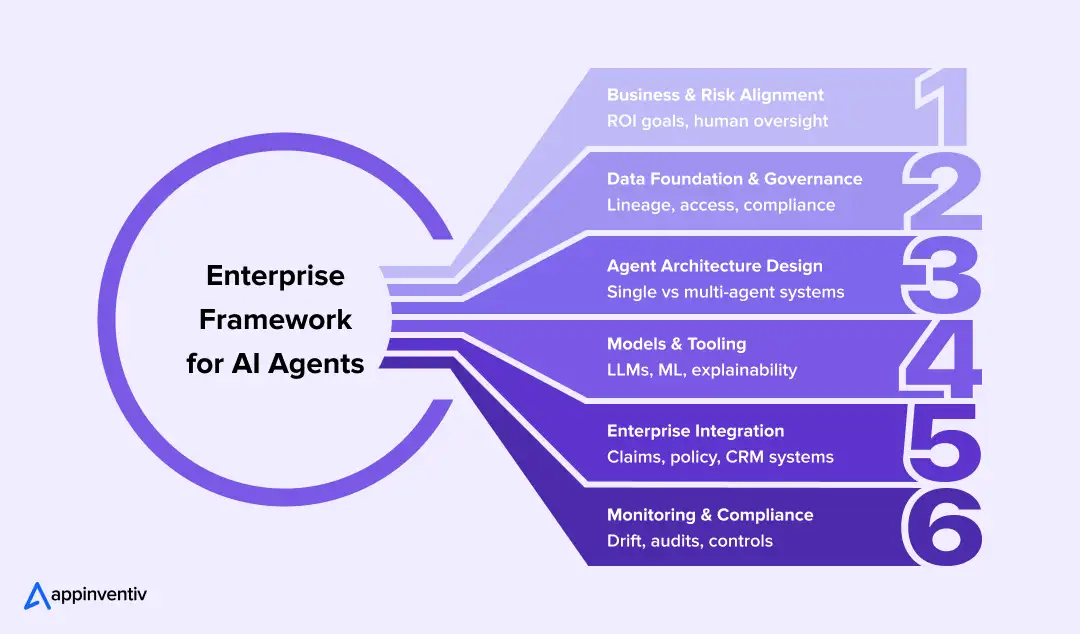
Stage 1: Business Objectives and Risk Alignment
Every successful AI agent program starts with clarity, not technology. At this stage, your team needs to align on where AI agents should intervene and, just as importantly, where they should not.
What teams typically define
- Priority workflows such as FNOL, claims triage, underwriting intake, fraud detection, or policy servicing
- Business outcomes tied to those workflows, reduced cycle time, lower cost per claim, higher underwriting capacity, fraud loss reduction
- Risk boundaries that determine when agents act autonomously and when humans must be involved
In practice, this alignment avoids downstream tension. Compliance, legal, and operations teams know upfront how decisions will be made and reviewed, which makes later approvals far smoother.
Stage 2: Data Foundation and Governance
AI agents are as reliable as the data they operate on. Enterprise insurance analytics data is rarely centralized. Policy details live in one system, claims in another, documents in shared drives, and risk signals come from third parties. This stage focuses on making that complexity manageable.
What this stage usually involves
- Assessing the readiness of structured data, such as policy attributes and claims fields
- Preparing unstructured data, including documents, images, and adjuster notes
- Establishing data lineage so every agent action can be traced back to its source
- Defining access controls, retention rules, and consent handling for sensitive data
Teams that rush past governance often see agents behave inconsistently once real-world data variability enters the system.
In regulated insurance environments, AI agents use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with secure vector databases to retrieve policy and claims data, reducing hallucinations and ensuring audit-ready, traceable decisions.
Stage 3: AI Agent Architecture Design
With objectives and data in place, architecture decisions take center stage. This is where your team defines how AI agents behave inside the enterprise.
Key questions addressed here
- Should a single agent handle the workflow, or do multiple agents collaborate across steps
- How agents trigger actions, call APIs, and hand off tasks to humans
- Where language models are used versus deterministic or predictive models
In insurance environments, hybrid designs are common. LLMs handle language-intensive tasks such as intake and summarization, while traditional ML models handle scoring, classification, and risk assessment. This balance improves reliability and auditability.
Insurance AI agents typically combine RAG-enabled LLMs with deterministic rules and predictive models, ensuring explainable decisions while maintaining strict control over underwriting and claims risk logic.
Stage 4: Model and Tooling Layer
This stage turns design into execution. AI tools for insurance agents are selected, trained, and validated based on their role in the workflow, not because they are new or popular.
What typically comes together
- NLP models for customer interactions and document understanding
- Computer vision models for images, scans, and damage assessment
- Anomaly detection models for fraud and risk monitoring
- Explainability tools to surface why decisions were made
For insurance teams, explainability is not a nice-to-have. Underwriting and claims decisions often need to be reviewed months later, sometimes by regulators, sometimes in disputes.
Stage 5: Enterprise Integration
AI agents do not replace core systems. They work through them. This stage ensures agents are embedded into existing insurance platforms rather than operating in parallel.
Common integration points
- Policy administration systems
- Claims management platforms
- CRM and contact center tools
- Data lakes, warehouses, and external data providers
When integration is done well, AI for insurance agents reduces manual navigation between systems. When it is not, teams bypass them entirely.
Stage 6: Regulatory-Compliant AI in Insurance – Security and Continuous Monitoring
Once agents are alive, governance becomes continuous. Models evolve. Data patterns shift. Regulations change.
What mature teams put in place
- Performance and drift monitoring to catch degradation early
- Detailed audit logs capturing inputs, decisions, and actions
- Human-in-the-loop checkpoints for high-risk scenarios
- Security controls aligned with enterprise and regulatory standards
This final stage enables AI agents to operate confidently at scale, not just during controlled pilots.
Build governed, scalable AI agents aligned with insurance operations
Technology Stack for Insurance AI Agent Development
Once teams agree on the framework, the next question usually comes quickly. What does the actual technology stack look like for insurance AI agent development when building systems meant to run inside an enterprise, not a sandbox?
There is no single “best” stack. What matters is how each layer supports reliability, auditability, and integration with systems you already depend on. Below is how mature insurance teams typically structure the stack, layer by layer.
Data Ingestion and Storage Layer
Insurance workflows generate a mix of structured and unstructured data. Policies, claims records, images, PDFs, call transcripts. All must be accessible without creating new silos. This layer focuses on making data usable and traceable.
What this layer handles
- Ingestion of policy, claims, and customer data from core systems
- Secure storage of documents, images, and interaction logs
- Versioning and lineage so agent decisions can be audited later
In practice, teams often prioritize reliability over speed here. Losing traceability later costs far more than a few milliseconds saved upfront.
ML Models and LLM Layer
This layer is where intelligence lives, but it should never operate in isolation. Insurance agents usually rely on a combination of models, each chosen for a specific role.
What typically runs here
- Language models for intake, summarization, and customer interaction
- Predictive models for risk scoring and classification
- Computer vision models for document and image analysis
- Anomaly detection models for fraud and risk signals
The key decision is not which model is most advanced. It is whether each model’s output can be explained, logged, and reviewed when needed.
Agent Orchestration and Workflow Layer
This is the insurance process orchestration layer that turns models into agents. Here, logic, state, and decision flows are defined so agents know what to do next and when to stop.
What this layer manages
- Task sequencing across multi-step AI-driven insurance workflows
- Tool and API calls based on agent decisions
- State management across long-running insurance processes
- Human handoffs for exceptions or high-risk cases
In real insurance operations, this orchestration layer often determines whether agents feel helpful or disruptive to teams.
Integration and API Layer
AI agents create value only when they operate within existing platforms. This layer connects agents to the systems your teams already use every day.
Common integration points
- Policy administration and claims management systems
- CRM and contact center platforms
- Billing, payments, and finance systems
- External data providers and third-party services
Strong integration reduces manual work. Weak integration creates parallel processes that people eventually avoid.
Security, Compliance, and Monitoring Layer
For insurance enterprises, this layer is non-negotiable. Agents must operate within strict security and regulatory boundaries while remaining observable.
What this layer supports
- Role-based access control and data encryption
- Audit logs capturing agent inputs, decisions, and actions
- Monitoring for performance degradation and model drift
- Alerts and controls for abnormal behavior
This is also where governance becomes visible. When regulators or internal auditors ask how decisions were made, this layer provides the answer.
Beyond deployment, production insurance AI agents require continuous monitoring, drift detection, and governance reviews to maintain accuracy, compliance, and long-term ROI.
ROI of AI Agents in Insurance: What Enterprises Actually Measure
The ROI of AI agents in insurance conversations tend to surface late in AI discussions. Often, by the time pilots are completed, expectations are already set. In insurance, that usually creates friction. Leaders want to know upfront where value shows up, how fast it compounds, and how reliably it can be measured.
When AI agents are deployed inside core insurance workflows, ROI becomes visible in operational metrics your teams already track. Not abstract AI scores. Real numbers are tied to cost, speed, and capacity.
Below is how enterprises typically evaluate returns.
Operational Cost Reduction Across Claims and Servicing
Cost savings rarely come from eliminating roles. They come from removing repetitive work.
AI agents reduce manual effort across intake, validation, routing, and follow-ups. In claims and servicing, that translates into fewer handoffs, less rework, and lower dependency on overtime or temporary staffing during peak periods.
Where cost reductions appear
- Fewer manual reviews for routine claims and requests
- Lower after-call work for service teams
- Reduced dependency on external processing vendors
Over time, teams see more predictable operating costs even as volumes fluctuate.
Claims Cycle Time and Backlog Reduction
Cycle time through claims lifecycle automation is one of the fastest indicators of AI agent impact. When AI agents for insurance claims processing manage FNOL, validate documents early, and route claims intelligently, bottlenecks start disappearing. Claims move forward with fewer pauses waiting for missing information or manual checks.
What improves in practice
- Faster initial claim acknowledgment
- Shorter time between submission and first decision
- Backlogs shrink without adding adjuster headcount
This improvement often shows up within weeks of deployment, which is why claims teams are usually early adopters.
Fraud Loss Prevention and Recovery Improvement
Fraud ROI looks different from operational savings. It is about avoiding losses and achieving better recovery rates.
AI agents surface fraud signals earlier in the lifecycle, while claims are still active. That timing matters. Intervening early prevents payouts that are difficult or impossible to recover later.
How value is measured
- Increase in fraud detection accuracy
- Reduction in false positives that waste investigation time
- Higher recovery rates through connected post-claim analysis
The compounding effect becomes clear over time as patterns strengthen and models adapt.
Underwriting Throughput and Decision Consistency
Underwriting ROI often shows up as capacity gain. AI agents for underwriting automation handle data collection, normalization, and first-pass assessments. Underwriters spend less time preparing and more time applying underwriting decision intelligence.
What changes for underwriting teams
- Higher submission throughput without sacrificing rigor
- More consistent decision rationale across cases
- Clear documentation is ready for audit or review
This consistency reduces risk exposure while allowing teams to scale without proportional hiring.
Customer Experience Impact
Customer experience improvements are often indirect, but measurable. As customers become more comfortable using AI agents across industries, expectations around speed, clarity, and continuity in insurance interactions continue to rise.
Faster claims resolution using top AI voice agents for insurance industry, fewer follow-ups, and smoother servicing interactions all contribute to higher satisfaction. AI agents help maintain context across channels and reduce friction during high-stress moments, such as claims filing.
Common CX indicators
- Improved CSAT and NPS scores
- Higher retention rates at renewal
- Fewer complaints related to delays or miscommunication
These gains reinforce operational ROI by reducing churn and service overhead.
Indicative Enterprise Benchmarks
Once AI agents move beyond pilots and into core insurance workflows, performance gains begin to show up in familiar metrics. The table below reflects ranges commonly observed across large insurance enterprises after production deployment, not best-case demos.
| Area of Impact | What Enterprises Typically See | Why It Improves |
|---|---|---|
| Claims handling time | 30–50% reduction | Agents manage FNOL, document checks, and routing early, reducing pauses and rework |
| Fraud detection effectiveness | 20–40% uplift | Continuous signal monitoring surfaces risk during processing, not after payout |
| Underwriting productivity | 25–35% improvement | Data aggregation and first-pass assessments free underwriters from prep work |
| Claims backlog volume | Meaningful reduction within weeks | Faster triage prevents accumulation during demand spikes |
| Service operation costs | Steady decline over time | Lower after-call work and fewer manual touchpoints across channels |
A single feature or model does not drive these benchmarks. They emerge when AI agents are embedded into workflows, monitored continuously, and governed with the same rigor as other enterprise systems.
Cost of Insurance AI Agent Development
By the time AI agents move from pilot to production, teams need a clear view of cost. Not an estimate built on theory, but one grounded in scope, integration depth, and compliance requirements.
Costs vary based on how many workflows are automated, how tightly agents integrate with core insurance systems, and the level of governance required.
Typical Cost Range for Insurance AI Agent Development
| Implementation Scope | What It Usually Covers | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Proof of concept or limited pilot | Single use case, basic workflows, limited integrations, controlled data scope | $40K – $80K |
| Department-level deployment | One function, such as claims or underwriting, deeper integrations, and governance controls | $80K – $180K |
| Multi-workflow implementation | Claims plus underwriting or servicing, orchestration layer, compliance-ready logging | $180K – $300K |
| Enterprise-scale rollout | Multiple lines of business, advanced orchestration, security, monitoring, and optimization | $300K – $400K |
These ranges typically cover core build and integration work. Ongoing expenses, such as cloud usage and model monitoring, are planned separately.
For most businesses, priority is not the lowest starting cost. It is building a system that can scale without repeated rebuilds as adoption grows.
Challenges in Scaling AI Agents Across Insurance Enterprises (And How to Address Them)
Most insurance leaders see early results from AI agents. The challenge with AI agent deployment in insurance enterprises is keeping those results consistent as usage grows.
What works with Insurance AI Agents in one line of business or one region often breaks down when exposed to real-world scale, subjected to regulatory scrutiny, and exposed to organizational complexity.
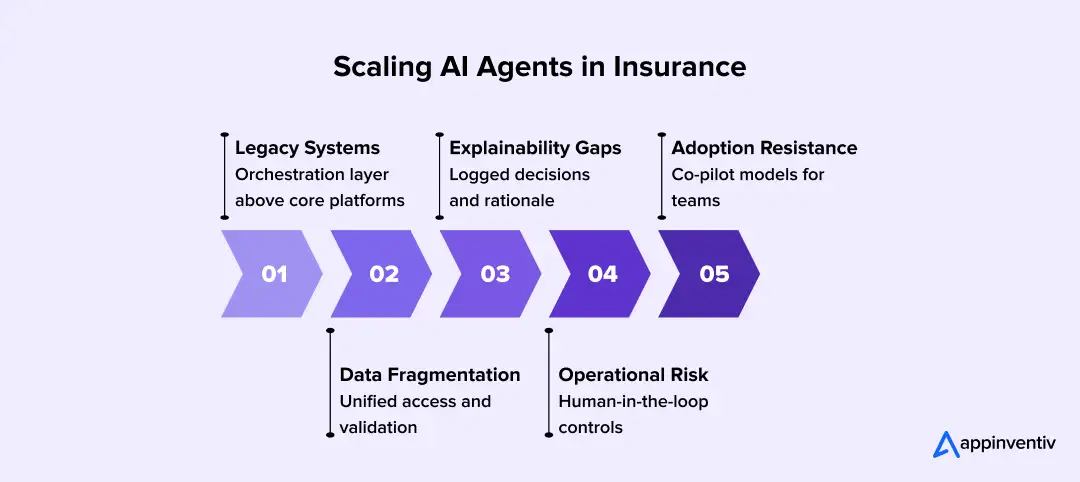
Below are the most common challenges enterprises encounter, along with the approaches that help resolve them.
Legacy System Complexity
Insurance environments are built on systems that were never designed to support autonomous agents. Policy administration platforms, claims systems, and billing tools often operate in isolation, with limited APIs and rigid workflows.
Agents struggle when they need to coordinate actions across systems that do not communicate well with one another. Teams end up creating workarounds that increase maintenance overhead.
How enterprises address it
- Introduce an orchestration layer that sits above core systems
- Use event-driven patterns instead of tightly coupled integrations
- Start with high-impact workflows before expanding across platforms
Data Quality and Fragmentation
AI agents rely on consistent, trustworthy data. In insurance, that data is often incomplete, duplicated, or spread across multiple repositories. Inconsistent data leads to conflicting decisions, which erodes trust quickly, especially in underwriting and claims.
How enterprises address it
- Establish a unified data access layer for agents
- Apply validation rules before data reaches models
- Prioritize lineage and traceability over raw volume
Explainability and Regulatory Scrutiny
Regulatory-compliant AI in insurance decisions are subject to internal reviews, customer disputes, and regulatory audits. Black-box behavior is not acceptable if teams cannot explain how an agent reached a decision; adoption stalls, regardless of performance.
How enterprises address it
- Combine LLMs with rule-based and predictive models
- Log inputs, outputs, and rationale for every decision
- Design workflows that surface explanations alongside outcomes
Managing Risk Without Slowing Everything Down
Autonomous systems introduce risk if they act without appropriate controls. At the same time, excessive oversight defeats the purpose of automation. Teams either over-constrain agents or hesitate to deploy them beyond pilots.
How enterprises address it
- Define clear autonomy boundaries for each workflow
- Use human-in-the-loop checkpoints for high-risk decisions
- Gradually expand agent responsibility as confidence grows
Organizational Adoption and Change Management
Even well-designed agents fail if teams do not trust or use them. Adjusters, underwriters, and service teams may see AI for insurance agents as disruptive rather than supportive..
How enterprises address it
- Position agents as co-pilots, not replacements
- Involve operational teams early in design and testing
- Measure and share performance improvements transparently
Maintaining Performance Over Time
Models drift. Data patterns change. Regulations evolve. What works at launch may degrade quietly until issues surface in audits or customer complaints.
How enterprises address it
- Monitor performance and drift continuously
- Schedule regular model reviews and retraining
- Treat AI agents as living systems, not one-time deployments
Scaling AI agents in insurance is less about overcoming one obstacle and more about managing several at once. Enterprises that succeed treat these challenges as part of the operating model, not exceptions.
Solve integration, governance, and adoption challenges before enterprise rollout
Future Trends and Innovations in AI for Insurance
AI agents for insurance are shifting from isolated automation to coordinated, real-time intelligence. The next phase of AI-powered insurance automation focuses on systems that continuously adapt, cleanly sit atop legacy infrastructure, and improve decision quality across the enterprise without forcing large-scale platform replacements.
Key trends to watch
- Multi-agent systems where conversational AI agents for insurance handle anomaly detection, fraud detection, and risk assessments in parallel. Effective AI agent interoperability enables these specialized agents to coordinate decisions without manual orchestration.
- AI insurance underwriting powered by real-time data insights rather than static applications, improving speed and consistency
- Advanced fraud detection using behavioral signals and network analysis instead of fixed rules
- Modular AI tech stacks that let insurers evolve capabilities without disrupting core systems
- Modular AI tech stacks that let insurers evolve capabilities without disrupting core systems. This mirrors agentic AI in SaaS platforms, where composable architectures enable rapid capability expansion.
- Enterprise insurance analytics for competitive intelligence and market analysis supported by AI agents tracking portfolio trends and external signals. Similar to AI trading agents in financial markets, insurance agents now leverage real-time data for dynamic risk assessment and pricing.
- Smarter integration with legacy infrastructure, where AI orchestrates workflows instead of replacing platforms. Successful implementations follow proven AI integration patterns that minimize disruption while maximizing value.
- While AI agents provide powerful automation capabilities, they work best when deployed through expert insurance technology consulting that addresses cloud infrastructure, data modernization, and process re-engineering simultaneously.
Together, these trends signal a move toward AI as an operational layer across the insurance industry. The next phase requires comprehensive enterprise AI agent deployment strategies that balance innovation with operational stability. One that enhances judgment, improves resilience, and keeps pace with changing risk, regulation, and customer expectations.
How Appinventiv Helps Insurance Enterprises Build Production-Grade AI Agents
Most insurers reach Appinventiv, a top AI agent development services company, after testing tools and pilots for building AI agents for insurance. At that stage, the insurance AI transformation strategy challenge is no longer whether AI works, but how to scale it responsibly across regulated workflows. Successful enterprise AI adoption requires balancing innovation velocity with risk management and governance requirements.
Our role is to guide insurance AI agent development with the right architectural and vendor decisions, then execute with discipline.
What Appinventiv brings to insurance AI programs
- Proven delivery of 100+ autonomous AI agents and 150+ custom AI models, built and deployed by 200+ data scientists and AI engineers
- Experience across 35+ industries, including compliance-heavy environments, where AI-powered decision-making must remain explainable
- Deep expertise in LLM-based AI agent design, combining generative AI with advanced algorithms and traditional machine learning
- Strong focus on natural language understanding for claims intake, underwriting summaries, and conversational AI systems
- Clear guidance on building or buying the best AI for insurance agents technology, helping teams evaluate off-the-shelf AI solutions versus custom development
- Hands-on support with technology vendor management, cloud service providers, and complex integration challenges
- Robust data management practices to ensure lineage, auditability, and long-term scalability. Our approach incorporates agentic AI data engineering principles to maintain data quality and governance at scale.
Business impact delivered
- 50% reduction in manual processes through claims lifecycle automation
- 90%+ agent task accuracy
- 2x scalability without linear cost growth
Just as important is governance. As an AI governance consulting company, Appinventiv designs compliance-ready architectures, decision logs, and human-in-the-loop controls from day one. This ensures AI agents remain trustworthy, auditable, and effective as adoption expands across the insurance enterprise. Let’s connect and start your AI program.
FAQs
Q. How can insurers use AI agents to automate claims and underwriting?
A. Insurers automate claims and underwriting by deploying AI agents that manage intake, validate documents, check coverage, aggregate risk data, and route cases intelligently. Agents escalate complex scenarios to humans while maintaining audit trails and explainable decisions across the workflow. This shortens cycle times and improves consistency without sacrificing compliance at scale.
Q. What is the ROI of deploying AI agents in insurance operations?
A. ROI is measured through operational savings, faster cycle times, and capacity gains rather than abstract AI metrics. Enterprises track reduced claims handling time, fraud loss prevention, underwriting throughput, and service efficiency. When agents are embedded into workflows, returns compound as volumes grow while operating costs remain stable and predictable over time.
Q. How do insurance enterprises safely deploy agentic AI at scale?
A. Safe deployment starts with clear autonomy boundaries, human-in-the-loop controls, and governance baked into design. Comprehensive AI agent security frameworks address both technical vulnerabilities and operational risks in production environments. Enterprises combine LLMs with deterministic models, log every decision, and continuously monitor performance.
Phased rollouts help teams validate behavior before expanding scope. This approach keeps systems compliant, auditable, and trusted by operations teams during real-world usage.
Q. What insurance AI implementation framework should insurers follow to build AI agents?
A. Insurers benefit from a staged framework that moves from business alignment to data readiness, architecture, and governance. This includes defining risk boundaries, designing hybrid agent architectures, integrating with core systems, and monitoring continuously. The focus remains on production reliability rather than experimentation, so deployments scale predictably across the enterprise over time.
Q. How can AI agents reduce operational costs in insurance?
A. AI agents reduce costs by removing repetitive manual work across claims, underwriting, and servicing workflows. They automate intake, validation, routing, and follow-ups while supporting human teams. This lowers handling time, reduces rework, and limits dependence on overtime or external vendors during demand spikes without compromising service quality or compliance expectations.
Q. How does Appinventiv help insurers build production-grade AI agents?
A. Appinventiv helps insurers design, build, and scale AI agents that operate reliably in regulated environments. Teams combine domain expertise, secure architectures, and governance-first delivery. From use-case prioritization to monitoring, solutions are built for long-term adoption, not short-term pilots. This ensures measurable ROI, compliance, and operational trust at scale across insurance operations.
Q. How should insurers select and evaluate AI tools and vendors for AI agent programs?
A. Insurers should evaluate AI tools for insurance agents based on how well they support AI-powered decision-making, integration with existing systems, and long-term governance. Teams must assess whether to build or buy AI technology, comparing off-the-shelf AI solutions with custom LLM-based AI agents.
Key factors include data management maturity, natural language understanding, machine learning capabilities, compatibility with cloud service providers, and the vendor’s approach to technology vendor management and integration challenges. Beyond technical evaluation, choosing AI development partners requires assessing domain expertise, delivery track record, and governance maturity.
Q. What types of AI agents are used in insurance? What key features should enterprises evaluate?
A. Insurance enterprises use multiple types of AI agents depending on the workflow. Conversational AI and virtual receptionist agents support policy inquiries, claims processing, and customer service operations. These AI-powered user interfaces are replacing traditional form-based interactions with natural conversation flows.
Pre-trained agents handle document and policy intelligence at scale, while specialized decision agents focus on fraud detection, risk assessment, and underwriting risk signals. Key features to evaluate include strong API integration, machine learning accuracy, and the ability to personalize recommendations within regulated insurance environments.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
Real Estate Chatbot Development: Adoption and Use Cases for Modern Property Management
Key takeaways: Generative AI could contribute $110 billion to $180 billion in value across real estate processes, including marketing, leasing, and asset management. AI chatbots can improve lead generation outcomes by responding instantly and qualifying prospects. Early adopters report faster response times and improved customer engagement across digital channels. Conversational automation is emerging as a…

AI Fraud Detection in Australia: Use Cases, Compliance Considerations, and Implementation Roadmap
Key takeaways: AI Fraud Detection in Australia is moving from static rule engines to real-time behavioural risk intelligence embedded directly into payment and identity flows. AI for financial fraud detection helps reduce false positives, accelerate response time, and protecting revenue without increasing customer friction. Australian institutions must align AI deployments with APRA CPS 234, ASIC…

Agentic RAG Implementation in Enterprises - Use Cases, Challenges, ROI
Key Highlights Agentic RAG improves decision accuracy while maintaining compliance, governance visibility, and enterprise data traceability. Enterprises deploying AI agents report strong ROI as operational efficiency and knowledge accessibility steadily improve. Hybrid retrieval plus agent reasoning enables scalable AI workflows across complex enterprise systems and datasets. Governance, observability, and security architecture determine whether enterprise AI…