- What Is Ambient Listening in Healthcare?
- From Dictation to True Ambient AI
- Inside an Ambient Listening System Architecture for Healthcare
- How Ambient Listening Is Changing Daily Clinical Work
- Relieving Documentation Overload and Burnout
- Boosting Coding Efficiency and Reimbursement
- Enhancing Patient Experience and Clinician Presence
- Smarter Team Collaboration and Workflow
- Quality Reporting, Analytics, and Population Health
- Real-World Use Cases: Ambient Listening in Action
- Mass General Brigham (Boston Area)
- Stanford Health Care (Stanford Medicine)
- Houston Methodist (Texas, USA)
- Cleveland Clinic (Ohio, USA)
- How to Keep Ambient Listening Safe, Compliant, and Transparent
- HIPAA, GDPR, and Everyday Compliance
- Consent, Transparency, and Opt-Out
- On-Device vs. Cloud and Audio Retention Policies
- Legal Discovery and Record Retention
- Building and Sustaining Patient Trust
- Integrating Ambient Listening Seamlessly into Existing Healthcare Systems
- EHR Interoperability and SMART on FHIR
- Security Controls and Endpoint Architecture
- Infrastructure and Environment Considerations
- Latency and Offline Mode
- Accuracy and Reliability Standards for Ambient Listening Systems
- Key Metrics to Track
- Shadow Pilots and Acceptance Thresholds
- Specialty Tuning and Edge Cases
- Balancing AI Power with Human Oversight
- Calculating the Real ROI of Ambient Listening in Healthcare
- Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership
- How to Measure ROI in the Real World
- Evaluating Vendors and Avoiding Hidden Costs
- Looking Beyond the Numbers
- How to Bring Ambient Listening Into Real Clinical Practice
- Start Small and Build Confidence
- Find Your Early Believers
- Keep Listening and Keep Improving
- Be Honest With Patients
- What’s Next for Ambient Listening in Healthcare
- Coordinating Care Without Extra Clicks
- Unlocking Insights for Population Health and Research
- A Changing Regulatory and Ethical Landscape
- Looking Ahead
- Shaping the Future of Connected Care — Together
- FAQs
Key Takeaways
- Ambient listening is helping doctors get back to what matters most, spending time with patients instead of screens.
- Hospitals using these tools are finding evenings a little freer, records a little cleaner, and teams a lot happier.
- When ambient listening connects with EHR systems, the paperwork finally starts taking care of itself.
- Real hospitals, from Mass General Brigham to Houston Methodist are already seeing how this technology saves time without losing the human touch.
- The next chapter of healthcare isn’t about more automation, it’s about quiet technology that listens, supports, and gives care its rhythm back.
“If I had two extra hours every day without being chained to the keyboard after the clinic, I’d call it a miracle.”
That’s what many doctors quietly say after long shifts. Healthcare today runs on screens and checkboxes, and that constant documentation demand has become its own form of exhaustion. What started as a way to improve recordkeeping now often keeps providers away from the very people they’re meant to help.
Ambient Listening Technology in Healthcare is changing that. Instead of typing or dictating, clinicians can simply focus on the patient while AI securely listens, interprets, and creates structured notes in real time. It captures what matters, organizes it for the record, and gives doctors back their time — time they can spend understanding, explaining, or just connecting.
Across hospitals and clinics, this quiet layer of AI is becoming the unseen assistant in the exam room — summarizing, coding, and supporting decisions without getting in the way. It’s not replacing clinicians; it’s removing the friction that technology once introduced.
The result? Fewer late-night charts, fewer clicks, and more meaningful care moments. But behind this promise lie real questions — about privacy, data accuracy, and how these systems fit into already complex healthcare operations. This article explores how ambient listening works, what it can fix, and what providers must prepare for before bringing it into their workflow.
Partner with Appinventiv to develop custom ambient listening software for hospitals and care providers.
What Is Ambient Listening in Healthcare?
For years, healthcare technology has done a good job of collecting data but not always of making life easier for the people using it. Every update to an EHR or workflow tool promised efficiency, yet somehow added another click or screen to manage. Ambient listening shifts the focus back to simplicity. Instead of asking doctors and nurses to fit into a system, it quietly fits into the way they already work. It listens in the background as natural conversations happen, turning them into useful, structured information. The technology almost disappears, allowing the human connection between doctor and patient to come through again.
From Dictation to True Ambient AI
Old dictation tools forced clinicians to pause mid-thought or repeat themselves into a recorder. Ambient listening, on the other hand, doesn’t wait for commands. It runs quietly during the visit, recognizing who’s speaking and capturing key details as the conversation unfolds. The result is a real-time, structured summary that can include notes, diagnoses, treatment plans, and billing codes.
It’s a small change on the surface but a big one in practice — moving from documenting after the visit to documenting as care happens. That shift is what makes ambient listening so different from traditional transcription.
This shift shows how ambient listening for medical transcription is evolving from passive dictation to active clinical understanding.
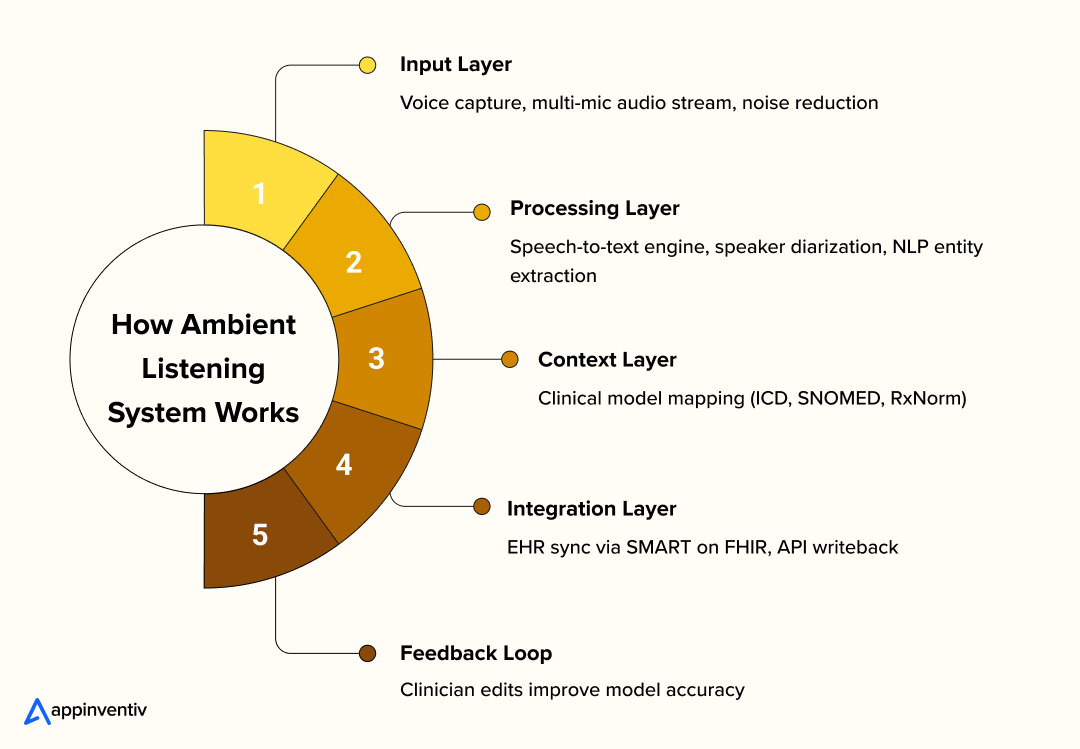
Inside an Ambient Listening System Architecture for Healthcare
Understanding how ambient listening in healthcare works helps providers see why it’s more than transcription, it’s intelligent interpretation. The pipeline typically involves:
- Speech recognition + diarization — separating speakers, transcribing the conversation
- NLP / concept extraction — mapping phrases to clinical concepts (symptoms, diagnoses, medicines, labs)
- Clinical context modeling — confirming relevant medical context (past history, allergies, medications)
- EHR writeback / suggestion layer — writing draft notes, aligning with EHR data models (Encounter, Observation, Medication, etc.)
- Feedback loop — clinician edits feed back into the learning model
Vendors differ in architecture: some do inference locally (on-device) to minimize audio transmission; others upload encrypted audio/streams to a cloud. Some never store raw audio (only final notes), others do (for QA or compliance). For example, Freed markets a “no-audio-retention” model.
Major players or proof-of-concept vendors include Nuance DAX, Abridge, Suki, Augmedix, and others. These early applications of ambient listening in healthcare are already proving how quiet, context-aware AI can simplify care delivery without disrupting the human connection.
How Ambient Listening Is Changing Daily Clinical Work
The real value of ambient listening technology in healthcare is not a flashy feature list. It is time back for clinicians and steadier workflows for teams. When notes write themselves in the background, visits feel less rushed, handoffs get cleaner, and evenings are not swallowed by unfinished charts.
Hospitals start seeing documentation as an area to improve, not just endure. The result is small but meaningful wins that add up across a day, a clinic, and a system. Many hospitals first explore ambient listening for medical transcription as an entry point before expanding to full workflow automation.
Relieving Documentation Overload and Burnout
Many clinicians still spend one to two extra hours after clinic finishing charts. That load chips away at rest and focus, and it is a major driver of burnout. McKinsey notes that automation and generative AI can take a meaningful share of administrative work off clinicians, allowing them to spend more time on core care tasks and judgment.
Deloitte reports similar signals from ambient speech pilots. Physicians describe fewer hours behind the screen and less need to finish charting at home, which often means better recovery and a healthier work rhythm.
Boosting Coding Efficiency and Reimbursement
Clear, complete notes are the foundation for accurate billing. Auto-structured narratives with suggested codes help improve E M level accuracy, reduce undercoding or overcoding, and bring denial rates down. The benefit is not only revenue. There are fewer back-and-forths between clinicians and coders, and faster, cleaner claims.
Enhancing Patient Experience and Clinician Presence
One of the key benefits of ambient listening technology in clinics is simple, it lets doctors be fully there with their patients. No typing, no clicking through screens, just a real conversation.
When a doctor can look up and truly listen, the visit feels different. The room slows down a little. There’s more warmth, more eye contact, and space for honest questions. Patients walk out feeling heard, and doctors end the day feeling like they actually practiced medicine, not paperwork.
Smarter Team Collaboration and Workflow
Care rarely ends at the exam room. Ambient notes that land in the EHR quickly help nurses, care coordinators, and pharmacists act without delay. Tasks get created automatically, orders are easier to review, and small issues can be flagged before they turn into bigger ones. The team moves together rather than in a line.
As these ambient listening services for hospital systems mature, they’re helping care teams communicate faster and reduce delays between departments.
Quality Reporting, Analytics, and Population Health
Responsibly captured conversation data can strengthen quality programs such as MIPS and HEDIS, and it supports research and population health work when de-identified and aggregated. Deloitte points to a future where these systems begin to suggest optimal care pathways in real time, informed by what patients say and what the data shows.
Real-World Use Cases: Ambient Listening in Action
Several leading health systems are already testing ambient listening in healthcare to understand how it fits within complex clinical workflows. Hearing about theoretical benefits is one thing.
The growing list of use cases of Ambient Listening Technology in Healthcare shows how hospitals are beginning to integrate AI-driven documentation tools into real clinical workflows.
Below are a few strong use cases where providers are already experimenting or operating with this technology.
| Health System | Focus Area | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Mass General Brigham | Multi-specialty pilot | 90% note accuracy, expanded to 800 clinicians |
| Stanford Medicine | DAX Copilot integration | Less admin work, more patient time |
| Houston Methodist | Inpatient + Outpatient | 2–4 hours saved daily, 90% focus improvement |
| Cleveland Clinic | 80+ specialties pilot | Vendor comparison & documentation ROI |
Mass General Brigham (Boston Area)
Mass General Brigham launched an ambient documentation pilot involving about 20 clinicians across multiple specialties. They securely record patient-clinician conversations and use AI to generate draft clinical notes, which clinicians then review and finalize. According to their reports:
- ~90% of the AI-drafted content ended up in the clinicians’ final notes, suggesting strong alignment and accuracy of the system’s outputs.
- The pilot expanded to ~800 clinicians over time.
Their experience demonstrates that ambient listening can scale across specialties once safety concerns and workflow alignment are addressed.
Stanford Health Care (Stanford Medicine)
Stanford Health Care is working with DAX Copilot (by Nuance / Microsoft) to integrate ambient listening into clinical documentation.
- Their pilot aimed to let the AI listen to patient interactions and generate draft notes that clinicians then review and edit.
- Leadership expressed belief that the technology can help clinicians “spend more time with patients and reduce the burden of administrative, nonclinical work.”
Stanford’s approach typifies the “assistive AI copilot” model, where the clinician maintains control but gets support.
Houston Methodist (Texas, USA)
Houston Methodist has expanded ambient listening into inpatient settings (ED, hospital floors) beyond outpatient clinics:
- Roughly 500 clinicians use ambient listening in outpatient specialties including primary care, orthopedics, OB/GYN, and gastroenterology.
- Early user feedback: some clinicians report reductions of 2 to 4 hours per day in time spent on notes.
- Their provider satisfaction metrics: ~90% said they were better able to focus on patients, 92% said charting time savings, 86% improved work-life balance.
- They are now testing adaptations for high-acuity care (ED) given the noise and rapid pace there.
Houston Methodist is one of the stronger public examples of expansion from outpatient to hospital settings.
Cleveland Clinic (Ohio, USA)
Cleveland Clinic carried out a robust pilot across 80+ specialties to evaluate multiple AI scribe vendors:
- They tested five AI scribe platforms against metrics like documentation quality, provider satisfaction, ease of implementation, and ROI.
- Following evaluation, they chose Ambience Healthcare’s AI platform for documentation, clinical documentation integrity, and point-of-care coding.
- The Clinic sees ambient listening as a vehicle to reduce administrative burden.
Cleveland Clinic’s careful vendor comparison and broad specialty testing make it a valuable reference for other health systems.
These examples show how ambient listening healthcare solutions are moving from small pilots to full-scale rollouts across diverse healthcare systems.
Let Appinventiv’s healthcare innovation team guide you, from strategy to full-scale ambient listening software development.
How to Keep Ambient Listening Safe, Compliant, and Transparent
Skipping this section is a guarantee of failure. No matter how advanced the technology is, ambient listening technology in healthcare will only work if patients and clinicians trust it. When a tool has access to clinical conversations, the stakes are higher than with any other kind of data. Privacy, security, and transparency have to be built in from the very first line of code.
At its heart, ambient listening technology in healthcare is still handling Protected Health Information (PHI) — the same sensitive data governed by laws like HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe. Providers that ignore compliance, or delay setting up the right safeguards, risk not only breaches but also reputational damage that can undo years of patient trust.
Teams planning to build healthcare ambient listening systems should prioritize compliance and communication from day one.
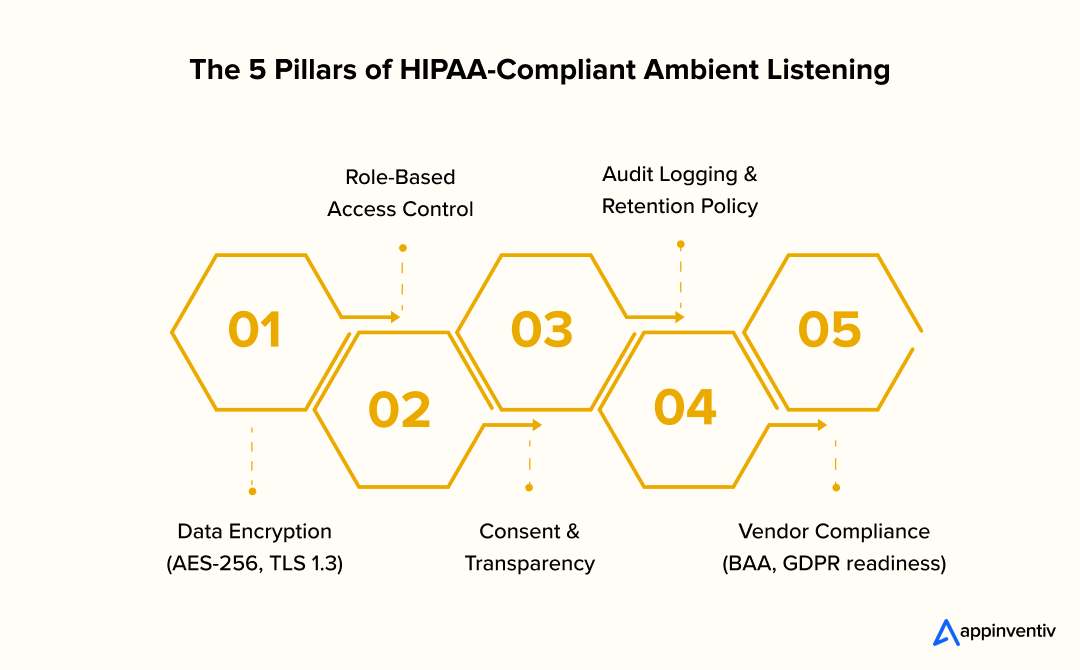
HIPAA, GDPR, and Everyday Compliance
When developing HIPAA-compliant ambient listening software, every safeguard — from encryption to access control, must meet the same standards as electronic health records.
Every ambient listening system must operate with the same discipline as a clinical record system. That means:
- Encryption in transit and at rest to secure both live audio and stored data
- Role-based access controls that restrict who can view or edit transcripts
- Comprehensive audit logs that record every action for accountability
- Data minimization so only the required information is processed
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with vendors that handle PHI
- Regular third-party security audits and penetration testing
It is also critical that ambient systems align with EHR security standards and interoperability frameworks such as SMART on FHIR, ensuring secure, standardized data exchange. You can read more about this on Building HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare Apps, which covers security controls and encryption protocols that apply directly to voice-enabled systems.
Consent, Transparency, and Opt-Out
Ambient listening sits closer to the patient than most technologies ever have. It hears the moments of diagnosis, decision, and reassurance. That closeness requires a new level of consent and communication.
Healthcare organizations should design clear consent workflows, including:
- Visible signage in clinics informing patients that conversations may be recorded for AI documentation
- Verbal consent scripts, such as: “We will record this session to help with documentation. You can pause or stop at any time.”
- Opt-out controls that allow clinicians or patients to disable recording easily
- Explicit consent for telehealth visits, where audio capture can feel less visible
- Defined retention rules, specifying how long raw audio, drafts, and final notes are stored and when they are deleted
This process should be part of the onboarding for both staff and patients. Teams must be trained to explain the technology in plain language, emphasizing control and choice rather than surveillance.
On-Device vs. Cloud and Audio Retention Policies
How an ambient system processes and stores data is one of the most important technical decisions a provider will make.
- On-device processing keeps conversations within the hospital or clinic network, minimizing external exposure. It is often the preferred model for high-sensitivity environments.
- Cloud-based systems provide scalability and richer AI processing but expand the surface area for security risks. Teams developing HIPAA-compliant ambient listening software must define how data is processed, stored, and deleted to stay within federal and regional compliance frameworks.
- Audio retention practices should be disclosed upfront. Some systems delete raw audio immediately after transcription, while others retain it temporarily for quality review or model training. Providers must define timelines for deletion, redaction protocols, and access review processes.
If you are exploring cloud-first solutions, read our guide on healthcare data security that outlines the right balance between AI capability and patient data protection.
Legal Discovery and Record Retention
During Healthcare ambient listening software development, providers must ensure generated transcripts and notes comply with legal standards for recordkeeping.
Once ambient listening becomes part of the clinical workflow, its outputs are treated like official records. That means they must comply with legal and operational standards for recordkeeping:
- Maintain complete logs of edits to transcripts or generated notes
- Enable export in standard formats that can integrate with EHR or legal systems
- Keep version control and audit trails for every modification
- Follow deletion and de-identification protocols after mandatory retention periods expire
- Support patient rights under HIPAA, such as data access, correction, or restriction requests
Hospitals should involve compliance officers early when evaluating vendors. Every system must pass risk assessments and data protection impact analyses (DPIAs) before full rollout.
Building and Sustaining Patient Trust
In the end, privacy compliance is only part of the story. Real trust comes from being transparent about how the technology works. Patients and caregivers need to know:
- What is being recorded — whether audio, transcript, or extracted clinical concepts
- How long it stays in the system and who is responsible for storage
- Who can see it, and for what purpose
- How errors are corrected and who reviews them
- What their rights are to review, pause, or delete data
When communication is open and control is clear, patients feel respected and clinicians feel confident using the technology. That’s what turns privacy from a compliance requirement into a competitive strength.
For a deeper look at how healthcare organizations can combine AI-driven innovation with patient data protection, you can explore our related blog on AI in Telemedicine: Enhancing Virtual Care with Compliance.
Integrating Ambient Listening Seamlessly into Existing Healthcare Systems
Successful Healthcare ambient listening software development depends on how well the system fits into existing health care systems and data security frameworks. That means talking to the EHR, following the same authentication standards, and maintaining security without slowing down care. Integration is not just a technical step, it is what makes the difference between a promising pilot and a usable clinical tool.
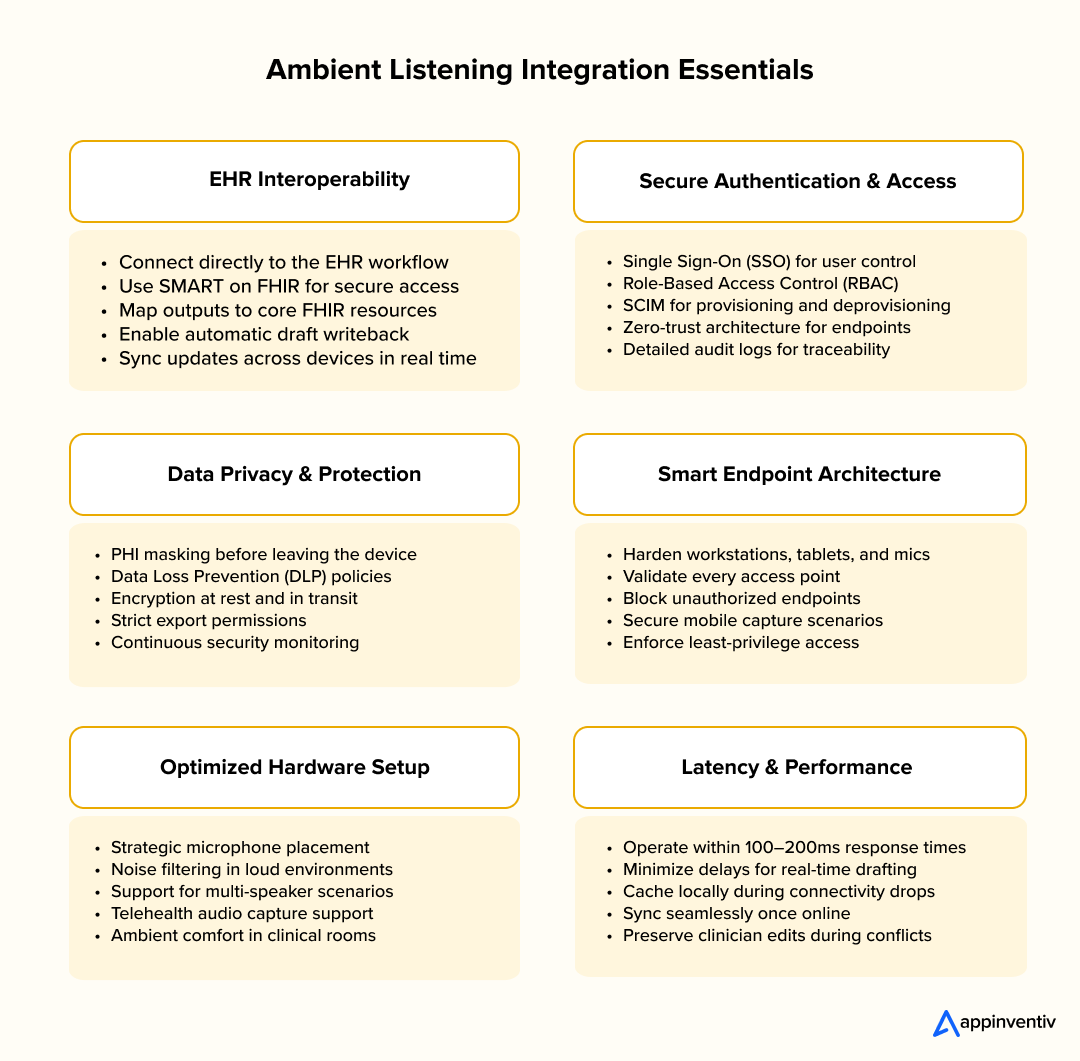
EHR Interoperability and SMART on FHIR
For ambient listening to truly add value, it must connect smoothly with the organization’s Electronic Health Record (EHR). These integrations ensure that what the AI hears becomes part of a clinician’s daily workflow instead of a separate system they have to manage.
To make that possible:
- Use SMART on FHIR for secure authentication and data access.
- Map outputs to key FHIR resources such as Encounter, Observation, MedicationRequest, Condition, and Procedure.
- Enable automatic writeback or ingestion of draft notes directly into the EHR.
- Maintain real-time synchronization so edits or updates reflect instantly across devices.
- Set up conflict resolution rules for concurrent edits by clinicians and the AI assistant.
When done right, strong ambient listening workflows and EHR integration ensure clinicians spend less time managing data and more time caring for patients.
Security Controls and Endpoint Architecture
Protecting patient data is non-negotiable. Every access point, whether it’s a workstation, mobile device, or microphone-enabled tablet, must follow strong security controls.
- Implement PHI redaction or masking before any data leaves the device.
- Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to limit exposure based on job roles.
- Set up Single Sign-On (SSO) and SCIM provisioning for easier user management.
- Deploy Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools and adopt a zero-trust architecture.
- Keep a record of every action through detailed audit logs of access, edits, and exports.
Infrastructure and Environment Considerations
Hardware and environment choices can make or break the quality of ambient capture. Even small setup details can affect transcription accuracy and user comfort.
- Place microphones strategically to minimize background noise.
- Use advanced noise filtering and speech enhancement models in loud settings such as ICUs and ERs.
- Account for multi-speaker scenarios (patients with family members, translators, or multiple caregivers).
- Enable telehealth audio capture for platforms such as Zoom or Teams.
- Build in failover or fallback modes for poor connectivity, allowing local caching until the system syncs again.
Latency and Offline Mode
Speed matters. Clinicians should never have to wait long for a note to appear.
- Real-time suggestions should process in under 100–200 milliseconds to stay in step with live conversations.
- In low-connectivity environments, enable offline buffering and background synchronization once the network stabilizes.
- Establish conflict-handling rules so that changes made while offline do not overwrite clinician edits after reconnection.
These seemingly small decisions determine how “invisible” the technology feels in practice. The smoother it runs, the more naturally clinicians will use it. When AI-based ambient listening technology integrates effortlessly with EHR systems, clinicians can focus more on patient care and less on administrative tasks.
Accuracy and Reliability Standards for Ambient Listening Systems
Getting documentation right is not just a technical requirement — it’s the foundation of patient safety and trust. When an AI system listens to clinical conversations, even a single misheard word or wrong speaker tag can change the meaning of a diagnosis or note. That’s why accuracy and reliability are at the heart of every ambient listening deployment in healthcare.
Unlike everyday voice assistants, these systems must perform in complex, unpredictable environments. Clinics are noisy, patients interrupt, and medical terms vary by specialty. The goal isn’t perfection — it’s consistent, verifiable accuracy that helps clinicians save time without compromising care.
Key Metrics to Track
To know if an ambient listening system is truly ready for clinical use, teams need to track more than just how “smart” it sounds. They should measure how it behaves in the real world, where voices overlap and time is limited. In practice, the same precision metrics that guide ambient listening for medical transcription apply when evaluating AI-generated clinical summaries.
- Word Error Rate (WER): Tracks how accurately the system transcribes spoken words. Lower WER means fewer misunderstandings and cleaner notes.
- Diarization Error: Checks whether the system can tell who’s speaking, which is a critical skill when both patient and clinician are talking.
- Concept Precision and Recall: Evaluates how well the AI captures and labels key medical information like symptoms, medications, and test results.
- Hallucination Rate: Measures how often the system adds false details that weren’t said, this is something that must stay close to zero.
- Edit Distance or Correction Rate: Shows how much a clinician needs to fix the AI’s output. The less editing needed, the stronger the system’s clinical readiness.
Tracking these metrics continuously, not just during setup, helps teams see where accuracy drops and where models need re-training or fine-tuning.
Shadow Pilots and Acceptance Thresholds
Before going live, most healthcare organizations run shadow pilots — short, real-world trials that compare AI-generated notes to those written by humans. This side-by-side testing helps teams understand accuracy in context rather than theory.
A typical pilot runs for two to four weeks and measures accuracy, editing time, and clinician satisfaction. Teams should set clear success benchmarks from the start. For example, no more than 10% editing required and at least 90% accuracy in identifying key medical terms.
Having clinicians review random samples daily during the pilot helps catch subtle errors early. This feedback loop is essential because it trains both the AI and the workflow to work in sync. The goal is not to remove humans from the process but to reduce repetitive work so clinicians can focus on patient care.
Specialty Tuning and Edge Cases
Every medical specialty has its own language and rhythm. A pediatrician’s visit sounds very different from an orthopedic consultation or a behavioral health session. That’s why a successful modern AI-enabled ambient listening systems must adapt to the unique language and rhythm of every specialty, from pediatrics to behavioral health.
- Pediatrics: Softer voices and multiple speakers, including parents, require models that can separate speech sources clearly.
- Behavioral Health: Conversations are sensitive and nuanced, demanding high accuracy and strong privacy controls.
- Emergency and ICU Environments: Constant noise and interruptions make reliable noise suppression and microphone placement essential.
- Accents and Multilingual Patients: Systems need to handle regional dialects and switch smoothly between languages when needed.
- Fallback Scenarios: Clinicians should be able to switch quickly to manual dictation or note entry if the system struggles in real time.
Fine-tuning for these edge cases makes the technology more inclusive and dependable across different care settings.
Balancing AI Power with Human Oversight
AI can process information fast, but it still needs human context to stay safe. In one study, fine-tuned large language models (LLMs) produced medical summaries that were rated “equivalent or superior” to human experts about 80–85% of the time.
That’s impressive progress, but not a reason to remove human review.
Every clinician edit adds value, it teaches the system what accuracy looks like in real practice. Over time, this feedback loop improves both reliability and trust. The safest deployments treat AI as a partner in documentation, not an autonomous scribe.
Modern AI-based ambient listening solutions rely on continuous feedback from clinicians to improve accuracy and reduce errors across specialties. When people and technology share accountability, the result is faster notes, better accuracy, and care that feels more personal again.
Calculating the Real ROI of Ambient Listening in Healthcare
Every hospital exploring new technology eventually faces the same question — is this worth it?
Ambient listening tools promise to make life easier for doctors, but decisions at this scale demand numbers, not just excitement. The real measure of success lies in what the technology gives back: time, focus, and energy that clinicians can reinvest in their patients. Getting to that answer requires an honest look at costs, savings, and the everyday impact on people who use it.
Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership
The cost of an ambient listening system is never just the subscription fee. What seems simple in a demo often becomes a mix of hardware, software, and change management once it reaches a real clinic.
To understand what you’re paying for, it helps to look at the full picture:
- Licensing or subscription plans that may vary by department or usage volume
- Hardware and infrastructure — microphones, tablets, and network setup
- Integration work to connect with the hospital’s EHR and keep data flowing safely
- Training and ongoing support for doctors, nurses, and IT teams
- Continuous model tuning as the AI adapts to different specialties and accents
- Administrative effort for compliance, vendor oversight, and workflow updates
These layers often decide whether the system runs smoothly or becomes another burden. Sometimes paying a little more upfront for a product that integrates easily and scales well ends up saving far more over time.
How to Measure ROI in the Real World
The value of ambient listening isn’t only about faster notes — it’s about giving clinicians back a part of their day. A practical way to measure that is through a simple formula:
ROI = (Clinician Hours Saved × Hourly Cost) + (Revenue from Coding Accuracy) – Total Cost of Ownership
It’s not perfect, but it helps paint a real picture.
For instance, if 40 doctors each save half an hour a day, and their average time is valued at $X per hour, that reclaimed time adds up quickly. Add in even a small boost in coding accuracy, and the benefits start outweighing the investment within months.
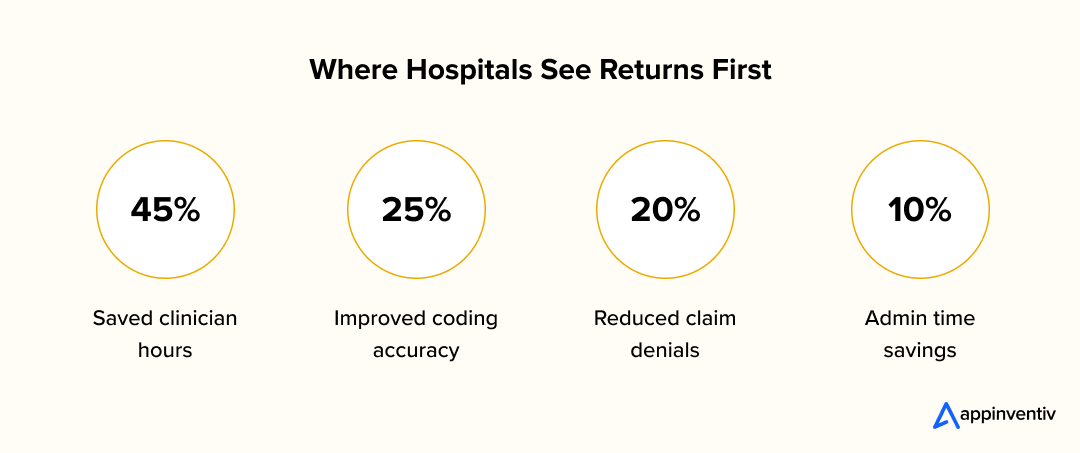
According to McKinsey, more than 70% of healthcare organizations are already using or testing generative AI to simplify administrative work. Another McKinsey report estimates that automation could unlock nearly $1 trillion in operational value across the industry. Those numbers don’t just point to cost savings — they show a shift in how hospitals think about technology: from expense to enabler.
Evaluating Vendors and Avoiding Hidden Costs
Picking the right vendor can make or break a rollout. The best systems don’t just sound accurate; they blend into daily work without friction. When evaluating options, look past glossy presentations and ask how well each solution fits your environment.
A good comparison checklist might include:
- Accuracy across different specialties and languages
- Data security and privacy controls, including encryption and retention policies
- Ease of integration with your EHR and existing infrastructure
- Administrative tools such as dashboards, audit logs, and user role controls
- Scalability and pricing structure, whether per clinician or enterprise-wide
- Support and SLA guarantees for uptime, updates, and maintenance
- Freedom to switch vendors without being locked into a single ecosystem
Hospitals that run short pilots with clear success metrics — rather than jumping straight to full deployment — tend to find the best long-term fit.
For reference, Appinventiv’s Guide to Healthcare App Development Costs breaks down how implementation, integration, and scaling affect overall spending in healthcare technology projects. The same principles apply to AI-powered documentation tools.
Looking Beyond the Numbers
For many clinicians, the biggest win from ambient listening for medical transcription isn’t just saved minutes, it’s the mental space to focus again on patient care.
The real return on ambient listening isn’t just measured in rupees or dollars, it’s measured in hours reclaimed and stress reduced. When doctors can finish their charts before dinner instead of after, when patients feel their provider is listening instead of typing, and when administrators see fewer billing delays, the impact is both financial and human.
That’s the kind of ROI that doesn’t always fit in a spreadsheet, but it’s the one that keeps hospitals moving forward.
How to Bring Ambient Listening Into Real Clinical Practice
Technology doesn’t change healthcare by itself. People do.
Even the smartest AI tool won’t make a difference if doctors don’t trust it or patients don’t feel comfortable with it.
Ambient listening is no different. While adoption brings clear benefits, there are also challenges implementing ambient listening in hospitals, from data privacy to workflow disruption and staff readiness.
The goal isn’t just to add new software. It’s to make daily work feel lighter, smoother, and a little more human again.
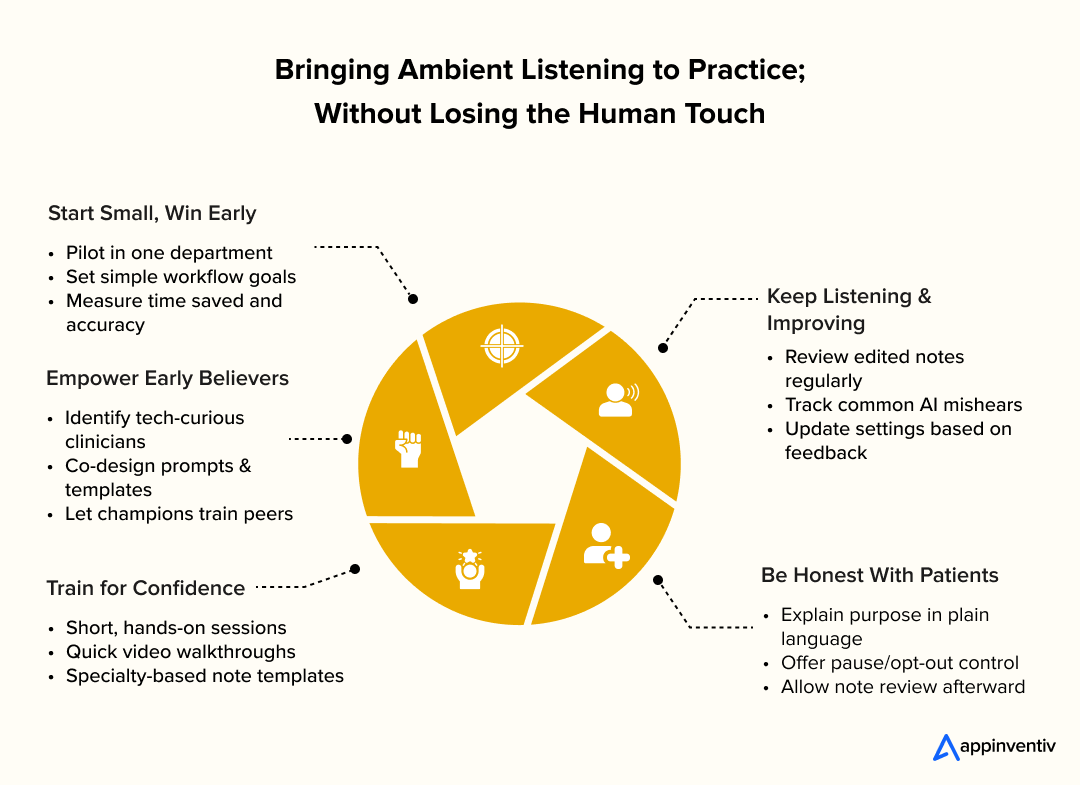
Start Small and Build Confidence
The best way to bring new technology into healthcare is slowly.
Pick one department or specialty where the team is open to innovation. Set simple goals — maybe it’s cutting down time spent on notes, improving accuracy, or just reducing after-hours charting.
Spend a few weeks observing how it fits into real workflows. Collect feedback often, and use it to refine templates or settings before you expand further. Once the system feels reliable and people are comfortable with it, roll it out to other departments.
This gradual approach helps everyone adjust. It replaces uncertainty with small wins — and those small wins are what make people trust the process.
Find Your Early Believers
Every hospital has a few people who make change possible. They’re the ones who stay curious, test new things first, and help their colleagues when something breaks. Those are your early adopters.
Invite them to be part of the design. Ask what kind of prompts, note styles, and workflows feel most natural for their specialty. When they see their input reflected in the system, they’ll take ownership of it.
Training doesn’t have to be complicated. A few hands-on sessions, short video walkthroughs, and a shared library of note templates go a long way. What matters most is that the learning feels relevant — not forced or technical.
Good training doesn’t tell people how to work. It helps them rediscover what good work feels like.
Keep Listening and Keep Improving
No system gets everything right the first time. What separates success from frustration is how feedback is handled.
Review a few notes each week and look for patterns such as words the AI mishears, details it misses, or edits that keep repeating. Talk to the clinicians using it every day. Ask what slows them down or what helps.
When their suggestions lead to visible improvements, it changes how they see the tool. It stops being “the AI” and starts being part of the team.
Be Honest With Patients
Patients deserve clarity. Let them know that the system is there to help their doctor focus on them, not the computer.
Put simple, friendly explanations in waiting areas or online FAQs. During the visit, use straightforward language: “This system helps me keep better notes so I can focus on our conversation. You can ask me to pause or stop it any time.”
Give patients the option to review their notes afterward. If something feels off, make it easy for them to share feedback.
When patients understand what’s happening and why, trust grows naturally. The purpose of AI-based ambient listening technology isn’t to automate care. It is to bring the focus back to listening, empathy, and human connection.
What’s Next for Ambient Listening in Healthcare
Most hospitals begin their ambient listening journey with a single goal and that is to make documentation easier. Understanding the future trends of ambient AI in healthcare helps providers plan for the next phase of automation and real-time clinical intelligence.
But that’s only the surface. Once the system learns to understand the flow of a clinical conversation, it can do more than record. It can help clinicians think ahead, spot gaps, and act faster.
Over the next few years, ambient listening services for hospital systems will likely expand from outpatient clinics to inpatient units, bringing real-time support across entire care ecosystems.
As AI-enabled ambient listening systems mature, they’ll evolve into real-time companions that quietly assist clinicians without interrupting the flow of care.
Real-Time Clinical Support That Feels Natural
In the next generation of deployments, ambient systems could become silent partners in care.
As a clinician discusses a treatment plan, the system could recognize context and gently prompt, “Consider checking kidney function before adjusting the dose,” or “Add DVT prophylaxis for this patient’s profile.”
These cues don’t make decisions for clinicians but they simply come-up as reminders at the right time. It’s a way to prevent small oversights before they turn into bigger problems.
Over time, this kind of real-time decision support could improve consistency across teams and give clinicians greater confidence that nothing important is slipping through the cracks.
Coordinating Care Without Extra Clicks
Today, most follow-ups, referrals, and test reminders depend on someone remembering to log them later. Ambient listening could change that.
By recognizing key phrases during the consultation — like “We’ll check your labs in two weeks” or “I’ll refer you to cardiology” — the system could automatically create tasks, reminders, or draft prescriptions.
All the clinician needs to do is review and confirm.
This kind of automation doesn’t just save time; it helps ensure that every patient gets timely follow-up, even on the busiest days. The technology fades into the background while care keeps moving forward.
Unlocking Insights for Population Health and Research
Beyond the exam room, de-identified conversational data could become a new source of insight. When analyzed responsibly, these datasets could help hospitals spot care gaps earlier, predict readmission risks, or understand how communication affects adherence and outcomes.
Researchers could also use this data to study how clinicians explain diagnoses or how patients describe symptoms — turning everyday language into a tool for improving empathy and clarity in care.
Of course, this must happen under strict privacy and governance frameworks. Patients’ voices should inform better healthcare, never compromise their confidentiality.
A Changing Regulatory and Ethical Landscape
As ambient listening becomes more capable, the rules that govern it will evolve too.
We can expect updates to HIPAA guidance on AI-driven voice capture, and even new definitions from the FDA on when such systems qualify as medical device software.
Globally, frameworks like the EU AI Act will set expectations for transparency, bias control, and model safety.
Deloitte’s Global Health Care Executive Outlook shows what many in the industry already feel that AI is moving from idea to impact. More than 80% of health leaders expect generative AI to influence their organizations this year, and nearly 9 in 10 believe digital transformation will pick up speed across health systems worldwide.
That means the focus now shifts from “Can we use this?” to “How do we use it responsibly?”
Looking Ahead
As AI-based ambient listening solutions evolve, they’ll move beyond transcription to active, real-time support that strengthens decision-making at the point of care. The next frontier of ambient listening won’t be about note-taking at all, it will be about understanding.
Systems that can listen, learn, and suggest in real time could help clinicians make safer choices, coordinate faster, and stay present with their patients.
The goal isn’t automation for efficiency’s sake, it’s to bring healthcare a little closer to what it’s meant to be: human, attentive, and connected.
Partner with Appinventiv to bring together ambient listening, AI, and EHR integration for faster, smarter clinical workflows.
Shaping the Future of Connected Care — Together
Healthcare is changing quietly but profoundly. The rise of ambient listening shows that technology doesn’t have to be loud to make a difference. When designed well, it simply fades into the background and gives doctors what they need most — more time with their patients.
At Appinventiv, that’s the kind of progress we believe in. Our work with healthcare organizations across the world has always focused on one thing: making innovation feel human. From helping providers build HIPAA-compliant healthcare apps to creating telemedicine platforms that blend seamlessly into daily practice, we’ve learned that the best systems are the ones that quietly remove friction from care.
Every healthcare team has its own pace and priorities. Some start with small pilots; others take on full-scale digital transformation. What matters most is a clear vision — to build solutions that are safe, simple, and centered on people.
Implementing ambient listening technology in healthcare is just one step in that direction. The future will connect everything: EHRs, AI assistants, and patient apps that work together as one. When these systems speak the same language, care becomes smoother, faster, and more personal.
If your team is looking for a custom healthcare software development company that balances automation with empathy, Appinventiv can help turn those ideas into real solutions.
Talk to our experts and see how we can help your team bring ambient listening and AI innovation into real-world healthcare settings.
FAQs
Q. What Is Ambient Listening, and How Is It Used In Healthcare?
A. Ambient Listening Technology in Healthcare is a quiet helper in the room. It listens as doctors talk with patients and turns those conversations into medical notes automatically. There’s no typing, no constant switching between screens. Doctors just talk, and the AI organizes what matters — the symptoms, the diagnosis, and the plan. Hospitals use it to save time, reduce mistakes, and bring the focus back to the patient sitting in front of the doctor.
Q. Why Is Ambient Listening Trending?
A. It’s catching on because doctors are tired. Many spend their evenings finishing charts after long days at the clinic. Ambient listening takes some of that weight off. It listens, learns, and writes, so they don’t have to. As the technology becomes more accurate and privacy standards catch up, more hospitals are realizing it’s not just convenient — it’s a relief. It gives clinicians a few hours back and lets them end their day when their patients do.
Q. How Is Ambient Listening Enhanced by EHR Integrations?
A. When ambient listening connects with a hospital’s EHR, it feels seamless. The AI writes notes and sends them straight into the right spot — prescriptions, diagnoses, or updates. No copying, no extra clicks. It keeps everything in one place and helps teams move faster. Using frameworks like SMART on FHIR, these integrations also stay secure and meet healthcare standards, so hospitals can trust the system as much as the people who use it.
Q. How AI and Ambient Listening Are Transforming Healthcare
A. AI and ambient listening are changing the quiet parts of medicine — the paperwork, the typing, the things no one sees but everyone feels. Instead of replacing doctors, the AI sits in the background, helping with notes, codes, and reminders. It catches small details and lets people focus on care again. The transformation isn’t loud or dramatic. It’s in the moments when a doctor looks up and listens, and the record is already being written.
Q. How This Technology Is Shaping Clinical Documentation
A. Before this, documentation meant hours of typing and editing. Now, with ambient listening, notes are finished by the time the appointment ends. Everything feels lighter — charts are cleaner, billing is smoother, and doctors can finally close their laptops before dinner. It’s not about flashy AI features. It’s about giving clinicians the freedom to listen to their patients without worrying about the next form to fill.
Q. What Healthcare Organizations Are Achieving with Ambient Listening AI
A. Hospitals using ambient listening AI are seeing small but important changes. Doctors are spending less time on screens and more time talking. Systems like Mass General Brigham and Stanford Medicine have reported shorter charting hours and higher satisfaction among clinicians. It’s not just about efficiency — it’s about breathing space. When the workday ends on time and care feels human again, that’s real progress.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
How to Build a Custom Pediatric EMR and EHR System?
Key takeaways: Clinical Precision: Custom systems accommodate pediatric-specific data points like percentile curves and weight-based longitudinal dosing. Interoperability: Seamless data exchange via HL7 FHIR ensures your practice stays connected to pharmacies, labs, and state registries. Regulatory Resilience: Built-in compliance with HIPAA, HITECH, and MACRA/MIPS reduces legal friction. Enhanced Engagement: Parent portals reduce administrative overhead by…

Change Management in Healthcare: Principles, Processes, and Models
Key Takeaways Change in healthcare fails quietly when ownership, workflow alignment, and follow-through are missing. Successful change management in healthcare focuses on adoption, not just system implementation. Clinical workflows and workforce capacity determine whether transformation sticks or stalls. Governance, clear accountability, and post-go-live support matter more than the model used. Sustainable healthcare transformation depends on…

A Practical Guide to Building Your Mental Health Chatbot - Use Cases, Cost, & ROI
Key takeaways: Mental health chatbots work when they know their limits. They’re most useful as a gentle first step, not as a stand-in for real care. Good chatbot design is more about judgment than AI. Clear boundaries, calm responses, and safety matter more than smart language models. Enterprises invest in chatbots to make support easier…