- AI’s Economic Impact and Market Size
- AU Gov-Led AI Regulations and Policy Frameworks
- A Practical Roadmap for Enterprise AI Implementation in 2026
- Step 1: Identify High-Friction Business Problems
- Step 2: Assess Data Readiness and Ownership
- Step 3: Choose the Right Model Approach
- Step 4: Integrate AI into Core Systems
- Step 5: Establish Governance, Monitoring, and ROI Tracking
- Step 6: Maintain and Scale
- Industry-Wise AI Implementation Use Cases in Australia
- AI in Mining
- AI in Energy and Utilities
- AI in Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
- AI in Banking and Finance
- AI in Retail and eCommerce
- AI in Logistics and Supply Chain
- Key Challenges Australian Businesses Face When Implementing AI
- Cost of Implementing AI in Australian Enterprises
- How Appinventiv Supports Enterprise-Grade AI Implementation in Australia?
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- 68% of Australian businesses have already integrated AI, with 23% planning to adopt it soon.
- AI transforms sectors like fintech, retail, and manufacturing, improving processes and innovation.
- The cost of AI implementation in Australia ranges from AUD 70,000 to AUD 700,000 or more.
AI implementation in Australia has crossed a structural threshold. What began as experimentation is now embedded into enterprise cost control, risk management, and operational resilience agendas.
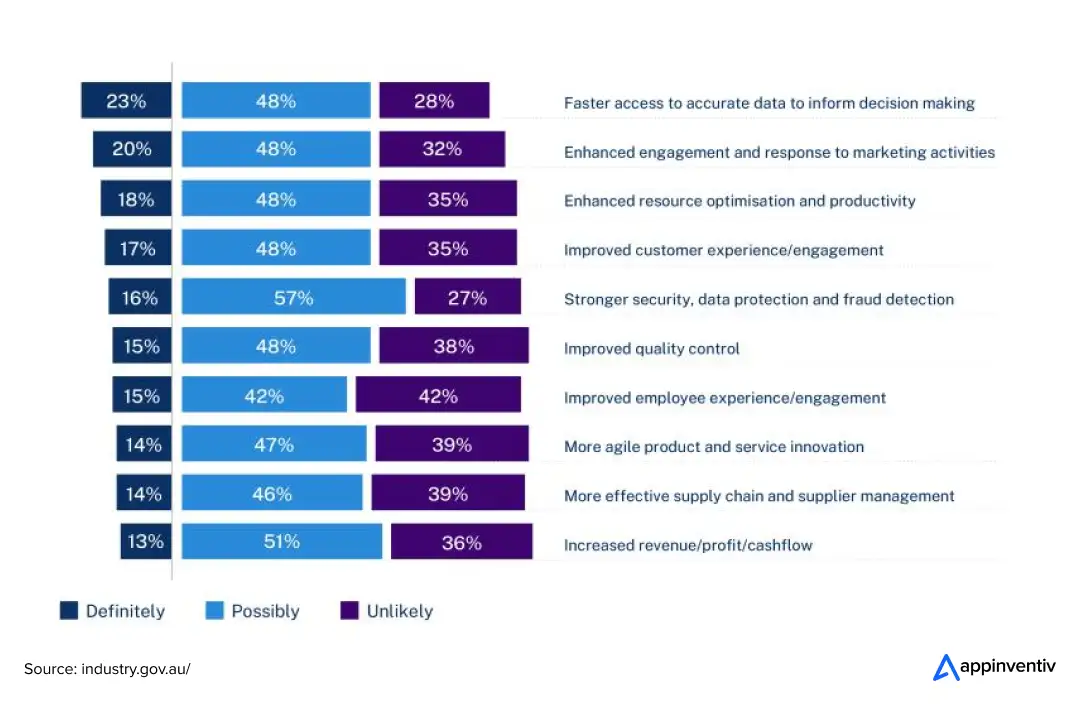
According to the Australian Government, over one-third of Australian businesses are already using or trialling AI, with adoption highest among large enterprises where productivity pressure, labour constraints, and compliance complexity intersect. And over half of organisations that harness AI technologies have cited positive business outcomes in several operational areas.
This shift is not driven by innovation narratives. It is driven by necessity. Rising operating costs, persistent skills shortages, fragmented data estates, and slower decision cycles are forcing enterprises to rewire how work gets done. AI is increasingly evaluated alongside ERP modernisation, cyber uplift, and platform consolidation, not as a standalone initiative.
What makes AI implementation in Australia distinct is the environment it must operate within. Data sovereignty expectations, sector-specific reporting obligations, and heightened board accountability for technology risk shape architectural decisions early. Systems must be explainable, auditable, and defensible under regulatory scrutiny. Models that cannot integrate seamlessly into existing governance frameworks rarely progress beyond pilot stages.
If you are looking to embark on or elevate your AI journey, our AI implementation guide for Australian businesses helps you identify high-value use cases, navigate governance and compliance expectations, and deploy AI systems that integrate safely with existing operations while delivering measurable, long-term value.
We can help you turn opportunities into outcomes!
AI’s Economic Impact and Market Size
Market signals and economic modelling now align on one point. AI has moved from experimental spend to a material driver of enterprise value in Australia. The Australian AI market is projected to exceed $80 billion in annual value by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 30%. This market growth is underpinned by broader economic impact.
According to CSIRO’s Data61 report, digital technologies, including artificial intelligence, could contribute around AUD 315 billion to Australia’s GDP by 2030, reflecting broad economic impact from productivity, efficiency, and digital transformation.
For enterprise leaders, this impact translates into a clear “why now” moment. Organisations that delay risk embedding face higher operating costs and slower decision cycles as AI becomes standard infrastructure across their industries.
AU Gov-Led AI Regulations and Policy Frameworks
The government is taking a proactive approach toward shaping a safe and trustworthy future of artificial intelligence in Australian businesses. The government has laid a strong foundation for regulating artificial intelligence through a mix of ethical guidelines, consultations, and existing legislation for businesses across sectors like mining, government, retail, logistics, and eCommerce.
To further support ethical and responsible use of AI in the government and other sectors, several new initiatives have been launched, including:
- National AI Centre (NAIC): Coordinates practical guidance for industry on responsible AI use and capability building.
- National AI Plan (2025): Sets long-term direction for safe adoption, skills development, and national AI capability.
- Australian Public Service AI Plan: Introduces mandatory governance and secure tooling that increasingly shapes enterprise standards.
- AI Safety Institute (Planned): Focused on testing and oversight of advanced AI systems.
- AI Adoption Program: Provides funding support to move AI from pilots into production.
- Responsible AI Network: Brings industry, researchers, and government together on ethical use.
- High-Risk AI Consultations: Examines where tighter controls are needed for sensitive AI applications.
- Sovereign Infrastructure Investment: Expands local data centre capacity for compliant AI workloads.
- Ethical and Data Governance Frameworks: Updates privacy and Indigenous data guidance for AI use.
- Australian AI Ethics Framework: Establishes Essential Eight principles for privacy, fairness, accountability, transparency, and human oversight in AI systems.
By aligning with these principles, frameworks and AI compliances in Australia, organisations across industries can ensure they are leading with ethical, responsible AI solutions.
For enterprises, the impact of AI adoption is practical. Adoption risk is lower. Data residency assumptions are clearer. Governance expectations are becoming consistent across the public and private sectors.
Most importantly, AI programs can now be designed for longevity. This policy stability allows Australian enterprises to move beyond contained trials and embed AI into core operating models with confidence.
A Practical Roadmap for Enterprise AI Implementation in 2026
AI implementation in 2026 is less about ambition and more about control. Rising regulatory expectations, legacy system complexity, and cost pressure require a structured approach that moves beyond pilots. A practical roadmap focuses on sequencing decisions around data readiness, integration, governance, and measurable outcomes, ensuring AI delivers value while remaining defensible at scale. Here are the key steps to implement artificial intelligence in Australian businesses:
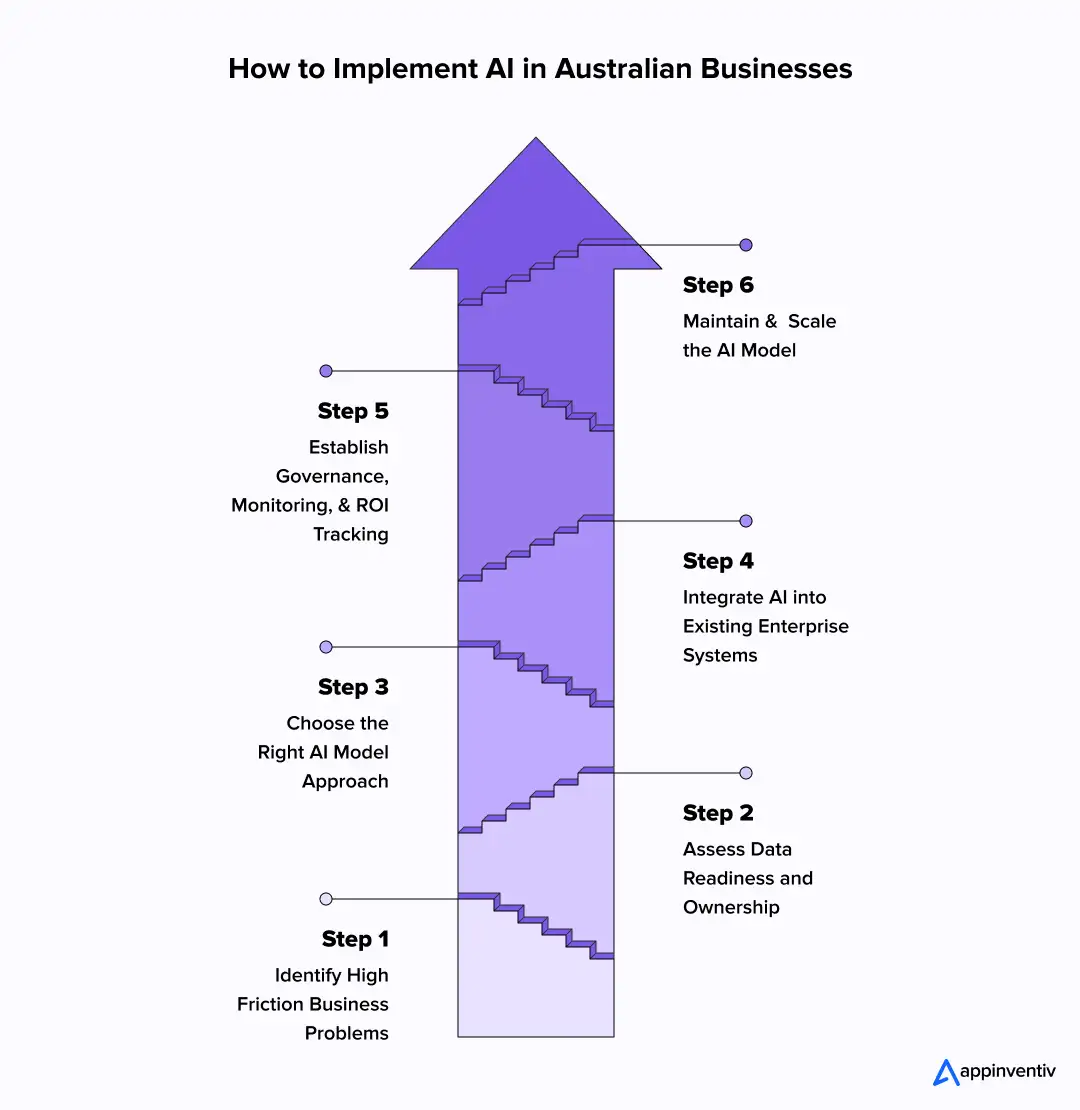
Step 1: Identify High-Friction Business Problems
AI delivers value when applied to persistent operational friction. Cost leakage, manual bottlenecks, compliance exposure, and scalability limits provide the strongest foundation. Thus, your first step is to figure out a practical use case and anchor that to measurable outcomes.
Step 2: Assess Data Readiness and Ownership
Data quality, lineage, and ownership determine feasibility. Australian enterprises must also evaluate where data resides, who controls it, and how it can be accessed without breaching internal or external obligations. This step often determines the timeline and cost more than model complexity.
Step 3: Choose the Right Model Approach
The next vital step is to choose the right AI model as per your defined use case. For instance, predictive models suit forecasting and risk scoring. Generative AI models in Australia support knowledge work and customer interaction. Optimisation models improve scheduling and asset utilisation. Computer vision enhances inspection and safety. The wrong choice creates cost without value.
Step 4: Integrate AI into Core Systems
AI that sits outside ERP, CRM, EHR, or asset management platforms rarely scales. Thus, you must integrate AI into existing legacy systems to ensure smooth adoption. Enterprises that embed AI outputs directly into existing workflows see faster value realisation.
Step 5: Establish Governance, Monitoring, and ROI Tracking
As AI systems move into production, governance becomes an operational requirement. Thus, enterprises must ensure models remain explainable, auditable, and aligned with security and AI compliance in Australia. Continuous performance monitoring and ROI tracking help leadership confirm that AI outcomes remain tied to cost control, risk reduction, and decision quality over time.
Step 6: Maintain and Scale
Models degrade. Regulations evolve. Business conditions shift and consumer demands evolve. Therefore, ongoing monitoring, retraining, and upgrading are essential to protect long-term returns.
Also Read: How to Build an AI App in Australia: A Complete Guide
Industry-Wise AI Implementation Use Cases in Australia
Across Australian industries, AI adoption is being driven by operational pressure rather than experimentation. Organisations are applying AI at points of persistent friction, such as capacity planning, risk detection, asset utilisation, and demand forecasting, with each industry shaping use cases around its regulatory and operating realities. Let’s delve deeper to comprehend industry-wide AI use cases for Australian businesses:
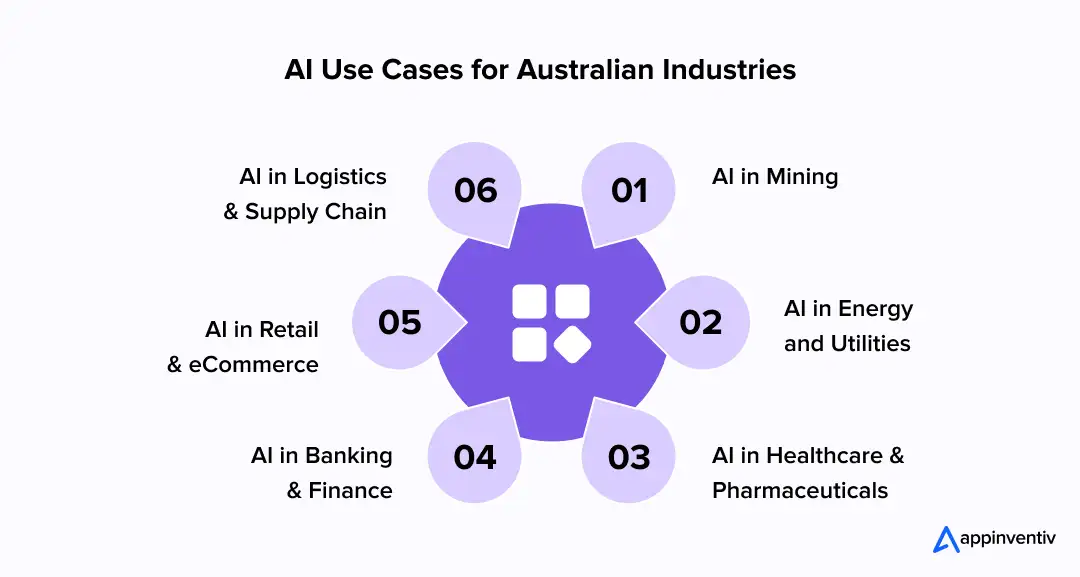
AI in Mining
Mining operations manage geographically dispersed assets under safety-critical conditions. Without Al for industrial automation in mining, operational strain typically appears as:
- Limited early warning of equipment degradation
- Safety risks identified only after near-miss events
- Production inefficiencies driven by static optimisation models
AI implementation delivers forward-looking operational control. Predictive models assess equipment health across fleets. Optimisation systems balance throughput, energy use, and maintenance windows. Safety analytics identify emerging risk patterns across sites. These capabilities are embedded into operational control environments rather than isolated dashboards.
Practical AI Use Case: Mining operators apply AI to fleet health monitoring, production optimisation, and safety compliance analytics within tightly governed operational systems.
Real World Example: Australian mining enterprises now predict critical equipment failures days in advance, improving uptime and workforce safety without disrupting production schedules.
AI in Energy and Utilities
Energy and utility providers operate under growing regulatory scrutiny while managing ageing infrastructure. Without AI, challenges commonly include:
- Inaccurate load forecasting during demand volatility
- Reactive asset maintenance increasing outage risk
- Limited predictive insight across network performance
AI implementation strengthens predictability and regulatory assurance. Load forecasting models improve demand accuracy. Asset optimisation systems extend infrastructure lifespan. Outage prediction supports faster response while maintaining compliance transparency.
Practical AI Use Case: Utilities and energy sectors deploy AI for demand forecasting, predictive maintenance of network assets, and regulatory performance monitoring aligned with Australian oversight expectations.
Real World Example: AGL Energy uses AI to manage electricity demand and supply, which is crucial for efficiently integrating renewable energy sources and minimising waste. This helps in supporting Australia’s sustainability goals.
AI in Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Healthcare systems and pharmaceutical operations in Australia experience persistent structural strain without AI. In day-to-day operations, this typically surfaces as:
- Capacity planning that reacts after bottlenecks form
- Clinicians working across fragmented patient and diagnostic systems
- Drug discovery and trial cycles slowed by regulatory review and cost escalation
AI implementation addresses these constraints by inserting predictive visibility and decision support at points where delay and risk accumulate. In hospital environments, forecasting models anticipate patient flow, staffing pressure, and bed utilisation. Within pharmaceutical, AI compresses early research timelines by narrowing viable compound pools while remaining aligned with Australian therapeutic governance standards.
Practical AI Use Case: Australian healthcare providers deploy AI-enabled imaging analysis, claims processing, and medical supply forecasting within tightly governed clinical data environments. Pharmaceutical firms apply machine learning to detect adverse drug events earlier and optimise national distribution networks without compromising compliance rigor.
Real World Example: The Royal Melbourne Hospital uses AI-assisted imaging analysis to accelerate diagnostic review, reducing turnaround time while preserving clinician oversight and auditability.

AI in Banking and Finance
Without AI, Australian banks and insurers operate under compounding operational pressure, typically driven by:
- Growing transaction volumes that overwhelm manual review processes
- Increasing fraud sophistication that outpaces static rule engines
- Expanding regulatory reporting obligations across multiple jurisdictions
AI implementation introduces adaptive risk intelligence across core financial operations. Transaction monitoring models learn evolving behavioural patterns rather than relying on fixed thresholds. Regulatory reporting automation lowers reconciliation effort while maintaining the explainability required by Australian supervisory bodies.
Practical AI Use Case: Financial institutions apply AI to real-time fraud detection, automated compliance reporting, and dynamic customer risk scoring, embedding outputs directly into core banking and case management platforms.
Real World Example: Commonwealth Bank, one of Australia’s largest banks, utilises artificial intelligence to monitor transaction patterns for signs of frauds and deploys AI chatbots to deliver 24/7 customer support and automate customer experience.
AI in Retail and eCommerce
Retail operations face persistent instability without AI-driven decision support. Common pressure points include:
- Demand volatility that renders historical forecasting unreliable
- Margin compression driven by overstocking and markdown dependency
- Inventory misalignment across channels and regions
AI implementation improves commercial precision rather than surface-level automation. Forecasting models continuously recalibrate to live demand signals. Pricing engines respond to elasticity changes. Personalisation systems align offers with intent rather than broad segments.
Practical AI Use Case: Australian retailers use AI for demand forecasting, assortment planning, pricing optimisation, and automated replenishment, tightly integrated with procurement and distribution systems.
Real World Example: Woolworths, the most famous retail app in Australia, uses AI to optimise stock levels and create custom marketing strategies as per consumer behaviour. This has helped them significantly enhance both sales and customer satisfaction.
AI in Logistics and Supply Chain
Supply chains without AI remain exposed to disruption and inefficiency. This mainly happens due to:
- Manual routing and planning that cannot adapt in real time
- Inventory imbalances across warehouses and regions
- Supplier risk visibility limited to historical performance
AI implementation introduces adaptive control across logistics networks. Routing models optimise delivery paths under live conditions. Inventory placement adjusts dynamically. Integration into transport and warehouse systems accelerates execution without expanding headcount.
Practical AI Use Case: Logistics providers apply AI to routing optimisation, warehouse automation, and supplier risk analytics embedded within transport management systems.
Real World Example: Toll Group, a leading logistics provider in Australia, uses AI-powered software to refine delivery routes and manage fleet operations.
Also Read: How Australian Businesses Can Build a Scalable eCommerce Logistics Strategy for Global Growth
Key Challenges Australian Businesses Face When Implementing AI
Despite the scale of opportunity, most Australian enterprises encounter friction during AI execution rather than ideation. These barriers are operational and structural, not technical, and tend to compound if not addressed early.
- Fragmented data estates that limit model reliability and delay production deployment
- Legacy system integration constraints that prevent AI from scaling beyond pilots
- Governance and compliance uncertainty, particularly around explainability, auditability, and accountability
- Board-level risk sensitivity, driven by unclear ownership and long-term liability models
- Workforce and skills gaps, where AI reduces manual workloads but increases demand for hybrid capability across data, domain knowledge, and risk management
Also Read: Melbourne’s Al Reality Check: 13 Industries That Chose Evolution
Cost of Implementing AI in Australian Enterprises
The cost of implementing AI in Australia varies widely, driven less by model complexity and more by enterprise readiness and governance expectations. On average, the cost to implement AI in businesses ranges from AUD 70,000 and AUD 700,000 or more. For most organisations, the primary cost drivers are not algorithms but the surrounding infrastructure and controls.
Typical cost components include:
| Cost Components | What It Covers in Practice | Indicative Cost Range (AUD) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Readiness & Governance | Data cleansing, lineage mapping, access controls, sovereignty alignment | $60,000 – $250,000 |
| AI Model Development | Model selection, training, validation, explainability design | $70,000 – $300,000 |
| System Integration | Embedding AI into ERP, CRM, operational and analytics platforms | $120,000 – $350,000 |
| Security & Compliance Controls | Audit logging, risk monitoring, regulatory alignment, approvals | $50,000 – $150,000 |
| Infrastructure & Ongoing Operations | Model retraining, performance monitoring, and infrastructure optimisation over time | $40,000 – $120,000 annually |
These ranges reflect typical AI implementation costs in Australia for mid-to-large enterprises. Final investment depends on integration depth, regulatory exposure, and long-term operating model decisions.
Also Read: How Australian Enterprises Are Using Intelligent Automation to Reduce Operational Cost
How Appinventiv Supports Enterprise-Grade AI Implementation in Australia?
For Australian enterprises, AI success is no longer about proving technical feasibility. That phase has passed. The real challenge in 2026 is executing AI programs that withstand regulatory scrutiny, integrate cleanly with legacy systems, and continue delivering value long after the first model goes live. This is where many initiatives stall. And that is the problem we help Australian organisations solve, quietly, rigorously, and with outcomes that hold up long after the initial deployment phase.
Appinventiv, as an experienced artificial intelligence development company in Australia, works with enterprises that view AI implementation in Australia as a balance sheet decision, not an innovation exercise. Our engagements typically begin at the point where internal teams recognise that experimentation alone will not survive audit, scale, or board review.
In practice, this means anchoring every AI program to a clearly defined source of business friction, such as cost leakage, compliance exposure, throughput constraints, or decision latency. From there, we design AI architectures that align with the Australian Data Privacy Act 1988, cyber maturity benchmarks, and board-level risk tolerance. Governance is designed into the operating model upfront, not introduced reactively once systems are already in use.
Our AI consulting solutions for Australia reflect this execution-first approach. With 5+ agile delivery centres nationwide, we support AI systems beyond initial deployment, including model retraining, governance updates, and performance optimisation as regulatory and operational conditions evolve.
For instance, we have deployed over 250 digital assets locally, many of them deeply integrated into ERP, asset management, clinical, and financial platforms. This level of integration is a key reason our client relationships with Australian brands like Lite N’ Easy, Multinail and Rapid Teachers tend to persist, reflected in a 96% retention rate across long-term engagements.
From an AI execution standpoint, our experience spans production environments rather than controlled pilots. Our AI work underpins platforms such as Vyrb, YouCOMM, Mudra, JobGet, and Chat & More, each requiring different balances of scale, security, user trust, and regulatory sensitivity.
These projects reinforce our ability to adapt AI architectures to distinct commercial and compliance contexts rather than applying a single pattern everywhere. In our 10+ years of APAC delivery experience, we have:
- 300+ AI-powered solutions delivered across enterprise use cases
- 150+ custom AI models trained and deployed in live environments
- 75+ enterprise AI integrations completed, often across legacy-heavy ecosystems
- 200+ data scientists and AI engineers supporting sustained delivery and scale
These capabilities translate into measurable business outcomes when applied correctly. Across Australian enterprise programs, AI deployments have contributed to efficiency improvements of around 35%, decision-making cycles accelerating by up to 75%, and average operating cost reductions approaching 40%, while maintaining a 99.5% compliance SLA across ISO and SOC2-aligned environments.
Share your AI vision with us and witness your idea taking shape.
FAQs
Q. How much does AI implementation cost in Australia?
A. The cost of AI implementation in Australian businesses can vary widely depending on the complexity of the project, the scope of the application, the AI use cases for Australian businesses, and more. Usually, prices may vary from AUD 70,000 to AUD 700,000 or more.
For an accurate estimate for AI implementation in Australia, it’s best to consult with AI development experts who can provide a tailored quote based on your specific requirements. Get in touch!
Q. How is Artificial Intelligence being used in Australia?
A. Across Australia, AI is being applied where operational pressure is highest. Enterprises use it to improve forecasting, detect risk earlier, optimise assets, automate reporting, and support faster decisions. Most deployments sit inside existing systems such as ERP, clinical platforms, banking cores, and asset management tools rather than as standalone products.
Q. How long does it take to implement an AI pilot?
A. The time it takes to implement an AI pilot ranges from 3 to 12 months or more. Timelines vary depending on data quality, integration scope, and governance approvals. Programs that move faster usually already have clean data and clear ownership.
Q. Is government support available for AI implementation in Australia?
A. Yes. Federal and state initiatives provide grants, research partnerships, and policy guidance to support responsible AI adoption. These programs reduce uncertainty, but enterprises remain fully accountable for security, compliance, and outcomes.
Q. Which Australian industries benefit most from AI implementation?
A. The benefits of AI adoption in Australia are visible across industries with complex operations and regulatory oversight. This includes but is not limited to:
- Banking and Finance
- Retail and eCommerce
- Manufacturing
- Mining
- Agriculture
- Energy and Utilities
- Logistics and Supply Chain
Q. How does AI implementation help Australian businesses?
A. AI improves efficiency by reducing manual work, increasing accuracy in forecasting and risk detection, and shortening decision cycles. When implemented correctly, it strengthens resilience and cost control rather than acting as a one-off productivity tool.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
Governance vs. Speed: Designing a Scalable RPA CoE for Enterprise Automation
Key takeaways: Enterprise RPA fails at scale due to operating model gaps, not automation technology limitations. A federated RPA CoE balances delivery speed with governance, avoiding bottlenecks and audit exposure. Governance embedded into execution enables faster automation without introducing enterprise risk. Scalable RPA requires clear ownership, defined escalation paths, and production-grade operational controls. Measuring RPA…
How AI Overhauling Industrial Automation in Australia
Key takeaways: AI is shifting industrial automation from rule-based to data-driven decision ecosystems Predictive and autonomous operations are improving efficiency and cost optimisation Australian industries are leveraging AI to solve workforce, sustainability, and compliance challenges Enterprises adopting AI early gain competitive, operational, and economic advantages Industrial automation in Australia is no longer just an engineering…
Implementing Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Healthcare Systems: Challenges, Use Cases & ROI
Key takeaways: RAG helps clinicians make better decisions by connecting AI responses to trusted clinical data sources. Healthcare organizations are gradually adopting domain-specific AI to improve efficiency, compliance, and operational clarity. Successful RAG deployment usually depends on strong governance, interoperability planning, and secure data practices. Retrieval-backed AI can ease documentation workload while improving accuracy, productivity,…