- Why Do Enterprises Struggle to Scale Automation Without an RPA Center of Excellence?
- What Are the Benefits of an RPA Center of Excellence?
- Why Simply “Having A CoE” Is Not Enough
- How Cost, Risk, And Control Compound At The Enterprise Scale
- Why The RPA CoE Acts As An Enterprise Automation Control Plane
- How Alignment Across Business, IT, And Risk Drives Scale
- How Should Enterprises Build and Structure an RPA CoE Team for Scale?
- Who Provides Sponsorship And Direction For The RPA CoE?
- What Role Does The RPA CoE Steering Committee Play?
- How Do RPA Champions And Process Analysts Enable Scale?
- Why Is The RPA Change Manager Critical At Enterprise Scale?
- How Does The Robotic Operating Team Support Day-to-Day Execution?
- How Should Enterprises Define Roles, Responsibilities, And Support Ownership?
- How Should Enterprises Build Technology and Infrastructure Foundations for a Scalable RPA CoE?
- What Roles Are Required To Operate RPA Infrastructure At Scale?
- How Should Development Environments And Software Infrastructure Be Designed?
- Why Do Performance, Connectivity, And Server Design Matter At Scale?
- How Should Maintenance And Support Be Handled In Enterprise RPA Programs?
- How Do CIOs Approach Balancing Speed and Governance in RPA When Choosing an Operating Model?
- Why Speed Breaks Without Governance
- Why Governance Fails When It Is Added Late
- How a Federated RPA CoE Resolves the Tradeoff
- How Should Enterprises Design an RPA Governance Framework That Scales?
- How Should Governing Bodies And Escalation Paths Be Structured?
- Why Are Role-Based Security And Segregation Of Duties Non-Negotiable?
- How Do Auditing Capabilities Protect Enterprise Automation Programs?
- Why Do Disaster Recovery And High Availability Matter Early?
- How Should Operations, Support, And Performance Be Governed?
- How Does Change Management Enable Successful RPA CoE Adoption Across the Enterprise?
- Why Is Organizational Change Management Critical For RPA Programs?
- How Do Change And Communication Plans Reduce Adoption Friction?
- Why Must RPA Change Management Align Closely With It?
- How Do Demand Management And Culture Affect Scale?
- How Can Enterprises Develop Skills and Training Within an RPA CoE?
- How Should Enterprises Design Training and Upskilling Programs for RPA?
- What Role Do Training Paths And Certifications Play In Maturity?
- How Does Enablement Strengthen The Core Robotic Operating Team?
- Why Do Reviews And Continuous Learning Matter At Scale?
- How Should Enterprises Identify and Prioritize Processes for RPA at Scale?
- How Do Enterprises Build A Reliable Automation Pipeline?
- What Role Do Business Analysts And Governance Boards Play?
- Why Is Structured Process Discovery Essential?
- How Should Proof-Of-Concept And Roi Guide Prioritization?
- How to Build an RPA Center of Excellence?
- How Should Enterprises Approach Readiness And Assessment?
- Why Does Operating Model Finalization Come Early?
- How Should Platform And Tooling Decisions Be Made?
- Why Are Pilots With Governance Guardrails Essential?
- How Do Enterprises Scale With Metrics And Controls?
- Why Is Continuous Optimization Part Of The Roadmap?
- How Should Enterprises Measure RPA CoE Performance and Drive Continuous Improvement?
- How Should ROI And Impact Assessments Be Structured?
- Which KPIs Matter At Enterprise Scale?
- Why Are Automation Audits And Governance Reviews Essential?
- How Do Risk Mitigation And Lessons Learned Drive Maturity?
- How Does Hyperautomation And Technology Evolution Fit In?
- How Can Enterprises Approach Integrating AI/ML Into RPA CoE With Governance?
- Where Do AI Use Cases Fit Safely Within RPA?
- What Governance Controls Are Required for AI-Enabled Bots?
- Why Do Explainability And Drift Management Matter?
- How Does Human-In-The-Loop Enforcement Preserve Enterprise Control?
- How Does Appinventiv Help Enterprises Design and Scale an RPA Center of Excellence?
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- Enterprise RPA fails at scale due to operating model gaps, not automation technology limitations.
- A federated RPA CoE balances delivery speed with governance, avoiding bottlenecks and audit exposure.
- Governance embedded into execution enables faster automation without introducing enterprise risk.
- Scalable RPA requires clear ownership, defined escalation paths, and production-grade operational controls.
- Measuring RPA success demands operational metrics like recovery time, stability, and sustained utilization.
- AI-enabled automation scales safely only with explainability, confidence thresholds, and human oversight.
Most enterprise automation initiatives start positively. A few high-impact bots deliver quick wins, cycle times improve, and manual effort drops. Confidence grows across teams, and robotic process automation begins to look like a dependable efficiency lever.
Challenges typically emerge within months. Governance gaps surface as automation expands, from credential management issues to deployments outside formal change control. Risk teams step in, delivery slows, and automation shifts from early momentum to operational friction.
At this stage, scaling is no longer a tooling exercise but an operating model challenge. Without a clear RPA CoE framework and a structured RPA Center of Excellence, gaps in ownership, decision rights, and accountability create technical and operational debt.
Are you already seeing these warning signals?
- Automation demand rising faster than delivery capacity
- Increasing bot maintenance effort
- Governance reviews happening post-deployment
- Unclear ownership of bot failures
If several apply, the priority becomes deciding how to build an RPA Center of Excellence that enables scale without increasing risk. The following sections examine how enterprises align governance with execution and design operating models that scale sustainably.
53% of enterprises already run RPA and face scaling decisions
Why Do Enterprises Struggle to Scale Automation Without an RPA Center of Excellence?
Enterprise robotics process automation center of excellence initiatives rarely break because bots stop working. They break because the operating model does. What enables speed during pilots becomes a liability when automation expands across systems, teams, and regions. Without a unifying RPA Center of Excellence, organizations accumulate risk faster than value.

This challenge is no longer limited to early adopters. A global survey by Deloitte found that 53% of enterprises have already implemented robotic process automation, increasing pressure to scale automation responsibly rather than experimentally.
| When RPA Scales Without a CoE | What Enterprises Start Seeing |
|---|---|
| Pilot-driven delivery model | Automation cannot keep up with enterprise complexity |
| No centralized ownership | Unclear accountability for bot failures and changes |
| Speed prioritized in isolation | Shadow automation outside IT visibility |
| Informal standards | Inconsistent credential and access handling |
| Reactive governance | Audit findings and delayed remediation |
| Tool-led expansion | RPA program governance was added too late |
As scaling RPA across the enterprise increases regulatory exposure, embedding controls early through a strong RPA governance framework prevents risk, delivery slowdowns, and trust erosion. Building an RPA Center of Excellence with clear governance, ownership, and metrics ensures automation scales with visibility, stability, and control.
What Are the Benefits of an RPA Center of Excellence?
At enterprise scale, a robust RPA CoE framework ensures automation success is no longer defined by how many bots are deployed. It is defined by how well automation holds up under cost pressure, regulatory scrutiny, and operational complexity.
This shift is reflected at the leadership level, where 98% of IT leaders now view automation as a critical driver of financial performance, not just operational efficiency. From RPA in finance and accounting to banking automation, industries with high compliance requirements demonstrate how governance enables value at scale.
This is where an enterprise-grade RPA Center of Excellence separates sustainable programs from stalled ones.
Why Simply “Having A CoE” Is Not Enough
Many organizations establish a CoE in name, but stop short of giving it real authority or structure. Without clear decision rights and enterprise scope, the CoE becomes a coordination layer rather than a control mechanism.
- Limited influence over automation standards
- No ownership of bot lifecycle or change control
- Reactive involvement after issues surface
How Cost, Risk, And Control Compound At The Enterprise Scale
As automation expands, small inefficiencies multiply. Bots that are cheap to build become expensive to maintain when controls, monitoring, and recovery are not designed upfront.
- Rising maintenance and support costs
- Increased audit and compliance remediation efforts
- Higher exposure to access and compliance risk
Why The RPA CoE Acts As An Enterprise Automation Control Plane
An enterprise-grade RPA CoE governance model does not centralize all delivery. It centralizes accountability. The CoE defines how automation operates, even when execution is distributed across teams.
- Standardized design and deployment practices
- Consistent lifecycle management
- Clear escalation and exception handling paths
How Alignment Across Business, IT, And Risk Drives Scale
Sustainable automation requires these functions to move together. The RPA CoE provides the structure that aligns priorities before conflicts emerge.
- Business gains predictable delivery and visibility
- IT maintains architectural stability and resilience
- Risk teams retain auditability and control
This alignment is what enables an enterprise RPA scaling strategy that grows automation without fragmenting the organization.
How Should Enterprises Build and Structure an RPA CoE Team for Scale?
This is often when ownership questions surface. Without clear accountability, it becomes difficult to build an RPA Center of Excellence that scales smoothly.
At the enterprise level, how to build an RPA Center of Excellence depends on defined decision rights, accountability, and coordinated workflows across business and IT.
Who Provides Sponsorship And Direction For The RPA CoE?
Every scalable RPA CoE framework starts with visible ownership at the top. An RPA sponsor provides executive backing, funding authority, and air cover when automation decisions cut across functions. This role is often paired with a Head of RPA who owns the day-to-day program, defines standards, and acts as the single point of accountability.
- Executive sponsorship tied to business outcomes
- Head of RPA accountable for delivery, risk, and scale
- Clear mandate that spans business and IT
What Role Does The RPA CoE Steering Committee Play?
As automation expands, decisions stop being purely technical. A steering committee provides structured governance for prioritization, funding, and risk acceptance. It prevents automation decisions from being made in isolation by any single function.
- Cross-functional representation from business, IT, and risk
- Approval authority for high-impact automations
- Alignment on priorities and escalation paths
How Do RPA Champions And Process Analysts Enable Scale?
RPA does not scale from the center alone. Champions embedded within business units surface demand and help translate operational pain points into automation candidates. From manufacturing automation workflows to insurance claims processing, process analysts work alongside champions to document processes, assess suitability, and reduce rework later.
- Business-owned demand intake
- Clear process definitions before automation starts
- Reduced friction between business intent and delivery
Why Is The RPA Change Manager Critical At Enterprise Scale?
Automation changes how work gets done, even when it runs quietly in the background. An RPA change manager ensures that communication, training, and adoption keep pace with delivery, especially as automation touches regulated processes in industries like healthcare and wealth management, or customer-facing processes.
- Change and communication planning
- Stakeholder alignment across teams
- Reduced resistance as automation footprint grows
How Does The Robotic Operating Team Support Day-to-Day Execution?
The robotic operating team is responsible for building, running, and maintaining automations under defined standards. This team typically operates in a centralized model for governance, while execution may be distributed depending on maturity.
- Bot development and testing
- Production monitoring and incident response
- Ongoing optimization and maintenance
How Should Enterprises Define Roles, Responsibilities, And Support Ownership?
Clarity here prevents scale from breaking. Enterprises must explicitly decide where they sit on the centralized versus decentralized approach, and how RPA service and support ownership is handled.
- Centralized standards with controlled decentralization of delivery
- Clear ownership for production support and upgrades
- Defined handoffs between business, IT, and the CoE
When these roles and responsibilities are designed deliberately, the RPA CoE operating model becomes scalable, not a bottleneck. That structure is what allows automation to scale predictably without losing control.
How Should Enterprises Build Technology and Infrastructure Foundations for a Scalable RPA CoE?
At enterprise scale, the robotics process automation center of excellence infrastructure is no longer a setup task. It becomes a shared production platform that must handle fluctuating demand, system changes, and operational failures without disrupting the business. Many automation programs struggle here because infrastructure decisions are treated as secondary to delivery speed.
A scalable foundation starts with enterprise-class architecture and IT infrastructure designed for resilience and operational continuity.
What Roles Are Required To Operate RPA Infrastructure At Scale?
Sustainable automation requires clear ownership beyond development teams.
- RPA infrastructure engineers manage environments, server capacity, orchestration health, and the coordination of automation workflows across enterprise systems.
- Deployment teams control releases, upgrades, and rollback procedures across environments
- RPA service support owns incident response, troubleshooting, and production continuity once bots go live
Without these roles clearly defined, automation reliability degrades as volume increases.
How Should Development Environments And Software Infrastructure Be Designed?
Enterprise RPA platforms must support change without fragility.
- Separate development, testing, and production environments with controlled promotion paths
- Standardized robotic configuration to reduce environment-specific failures
- Software infrastructure aligned to enterprise security, networking, and identity standards
This ensures new automations do not introduce instability into existing workflows.
Why Do Performance, Connectivity, And Server Design Matter At Scale?
As bots interact with multiple enterprise systems, infrastructure limitations surface quickly.
- Server installation and capacity planning aligned to automation throughput, not static estimates
- Continuous monitoring of performance and connectivity to upstream systems
- Proactive troubleshooting before failures cascade into outages
These controls prevent automation from becoming brittle under real-world load.
How Should Maintenance And Support Be Handled In Enterprise RPA Programs?
RPA programs that scale successfully plan for operations from the beginning. They evaluate enterprise maintenance costs and support needed early on
- Defined maintenance and support models with ownership clarity
- Standard troubleshooting workflows and escalation paths
- Regular infrastructure health reviews tied to automation growth
Strong technical foundations allow RPA to scale as a platform, not a collection of scripts.
How Do CIOs Approach Balancing Speed and Governance in RPA When Choosing an Operating Model?
Balancing speed and governance in an RPA Center of Excellence is not a cultural or tooling challenge. It is an RPA CoE governance model decision. At enterprise scale, automation pressure comes from volume. Demand grows across business units, systems, and regions, and the way the CoE is structured determines whether automation accelerates or stalls.
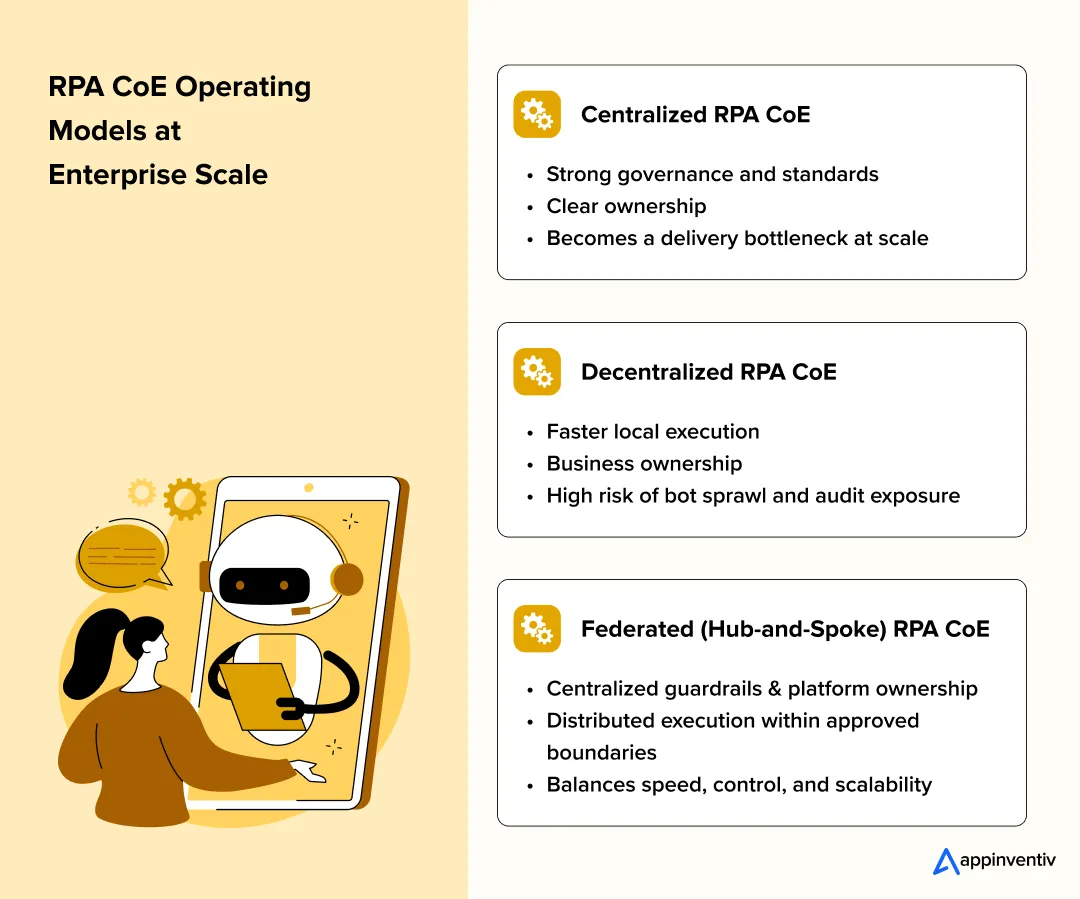
When speed and control are treated as opposing goals, enterprises predictably land in one of two failure states: delivery slows under excessive centralization, or automation moves fast enough to create audit, security, and operational risk. The operating model is where this tension is resolved.
RPA CoE Models and the Speed–Governance Tradeoff
For most CIOs, the decision ultimately comes down to a centralized vs federated RPA CoE model, with speed, governance, and scalability pulling in different directions.
| RPA CoE Model | Impact on Speed | Impact on Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized CoE | Slows as demand increases | Strong control and standardization |
| Decentralized CoE | Faster local execution | Bot sprawl, inconsistent controls, audit exposure |
This comparison of RPA CoE models explains why neither extreme scales cleanly across large enterprises. Centralized models struggle to keep up with demand. Decentralized models move faster but erode consistency and control as automation expands.
Why Speed Breaks Without Governance
Unrestricted execution works briefly, then destabilizes the program. As automation spreads across systems and regions, gaps in standards and ownership surface quickly.
- Bots fail more frequently after upstream system changes
- Maintenance effort overtakes new delivery
- Security and audit issues emerge under regulatory scrutiny
Why Governance Fails When It Is Added Late
When governance is introduced late, automation often reaches a point where delivery slows under audit pressure, maintenance costs spike, and business trust declines. At this stage, enterprises spend more time stabilizing automation than expanding it.
Governance becomes a constraint when it is imposed after automation is already in motion. Long approval cycles and late-stage reviews introduce friction rather than protection.
- Automation requests stall in review queues
- Design changes happen late, driving rework
- Delivery timelines become unpredictable
How a Federated RPA CoE Resolves the Tradeoff
A federated, hub-and-spoke RPA delivery model for enterprises addresses this structural tension by separating policy, platform, and execution.
- Governance, standards, and platform ownership remain centralized
- Execution is distributed within defined guardrails
- Quality gates ensure consistency without centralizing delivery
This approach embeds governance into execution rather than layering it on afterward. Speed is preserved because teams operate within clear boundaries. Control is maintained because standards, access, and escalation paths are enforced centrally.
Also Read: How AI is Revolutionizing Data Governance for Enterprises and How to Do It Right?
For CIOs, this is the inflection point where the benefits of the RPA Center of Excellence become clear. Automation stops being a scaling risk and becomes a repeatable enterprise capability. When the operating model is aligned to organizational complexity and risk exposure, automation can expand without creating operational debt.
Align CoE structure with enterprise scale, risk exposure, and delivery velocity
How Should Enterprises Design an RPA Governance Framework That Scales?
This is where RPA program governance stabilizes or slows enterprise automation. A scalable RPA governance framework is the foundation of enterprise automation governance, defining how automation is designed, deployed, and operated as scale and complexity increase. When governance is practical and embedded, teams move faster with fewer surprises.
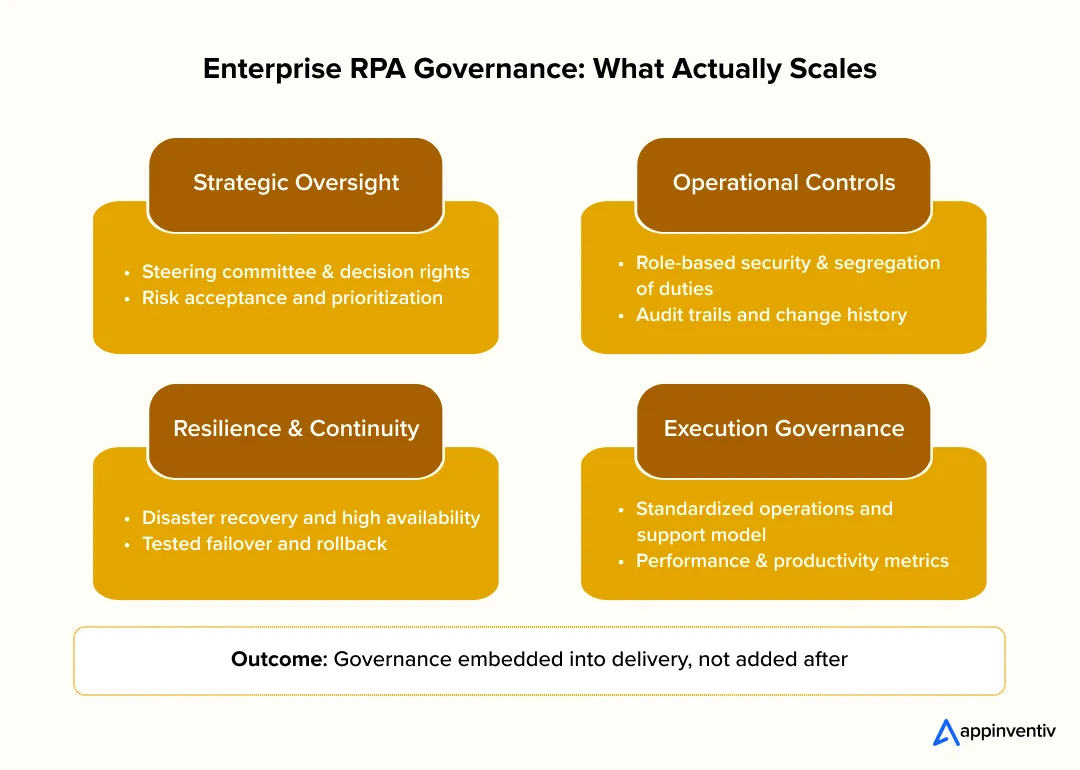
How Should Governing Bodies And Escalation Paths Be Structured?
An effective RPA CoE governance model works when decision rights are clear before issues arise. In enterprise programs we support, the absence of predefined escalation paths is usually what forces risk teams to intervene late and slow delivery. Designing those paths early allows automation teams to move faster without triggering reactive controls.
- RPA governance structure defines how the CoE owns standards and lifecycle policies
- Steering or governance boards handle prioritization and risk acceptance
- Escalation paths exist for exceptions, not every release
Why Are Role-Based Security And Segregation Of Duties Non-Negotiable?
As bots access sensitive systems, access control becomes a primary risk surface. Governance must enforce separation between build, approve, and operate functions.
- Role-based access for developers, operators, and reviewers
- Segregation between bot development and production credentials
- Periodic access reviews aligned with enterprise security policies
How Do Auditing Capabilities Protect Enterprise Automation Programs?
Strong RPA program governance through auditability is not just for compliance teams. It protects delivery teams from rework and disruption when scrutiny increases.
- Traceable approvals and change history
- Logged bot actions and exception handling
- Evidence-ready documentation for audits
Why Do Disaster Recovery And High Availability Matter Early?
Automation becomes embedded faster than most teams expect. Governance must assume failures will happen.
- Defined recovery objectives for critical automations
- High availability for orchestration and runtime components
- Tested failover and rollback procedures
How Should Operations, Support, And Performance Be Governed?
Sustainable RPA automation governance extends into day-to-day operations.
- Clear operations and support model with ownership defined
- Performance and productivity metrics tied to business outcomes
- Ongoing monitoring to catch degradation early
A well-designed robotic process automation governance framework enables scale by reducing friction, not adding it.
How Does Change Management Enable Successful RPA CoE Adoption Across the Enterprise?
Automation rarely fails because of code. It fails because people, processes, and expectations move out of sync. At enterprise scale, change management is the mechanism that keeps automation adoption stable as delivery accelerates.
This human dimension matters. Studies consistently show that 89% of employees report higher job satisfaction when automation removes repetitive, low-value work, making adoption as much an organizational priority as a technical one.
Without it, even a well-designed RPA CoE governance model struggles to gain traction
Why Is Organizational Change Management Critical For RPA Programs?
RPA alters how work flows across teams, often without changing job titles or org charts. That subtle shift creates uncertainty if it is not managed deliberately.
- Clear ownership of automation impacts across roles
- Early identification of operational and control risks
- Structured onboarding as automation expands into new teams
An RPA change manager anchors these efforts and ensures change is treated as part of delivery, not an afterthought.
How Do Change And Communication Plans Reduce Adoption Friction?
Enterprises underestimate how much confusion automation can create when communication is inconsistent. A formal plan sets expectations before resistance builds.
- Transparent messaging on what automation will and will not change
- Role-specific communication for business, IT, and operations
- Timely updates tied to releases, not post-deployment
Why Must RPA Change Management Align Closely With It?
RPA does not operate outside the enterprise technology landscape. Collaboration with IT ensures automation aligns with existing controls and operating rhythms.
- Integration with IT service management processes
- CMDB alignment for bot assets and dependencies
- Shared incident, change, and release workflows
How Do Demand Management And Culture Affect Scale?
As demand grows, unmanaged intake overwhelms delivery teams and fuels shadow automation. Cultural resistance often follows when expectations are missed.
- Structured demand management process
- Clear intake and prioritization criteria
- Organizational redesign recommendations where roles shift
Change management transforms automation from a technical initiative into an enterprise capability that people trust and adopt at scale.
How Can Enterprises Develop Skills and Training Within an RPA CoE?
Automation maturity is not sustained by tools alone. People who understand how to design, run, and evolve automation safely as scale increases sustain it. Enterprises that invest early in skills and training avoid the delivery slowdowns and operational risk that appear when knowledge remains concentrated in a few individuals.
A strong skills strategy is a core part of RPA CoE best practices, not a supporting activity.
How Should Enterprises Design Training and Upskilling Programs for RPA?
Enterprise RPA teams require more than basic tool familiarity. Training must cover design standards, operational resilience, and governance expectations alongside development skills.
- Structured onboarding for new CoE members
- Role-specific training for developers, analysts, and operators
- Ongoing refreshers aligned with platform updates
This creates consistency as automation scales across teams.
What Role Do Training Paths And Certifications Play In Maturity?
Formal training paths bring discipline to skill development and reduce dependency on informal knowledge transfer. Certification programs, including SS&C Blue Prism certification tracks where applicable, provide a shared baseline for quality and standards.
- Defined progression from foundational to advanced roles
- Clear expectations for skill readiness before production access
- Reduced variation in build and support quality
How Does Enablement Strengthen The Core Robotic Operating Team?
The core robotic operating team carries responsibility for production stability. Enablement focuses on operational readiness, not building capability.
- Monitoring, incident response, and recovery training
- Exposure to real production scenarios
- Cross-training to reduce single points of failure
Why Do Reviews And Continuous Learning Matter At Scale?
Before-action and after-action reviews help teams anticipate risk and capture lessons without slowing delivery. Over time, these practices support the progression of the RPA CoE maturity model.
- Structured learning loops tied to delivery outcomes
- Mentorship to spread experience across teams
- Innovation strategy aligned with governance boundaries
Together, these practices embed robotic process automation best practices into the CoE and support long-term enterprise scale.
How Should Enterprises Identify and Prioritize Processes for RPA at Scale?
This is where many RPA programs quietly lose momentum. Not because teams cannot automate, but because they automate the wrong things first. At scale, process identification is less about enthusiasm and more about discipline. The goal is to build a pipeline that consistently feeds high-value automation into delivery without creating noise or rework.
A structured approach keeps automation focused on outcomes, not activity.
How Do Enterprises Build A Reliable Automation Pipeline?
Process identification starts with intent. Enterprises need a steady flow of automation candidates that are evaluated the same way every time, regardless of which team submits them.
- Centralized automation pipeline owned by the CoE
- Standard intake criteria for all business units
- Early screening for technical feasibility and risk
This prevents low-value or high-risk work from entering delivery.
What Role Do Business Analysts And Governance Boards Play?
Business analysts translate operational pain into automation-ready inputs. Governance boards ensure prioritization decisions align with enterprise goals, not local urgency.
- Clear process definitions before approval
- Governance board oversight for prioritization and sequencing
- Alignment between business value and delivery capacity
Why Is Structured Process Discovery Essential?
Automating poorly understood processes only accelerates inefficiency. Discovery and selection must happen before design begins.
- Documented process maps with variations identified
- Defined inputs, outputs, and exception paths
- Agreement on process ownership
How Should Proof-Of-Concept And Roi Guide Prioritization?
Proof-of-concept validation reduces risk before full investment. ROI calculations then determine sequencing.
- POCs used to validate assumptions, not showcase tools
- ROI calculations based on effort saved, risk reduced, and scale potential
- Prioritization guidelines applied consistently across the portfolio
This robotic process automation assessment framework ensures enterprises scale automation where it delivers measurable value, not just visible activity.
How to Build an RPA Center of Excellence?
An enterprise roadmap is no checklist. It is a sequence of decisions that reduce risk as automation expands. The order matters. Skipping steps usually feels faster in the short term, but it’s up later as rework, control gaps, or stalled delivery. A practical roadmap keeps execution moving while governance matures alongside it.
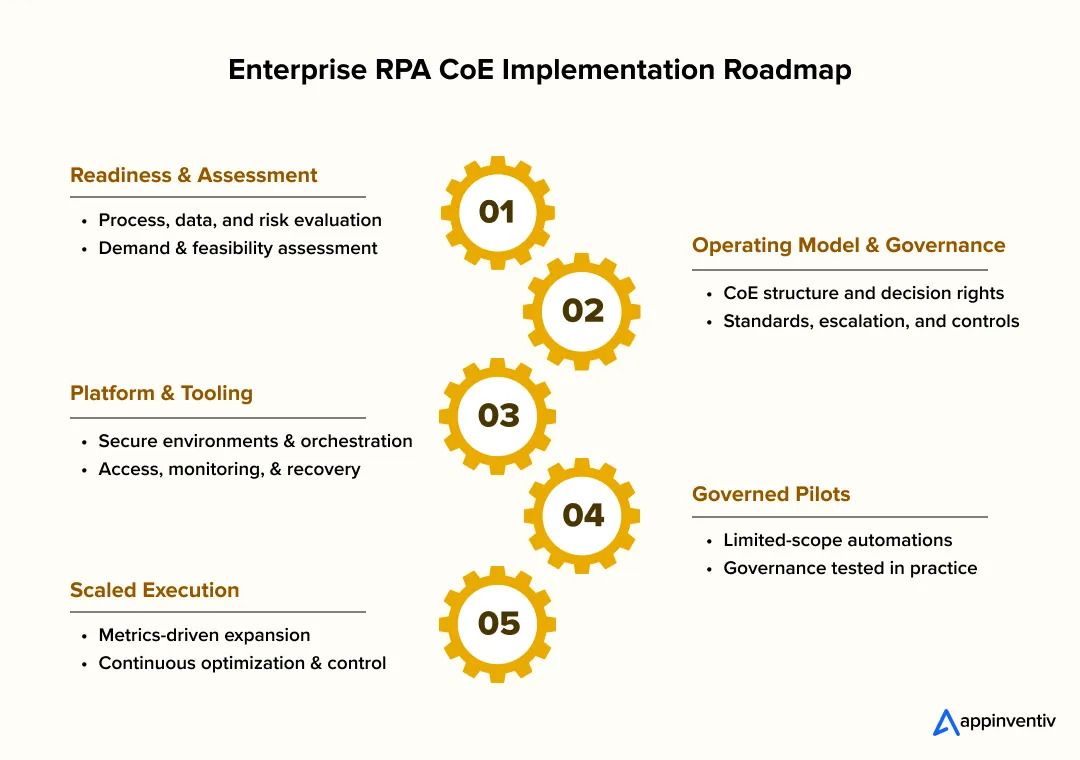
How Should Enterprises Approach Readiness And Assessment?
Before design begins, leaders need a clear view of where automation can safely start and where it cannot. This phase sets boundaries and avoids false starts.
- Enterprise readiness assessment across processes, enterprise data architecture, and controls
- Initial inventory of automation demand and risk exposure
- Agreement on success criteria and constraints
Why Does Operating Model Finalization Come Early?
The RPA CoE operating model determines who decides, who builds, and who supports. Finalizing it early prevents confusion once delivery begins.
- Clear centralized versus decentralized responsibilities
- Defined escalation paths and approval authority
- Alignment between business, IT, and risk teams
How Should Platform And Tooling Decisions Be Made?
The RPA delivery model for enterprises should be reinforced by tooling, not dictated by it. Decisions here focus on standardization and scale readiness.
- Selection aligned to security and integration requirements
- Environment strategy for development, testing, and production
- Built-in controls for access, monitoring, and recovery
Why Are Pilots With Governance Guardrails Essential?
Pilots validate more than technical feasibility. They test how governance works in practice.
- Limited-scope pilots under full standards
- Early feedback on intake, review, and release flows
- Adjustments before scale increases
How Do Enterprises Scale With Metrics And Controls?
Once pilots stabilize, scale follows discipline, not acceleration.
- Metrics tied to delivery speed, stability, and value
- Controls enforced through platforms, not manual checks
- Visibility into performance and risk
Why Is Continuous Optimization Part Of The Roadmap?
An effective RPA CoE implementation roadmap assumes change. Optimization keeps automation relevant as the enterprise evolves.
- Regular reviews of performance and controls
- Refinement of standards and processes
- Incremental expansion without disrupting operations
This is how enterprises build an RPA Center of Excellence that scales predictably instead of reactively.
Translate strategy into a phased, governance-led automation roadmap
How Should Enterprises Measure RPA CoE Performance and Drive Continuous Improvement?
Once automation moves beyond pilots, measurement becomes the difference between sustained value and silent operational risk. At enterprise scale, bot counts and hours saved provide limited insight. What leadership needs are operational signals that show whether automation is stable, recoverable, and safe to expand across critical workflows.
This is where measurement becomes a core part of the enterprise RPA scaling strategy, not a reporting exercise.
How Should ROI And Impact Assessments Be Structured?
ROI must reflect business reality, not optimistic projections. Mature CoEs assess value across efficiency, risk reduction, and operational resilience.
- Effort and cycle time reduction are valid post-deployment
- Cost avoidance from reduced errors and rework
- Impact on compliance and control effectiveness
Which KPIs Matter At Enterprise Scale?
Enterprise RPA programs rely on a focused set of operational KPIs that reflect real system behavior under load. These indicators help CoE leaders detect risk early and make informed scaling decisions.
| Metric | Business Impact |
|---|---|
| Mean Time to Recover (MTTR) | Indicates operational resilience and how quickly automations are restored after failures |
| Automation Success and Exception Rates | Reveal design quality, data stability, and upstream system reliability |
| Throughput Versus Backlog Growth | Shows whether automation delivery capacity is keeping pace with enterprise demand |
| Bot Utilization Trends | Measures efficiency of bot capacity across environments and identifies over or underuse |
Together, these metrics form a performance framework that supports scale without masking instability.
Why Are Automation Audits And Governance Reviews Essential?
At enterprise scale, audits and governance reviews act as early-warning mechanisms rather than corrective actions. They help CoE leaders identify systemic issues before failures impact critical operations.
- Regular reviews of access, change history, and control effectiveness
- Operational governance reviews aligned to risk exposure and system criticality
- Remediation actions tracked to closure, not documentation alone
How Do Risk Mitigation And Lessons Learned Drive Maturity?
Continuous improvement depends on feedback loops that teams actually use.
- Lessons learned and captured after incidents and releases
- Risk patterns tracked across the automation portfolio
- Preventive controls refined over time
Also Read: Harnessing the Power of AI for Enhanced Risk Management in Business
How Does Hyperautomation And Technology Evolution Fit In?
As enterprises move toward hyperautomation, combining RPA with AI, analytics, and orchestration, the RPA CoE maturity model must adapt to govern increasingly interconnected automation workflows.
- Measured introduction of new capabilities
- Governance extended to emerging technologies
- Continuous alignment with business priorities
This is how RPA CoEs progress through maturity stages while preserving control and value.
How Can Enterprises Approach Integrating AI/ML Into RPA CoE With Governance?
Integrating AI/ML into RPA CoE often begins as incremental improvements but quickly introduces probabilistic decision-making into deterministic workflows. Achieving enterprise AI at scale requires strong governance, clear oversight, and robust data governance controls to ensure automation scales safely without increasing operational or compliance risk.
Where Do AI Use Cases Fit Safely Within RPA?
AI adds value when it augments decision points rather than replaces control, forming the foundation of intelligent automation within governed enterprise workflows. Mature enterprises introduce intelligence at well-defined stages of the automation lifecycle.
- Document classification and data extraction
- Predictive routing and prioritization
- Assisted exception handling
These use cases expand capability without destabilizing core processes.
What Governance Controls Are Required for AI-Enabled Bots?
Integrating AI and ML changes automation from deterministic behavior to probabilistic outcomes. This shift requires explicit controls to ensure decisions remain explainable, auditable, and defensible under scrutiny.
- Confidence thresholds: Bots act autonomously only when model confidence exceeds predefined limits, routing low-confidence outcomes to human review.
- Explainability and audit trails: AI execution logs capture input data, model versions, and decision rationale to support compliance reviews.
- Lifecycle separation: Model training, validation, and production deployment are managed as distinct stages with controlled promotion paths.
- Drift monitoring: Performance is continuously tracked to detect degradation and trigger retraining or rollback before impact escalates.
Also Read: AI Integration Consulting in 2026: Why Enterprises Can’t Ignore It?
Why Do Explainability And Drift Management Matter?
Enterprises need to understand why automation behaves a certain way, especially under audit or failure conditions.
- Model explainability for regulated workflows
- Drift detection to catch performance degradation
- Defined thresholds for retraining or rollback
How Does Human-In-The-Loop Enforcement Preserve Enterprise Control?
In enterprise environments, human oversight is not a fallback. It is a deliberate control mechanism. High-impact decisions must remain reviewable even when AI confidence is high.
- Mandatory human review for financial, regulatory, or customer-impacting decisions
- Exception routing is integrated directly into automation workflows
- Defined escalation paths aligned with governance and risk thresholds
This approach allows enterprises to integrate AI and ML into an RPA CoE without sacrificing trust or control.
Also Read: How Explainable AI can Unlock Accountable and Ethical Development of Artificial Intelligence
Identify governance gaps before automation debt limits enterprise growth
How Does Appinventiv Help Enterprises Design and Scale an RPA Center of Excellence?
Most enterprises engage our RPA development services once automation proves value, but before resilience is fully tested. Bots deliver measurable impact, yet confidence depends on whether programs can withstand audit pressure, system changes, and growing enterprise demand.
Our approach to building an RPA Center of Excellence prioritizes governance-first operating models, clear decision rights, and lifecycle ownership. We design vendor-agnostic automation environments that avoid platform lock-in, embed compliance through access controls and audit trails, and support stable enterprise-scale adoption.
As an AI governance consulting company, we help enterprises introduce AI responsibly using explainability, confidence thresholds, and human oversight. With 300+ AI-powered solutions delivered for global enterprises, including IKEA and Domino’s, we support scalable, risk-aware automation.
FAQs
Q. What is an enterprise-grade RPA Center of Excellence?
A. An enterprise-grade RPA Center of Excellence is a centralized governance and operating structure that defines how automation is designed, approved, deployed, and supported at scale. It goes beyond delivery to include ownership models, security controls, audit readiness, performance measurement, and alignment across business, IT, and risk functions. The benefits of the RPA Center of Excellence include reduced operational risk, improved audit readiness, and sustainable automation at scale.
Q. How can enterprises scale RPA without losing governance control?
A. Enterprises scale RPA by embedding governance into the operating model rather than adding it later. This includes clear decision rights, standardized intake and prioritization, platform-enforced controls, and defined escalation paths. When governance is built into execution, automation can scale quickly without increasing risk or rework.
Q. What is the right RPA CoE model for large enterprises?
A. Among various RPA CoE models, most large enterprises succeed with a hybrid or hub-and-spoke approach. Governance, standards, and platform ownership remain centralized, while execution is distributed across business units. This approach balances delivery speed with consistency, auditability, and enterprise-wide control as automation scales.
Q. How do CIOs balance speed and control in RPA programs?
A. CIOs balance speed and control by separating policy, platform, and execution. Governance defines the rules, platforms enforce them automatically, and delivery teams operate within clear guardrails. This removes friction from day-to-day delivery while preserving oversight, stability, and compliance as automation expands.
Q. Why do RPA initiatives fail to scale across enterprises?
A. RPA initiatives fail to scale when they are tool-led instead of operating-model-led. Common causes include unclear ownership, reactive governance, unmanaged change, and lack of performance metrics. Without a CoE to align delivery, control, and accountability, early automation success turns into operational drag.
Q. What governance frameworks work best for enterprise RPA?
A. Effective enterprise RPA governance frameworks combine strategic oversight, security controls, operational standards, and performance management. They include governing bodies, role-based access, audit trails, disaster recovery planning, and continuous governance reviews. The goal is consistency and resilience, not a heavy process.
Q. How does Appinventiv help enterprises design scalable RPA CoEs?
A. Appinventiv helps enterprises design RPA CoEs that scale through governance-first operating models, vendor-agnostic architectures, and compliance-ready automation programs. We align business, IT, and risk priorities early, introduce AI in a controlled manner, and focus on long-term stability alongside delivery.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Top Enterprise Use Cases for Agentic RAG in eCommerce Transformation
Key takeaways: Agentic RAG in eCommerce combines retrieval, generation, and autonomous decision-making, enabling AI systems to plan, reason, and act on real-time data for smarter automation and personalization. This approach powers advanced use cases like dynamic merchandising, personalized recommendations, automated customer care, and intelligent pricing, improving efficiency and customer experience. Enterprises benefit from enhanced operational…

Build AI Chatbot With RAG Integration: Appinventiv’s End-To-End Development Framework
Key takeaways: RAG chatbots improve enterprise AI accuracy by grounding responses in verified internal business knowledge. Governance, security, and explainability become critical as AI shifts from pilots to enterprise infrastructure. Investment typically ranges $50K–$500K depending on data integration, compliance, and deployment complexity. Strong data engineering and architecture discipline matter more than standalone model capability for…

The Enterprise Buyer’s Checklist Before Hiring an AI Development Partner
Key takeaways: Choosing an AI development partner is less about technical demos and more about real-world fit, governance, and operational reliability. Internal alignment on outcomes, data ownership, and integration realities is essential before engaging any enterprise AI partner. Strong partners demonstrate delivery maturity through governance controls, security discipline, and lifecycle management, not just model accuracy.…