- Overview of Infrastructure Management
- Components of IT Infrastructure Management
- 1. Hardware Management
- 2. Software Management
- 3. Network Management
- 4. Data Storage and Management
- 5. Cloud Services Management
- 6. Security Management
- 7. Facilities Management
- Benefits of IT Infrastructure Management
- 1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
- 2. Strengthened Security Posture
- 3. Improved Business Agility
- 4. Facilitated Innovation
- 5. Scalability for Growth
- 6. Optimized Return on Investment
- 7. Ensured Business Continuity
- 8. Compliance and Risk Management
- Key Features of Effective IT Infrastructure Management
- 1. Comprehensive Monitoring and Reporting
- 2. Automation Capabilities
- 2. Scalability
- 3. Advanced Security Features
- 4. User-Friendly User Interface
- 5. Integration Capabilities
- Best Practices and Strategies for IT Infrastructure Management
- 1. Continuous Monitoring and System Health Checks
- 2. Streamlining Operations Through Automation
- 3. Maintaining Consistency with Configuration Management
- 4. Leveraging the Cloud for Enhanced IT Flexibility
- 5. Maximizing Resources with Virtualization
- 6. Developing Robust Disaster Recovery Plans
- 7. Driving Operational Efficiency Through Standardization
- 8. Building a Knowledge Base Through Comprehensive Documentation
- 9. Ensuring System Security with Regular Updates and Patches
- 10. Facilitating Teamwork with Effective Communication
- 11. Identifying Core Issues with Root Cause Analysis
- 12. Strengthening IT Defense with Advanced Security Practices
- 13. Building Resilience with Hybrid IT Environments
- 14. Optimizing Network Performance for Seamless Connectivity
- 15. Accelerating IT Delivery with DevOps Integration
- 16. Planning for Growth with Scalable Infrastructure
- IT Infrastructure Management Implementation Roadmap
- 1. Evaluate the Current State of IT Infrastructure
- 2. Set Clear Infrastructure Goals – Planning and Documentation
- 3. Allocate Resources for Infrastructure Needs
- 4. Define Success Metrics and Key Performance Indicators
- 5. Implement Continuous Monitoring and Alert Systems
- 6. Ensure Comprehensive Security and Compliance
- Key Focus Areas For Effective IT Infrastructure Management Implementation
- 1. Dynamic Configuration Management
- 2. Unified Analysis and Monitoring for Seamless Insights
- 3. AI-driven Insights for Enhanced Decision Making
- 4. Scalability for Future Growth and Demands
- 5. Automation to Optimize Performance and Efficiency
- Overcoming Challenges in IT Infrastructure Management
- 1. Managing the Complexity of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
- 2. Straining Resources and Budget Limitations
- 3. Navigating Evolving Cybersecurity Risks
- 4. Staying Ahead of Technological Advancements
- 5. Achieving Scalability Without Disrupting Operations
- 6. Ensuring Consistent Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
- Appinventiv: For Your Seamlessly Integrated Service for IT Infrastructure Management
- FAQs
In the fast-paced, high-stakes world of enterprise operations, IT infrastructure is the backbone that keeps businesses running smoothly. Yet, as digital ecosystems grow more complex, managing this infrastructure has become a daunting challenge since enterprises today face mounting pressure to ensure seamless connectivity, bulletproof security, and scalability – all while meeting the demands of global customers and partners.
Consider this: a single outage or security breach can disrupt operations and erode years of built trust with stakeholders. Thus, it’s not just about maintaining systems anymore; it’s about driving business resilience, agility, and competitive advantage.
This article delves into the best practices and actionable strategies that empower enterprises to manage their IT infrastructure efficiently. Whether you’re grappling with hybrid cloud environments, managing sprawling networks, or ensuring compliance, IT infrastructure development will provide a clear pathway to optimizing operations.
Let’s explore how enterprises can transform IT infrastructure management systems from a cost center into a strategic growth enabler.
Overview of Infrastructure Management
IT infrastructure management software refers to strategically coordinating and administrating the core technological components that power an enterprise’s operations. Components which form the architecture include hardware, software, networks, data storage, and cloud computing services, all of which must function cohesively to support business objectives.
IT infrastructure management solutions set the foundation for operational efficiency and technological resilience; however, understanding its scope requires breaking down the various components that drive its effectiveness. From physical assets to cloud services and security measures, each element plays a vital role in ensuring the seamless functioning of enterprise IT ecosystems.
Let’s get your modern enterprise running like clockwork! Chat with our IT gurus to discover how our tailored IT consulting services can optimize your operations and boost your ROI.
Components of IT Infrastructure Management
Effective IT infrastructure management encompasses several critical components that collectively ensure the seamless operation of an enterprise’s technology environment.
1. Hardware Management
Hardware management oversees the physical devices that form the foundation of an enterprise’s IT system infrastructure environment, including servers, computers, storage devices, networking equipment, and data center infrastructure.
This involves monitoring the health and performance of each device, ensuring regular maintenance schedules, and upgrading components as needed to prevent failures or obsolescence. Enterprises must also manage warranties, procurements, and asset lifecycle planning to align hardware capabilities with current and future business requirements.
2. Software Management
Software management ensures that all applications, operating systems, and software tools within the enterprise are up-to-date, secure, and functioning as intended. This includes managing licenses, monitoring usage, and deploying updates or patches to address vulnerabilities and improve performance.
Enterprises often rely on centralized information technology and infrastructure management tools to streamline software inventory and automate routine maintenance tasks, ensuring compliance with vendor requirements and optimizing software investments.
Also Read: How Much Does it Cost to Maintain a Software
3. Network Management
Network management covers the configuration, monitoring, and optimization of an organization’s network infrastructure, which includes routers, switches, firewalls, and wireless systems.
With the help of IT teams that implement strategies to monitor bandwidth usage, address latency issues, and enforce security protocols to protect against unauthorized access, this component ensures reliable connectivity across on-premises locations, remote offices, and cloud environments.
4. Data Storage and Management
Data storage and management involve the entire organization, especially since every department is concerned withthe storage, retrieval, and protection of enterprise data.
To build upon a strategic data management approach, enterprises must balance on-premises storage solutions, such as servers and NAS (Network Attached Storage), with scalable cloud storage options to meet their growing data needs. Backup and disaster recovery strategies should also be implemented to minimize downtime and ensure data availability during unexpected events.
Lastly, any conversation around data storage and management will be incomplete without the mention of compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, so the IT infrastructure management tool or process must implement a stringent governance and encryption measure.
5. Cloud Services Management
As enterprises increasingly adopt cloud-based solutions, managing these services become an integral part of IT system infrastructure, which includes overseeing Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service model to ensure optimal resource utilization.
Cloud management, here, involves monitoring usage, controlling costs, maintaining security, and integrating cloud services with existing on-premises systems.
6. Security Management
Security management is dedicated to protecting enterprise IT infrastructure management components from a wide range of threats, including cyberattacks, unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cloud security risks.
To prevent this, IT teams implement firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, endpoint protection tools, and encryption technologies for safeguarding sensitive information while performing regular audits, vulnerability assessments, and incident response plans to stay ahead of emerging threats. Additionally, they extend security management to employee training, ensuring staff are aware of and adhere to best practices for cybersecurity.
7. Facilities Management
Facilities management software encompasses the physical environment that supports IT infrastructure management for enterprises, including data centers, server rooms, power supplies, cooling systems, and physical security measures such as access controls and surveillance.
Ensuring a stable and secure environment involves monitoring environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, to prevent damage to hardware while investing in backup power solutions, like UPS and generators, which are equally critical for maintaining operations during power outages.
By thoroughly addressing each of these components, enterprises can establish a robust, agile, and secure managed IT infrastructure that meets current operational needs and supports long-term strategic goals.
Having explored the fundamental components of IT infrastructure management, it becomes clear how each element contributes to the stability and functionality of an enterprise’s technology ecosystem.
However, the value of well-managed infrastructure operations goes beyond its parts. When these components are effectively integrated and optimized, they unlock many benefits that empower businesses to operate more efficiently, innovate faster, and maintain a competitive edge in an ever-evolving market.
Let’s dive deep into these advantages, highlighting how enterprises can leverage robust IT infrastructure management to achieve long-term success and resilience.
Benefits of IT Infrastructure Management
On a high level, implementing robust IT infrastructure management for enterprises means witnessing significant advantages and fostering resilience, efficiency, and growth. But what does this mean on a micro level? Let’s delve into the key benefits in detail:
1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
By streamlining the management of IT resources, enterprises can address operational bottlenecks while reducing downtime. This begins with proactive monitoring and maintenance, which ensures that systems consistently perform at peak levels and minimizes the risk of disruptions.
As a result, employees can remain focused on their core responsibilities without being derailed by technical issues. Moreover, using automation tools and centralized management systems further enhances efficiency by optimizing resource allocation. These tools eliminate redundancies, improve collaboration, and maximize productivity across departments, creating a cohesive and well-functioning IT ecosystem.
2. Strengthened Security Posture
A well-managed IT infrastructure management system places security at the forefront, ensuring that sensitive data and critical systems are protected from evolving threats. This involves strategically deploying firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular vulnerability assessments, which work together to establish a robust defense against cyberattacks. To further strengthen this security framework, automated updates, and timely patches are implemented to close potential vulnerabilities.
These cybersecurity measures ensure compliance with industry regulations and significantly reduce the likelihood of data breaches or unauthorized access, providing enterprises with a secure and resilient IT environment.
3. Improved Business Agility
In today’s dynamic business landscape, enterprises must remain agile to effectively respond to market shifts, evolving customer demands, and emerging trends. A robust IT infrastructure management software is the backbone of this agility, enabling the rapid deployment of new applications, seamless scalability of existing systems, and effortless integration of innovative technologies.
By empowering businesses to adapt quickly to changing circumstances, such a system ensures operational continuity and helps maintain a competitive edge, even in the face of volatile and unpredictable environments.
4. Facilitated Innovation
Efficient infrastructure management relieves IT teams from time-consuming maintenance tasks, enabling them to redirect their efforts toward innovation and strategic initiatives. This shift cultivates a culture of creativity and exploration, where teams can experiment with emerging technologies and implement forward-thinking processes to propel business transformation.
Whether harnessing the power of artificial intelligence for IT operations or integrating IoT solutions, a well-managed infrastructure becomes the foundation for driving cutting-edge advancements that keep enterprises ahead in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
5. Scalability for Growth
As companies expand, their enterprise infrastructure management requirements grow exponentially, demanding more sophisticated solutions. Effective infrastructure management ensures seamless scalability, enabling organizations to handle increased workloads, accommodate additional users, or support geographic expansion without disruption.
By leveraging cloud-based solutions, hybrid architectures, or modular systems, enterprises can scale their IT resources to align with their growth. Importantly, scalability is not just about increasing capacity; it’s about achieving this growth efficiently without compromising performance, reliability, or the overall user experience.
6. Optimized Return on Investment
Managed IT infrastructure represents a significant financial investment for enterprises. Effective management ensures that these assets are utilized to their full potential, avoiding wastage and reducing unnecessary expenditures.
By leveraging managed IT services, oOrganizations can achieve a higher ROI on their technology investments by maintaining system performance and preventing costly downtime. Additionally, cost savings achieved through automation and energy-efficient systems can further enhance profitability.
7. Ensured Business Continuity
Unexpected disruptions, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or hardware failures, have the potential to cripple business operations. A well-planned IT infrastructure strategy mitigates these risks by incorporating robust disaster recovery and backup solutions designed to minimize downtime and prevent data loss.
By regularly testing recovery protocols, enterprises can ensure that critical business functions remain operational during the most challenging circumstances. This proactive approach safeguards customer trust and helps minimize financial losses, reinforcing the organization’s resilience.
8. Compliance and Risk Management
Enterprises operate within a complex regulatory landscape, where non-compliance can result in severe penalties and damage their reputation. IT risk management involves integrating compliance protocols and robust strategies to proactively identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Regular audits, advanced encryption measures, and stringent access controls are crucial in ensuring adherence to legal requirements while mitigating the risk of internal and external threats. This comprehensive approach safeguards the organization’s operations and reinforces stakeholder trust.
While the benefits of IT infrastructure management highlight its strategic value, the underlying features provide the tools and functionalities that make those benefits possible.
Next, we will explore those key features of infrastructure management solutions in greater detail, demonstrating how they collectively contribute to building a resilient and agile IT environment.
Key Features of Effective IT Infrastructure Management
A robust IT infrastructure management system is built on functionalities designed to enhance performance, security, and adaptability. Features of infrastructure management solutions that enable enterprises to maintain seamless operations while preparing for future growth and technological advancements.
1. Comprehensive Monitoring and Reporting
One of the cornerstones of IT infrastructure management for enterprises is the capability to monitor and analyze the performance of all systems and components in real-time. By leveraging comprehensive monitoring tools, organizations gain visibility into critical aspects such as hardware health, software efficiency, network traffic, and security alerts.
Detailed reporting complements this monitoring by delivering actionable insights into trends, anomalies, and potential risks, empowering IT teams to address issues proactively before they escalate. Additionally, intuitive dashboards that aggregate data from multiple sources streamline decision-making and highlight opportunities for optimization, ensuring that enterprise systems run smoothly and efficiently.
2. Automation Capabilities
Automation is crucial for streamlining repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as patch management, system updates, and resource allocation. By integrating automation capabilities, enterprises can reduce human error, improve response times, and free up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives.
Workflow automation also ensures consistency across processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. For instance, automated alert systems can notify teams about potential issues, enabling quicker resolutions and reducing downtime.
2. Scalability
Enterprises operate in dynamic environments that demand flexibility and the ability to scale seamlessly. Strategically managing IT infrastructure allows organizations to adjust resources efficiently, ensuring that operations remain uninterrupted during periods of growth or change.
Whether it involves supporting a growing user base, expanding network capacity, or increasing data storage, scalability ensures businesses can meet evolving demands without disruption. By leveraging advanced solutions like hybrid cloud integrations and modular architectures, enterprises can scale incrementally, maintaining performance and cost efficiency as they adapt to new opportunities and challenges.
3. Advanced Security Features
Maintaining IT infrastructure is a critical task where security is a non-negotiable priority. Integrated security features like firewalls, encryption technology, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection systems are essential in safeguarding sensitive data and critical assets from evolving cyber threats.
Alongside these proactive measures, real-time threat detection and automated incident response tools play a key role in minimizing the impact of potential breaches, ensuring rapid mitigation. Additionally, IT compliance regulation with industry-specific regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA is facilitated through robust security integrations, helping enterprises stay aligned with legal requirements while protecting their reputation and data integrity.
4. User-Friendly User Interface
A user-friendly interface enables IT teams to navigate, manage, and troubleshoot systems efficiently. Intuitive dashboards, customizable views, and simplified workflows make it easier to oversee complex IT environments.
To enable this features like drag-and-drop functionality, quick access to key metrics, and seamless navigation reduce the learning curve for IT personnel. Additionally, a well-designed user interface can increase productivity by minimizing time spent searching for information or configuring tools.
5. Integration Capabilities
IT system infrastructure is the backbone of modern enterprises, supporting various software and hardware solutions to optimize operations. With robust data integration capabilities, IT infrastructure enables seamless connectivity between third-party applications, cloud services, and legacy systems.
This integrated approach eliminates silos and fosters a unified IT environment, ensuring smooth data flow across platforms. By facilitating better coordination and sharing of information, integration empowers IT teams to derive actionable insights and implement cohesive strategies that enhance operational efficiency and drive organizational success.
While the key features of IT infrastructure management solutions play a pivotal role in ensuring efficiency, scalability, and security, implementing the right strategies is equally crucial for unlocking their full potential.
Let us revamp your IT infrastructure with cutting-edge, custom-built solutions tailored for peak performance. Don’t just keep up—level up.
In the next section, we will explore the best practices and strategies that leverage these features effectively, ensuring that your IT infrastructure remains agile, secure, and future-ready. From proactive monitoring to disaster recovery, effective IT infrastructure management strategies will enable your organization to maintain seamless operations and stay ahead of the competition.
Best Practices and Strategies for IT Infrastructure Management
To maximize the benefits of the process, enterprises must adopt a combination of strategies and approaches that ensure their IT environments remain secure, efficient, and scalable. The following IT infrastructure management best practices are essential for optimizing infrastructure performance, minimizing risks, and enhancing operational efficiency.

1. Continuous Monitoring and System Health Checks
Continuous monitoring systems enable enterprises to closely monitor the health of hardware, software, networks, and security systems, ensuring everything runs smoothly in real-time. By leveraging tools for IT infrastructure management like SolarWinds, Nagios, and Datadog, businesses can track infrastructure performance and receive alerts when something’s off, allowing IT teams to take action quickly.
Along with continuous monitoring, regular maintenance routines, such as timely updates and system diagnostics, are essential to ensure optimal performance, reduce downtime, and prevent costly disruptions to business operations.
2. Streamlining Operations Through Automation
Automating routine tasks such as system updates, patch management, and resource allocation is a critical practice for reducing operational complexity and human error. Tools like Ansible, Chef, and Puppet allow enterprises to automate the deployment and management of IT infrastructure. At the same time, platforms such as Jenkins and GitLab are valuable for automating DevOps methodologies, helping IT teams to focus on higher-priority tasks.
3. Maintaining Consistency with Configuration Management
Consistency across all systems is key to avoiding configuration errors and ensuring smooth operations. By implementing configuration management tools, enterprises can define, document, and automate the deployment of standardized configurations across their infrastructure.
Terraform and Ansible are popular IT infrastructure management tools used primarily for automating infrastructure provisioning, while Puppet and Chef help maintain consistency and configuration standards.
4. Leveraging the Cloud for Enhanced IT Flexibility
Adopting cloud computing solutions is another one of the strategies for effective IT infrastructure management that enables enterprises to scale their IT infrastructure efficiently. With cloud services, businesses can rapidly adjust their capacity based on demand, avoiding the high upfront costs of traditional on-premises infrastructure while benefiting from advanced services such as AI, machine learning, and data analytics.
Tools such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are considered one of the top platforms enterprises choose to offer flexible and scalable cloud environments.
5. Maximizing Resources with Virtualization
Virtualization enables enterprises to optimize their IT infrastructure by running multiple virtual systems on a single physical server, significantly improving resource utilization and reducing hardware costs.
Through virtualization in the cloud, companies can consolidate their infrastructure, streamline operations, and enhance disaster recovery strategies. Tools like VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and KVM help facilitate this process, allowing businesses to allocate resources more efficiently and manage workloads flexibly.
6. Developing Robust Disaster Recovery Plans
Another IT infrastructure management best practice includes having a robust disaster recovery plan, which is crucial for maintaining business continuity during system failures or unexpected disruptions. A well-defined disaster recovery strategy typically incorporates backup solutions, data redundancy, and failover mechanisms to minimize downtime and prevent data loss.
To power this, businesses use tools like Veeam, Zerto, and Commvault that are pivotal in automating backup and disaster recovery processes, ensuring that critical applications and data can be swiftly restored when needed. Additionally, regular testing of recovery protocols should be planned to ensure that enterprises can quickly recover their services and data, allowing them to maintain operations even during crises.
7. Driving Operational Efficiency Through Standardization
Standardizing hardware, software, and processes across the enterprise helps streamline IT management, reduce complexity, and enhance efficiency while providing uniformity in performance and security practices. With standardized systems, teams can manage infrastructure more effectively, ensuring quicker responses to issues and smoother updates or migrations.
To streamline the process, the team also uses IT systems infrastructure tools like Microsoft System Center and Chef Automate to establish standard configurations and processes across the enterprise and ensure consistency.
8. Building a Knowledge Base Through Comprehensive Documentation
Comprehensive documentation is a cornerstone of effective information technology and infrastructure management. Well-documented processes, system configurations, and procedures help ensure that all the team members are aligned and that there is a clear record of actions taken while playing a critical role in troubleshooting and providing IT teams with a reference guide for resolving issues quickly.
9. Ensuring System Security with Regular Updates and Patches
Keeping systems up-to-date with the latest security patches and software updates is a fundamental best practice for maintaining secure and reliable IT infrastructure operations, specifically to improve system stability and address known security flaws before they can be exploited.
To automate updates and patches, businesses use various automated patch management tools like ManageEngine, Ivanti, and WSUS (Windows Server Update Services) to ensure updates are deployed consistently across all systems.
10. Facilitating Teamwork with Effective Communication
Effective collaboration between IT teams, other departments, and external partners is essential for successful infrastructure management. Regular communication would help align IT initiatives with business goals while guaranteeing that the issues get addressed promptly.
To enable this, collaboration tools such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Trello are typically used to help streamline communication, improve efficiency across the organization, and foster a more integrated approach to maintaining IT infrastructure.
11. Identifying Core Issues with Root Cause Analysis
Post system failures or performance issues, the first focus of enterprises becomes conducting a thorough root cause analysis to identify the underlying factors. Tools like Splunk, New Relic, and ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) provide real-time monitoring and log management.
These are handy here to help IT teams quickly identify and address the source of system disruptions. By investigating and understanding the source of the problem through the help of these tools, enterprises can implement long-term solutions that can prevent future occurrences.
12. Strengthening IT Defense with Advanced Security Practices
Ensuring the security of IT infrastructure strategy is critical in protecting sensitive data and maintaining trust with customers and partners. Generally, a multi-layered security strategy involving firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, regular security audits, penetration testing, and employee training and access control measures is formed to help safeguard systems from cyber threats.
Tools such as Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet, and CrowdStrike offer comprehensive security solutions, including threat detection, prevention, and response.
13. Building Resilience with Hybrid IT Environments
Adopting a hybrid IT environment – integrating on-premises infrastructure with cloud services – provides businesses with a great deal of flexibility and resilience by optimizing the process of managing IT infrastructure based on performance, cost, and compliance requirements.
Platforms like VMware vCloud and Microsoft Azure Stack enable businesses to seamlessly manage and integrate hybrid IT infrastructures, giving them the agility to handle dynamic workloads.
14. Optimizing Network Performance for Seamless Connectivity
Optimizing the network ensures fast, reliable, and secure data transmission across the enterprise. The IT teams typically apply techniques such as load balancing, traffic shaping, and the use of content delivery networks to help minimize latency, improve application performance, and ensure reliable connectivity.
Additionally, network optimization tools like Cisco Meraki, SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, and Riverbed help improve network visibility and performance, ultimately ensuring a seamless IT environment.
15. Accelerating IT Delivery with DevOps Integration
DevOps adoption and implementation promote better collaboration between development and operations teams by breaking down silos between them – ultimately fostering a culture of innovation and agility that leads to faster deployment cycles and improved system reliability.
The approach, by emphasizing continuous integration, continuous delivery, and automation, helps enterprises streamline the development lifecycle and enhance the efficiency of their IT operations. Tools such as Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and GitLab facilitate DevOps practices, automating deployment pipelines and improving collaboration across teams.
16. Planning for Growth with Scalable Infrastructure
Planning for future growth is essential to avoid overloading IT resources or underutilizing them. When it comes to growth strategizing, enterprises’ primary agenda is scalability and capacity planning, which typically involves forecasting future infrastructure needs based on business growth and technological advancements.
Tools like CloudHealth by VMware, Capacity Planner, and Turbonomic help companies manage and optimize capacity, ensuring that their IT infrastructure management for enterprise processes can scale seamlessly and meet growing demands without sacrificing performance or efficiency.
While the strategies and best practices outlined lay the foundation for a successful IT system infrastructure plan, carefully implementing them transforms them into tangible results. And the road to success begins with a clear, structured approach to implementing these practices.
In the next section, we will explore the steps involved in assessing, planning, and executing these strategies to create robust and agile IT infrastructure management solutions that drive operational efficiency, enhance security, and support long-term business objectives.
IT Infrastructure Management Implementation Roadmap
A strategic implementation roadmap ensures the IT infrastructure meets its evolving business needs. For an enterprise, the journey begins with a thorough assessment, followed by well-planned execution phases to optimize performance, enhance security, and support long-term scalability.
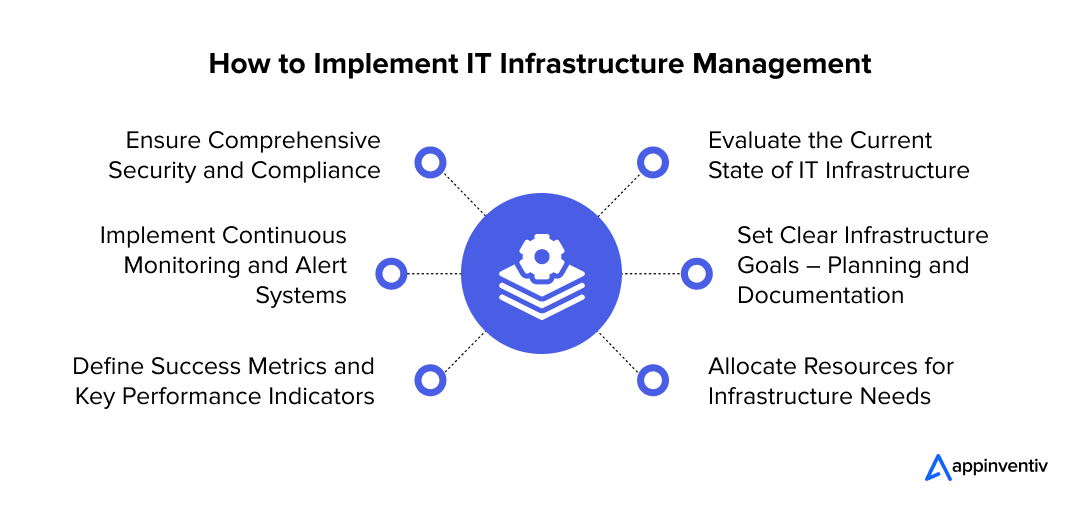
1. Evaluate the Current State of IT Infrastructure
The foundation for maintaining IT infrastructure is a clear understanding of the current environment. This involves conducting a detailed assessment to evaluate the effectiveness of existing hardware, software, networks, and security protocols.
At this stage, businesses can determine the necessary improvements and upgrades to align their infrastructure with strategic goals by identifying bottlenecks, performance gaps, and inefficiencies.
2. Set Clear Infrastructure Goals – Planning and Documentation
Defining specific objectives for the IT infrastructure is crucial for ensuring that technology investments align with business goals. This phase involves documenting the current infrastructure landscape and outlining the desired outcomes, such as enhanced system performance, better security, or scalability.
Well-documented plans made here also serve as a reference point for all future decisions and initiatives, ensuring continuity and consistency across the organization’s IT infrastructure strategy.
3. Allocate Resources for Infrastructure Needs
Adequate resource allocation is key to supporting infrastructure improvements and maintaining ongoing operations. This includes assigning the necessary budget, equipment, and personnel to meet the infrastructure objectives.
Proper resource planning that you do here will ensure that every aspect of the infrastructure is well-supported and capable of scaling to accommodate future growth.
4. Define Success Metrics and Key Performance Indicators
To track the progress and success of the infrastructure management strategy, businesses must establish clear, measurable KPIs. These metrics could include system uptime, response times, security breach frequencies, or resource utilization rates.
By aligning KPIs with the organization’s broader goals, IT leaders can assess the effectiveness of their infrastructure investments and adjust strategies accordingly.
5. Implement Continuous Monitoring and Alert Systems
Proactive monitoring is essential to detect issues early and minimize disruptions. By setting up continuous monitoring for performance, security, and system health, organizations can identify potential problems before they impact business operations.
This managed IT infrastructure approach allows for quick intervention and reduces the risk of downtime, ensuring smooth and efficient infrastructure performance.
6. Ensure Comprehensive Security and Compliance
As cyber threats continue to rise and regulatory requirements become more stringent, securing the IT infrastructure and ensuring compliance are no longer optional but essential priorities.
This involves implementing robust security protocols to protect against external and internal risks while ensuring adherence to industry-specific standards and regulations. A strong security posture mitigates the risk of data breaches and fortifies the infrastructure, supporting long-term operational resilience and maintaining the integrity of critical business functions.
Key Focus Areas For Effective IT Infrastructure Management Implementation
Successfully executing an enterprise infrastructure management process requires more than just following a roadmap. Key focus areas help drive the implementation process and ensure that the infrastructure is adaptable and future-ready. Areas which play a critical role in aligning technology investments with business objectives, improving system performance, and facilitating long-term growth:
1. Dynamic Configuration Management
Flexibility in configuration management is vital for optimizing IT infrastructure performance. By implementing dynamic configuration processes, organizations can adapt quickly to changing requirements and adjust based on real-time needs.
This also ensures that infrastructure components always align with the business objectives, improving operational efficiency and minimizing downtime.
2. Unified Analysis and Monitoring for Seamless Insights
A unified approach to analysis and monitoring provides a comprehensive view of the entire IT ecosystem. By centralizing data from various systems into a single platform, businesses can allow for seamless analysis, enabling organizations to proactively identify trends, track performance, and respond to issues.
This unified approach can enhance decision-making and provide a holistic view of the infrastructure’s health.
3. AI-driven Insights for Enhanced Decision Making
Integrating artificial intelligence into IT infrastructure management enables businesses to analyze vast amounts of data and make intelligent, data-driven decisions. Through AI, companies can identify patterns, predict potential issues, and automate routine tasks, thus improving system performance and reducing manual interventions. This forward-thinking approach enhances both operational efficiency and scalability.
4. Scalability for Future Growth and Demands
Scalability is another crucial component of successful infrastructure management software. As businesses grow, their infrastructure must be designed to handle increasing demands, and by building a scalable infrastructure, organizations can seamlessly accommodate growth, whether through additional resources, enhanced capacity, or new technologies, ensuring long-term flexibility.
5. Automation to Optimize Performance and Efficiency
Automation simplifies infrastructure management systems by handling repetitive tasks, reducing manual errors, and speeding up processes. By automating routine maintenance, updates, and monitoring, enterprises can free up valuable resources for more strategic initiatives, enhancing consistency and reliability, contributing to overall infrastructure stability.
Let’s partner up to create an IT roadmap tailored to your unique needs. From streamlining operations to scaling your business, we’ve got the expertise to make your goals a reality.
While adopting the right strategies and best practices sets the stage for a strong IT infrastructure, enterprises must also be prepared to tackle the inherent challenges that come with it. The strategies we’ve discussed is designed to help businesses optimize their infrastructure management system, but these solutions often need to be adapted to organizations’ unique difficulties.
From the increasing complexity of hybrid environments to the constant evolution of cybersecurity threats, managing IT infrastructure at an enterprise level requires overcoming numerous obstacles.
Understanding these challenges can be key to refining your approach and ensuring your strategies are resilient enough to drive long-term success. In the next section, we will explore the common hurdles organizations face and provide insights on how to mitigate them while maintaining an efficient, secure, and scalable IT framework.
Overcoming Challenges in IT Infrastructure Management
Managing IT infrastructure on an enterprise-level IT infrastructure comes with its own set of unique challenges. From dealing with the growing complexity of modern systems to securing data from ever-evolving cyber threats, organizations must proactively address potential issues to ensure the stability, scalability, and security of their IT operations.
1. Managing the Complexity of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
As businesses adopt hybrid IT environments combining both on-premise and cloud-based solutions, managing the complexity of these systems becomes a significant challenge. With multiple cloud providers, on-premise infrastructure, and SaaS applications, enterprises face difficulties in achieving seamless integration across these varied components, which can lead to operational inefficiencies, system incompatibilities, and increased risk of data silos.
Solution: To manage such complexities, businesses need robust integration frameworks and a clear cloud strategy to optimize performance, reduce costs, and improve scalability across all platforms.
2. Straining Resources and Budget Limitations
IT infrastructure management for enterprises often requires a large allocation of resources, which may not always be available. Budget constraints are one of the most common challenges enterprises face when maintaining an optimal IT setup. With the rapid pace of technological innovation and rising costs of infrastructure upgrades, organizations can struggle to allocate sufficient funds for necessary improvements.
Solution: Skilled IT professionals can manage complex systems, leading to operational efficiencies or remove delays in executing essential updates and improvements.
Hiring IT outsourcing services can help businesses reduce expenses on hiring, training, and retention while providing access to expert-managed services on demand, ensuring efficiency and scalability.
3. Navigating Evolving Cybersecurity Risks
With cybersecurity threats growing more sophisticated, the increasing digital presence and expanded use of cloud-based solutions by businesses have significantly widened the attack surface. Ensuring a secure infrastructure has become paramount, with breaches posing severe risks such as financial loss, data exposure, and reputational damage.
Solution: The challenge is compounded by the need to manage security across diverse devices, endpoints, and networks while simultaneously adhering to stringent industry regulations. To address these complexities, enterprises must implement end-to-end security measures, invest in advanced security technologies, and adopt a proactive approach to mitigate potential risks effectively.
4. Staying Ahead of Technological Advancements
The rapid pace of technological change presents a constant challenge for IT infrastructure management. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, automation, and the Internet of Things bring potential improvements but also require continuous investment and adaptation. Plus, organizations often struggle to integrate these new technologies with legacy systems, which can result in compatibility issues and hinder performance.
Solution: To address this, regular training, strategic adoption of new technologies, and phased integration are crucial for staying competitive without compromising system stability.
5. Achieving Scalability Without Disrupting Operations
The demand for a robust IT infrastructure is directly synced up with the growth trajectory of an enterprise. Ensuring that the infrastructure is scalable to meet future needs – such as increased data processing, higher user demands, and expanding workloads – without disrupting ongoing operations is a delicate balance. Overprovisioning can lead to unnecessary costs, while underprovisioning can cause performance bottlenecks.
Solution: Effective capacity planning, real-time monitoring, and flexible infrastructure solutions are necessary to accommodate growth and avoid operational disruptions.
6. Ensuring Consistent Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
Enterprises must adhere to many industry-specific regulations and compliance standards to avoid fines, legal penalties, and loss of consumer trust. The challenge here is ensuring that infrastructure management supports compliance and keeps up with changing regulations.
Solution: Managing these high-grade security standards, data privacy laws, and international compliance requirements requires constant vigilance and dedicated resources.
Appinventiv: For Your Seamlessly Integrated Service for IT Infrastructure Management
Effective IT infrastructure management is imperative for enterprises aspiring to be ahead of the game in today’s fast-paced, tech-driven landscape. Be it the integration, security, scalability, and cost-efficiency, managing IT systems involves strategic thinking and knowledge about adapting to evolving challenges.
Appinventiv delivers robust IT consulting services to streamline and improve infrastructure management. As technology evolves at unprecedented speeds, IT systems become more complex. Our team is there to help you overcome these complexities with a well-crafted roadmap and a proactive mindset, capitalizing on new opportunities and staying ahead of the curve.
When you join forces with us, you’ll unlock expertise that lets your business innovate faster, maintain an edge over competitors, and get the best possible outcomes out of its IT environment. Want to revolutionize your IT landscape? Contact us at Appinventiv now.
FAQs
Q. What is Infrastructure Management?
A. Infrastructure management refers to overseeing and maintaining the essential components that form the foundation of an organization’s IT environment, which includes hardware, software, networks, data storage, and cloud services. Infrastructure management aims to ensure that these components operate efficiently and securely and are aligned with the business’s needs and goals. It involves monitoring performance, handling configuration management, addressing security issues, managing resources, and ensuring system uptime to support the organization’s operations.
Q. What Does an IT Infrastructure Manager Do?
A. An IT infrastructure manager oversees an organization’s IT infrastructure’s planning, implementation, maintenance, and optimization. This role ensures that all hardware, software, networks, and data storage solutions function properly and efficiently.
They also monitor system performance, address issues as they arise, manage the integration of new technologies, and ensure compliance with security standards and regulations. Additionally, an IT infrastructure manager works closely with other departments to align IT capabilities with business objectives, providing the infrastructure that supports the organization’s growth, scalability, and overall strategic goals.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Why Partnering with an IT Consulting Company in Dubai is Essential for Your Business
Dubai's rapid evolution into a global business hub is a testament to its strategic digital transformation initiatives, many of which have been propelled through IT outsourcing partnerships. In recent years, the UAE's technology sector has experienced significant growth, driven by ambitious government programs such as the Dubai 10X initiative and the UAE Artificial Intelligence Strategy…

10 Business-Critical Benefits of Managed Security Services
Every business today, regardless of size or industry, operates in a digital battlefield. Cyber threats are evolving at an unprecedented pace, outstripping the capabilities of traditional security measures. A single breach can trigger financial losses, operational disruptions, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties - impacts that extend far beyond IT teams and into the core of…

Managed IT Services for Manufacturing - An Explorative Guide for CIOs
Key takeaways: The IT services provided can maximize production process efficiency through proactive monitoring, reduced downtime, and faster operations. Latent cybersecurity safeguards correspond to the intellectual assets and intelligence within the business relating to business continuity in a virtual reality. With fixed-price models, unforeseen IT costs are eliminated, allowing for the consolidation of resources and…


















