- What Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Healthcare Means From a Technical Perspective?
- How RAG in Healthcare Systems Differs From Enterprise AI Deployments?
- How Do RAG Use Cases In Healthcare Drive Clinical And Operational Value?
- Clinical Decision Support
- Medical Knowledge Retrieval and Research Assistance
- Medical Documentation Automation
- Healthcare Conversational AI and Patient Engagement
- Administrative and Revenue Cycle Optimization
- Real World Example of RAG in Healthcare
- How Does RAG Implementation In Healthcare Enterprises Typically Work?
- Phase 1: Readiness and Strategy Alignment
- Phase 2: Architecture and Integration Planning
- Phase 3: Pilot Deployment
- Phase 4: Enterprise Scaling
- Quick Timeline Snapshot
- Stakeholder Alignment Matters Early
- How Do The Benefits Of RAG In Healthcare Systems Improve Clinical And Operational Outcomes?
- Improved Diagnostic Confidence
- Reduced Administrative Burden
- Enhanced Patient Engagement
- Lower Operational Costs
- How Can Enterprises Address Challenges Of RAG Implementation In Healthcare?
- Data Interoperability and Silos
- Compliance and Security Complexity
- Data Quality and Bias Management
- Integration With Legacy Infrastructure
- User Adoption and Workflow Alignment
- How Is Agentic RAG Shaping The Future Of RAG In Healthcare Systems?
- How Should RAG Architecture In Healthcare Systems Be Designed Effectively?
- Reference Architecture Overview
- Scalability Considerations
- How Much Does RAG Implementation Cost In Healthcare For Enterprises?
- Key Cost Drivers
- How Can Enterprises Measure ROI Of RAG In Healthcare Effectively?
- How Should Compliance, Security, And Ethical Considerations Be Managed For RAG In Healthcare?
- HIPAA Compliance Strategies
- Data Anonymization and Privacy Controls
- Auditability and Traceability
- Responsible AI Governance
- How Will The Future Of RAG In Healthcare Systems Evolve?
- Choosing the Right RAG Technology Partner
- Business Associate Agreements and Vendor Accountability
- How Appinventiv Can Help with RAG in Healthcare Systems Development
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key takeaways:
- RAG helps clinicians make better decisions by connecting AI responses to trusted clinical data sources.
- Healthcare organizations are gradually adopting domain-specific AI to improve efficiency, compliance, and operational clarity.
- Successful RAG deployment usually depends on strong governance, interoperability planning, and secure data practices.
- Retrieval-backed AI can ease documentation workload while improving accuracy, productivity, and patient communication.
- Enterprise RAG initiatives often support scalable AI infrastructure aligned with compliance and long-term digital transformation priorities.
Most healthcare IT teams hit a point where data stops being helpful and starts slowing things down. A physician searches for past case notes, someone checks treatment guidelines, and another team looks for billing documentation. Information exists, but finding the right piece at the right time is rarely simple.
That growing friction is one reason RAG in healthcare is getting serious attention. Retrieval-augmented generation in healthcare connects AI models to trusted medical data sources. Hence, the output reflects current clinical knowledge rather than generic internet-scale training data. In US healthcare systems, where compliance and accuracy carry real consequences, this matters.
If your organization is already experimenting with AI, you may have noticed the limits of standalone models. They generate fluent answers but often miss institutional protocols, up-to-date patient context, or specialty-specific knowledge. That gap can slow adoption even when leadership is interested.
This is where modern healthcare AI retrieval systems highlight the role of RAG in healthcare, bringing relevant clinical data into AI workflows while maintaining traceability. They bring relevant data into the AI workflow while maintaining traceability. The rest of this blog looks at how retrieval-augmented generation in healthcare actually gets implemented, where it delivers value, and what it takes to make it work reliably.
30–40% documentation time savings show how retrieval-backed AI improves healthcare workflows.
What Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Healthcare Means From a Technical Perspective?
If you look closely at how hospitals are adopting AI today, momentum is clearly building. Around 22% of healthcare organizations already use domain-specific AI tools, with adoption highest among health systems at roughly 27%, followed by outpatient providers at 18% and payers near 14%.
Still, many deployments struggle when models lack a reliable clinical context. That is where RAG pipelines for healthcare data come in. They connect clinical systems with generative models while keeping outputs traceable and grounded in verified medical sources.
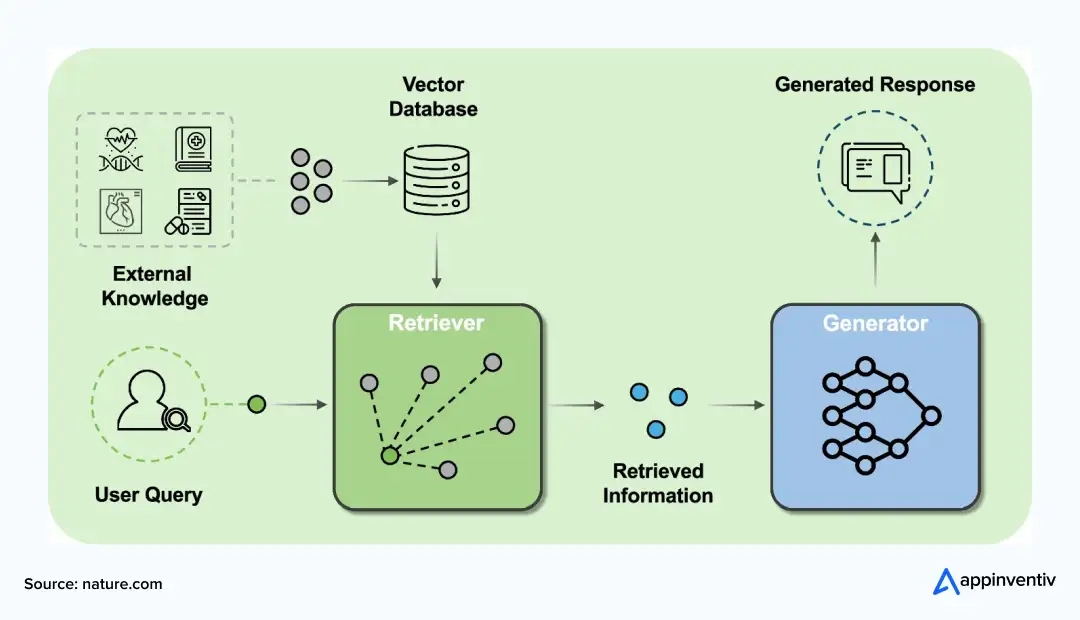
Typical healthcare RAG pipeline includes:
- Data ingestion from EHRs, PACS imaging systems, clinical research repositories, and insurance claims
- Medical-term embeddings aligned with ontologies like ICD-10 or SNOMED CT
- Retrieval orchestration using hybrid semantic and keyword search
- Grounded responses from RAG-based models in healthcare, backed by verified sources
Explainability remains critical. Healthcare AI retrieval systems must show where information came from, not just generate answers.
How RAG in Healthcare Systems Differs From Enterprise AI Deployments?
If you have worked with enterprise AI before, healthcare feels noticeably different. Data is messier, compliance expectations are stricter, and error tolerance is extremely low. That reality shapes how retrieval-augmented generation in healthcare gets designed compared with typical enterprise deployments.
| Aspect | Healthcare RAG Reality | Typical Enterprise RAG |
|---|---|---|
| Data Diversity | Clinical notes, imaging, claims, and research data are mixed | Mostly structured business data |
| Ontology Integration | ICD-10, SNOMED CT, and CPT are required for accuracy | Usually optional taxonomy |
| Privacy Constraints | HIPAA PHI handling and audit trails are essential | Standard enterprise security |
| Response Latency | Often near real-time for clinical decisions | Moderate latency acceptable |
| Accuracy Tolerance | Very high, patient impact risk | Generally lower stakes |
This context is why healthcare AI projects demand stronger governance, careful data alignment, and deeper validation before deployment.
How Do RAG Use Cases In Healthcare Drive Clinical And Operational Value?
Once you start looking at real hospital workflows, the value of retrieval-augmented generation becomes easier to see. Most medical delays are not due to a lack of expertise. They come from scattered information, documentation overhead, or slow access to knowledge. That is where RAG is quietly moving from pilot projects to operational systems.
Clinical Decision Support
Clinical teams rarely make decisions in isolation. They cross-check guidelines, patient history, and research literature before finalizing treatment.
- Evidence retrieval directly during consultations
- Treatment pathway optimization using updated clinical sources
- Drug interaction validation grounded in verified datasets
For example, RAG-based clinical decision support systems can integrate curated medical content to deliver context-aware insights at the point of care, reducing time spent searching across references.
This is why RAG for clinical decision support systems is gaining traction in large US healthcare networks.
Medical Knowledge Retrieval and Research Assistance
Healthcare professionals constantly work against time when accessing medical knowledge. Research evolves quickly, and institutional protocols change often.
- Automated literature retrieval for clinical research
- Protocol standardization across departments
- AI copilots assisting physicians during case reviews
Research shows that RAG improves factual consistency by retrieving domain-specific knowledge before generating responses, thereby reducing hallucinations in medical AI outputs.
That capability is driving the adoption of RAG for medical data retrieval and broader RAG in medicine initiatives.
Effective retrieval systems rely on unified healthcare data. Many organizations start by consolidating patient information across devices, records, and assessments to support future AI use cases.
Appinventiv partnered with a digital health platform to unify wellness data from connected devices, improving interoperability, enabling structured assessments, and supporting ongoing health analytics initiatives.
Medical Documentation Automation
Documentation pressure remains one of the biggest operational issues in healthcare. Clinicians often spend hours summarizing consultations and updating records.
- Clinical note summarization from multiple data sources
- Discharge documentation support
- Coding assistance tied to validated clinical references
Real adoption is already visible. AI documentation platforms are being used across US healthcare systems to automate clinical notes and reduce administrative burden, allowing clinicians to focus more on patient care. This explains the rising interest in RAG for medical documentation automation.
Healthcare Conversational AI and Patient Engagement
Patient communication is another area seeing steady adoption.
- Intelligent patient assistants for FAQs and care guidance
- Appointment triage automation
- Post-discharge continuity bots
Studies indicate that RAG improves the reliability of conversational healthcare AI by grounding responses in domain-specific knowledge rather than generic training data.
That reliability is driving investment in RAG for healthcare chatbots and broader RAG applications in healthcare.
Administrative and Revenue Cycle Optimization
Operational workflows often deliver the fastest ROI.
- Claims validation using policy knowledge bases
- Prior authorization automation
- Compliance documentation retrieval
These use cases reduce administrative overhead while improving accuracy in regulated workflows.
Real World Example of RAG in Healthcare
If you look at how healthcare AI is actually being rolled out today, the shift toward data-grounded systems is already visible. Hospitals are not just testing generative AI. They want tools that work with clinical records, workflows, and compliance realities.
Take Microsoft Nuance’s Dragon Copilot. It listens to clinician-patient conversations and helps turn them into structured clinical documentation while surfacing relevant information during workflows. The goal is simple: less time typing notes, more time focused on care. Many US health systems are already exploring similar documentation assistants.
Abridge offers another practical example. Its platform captures clinical conversations and converts them into structured medical notes that integrate with EHR systems like Epic. Physicians use it during consultations, not after hours, thereby reducing documentation fatigue.
When AI stays connected to trusted clinical data, adoption tends to follow. Accuracy improves, workflows feel more natural, and teams become more willing to scale usage.
How Does RAG Implementation In Healthcare Enterprises Typically Work?
If you are evaluating RAG implementation in healthcare, the biggest mistake teams make is jumping straight into tools or models without first understanding the problem. Healthcare environments are layered with legacy systems, compliance constraints, and clinical workflows that cannot be disrupted. A phased rollout usually works better, giving your team space to validate accuracy, security, and real-world usability before scaling.
Phase 1: Readiness and Strategy Alignment
This phase is less about AI and more about clarity. Healthcare data often lives across EHR platforms, imaging systems, claims software, and research databases. Understanding what data exists, how clean it is, and where gaps sit helps avoid downstream issues.
- Assess data maturity across clinical and operational systems
- Prioritize use cases where retrieval delays affect outcomes or productivity
- Review compliance posture, especially HIPAA handling and audit readiness
Many long-term RAG development in the healthcare industry initiatives begin here.
Phase 2: Architecture and Integration Planning
Once priorities are clear, technical design takes center stage. Healthcare systems rarely operate in isolation, so integration planning becomes critical.
- Design RAG pipelines aligned with clinical workflows
- Define security architecture, access controls, and audit logging
- Plan integration with legacy healthcare IT systems and data repositories
This stage often determines how smoothly RAG in healthcare systems scales later.
Phase 3: Pilot Deployment
Pilots allow controlled experimentation without risking clinical operations. A limited environment helps validate whether retrieval quality and response accuracy meet expectations.
- Test within a clinical or operational sandbox
- Validate KPIs such as response accuracy, latency, and clinician usability
Insights gathered here usually shape enterprise rollout decisions.
Phase 4: Enterprise Scaling
Scaling involves more than adding infrastructure. Governance, monitoring, and continuous refinement become essential as adoption grows.
- Implement monitoring frameworks and governance policies
- Establish retraining cycles and retrieval optimization processes
This phased path keeps implementation structured while reducing operational risk.
Quick Timeline Snapshot
Typical enterprise rollouts follow a staged timeline:
- Months 1–2: Data assessment, compliance review, use case selection
- Months 3–5: Infrastructure setup, pipeline design, security configuration
- Months 6–8: Pilot deployment with controlled clinical workflows
- Months 9–12: Gradual enterprise scaling with governance controls
Timelines vary, but structured phasing reduces adoption risk.
Stakeholder Alignment Matters Early
Successful healthcare AI rollouts rarely stay technical. Clinical leadership, compliance teams, IT architects, and executive sponsors usually need alignment early.
Common engagement practices:
- Clinical stakeholder input during use case selection
- IT and security teams are involved in architecture planning
- Compliance oversight throughout implementation
- Executive sponsorship to sustain adoption momentum
This alignment often reduces resistance and speeds enterprise adoption.
How Do The Benefits Of RAG In Healthcare Systems Improve Clinical And Operational Outcomes?
If your team is evaluating generative AI in clinical settings, you are not alone. About 84% of healthcare leaders see AI as a major driver of innovation, and nearly 44% expect to adopt new AI capabilities within the next year. The real conversation now is less about experimentation and more about measurable outcomes, including accuracy, efficiency, patient experience, and cost control. That is where the benefits of RAG in healthcare start becoming tangible.
Improved Diagnostic Confidence
Clinicians often juggle patient history, imaging reports, treatment protocols, and research literature. RAG systems pull relevant context together quickly. Instead of searching across multiple platforms, physicians get grounded insights linked to verifiable sources. That tends to improve diagnostic confidence while reducing information gaps.
Reduced Administrative Burden
Documentation remains one of healthcare’s biggest operational pressures. RAG helps summarize clinical notes, retrieve coding references, and support discharge documentation. The result is less manual searching and fewer repetitive documentation cycles. Many organizations view this as one of the key advantages of implementing RAG in healthcare.
Enhanced Patient Engagement
Patient communication also benefits. Intelligent assistants powered by retrieval-backed AI can answer questions using institutional knowledge bases rather than generic data. That helps maintain consistency in patient messaging while improving response speed and accessibility.
Lower Operational Costs
Operational impact usually follows efficiency gains. Faster documentation, reduced duplicate testing due to better information access, and improved administrative workflows can translate into measurable cost savings. Over time, this broader impact of RAG in healthcare often supports both clinical productivity and financial sustainability.
For many healthcare enterprises, these benefits make RAG less of an experimental AI project and more of a practical infrastructure investment.
Also Read: How to Develop a RAG-Powered Application: Process and Costs
How Can Enterprises Address Challenges Of RAG Implementation In Healthcare?
Most healthcare AI projects look straightforward on slides but reality usually feels different once clinical data, compliance rules, and legacy systems come into play. The challenges of RAG in healthcare often come from data environments and operational constraints rather than the AI model itself.
Data Interoperability and Silos
Healthcare data rarely resides in a single unified system. EHRs, imaging platforms, claims databases, and research repositories often operate independently. This fragmentation slows retrieval accuracy and complicates integration.
What helps:
- Interoperability standards like HL7 and FHIR
- Data integration platforms that unify fragmented sources
- Clear data governance policies to maintain consistency
Compliance and Security Complexity
Healthcare AI must align with strict regulatory expectations. Managing PHI, maintaining audit trails, and ensuring secure access create ongoing RAG healthcare compliance challenges.
What helps:
- Continuous compliance auditing frameworks
- Strong encryption and access control practices
- Governance processes aligned with regulatory requirements
Data Quality and Bias Management
Clinical AI systems depend heavily on data quality. Incomplete records, outdated information, or biased datasets can affect the reliability of the output.
What helps:
- Structured data quality assessment practices
- Bias detection algorithms and fairness checks
- Regular dataset updates tied to clinical standards
Integration With Legacy Infrastructure
Many healthcare organizations still rely on older IT systems. Connecting RAG pipelines with legacy infrastructure often requires careful planning.
What helps:
- Middleware or data abstraction layers
- Incremental modernization instead of full replacement
- Scalable technical infrastructure planning
Also Read: How to Integrate RAG in Your Application? Process and Costs
User Adoption and Workflow Alignment
Even technically sound systems can struggle if they disrupt clinical workflows. Trust and usability influence adoption significantly.
What helps:
- Alignment with existing clinical workflows
- Practical training for healthcare teams
- Clear explainability in AI-generated outputs
Addressing these areas early usually makes RAG deployments more stable and easier to scale across healthcare environments.
Also Read: Navigating the AI Challenges in Healthcare – Insights and Success Strategies for Enterprises
For example, one hospital network struggled with fragmented clinical data across legacy systems. By implementing a FHIR-based integration layer before deploying RAG, they improved retrieval accuracy and clinician adoption within months.
Healthcare data silos, compliance gaps, and integration challenges require structured enterprise implementation planning.
How Is Agentic RAG Shaping The Future Of RAG In Healthcare Systems?
Most healthcare RAG deployments today focus on retrieving information when someone asks for it. The next shift is making those systems more proactive. That is where agentic RAG in healthcare is starting to move from concept to experimentation.
Instead of a single retrieval layer, organizations are exploring coordinated AI agents that handle different responsibilities across clinical and operational workflows.
What this evolution typically involves:
- Autonomous clinical AI agents monitoring context and surfacing relevant insights
- Multi-agent retrieval ecosystems where separate agents handle retrieval, validation, and response generation
- Workflow automation opportunities across documentation, decision support, and administrative tasks
The future of RAG in healthcare will likely include more embedded AI copilots and operational assistants. Adoption is still early, but healthcare enterprises are beginning to test these models in controlled environments before broader rollout.
Also Read: How Agentic AI in Healthcare Is Bringing in Industry-level Transformation
How Should RAG Architecture In Healthcare Systems Be Designed Effectively?
Once teams move from pilots to production, architecture decisions start carrying real weight. Healthcare environments are not forgiving if latency spikes or audit trails break. A well-planned RAG architecture in healthcare systems usually focuses as much on governance and scalability as on model performance.
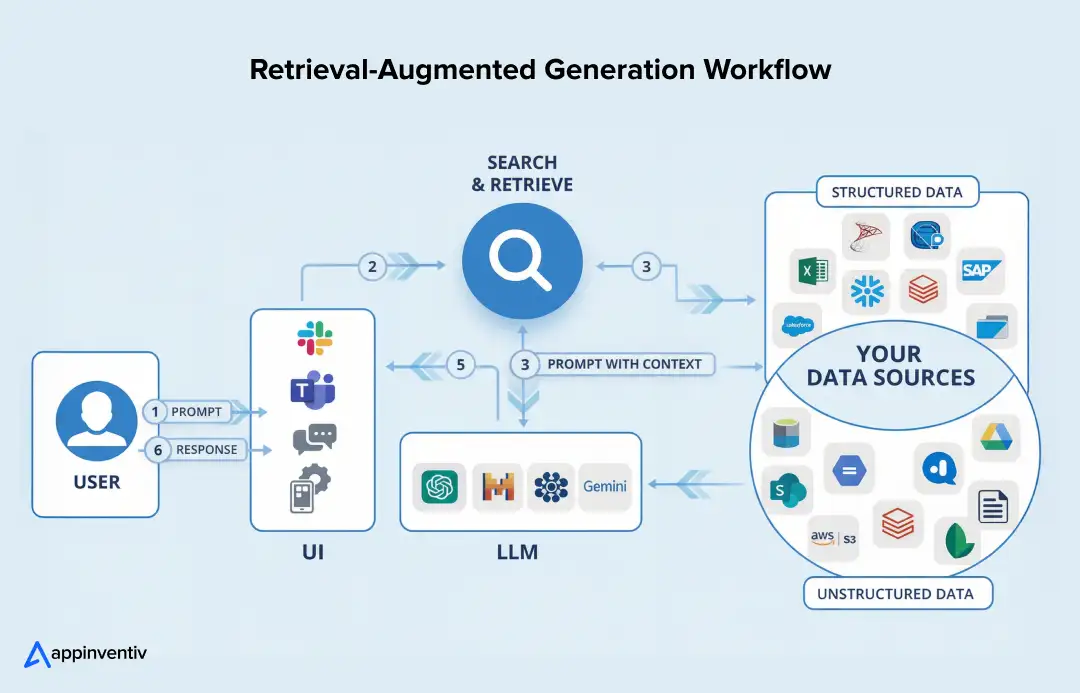
Reference Architecture Overview
Most healthcare RAG deployments follow a layered structure. Each layer supports reliability, compliance, and explainability.
Typical architecture components:
- Ingestion layer: Pulls data from EHRs, PACS imaging systems, research databases, and claims platforms while maintaining structured metadata
- Embedding layer: Converts clinical text, codes, and documents into vector representations aligned with medical terminology
- Vector database: Stores embeddings for fast semantic retrieval, often optimized for healthcare scale and compliance
- Orchestration layer: Connects retrieval pipelines with LLM workflows, manages prompts, validation, and response assembly
- Application interface: Clinical copilots, patient assistants, analytics dashboards, or internal knowledge tools
- Monitoring and governance: Audit logging, performance tracking, access controls, and compliance oversight
Scalability Considerations
Healthcare data volume grows quickly. Systems must handle rising query loads without compromising accuracy or response time.
Common focus areas:
- Distributed vector storage and cloud scaling
- Retrieval latency optimization
- Continuous model evaluation and retraining
Strong architecture decisions early usually determine how smoothly RAG scales across healthcare environments.
Healthcare AI adoption often depends on infrastructure readiness as much as model capability. Many organizations prioritize scalability, reliability, and secure data access before advancing AI initiatives.
Appinventiv supported a diabetes management platform in modernizing its cloud infrastructure to improve scalability, system reliability, and secure patient data access while optimizing operational costs.
How Much Does RAG Implementation Cost In Healthcare For Enterprises?
If you are evaluating AI investments right now, cost clarity probably sits high on your checklist. The RAG implementation cost in healthcare varies widely because no two healthcare IT environments look the same. Data readiness, compliance scope, integration depth, and scaling goals usually shape the final investment more than the AI model itself.
| Implementation Stage | Typical US Cost Range | What It Usually Covers |
|---|---|---|
| Pilot deployment | $150K–$500K | Limited use case validation, initial data pipelines, basic compliance controls |
| Department rollout | $500K–$1.5M | Expanded integrations, workflow customization, and security hardening |
| Enterprise transformation | $2M+ | Full system integration, governance frameworks, scalable infrastructure |
Also Read: How Much Does It Cost to Build a Healthcare App?
Key Cost Drivers
Costs often shift depending on how mature your data environment and compliance posture already are.
Common drivers include:
- Infrastructure provisioning, including compute, storage, and vector databases
- Integration complexity across EHRs, imaging systems, and legacy platforms
- Data engineering work, such as cleaning, normalization, and metadata structuring
- Compliance and security investments, especially HIPAA-aligned safeguards
- Ongoing operational costs like monitoring, retraining, and system optimization
How Can Enterprises Measure ROI Of RAG In Healthcare Effectively?
ROI conversations in healthcare rarely stay theoretical for long. Leaders usually want clear signals, where time improves, where costs drop, and whether patient care actually benefits. The ROI of RAG in healthcare typically shows up across both clinical and operational metrics.
| Impact Area | What Changes | Typical Enterprise Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Productivity | Faster access to relevant patient and research data | Reduced clinician search time |
| Documentation Efficiency | Retrieval-backed note summaries and coding support | Less administrative burden |
| Administrative Costs | Streamlined claims, authorizations, and compliance retrieval | Lower processing overhead |
| Patient Experience | Faster responses and consistent information delivery | Higher engagement and satisfaction |
| AI Maturity | Stronger data retrieval foundation for future AI initiatives | Easier scaling of AI programs |
Most organizations track these indicators over time rather than expecting immediate financial returns. Once retrieval reliability improves, both efficiency and decision quality usually follow.
Quick Quantitative ROI Metrics Table:
| Metric | Observed Industry Impact |
|---|---|
| Clinical documentation time | 30–40% reduction |
| Information retrieval time | 20–25% faster |
| Prior authorization speed | Up to 60% faster |
| Diagnostic confidence | Noticeable improvement |
Quick KPI list:
Common KPIs healthcare organizations track:
- Time to clinical information retrieval
- Documentation turnaround time
- Administrative processing cost
- Patient satisfaction scores
- System uptime and response latency
These metrics help justify scaling decisions.
How Should Compliance, Security, And Ethical Considerations Be Managed For RAG In Healthcare?
Talk to anyone running AI inside a US hospital system, and the same concern comes up quickly: compliance. Not performance, not features, but whether patient data stays protected and decisions remain explainable. That reality shapes how retrieval-augmented systems are built from the start, not after deployment.
HIPAA Compliance Strategies
HIPAA affects everyday technical choices. Data access, storage, and transmission all need clear safeguards so clinicians can use AI without risking patient privacy.
- Administrative safeguards: workforce training, access policies, AI oversight roles
- Technical safeguards: encryption, audit logs, secure APIs, identity management
- Physical safeguards: secure data hosting environments and controlled access
These layers help maintain HIPAA alignment as AI systems scale.
Data Anonymization and Privacy Controls
Many teams reduce risk before data reaches the AI pipeline. Removing identifiers allows analysis while keeping exposure low, especially during testing or model tuning.
- De-identification of clinical notes and records
- Masking sensitive attributes where possible
- Secure environments for controlled experimentation
Also Read: Navigating Healthcare Data Security: Common Challenges and Proven Best Practices
Auditability and Traceability
Clinicians usually want to know where an answer came from. Regulators do too. Traceability helps both.
- Clear source attribution for generated responses
- Version tracking for models and knowledge bases
- Maintainable audit logs for reviews
Responsible AI Governance
Governance also covers how AI behaves in practice. Fairness, validation, and oversight matter just as much as security.
- Bias monitoring across patient populations
- Clinical review checkpoints before wider rollout
- Defined escalation paths when uncertainty appears
Most healthcare organizations find adoption smoother once these guardrails are built in early.
Healthcare organizations increasingly evaluate vendors based on certifications such as SOC 2, HIPAA alignment programs, and ongoing security audits. These signals often accelerate stakeholder trust during procurement discussions.
Also Read: Responsible AI – Addressing Adoption Challenges With Guiding Principles and Strategies
How Will The Future Of RAG In Healthcare Systems Evolve?
Healthcare AI has been moving in small, careful steps. First basic automation, then predictive analytics, and now retrieval-backed generative systems. The future of retrieval-augmented generation for generative artificial intelligence in healthcare is shaping up around deeper clinical integration rather than standalone AI tools.
Some RAG in healthcare future trends are already becoming visible:
- Multimodal AI combining clinical notes, imaging scans, lab reports, and structured patient data in one retrieval workflow
- Real-time clinical copilots that surface relevant guidance during consultations, rather than after documentation is complete.
- Precision medicine support where patient-specific context connects with research literature and treatment pathways
- Early experiments with automated hospital operations, such as scheduling support or resource planning
Predictive RAG is also emerging. Instead of responding only to queries, systems can proactively surface insights, such as potential readmission risks or care pathway recommendations, by combining historical data retrieval with predictive analytics.
Advances in domain-trained models, faster retrieval infrastructure, and improved data interoperability will shape how RAG-based models in healthcare evolve. Adoption will likely remain cautious but steady as healthcare systems balance innovation with clinical reliability.
Evaluate ROI, scalability strategy, and compliance readiness before deploying healthcare AI systems.
Choosing the Right RAG Technology Partner
Healthcare enterprises usually evaluate more than technical capability when selecting an artificial intelligence development company, especially in regulated healthcare environments.
Common selection criteria include:
- Proven healthcare domain experience
- Strong compliance and security posture
- Integration capability with EHR, PACS, and clinical systems
- Clear governance and auditability practices
- Track record with enterprise-scale deployments
These factors often influence long-term project success more than tooling alone.
Business Associate Agreements and Vendor Accountability
When third-party AI vendors handle protected health information, Business Associate Agreements are typically required. These agreements clarify data handling responsibilities, breach response protocols, and compliance obligations.
Many healthcare organizations treat BAAs as a prerequisite before production deployment, especially when retrieval systems access clinical records.
How Appinventiv Can Help with RAG in Healthcare Systems Development
If your team is exploring retrieval-backed AI in healthcare, implementation rarely succeeds with generic tooling alone. Clinical data complexity, compliance expectations, and system interoperability usually demand a partner that understands both healthcare workflows and enterprise AI architecture.
That is where Appinventiv, a top RAG development company, typically supports healthcare organizations.
Over the last decade, our teams have worked across hospitals, digital health platforms, and connected device ecosystems. Some relevant experience indicators:
- 500+ digital health platforms delivered
- 450+ healthcare clients served
- 10+ years working on HealthTech initiatives
- Integration of 300+ connected medical devices
- 99.90% uptime maintained for critical systems
- Up to 45% operational efficiency gains reported
- 90% plus clinical data accuracy in deployed solutions
- Around 95% patient satisfaction across healthcare apps
From consulting to deployment, the focus stays on compliance-first architecture, secure data pipelines, and scalable RAG infrastructure. This includes healthcare AI consulting, integration with enterprise clinical systems, and ongoing optimization.
If you are evaluating RAG adoption in healthcare systems, a focused consultation can clarify feasibility, costs, and rollout strategy. Let’s connect.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How to build a multimodal RAG app for medical applications?
A. Building a multimodal RAG app typically starts by integrating diverse healthcare data, such as clinical notes, imaging, lab reports, and research literature. The next step involves creating embeddings aligned with medical terminology, setting up secure retrieval pipelines, grounding responses with trusted datasets, and validating outputs through clinical testing before scaling.
Q. How can Healthcare RAG systems be customized to support different medical specialties?
A. Customization typically involves specialty-specific datasets, clinical guidelines, and terminology models. Cardiology, oncology, or radiology teams often require tailored retrieval sources and validation workflows. Fine-tuning prompts, integrating departmental protocols, and aligning outputs with clinical workflows usually make adoption smoother and more relevant.
Q. How much does it cost to implement RAG in healthcare?
A. Costs vary based on data readiness, compliance requirements, and integration scope. Pilot implementations may range from about $150K to $500K, while enterprise-wide deployments can exceed $2M. Infrastructure, data engineering, security controls, and ongoing maintenance usually account for most of the investment.
Q. How RAG elevates clinical use cases?
A. RAG improves clinical workflows by grounding AI outputs in verified medical data. This helps clinicians access research, patient histories, and treatment protocols more quickly. The result often includes better decision support, reduced documentation time, and more consistent clinical insights across departments.
Q. How does retrieval-augmented generation support healthcare AI initiatives?
A. Retrieval-augmented generation strengthens AI reliability by connecting models to institutional knowledge, clinical databases, and up-to-date research sources. This approach supports safer automation, improves explainability, and helps healthcare organizations expand AI adoption while maintaining compliance and operational trust.
Q. How is retrieval-augmented generation transforming access to medical knowledge?
A. Medical knowledge is expanding rapidly, and traditional search methods can slow clinicians down. RAG systems retrieve relevant information directly from trusted sources and present it contextually. This typically improves access to research insights, clinical protocols, and patient-specific data without the need for extensive manual searching.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Top Enterprise Use Cases for Agentic RAG in eCommerce Transformation
Key takeaways: Agentic RAG in eCommerce combines retrieval, generation, and autonomous decision-making, enabling AI systems to plan, reason, and act on real-time data for smarter automation and personalization. This approach powers advanced use cases like dynamic merchandising, personalized recommendations, automated customer care, and intelligent pricing, improving efficiency and customer experience. Enterprises benefit from enhanced operational…

Build AI Chatbot With RAG Integration: Appinventiv’s End-To-End Development Framework
Key takeaways: RAG chatbots improve enterprise AI accuracy by grounding responses in verified internal business knowledge. Governance, security, and explainability become critical as AI shifts from pilots to enterprise infrastructure. Investment typically ranges $50K–$500K depending on data integration, compliance, and deployment complexity. Strong data engineering and architecture discipline matter more than standalone model capability for…

The Enterprise Buyer’s Checklist Before Hiring an AI Development Partner
Key takeaways: Choosing an AI development partner is less about technical demos and more about real-world fit, governance, and operational reliability. Internal alignment on outcomes, data ownership, and integration realities is essential before engaging any enterprise AI partner. Strong partners demonstrate delivery maturity through governance controls, security discipline, and lifecycle management, not just model accuracy.…