- Understanding the Role of ML in Manufacturing
- How Different Industry Verticals are Leveraging Machine Learning For Manufacturing
- Pharmaceutical
- Food and Beverage
- Automotive
- Retail
- Machine Learning for Manufacturing: Use Cases and Examples
- Predictive Maintenance
- Virtual-Physical Integration
- Advanced Quality Control
- Supply Chain Management
- ML-Driven Product Design
- Smart Inventory Management
- Anomaly Detection and Cybersecurity
- Self-Driving Cars
- Energy Management
- Mass Customization
- The Roadmap for Integrating Machine Learning into Manufacturing
- Clearly Define Your Business Goals
- Data Collection and Preprocessing
- Select and Train the ML Model
- Evaluate and Validate the Model
- Integrate ML Models into Production Systems
- Monitor and Update the Model
- Practical Solutions to Common Machine Learning Adoption Challenges
- High Implementation Costs
- System Integration Challenges
- Data Quality and Availability
- Model Interpretability and Explainability
- Future of Machine Learning in Manufacturing
- Get Started with Manufacturing Machine Learning with Appinventiv
- FAQs
- Q. How is ML used in the manufacturing industry?
- Q. What are the emerging trends of machine learning in the manufacturing industry?
- Q. What are the advantages of machine learning in manufacturing?
The world is entering the fifth industrial revolution—Industry 5.0—which is giving rise to smart manufacturing that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. Machine learning in manufacturing is not just a buzzword—it is a game-changer.
According to MarketsAndMarkets, the Industry 5.0 market is projected to reach $255.7 billion in value by 2029, and machine learning has a key role to play here. A 2023 survey conducted by the Manufacturing Leadership Council (MLC) reveals that over a quarter of manufacturing companies are already implementing AI and ML in their potential to transform the future of the industry as it approaches 2030.
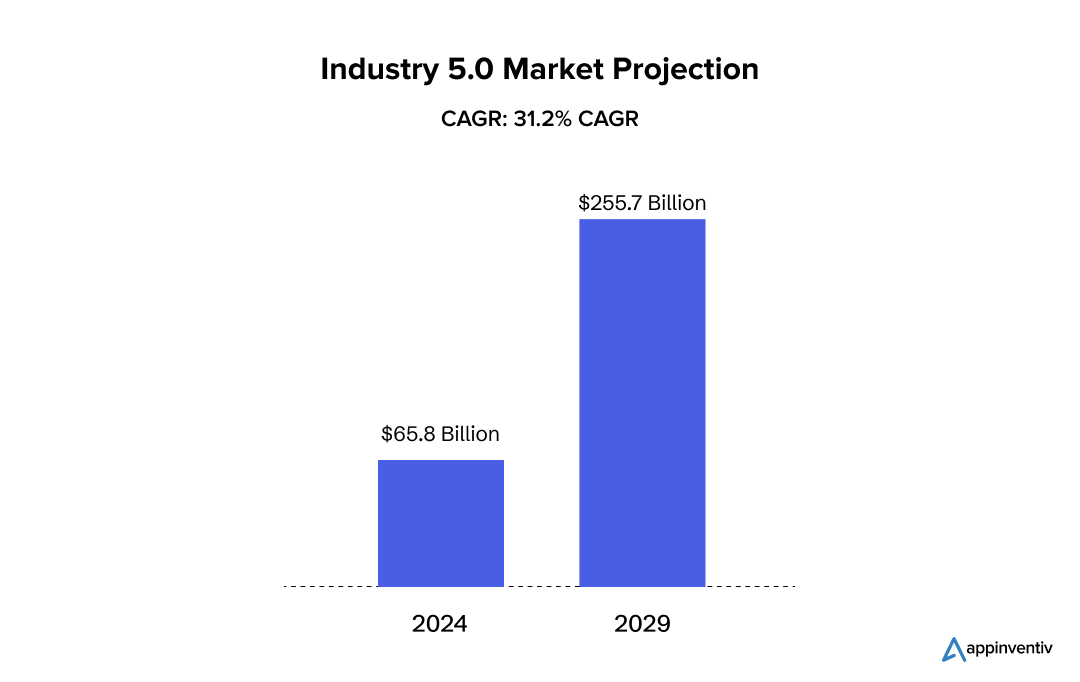
These insights underscore the increasing influence of AI and ML in manufacturing, making the industry more resilient, smarter, and agile. From removing the root causes of production losses and increasing workforce productivity to strengthening security and improving product quality, manufacturing machine learning is setting new standards and redefining the landscape of modern manufacturing.
Unsurprisingly, ML in manufacturing is one of the key drivers of digital transformation, poised to redefine labor-intensive processes and improve operational efficiency.
But how AI and ML technologies transform the present and future of the manufacturing industry? Let’s delve into the ten compelling use cases of machine learning in manufacturing industry, illustrating how ML algorithms are setting new benchmarks in the era of Industry 5.0.
Understanding the Role of ML in Manufacturing
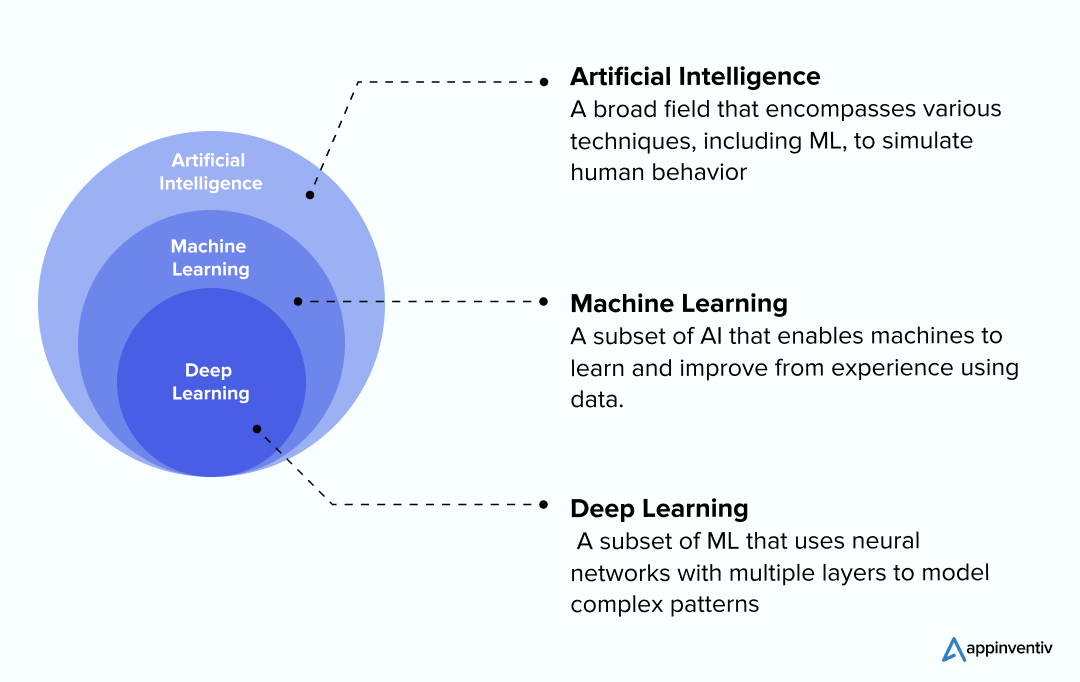
To gain an in-depth understanding of machine learning’s role in manufacturing, it is crucial to distinguish it from related concepts like Artificial intelligence and deep learning. Even if in the realm of manufacturing, terms like AI, ML, and deep learning are often used interchangeably and are closely related to one another, they refer to distinct concepts. To clarify:
- Artificial intelligence in manufacturing is a broad field that encompasses various technologies aimed at creating machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. This includes problem-solving, reasoning, and understanding language.
- Machine Learning is a subset of AI focused on developing algorithms that enable machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed. ML systems identify patterns in data and use these patterns to make predictions or decisions.
- Deep Learning is a further subset of ML involving neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”). It excels in processing large volumes of unstructured data, such as images and text, and is particularly useful for complex tasks like image recognition and natural language processing.
Machine learning for manufacturing aims to automate complex and repetitive tasks by endowing machines with cognitive abilities. This involves:
- Data Collection: Gathering vast amounts of data from various manufacturing processes and workflows.
- Pattern Recognition: Analyzing this data to identify useful patterns and trends.
- Automation: Using these patterns to automate tasks, predict maintenance needs, optimize workflows, and enhance operational efficiency.
The goal of machine learning manufacturing trends is to provide manufacturers with new ways to streamline operations, cut costs, increase workforce productivity, strengthen safety, enhance product quality, and automate tasks previously managed by humans only.
Now that we know what ML is in manufacturing and how the technology transforms the industry, let’s discover the diverse manufacturing machine learning use cases.
How Different Industry Verticals are Leveraging Machine Learning For Manufacturing
Machine learning transforms manufacturing by driving efficiency, enhancing quality control, and enabling predictive maintenance. Harnessing data insights optimizes production, minimizes downtime, and streamlines operations across various processes. Here are some of the top industries utilizing ML in their processes.

Pharmaceutical
Pharmaceutical manufacturing uses ML to streamline drug discovery, optimize formulations, and improve production processes. Algorithms accelerate R&D by predicting chemical interactions, while ML in the healthcare & pharmaceutical industry ensures compliance with regulatory standards and enables predictive equipment maintenance.
Food and Beverage
The food sector employs ML to ensure consistent quality, optimize supply chains, and manage inventory. Automated sorting systems powered by ML reduce waste and improve product grading, while predictive analytics assist in accurate demand forecasting.
Automotive
The automotive sector applies machine learning for predictive maintenance, quality assurance, and optimizing assembly lines. ML-powered robotics aid in manufacturing precision components, while advanced data analytics enhance supply chain operations. Autonomous vehicle technologies also rely on ML for real-time decision-making.
Retail
Machine learning in retail enhances defect detection, predictive maintenance, and pattern recognition within textile manufacturing. It optimizes production schedules, improves fabric quality, and helps predict consumer trends, leading to better product designs and more informed decision-making.
Machine Learning for Manufacturing: Use Cases and Examples
ML in manufacturing is reshaping the industry with its diverse applications and advantages. From predictive maintenance to optimized supply chains, machine learning applications in manufacturing are driving innovation and productivity across the industry. Here are some of the most remarkable machine learning use cases in manufacturing with their real-world examples:
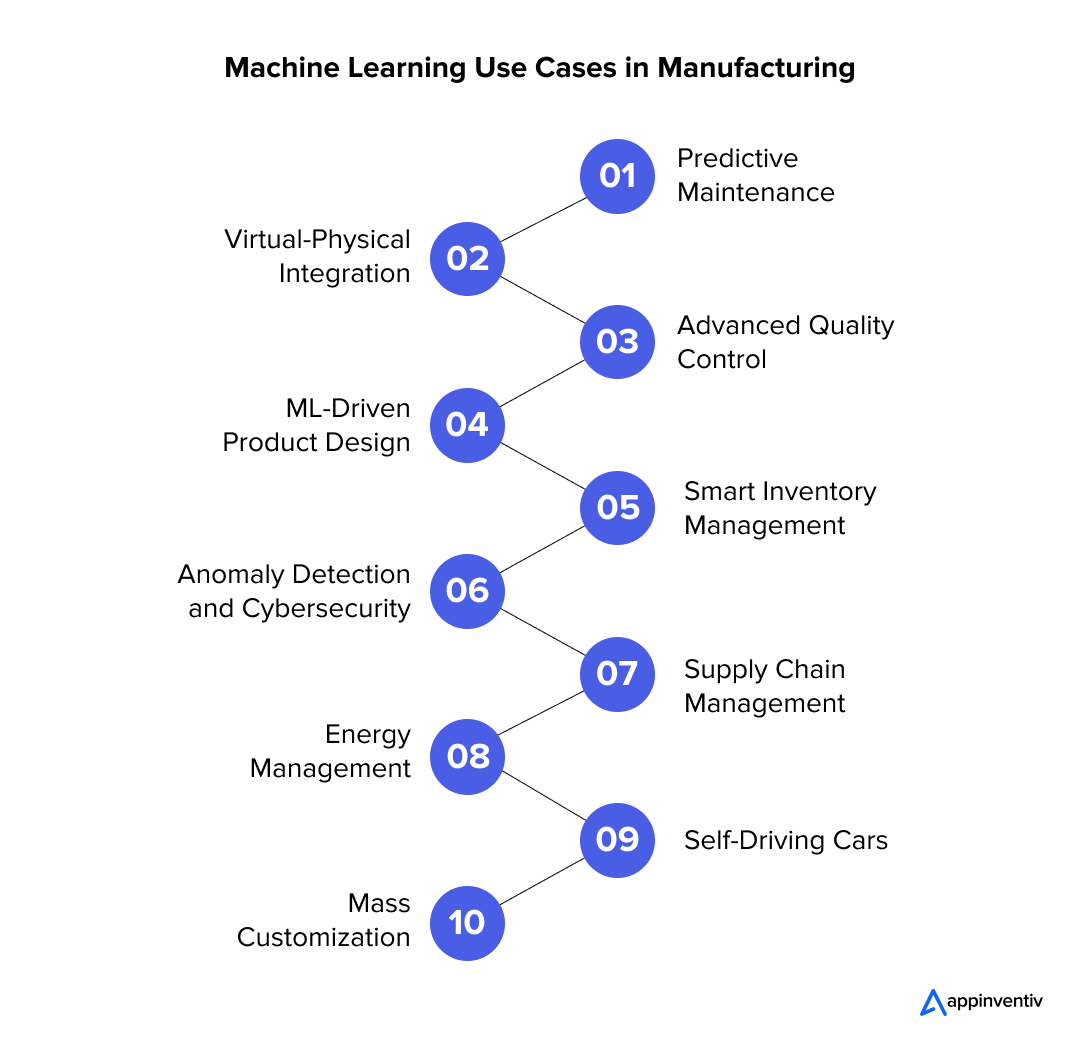
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is one of the key applications of machine learning in the manufacturing industry. ML models can efficiently analyze vast amounts of sensor data from equipment to identify patterns that indicate impending failures. By forecasting when a machine is likely to fail, manufacturers can perform maintenance just in time to prevent costly breakdowns.
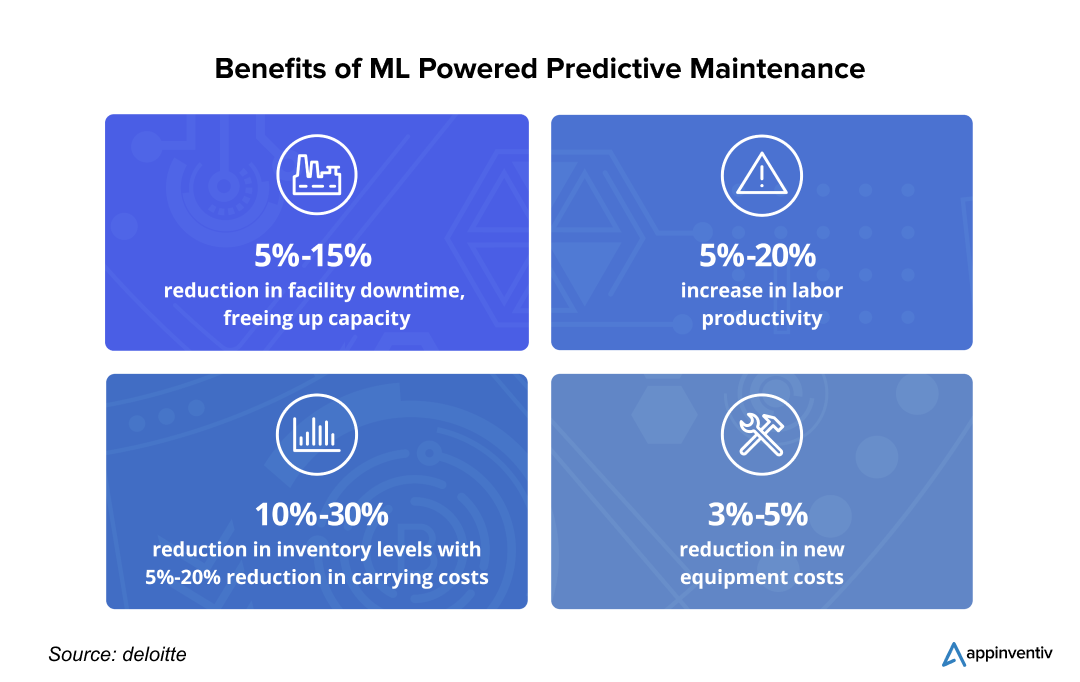
Real World Example: General Motors, one of the biggest vehicle manufacturers in the US, is one of the earliest advocates of leveraging ML, AI, IoT, and other emerging technologies. GM uses AI and ML to monitor the health of its assembly-line robots.
Using machine learning for manufacturing process optimization, GM can efficiently identify early signs of equipment wear, preventing unplanned downtime and extending machinery lifespan. As a result, GM reduced unexpected downtime by 15% and saved around $20 million annually in maintenance costs.
Virtual-Physical Integration
ML-enabled digital twins, which are virtual replicas of physical assets, create dynamic models of manufacturing systems and are one of the most important machine learning use cases in manufacturing. These models enable real-time monitoring, simulation, and optimization. This integration allows manufacturers to carry out instant diagnostics, predict system performance, identify potential issues before they occur, and fine-tune operations.
For instance, you can develop virtual prototypes of physical production to spot potential issues early on. Additionally, you can anticipate maintenance needs, preventing unexpected breakdowns and minimizing downtime.
Real World Example: Siemens, a world-renowned company, uses digital twins to simulate entire production lines and enhance processes. This approach has minimized operational disruptions and enhanced efficiency.
Advanced Quality Control
Traditional quality control methods can miss subtle defects. ML-powered inspection systems use advanced image recognition and sensor data to detect defects and anomalies in real-time, surpassing the accuracy and speed of human inspectors. This ensures higher product quality and reduces the risk of defective products reaching customers.
Real World Example: Fanuc and Preferred Networks, Inc. (PFN), a leader in robotics, integrates ML into its robotic arms to detect tiny defects during the assembly process, reducing the production of defective products and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Supply Chain Management
One of the notable applications of machine learning in manufacturing is supply chain management. The rise of IIoT technologies is set to transform smart supply chains, revolutionizing manufacturing operations. While automation is just the beginning, the future holds the promise of fully “cognitive” supply chains. These advanced systems will leverage AI and ML to automatically analyze extensive datasets and manage complex supply chains, including shipments, inventory, consumer preferences, market trends, and weather forecasts.
Real World Example: DHL leverages ML and advanced data analytics to predict logistics demand spikes during peak seasons, automating workflows, optimizing resource allocation, reducing delays, and ensuring a more efficient supply chain.
You may like reading: AI-Based Demand Forecasting: Optimizing Supply Chains
ML-Driven Product Design
Machine learning in design leverages generative design algorithms to create optimized product designs based on predefined criteria such as material strength, size, weight, and cost. This speeds up the design process and results in more innovative and efficient products.
With the new-age ML-driven designs, automakers can quickly explore countless design options for future vehicles, selecting the most optimal ones to streamline production and speed up delivery timelines.
Real World Example: Automotive leaders like Nissan and Volkswagen leverage machine learning technology to rapidly generate impressive and innovative designs, transforming their creative processes with unprecedented speed.
Also Read: How to Use AI to Design Better Mobile App User Experience?
Smart Inventory Management
Inventory management is not easy in manufacturing. With a vast number of products and components stored at warehouses, understocking and overstocking become serious challenges. Machine learning for manufacturing offers a solution that automates key aspects of warehouse management.
Real World Example: Amazon uses machine learning in its logistics operations to manage real-time inventory and gain a competitive edge in the market. The company optimizes its warehouse operations by analyzing customer demand, inventory levels, and shipping routes, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and shortening delivery times.
Related Article: 10 Ways to Unlock the Power of AI in Inventory Management
Anomaly Detection and Cybersecurity
Modern manufacturing companies heavily rely on advanced technologies like IoT, AI, cloud computing, and other digital systems, which are the prime targets of cyberattacks. Traditional cybersecurity measures may fall short of addressing the burgeoning challenges of cyberattacks.
Machine learning models can efficiently detect anomalies in network traffic and operational data. They can identify potential cybersecurity threats or process irregularities before they cause significant harm.
Real World Example: Rolls-Royce employs machine learning for manufacturing to monitor its digital infrastructure, identifying possible cyber threats in real-time and protecting sensitive data and operations.
Self-Driving Cars
Machine learning and AI are at the forefront of the evolution of self-driving cars, which are projected to account for 10 to 15% of global car sales by 2030. These technologies enable vehicles to navigate autonomously by processing data from sensors, cameras, and radar in real time, allowing them to identify objects, interpret road signs, and understand road conditions.
This enhances road safety and accelerates manufacturing processes, from automating assembly lines to optimizing conveyor belts, thus reducing time-to-market for new vehicles.
Real World Example: Waymo, an automotive giant, uses advanced ML and AI to power its autonomous vehicle technology. Its self-driving cars have accumulated millions of miles of road experience, leading to a significant reduction in accidents and an efficient transportation experience.
Also Read: Benefits and Use Cases of AI in the Automotive Industry

Energy Management
In energy-intensive manufacturing processes, machine learning algorithms can significantly enhance energy management. By analyzing data from various parameters such as temperature, lighting, and movement within a facility, these technologies can create predictive models to forecast future energy consumption. This approach enables manufacturers to optimize energy use, identify inefficiencies, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and reduce overall consumption, contributing to a more sustainable operation.
Real World Example: Google DeepMind partnered with National Grid to utilize ML to optimize energy management. The goal is to improve the efficiency of the electricity grid by forecasting and balancing energy demand through sophisticated ML algorithms.
Mass Customization
Machine learning enables manufacturers to offer personalized products at scale. By analyzing extensive customer data and preferences, ML algorithms tailor production processes to meet individual specifications while maintaining operational efficiency. This capability enhances customer satisfaction by providing bespoke solutions and optimizes production workflows.
Real World Example: Adidas uses AI and ML to manage its “Speedfactory” operations, allowing it to produce custom footwear in days rather than weeks. This approach has led to a significant increase in customer satisfaction due to the personalized fit and design.
You may like to know: How we helped Adidas expand its mobile presence globally
The Roadmap for Integrating Machine Learning into Manufacturing
Implementing ML in manufacturing processes can optimize production efficiency, improve quality, and reduce costs. Here’s a step-by-step guide for successful ML adoption in manufacturing:

Clearly Define Your Business Goals
Start by clearly outlining your goals for implementing machine learning in your manufacturing processes. Whether it’s improving maintenance, enhancing quality, or optimizing schedules, ensure these goals align with your business priorities.
Identify the key challenges you face and set measurable KPIs, such as uptime, yield rate, or cost reduction, to track the success of your ML efforts.
Data Collection and Preprocessing
Collect relevant data from various sources, including sensors, machinery logs, and production records. The quality of this data is crucial to the success of your ML model, so ensure it is clean and formatted properly.
Preprocess the data by handling missing values, normalizing them, and removing outliers to improve model performance and accuracy.
Select and Train the ML Model
Start by selecting the machine learning model that best addresses your problem. For predictive maintenance, consider supervised learning; unsupervised learning may be more suitable for anomaly detection, and reinforcement learning works well for optimizing processes like supply chains.
Once the model is chosen, historical data will be used to train it. Split the data into training and testing sets to assess accuracy and focus on selecting the most relevant features.
Evaluate and Validate the Model
Test the trained model’s performance with unseen data to ensure it can generalize well. Use cross-validation techniques to confirm that the model works consistently across different datasets.
If the model isn’t performing as expected, revisit data preprocessing, feature engineering, or model selection to improve its accuracy.
Integrate ML Models into Production Systems
After validation, integrate the model into your production systems. This may involve collaboration with IT teams to ensure the model is compatible with existing software.
Set up systems for real-time predictions, such as automating maintenance schedules or quality control checks, to improve operational efficiency and decision-making.
Monitor and Update the Model
Ongoing monitoring is essential to maintain the model’s performance. Track its effectiveness and watch for any decline in accuracy over time. As new data comes in, periodically retrain the model to ensure it stays relevant and adapts to changes in your manufacturing processes.
Practical Solutions to Common Machine Learning Adoption Challenges
Machine learning adoption presents several hurdles, but organizations can effectively overcome them with the right strategies in place. With appropriate solutions, businesses can unlock the full potential of machine learning to drive innovation and enhance growth. Let’s have a look at those.

High Implementation Costs
Problem: The cost of developing and implementing machine learning solutions is another common obstacle, as it often involves substantial investment in infrastructure and expertise.
Solution: Cloud-based machine learning platforms provide a cost-effective alternative, eliminating the need for upfront infrastructure investments. Starting with small pilot projects allows organizations to evaluate the potential impact of machine learning before scaling. Open-source tools and frameworks also offer a cost-efficient way to build models without compromising quality or functionality.
System Integration Challenges
Problem: Integrating machine learning into existing systems and workflows can be complex and technically challenging.
Solution: Organizations can simplify this process by utilizing APIs and middleware to connect ML solutions with current software. Engaging third-party experts can further streamline deployment and minimize disruptions. Choosing scalable, integration-ready ML platforms ensures smoother adoption and reduces compatibility issues.
Data Quality and Availability
Problem: The lack of high-quality, reliable data is a critical hurdle in adopting machine learning. Machine learning models require extensive datasets, but these are often incomplete, unstructured, or inconsistent.
Solution: To overcome this, organizations should implement effective data governance strategies to ensure data accuracy and reliability. Preprocessing methods like data cleaning, normalization, and transformation are essential to prepare datasets for training.
Model Interpretability and Explainability
Problem: Understanding and trusting the predictions of machine learning models, especially in critical fields like healthcare and finance, is a persistent challenge.
Solution: This can be addressed using simpler, more interpretable models, such as decision trees or linear regression, for specific use cases. For complex models, explainability tools like LIME (Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations) and SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) can make predictions more transparent.
Future of Machine Learning in Manufacturing
The future of ML in manufacturing is set to revolutionize the industry, bringing about smarter, more efficient, and adaptive production processes. As ML technologies advance, they will increasingly integrate with other cutting-edge innovations like AI, IoT, digital twins, and robotics, leading to fully automated and self-optimizing factories. Here is what to expect from the manufacturing and machine learning collaboration in the coming years:
- AI-driven insights will become more accessible and understandable for the everyday worker, empowering them to make data-driven decisions on the factory floor.
- Digital twins, already making significant contributions to production, will further ensure the reliability of manufacturing processes by simulating and testing systems before physical implementation.
- ML will empower manufacturing robots to adapt to changes in real time, enhancing safety and precision by enabling them to navigate obstacles and make intelligent decisions on the go.
- Predictive analytics and real-time quality control will work together to virtually eliminate manufacturing defects, ensuring products meet the highest standards.
- Sustainability will also be a key focus, with Green AI and ML optimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental impact.
As a result, the manufacturing industry will not only become more resilient and agile but also more environmentally responsible, paving the way for a future where data-driven decision-making and sustainable practices are at the core of production.
Get Started with Manufacturing Machine Learning with Appinventiv
Machine learning is transforming manufacturing, offering powerful tools to enhance efficiency, solve critical challenges, and improve the bottom line across departments. Whether you are a process engineer, data scientist, analyst, or factory floor manager focused on continuous improvement, integrating ML into your operations can drive significant advancements.
However, to leverage the maximum potential of machine learning in manufacturing, it is essential to set clear business objectives and partner with a reputed machine learning development company.
At Appinventiv, we specialize in rearchitecting digital landscapes and creating highly connected ecosystems with AI, ML, and other digital technologies. Our global team of 1600+ experts empowers each of our clients to maximize the value of their technology investments.
We offer IT solutions for the manufacturing industry to strategically integrate machine learning, ensuring precision and streamlined workflows. Whether you need to develop a custom ML model or integrate it into your existing systems, we provide advanced ML services tailored to your needs. Connect with us to discover how we can help your business thrive with cutting-edge digital technologies.
FAQs
Q. How is ML used in the manufacturing industry?
A. Machine learning is used in the manufacturing industry by collecting vast amounts of data from various processes, identifying key patterns and trends, and then using those insights to automate tasks, predict maintenance needs, and optimize workflows. It enables manufacturers to make data-driven decisions, reduce operational costs, and enhance efficiency.
Q. What are the emerging trends of machine learning in the manufacturing industry?
A. The key trends of machine learning in manufacturing industry include:
- Predictive Maintenance
- Quality Control
- Digital Twins
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Energy Management
- Robotics and Automation
- Inventory Management
- Mass Customization
- Human-Robot Collaboration
- Sustainability Initiatives
- AI-Driven Design
- Self Driving Cars
- Anomaly Detection and Cybersecurity
To gain an in-depth understanding of these emerging manufacturing machine learning manufacturing trends, please refer to the above blog. It will give you a comprehensive overview of applications, examples, and features of ML in manufacturing.
Q. What are the advantages of machine learning in manufacturing?
A. The benefits of manufacturing machine learning are innumerable and undeniable, revolutionizing the industry in various ways. Here are some of the most remarkable benefits of ML in manufacturing:
Reduce Cost: AI/ML helps reduce costs by optimizing inventory, automating tasks, planning maintenance, extending equipment life, and minimizing defects.
Improve Quality: ML algorithms enhance product quality by detecting and addressing defects swiftly, leading to fewer returns and a stronger reputation.
Enhance Efficiency: Machine learning analyzes large datasets to streamline processes, cut downtime, and ensure a smooth production flow, thus improving efficiency.
Improve Worker Safety: ML-powered predictive analytics and sensor systems improve worker safety by identifying patterns in the workplace and monitoring equipment health conditions.
Informed Decision-Making: ML enables real-time data analysis, allowing for quick adjustments in production, inventory management, and quality control to stay ahead of market changes.


10 Use Cases and Examples of How Machine Learning is Transforming the Logistics Industry
The widespread adoption of ML has resulted in the explosion of data from sensors, customer interactions, and digital platforms across different domains. More and more businesses are leveraging machine learning in logistics to improve their strategic decision-making expertise centered around tailoring customer experience, improving productivity, increasing engagement, and preventing fraud. According to the McKinsey Global…

How Machine Learning in Retail is Redefining the Sector - Key Business Opportunities and Challenge
In the last few years, the retail industry has faced some critical challenges like the global pandemic — COVID-19, supply chain disruptions, curfews, energy crunches, sustainability pressures, cybersecurity threats, eCommerce apocalypse, and so on. Despite these obstacles, the industry has shown remarkable resilience, transforming its operations to meet the demands of a rapidly changing retail…

Machine Learning in Banking - Use Cases and Implementation Process
The speed at which fintech transformation is happening is nothing short of a never-seen-before revolution. With the advent of technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence, metaverse, and edge computing, the fintech space - as we know it - has drastically changed. This transformation's intrinsic change can be seen in how comfortable users have gotten with on-the-move…


















