- Kuwait’s Software Development Landscape: Where Demand Is Coming From
- Common Hiring Barriers That Slow Down Software Initiatives in Kuwait
- Limited Talent, Expensive Hiring Cycles
- Compliance Blind Spots
- Arabic UX Still Treated as Secondary
- Varying Development Discipline
- Contracts That Don’t Protect You
- Things to Consider Before Hiring a Software Company in Kuwait (Internal Prep)
- 1. Define Outcomes, Not Just Features
- 2. Map Mandatory Integrations
- 3. Decide Procurement Model
- 4. Set Budget Guardrails and Contingency
- 5. Governance, Sign-offs and Roles
- What to Really Evaluate Before Signing With a Software Partner
- 1. Clear Contracts and Commercial Terms
- 2. Technical Competence and Execution Approach
- 3. Team Strength and Stability
- 4. Security Readiness and Compliance Experience
- 5. Arabic UX, Accessibility, and Regional Adaptation
- 6. QA Discipline, Performance Readiness, and Monitoring
- 7. Post-Launch Support and Operational Readiness
- Build a Vendor Scorecard
- Choosing the Right Delivery Model: Local, Offshore, or Hybrid
- When Local Development Makes Sense
- When Offshore is a Viable Option
- Hybrid: Often the Most Practical Middle Ground
- Quick Decision Guide
- What Software Development in Kuwait Typically Costs and How Long It Takes
- Estimated Software Development Cost & Timeline Bands
- What Impacts the Final Number
- Structuring Contracts to Manage Cost
- Structuring the RFP and Vendor Interview: What to Include, What to Ask
- RFP Essentials Checklist
- Sample Interview Questions by Category
- Red Flags to Watch For
- Running a Pilot That Minimizes Risk and Reveals Fit
- What Are the Common Mistakes When Hiring a Software Company in Kuwait?
- 1. Choosing Based on Price Alone
- 2. Skipping Reference Checks
- 3. Ignoring Data Security and Compliance
- 4. Vague Contracts or Missing IP Clauses
- 5. No Transition or Handover Planning
- A Delivery Partner That Builds What Kuwait’s Market Demands
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q. How to choose a software development company in Kuwait?
- Q. What are the main challenges of hiring a software development company in Kuwait?
- Q. What factors should be considered before hiring a software development company in Kuwait?
- Q. Is it better to choose a local or offshore software development company in Kuwait?
- Q. How can businesses evaluate software development companies in Kuwait?
- Q. What industries are investing most in software development in Kuwait?
- Q. How does the Kuwait software development market differ from other regions?
- Q. How important is data security and compliance when hiring a software company in Kuwait?
- Q. How long does it typically take to develop enterprise software in Kuwait?
- Q. Why are AI-powered software solutions gaining traction in Kuwait?
- Use a scorecard-driven RFP and a technical assessment to compare vendors on capability, compliance, and delivery risk.
- Local partners provide regulatory and cultural alignment; hybrid teams often pair that with offshore cost efficiency.
- Start with a scoped pilot or MVP, milestone-based contracts, and clear IP/SLAs to reduce procurement risk.
- Require demonstrable security controls, repeatable QA artefacts, and a firm post-launch support plan.
- Evaluate vendors by evidence (code samples, CI/CD proof, audit reports), not by portfolio polish or price alone.
Software development in Kuwait has moved well beyond “nice-to-have.” Government programs and private enterprises are investing in customer portals, payments, clinical systems, logistics platforms, and automation tools. The intent is practical: reduce manual work, speed up service delivery, and ship systems that survive audits and day-two operations.
The catch is that building here comes with predictable pressure points. Senior local talent is limited, and vendor maturity isn’t consistent. Arabic UX is still underestimated. Data residency and compliance assumptions get left vague until late. And the moment you add integrations with core systems, timelines and budgets can stretch in ways that nobody planned for.
When you pick the right partner, the outcome is usually straightforward: fewer manual tasks, faster delivery cycles, new digital channels, and measurable efficiency gains. The safest way to get there is not “trusting the pitch.” Pilot first, tie payments to milestones, lock down IP early, and treat discovery as the place where you buy clarity.
If you want a fast sanity check before you commit, a short technical discovery or an RFP review, it typically saves more time (and stress) than people expect.
Choose Appinventiv for service delivery
Kuwait’s Software Development Landscape: Where Demand Is Coming From
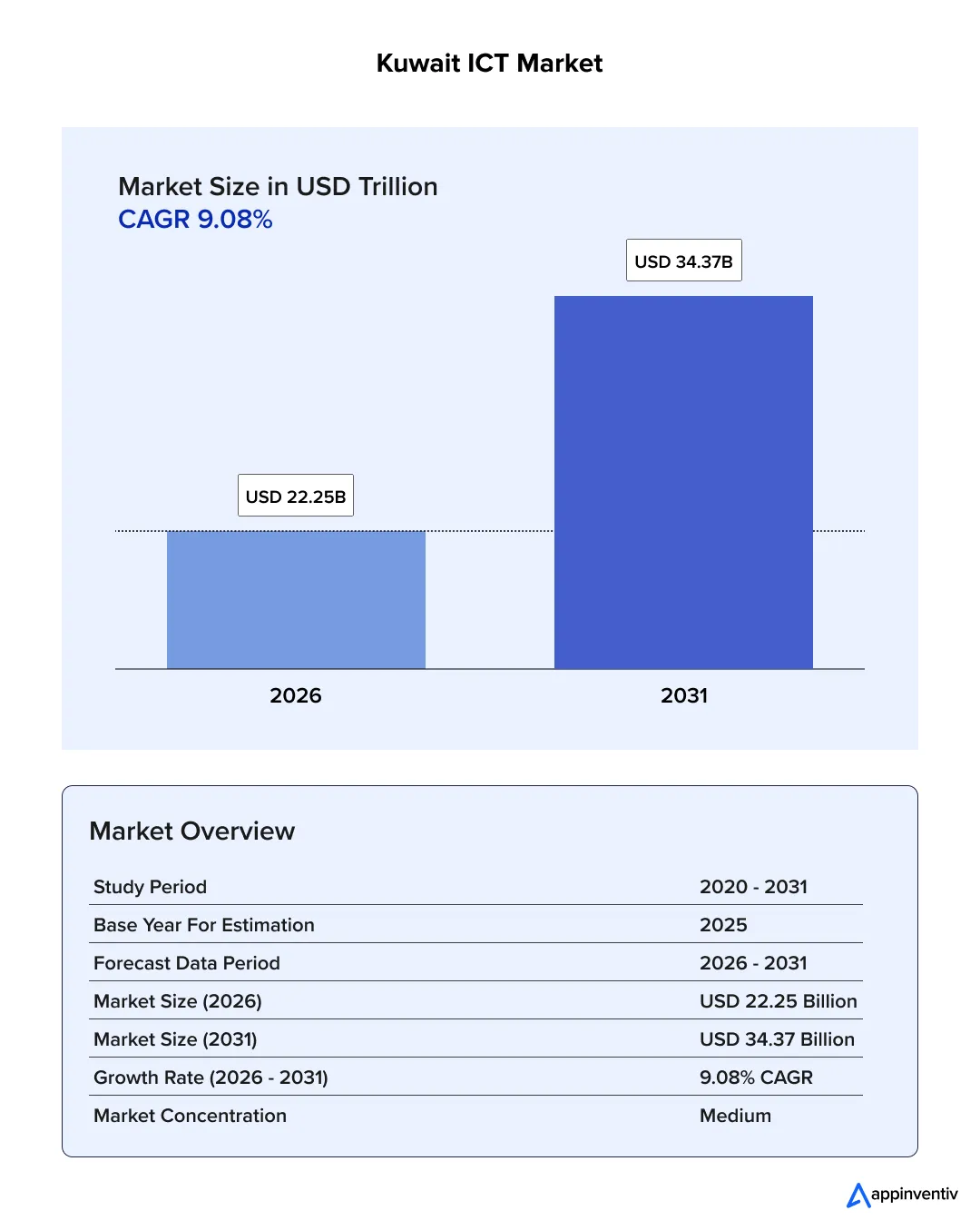
Kuwait’s ICT market is on a clear growth path. Mordor Intelligence projects a continued uptick through 2029, driven by public-sector digitisation and private firms pushing for faster, more consistent customer experiences.
Where demand shows up is not a mystery. It clusters by software development for different industries:
- Banking and fintech teams need secure transaction workflows, audited logs, and resilient rails.
- Healthcare teams need privacy, clinical integrations, and operational continuity.
- Retail and logistics teams want multi-channel systems that do not fall apart under traffic spikes.
- Energy and industrial environments increasingly ask for edge-to-cloud telemetry and secure analytics.
Government & G2C Services: With the mass adoption of the Sahel and Sahel Business apps, private enterprises (especially in insurance, banking, and real-time services) are seeking partners who can build “Sahel-ready” modules. This requires a deep understanding of Kuwait’s unified digital government framework and identity authentication protocols (like Hawiyati).
This surge is anchored by the “New Kuwait” Vision 2035, which prioritizes a “Sustainable Diversified Economy” and “Developed Infrastructure.” For enterprise buyers, this means digital transformation is no longer siloed, it is a mandate to integrate with national initiatives.
Any partner you hire must align with these macro-goals, particularly regarding Citizen Experience (CX) and the modernization of non-oil sectors like Fintech and Healthcare.
The market appetite is for production systems, not demos. Kuwait buyers are also becoming more discerning. They want speed, yes, but they want software audit readiness and operational discipline alongside it.
Who usually buys? It is typically a mix of IT, product, and operations. Procurement and legal steps are initiated early for larger budgets, especially where IP, SLAs, data residency, and compliance are involved. Priorities vary, but the pattern is consistent: buyers want fast delivery without introducing regulatory or reputational risk.
A practical point that matters: software outsourcing in Kuwait is now common, especially when organisations combine local governance with offshore engineering capacity. That model tends to hold budgets steady while keeping control where it matters.
Common Hiring Barriers That Slow Down Software Initiatives in Kuwait
Selecting a software development company in Kuwait is rarely about “finding a developer.” The real challenge is avoiding delivery inconsistency and compliance surprises that surface halfway through the build.
Here are the most common barriers that slow down custom software development in Kuwait.
Limited Talent, Expensive Hiring Cycles
Senior architects, DevOps leads, and experienced platform engineers are hard to hire locally. Junior talent is more available, but senior capability is what stabilises delivery and prevents rework. This is why many teams choose hybrid staffing: local leadership and stakeholder management, paired with offshore delivery to keep capacity scalable and budgets defensible.
Compliance Blind Spots
Finance and healthcare projects typically require documented compliance, not verbal assurances. Data residency expectations, encryption standards, access controls, and software audit trails should be designed and documented early. If deliverables fail compliance checks, approvals stall, and release schedules slip.
In 2026, compliance isn’t just a checklist; it’s a legal barrier. For projects in Kuwait, your vendor must demonstrate specific readiness for:
- CITRA Regulation 26/2024: Ensuring mandatory data confidentiality and user-consent audits for IT service providers.
- CBK’s Cyber & Operational Resilience Framework (CORF): Essential for any fintech or banking integration to ensure “always-on” availability and data sovereignty.
- Data Residency: Confirming whether Tier 3 or Tier 4 data will be hosted on-shore within Kuwaiti borders to satisfy National Cybersecurity Center (NCSC) classifications.
Arabic UX Still Treated as Secondary
Arabic UX in the MENA region is not translation work. RTL layouts affect spacing, navigation behaviour, typography, and even icon direction. When teams treat it as “we’ll localise later,” adoption suffers, and redesign cycles follow. Service localisation belongs in design and QA, not just content.
Varying Development Discipline
Some vendors run mature delivery: CI/CD pipelines, automated tests, structured retrospectives, and consistent release practices. Others operate in a largely manual mode. This difference becomes apparent when projects reach a certain level of complexity.
Ask vendors to share, under NDA if needed:
- build and release artefacts
- sample test reports and test coverage summaries
- sprint retrospectives (redacted is fine)
- rollback approach and incident response flow
If a vendor refuses to share any artefacts, even anonymised ones, treat that as a signal to probe further.
Contracts That Don’t Protect You
Weak contracts create expensive lock-in. The common culprits are vague IP terms, thin SLAs, and missing exit or transition clauses. You should confirm IP assignment early, and for larger initiatives, consider source-code escrow.
Risk signals to watch for:
- NDA signed before deep talks
- encryption and data-flow artefacts available
- IP terms are clearly defined in the contract
- Arabic UX samples that show real RTL work
- SLAs with explicit response and resolution times
- CI/CD visibility
- pilot before full commitment
Our Kuwait-aligned delivery model ensures local oversight with scalable offshore execution.
Things to Consider Before Hiring a Software Company in Kuwait (Internal Prep)
A strong software development vendor selection process usually starts with internal clarity. If your RFP is vague, your vendor responses will be vague too. A disciplined internal scoping exercise reduces friction later and makes comparisons fair.
1. Define Outcomes, Not Just Features
Feature lists are easy to write. Outcomes are harder to achieve, but they make delivery measurable. Instead of “improve onboarding,” define what success looks like. For example, reduce signup time from 72 hours to 24, or raise completion rates from X to Y. Vendors estimate better when you describe the business result.
2. Map Mandatory Integrations
List target systems and be specific about integration patterns (API, SFTP, messaging), security expectations, and constraints. If an ERP requires a custom connector, say that plainly. Integration ambiguity is a common reason cost estimates blow out later.
3. Decide Procurement Model
- Fixed price: works best when the scope is stable and bounded. Use caution for long-running initiatives.
- Time and material: suitable when the scope evolves, but only with governance and monthly burn reviews.
- Outcome-based: useful when accountability can be measured clearly and enforced contractually.
Also Read: White-Label Enterprise Procurement Software Development Cost
4. Set Budget Guardrails and Contingency
Some costs rarely appear in initial estimates: licences, approval fees, compliance documentation, and hosting choices driven by residency requirements. Keep a contingency reserve of around 10–20% for integration surprises and compliance-driven adjustments.
5. Governance, Sign-offs and Roles
Define who signs off on deliverables, who owns security and legal checks, and how change requests are handled. Name primary contacts and backups in the RFP. Unclear ownership slows approvals and creates last-minute conflict.
Project-intent table (simple template for RFP)
Project goal → Target KPI → Mandatory integrations → Budget band → Timeline
What to Really Evaluate Before Signing With a Software Partner
RFPs can look impressive and slide decks can be persuasive. But, delivery quality shows up in evidence: how teams design, test, release, and support software when reality gets messy.
Below are factors to consider when hiring company developers built around seven areas. It helps you spot gaps early and choose a partner that can deliver under real conditions, not just ideal ones.
1. Clear Contracts and Commercial Terms
Start with the agreement, because it defines everything downstream. Look for contracts that specify:
- deliverables and acceptance criteria
- milestone-linked payment terms
- IP ownership terms and handover expectations
- change request handling
- service levels and support scope
Be cautious when pricing is open-ended without boundaries, or when IP is vague. If you are funding custom software development in Kuwait, code ownership should be explicit.
2. Technical Competence and Execution Approach
Move past the pitch and ask for proof. Architecture diagrams, sample API designs, and CI/CD walkthroughs reveal how teams actually build and run systems.
For larger projects, ask for:
- A draft sprint plan
- An early-stage product backlog
- How they estimate and re-estimate scope
- What they do when requirements shift
If a vendor cannot share anonymised examples under NDA, treat it as a prompt for deeper scrutiny.
Expert Note: The Artifact Walkthrough
Don’t just look at high-level architecture. Request a “Day 2” Operational Plan. Ask the vendor: “If our Knet payment gateway integration fails at 2:00 AM on a Friday, what is the specific automated alert flow and MTTR (Mean Time to Recovery) protocol?” If they cannot show a runbook or an automated monitoring dashboard (Datadog, New Relic, etc.), they are building a “demo,” not a production system.
3. Team Strength and Stability
Delivery depends on the actual team, not the logo on the proposal. Ask for:
- project org chart
- CVs of key leads (PM, architect, lead developer)
- clarity on whether key roles are internal or subcontracted
- continuity plan if a key person leaves
Turnover can disrupt momentum. A reliable vendor should be transparent about succession planning.
4. Security Readiness and Compliance Experience
For finance, healthcare, telecom, and government-linked projects, security is not optional. Ask vendors to show evidence, not intent:
- pen test reports or summaries (anonymised is fine)
- data handling policies
- relevant certifications like ISO 27001 or SOC 2, where applicable
- data residency approach, if your environment requires it
Do not leave this for later. Compliance retrofits are expensive and usually have a slow go-live.
5. Arabic UX, Accessibility, and Regional Adaptation
Arabic-first UX is specialised design work. RTL interfaces change navigation flow, spacing, typography, and interaction patterns. Ask for real-world examples of Arabic-first UX, and confirm that designers have tested with Arabic-speaking users.
In public services, education, and healthcare, localisation and accessibility often connect directly to adoption and usability. Sometimes they intersect with compliance, too.
6. QA Discipline, Performance Readiness, and Monitoring
Manual testing alone is rarely enough for systems with integrations and workflows. Ask:
- What is automated and what is not
- How frequently tests run
- What coverage levels are typical
- Performance benchmarks and load testing approach
- How production monitoring is handled (logs, alerts, dashboards)
Also, clarify how post-launch issues are tracked and resolved.
7. Post-Launch Support and Operational Readiness
Support is where many projects struggle. Avoid post-launch app mistakes, ask for:
- support tiers and escalation paths
- patch timelines
- response and resolution SLAs
- runbooks, documentation, and the handover process at go-live
This is often what separates short-term builders from long-term partners.
Build a Vendor Scorecard
Use a weighted scorecard so your team evaluates consistently.
| Criteria | Weight | Example Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Capability | 25% | Architecture diagrams, sprint plan, CI/CD access |
| Security & Compliance | 20% | Pen-test summary, ISO cert, data flow diagrams |
| Commercial & Contractual | 15% | SOW, milestone plan, IP clauses |
| Team Quality & Continuity | 15% | Org chart, team CVs, attrition data |
| UX/Arabic Localisation | 10% | RTL design samples, accessibility test results |
| QA & Monitoring | 10% | Test coverage, performance metrics, tooling |
| Support & Maintenance | 5% | SLA document, response times, runbooks |
Score each category from 1 to 5, apply weights, and shortlist based on alignment, not presentation polish.
If you need a second set of eyes on proposal gaps or vendor claims, a short review by a team familiar with Kuwait delivery realities often exposes risks that slide decks hide.
Choosing the Right Delivery Model: Local, Offshore, or Hybrid
Once goals and vendor shortlists are clear, the next decision is the delivery model. Most enterprises compare three setups: hybrid vs. offshore vs. local software development in Kuwait.
Cost matters, but the bigger impact is coordination, speed of issue resolution, and whether compliance and language expectations are met in production.
When Local Development Makes Sense
Sensitive data, government workflows, and sector compliance typically benefit from local teams. Local teams tend to understand regulatory expectations and Arabic UX requirements more naturally. The trade-off is capacity and cost, which can become a constraint in multi-phase initiatives.
When Offshore is a Viable Option
Offshore software development can offer cost advantages and access to specialised skills. It fits best when the scope is clearly defined, and regulatory pressure is lower. The risk is drift: time zones, unclear feedback loops, and gaps in local context can slow projects unless governance is strong.
If you go offshore, structure matters: daily syncs, shared tooling, clear documentation, and local oversight.
Hybrid: Often the Most Practical Middle Ground
Hybrid models combine local oversight with offshore execution. A local PM or BA bridges compliance, Arabic UX feedback, approvals, and stakeholder alignment while offshore teams handle engineering and QA at scale.
For many Kuwait organisations, this is the model that balances speed, quality, and budget control.
Quick Decision Guide
Here’s a quick guide to help you make a decision as per your business needs.
| Priority | Recommended Model |
|---|---|
| Data Compliance | Local / Hybrid |
| Cost Efficiency | Offshore / Hybrid |
| Stakeholder Access | Local / Hybrid |
| Niche Skills | Offshore / Hybrid |
| Multilingual UX | Local / Hybrid |
A short discovery sprint is a smart step before you lock the model. It tests collaboration, exposes alignment gaps early, and validates technical assumptions before full commitment.
What Software Development in Kuwait Typically Costs and How Long It Takes
There is no single price tag for the cost to hire a software development partner in Kuwait. Scope, compliance, integrations, team composition, and delivery model all move the number. Still, typical ranges do exist, especially when mapped to project type.
When evaluating costs, focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than the initial build price. In Kuwait’s high-growth market, “Technical Debt” is the most expensive hidden cost. A cheap vendor might save you $10,000 today, but cost you $100,000 in legacy migrations or security patches three years from now as CITRA regulations evolve.
Estimated Software Development Cost & Timeline Bands
The software development cost in Kuwait depends on the project scope. Here’s a quick estimated breakdown:
| Project Scope | Cost Range (USD) | Timeline (Weeks) | Key Cost Drivers | Recommended Contract Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic MVP (limited features, 1 platform) | $3,500 – $20,000+ | 4–8 weeks | Single user journey, no integrations, fixed UI flows | Fixed-price or time-boxed sprint |
| Standard product (multi-platform, moderate backend) | $20,000 – $80,000+ | 8–16 weeks | API integrations, role-based access, admin workflows | Milestone-based fixed-price |
| Mid-complexity system (custom workflows, dashboards) | $80,000 – $180,000+ | 16–28 weeks | Analytics, workflow automation, third-party systems | Hybrid: fixed for knowns, T&M for change |
| Large platform (multi-module, compliance-heavy) | $180,000 – $400,000+ | 28–52+ weeks | Regulatory audits, encryption, data residency, multi-tenant logic | Phase-based contract with SLA |
What Impacts the Final Number
Two projects can look similar on paper and still price very differently. The usual drivers are:
- Regulatory compliance: encryption, access control, audit trails, documentation, and validation cycles increase effort.
- Third-party integrations: ERP/CRM/payment gateway connections add build time and testing complexity.
- UX and language support: bilingual UI and Arabic-first design require additional design and RTL testing cycles.
- AI/ML components: intelligent workflows and predictive analytics require pipelines, infrastructure, and validation effort.
- Ongoing support: monitoring, incident response, and security maintenance create a recurring scope.
Structuring Contracts to Manage Cost
A phased approach works best for most Kuwait enterprise software development market scenarios. This typically includes:
- Discovery and architecture sprint
- Pilot or MVP phase
- Full build after early milestones validate scope
- Support phase with SLAs and security maintenance
If requirements are still fluid, a paid discovery sprint is usually the fastest way to reduce assumptions and align stakeholders without overcommitting budget.
Structuring the RFP and Vendor Interview: What to Include, What to Ask
A structured RFP works as a filter and a guidepost. It helps you eliminate mismatched vendors and gives serious teams what they need to propose responsibly.
Interviews should focus on delivery reality: how vendors handle pressure, scope changes, and quality control when the project stops behaving like the plan.
RFP Essentials Checklist
When preparing an RFP for a software partner, especially in sectors like banking, healthcare, or logistics, clarity is non-negotiable. Here’s what to include:
- Business context and outcomes tied to KPIs (reduce turnaround time by 50%, raise uptime to 99.9%, etc.)
- Scope boundaries and success criteria
- System integrations (ERP, CRM, payments, legacy platforms)
- Compliance and data expectations (residency, audit readiness, sector regulations)
- Security standards (encryption, access roles, audit logs)
- Acceptance criteria and sign-off flow
- Support expectations, SLAs, and escalation paths
- IP and ownership clauses (source code and documentation ownership)
- Milestones and payment structure tied to deliverables
- Evaluation criteria and scoring method
If the scope is not stable yet, start with discovery. It sharpens requirements and prevents proposal mismatch.
Sample Interview Questions by Category
Once proposals are in, your shortlisting should include a live interview, preferably with both technical and operational leads from the vendor side.
Technical Depth
- Walk us through your architecture for a similar solution.
- How do you manage release automation and CI/CD?
- What tools do you use for test automation, and what coverage is typical?
- What is your rollback plan if production issues occur?
Delivery Process
- What does your sprint cycle look like, and how do you manage backlogs?
- How do you handle scope changes without losing control of timelines?
- Share an example where a project slipped. What did you change to recover?
Security & Compliance
- Have you completed third-party pen tests? Can you share anonymised results?
- How do you handle secrets, keys, and access credentials during deployment?
- What is your incident response protocol, and who owns it?
Commercial & Contractual
- What is your policy on code ownership and escrow?
- How do you handle failed acceptance tests or resourcing gaps?
- Do you offer phased fixed bids with milestone approvals?
Arabic Localisation & Cultural Fit
- Show examples of RTL interfaces and Arabic-first UX.
- How do you validate Arabic layouts and translations with real users?
- How do you manage stakeholder feedback across time zones?
Red Flags to Watch For
A few red flags that cannot be overlooked includes:
- Refusal to share architecture or CI/CD details under NDA
- Sales-heavy calls without access to technical leads
- No SLAs or vague support commitments
- Generic compliance answers with no evidence
- One-size proposals that ignore your domain constraints
A detailed vendor scorecard used during interviews can help your team evaluate consistently.
Running a Pilot That Minimizes Risk and Reveals Fit
A pilot is the most reliable way to test vendor fit without gambling the full program. It is not a sales exercise, but a delivery test.
A well-scoped pilot usually runs 4–12 weeks and focuses on one or two workflows that expose delivery reality, such as:
- A core API integration
- A role-based user journey
- A dashboard backed by real data
- A CI/CD pipeline with repeatable releases
The aim is not feature completeness; it is to see how the team builds, communicates, and protects quality when decisions and changes happen.
Set pass/fail criteria early:
- Working CI/CD
- Minimum test coverage targets
- Performance benchmarks
- Integration with a test system
- Weekly demos and codebase visibility
What to include in a pilot contract:
- Time-boxed scope and measurable goals
- IP ownership for pilot code
- Milestone-based payments
- Termination or rollback clauses
- Acceptance metrics and review checkpoints
A pilot is not a sales exercise but an operational test. If you want to structure a pilot properly, a short discovery consultation can help define scope and governance before you sign a long vendor agreement.
What Are the Common Mistakes When Hiring a Software Company in Kuwait?
Even mature teams miss things during procurement. The small gaps usually become expensive later.
1. Choosing Based on Price Alone
Low quotes often hide missing scope, thin QA, weak documentation, or a delivery model that cannot scale. Cheap upfront rarely means low total cost.
Fix: request a milestone breakdown, include support scope, and evaluate price alongside technical clarity.
2. Skipping Reference Checks
Portfolios can be outdated. Without reference calls, you cannot see how teams handle delays, pressure, or scope changes.
Fix: speak to at least two references and ask about communication, issue resolution, and maintainability.
3. Ignoring Data Security and Compliance
Treating security as “later” is risky in finance, healthcare, and government-linked work.
Fix: make security and compliance evidence part of the RFP and interviews. Ask for real artefacts, not promises.
4. Vague Contracts or Missing IP Clauses
Unclear ownership and acceptance terms create disputes during handover or vendor changes.
Fix: define SOWs, IP, exit terms, and delivery-based payments. Avoid verbal agreements.
5. No Transition or Handover Planning
Teams focus on go-live and forget what happens after. Knowledge transfer becomes a scramble.
Fix: require documentation, runbooks, and a support onboarding period after launch.
Most of these mistakes are preventable with a scorecard-driven process and a short pilot. If time is tight, a second-opinion review of proposals can catch risks before they turn into delays.
We assist teams in Kuwait with pilot reviews, compliance audits, and mid-project course corrections, without locking you in.
A Delivery Partner That Builds What Kuwait’s Market Demands
Appinventiv is a well-known software and app development company in Kuwait. We help businesses turn complex software goals into working systems that are secure, scalable, and ready for production. The difference is not just delivery, it is delivery discipline.
What we bring:
- 3,000+ solutions designed and delivered across critical sectors
- 500+ legacy systems modernised with audit-ready infrastructure
- 150+ AI models deployed in live, high-traffic environments
- 35+ industries served, from finance and healthcare to mobility and energy
- 1,600+ engineers, architects, and QA professionals available to scale delivery quickly
For Kuwait engagements, we typically support:
- Local consulting and stakeholder alignment
- Hybrid delivery with onshore planning and offshore execution
- Regulatory-aware architecture with residency and encryption controls
- Arabic UX and RTL interface support
- CI/CD pipelines, QA automation, and monitoring built into the workflow
We start with technical discovery and operate with milestone-linked plans so delivery stays predictable.
If you are evaluating vendors and want a second opinion on your RFP, pilot scope, or estimate assumptions, we can help.
(Tell us your project scope, preferred go-live window, and budget band. We will send a checklist and a timeline alignment sheet.)
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How to choose a software development company in Kuwait?
A. Choose a company with proven vertical expertise in your industry. For example, a vendor experienced in eCommerce may not understand the Cybersecurity Framework requirements of a Kuwaiti bank.
Prioritize firms that conduct a structured Technical Discovery Sprint to map regulatory, hosting, and integration needs specific to Kuwait before contract finalization. Always validate real project evidence, not just presentations.
Q. What are the main challenges of hiring a software development company in Kuwait?
A. The biggest challenge is the senior talent gap. Many firms have capable junior developers, but experienced architects with expertise in Sahel integrations, Arabic-first UX, or regulator-facing systems are limited. Successful enterprises in Kuwait often use a hybrid delivery model, combining local governance with offshore engineering teams to ensure both compliance alignment and scalability.
Q. What factors should be considered before hiring a software development company in Kuwait?
A. Evaluate technical capability, regulatory experience, IP ownership terms, exit clauses, and post-launch support models. Confirm that the company has delivered systems in your industry in Kuwait or in similar regulatory environments. Review change request handling processes and ask for live system demos or artefacts under NDA rather than relying solely on pitch decks.
Q. Is it better to choose a local or offshore software development company in Kuwait?
A. Local companies are better suited for regulator-facing projects, government programs, and initiatives requiring strong Arabic localisation. Offshore teams can reduce cost and provide niche technical skills for clearly defined scopes. In Kuwait, hybrid models are often most effective, combining local stakeholder management with scalable offshore execution.
Q. How can businesses evaluate software development companies in Kuwait?
A. Use a structured evaluation framework that assesses technical depth, compliance readiness, UX capability, QA processes, and team continuity. Interview delivery managers and technical leads, not just sales representatives. Request documentation, including architecture diagrams, security protocols, and deployment workflows, to validate operational maturity.
Q. What industries are investing most in software development in Kuwait?
A. Finance, healthcare, public services, retail, logistics, and energy are leading investment sectors. Most projects focus on modernizing legacy systems, automating workflows, and integrating customer-facing platforms with core enterprise systems. Regulatory alignment and digital service improvement are major drivers.
Q. How does the Kuwait software development market differ from other regions?
A. The Kuwaiti market places strong emphasis on Arabic-first UX, bilingual system support, and compliance readiness. Procurement often requires local engagement, and hosting or residency considerations may affect system architecture. Enterprise buyers typically prioritize governance and regulator alignment more heavily than in many other regions.
Q. How important is data security and compliance when hiring a software company in Kuwait?
A. Data security and compliance are critical, particularly in banking, healthcare, and government-linked sectors. Vendors should provide documented evidence such as penetration test summaries, data flow diagrams, encryption standards, and audit support plans. Security architecture should be defined during the discovery phase, not after development begins.
Q. How long does it typically take to develop enterprise software in Kuwait?
A. Timelines vary by scope and regulatory complexity. Small MVPs may take 1–2 months, mid-sized enterprise platforms typically require 3–6 months, and complex multi-system programs can extend to 9–12 months or longer. Compliance approvals and stakeholder reviews often influence the overall timeline.
Q. Why are AI-powered software solutions gaining traction in Kuwait?
A. AI adoption in Kuwait is driven by measurable operational value. Enterprises use AI to automate manual processes, detect anomalies, generate predictive insights, and enhance decision-making dashboards. Adoption increases when AI solutions are implemented within clear governance frameworks and produce quantifiable efficiency gains.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

The ROI of Strategic Insurance Technology Consulting for Legacy Modernization
Key takeaways: Insurance technology consulting delivers ROI only when modernization is tied to real workflows, not system replacement. Most legacy modernization failures stem from weak ROI definition and tracking, not from technology limitations. The strongest returns come from reduced operational friction, faster change cycles, and tighter claims and underwriting control. Delaying modernization incurs hidden costs…

A Strategic Framework for Proof of Concept Software Development
Key takeaways: Most enterprise PoCs fail due to a lack of decision clarity, not technical feasibility or innovation potential. A disciplined PoC framework reduces delivery risk before budgets, teams, and timelines are committed. Enterprise-grade PoCs validate feasibility, compliance, and scale assumptions under realistic operating constraints. Clear success metrics and governance turn PoCs into reliable inputs…

Top UK Software Development Trends Shaping 2026: Insights for Business Leaders
Key takeaways: 2026 is about fixing friction, not chasing trends. UK software teams are prioritising reliability, clarity, and systems that are easier to change over flashy new tooling. AI is becoming background support, not the main act. Its value shows up in routine work like testing, reviews, and documentation, while people still make decisions. Architecture…