- Understanding the Role of Edge Computing in IoT App Development
- Edge vs. Cloud: A Tale of Two Libraries
- How Edge Computing Architecture Powers IoT
- Different Types of Edge IoT Devices
- The Edge Advantage: Why Your IoT Application Demands This Upgrade
- Reduced Latency
- Improved Bandwidth Efficiency
- Real-Time Data Processing
- Offline Functionality and Uptime
- Cost Reduction
- Security & Reliability
- Edge Computing and IoT Use Cases in Different Industries
- Smart Cities: From Gridlock to Intelligent Flow
- Healthcare: Bringing the Hospital Home
- Manufacturing: Welcome to Industry 5.0
- Retail: The Revenge of Brick-and-Mortar
- Finance: Securing and Speeding Up Transactions
- Real World Examples of Companies Using Edge Computing in the IoT Market
- John Deere
- Amazon Go
- NVIDIA
- Challenges of Implementing Edge Computing for IoT & How to Overcome Them
- Scalability: Managing Distributed Infrastructure
- Security: Protecting Distributed Data and Systems
- Integration: Harmonizing Existing Infrastructure
- Cost Considerations: Upfront vs. Long-Term Savings
- Interoperability: Making Devices Speak the Same Language
- The Future of IoT is at the Edge: Emerging Trends and Technologies
- AI and Machine Learning at the Edge
- 5G Network Integration
- Quantum Computing
- Partner with Appinventiv: Your Next Move in the Edge-IoT Revolution
- FAQs
- Edge computing kills latency by processing data on the spot, paving the way for real-time magic in things like autonomous cars and factory robots.
- By analyzing data at the source, you can slash your bandwidth and cloud storage bills. It’s just a more efficient way to run your IoT ecosystem.
- Your IoT setup can keep humming along even if the internet connection drops. Edge offers a new level of reliability for critical operations.
- Processing sensitive data locally means less risk of it being snatched in transit to the cloud. It’s a huge security win.
- The trio of AI, 5G, and edge computing is creating a new wave of smart, autonomous systems that will completely redefine how industries operate.
Picture this: Imagine an autonomous car cruising down the highway. Suddenly, a pedestrian steps onto the road. The car’s sensors detect the obstacle and need to make a split-second decision: brake. Now, what if that decision had to travel hundreds of miles to a centralized cloud server, get processed, and then travel all the way back to the car’s braking system? That fraction of a second, that tiny delay, is the difference between a close call and a catastrophe.
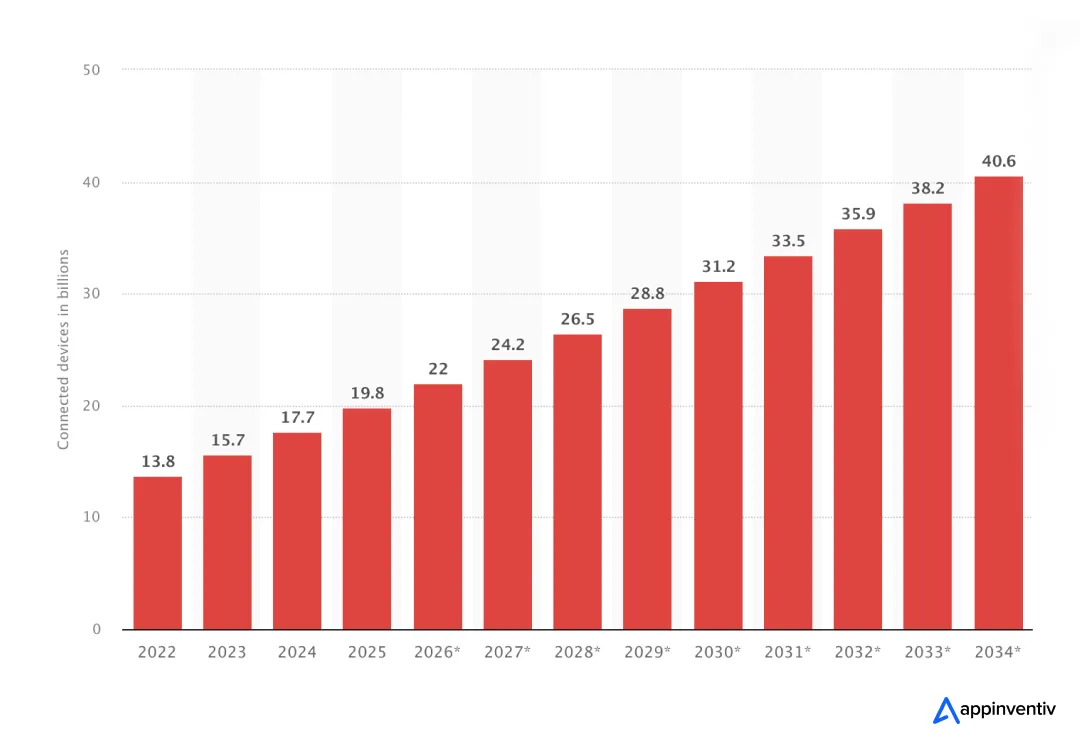
This scenario isn’t a hypothetical edge case; it’s the core challenge defining the limits of the Internet of Things (IoT) systems. We’re deploying connected devices at a blistering pace, with projections pointing to the number of IoT connections worldwide will double from 19.8 billion in 2025 to over 40.6 billion by 2034. Together, these IoT devices produce a deluge of data.
However, the traditional model of funneling everything to a central cloud for analysis is proving too slow, too expensive, and too vulnerable for the demands of a real-time world. The solution isn’t to get rid of the cloud, but to give it some local help.
This is where edge computing walks in and changes the game. The solution isn’t to fire the cloud. It’s to give it a team of brilliant, local deputies. By moving computation from distant cloud servers to local edge devices, we’re witnessing a transformation in how IoT applications perform, scale, and deliver value.
This approach to edge computing in IoT app development isn’t just an incremental improvement; it’s a fundamental reimagining of how we architect intelligent systems. Interested in exploring more about the role of edge computing in IoT and leveraging its transformative potential? Then this blog is for you.
In this blog, we’re going to pull back the curtain on how edge computing in IoT app development is more than just an upgrade. It’s a complete rewrite of the rules. We’ll look at what it is, why it’s a massive win for your apps, and how it’s already making waves in real-world businesses across industries.
As IoT connections are set to soar to 40.6 billion by 2034, it’s time to future-proof your business with edge computing.
Understanding the Role of Edge Computing in IoT App Development
To understand the role of edge computing in IoT, it helps to know what edge computing is. At its core, edge computing means processing data closer to the source where it’s generated. This could be a sensor, a camera, or any device that collects data for an IoT application. Rather than sending all the data to a cloud server to be processed, it’s analyzed on local devices or edge nodes.
This differs from traditional cloud computing for IoT, where data is sent to remote servers for processing. With edge computing for IoT, the idea is simple: the closer you are to the source of the data, the faster you can act on it. By processing this data on the edge devices themselves or at nearby nodes, businesses can reduce latency, improve performance, and increase the overall efficiency of their IoT systems.
Edge vs. Cloud: A Tale of Two Libraries
The best way to get your head around the edge is to see it side-by-side with the cloud.
- Cloud Computing: Imagine the cloud is a massive, central national library. It’s incredible. It has every book imaginable. But if you live in a small town and need to check a fact, you have to send a courier all the way there and wait for them to come back. For deep research, it’s unbeatable. For a quick answer? Not so much. That travel time is latency.
- Edge Computing: Now, imagine that the factory has its own technical reference room on-site. This room contains all the essential manuals, schematics, and operational data needed for 95% of daily tasks. The staff can get answers instantly. They only need to contact the central research library for large-scale historical analysis or to archive their findings. That on-site reference room is the edge. It’s fast, efficient, and keeps the main lines of communication to the central library clear for strategic data.
Here is a brief table outlining the key differences between cloud and edge computing:
| Feature | Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Analogy | A massive, central national library. | A local factory’s technical reference room. |
| Data Processing Location | Centralized, distant from the user/device. | Local, closer to the user/device. |
| Speed (Latency) | High latency due to data needing to travel to and from the cloud. | Low latency, with instant access to data on-site. |
| Efficiency | Best for deep research and large-scale data analysis. | Best for real-time, daily operational tasks. |
| Data Handling | Processes large volumes of data and stores everything. | Handles the majority of data locally, sending only relevant information to the cloud. |
| Communication | Requires constant communication with the cloud for even small queries. | Only communicates with the cloud for big data analysis or archiving. |
| Use Case | Ideal for deep analysis, historical data, and large data storage. | Ideal for quick responses, real-time operations, and reducing reliance on the cloud. |
How Edge Computing Architecture Powers IoT
To truly unlock the benefits of edge computing in IoT, it helps to understand how the pieces fit together. This distributed setup is the heart of the edge computing architecture in IoT. It typically creates three interconnected tiers of operation:
- The Things (Your Devices): This is where data originates with the billions of sensors, cameras, and machines that interact with the physical world.
- The Edge (The Local Brains): This is the local library branch. It could be a small, rugged server on a factory floor, a smart gateway in your office, or even a powerful chip inside the device itself. This is where the immediate thinking happens.
- The Cloud (The Central HQ): The cloud doesn’t go away; its job just gets smarter. It’s where you send the important summaries for long-term storage and big-picture analysis. It’s the brain trust, not the mailroom.
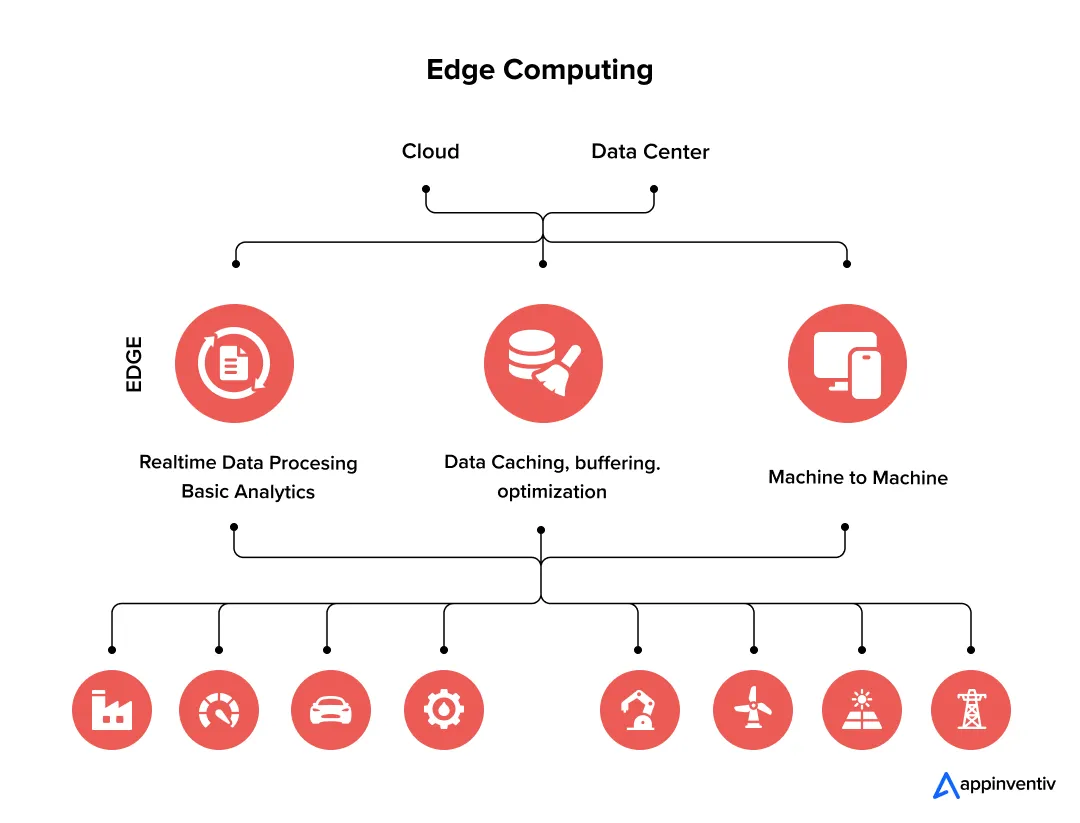
This powerful edge computing architecture in IoT delivers a hybrid solution: the instant reflexes of local processing and the heavyweight analytical power of the cloud.
Also Read: How To Make Your IoT Project Successful?
Different Types of Edge IoT Devices
In the context of edge computing, the devices that collect and process data are just as important as the infrastructure itself. Though the official list of types of edge IoT devices is always growing, here are some examples of edge IoT devices that play a crucial role in the ecosystem:
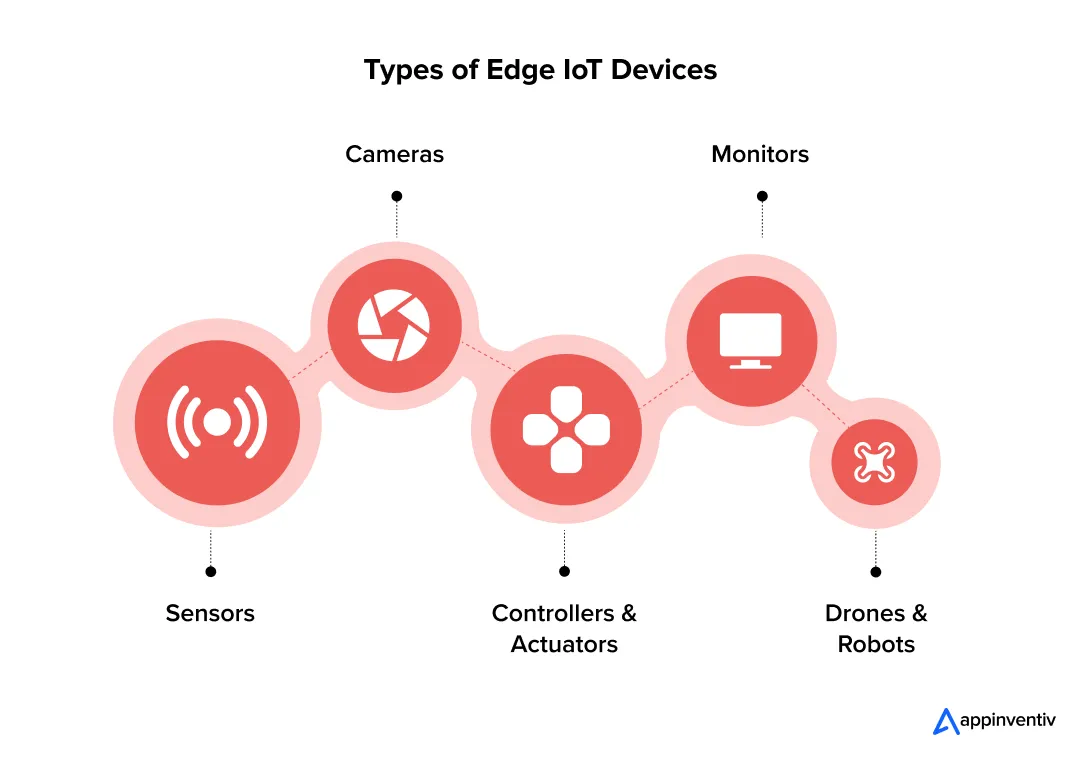
These are the digital nerves of an operation. They feel critical things like temperature, motion, and pressure, and turn them into data. An edge-powered sensor doesn’t just say, “It’s 102 degrees.” It says, “It’s 102 degrees, which is above the safety limit, so I’m triggering the local cooling system right now.”
Cameras
A modern camera is a data firehose. Trying to stream 4K video to the cloud 24/7 is a great way to bankrupt your company on bandwidth costs. An edge camera is smarter. It watches the feed itself and only bothers to send an alert when it spots something genuinely important, like a person in a restricted area.
Monitors
These are the faces of the edge, giving humans a real-time window into what’s happening. A monitor on a piece of heavy machinery can show an operator live performance stats, crunched by an edge server sitting five feet away, not from a data center five states away.
Controllers & Actuators
These are the hands. They get instructions and make something happen in the real world, like flip a switch, turn a valve, or lock a door. With edge, the command comes from the local node, so the action is immediate and reliable.
Drones & Robots
These aren’t just devices; they’re mobile edge platforms. An IoT and AI powered drone flying over a farm can analyze crop health imagery as it flies, making on-the-spot decisions about where to spray fertilizer, all without needing to land and upload massive files.
Together, these devices are the foundation of a more responsive world, all thanks to the powerful combination of IoT and edge computing.
The Edge Advantage: Why Your IoT Application Demands This Upgrade
Moving to an edge model isn’t just swapping one technology for another. It’s a strategic move that delivers some serious, tangible perks. The benefits of edge computing for IoT app performance are huge, hitting everything from your app’s responsiveness to your company’s bank account.
Reduced Latency
In the world of IoT, lag isn’t just annoying; it can be downright dangerous. That delay, or latency, can make or break an application. By putting the processing power right where the data is, edge computing cuts out the long, slow trip to the cloud. We’re talking about shrinking response times from seconds to mere milliseconds. For an industrial robot, a remote surgery tool, or a self-driving car, that’s everything.
Improved Bandwidth Efficiency
A single smart factory can generate terabytes of data every day. Transmitting all of that raw information to the cloud can quickly burn through cash and choke your network. Edge computing acts as an intelligent filter at the source. It analyzes the data flood locally, and transmits only valuable, summarized insights. This dramatically reduces bandwidth consumption and the associated operational costs.
Also Read: How Interconnection Bandwidth Enhances App Delivery
Real-Time Data Processing
The true value of data diminishes over time. The ability to analyze it the moment it is created unlocks profound operational advantages. It’s the difference between a report that tells you a machine failed yesterday and an alert that tells you it will likely fail in the next hour. This is the core value proposition of the role of edge computing in modern IoT solutions: it closes the gap between data collection and actionable intelligence.
Offline Functionality and Uptime
What is the contingency plan for your smart facility when its internet connection is severed? For cloud-dependent systems, the answer is often a complete shutdown. Edge computing for IoT, however, provides inherent resilience. Since the core logic and decision-making can happen locally, your critical operations can keep running even when the cloud is out of reach. This level of operational continuity is non-negotiable for any mission-critical system.
Cost Reduction
Yes, there’s an upfront cost to edge hardware. But the long-term savings are often staggering. By reducing the need for constant cloud processing and minimizing data transfers, edge computing in IoT can lower operational costs for businesses. They don’t have to worry as much about cloud storage fees, data transfer costs, or maintaining powerful cloud servers.
Security & Reliability
Every piece of data you send to the cloud is a potential target of cyber theft. Sending sensitive information from thousands of devices creates a huge surface for attackers to poke at. By processing data at the edge, you keep your most valuable information, be it patient health records or secret manufacturing formulas, off the open road. It’s a fundamentally more secure way to design your system.
In short and simple terms, the benefits of edge computing in IoT app development are too compelling to ignore: the speed, the cost savings, the reliability, and the security. They add up to a massive competitive advantage.
Edge Computing and IoT Use Cases in Different Industries
The fusion of IoT and edge computing is not a future-state vision; it is a present-day reality that is actively creating value. These Edge Computing and IoT Use Cases show how this tech is solving real problems in different sectors.

Smart Cities: From Gridlock to Intelligent Flow
IoT-driven Smart cities are becoming living organisms of data. Edge computing is the nervous system that lets them react and adapt.
- Intelligent Traffic Flows: Instead of relying on static timers, edge nodes hooked up to traffic cameras can analyze the flow of cars and pedestrians in real time. This allows traffic signals to adapt dynamically to clear congestion or create a “green wave” for an approaching ambulance.
- Smarter Public Safety: An AI-powered camera in a subway station can identify an unattended bag and instantly alert security, without a human having to watch thousands of hours of boring footage. The analysis happens right there, on the camera.
Healthcare: Bringing the Hospital Home
In medicine, speed intervention can mean life or death situations. Edge computing is making high-tech patient care possible that extends beyond the hospital walls
- Proactive Health Monitoring: Imagine a wearable sensor for a cardiac patient. Instead of just streaming raw heart rate data, an edge device in the home analyzes the patterns. It can detect the subtle signs of an impending cardiac event and alert caregivers before it happens, all while keeping the patient’s private health data securely inside their own home.
- Surgical Robots: Surgical robotics enhanced with edge computing provides surgeons with real-time feedback and precision control that wouldn’t be possible with cloud-dependent systems. The microsecond-level responsiveness required for delicate procedures demands local processing capabilities that only edge computing can deliver.
Manufacturing: Welcome to Industry 5.0
The modern factory is a playground for edge computing for IoT applications, where real-time data processing enables faster decision-making, improved efficiency, and reduced downtime.
- Machines That Predict Their Own Future: Sensors on a giant press can “listen” for tiny vibrations that signal a bearing is about to fail. An edge gateway right on the factory floor crunches this data, flags the issue, and schedules maintenance, preventing a costly, catastrophic breakdown.
- Flawless Quality Control: A high-speed camera powered by edge AI can spot a microscopic defect on a product whizzing by on a conveyor belt. This feat is too fast for the human eye and too data-intensive for a slow cloud connection.
Also Read: IoT in Manufacturing: Ley Trends & innovations
Retail: The Revenge of Brick-and-Mortar
Physical retail stores are using the edge to create experiences to fight back against eCommerce.
- Stores That Understand You: In-store sensors and cameras can figure out which displays are popular and where the bottlenecks are. Store managers get a live dashboard, powered by local processing, that helps them optimize the layout in real time.
- The Perfect, Spontaneous Offer: By connecting this data to a loyalty app, a store’s edge system can see the consumers lingering in the shoe department and instantly ping their phone with a 15% off coupon for that exact pair.
Finance: Securing and Speeding Up Transactions
Even the finance industry is leveraging edge computing for fraud detection, risk assessment, and customer authentication.
- Fraud Detection: ATMs and point-of-sale systems can use edge computing to run complex fraud detection algorithms locally. This allows them to identify and flag suspicious transactions in milliseconds, without the delay of querying a central cloud server, enhancing security for consumers.
- Customer Authentication: Branch automation systems utilize edge computing for customer identification, service personalization, and security monitoring. This creates efficient banking experiences while maintaining strict security protocols.
These Use Cases for Edge Computing in IoT are just scratching the surface. As the tech gets better and cheaper, the possibilities are endless.
Also Read: IoT App Development Costs: Guide to Budgeting in 2025
Real World Examples of Companies Using Edge Computing in the IoT Market
It’s one thing to talk about potential; it’s another to see it in action. Exploring how leading companies are implementing edge solutions truly highlights their power. These Examples of Edge Computing in IoT showcase the practical and profitable application of this technology.
John Deere
The agricultural giant has transformed farming with its autonomous tractors and combines. These vehicles are packed with sensors and cameras that generate over a gigabyte of data per second. It’s completely impractical to send that to the cloud from a field with spotty connectivity.
Instead, the vehicles use powerful onboard edge computers to process image data in real-time, distinguishing crops from weeds and precisely controlling sprayers. This is a perfect example of edge computing in IoT delivering real-world value.
Amazon Go
Amazon’s cashierless retail stores are a masterclass in edge computing. A complex web of cameras and sensors tracks every item a shopper picks up or puts back. This massive amount of data is processed by on-premise servers (the edge) within the store itself. This local processing is what enables the seamless “just walk out” experience; waiting for cloud confirmation for every item would create an impossibly long delay.
NVIDIA
While known for GPUs, NVIDIA is a major player in the edge AI space. Their Metropolis platform is used in smart cities and retail environments. It allows cameras to perform complex AI tasks like object tracking and behavior analysis right on the device.
For example, a city can use Metropolis-powered cameras to identify open parking spaces, or a retailer can analyze which displays attract the most attention, all processed at the edge for instant results.
These Real-World Applications of edge computing in IoT prove this isn’t some far-off trend. It’s happening now, and it’s creating real value.
Build faster, smarter, and more secure IoT applications with edge computing today.
Challenges of Implementing Edge Computing for IoT & How to Overcome Them
While the payoff is huge, there are some common challenges in integrating edge computing with IoT. The good news? For every barrier, there’s a smart path forward. Understanding these obstacles and their solutions is crucial for planning effective edge computing strategies.
Scalability: Managing Distributed Infrastructure
Challenge: Managing a few servers in a data center is one thing. But how do you manage, update, and monitor thousands or even millions of devices scattered all over the world? It can feel like herding cats.
The Path Forward: The answer is a solid device management platform. Think of it as a central remote control for your entire edge army. Tools like AWS IoT Greengrass or Microsoft Azure IoT Edge, along with container tech like Kubernetes, are built for this. They let you manage your fleet from one place, making IoT app scalability using edge computing a manageable reality.
Security: Protecting Distributed Data and Systems
Challenge: Every single device at the edge is a tiny door into your network. Securing thousands of these doors is a whole lot harder than just fortifying one big castle (the cloud).
- The Path Forward: Adopt a “zero-trust” approach. Assume nothing is safe. Every device, user, and app needs to prove who they are, every single time. End-to-end encryption is a must. And using hardware-level security, like special security chips on your devices, adds a much-needed layer of armor.
Integration: Harmonizing Existing Infrastructure
Challenge: Most enterprises aren’t starting from scratch. They have existing cloud infrastructure, legacy applications, and established data workflows that have been around for years. How do you plug in a new edge system without breaking everything?
The Path Forward: It’s all about building bridges, not walls. Use open standards and well-documented APIs to let your old and new systems talk to each other. You can start with a hybrid model: let the edge handle the fast, real-time stuff, and then feed the important summaries into the cloud systems you already have. This kind of thoughtful integration is key to achieving IoT app scalability using edge computing without the headaches.
Cost Considerations: Upfront vs. Long-Term Savings
Challenge: Edge hardware deployment hits you with bigger upfront costs than sticking with cloud-only setups. You’re buying devices, gateways, and local servers that need real money invested.
The Path Forward: Keep your eyes on the long game, i.e., reduced bandwidth bills, smaller cloud storage costs, and fewer expensive outages. Most companies discover that the operational perks and cost cuts pay back the initial investment faster than expected.
Interoperability: Making Devices Speak the Same Language
Challenge: IoT setups typically mix devices from different manufacturers, each speaking its own technical language and using different communication methods.
The Path Forward: Stick with open standards and platforms that handle multiple protocols like MQTT, CoAP, ZigBee, and Bluetooth. This approach keeps devices talking to each other smoothly and protects your investment when you expand your IoT network down the road.
The Future of IoT is at the Edge: Emerging Trends and Technologies
The synergy for IoT and edge computing is clear and accelerating. A confluence of powerful technologies is set to make this partnership even more transformative. The observation by Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella that “We are moving from a mobile-first, cloud-first world to a new world that is going to be made up of an intelligent cloud and an intelligent edge” is not just a marketing phrase; it is an accurate description of the next era of computing architecture. Let’s see how:
AI and Machine Learning at the Edge
AI and machine learning will soon operate completely on edge devices, handling complex analysis and making autonomous decisions without cloud connections. Tomorrow’s edge AI will drive advanced computer vision for instant object recognition, smart natural language processing for conversational controls, and predictive analytics that catch equipment problems early.
Edge devices are shifting from simple data collectors to intelligent systems that learn and improve continuously. Next-gen machine learning models will train right on edge hardware, learning from real-world usage while keeping data private and cutting bandwidth needs.
Also Read: AI and IoT in business driving innovation across industries
5G Network Integration
5G networks will transform edge computing through ultra-fast connections, massive IoT device support, and lightning-quick communication between edge points and cloud systems. This synergy of 5G and IoT will power breakthrough apps needing instant local processing plus seamless connectivity – think immersive AR experiences and fully autonomous robots working together.
5G network slicing will let companies build custom network segments tuned for specific IoT needs, ensuring rock-solid performance and security for critical edge deployments.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing will eventually transform edge processing, handling incredibly complex calculations that regular computers can’t touch. Future quantum edge apps will tackle advanced encryption, multi-dimensional optimization challenges, and real-time simulations that tap into quantum computing’s unique strengths.
The integration of AI, ML, 5G, and quantum computing will create seamless digital experiences that respond instantaneously to user needs and environmental changes.
Partner with Appinventiv: Your Next Move in the Edge-IoT Revolution
The debate is over. The question is no longer if you should be thinking about the edge, but what your edge strategy is going to be. The old cloud-only model is already groaning under the weight of a world that demands instant, reliable, and secure data processing. The future clearly lies in edge computing in IoT app development.
Making this leap requires a trusted tech partner who gets it, someone who knows the nitty-gritty of technical details and can provide strategic guidance. This is where we come in. At Appinventiv, we bring 10+ years of industry experience to implement reliable edge computing solutions, ensuring that your IoT systems run at peak performance while overcoming common integration challenges.
As a leading IoT app development company, we have successfully guided numerous organizations through edge computing deployments. Our team of 1600+ tech experts brings a deep understanding of both IoT connectivity technologies and edge computing platforms, ensuring that your implementation achieves optimal performance while maintaining scalability and security.
From initial strategy development through deployment and ongoing optimization, we offer comprehensive support at every step. Our proven track record speaks for itself, helping businesses realize their vision with real-world, impactful results.
The future belongs to organizations that can process data instantly, respond to changes immediately, and deliver experiences that exceed user expectations. Edge computing for IoT provides the foundation for this future, and Appinventiv provides the expertise to build upon that foundation.
Whether you’re planning your first IoT development project or looking to enhance existing systems with edge computing capabilities, our team is ready to help you navigate the complexities and maximize the opportunities. The edge computing revolution is here; let us help you lead it with confidence.
FAQs
Q. What is edge computing in IoT?
A. Edge computing in IoT app development refers to the practice of processing data locally on or near IoT devices rather than sending all data to centralized cloud servers. This approach brings computational power closer to data sources, enabling real-time processing, reduced latency, and improved application performance while maintaining connectivity to cloud infrastructure for advanced analytics and storage.
Q. What is the purpose of edge computing in IoT?
A. The primary purpose of edge computing in IoT is to overcome the limitations of traditional cloud-based architectures by reducing latency, improving bandwidth efficiency, and enabling real-time decision-making. This technology combination supports mission-critical applications that require instant responses, reduces network congestion, and provides reliable operation even during connectivity interruptions.
Q. How does Edge computing enhance IoT performance?
A. Edge computing supercharges IoT performance in several key ways:
- Speed boost: Responses happen almost instantly since you’re not waiting for data to travel to distant servers and back
- Cost savings: You spend way less on bandwidth and cloud storage by only sending the truly important stuff
- Better reliability: Systems keep working locally even when the internet goes down
- Enhanced security: Less sensitive data traveling means fewer chances for hackers to grab it
Q. How is artificial intelligence used with IoT in edge technology?
A. AI makes edge computing for IoT much smarter by handling intelligent data analysis, spotting patterns, and making automated decisions right on the device. AI algorithms running on edge hardware can examine sensor readings instantly, predict when equipment might fail, tune system performance, and adjust to changing situations without needing cloud connections. This creates truly independent systems that learn and get better over time.
Q. What are the security benefits of edge computing in IoT applications?
A. Edge computing delivers multiple security wins for IoT setups, such as edge computing in IoT:
- Reduces data transmission across networks, limiting attack surface exposure
- Keeps sensitive information processed locally rather than sent to remote servers
- Creates a distributed architecture that eliminates single points of failure
- Enables real-time threat detection and response directly at the device level
- Provides encrypted communication channels between edge devices and cloud systems
- Minimizes exposure to network-based security vulnerabilities and breaches
- Enhances data privacy through localized processing and storage capabilities
- Delivers faster security responses without dependencies on cloud connectivity
Q. How to implement edge computing in IoT app development?
A. Here’s a step-by-step process to guide your implementation journey:
- Define Your Use Case: Map out what your application actually needs in real-time and how data moves through your system. Which specific headaches will edge computing fix: slow responses, expensive bandwidth, or data security risks?
- Select the Right Edge Devices: Match your hardware choices to actual requirements for processing power, network connections, and operating environments. Basic sensors handle simple tasks, while gateways manage moderate workloads, and edge servers tackle heavy computation.
- Plan Local Data Processing: Split your data smartly between what gets handled locally versus what travels to cloud servers. Time-sensitive stuff stays at the edge, while detailed analysis can happen remotely. Add local AI models when instant decisions matter.
- Ensure Security: Lock down your edge nodes with proper device authentication, strong encryption for data movement and storage, plus scheduled firmware updates to patch vulnerabilities.
- Design for Scalability: Build management capabilities from day one using device management platforms and container tech like Kubernetes. This lets you handle distributed edge networks without manual headaches.
- Monitor and Maintain: Set up monitoring dashboards and automated diagnostics so you catch problems before users notice them. Remote troubleshooting becomes essential when devices sit in hard-to-reach locations.
This approach builds edge-powered IoT solutions that actually work reliably and grow with your business needs.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
IoT in Wearables: An Enterprise Guide to Architecture, Integration, and Scalable Deployment
Key Takeaways IoT wearables are shifting from pilot projects to enterprise infrastructure across the healthcare, industrial, and logistics sectors. Secure integration, compliance readiness, and data architecture determine wearable success more than device hardware alone. Continuous wearable data enables predictive healthcare, workforce safety optimization, and new enterprise operational intelligence capabilities. AI-driven analytics are transforming wearable data…
IoT in Mining: Modernizing Operations for Enterprise Efficiency and Safety
Key takeaways: The Internet of Things in mining turns scattered operational signals into live, decision-ready visibility across fleets, fixed plants, people, and the environment. The biggest wins usually show up first in uptime, then in safety response, and finally in energy and process stability. “More data” does not automatically mean better performance. Value comes when…

IoT in Banking Industry: Use Cases, Examples, ROI
Key takeaways: IoT in banking creates real value only when it is treated as a software and integration problem, not a hardware initiative. Security, governance, and audit readiness determine whether IoT programs scale or quietly stall in regulated environments. IoT implementation in banking typically ranges from $40,000 to $600,000+, with cost driven more by integration…