- What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
- Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
- By Deployment
- By Distribution
- What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
- Lowers Healthcare Cost
- Easy Interoperability
- Ownership of Patients' Data
- Improves Collaboration
- Reinforces Security
- Facilitates Regulatory Compliance
- Increases Disaster Recovery Capabilities
- Supports Advanced Analytical Capabilities
- Promotes Environmental Sustainability
- Cloud Computing for Patient Experiences: Managing Patient Care, Not Just Data
- Personalized Patient Interactions
- Enhanced Patient Monitoring
- Streamlined Patient Care Coordination
- Improved Access to Healthcare Services
- Real-World Use Cases of Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry
- Telemedicine
- Medical Imaging
- Health Information Exchange
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
- Research and Development
- Challenges of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards
- Integration with Existing IT Infrastructure
- Downtime and Service Disruptions
- Managing Costs
- Skill Gaps and Training Needs
- Future of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
- Increased Adoption Across the Board
- Enhanced Data Analytics Capabilities
- Greater Focus on Personalized Medicine
- Improved Interoperability and Collaboration
- Integration with IoT and Wearable Devices
- Edge Computing for Real-Time Processing
- Expansion of IoT and IoMT
- How Can Appinventiv Help You Adopt Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
- FAQs
- Q. How much does it cost to avail cloud solutions for the healthcare industry?
- Q. How does cloud computing help with data sharing and interoperability in healthcare?
- Q. What are the risks of using cloud computing in healthcare?
- Q. Which cloud models are commonly used in healthcare?
Key Takeaways
- Healthcare teams can store and use patient data online instead of keeping it all on hospital computers.
- Using online data tools can lower costs and avoid big investments in hardware.
- Patients can get care from home, especially when doctors use connected devices and online services.
- It’s still important to keep patient information safe, follow rules, connect old and new systems, and train staff.
- In the future, more clinics will use these tools. Big data, wearable devices, and even faster processing will make care more personal and more efficient.
Imagine a scenario where a multi-hospital system faces the daunting challenge of maintaining the efficiency and reliability of its IT infrastructure amidst the increasing data demands and regulatory pressures. Each hospital in the system manages thousands of patient records, imaging data, and complex scheduling details.
The traditional IT setup struggles with these demands, leading to delays and potential errors that could affect patient care and operational efficiency. Now, entering to the rescue this issue is cloud computing, acting as a transformative solution that not only addresses these challenges but also streamlines communications across the network.
With cloud computing, this healthcare network can centralize its data management and allow seamless access to critical information across all facilities, ensuring that every unit operates with up-to-date information. This shift enhances patient care by providing consistent and quick access to patient histories and also reduces the redundancy and potential for errors that often come with decentralized data management.
Moreover, the scalability offered by leveraging cloud computing in healthcare allows businesses to adjust their data storage needs based on current demands without the need for significant upfront capital investment in physical infrastructure. This scalability is crucial in handling fluctuating data volumes, such as during a health crisis when rapid and expansive data processing becomes vital.
Given all this, the question for healthcare business leaders isn’t whether to adopt cloud computing but rather how quickly and effectively they can integrate it into their existing systems. The transition to cloud computing requires a strategic investment in technology that not only supports current operational needs but also anticipates future demands. For healthcare businesses, this means partnering with cloud providers who understand the nuances of healthcare regulations and can offer tailored solutions that enhance data interoperability across various health systems.
Investing in cloud computing enables healthcare businesses to embrace digital transformation and maintain agility in this evolving ecosystem.This move facilitates the adoption of cloud-based healthcare solutions like telemedicine, real-time data analytics, and patient-centered technologies, all of which are crucial for delivering top-notch healthcare.
This blog will explore how cloud computing is not just an option but a necessity for modern healthcare businesses, detailing its role in operational excellence, compliance adherence, and technological advancements in patient care. So, let’s begin.
Let’s step into the future of healthcare with cloud computing and transform your patient outcomes today!
What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
Cloud computing for the healthcare industry is primarily about implementing remote server access via the Internet to store, manage, and process medical data. This process provides a flexible solution for healthcare stakeholders to access servers where the data is hosted remotely. The remote accessibility of healthcare data breaks down the location barriers to accessing medical services.
Cloud computing for healthcare comes with two-fold applications for patients and healthcare providers, enabling them to use a massive amount of data securely from anywhere, anytime, improve patient care, streamline operations, and automate various processes.
For medical institutions, virtualization in cloud computing helps lower operational spend while enabling them to deliver high-quality and personalized care. The patients, conversely, are getting accustomed to the instant delivery of healthcare services.
As the healthcare sector faces growing demands for data management, cloud computing steps in as a crucial solution. According to McKinsey, industries like healthcare are set to gain significant value from cloud technology, with potential global gains of up to $3 trillion by 2030.
Furthermore, the market for healthcare cloud computing is expected to skyrocket from $58.93 billion in 2024 to $170.82 billion by 2030. This rapid growth highlights the critical need for robust data handling solutions, which cloud computing provides through improved storage, management, and processing capabilities.
Thus, healthcare businesses looking to streamline operations and enhance patient care should consider investing in cloud computing now. This move is not just about keeping up with current trends but also about adapting to the digital age where quick, reliable access to healthcare data is essential.
Cloud computing offers a scalable solution that can manage growing data needs while reducing costs by reducing the need for extensive physical infrastructure. With the healthcare cloud computing market expected to witness substantial growth, investing now means setting up for future success, ensuring businesses can expand and adapt without major new investments in physical resources.
Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing in healthcare is categorized into two main models: Deployment and Distribution. Each offers distinct features and benefits tailored to the specific needs of healthcare organizations. Let’s look into the various types of cloud computing in healthcare in detail below.
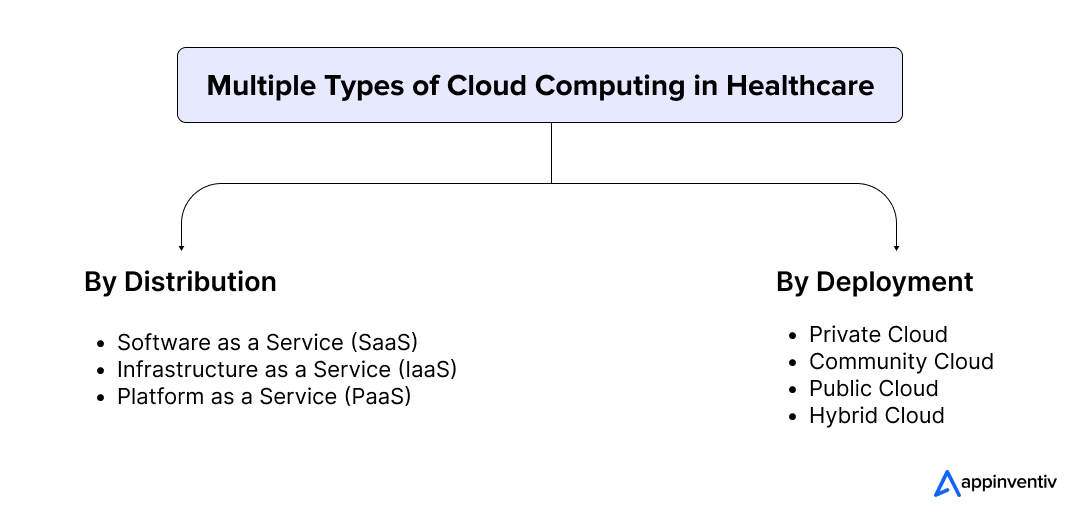
By Deployment
Private Cloud
In a private cloud model, a single healthcare organization exclusively uses the cloud infrastructure. This setup provides enhanced control over data and resources, ensuring higher security levels and customization. It’s particularly suitable for large healthcare systems that require stringent data control and privacy.
Community Cloud
The community cloud involves a shared infrastructure used by a group of healthcare organizations with common concerns and requirements. This model helps reduce costs through shared resources while offering a certain level of privacy and security better than public clouds.
Public Cloud
Third-party cloud service providers operate public clouds and are available to any organization that wants to use or purchase them. This model is cost-effective and offers high scalability, making it ideal for healthcare providers needing extensive computing resources without heavy investments in infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines private, community, and public clouds, allowing healthcare organizations to manage their cloud usage based on specific needs. This model offers flexibility, scalability, and security by enabling data and applications to move between private and public environments as required.
By Distribution
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS allows healthcare providers to use applications hosted online by a third-party vendor, eliminating the need for installation or maintenance. This model is ideal for managing Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and patient systems that require regular updates, simplifying technical operations, and ensuring security.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides essential computing resources like servers, storage, and networking from a third-party provider, while the healthcare organization manages the software and data. This model offers flexibility and control over the infrastructure without the heavy investment in physical hardware.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides healthcare organizations with a complete platform that includes tools, infrastructure, and support to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure. It is useful for developing bespoke applications like healthcare analytics and patient engagement.
Also Read: The key differences between IaaS and PaaS
What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
Cloud computing for healthcare, with its on-demand availability, high-data accessibility, and internet-based services, has transformed the entire healthcare industry. It is why tech-savvy medical professionals increasingly embrace cloud technology in healthcare for all its benefits to address patients’ and business needs effectively. Here are some benefits of cloud computing in healthcare.
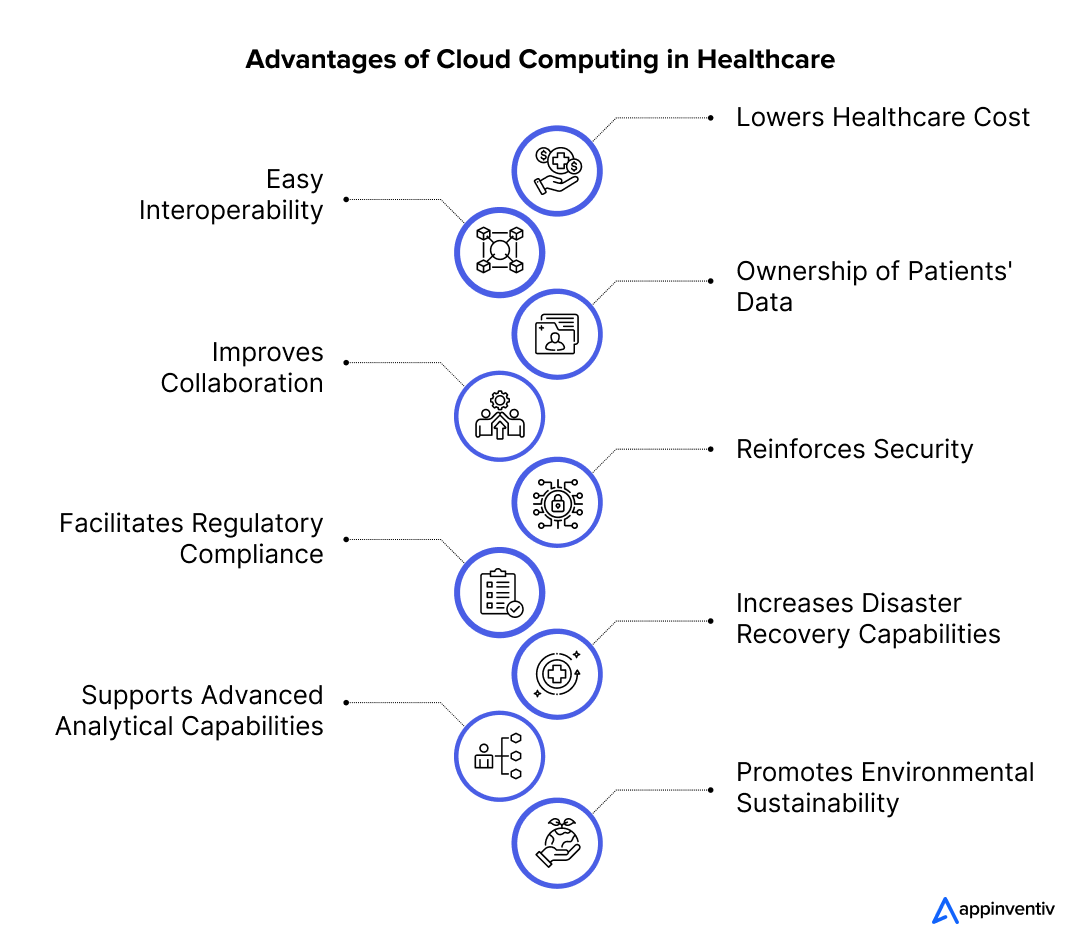
Lowers Healthcare Cost
The primary benefits of cloud computing in healthcare are the real-time availability of resources such as data storage and computing power. Also, there are no upfront charges linked with the healthcare cloud adoption; they will only have to pay for the resources they use.
Furthermore, cloud computing in healthcare provides an optimum environment for scaling without burning a hole in the pocket. With the patient’s data flowing in from several sources like EMRs, healthcare apps, and wearables….., a cloud solution for healthcare makes it possible to scale the storage while keeping the costs low.
Easy Interoperability
One of the major benefits that highlights the importance of cloud computing in healthcare is easy interoperability. It focuses on establishing data integrations through the entire healthcare system, irrespective of the origin or where the data is stored. It makes patients’ data available for easy distribution and for getting insights to aid healthcare delivery. Also, cloud computing for healthcare enables medical professionals to access a varied range of patient data, share it with key stakeholders, and deliver timely protocols.
Ownership of Patients’ Data
The applications of cloud computing in the healthcare industry democratize data and empower patients to control their health. It facilitates patients’ participation in making crucial decisions related to their health, working as a tool to better patient engagement and education. Also, with cloud-based healthcare solutions, medical data can be archived and retrieved easily. And with an increase in the system uptime, the data redundancy is reduced to a huge extent, and data recovery also becomes easier.
Improves Collaboration
Healthcare cloud adoption significantly boosts collaboration between healthcare stakeholders, providers, and patients. By saving the Electronic Health Records in the cloud, patients no longer need to carry their medical records to every doctor visit. The doctors can easily view the information, see the outcome of previous interactions, and even share information with one another in real-time. This, in turn, enables them to provide more personalized and better treatment.
Also Read: EMR Vs. EHR Development – What Should You Choose for Your Healthcare Business?
Reinforces Security
Enhanced security is one of the most important benefits of healthcare cloud computing. The healthcare industry deals with a massive amount of data daily, making it a focal point of attraction to malicious attackers, which increases the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. With the applications of cloud computing in healthcare, medical institutions and healthcare providers can ensure failsafe cybersecurity as these applications can proactively inform you about suspicious attempts.
Facilitates Regulatory Compliance
Cloud computing makes it easier for healthcare organizations to comply with complex regulations. Cloud providers often have robust systems and processes in place that are specifically designed to meet standards such as HIPAA in the U.S. or GDPR in Europe. By using these cloud services for healthcare, providers can ensure that they meet the required compliance benchmarks with less effort and lower risk of penalties.
Increases Disaster Recovery Capabilities
In a natural disaster or system failure, storing data in the cloud ensures that it remains safe and can be quickly restored. Cloud technology in healthcare software or apps provides organizations with robust disaster recovery plans, which are essential for maintaining continuity of care and protecting sensitive patient information against unexpected disruptions.
Supports Advanced Analytical Capabilities
Cloud computing can enhance healthcare analytics by providing the computational power needed to process large datasets quickly and efficiently. This enables healthcare providers to utilize advanced analytical tools and techniques like predictive analytics and machine learning to derive actionable insights from their data. These insights can lead to better patient outcomes, more effective treatment plans, and optimize operational efficiencies.
Promotes Environmental Sustainability
By reducing the need for physical data centers and the associated energy consumption, cloud computing can help healthcare organizations reduce their carbon footprint. This shift supports sustainability initiatives and aligns with global efforts to reduce energy usage and promote environmental responsibility in the healthcare sector.
Cloud Computing for Patient Experiences: Managing Patient Care, Not Just Data
Cloud computing transforms patient care by enabling more than just efficient data management and enhancing the overall patient experience. Let’s explore how cloud technology is being used to directly improve patient interactions, care delivery, and outcomes.
Personalized Patient Interactions
Cloud computing in the medical field allows healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient data in real-time, enabling personalized interactions. This personalized approach helps address patient concerns more effectively, leading to higher satisfaction and better patient engagement.
Enhanced Patient Monitoring
With cloud technology in healthcare, continuous monitoring of patients’ health becomes simpler and more effective, especially for those with chronic conditions. Real-time data collected from IoT devices can be analyzed instantly to provide actionable insights, alerting healthcare providers to potential health issues before they become critical.
Discover how we developed YouCOMM, a dedicated healthcare app that allows the patients to connect with hospital staff with just voice commands and head gestures
Streamlined Patient Care Coordination
Cloud computing facilitates better coordination among different healthcare professionals involved in a patient’s care. Seamless sharing of patient data across platforms ensures that all care providers have up-to-date information, which is crucial for effective treatment planning and execution.
Improved Access to Healthcare Services
Healthcare cloud computing breaks down geographical barriers by enabling telehealth services. This allows patients in remote or underserved areas to receive high-quality care from specialists without traveling.
Real-World Use Cases of Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry
Cloud computing revolutionizes the healthcare industry by offering scalable solutions that improve service delivery and operational efficiency. Here are some key applications of cloud computing in healthcare.
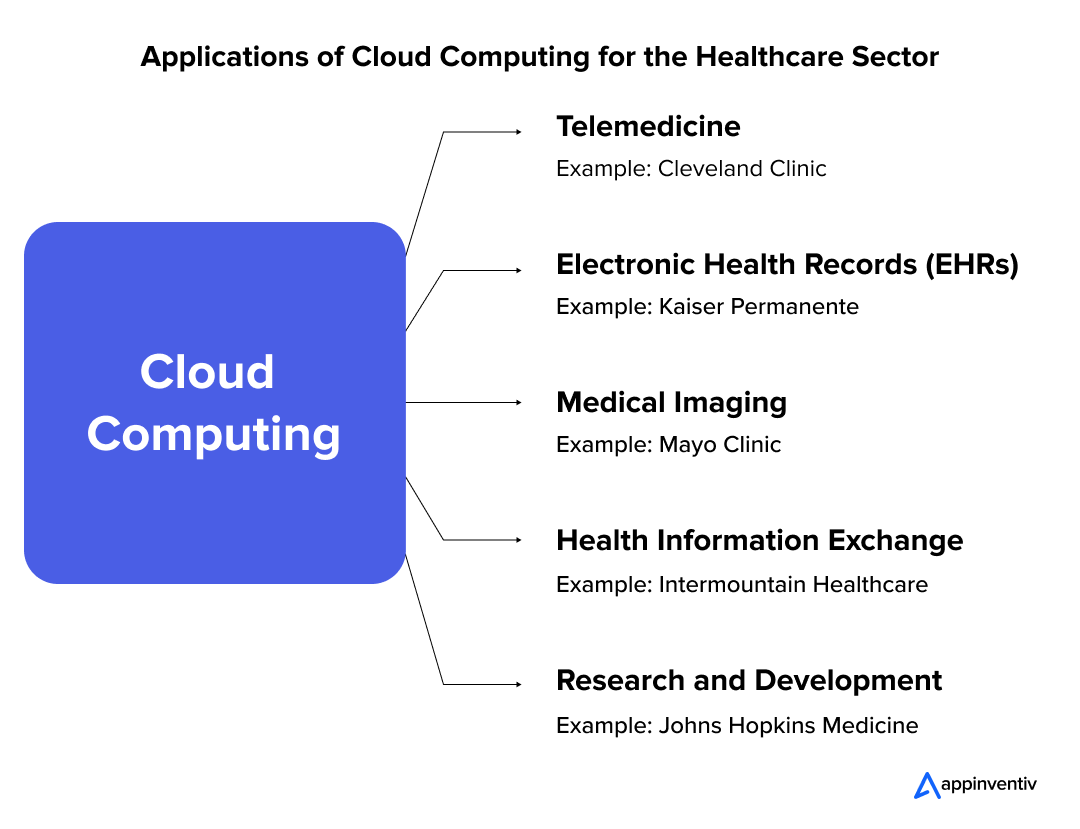
Telemedicine
Cloud computing has enabled the widespread adoption of telemedicine, allowing healthcare providers to offer remote consultations, diagnostics, and treatment. This technology uses cloud-based platforms to facilitate HD video conferencing, secure sharing of patient data, and real-time communication between patients and medical professionals. This extends the reach of healthcare services to rural areas, enhances patient convenience, and reduces the strain on traditional medical facilities.
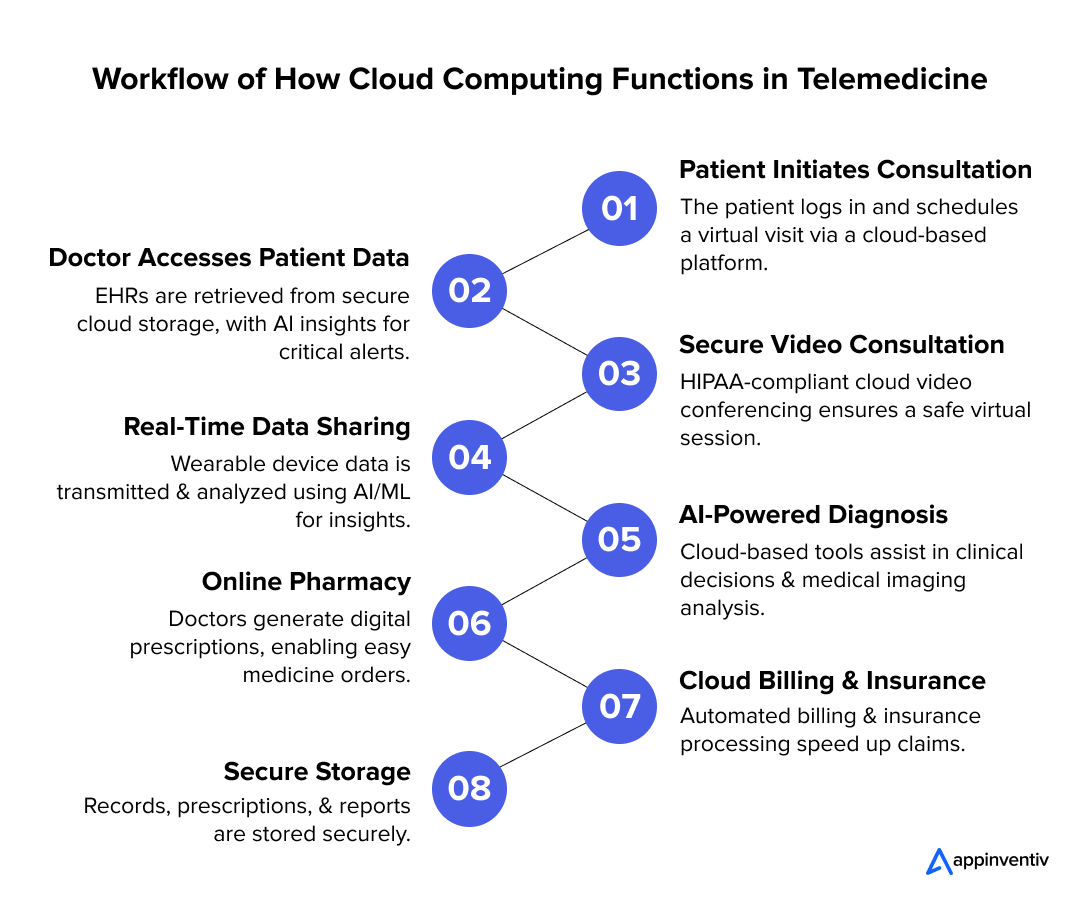
Example: Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic utilizes cloud computing to power its telemedicine services, providing patients with remote access to healthcare consultations and specialized medical advice, thereby improving patient engagement and care continuity.
Medical Imaging
Healthcare cloud computing has significantly advanced the field of medical imaging by providing powerful tools for storing, accessing, and analyzing large imaging files. Cloud-based healthcare solutions offer professionals the ability to access medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, in real-time, facilitating quicker diagnoses and treatment plans.
Example: Mayo Clinic
Uses cloud services for healthcare to manage and analyze medical imaging data, enhancing the speed and accuracy of diagnostic processes across its facilities.
Health Information Exchange
Health information exchange through the cloud enables healthcare facilities to share patient information securely and efficiently. This interoperability improves the quality of care by ensuring that all healthcare providers have access to complete and up-to-date patient information, facilitating informed decision-making, and reducing duplication of tests.
Example: Intermountain Healthcare
Intermountain Healthcare leverages cloud-based health information exchange systems to connect with other healthcare providers and share critical patient information securely, improving care coordination and patient outcomes.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Cloud-based electronic health records are transforming data management in healthcare. These systems allow for the secure storage, retrieval, and management of health records on cloud platforms, making patient data accessible to authorized healthcare providers from any location. This facilitates better coordination among different healthcare providers, leading to improved treatment outcomes and optimized patient management.
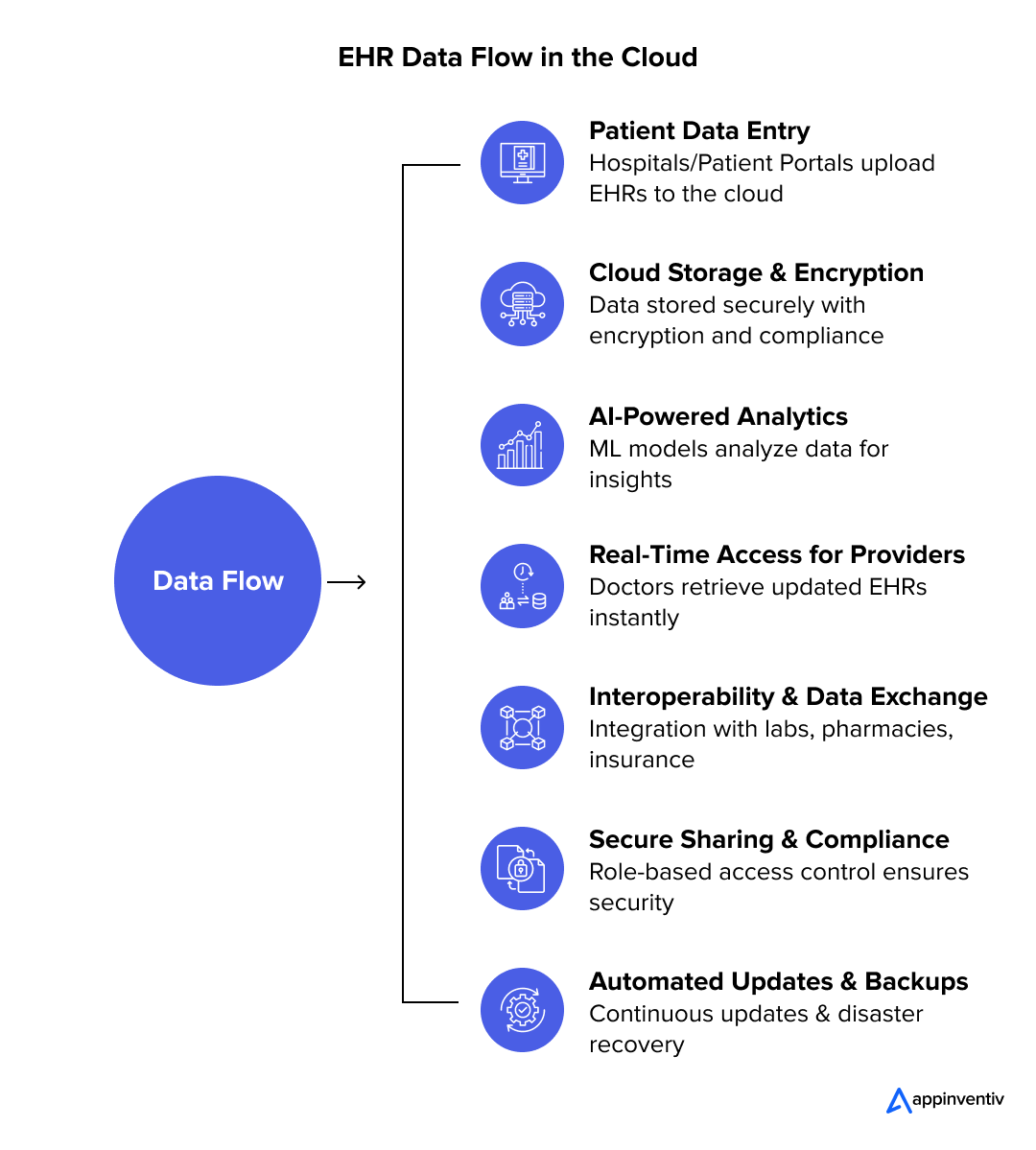
Example: Kaiser Permanente
Kaiser Permanente has integrated cloud-based EHRs across its network, enabling seamless access to patient records that help in providing coordinated and efficient care.
Research and Development
Cloud technology in healthcare supports R&D in the sector by providing a scalable environment to conduct extensive research and trials. Researchers can utilize cloud platforms to collaborate, share data, and use high-powered analytics tools to develop new treatments and drugs.
Example: Johns Hopkins Medicine
Johns Hopkins Medicine utilizes cloud computing for genomic research, allowing scientists to store and analyze vast amounts of genetic data, accelerating the development of personalized medicine strategies.
After looking into the multiple use cases and cloud computing in healthcare examples, let’s move ahead and understand the various risks of cloud computing in healthcare.
Challenges of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
While cloud computing for healthcare offers numerous advantages to businesses and patients alike, the technology also combines some significant risks and challenges. Let’s have a look at them below.
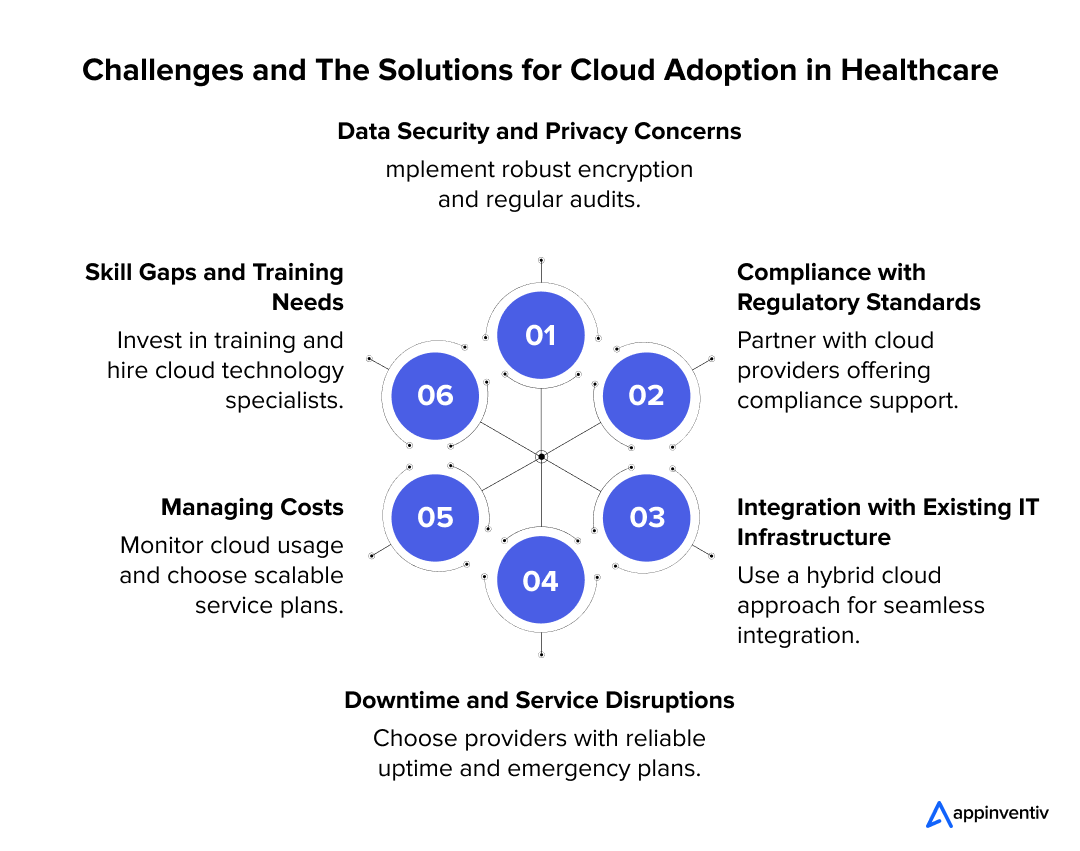
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
The handling of sensitive patient data on cloud solutions for the healthcare industry raises significant security and privacy concerns. Healthcare providers must ensure that data is protected against breaches and unauthorized access. For instance, integrating secure Medical Courier Apps can streamline the safe transport of physical medical records or specimens while maintaining strict data encryption and access controls.
Solution: Implementing robust encryption methods, regular security audits, and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA can enhance data security and build trust.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Healthcare is a heavily regulated industry, and meeting the compliance requirements for data protection standards can be complex.
Solution: Partnering with cloud providers that offer compliance support services can simplify adherence to legal requirements.
Integration with Existing IT Infrastructure
Integrating cloud solutions with existing on-premise IT infrastructure can be technically challenging and disruptive.
Solution: Employing a hybrid cloud approach allows for a gradual migration and seamless integration, minimizing operational disruption.
Downtime and Service Disruptions
Dependence on cloud services for healthcare can lead to vulnerabilities, such as downtime or service disruptions, affecting access to critical applications and data.
Solution: Choosing healthcare cloud providers with reliable uptime records and having emergency plans in place, such as redundant data storage, can mitigate these risks.
Managing Costs
Although medical cloud computing can be cost-effective, unexpected expenses such as data transfer fees and services can add up.
Solution: Careful planning and monitoring of cloud usage and costs, along with choosing scalable service plans that match the healthcare organization’s needs, can control expenditures.
Skill Gaps and Training Needs
There can be a lack of expertise among staff regarding the use of cloud technologies, which can hinder the effective adoption of cloud solutions.
Solution: Investing in training programs to enhance the cloud computing skills of existing staff, or hiring specialists, can ensure the healthcare organization maximizes the benefits of cloud technology.
Future of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
The future of cloud computing in healthcare looks promising, with technological advances and increased adoption set to transform how services are delivered. Here’s what we can expect in the coming years.
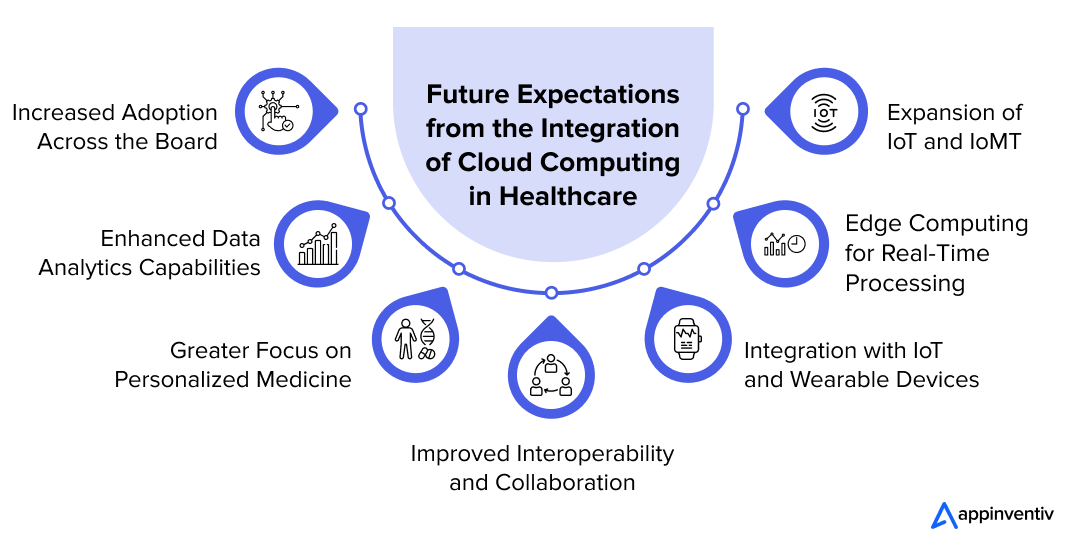
Increased Adoption Across the Board
As more healthcare organizations realize the benefits of cloud computing, its adoption is expected to grow exponentially. This will be driven by the need for more robust data management solutions and the desire to enhance patient care through more accessible and integrated health services. Over time, even smaller clinics and healthcare facilities will begin to leverage cloud solutions, making high-quality healthcare more widespread and efficient.
Enhanced Data Analytics Capabilities
With the accumulation of vast amounts of health data, medical cloud computing is bound to enhance its analytical capabilities significantly. Advanced analytics and machine learning models running on cloud platforms will provide deeper insights into patient care, disease patterns, and operational efficiency. This will improve outcomes and also empower healthcare providers to deliver predictive and preventive healthcare services.
Greater Focus on Personalized Medicine
Cloud computing will play a crucial role in the advancement of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual genetic profiles. By facilitating the storage and analysis of large genomic datasets, cloud technologies will enable faster and more accurate genetic profiling, leading to more effective and personalized treatment plans.
Improved Interoperability and Collaboration
Future cloud platforms are expected to enhance interoperability between different healthcare systems and tools. This will allow for seamless communication and data sharing among healthcare providers, insurers, and patients, improving care coordination and optimizing health outcomes.
Integration with IoT and Wearable Devices
The integration of cloud computing with IoT and wearable technology is set to increase. This combination will facilitate real-time health monitoring and data collection, providing continuous patient data to healthcare providers.
Edge Computing for Real-Time Processing
Edge computing will enhance cloud capabilities in healthcare by processing data closer to its source. This improvement drastically reduces delays and boosts the efficiency of critical applications, including telemedicine and remote surgical operations, ensuring faster and more reliable healthcare delivery.
Expansion of IoT and IoMT
The Internet of Things (IoT) and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) are set to expand significantly. A growing network of connected devices and sensors will stream health data continuously, enhancing remote patient monitoring, chronic disease management, and the effectiveness of emergency response systems.
How Can Appinventiv Help You Adopt Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
We hope this blog has made you understand the impact of cloud computing on healthcare. If you are a business looking for risk-proof cloud solutions for healthcare, now is the ideal time to partner with us. We will help you leverage the full potential of cloud computing in the form of streamlined delivery, high security, optimal performance, and reduced costs.
Being a renowned provider of healthcare mobile app development services, we have a team of 600+ cloud specialists who have successfully delivered more than 350 cloud applications for businesses across the globe. As a leading healthcare cloud-managed services provider, our experts build custom solutions around the common risks associated with 80% of healthcare cloud projects – compliance checks, data security, and chances of downtime.
Our custom range of services includes cloud consulting, cloud architecture design, cloud infrastructure configuration, cloud managed services, and code reviews.
From streamlining everyday processes to integrating innovation across the system, our healthcare cloud consulting services tackle all the industry challenges and support your business at every stage of transformation.
For instance, we recently developed Soniphi, the very first resonant frequencies-based personal wellness system that uses the cloud to provide patients with a complete well-being analysis report on their personal healthcare apps. The app’s cloud infrastructure supports early disease diagnosis, remote patient monitoring, and telehealth consultations.
Contact us now to adopt cloud computing in healthcare and overcome technical issues.
FAQs
Q. What is cloud computing in healthcare?
A. Cloud computing in healthcare refers to using remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process healthcare data rather than using local servers or personal computers. This technology enables healthcare providers to access medical records and applications anytime and anywhere, facilitating more flexible and immediate care. It supports a range of services from data storage and backup to hosting complex applications for patient management systems, telemedicine, electronic health records (EHRs), and medical imaging services.
Q. How is cloud computing used in healthcare?
A. Cloud computing is used in healthcare to streamline and enhance various operations by storing data and applications on remote servers that healthcare providers can access over the internet. This allows for efficient management of medical records, patient data, and imaging files, enabling doctors and healthcare professionals to access and share vital information quickly and securely, regardless of their location. Additionally, cloud computing supports telemedicine, which facilitates remote consultations and treatments, improving access to healthcare services, especially in underserved areas. It also enables real-time data analysis and supports the integration of AI technologies for better disease prediction, patient care personalization, and operational efficiency in healthcare facilities.
Q. How much does it cost to avail cloud solutions for the healthcare industry?
A. Businesses in the healthcare sector looking to adopt cloud computing can work with cloud consulting services, where costs generally range from $30,000 to $150,000 or more. This price variation is due to factors like the size of the required cloud infrastructure, the complexity of transferring data, compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA, and the level of ongoing support and maintenance needed. Prices are often based on customized solutions and detailed consultations to ensure that the services meet the specific operational and security requirements of healthcare providers.
Q. How does cloud computing help with data sharing and interoperability in healthcare?
A.Cloud systems store patient information in one safe, online place.
This makes it easier for hospitals, clinics, and labs to access the same files when needed.
Doctors can see updated records in real time and avoid repeating tests.
It also reduces errors because everyone works with the same information.
Overall, it helps different healthcare teams work together smoothly.
Q. What are the risks of using cloud computing in healthcare?
A. The main risk is data theft if security rules are not followed. There can also be service outages that slow down access to patient files.
Some providers may worry about losing control over where data is stored. If old systems don’t match well with cloud systems, it can cause delays. These risks can be managed with strong security, good planning, and regular checks.
Q. Which cloud models are commonly used in healthcare?
A. Healthcare teams mostly use three types of cloud models:
- Public cloud: Shared systems used by many organizations. It is good for general storage and basic services.
- Private cloud: Built only for one organization. It offers more control and fits settings that handle very sensitive data.
- Hybrid cloud: A mix of public and private models. It helps teams use both flexibility and strong control where needed.
These models help hospitals choose what works best for their data, budget, and security needs.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

How Cloud Services Accelerate Product Development for Businesses
Key takeaways: Cloud product development changes the speed, cost, and risk profile of modern software delivery. The cost of cloud product development ranges between $40,000 and $400,000 or more. Cloud platforms give you instant access to AI/ML, edge computing, and advanced analytics without dropping tons of money upfront. Appinventiv supports enterprise cloud product development through…
Green Cloud - How Cloud Adoption Helps Improve Sustainability/ESG Goals of Enterprises
Key takeaways: Adopting green cloud solutions lowers energy consumption, cuts emissions, and reduces operational costs. Companies like UEM Edgenta and Bharti Airtel have seen measurable improvements in sustainability and efficiency. AI Enhances Green Cloud Efficiency. AI optimizes energy use, predicts demand, and minimizes waste in cloud infrastructure. Your Green Cloud Roadmap. Start with an infrastructure…

Cloud Migration Strategy for Enterprises in Australia: Benefits, Implementation Process and Tools
Key takeaways: Cloud migration in Australia is accelerating as enterprises modernize aging systems and prepare for AI-driven workloads. Local cloud regions in Sydney, Melbourne and Brisbane make compliance and performance far easier for large-scale migrations. A strong cloud migration strategy for enterprises in Australia depends on clear assessment, the right tools and ongoing optimization. Industry…