- The Core of XR Experiences
- The Evolution of XR: From Sci-Fi to Mainstream Adoption
- The Future of XR Technology: What’s Next?
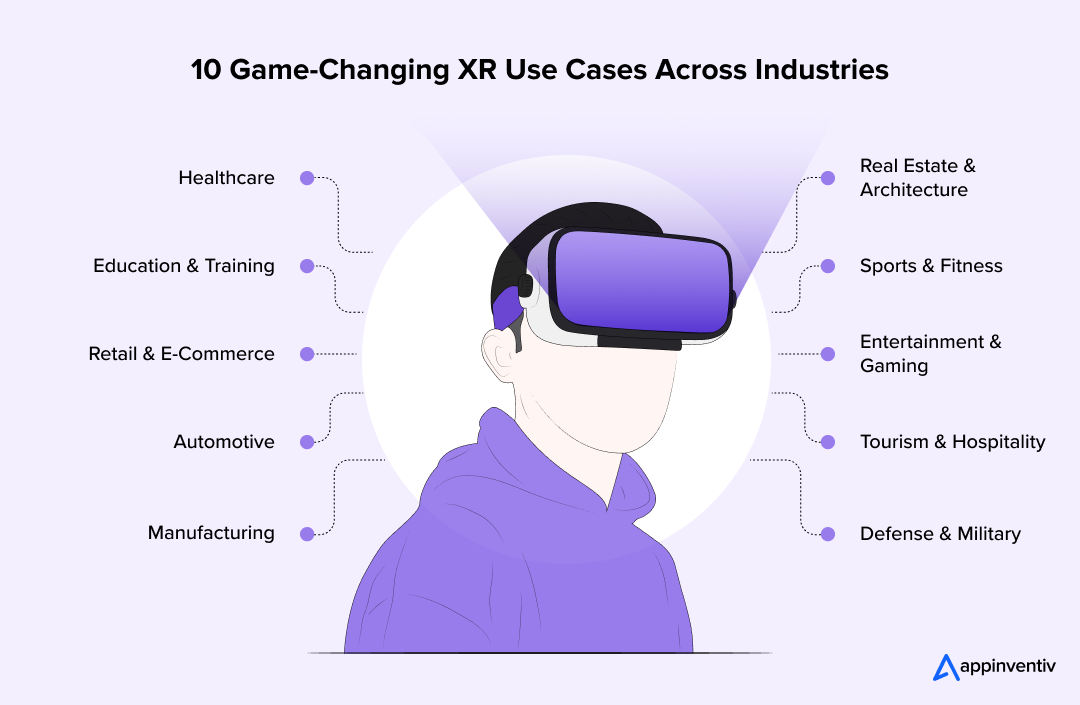
- 10 XR Use Cases That Are Transforming Industries
- Healthcare
- Education and Training
- Retail and E-Commerce
- Automotive
- Manufacturing
- Real Estate and Architecture
- Sports and Fitness
- Entertainment and Gaming
- Tourism and Hospitality
- Defense and Military
- Appinventiv - Grab Your Tech Buddy for XR Dreams
- FAQs
Imagine a factory where engineers diagnose machinery issues using 3D holograms or a hospital where surgeons rehearse complex procedures in a fully immersive virtual space before operating on a real patient. These scenarios are not distant possibilities – they are happening today and are powered by Extended Reality – XR use cases.
As a convergence of Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), extended reality applications are transforming industries by bridging the gap between digital and physical experiences.
It enables businesses to enhance efficiency, improve training, and revolutionize customer interactions. Whether it’s a retailer offering virtual try-ons, an architect presenting a 3D walkthrough of a future building, or a defense agency training soldiers in hyper-realistic simulations, XR is reshaping how we work, learn, and engage with the world.
The impact of digitally extended realities extends far beyond entertainment and gaming – industries like healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and education are already leveraging their capabilities to drive innovation, reduce costs, and improve outcomes.
In this article, we’ll explore some of the most compelling use cases of XR-powered virtual reality applications, along with real-world examples that showcase how this technology is redefining the future of various sectors.
The Core of XR Experiences
Extended Reality is not a single technology but a spectrum of immersive experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds. It includes Virtual, Augmented, and Mixed Reality, each offering unique ways to interact with digital content.
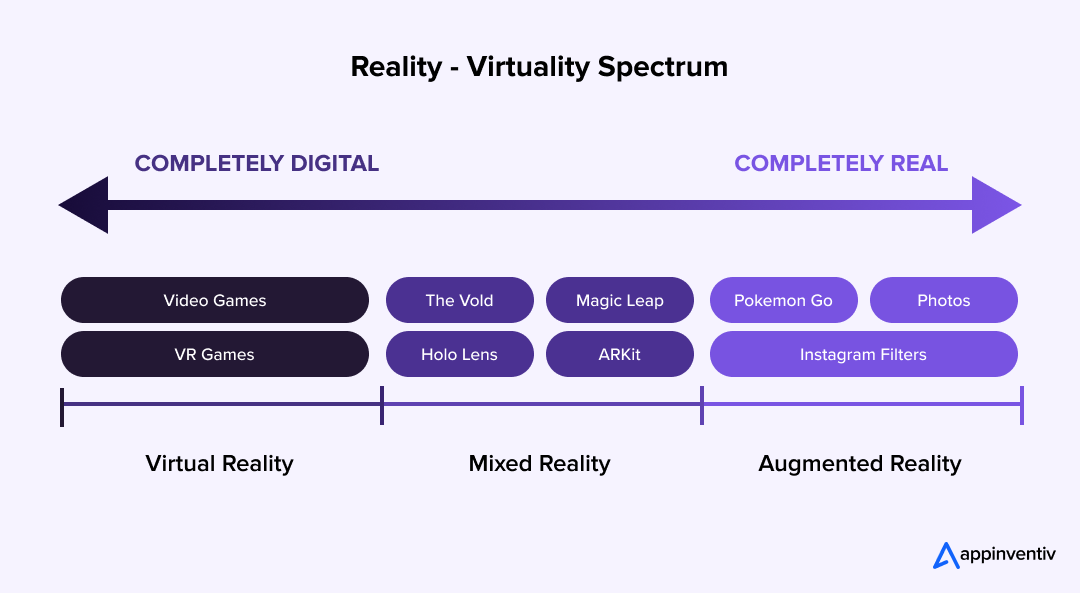
- VR: Virtual Reality use cases fully immerse users in a simulated environment, replacing the real world entirely. It’s widely used in gaming, training, and remote collaboration.
- AR: Overlays digital elements onto the real world, enhancing what users see with additional information, 3D objects, or interactive visuals.
Bonus Read: Augmented Reality for Business: Use Cases and Benefits
- MR: Mixed Reality applications merge digital and physical objects to interact in real-time, allowing users to manipulate virtual elements as if they were part of their environment. The adaptability of Mixed Reality makes it a choice for surgery in healthcare.
Together, these technologies form the backbone of XR’s extended reality, reshaping industries by improving efficiency, engagement, and problem-solving capabilities.
The Evolution of XR: From Sci-Fi to Mainstream Adoption
The idea of an immersive extended reality platform has existed for decades. Early experiments in Virtual Reality date back to the 1960s, with devices like the Sensorama offering multi-sensory experiences. The 1980s and 1990s saw the rise of VR headsets, such as those developed by NASA and early gaming companies, but limitations in computing power, resolution, and user comfort slowed mainstream adoption.
- The 2000s marked a turning point with advancements in augmented reality, driven by smartphones and computer vision.
- The launch of Google Glass in 2013 and the popularity of Pokémon GO in 2016 showcased AR’s potential to blend digital experiences with the real world.
Meanwhile, VR made a strong comeback by introducing Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR, offering higher-resolution displays and improved motion tracking.
By the late 2010s and early 2020s, XR augmented reality had moved beyond gaming and entertainment, finding its place in healthcare, education, industrial training, and remote collaboration.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated adoption as businesses sought immersive solutions for shopping, remote work, product design, and customer engagement. Today, Apple Vision Pro, Meta Quest, and Microsoft HoloLens are pushing the boundaries of XR, making it more intuitive and powerful than ever.
The Future of XR Technology: What’s Next?
The next decade of XR will be defined by smarter, more personalized, and more accessible experiences. Several key trends will shape its evolution towards the future of extended reality:
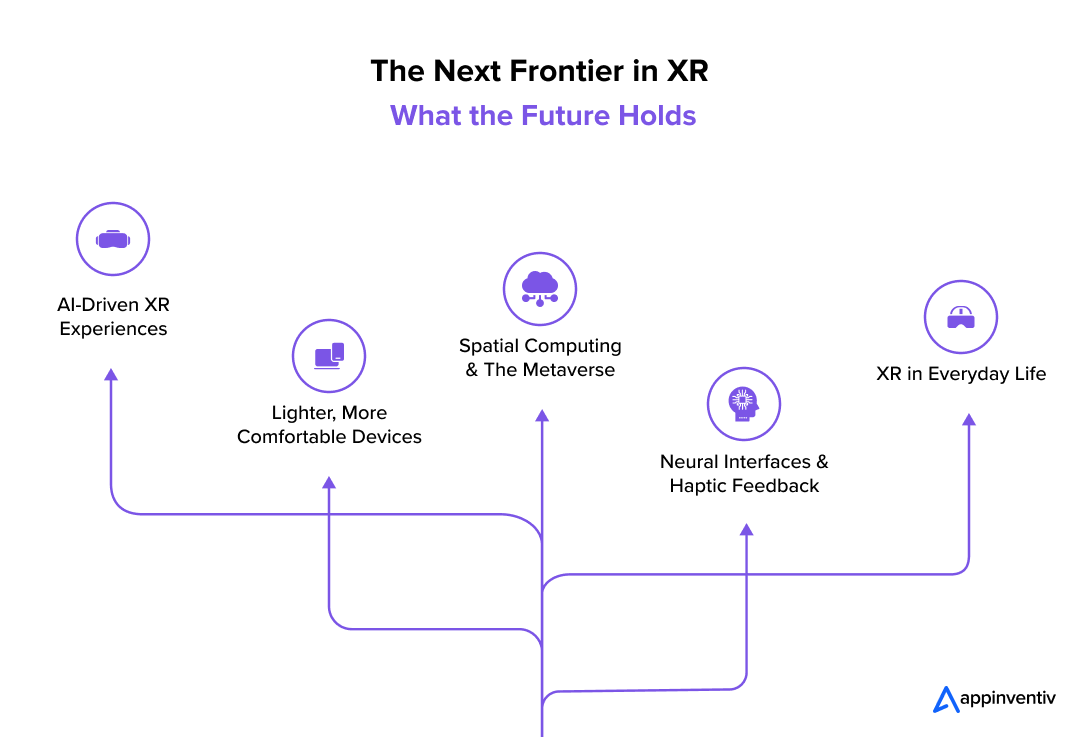
- AI-Driven XR Experiences – AI will enhance XR by enabling more intuitive interactions, real-time translations, and intelligent avatars that can respond naturally to human input.
- Lighter, More Comfortable Devices – Advances in hardware will lead to thinner, wireless headsets with improved battery life, reducing the barriers to widespread adoption.
- Spatial Computing & The Metaverse – Companies like Meta, Apple, and Google are developing metaverse AR/VR ecosystems, where virtual offices, digital storefronts, and social interactions become mainstream.
- Neural Interfaces & Haptic Feedback – Brain-computer interfaces and touch-based feedback systems will make XR more immersive, allowing users to control digital environments with their thoughts or feel virtual objects as real.
- XR in Everyday Life – From virtual tourism to AR-enhanced shopping experiences, extended reality XR application development will become part of daily routines, blurring the line between the real and digital worlds.
As extended reality development advances, businesses and industries are already harnessing their power to create new revenue streams, optimize operations, and enhance customer experiences.
The following sections will explore some of the most impactful XR applications that validate the unmissable benefits of extended reality, along with real-world examples demonstrating how the technology has revolutionized various industries.
10 XR Use Cases That Are Transforming Industries
Extended Reality XR application development is no longer just a futuristic concept – it is actively reshaping industries by enhancing efficiency, improving safety, and delivering immersive experiences. From revolutionizing medical procedures to redefining customer engagement in retail, XR is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Businesses are integrating virtual reality applications, XR augmented reality, and Mixed Reality to solve real-world challenges, optimize workflows, and create new revenue streams. While some industries invest in extended reality development for training and simulations, others leverage it for interactive product visualization, remote collaboration, and customer experiences that were once unimaginable.
The following sections explore how XR extended reality drives innovation across ten key industries, highlighting practical use cases and real-world examples that showcase its growing impact.
Healthcare
Extended Reality applications are revolutionizing healthcare by improving medical training, enhancing surgical precision, and transforming patient care. Traditionally, doctors relied on 2D imaging and physical training to prepare for complex procedures. Now, XR enables medical professionals to interact with 3D models of organs and practice surgeries in a risk-free virtual environment.
Mixed Reality applications also aid in real-time surgeries, overlaying critical patient data onto the surgeon’s field of view. In addition, XR plays a role in mental health therapy, pain management, and rehabilitation, offering immersive experiences that help patients recover faster. Extended Reality applications are also revolutionizing healthcare by improving medical training, enhancing surgical precision, and transforming patient care through AI-powered virtual environments that adapt to individual learning needs.
Use Cases:
- Surgical Training and Assistance: VR allows surgeons to simulate operations, while AR provides real-time visual overlays to guide precision surgeries.
- Telemedicine and Remote Consultations: XR enhances doctor-patient interactions, enabling 3D visualization of medical scans for more accurate diagnoses.
- Pain Management and Rehabilitation: Virtual reality use cases can be seen through therapy, which helps alleviate chronic pain and speeds up physical recovery with engaging rehabilitation exercises.
Real Example: Johns Hopkins Hospital
Johns Hopkins Hospital successfully performed a spinal surgery using AR, allowing surgeons to visualize internal structures in real-time, increasing accuracy and reducing operation time.
Education and Training
XR technology examples can also be seen in how it reshapes education by making learning more interactive and engaging. Instead of relying solely on books and lectures, students can now explore historical sites in VR, conduct virtual science experiments, and interact with 3D anatomical models.
Companies use XR simulations in corporate settings to train employees in high-risk industries like aviation, healthcare, and manufacturing. This ensures hands-on learning experiences without real-world consequences.
Use Cases:
- Virtual Classrooms: Through digitally extended realities, students can engage with interactive 3D environments, making complex subjects like physics and engineering more accessible.
- Corporate Training and Safety Drills: VR employee training prepares employees for real-world crises, such as handling hazardous materials or responding to emergencies.
- Soft Skills Development: XR experiences-powered AI avatars help employees refine communication, leadership, and negotiation skills in realistic business scenarios.
Example: Walmart
Walmart uses VR to train employees for high-stress situations like Black Friday sales, helping them practice crowd management and customer service.
Retail and E-Commerce
Extended reality examples are redefining how consumers shop online and in physical stores. With AR apps, customers can try on clothes, glasses, and makeup virtually, reducing returns and increasing confidence in purchases.
In furniture retail, XR applications allow shoppers to see how products will look in their homes before purchasing. Some brands have even launched virtual stores where customers can browse and interact with products in 3D.
Use Cases:
- Virtual Try-Ons: Store owners and shop owners have invested in Virtual Try-on App Development, allowing shoppers to see how clothes, accessories, or furniture fit into their spaces without physically trying them.
- Immersive Shopping Experiences: One of the top virtual reality applications – VR-powered showrooms – lets customers explore products like a real store.
- Retail Staff Training: XR helps train employees in customer service, merchandising, and store management.
Real Example: IKEA
The IKEA app lets users visualize furniture in their homes using AR, improving shopping experiences and reducing return rates.
Automotive
Extended reality applications are reshaping the automotive industry by improving design, manufacturing, and driving experiences. On one hand, engineers are using virtual reality applications to prototype cars, reducing the need for costly physical models.
On the other hand, AR-powered heads-ups are also being explored to enhance driver safety by overlaying navigation and hazard alerts onto windshields.
Use Cases:
- Design and Prototyping: XR use cases allow for rapid development and testing of vehicle models.
- Driver Assistance: AR HUDs display real-time navigation, traffic alerts, and road conditions.
- Maintenance and Training: AR overlays guide technicians through complex vehicle repairs.
Real Example: WayRay
WayRay’s Holograktor car features a True AR HUD that projects interactive visuals onto the windshield.
Manufacturing
XR solutions for heavy machinery and process optimization enhance manufacturing efficiency by streamlining assembly, reducing errors, and improving worker training. AR-powered work instructions help factory workers complete tasks precisely, while VR simulations optimize production workflows before implementation.
Use Cases:
- Assembly Guidance: Mixed Reality Applications provide step-by-step assembly instructions.
- Predictive Maintenance: XR extended reality helps technicians diagnose equipment failures before they happen.
- Quality Control: AI-powered AR detects product defects in real-time.
Real Example: Boeing
Boeing uses AR overlays to assist technicians in wiring aircraft, improving accuracy and reducing errors.
Real Estate and Architecture
There are plenty of extended reality examples in the property market, the most commonly found in how technology transforms real estate by enabling virtual property tours and interactive design previews.
Homebuyers can explore properties remotely, while architects can create and modify 3D building models before construction begins. These innovations ultimately make collaboration between designers, builders, and clients more efficient, reducing costs and project timelines.
Use Cases:
- Virtual Property Tours: Buyers can explore homes remotely without needing in-person visits.
- Architectural Visualization: AR-focused extended reality platform’s overlays allow designers to see how different design elements will look in real-time.
- Construction Planning and Safety: XR improves project planning, ensuring structural integrity before breaking ground.
Real Example: Zillow
Zillow’s 3D Home Tours provide an interactive real estate browsing experience, allowing buyers to walk through homes virtually.
Sports and Fitness
XR technology examples are also evident in how it transforms how athletes train, how fans experience sports, and how fitness enthusiasts stay engaged. Athletes can refine their techniques with real-time biomechanical feedback by integrating AR and VR into training routines.
Meanwhile, fitness apps use XR cases to create immersive workout experiences, keeping users motivated and engaged. On the other end of the spectrum, stadiums and broadcasters also leverage virtual reality applications to offer interactive viewing experiences, allowing fans to see real-time stats and player insights overlaid on live games.
Use Cases:
- Athlete Training and Performance Analysis: Extended reality applications enable players to simulate real game scenarios and refine their techniques with AI-powered insights.
- Immersive Home Workouts: Virtual fitness classes and AR-powered personal trainers help users maintain their exercise routines.
- Enhanced Fan Engagement: Stadiums and broadcasters use AR overlays to give fans real-time stats and in-depth game analysis.
Real Example: STRIVR
STRIVR provides VR training simulations for NFL teams, helping quarterbacks improve decision-making by running plays in virtual environments.
Entertainment and Gaming
Gaming was one of the earliest adopters of extended reality in business, but the technology has now expanded into being used in film, live events, and theme parks. XR-powered experiences create hyper-immersive worlds where users can interact naturally. Virtual filmmaking allows directors to shoot scenes in digitally generated environments, saving time and production costs.
Use Cases:
- Immersive Gaming: By correctly incorporating virtual reality use cases, gaming platforms transport players into lifelike digital worlds, enhancing engagement.
- Virtual Film Production: Directors can create entire scenes without expensive physical sets.
- XR Concerts and Events: Fans can attend live concerts or sports matches in VR with 360-degree views.
Real Example: Fortnite’s Travis Scott
Fortnite’s Travis Scott concert in VR attracted over 12 million viewers, setting a precedent for interactive digital performances.
Tourism and Hospitality
The tourism industry is redefining XR technology examples to provide virtual travel experiences, allowing customers to preview destinations before booking. Moreover, museums and historical sites have also started using AR to bring exhibits to life, offering interactive learning experiences.
Use Cases:
- Virtual Travel Previews: Travelers can explore hotels, resorts, and tourist spots before making reservations.
- AR Museum and Heritage Tours: Visitors receive interactive information overlays on historical sites.
- Smart Hotel Services: AR-powered XR use cases like concierge services are known to personalize guest experiences.
Real Example: The British Museum uses AR
The British Museum uses AR to provide interactive historical insights for visitors.
Bonus Read: How is Augmented Reality Transforming Travel & Tourism
Defense and Military
XR applications are a game-changer for defense by improving combat training, mission planning, and situational awareness. Soldiers can train in simulated combat environments, replicating real-world battle conditions while their AR headsets provide live battlefield data, helping them make quick tactical decisions.
Use Cases:
- Combat Simulations: VR-based military drills enhance battlefield readiness.
- Mission Planning: XR technology examples can also be seen helping strategists visualize terrain and enemy movements in 3D.
- Remote Maintenance: AR assists in troubleshooting and repairing military equipment.
Real Example: US Army’s IVAS system
The US Army’s IVAS system, built using Microsoft HoloLens, provides soldiers with real-time battlefield data.
Appinventiv – Grab Your Tech Buddy for XR Dreams
Extended Reality (XR) keeps changing games for many sectors like healthcare, teaching, shops, and the military.
Do you want to boost how things run, make experiences that draw people in, or flip training? Our AR VR app development services are the magic you need to tap into everything XR offers. Enter Appinventiv.
We come with solid experience from over 3000 tasks, dishing out state-of-the-art fixes made just right for a whole range of sectors. You can see our reputation glow when we team up with huge names like KFC, IKEA, Pizza Hut, Domino’s, and Adidas. It’s the same deal when we give a hand to newbies like JobGet, EdFundo, and Vyrb, helping them grab big bucks in investments.
Our team of more than 1600 experts is about blending creative flair with tech skills and deep knowledge of different industries to make XR stuff that changes things. We’re super into Agile ways of doing stuff, so we can stay nimble and tweak things fast as everything changes, and we don’t drop the ball on talking to you, so the work we do fits what you want like a glove.
When we snagged the ‘Tech Company of the Year’ title at the Times Business Awards 2023, it was like a big shout-out for our smarts and top-notch work. We’ve got a whole bunch of happy client shout-outs that show we know our stuff, helping businesses all over the place to level up with cool software that breaks the mold.
Are you geared up to make your XR dreams a reality? Team up with us, and we’ll craft groundbreaking extended reality experiences that push the boundaries of the imaginable.
FAQs
Q. What is XR technology?
A. Extended Reality is an umbrella term that includes Virtual, Augmented, and Mixed Reality. It encompasses technologies that blend digital and physical environments, creating immersive experiences for various applications. XR is used across industries for training, simulations, remote collaboration, entertainment, and customer engagement.
Q. What are the applications of XR training?
A. XR use cases around training are widely adopted in industries that require hands-on learning, real-world simulations, or risk-free environments for practice. Some key applications include:
- Healthcare: Surgical simulations and patient diagnostics.
- Manufacturing: Equipment maintenance and assembly training.
- Aerospace & Defense: Flight simulations and combat training.
- Corporate Training: Soft skills development and employee onboarding.
- Retail & Customer Service: Interactive product training and sales coaching.
Q. What are the future applications of XR?
A. As technology evolves, XR is expected to have broader applications, including:
- Metaverse-driven Collaboration: Fully immersive virtual workspaces.
- AI-Powered Personalization: Adaptive training and customer experiences.
- Advanced Healthcare Solutions: Remote surgeries using XR-guided robotics.
- Smart Cities & Infrastructure Planning: Virtual city modeling for urban development.
- Next-Gen Retail: Personalized AR shopping with AI-driven recommendations.
Q. What is XR technology used for?
A. XR technology is used for creating interactive and immersive experiences across multiple sectors; some of the extended reality examples include:
- Education and Training: Enhancing learning with realistic simulations.
- Healthcare: Assisting in surgeries, therapy, and patient engagement.
- Retail & E-commerce: Enabling virtual try-ons and interactive shopping.
- Entertainment & Gaming: Delivering immersive storytelling and gameplay.
- Engineering & Design: Visualizing prototypes and architectural models in 3D.
Q. How does Extended Reality work?
A. Extended Reality works by merging digital and physical elements through advanced hardware and software. The core components include:
- Headsets & Smart Glasses: Devices like VR headsets (e.g., Oculus, HTC Vive) and AR glasses (e.g., HoloLens) that enable immersive interactions.
- Sensors & Cameras: Tracking systems that map real-world environments and detect user movements.
- AI & Machine Learning: Enhancing experiences with real-time data analysis and interaction.
- Cloud & 5G Technology: Supporting seamless, high-speed XR applications for remote collaboration and processing.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

How to Integrate AR/VR into Your Fitness Offerings for Business Growth?
Key Takeaways AR/VR in fitness is transforming exercise with engaging, interactive, and custom workouts that enhance engagement and retention. It is estimated that the global AR/VR market will reach $589 billion by 2035. AR/VR helps companies to go international with online classes and personalized distance training. AR/VR contributes to better outcomes and user satisfaction in…

13 Use Cases and Examples of How Adaptive AI is Transforming Industries
Slashing downtime, boosting margins, automating workflow, and stealing your market share. You must be thinking that these buzzwords are Silicon Valley’s hype. No, these are the silent revolutions hitting Main Street industries. From manufacturing deploying demand forecasting to controlling production lines, healthcare tailoring predictive care and driving better outcomes. The success mantra—these industries are quietly…

AR/VR in Construction - 10 Use Cases of How Augmented and Virtual Reality is Shaping the Industry
The use of extended reality technologies is one of the growing trends in the expanding domain of construction technology. As the sector gradually adopts more sophisticated practices, virtual and augmented reality in construction have emerged as revolutionary solutions. With compelling advantages like planning, marketing, and training, AR/VR technologies are transforming the face of construction. Prescient…