- Why Should Organisations Invest in Developing Financial Software?
- What Types of Financial Software Systems Do Enterprises Build
- What Are the Key Benefits of Financial Software Development
- Greater Operational Control and Process Accuracy
- Improved Compliance and Risk Management
- Better Scalability and Long-Term System Stability
- Faster Product and Service Expansion
- Stronger Data Visibility and Decision Support
- Long-Term Cost Efficiency
- Better Alignment with Business Goals
- What Features Must a Financial Software System Include?
- Security Embedded at the Architecture Level
- Identity, Access, and Permission Management
- Compliance Controls and Audit Readiness
- Real-Time Transaction Processing Engine
- Integration and Interoperability Layer
- Scalable and Fault-Tolerant System Design
- Operationally Efficient User Interfaces
- How Do You Choose the Right Financial Tech Stack?
- Backend Technologies
- Frontend Technologies
- Databases and Data Storage
- Cloud and Infrastructure Platforms
- Integration and API Management
- Security and Compliance Tooling
- Payment and Financial Integrations
- What Are the Stages of Financial Software Development?
- 1. Discovery and Requirement Gathering
- 2. Planning and Prototyping
- 3. Architecture and System Design
- 4. Development and Implementation
- 5. Testing and Quality Assurance
- 6. Deployment and Integration
- 7. Ongoing Support and Maintenance
- How Much Does it Cost to Build Financial Software?
- Key Factors That Influence Financial Software Development Cost
- Where Does the Financial Software Development Budget Go?
- Typical Cost Scenarios by Business Need
- Indicative Financial Software Development Cost Breakdown
- Cost Planning Consideration
- Key Tech Trends of Financial Software Development
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Financial Systems
- Real-Time Payments and Instant Settlement
- Open Banking and API-Driven Ecosystems
- Embedded Finance Across Digital Platforms
- Blockchain for Traceability and Process Integrity
- Automation of Financial Operations
- Cross-Border and Multi-Currency Enablement
- Financial Software Development Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Managing Security Risks in Financial Systems
- Navigating Regulatory and Compliance Complexity
- Controlling System Scope and Complexity
- Integrating with Legacy Systems and Third-Party Services
- Adopting New Technologies Without Disruption
- Choosing the Right Financial Software Development Company
- Start With Accountability, Not Just Capability
- Evaluate How the Partner Thinks About Risk
- Look Beyond Initial Delivery
- Assess Process Discipline and Communication
- Treat the Relationship as a Long-Term Partnership
- Why Appinventiv is the Right Partner for Financial Software Development
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key takeaways:
- Financial software underpins daily operations, from transactions and reporting to customer-facing services.
- Custom-built systems reduce manual work, improve accuracy, and support evolving regulatory requirements.
- Security and compliance standards such as PCI-DSS, KYC, and data protection directly influence system design.
- Architecture and technology choices determine scalability, resilience, and long-term adaptability.
- Development costs vary by complexity and compliance scope; long-term value matters more than initial spend.
- The right development partner is critical to system reliability, compliance confidence, and delivery outcomes.
Financial organisations operate in environments where there is little room for error. Accuracy, compliance, and reliability are not just expectations—they are requirements. When financial software fails, the impact is immediate. Operations slow or stop, regulatory exposure increases, and customer trust is put at risk.
Many organisations struggle not because their business ideas are flawed, but because the systems supporting them are not built to scale or endure. Legacy platforms restrict change. Manual processes increase cost and operational risk. Security gaps create constant uncertainty for leadership teams.
Custom financial software development addresses these issues at the foundation level. It gives organisations control over how systems are designed, how compliance is handled, and how growth is supported. Instead of forcing business processes to fit rigid tools, teams can build banking, payments, lending, and wealth management platforms that reflect real workflows, regulatory responsibilities, and long-term plans.
This guide outlines how financial software is built in practice. It looks at the types of systems organisations build, the technology decisions behind them, the stages involved in development, and the cost and risk factors leaders need to understand to make confident, informed decisions.
The real question is whether your financial systems are ready to scale with it.
Why Should Organisations Invest in Developing Financial Software?
Financial software has become a board-level consideration. Customer expectations keep rising, while regulatory and security demands grow more complex each year. Systems built only a few years ago often fall short of today’s operational needs.
Global FinTech revenue is projected to reach $1.5 trillion by 2030, signaling a clear shift in how financial services are delivered. Digital payments, real-time services, automation, and data-driven decisions are shaping this growth.
Several structural changes are pushing organisations to invest in custom financial software development:
- Shift to digital payments: Cash and batch-based processes are being replaced by instant transactions that demand secure, reliable systems.
- Rising compliance complexity: Regulations across regions continue to expand, increasing the need for software that supports reporting, monitoring, and audit readiness.
- Demand for real-time data: Businesses and customers expect immediate access to balances, transactions, and insights, making real-time processing essential.
For organisations, the implication is clear. The benefits of financial software development investment are no longer limited to innovation initiatives. It directly affects cost control, compliance readiness, and the ability to scale products and services with confidence.
What Types of Financial Software Systems Do Enterprises Build
Software development for financial services focuses on building systems that manage transactions, data, and operations within secure, regulated environments. Each system type serves a specific business purpose and addresses distinct software operational and financial compliance requirements.
Unlike general financial application development, software development must operate with high accuracy, low latency, and strict security controls. Errors are not just technical issues. They create financial risk, regulatory exposure, and loss of customer trust.
The table below outlines the types of financial software systems organisations build today. Each category serves a distinct business purpose and comes with different technical and compliance requirements.
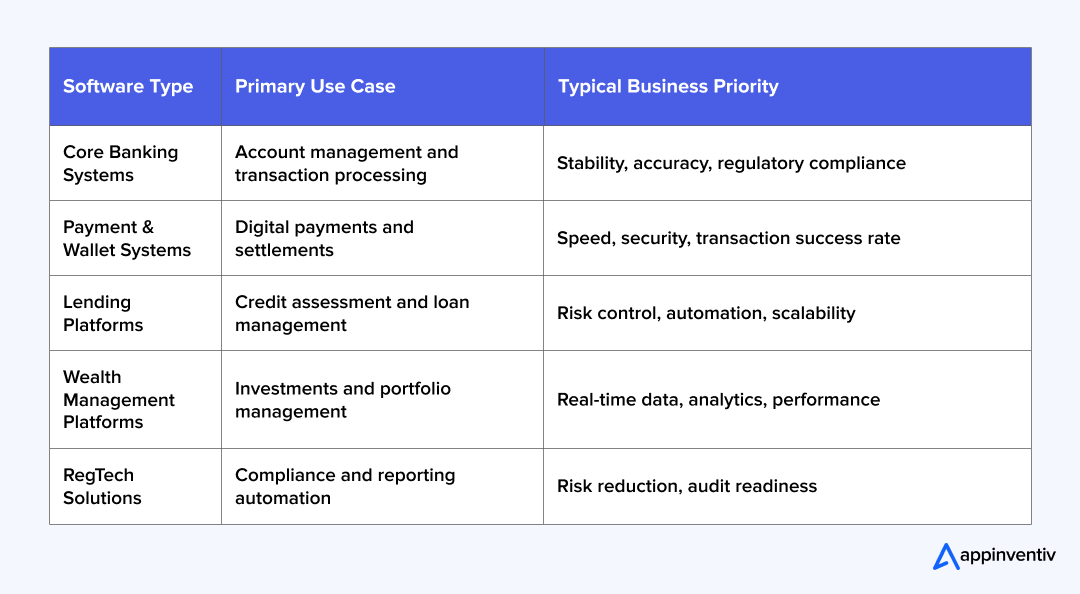
Larger organisations tend to prioritise systems built for scale, resilience, and regulatory alignment, such as core banking, payment processing, and RegTech platforms. These systems support high transaction volumes and require strong governance.
Startups and mid-sized businesses usually begin with more focused platforms, such as digital wallets, lending applications, or personal finance tools. These products help validate the business model and enter the market quickly, with room to scale over time.
Also Read: How Much Does Loan Lending App Development Cost?
Choosing the right type of financial software depends on business goals, risk tolerance, and long-term growth plans.
Edfundo: Financial Literacy Platform
Appinventiv built a market-focused financial-education platform for young users. The product combined learning modules with simple account controls to boost early financial behaviour.
Outcomes
- Raised $500,000 in pre-seed funding.
- Recognised as FinTech Startup of the Year (product traction and investor interest).
What Are the Key Benefits of Financial Software Development
A custom financial software development delivers value beyond technology upgrades. For enterprises, it directly improves how financial operations run, how risks are managed, and how systems scale over time. When built correctly, it becomes a long-term business asset rather than a short-term IT expense.
Below are the most relevant benefits organisations see from well-planned software development for financial services.
Greater Operational Control and Process Accuracy
Financial systems handle sensitive data and high transaction volumes. Even small inefficiencies can create large downstream risks. Custom financial software development allows organisations to design workflows around their actual operating model instead of adapting to generic tools.
This results in:
- Fewer manual handoffs between systems
- Improved data consistency across departments
- Better visibility into transactions and exceptions
For enterprises managing payments, lending, or investment operations, this level of control improves accuracy and reduces operational friction.
Improved Compliance and Risk Management
Regulatory requirements are constant and continue to evolve across regions. Many off-the-shelf tools struggle to keep up. Custom financial services software development allows compliance controls to be built into the system from the outset.
This typically includes:
- Automated audit trails and reporting
- Enforced access controls and data policies
- Faster adaptation to regulatory changes
By embedding compliance into the architecture, organisations reduce regulatory exposure and lower ongoing compliance management costs.
Better Scalability and Long-Term System Stability
As transaction volumes increase, systems must scale without sacrificing performance. Many organisations face breakdowns because their existing platforms were not designed for expansion. Financial industry software development addresses this by using architectures that support growth without constant rework.
Scalable systems allow organisations to:
- Handle peak transaction loads reliably
- Add new products or markets without disrupting operations
- Maintain performance as user numbers increase
This is especially critical for banking and financial software projects, where downtime or delays directly affect customer trust.
Faster Product and Service Expansion
Custom financial software gives teams more control than packaged solutions. New features, integrations, and services can be added without waiting on vendor roadmaps.
This enables:
- Faster launch of new financial products
- Easier integration with third-party platforms and APIs
- Closer alignment between business strategy and system capabilities
For organisations of all sizes, this flexibility supports growth while keeping costs and risks manageable.
Stronger Data Visibility and Decision Support
Financial software developers help organisations centralise data and produce insights that support informed decisions. Real-time access to financial information allows leaders to respond quickly to operational and market changes.
This includes:
- Clear visibility into transaction flows and performance
- Better monitoring of risks and anomalies
- More accurate forecasting and planning
When paired with analytics or AI & ML in financial software development, these systems further improve the quality of insights without adding complexity for users.
Long-Term Cost Efficiency
While the upfront cost of financial software development varies, well-designed systems often reduce total operating costs over time. Custom solutions minimize dependency on multiple vendors, reduce integration and maintenance overhead.
Cost-related benefits include:
- Lower manual processing costs
- Reduced reliance on third-party tools
- Fewer system failures and emergency fixes
For organisations evaluating cost, long-term efficiency is often a stronger driver than initial build expenses.
Better Alignment with Business Goals
Every organisation operates differently. Financial custom software development ensures systems reflect real business priorities, risk tolerance, and growth plans.
This alignment helps:
- Ensure technology supports strategic objectives
- Improve collaboration between business and technology teams
- Reduce gaps between operations and IT
Selecting the right financial software development company is critical, as domain experience and industry understanding directly affect solution quality.
What Features Must a Financial Software System Include?
Enterprise financial software is defined by how it is built, not by promises alone. The following features form the technical baseline for reliable software across banking, payments, lending, and investment platforms.
Security Embedded at the Architecture Level
In financial software, security cannot be layered on after development. It must be part of the core architecture, covering infrastructure, application logic, and data flows.
Key security capabilities include:
- Encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Secure key storage and rotation mechanisms
- Tokenization for sensitive financial data
- Continuous monitoring for abnormal system behaviour
These controls support both threat prevention and post-incident investigation.
Identity, Access, and Permission Management
Financial platforms serve customers, internal teams, and external partners with different access needs. Strong identity management ensures access remains controlled, auditable, and aligned with defined roles.
Essential capabilities include:
- Role-based access control across system modules
- Multi-factor authentication for high-risk actions
- Session monitoring and access logs for audits
This structure reduces internal misuse risk and supports regulatory oversight.
Compliance Controls and Audit Readiness
Financial industry software development must treat compliance as a built-in operational function, not a manual task. Systems should produce clear, audit-ready records without interrupting day-to-day operations.
Core compliance features include:
- Automated transaction logging and audit trails
- Policy-based enforcement for data handling and access
- Configurable reporting aligned with regulatory requirements
These controls allow businesses to adapt to regulatory changes without redesigning core systems.
Real-Time Transaction Processing Engine
Modern financial platforms must process transactions continuously, with immediate confirmation and visibility. This requires infrastructure built for low latency and consistent performance under load.
Key capabilities include:
- Real-time validation and transaction execution
- Immediate status updates and exception handling
- Consistency controls to prevent duplication or loss
This feature is foundational for payments, trading, and digital banking systems.
Integration and Interoperability Layer
Finance software development rarely operates independently. It must exchange data with banks, payment processors, data providers, and internal platforms.
Integration capabilities typically include:
- API-first architecture for external services
- Secure data exchange with legacy systems
- Event-driven messaging for high-volume workflows
A strong integration layer reduces manual intervention and supports future expansion.
Scalable and Fault-Tolerant System Design
Transaction volumes and user activity fluctuate. Financial industry software development must scale predictably while maintaining availability.
This is achieved through:
- Modular system components
- Load balancing and redundancy mechanisms
- Controlled failure handling and recovery processes
These design choices support long-term system reliability.
Operationally Efficient User Interfaces
In financial software, user experience focuses on clarity and accuracy rather than visual complexity. Interfaces must support fast decision-making and reduce operational errors.
Key considerations include:
- Clear workflows for critical financial actions
- Consistent behaviour across devices and roles
- Accessibility for diverse user groups
Efficient interfaces reduce support overhead and training effort.
How these features are implemented depends largely on system architecture and technology choices, making tech stack selection a critical step in the development process.
How Do You Choose the Right Financial Tech Stack?
The financial technology for software development you choose directly affects how secure, scalable, and maintainable the system will be over time. In financial software development solutions, technology choices affect transaction accuracy, system availability, and compliance readiness.
There is no single technology stack that suits every organisation. The right combination depends on transaction volumes, regulatory scope, integration requirements, and long-term growth plans.
Below are the core layers of a financial software technology stack commonly used in enterprise environments.
Backend Technologies
The backend manages transaction processing, business logic, and system integrations. It must handle high concurrency, ensure consistency, and remain fault tolerant.
Common backend technologies include:
- Java for large-scale, transaction-heavy banking systems
- Node.js for API-driven platforms and real-time services
- .NET for enterprises aligned with Microsoft ecosystems
- Python for analytics-driven modules and risk engines
In banking and financial software development, Java and .NET are often chosen for their maturity, stability, and strong ecosystem support.
Frontend Technologies
Frontend technologies define how users interact with financial systems. The emphasis is on clarity, performance, and reliability rather than visual complexity.
Common choices include:
- React for web-based financial platforms
- Angular for complex, enterprise-grade dashboards
- Flutter and Swift/Kotlin for mobile banking and wallet applications
These frameworks support responsive interfaces and consistent user experiences across devices.
Databases and Data Storage
Financial systems require accurate data storage with strong consistency and audit support.
Typical database technologies include:
- PostgreSQL and MySQL for transactional data
- Oracle Database for large enterprise environments
- MongoDB for semi-structured data and logs
- Redis for caching and session management
Enterprises often use a combination of relational and non-relational databases to balance performance and reliability.
Cloud and Infrastructure Platforms
Infrastructure choices influence system availability, disaster recovery, and cost control.
Common platforms include:
- AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform
- Containerisation using Docker
- Orchestration with Kubernetes
For regulated environments, hybrid or private cloud setups are also common to address data residency requirements.
Integration and API Management
Financial services software development depends on integrations with banks, payment providers, and third-party services.
Key technologies include:
- REST and GraphQL APIs
- API gateways such as AWS API Gateway or Apigee
- Message brokers like Kafka and RabbitMQ for event-driven processing
These tools support reliable communication between systems and improve scalability.
Security and Compliance Tooling
Security tools are a core part of the tech stack, not an add-on.
Commonly used technologies include:
- OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect for authentication
- Vault and cloud-native key management services
- TLS for secure data transmission
These tools help meet requirements related to PCI-DSS, KYC, and data protection laws.
Payment and Financial Integrations
Many platforms rely on established providers rather than building payment infrastructure from scratch.
Common integrations include:
- Stripe, Adyen, and PayPal for payments
- Plaid and Yodlee for financial data aggregation
- Core banking systems and regional payment networks
Choosing widely adopted providers reduces integration risk and speeds up implementation.
The right financial technology software development approach balances proven tools with flexibility for future change. An experienced financial software partner ensures the stack supports compliance, scale, and long-term business goals.
What Are the Stages of Financial Software Development?
Building a financial software needs to follow a structured process to manage risk, ensure accuracy, and meet regulatory expectations. Each stage reduces uncertainty and prepares the system for real-world financial operations.
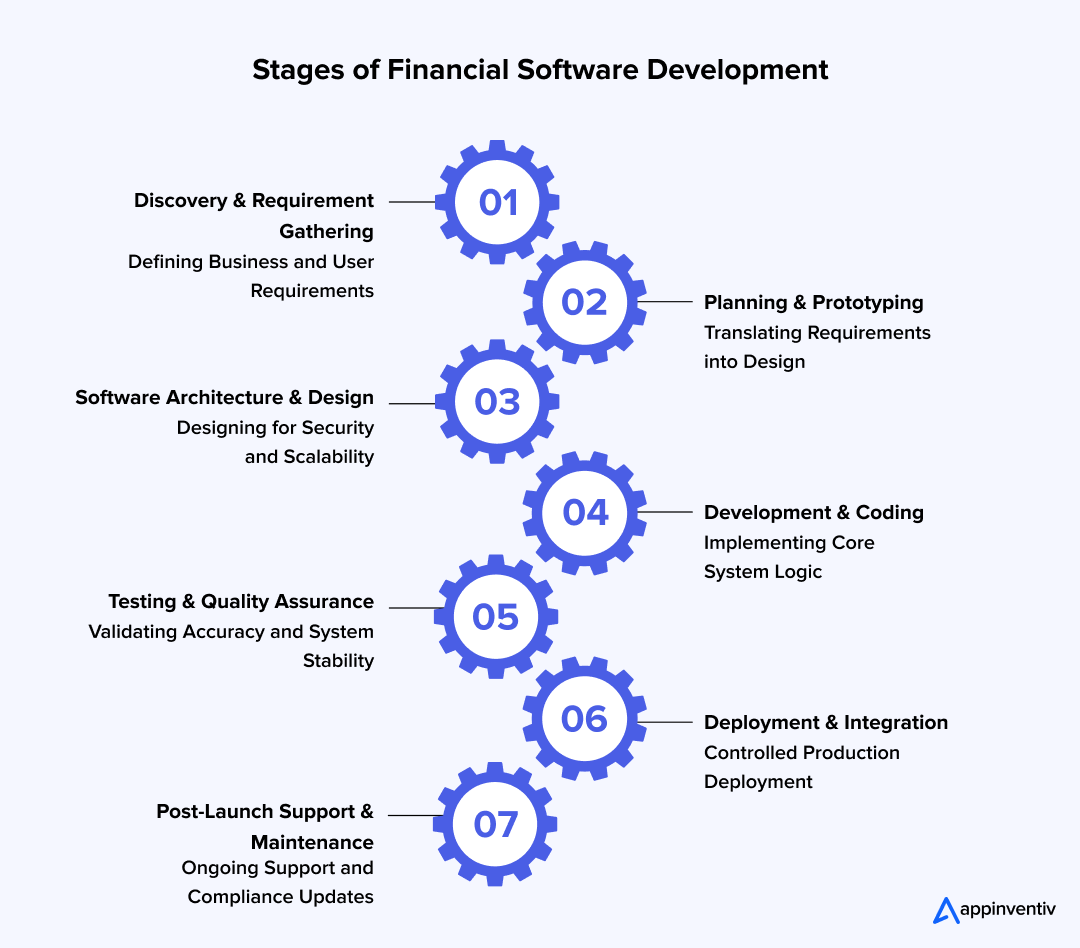
1. Discovery and Requirement Gathering
This stage focuses on understanding business goals, user needs, and regulatory constraints. It sets the direction for the entire project.
Key activities include:
- Defining business and operational goals
- Identifying regulatory and compliance requirements
- Mapping user journeys and edge cases
Outcome:
A clear, validated scope that aligns technology decisions with business and compliance needs.
2. Planning and Prototyping
Planning translates requirements into an actionable roadmap. Design decisions are evaluated early to avoid rework later.
Key activities include:
- Defining system scope and delivery milestones
- Designing user flows and core system behaviour
- Reviewing security and compliance considerations
Outcome:
A practical delivery plan and design framework that guides development and testing.
3. Architecture and System Design
This stage of the financial software development lifecycle defines how the system will operate at scale. The focus is on reliability, security, and long-term stability.
Key activities include:
- Designing system components and data flows
- Planning for fault tolerance and system resilience
- Defining integration points with internal and external systems
Outcome:
A secure and scalable architecture that supports current needs and future growth.
4. Development and Implementation
Development focuses on building core functionality with strong controls around accuracy and security.
Key activities include:
- Implementing business logic and transaction handling
- Integrating required third-party and internal systems
- Applying secure coding practices throughout development
Outcome:
A functional system that reflects approved designs and business rules.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing ensures the system performs reliably under real operating conditions. This stage is critical in financial software development.
Key activities include:
- Functional testing across standard and edge cases
- Security and vulnerability testing
- Performance and load validation
Outcome:
A stable and secure system ready for controlled deployment.
6. Deployment and Integration
Deployment moves the system into the live environment with safeguards in place to minimise risk.
Key activities include:
- Configuring production environments
- Validating integrations with financial institutions and services
- Establishing monitoring and rollback procedures
Outcome:
A controlled launch with operational visibility and response mechanisms.
7. Ongoing Support and Maintenance
Financial software requires continuous oversight after launch. Regulatory changes and evolving risks make maintenance essential.
Key activities include:
- Monitoring system performance and security
- Applying updates for compliance and risk mitigation
- Improving system efficiency as usage grows
Outcome:
A reliable system that remains compliant, secure, and aligned with business needs over time.
A structured development approach reduces risk and improves delivery outcomes. Understanding how costs take shape across these stages helps organisations plan investments more effectively, leading to development cost and budgeting.
Our teams design and deliver secure financial systems built for real transaction volumes and regulatory scrutiny.
How Much Does it Cost to Build Financial Software?
The cost of financial software development varies based on scope, regulatory exposure, and system scale. There is no fixed price because financial systems differ widely in complexity and compliance needs.
As a broad guide, the cost can range from $30,000 to $500,000 or more, depending on scope and deployment. Enterprise-grade platforms typically sit at the higher end due to security, compliance, and scalability requirements.
Instead of focusing on a single number, it is more helpful to understand what drives cost and how budgets are distributed.
Key Factors That Influence Financial Software Development Cost
Several variables shape the overall financial custom software development investment:
System complexity
Real-time payments, core banking, and risk management systems require deeper engineering and testing.
Feature scope
Capabilities such as multi-currency support, analytics, reporting, and automation increase build effort.
Compliance requirements
Standards such as PCI-DSS, KYC, GDPR compliance, and regional financial regulations increase design, testing, and validation efforts.
Integrations
Connections with banks, payment gateways, credit bureaus, and third-party services influence timelines and overall cost.
Scalability expectations
Systems built for high transaction volumes and future growth require more rigorous infrastructure planning.
These factors apply across finance software development, whether the product serves consumers, large organisations, or financial institutions.
Where Does the Financial Software Development Budget Go?
Financial software development costs extend well beyond coding. Each phase contributes to system stability, compliance readiness, and long-term maintainability.
A typical budget includes the following areas:
| Development Phase | Purpose and Cost Drivers |
|---|---|
| Discovery and planning | Business analysis, requirement definition, and early regulatory assessment to reduce scope and compliance risk. |
| Design and system planning | Application design, user experience planning, and security considerations that guide reliable development. |
| Development and integrations | Building core functionality and connecting with payment systems, banks, and third-party services. |
| Testing and compliance validation | Functional testing, security reviews, and checks to ensure accuracy and regulatory alignment. |
| Deployment and ongoing support | Production setup, monitoring, updates, and maintenance to keep systems stable after launch. |
Skipping or rushing early phases often leads to higher costs later through rework, delays, and compliance issues.
Typical Cost Scenarios by Business Need
Finance software development costs also vary by business maturity and system purpose.
Focused financial applications
Examples include digital wallets, lending MVPs, or personal finance platforms. These typically have a limited feature set, fewer integrations, and single-region deployment.
Mid-scale financial platforms
Examples include payment systems, investment platforms, or RegTech solutions. These require stronger compliance controls, broader integrations, and greater operational resilience.
Enterprise-grade financial systems
Examples include core banking platforms, large payment infrastructures, or risk management systems. These demand high availability, multi-region compliance, and long-term scalability.
Each scenario carries different cost software development for finance implications based on risk tolerance and growth plans.
Indicative Financial Software Development Cost Breakdown
| Type of Financial Software | Typical Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Banking software | $50,000 to $300,000 |
| Investment platforms | $55,000 to $65,000 |
| Consumer finance apps | $70,000 to $90,000 |
| Insurance platforms | $50,000 to $700,000 |
| Lending software | $80,000 to $100,000 |
| Financial risk management systems | $80,000 to $200,000 |
These ranges are indicative. Actual costs depend on scope, compliance requirements, and system scale.
Cost Planning Consideration
Financial software should be viewed as a long-term investment. Initial development is only one part of total ownership cost. Ongoing compliance updates, security improvements, and performance optimisation also influence spend over time.
An experienced financial services software development agency helps organisations plan budgets realistically and avoid hidden costs caused by rework or compliance gaps.
This cost clarity sets the stage for understanding how emerging technologies are shaping the next phase.
Key Tech Trends of Financial Software Development
Financial software is being shaped by a small set of technologies moving from experimentation to enterprise adoption. These trends are no longer optional for organisations modernising financial systems. They directly shape system design, security, and long-term competitiveness.
Below are the fintech technology trends that matter most today.
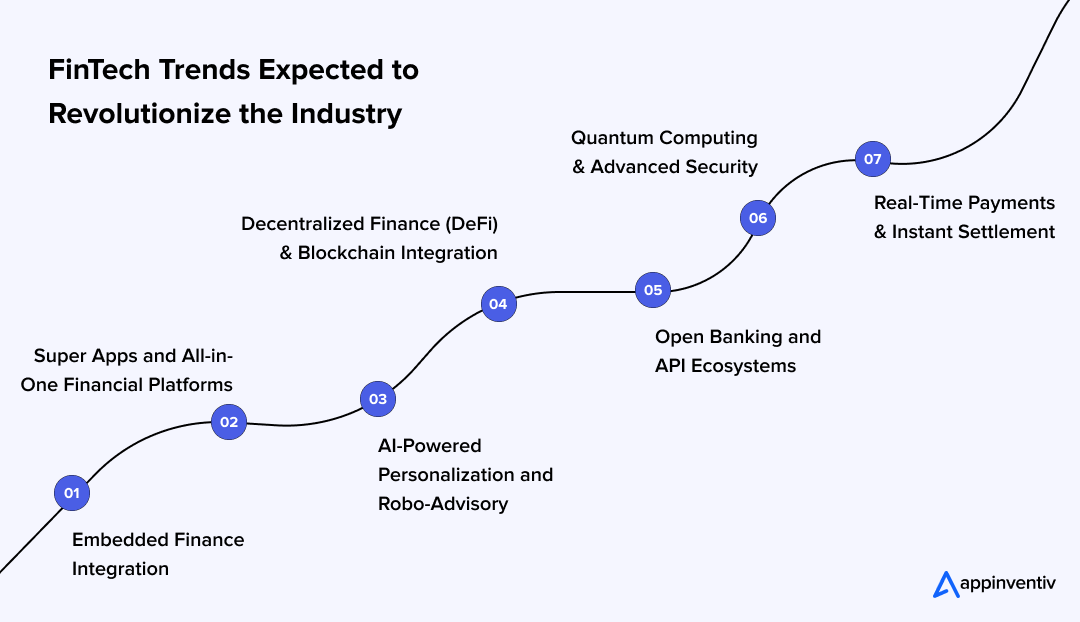
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Financial Systems
AI and machine learning are now embedded into core financial workflows. Their role has expanded beyond chatbots and automation into risk assessment, fraud detection, and decision support.
AI and ML in financial software development are commonly used to:
- Detect suspicious transactions in real time
- Improve credit assessment and underwriting accuracy
- Support personalised financial recommendations
- Reduce manual review in compliance and operations
For enterprises, the value lies in controlled, explainable use of these models rather than broad experimentation.
Mudra: AI-driven Budget Management
Mudra uses ML to deliver personalised budgeting and real-time insights. The app shows how targeted AI capabilities can improve user engagement across markets without adding unnecessary complexity.
Outcomes
- Launched across 12+ countries.
- Improved user adoption through tailored recommendations.
Real-Time Payments and Instant Settlement
Customer and business expectations now centre on immediate transaction processing. Financial software solutions are increasingly expected to support real-time payments and instant settlement.
This trend impacts:
- Payment processing infrastructure
- Transaction monitoring and reconciliation
- System performance and reliability
Financial software must process transactions quickly while maintaining accuracy and regulatory compliance. Systems not built for real-time execution often struggle to scale.
Open Banking and API-Driven Ecosystems
Open banking regulations and API-first architectures have changed how financial systems interact. APIs now form the backbone for data sharing, payments, and third-party integrations.
Key implications for building a financial software include:
- Secure access to banking and financial data
- Faster onboarding of partners and services
- Modular system design that supports expansion
Organisations that adopt API-driven architectures gain flexibility without rebuilding core systems.
Embedded Finance Across Digital Platforms
Embedded finance allows financial software development services expertise to be delivered within non-financial platforms. Payments, lending, and insurance are increasingly offered as integrated services rather than standalone products.
From a development perspective, this trend requires:
- Scalable APIs
- Secure identity and payment handling
- Tight integration with existing business platforms
For enterprises, embedded finance creates new revenue paths but also raises expectations around reliability and compliance.
Blockchain for Traceability and Process Integrity
Blockchain adoption in financial software has shifted from experimentation to selective use cases. Its primary value lies in transparency, traceability, and data integrity.
Common enterprise use cases include:
- Transaction traceability across multiple parties
- Secure record keeping and audit trails
- Smart contract-based process automation
Blockchain is typically used alongside traditional systems rather than replacing them entirely.
Automation of Financial Operations
Robotic process automation in Fintech is increasingly used to manage repetitive, rule-based tasks within financial systems.
In practice, automation supports:
- KYC and onboarding workflows
- Reconciliation and reporting processes
- Compliance checks and data validation
This trend improves operational efficiency when applied to clearly defined processes with strong controls.
Cross-Border and Multi-Currency Enablement
As software development for finance expands across regions, systems must support cross-border payments and multi-currency operations.
This trend affects:
- Currency conversion and settlement logic
- Regional compliance handling
- Transaction reporting and reconciliation
Financial software must account for regulatory differences and operational complexity across markets.
These trends shape how modern financial systems are designed, built, and maintained. Organisations that adopt them effectively prioritise stability, compliance, and integration over novelty.
Financial Software Development Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Financial software must balance accuracy, security, and compliance while supporting high transaction volumes. Even well-structured projects encounter challenges that can affect timelines, costs, and long-term reliability.
Identifying these challenges early helps organisations manage risk and make more informed technology decisions.
Managing Security Risks in Financial Systems
Financial software is a common target for cyber threats due to the sensitive data and transactions it handles. Security gaps can result in data exposure, service disruption, and loss of trust.
How organisations address this challenge:
- Applying secure development practices from the start
- Implementing strong access controls and encryption
- Conducting regular security reviews and updates
Security must be embedded in the system, not added after development.
Navigating Regulatory and Compliance Complexity
Financial systems must meet multiple regulations that vary by region and business model. Requirements around data protection, identity verification, and payment security continue to change.
Common compliance areas include:
- Data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA
- Identity and fraud controls like KYC and AML
- Payment security standards such as PCI-DSS
- Regional financial regulations affecting reporting and disclosures
How organisations manage compliance:
- Designing systems with compliance in mind
- Automating reporting and monitoring where possible
- Working with development teams familiar with financial regulations
Early compliance planning reduces rework and audit risk.
Controlling System Scope and Complexity
Financial software often grows in scope over time. New features, integrations, and regulatory updates can increase system complexity if not managed carefully.
How organisations control this risk:
- Prioritising features based on business impact
- Using modular system designs that support change
- Reviewing the scope regularly against operational goals
Clear scope management helps control cost and maintain system stability.
Integrating with Legacy Systems and Third-Party Services
Most financial platforms depend on existing banking systems, payment providers, and external services. These integrations often introduce delays and technical complexity.
How organisations reduce integration risk:
- Planning integrations early in the project
- Using standardised APIs and proven connectors
- Allowing time for certification and testing
Careful integration planning improves reliability and performance.
Adopting New Technologies Without Disruption
Technologies such as AI, automation, and data analytics can add measurable value in financial software. When poorly implemented, however, they increase complexity without improving results.
How organisations approach technology adoption:
- Aligning technology choices with business objectives
- Introducing new capabilities in controlled phases
- Ensuring teams have the right technical expertise
Technology should support operations, not add friction
Most challenges in software development for finance can be addressed with sound planning and relevant experience. Organisations that treat security, compliance, and scalability as core requirements are better positioned for long-term success.
Selecting financial software development companies with proven domain experience helps reduce risk, control cost, and ensure systems remain reliable as business needs change.
Choosing the Right Financial Software Development Company
For financial software, execution quality matters as much as the idea itself. Systems operate under constant regulatory scrutiny, process high transaction volumes, and carry direct business risk. The development partner you choose plays a central role in how well these systems perform over time.
For business leaders, the decision is less about vendor selection and more about risk ownership.
Start With Accountability, Not Just Capability
A reliable development company does more than build features. It takes responsibility for outcomes such as system stability, security posture, and regulatory readiness.
Organisations should ask financial software development consultants whether a partner:
- Has delivered financial systems that operate in production environments
- Understands the operational impact of system failures
- Is comfortable working with compliance, audit, and security teams
This level of accountability is difficult to assess without proven financial domain experience.
Evaluate How the Partner Thinks About Risk
Financial software is defined by risk management. Design decisions affect data exposure, transaction accuracy, and regulatory compliance.
A capable partner demonstrates:
- A clear approach to handling sensitive financial data
- Experience designing systems that support audits and controls
- Awareness of how regulations influence architecture and integrations
Risk-aware teams build systems that are resilient under pressure.
Look Beyond Initial Delivery
Many financial platforms fail not at launch, but months later when transaction volumes increase or regulatory requirements change.
When assessing a development partner, it is important to understand:
- How systems are designed to scale over time
- How integrations are maintained as dependencies evolve
- How updates and fixes are managed without disrupting operations
Long-term thinking protects investment and reduces operational surprises.
Assess Process Discipline and Communication
Enterprise financial projects involve multiple stakeholders and decision layers. Clear communication and structured delivery are essential.
A strong development partner provides:
- Defined delivery processes and reporting
- Clear ownership of decisions and changes
- Consistent documentation for internal and regulatory use
This discipline helps teams stay aligned throughout the project lifecycle.
Treat the Relationship as a Long-Term Partnership
Financial software is rarely static. Regulations change, security risks evolve, and business requirements continue to shift.
The right partner:
- Supports continuous system improvement
- Responds quickly to security and compliance needs
- Works closely with internal teams
This partnership approach lowers risk and supports sustainable growth.
Choosing a financial software development company is a strategic decision. It influences system reliability, compliance confidence, and the ability to scale without disruption.
Organisations that prioritise experience, accountability, and long-term support are better positioned to build financial software that remains dependable as business and regulatory demands evolve.
Enterprise Bank Modernisation — AI & Operations
Appinventiv modernised a European bank’s customer operations with multilingual automation and ML-driven scoring. The work shows how an experienced partner reduces churn and improves operational metrics.
Outcomes
- 20% improvement in customer retention for key portfolios.
- 92% improvement in ATM service levels and 35% reduction in manual processes.
A short conversation can help clarify feasibility, timelines, and risk before commitments are made.
Why Appinventiv is the Right Partner for Financial Software Development
Financial software leaves little margin for error. Systems must stay stable under heavy load, meet strict compliance requirements, and protect sensitive data at every layer. Choosing the right partner directly shapes business risk, delivery timelines, and long-term system health.
Appinventiv works with regulated institutions, large organisations, and growing FinTech firms that require dependable financial software development services. Our teams build custom financial software designed for real transaction volumes, real users, and real regulatory scrutiny.
Our financial software expertise brings depth where it matters most:
- 35+ industries mastered, including banking, payments, lending, insurance, and wealth platforms
- 1600+ technology specialists, covering backend systems, cloud, security, data, and compliance-led engineering
- 150+ AI models deployed, supporting fraud detection, scoring, automation, and decision systems
- 3000+ digital solutions delivered, many operating at enterprise scale
- 500+ legacy processes transformed, reducing operational risk and manual dependency
Our financial software development consultants work closely with business and technology leaders from the start. We focus on system architecture, security design, compliance alignment, and scalability planning before development begins. This approach reduces rework, improves delivery predictability, and keeps long-term operating costs under control.
Appinventiv is also recognised for consistent execution and governance. We are ISO-certified and a Deloitte Technology Fast 50 company. Our work has been acknowledged through Clutch Global Awards, ET Leadership Excellence, and industry-led recognitions for Android, chatbot, and AI development.
More importantly, our experience spans outcomes. We have helped global banks improve retention, supported FinTech platforms scaling across multiple regions, and delivered financial software that continues to perform under regulatory and operational pressure.
If you are planning new financial software development or updating existing systems, Appinventiv brings the technical depth, domain understanding, and delivery discipline needed for enterprise-grade results. Schedule a discussion with us.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Why is custom financial software important for FinTech businesses?
A. Off-the-shelf solutions often struggle in regulated, high-volume environments. Custom financial software allows organisations to design systems around their workflows, compliance requirements, and growth plans.
Custom platforms offer better transaction control, smoother integrations, and stronger security. They also reduce long-term risk by avoiding temporary workarounds that become costly as transaction volumes grow and regulatory oversight increases.
Q. What technologies are commonly used in financial software development?
A. Financial software development relies on stable, secure, and scalable technologies. The exact stack depends on the system type and compliance scope.
Common technologies include:
- Backend: Java, Node.js, Python
- Frontend: React, Angular
- Databases: PostgreSQL, MongoDB
- Cloud infrastructure: AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud
- Integrations: API gateways, open banking APIs
- Security: Encryption frameworks, identity and access management tools
Experienced financial software developers select technologies based on reliability, regulatory needs, and long-term system performance.
Q. How does financial software development support regulatory compliance?
A. Compliance is built into the system design, not added later. Financial services software development includes controls that help organisations meet regulatory and audit requirements.
This typically involves:
- Automated checks for KYC, AML, GDPR, and PCI-DSS
- Secure data storage with encryption and access controls
- Detailed audit trails for transactions and user activity
- Regular system updates to reflect regulatory changes
This approach reduces compliance risk and supports business continuity.
Q. How is security managed in financial software applications?
A. Security is a core requirement in financial software application development. Systems are designed to protect data, transactions, and user access from day one.
Key security measures include:
- End-to-end encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Multi-factor authentication and role-based access
- Regular security testing and vulnerability assessments
- Secure coding standards across all development stages
These practices help prevent breaches and maintain trust with users and regulators.
Q. How long does it take to develop a financial software system?
A. The timeline for financial software development depends on scope, compliance needs, and system complexity.
- Basic platforms: 3–5 months
- Mid-scale systems with integrations: 6–9 months
- Enterprise-grade financial software: 9–12 months or more
Discovery, architecture design, testing, and compliance reviews account for a significant part of the timeline. Rushing these stages often increases risk and long-term cost.
Q. How is financial software developed for different financial industry segments?
A. Financial software development varies by sub-industry due to differences in risk, regulation, and transaction complexity. The financial industry broadly includes BFSI, banking, payments, insurance, lending, and investment platforms.
Development approaches are tailored based on:
- Regulatory requirements specific to each segment
- Transaction volume and processing speed
- Data sensitivity and security controls
- Integration needs with third-party systems
This ensures software aligns with operational realities across financial services.
Q. Does financial software development include post-launch support and maintenance?
A. Yes. Financial software requires ongoing support after launch to remain secure, compliant, and stable.
Post-launch activities typically include:
- Performance monitoring and issue resolution
- Security updates and vulnerability management
- Regulatory updates and compliance changes
- System enhancements based on usage patterns
Ongoing maintenance is critical for long-term reliability and business continuity.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Key takeaways: Every healthcare app in Australia must comply with the Privacy Act 1988, Australian Privacy Principles (APPs), and in some cases TGA (SaMD) regulations. Core integrations include My Health Record, the Healthcare Identifiers Service, Medicare/PBS systems, and pathology/imaging providers. It increases development scope but is crucial for adoption. Healthcare solutions must embed encryption, access…

Retail businesses today operate across stores, mobile apps, websites, marketplaces, and fulfillment partners. Each channel generates data, transactions, and customer interactions. When these systems do not work together, growth slows, costs rise, and decision-making becomes reactive. Retail software development has moved far beyond basic POS or eCommerce tools. For many organizations, it now supports pricing,…

Key takeaways: With 6.05 billion users expected by 2028, social media apps are growing fast, creating opportunities for new entrants. Essential and advanced features for social media apps include profiles, feeds, media sharing, messaging, notifications, security, AR filters, and analytics. AI-driven personalization, social commerce, and AR/VR experiences are some of the emerging trends in social…





































