- What Makes A Fintech Super App Unique?
- Market performance
- Comprehensive Cost Breakdown to Build a Fintech Super App
- Cost by Complexity
- Basic multi service fintech app
- Mid range super app
- Enterprise grade fintech super app
- Cost by Development Stages
- Detailed Breakdown
- Cost by Region
- 10 Key Factors Affecting Fintech Super App Development Cost
- 1. UI and UX complexity
- 2. Number of financial modules being integrated
- 3. Backend architecture and performance engineering
- 4. Third party integrations
- 5. AI and analytics
- 6. Security layers
- 7. Compliance layers
- 8. Choice of platform and tech stack
- 9. Scalability and cloud infrastructure
- 10. API ecosystem and microservices
- Hidden or Underestimated Costs
- Cost Optimization Strategies When Building Your Fintech Super App
- How to Develop a Fintech Super App
- Discovery and requirement mapping
- Compliance planning
- UX workflow creation
- Architecture and tech setup
- Development of core modules
- API and payment integrations
- Security implementation
- QA and testing cycles
- Deployment
- Monitoring and enhancements
- 7 Ways to Build a Better Fintech Super App
- Key Features of Fintech Super Apps
- Benefits of Fintech Super Apps
- Challenges in Developing Fintech Super Apps
- Security and privacy concerns
- Tough regulatory expectations
- Getting multiple services to work together
- Keeping the design simple
- Real time performance
- Depending on external APIs
- How Appinventiv Built a Fintech Platform: The Mudra Story
- Key challenge
- Our approach
- Technology backbone
- Results achieved
- 8 Ways to Generate Revenue From Your Fintech Super App
- The Future of Fintech Super Apps
- Why Partner with Appinventiv for Your Fintech Super App
- FAQs
Key Takeaways
- Building a fintech super app costs between $40,000 and $400,000, depending on modules, compliance, and integrations.
- Backend architecture, compliance, and third party APIs are the biggest cost drivers in any super app build.
- AI, lending, investments, and insurance instantly push the project into the enterprise cost range.
- Hidden costs like audits, cloud hosting, security updates, and scaling play a major role after launch.
- An MVP first approach, modular architecture, and ready made financial APIs help reduce the long term fintech super app development cost.
The global financial ecosystem is undergoing one of its most significant shifts as consumers move toward consolidated digital platforms. McKinsey’s latest Global Payments Report highlights how digital payments, embedded finance, and AI enabled financial services are accelerating faster than traditional financial products, reshaping how people manage money across markets. This momentum is creating fertile ground for fintech super apps that bring multiple financial services into a single, integrated experience.
With this rise, one question comes up often for founders, banks, and enterprises: what is the actual cost to build a fintech super app?
The answer is not straightforward. The fintech super app development cost varies widely depending on the app’s scope, the number of financial modules, compliance requirements, AI capabilities, backend architecture, and the regions where development takes place. A simple version can sit at one end of the spectrum, while a feature heavy, enterprise grade financial ecosystem can sit at the other.
This guide breaks down those variables clearly. You will learn how much different levels of complexity cost, how integrations and compliance impact pricing, where hidden costs show up, and what it takes to plan a realistic budget. By the end, you will have a detailed framework to understand the true cost to build a fintech super app and how to approach development with clarity.
What Makes A Fintech Super App Unique?
A fintech super app stands out because it brings multiple financial services together inside one connected platform. Users do not need separate apps for payments, wealth, lending, or insurance. Everything works through a unified experience where every service talks to each other through a shared backend.
This creates an all-in-one financial ecosystem built around a single user identity.
Key elements of a unified money management stack include:
- Payments
- Mobile wallet
- Investment and wealth tools
- Lending and credit services
- Insurance access
- Cross border remittance
- Personal finance management
This combination makes the platform sticky, improves engagement, and increases the frequency of financial interactions.
Market performance
The global push toward digital finance is helping fintech super apps grow at a steady pace. Consumers prefer platforms that simplify how they manage money and reduce the clutter of juggling multiple apps.
Current adoption trends show:
- Rising usage of digital wallets and instant payments across APAC, the Middle East, and Europe
- Strong interest from financial institutions that want to offer bundled financial services
- Increasing willingness from users to adopt multi service financial platforms for everyday money tasks
This shift is also leading to higher financial impact and user growth. Super apps benefit from better retention, increased transaction volumes, and stronger cross selling opportunities because users stay inside the same environment for diverse financial needs.
Comprehensive Cost Breakdown to Build a Fintech Super App
Estimating the fintech super app development cost requires a structured view of how features, compliance, backend engineering, AI capabilities, and integrations influence the final budget. A financial super app is not a single module. It is a large ecosystem that handles identity, payments, investments, lending, insurance, analytics, fraud monitoring, and regulated data. This interconnected scope directly affects the cost to build a fintech super app.
Based on current benchmarks and typical development patterns, the overall cost sits between $40,000 and $400,000.
Below is a detailed breakdown of how that cost distributes across complexity levels, development stages, regions, and engineering effort.
Cost by Complexity
The complexity of the app determines the size of the architecture, number of modules, scope of compliance, and the engineering scale needed for building fintech super apps.
| Complexity Level | What It Includes | Estimated Hours | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic multi service fintech app | Wallet, payments, onboarding, basic KYC | 800 to 1200 hours | $40,000 to $80,000 |
| Mid range financial super app | Wallet, payments, P2P, bill pay, budgeting, analytics | 1500 to 2800 hours | $80,000 to $200,000 |
| Enterprise grade fintech super app | Lending, investments, insurance, BNPL, AI, fraud detection, remittance | 3000 to 6000+ hours | $200,000 to $400,000+ |
Basic multi service fintech app
A starter version for early validation. This level is chosen by teams developing financial super app MVPs.
Includes:
- Payments
- Wallet
- Basic KYC
- Simple transfers
- Transaction records
- Basic notifications
Why costs stay low: Limited compliance, fewer integrations, lighter backend.
Budget: $40,000 to $80,000
Mid range super app
Suitable for teams building financial super app versions with broader utility.
Includes:
- Payments and wallet
- KYC and AML screening
- Bill pay
- Budgeting
- Analytics
- Multi level support
- Improved dashboards
- Digital identity
Budget: $80,000 to $200,000
Enterprise grade fintech super app
The top tier of fintech super app development pricing. This is chosen by banks, global fintechs, or enterprises targeting scale.
Includes:
- Lending and loan management
- BNPL
- Investments and stock trading
- Insurance marketplace
- Cross border remittance
- AI fraud detection
- AI based credit scoring
- Multi currency wallet
- Advanced analytics and personal finance automation
- Compliance automation
- Risk engines
Budget: $200,000 to $400,000+
Cost by Development Stages
Every stage has a unique cost influence. The deeper the ecosystem, the more hours are required.
| Stage | What Happens Here | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery and planning | Feature mapping, user flows, compliance mapping | Medium |
| UX and UI design | Screens, journeys, finance UI patterns | Medium |
| Architecture and backend | Microservices, databases, core logic, security | Very high |
| APIs and integrations | Payment gateway, KYC, AML, credit scoring | High |
| Compliance and security | AML, KYC, PCI DSS, GDPR | High |
| Testing and QA | Functional, security, regression, stress testing | Medium |
| Deployment | Cloud, CI/CD, production rollout | Medium |
| Maintenance and updates | Ongoing upgrades, patches, compliance updates | High |
Detailed Breakdown
Building a fintech super app involves several interconnected stages, each contributing to the overall budget. These stages determine the engineering depth, compliance effort, integrations, and long term scalability of the platform. Here is a short look at how each phase impacts cost.
- Discovery and planning: This stage defines the scope and overall understanding of fintech super app development cost. Teams map regulatory requirements, outline data flows, select features, and categorize the project into basic, mid range, or enterprise complexity.
- UX and UI design: Fintech UX focuses on clarity, trust, and low friction. Designers craft financial grade interfaces, smooth navigation patterns, and multi-step flows for onboarding, payments, lending, and investments.
- Architecture and backend: This is one of the largest cost contributors. The tech stack in finance super app development process includes microservices, API gateways, encryption, event driven systems, and high concurrency transaction engines to support secure real time operations.
- APIs and integrations: Fintech super apps rely on multiple external partners. API Integrations like payment gateways, KYC and AML services, credit scoring, remittance networks, and investment APIs increase development time, testing scope, and compliance checks.
- Compliance and security: A major cost segment in developing financial super app platforms. Requirements include PCI DSS, AML, KYC, GDPR, and data residency rules. Security layers involve encryption, role based access, logs, secure cloud setups, and continuous monitoring.
- Testing and QA: Financial apps require extensive QA to ensure accuracy and stability. Testing includes functional checks, regression tests, penetration tests, stress testing, and validation of sensitive financial flows such as transfers, withdrawals, and loan approvals.
- Maintenance and updates: Recurring costs appear after launch. These include framework updates, compliance renewals, fraud monitoring, feature scaling, and continuous performance improvements as user volume grows.
Cost by Region
Regional rates influence fintech super app development pricing more than any other external variable.
| Region | Average Hourly Rate | Impact on Total Cost |
|---|---|---|
| US | $120 to $180 | Very high |
| Western Europe | $100 to $150 | High |
| Eastern Europe | $80 to $120 | Moderate |
| Middle East | $70 to $120 | Moderate to high |
| India | $25 to $40 | Most cost efficient |
| Australia | $90 to $150 | High |
India remains the strongest region for cost to build a fintech super app due to high fintech engineering maturity and competitive rates.
10 Key Factors Affecting Fintech Super App Development Cost
The cost to build a fintech super app depends on how many financial services you include, how deep the backend needs to be, and how strict the compliance environment is. Each layer adds its own engineering effort and shapes the final budget. Below are the core factors influencing the cost to build a fintech super app.
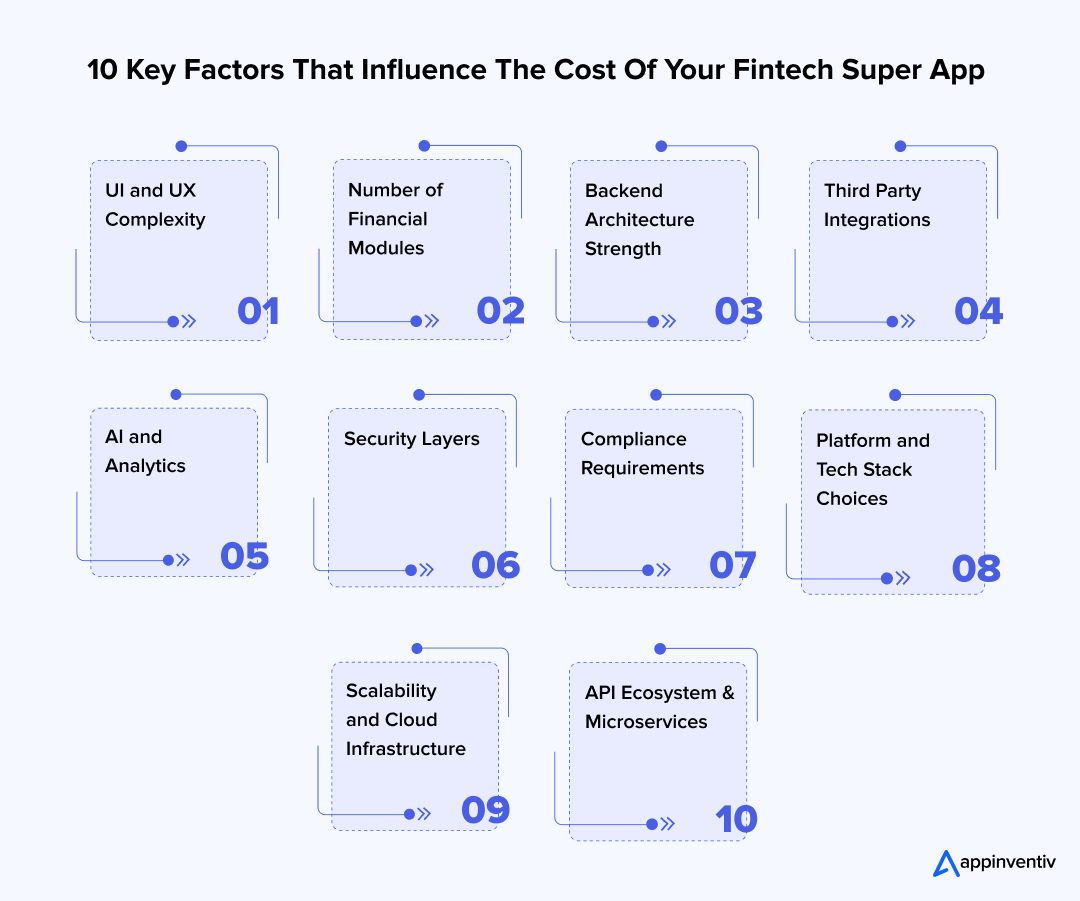
1. UI and UX complexity
A financial super app requires a design that feels secure, fast, and intuitive. The more screens, micro interactions, and multi step flows you add, the higher the design cost.
Cost drivers:
- Clean financial grade layouts
- Multi step onboarding flows
- Smooth transaction journeys
- High trust interface elements
2. Number of financial modules being integrated
Every new financial service adds backend logic, compliance, and testing cycles. A two module app costs far less than a platform with payments, lending, investments, and insurance.
Modules that increase cost:
- Wallet and payments
- Lending and BNPL
- Insurance marketplace
- Investments and trading
- Cross border remittance
3. Backend architecture and performance engineering
Fintech apps operate in real time. This demands a backend that is secure, scalable, and able to process high volume transactions.
Key architecture components include:
- Microservices
- Transaction engine
- API gateway
- High concurrency processing
- Event driven workflows
A stronger architecture increases reliability but also adds development hours.
4. Third party integrations
Fintech ecosystems rely heavily on external APIs. Each integration adds custom logic and testing effort.
Common integrations:
- Payment gateways
- KYC and AML services
- Credit scoring APIs
- Remittance partners
- Investment and brokerage APIs
More integrations mean higher development and compliance effort.
5. AI and analytics
AI adds intelligence to the platform but also increases cost due to data pipelines, model training, and validation.
AI use cases that add cost:
- AI powered fraud detection
- Credit scoring
- Personalized recommendations
- Risk scoring
- Behavioral analytics
6. Security layers
Stronger security results in higher development time, but it is essential for financial apps.
Security layers that impact cost:
- Encryption and tokenization
- Secure key management
- Multi factor authentication
- Fraud monitoring
- Audit logging
7. Compliance layers
Regulatory frameworks play a major role in fintech super app development cost. Every compliance rule creates extra engineering work.
Compliance requirements include:
- PCI DSS
- AML and KYC
- GDPR or CCPA
- Data residency rules
- eKYC standards
Each compliance layer adds tests, documentation, and architecture constraints.
8. Choice of platform and tech stack
Launching on iOS, Android, and web increases both cost and engineering time. The tech stack also determines scalability and security.
Cost factors:
- Native vs cross platform
- Number of platforms
- Frameworks and libraries used
9. Scalability and cloud infrastructure
A fintech super app must scale as users and transactions grow.
Cost drivers include:
- Cloud hosting
- Auto-scaling
- Monitoring and alerts
- Load balancing
- Multi-region deployment
10. API ecosystem and microservices
A microservices ecosystem supports long term growth but requires more upfront engineering.
Impact areas:
- Independent service development
- Containerization
- Service level security
- Inter service communication
Hidden or Underestimated Costs
Even after the main development is done, a fintech super app continues to generate a set of expenses that most teams do not think about in the beginning. These costs show up slowly, usually once the app starts growing, and they become a regular part of running a financial platform.
- Infrastructure and cloud hosting: As more users join and transaction volume goes up, the cloud bill follows. Higher traffic, more storage, and multi region hosting all push the monthly costs upward.
- Annual compliance audits: Fintech apps cannot skip audits. Every year, the platform has to go through checks for AML, KYC, PCI DSS, GDPR, and other rules. If you expand into new markets or add more financial products, the audit work naturally becomes heavier.
- Ongoing security patches: Security never stays still. Teams need to update libraries, fix vulnerabilities, and refresh encryption to keep the app safe. It is a quiet but constant expense.
- Monitoring and incident response: Someone has to keep an eye on how the app behaves. Downtime, suspicious activity, or stuck transactions need quick attention, and that requires monitoring tools and on call experts.
- Version upgrades: Whenever iOS, Android, or a third party SDK releases something new, the app needs updates too. Staying compatible saves you from performance issues or rejection during app store reviews.
- Third party SaaS tools: KYC checks, AML screening, analytics platforms, and support tools all come with subscription or per transaction charges. As your user base grows, these tools start taking a bigger share of the budget.
- App store charges: Developer accounts, app listing maintenance, and specific transaction related fees add up over the year. It is not huge individually, but it becomes noticeable over time.
- Customer support and agent training: Once real users start managing money on your app, questions, disputes, and issues will follow. Support teams need training, better tools, and eventually more people as usage increases.
- Scaling related costs: More users mean more compute power, stronger databases, caching layers, and load balancing. Scaling is great for growth, but it brings extra expenses on the infrastructure side.
- Additional cost for new features or financial modules: Every time you add a new module like BNPL, lending, or insurance, the app needs fresh development, new integrations, and new compliance checks. Each upgrade adds a new layer of cost.
Cost Optimization Strategies When Building Your Fintech Super App
Managing the fintech super app development cost becomes easier when the project follows a structured, efficient approach. Small decisions made early can significantly reduce long term spending without compromising product quality.
- Start with an MVP and scale in phases: Launching with an MVP helps validate demand before investing in every financial module. Once the core experience works, new features can be added gradually.
- Prioritize critical financial modules: Focusing only on essential services in the first release keeps development lean. Payments, wallet, and onboarding usually come first, while lending or investments can follow later.
- Use cross platform development: Building once for both iOS and Android lowers engineering effort and shortens time to market, especially for early stage versions.
- Choose modular architecture: A modular setup lets teams add or upgrade features without rebuilding the entire system. This keeps long term engineering costs predictable and efficient.
- Outsource to cost efficient regions: Working with teams in cost friendly regions helps control budget while still accessing strong fintech engineering expertise.
- Use managed cloud services: Managed cloud tools reduce configuration time, improve security, and cut down on infrastructure overhead through automated scaling and monitoring.
- Automate testing and CI workflows: Automated testing lowers QA effort and reduces the number of regressions, helping maintain quality while keeping development efficient.
- Use ready made financial APIs: Integrating existing APIs for KYC, AML, payments, or identity verification avoids building complex systems from scratch and significantly reduces overall cost.
How to Develop a Fintech Super App
Building a fintech super app is a structured process. Each stage ensures the platform stays compliant, scalable, and stable as more financial modules are added. Below is a simple overview of how teams move from concept to launch.
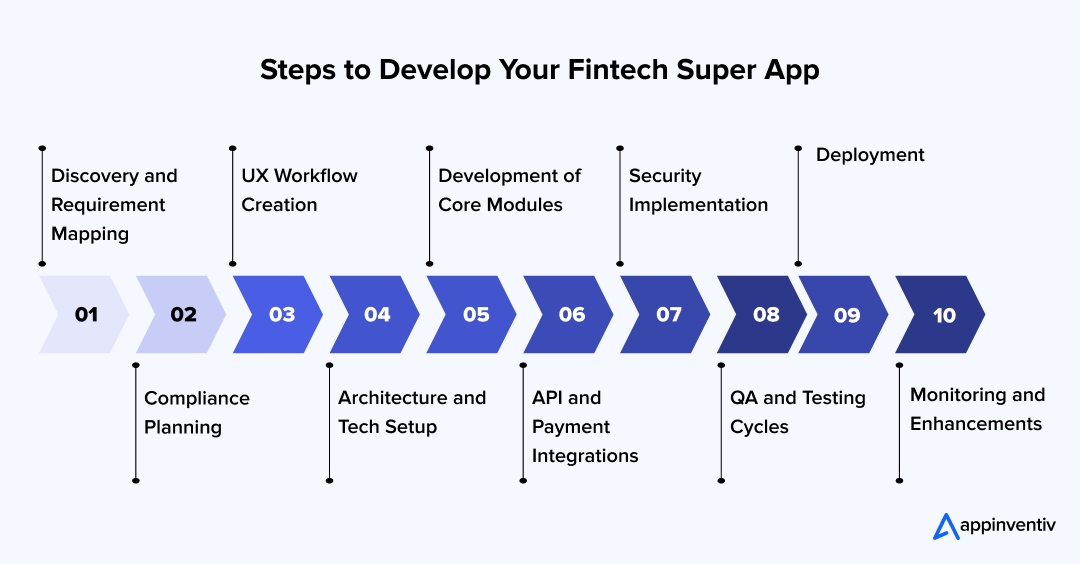
Discovery and requirement mapping
This stage defines what the app needs to achieve. Teams gather user expectations, list core financial services, outline flows, and finalize initial scope. Clear requirements keep the project aligned and prevent unnecessary features from entering early stages.
Compliance planning
Fintech platforms must follow strict rules. Compliance planning identifies the regulations required for each module, whether it is payments, lending, identity verification, or data protection. Early planning avoids costly rework later.
UX workflow creation
Design teams map user journeys and create flows for onboarding, KYC, payments, transfers, and other financial actions. A smooth experience increases trust and reduces drop offs.
Architecture and tech setup
A stable architecture supports real time finance operations. Engineers set up the backend, choose the tech stack, create microservices, and prepare the environment for secure and scalable operations.
Development of core modules
This is where the first version takes shape. Developers build the primary features such as digital wallet, online payments, identity management, and basic account functions. Each module is tested in isolation before integration.
API and payment integrations
Fintech products rely on external APIs. Integrations include payment gateways, KYC and AML services, credit scoring platforms, and sometimes investment or insurance partners. These integrations connect the app to real financial infrastructure.
Security implementation
Security layers are added once the core system is stable. This includes encryption, access control, fraud checks, secure API communication, and threat monitoring. Strong security is essential for financial trust.
QA and testing cycles
The app undergoes functional tests, regression tests, and performance checks. Financial flows such as transfers, deposits, and withdrawals are validated repeatedly to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Deployment
Once tested, the app is deployed to cloud environments and published to app stores. This stage includes setting up environments, CI pipelines, and release processes.
Monitoring and enhancements
After launch, teams track system performance and user behavior. Continuous improvements, new modules, compliance updates, and optimizations help the super app scale steadily.
7 Ways to Build a Better Fintech Super App
A good fintech super app handles transactions well. A great one feels easy, fast, and smart every time a user interacts with it. Improving a few key areas can create a noticeable difference in how people use and trust the platform.
- Superior UX and navigation: A simple, well-structured interface often matters more than a long feature list. Clear screens, predictable journeys, and smooth transitions help users stay comfortable while managing their money.
- Faster onboarding flows: People drop off when onboarding feels slow or confusing. Shorter steps, smooth KYC, and guided prompts make account setup quick, which increases the chance of users coming back.
- AI driven personalization: AI can turn financial data into useful insights. Personalized budgets, spending alerts, and smart suggestions help users feel supported rather than overloaded with information.
- Stronger fraud protection: Safety builds trust. Real time monitoring, risk scoring, and behavior analysis protect users without slowing them down, keeping the platform secure and reliable.
- Wider service integrations: The more services the app brings together, the more value it offers. Payments, lending, investments, insurance, and bill pay inside a single platform make the app a daily finance companion.
- Real time analytics: Instant updates and financial summaries help users stay aware of their activity. Clear, real time insights improve decision making and increase engagement.
- More fluid cross border payments: Fast and affordable international transfers are a growing expectation. Multi currency wallets and streamlined remittance flows make the app appealing to global users and frequent travelers.
Key Features of Fintech Super Apps
A good super app keeps everything about money in one place, so users do not have to bounce between different apps just to pay bills, track spending, or check investments. The best ones feel simple on the surface even though a lot is happening in the background.
- Digital payments: Most people start using a super app for quick payments. Whether it is bill payments, QR scans, or sending money to a friend, the idea is to make the process feel quick and predictable.
- Investment management: Many super apps let users look after their investments too. Simple charts, market updates, and easy buying and selling options help people manage their money without needing a separate investment app.
- Personal financial management: Budgeting tools play a big role. Expense categories, small nudges, reminders, and monthly summaries help users understand where their money is going and what they need to fix.
- Multi-service convenience: Lending, insurance, remittances, savings products, and other services come together inside one platform. This saves users from juggling five or six apps for basic financial tasks.
- Seamless user experience: Even with many features, the app still needs to feel light. Clear screens, simple journeys, and predictable steps keep the experience comfortable instead of overwhelming.
Benefits of Fintech Super Apps
The biggest strength of a fintech super app is that it saves people time. Instead of opening five different apps for simple money tasks, everything sits inside one place. That alone changes how people manage their day to day finances.
- Enhanced user convenience: Most users just want something that works without making them think too much. When they can pay a bill, send money, or check their expenses from the same screen, it feels easier and more natural. It cuts down on the small frustrations that usually come with managing money online.
- Increased customer engagement: Super apps slowly become part of the user’s routine. They notice spending alerts, small suggestions, reminders, or offers that match their habits. These little touchpoints keep people involved without forcing them to stay active.
- Better personalization: When all financial activity passes through one place, the app starts understanding patterns. It can point out where the user is overspending, when a bill is coming up, or how much they could save. These insights feel helpful, not intrusive.
- Faster access to financial services: Loans, insurance, savings products, or investments are usually messy and time consuming. Inside a super app, the process becomes shorter. Users get what they need without dealing with long forms or different platforms.
- Stronger loyalty over time: Once someone gets used to managing everything inside one app, switching becomes inconvenient. The comfort and familiarity build a quiet kind of trust, and that is what keeps people around for years.
Challenges in Developing Fintech Super Apps
Anyone who has tried building a fintech super app knows it is not a straight road. You bring payments, lending, saving, insurance, and a dozen other pieces into one place, and suddenly every small decision feels twice as heavy. Below are the common hurdles teams run into, written the way people actually talk about them.
Security and privacy concerns
The moment money is involved, everyone becomes cautious. Users want to feel safe, and developers cannot afford even a small slip. Fraud, data leaks, and account misuse are real possibilities, and that pressure never really goes away.
The only way to handle this is by treating security like daily hygiene. Regular checks, stronger logins, constant updates, and clear communication help people trust the app and feel comfortable using it.
Tough regulatory expectations
Every financial feature invites a fresh set of rules. One module needs KYC, another demands AML checks, and new markets bring their own lists of approvals. It gets confusing quickly.
Teams that stay ahead usually map these rules early. They involve legal experts from day one and keep the system flexible so new requirements can slide in without breaking everything else.
Getting multiple services to work together
A super app sounds smooth on paper, but in reality, every service has its own behaviour. Payments move fast, investments require more checks, insurance flows are lengthy. Keeping all of this in sync is never simple.
Breaking features into small, independent parts helps. When each service runs on its own, fixing or improving one does not disturb the rest of the platform.
Keeping the design simple
As features pile up, screens start feeling crowded. Users just want the important things in front of them without digging around.
A tidy layout and predictable flow usually solve most of the clutter. Grouping related services and guiding people through tricky steps keeps the experience comfortable.
Real time performance
Financial apps cannot afford slow moments. People expect their balance to update instantly and transactions to reflect right away. Even a tiny delay makes users lose confidence.
Strong backend planning, smart caching, and a system that can stretch during busy hours help the app stay steady when activity spikes.
Depending on external APIs
Super apps rely heavily on outside services. If a payment gateway slows down or a KYC provider goes offline, users blame the app, not the partner.
Most teams deal with this by keeping backup options ready or building small safety nets so the app does not freeze when one partner has issues.
How Appinventiv Built a Fintech Platform: The Mudra Story
When the team behind Mudra approached us, they had a simple but bold goal: make budgeting intuitive and engaging for millennials. They wanted to move away from spreadsheets and manual tracking — and instead, offer a smarter, AI-powered alternative that feels fresh, playful, and reliable.
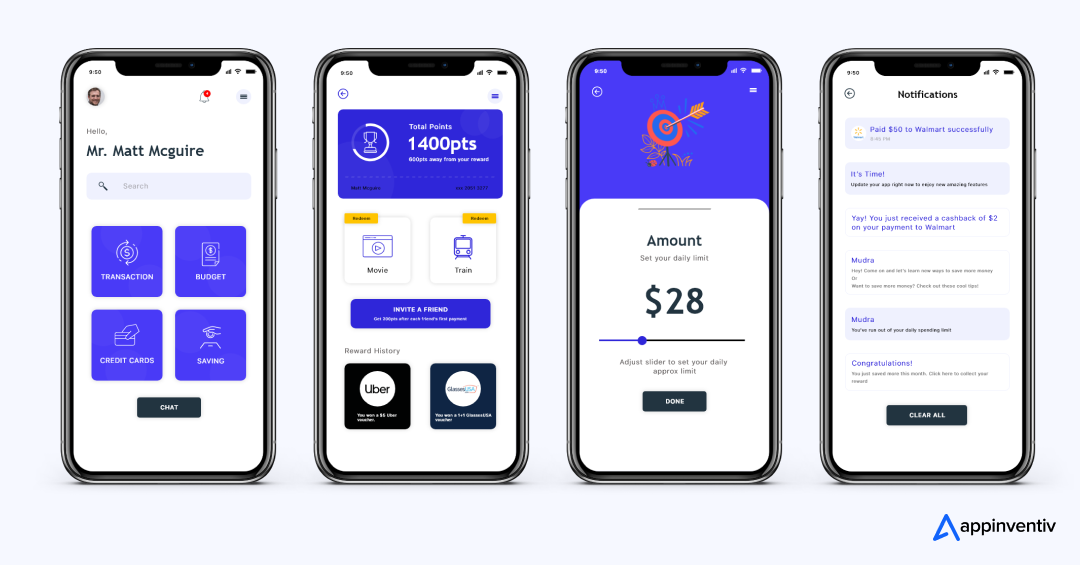
Key challenge
Mudra needed to replace a tedious, manual budgeting process with something that people would actually enjoy using. That meant balancing usability with serious financial logic, while making sure the app stayed lightweight and intuitive enough for millennials often turned off by conventional finance tools.
Our approach
We proposed a chatbot-centric architecture that blends budgeting logic with conversational design. By modeling user behaviour and preferences, Mudra could track expenses, alert users when they go off budget, and deliver financial insights — all via a friendly, chat-based interface. The goal was to turn budgeting from a chore into a habit.
Technology backbone
The build combined a modular backend, secure data storage, and integration of payment-card data (for spending tracking). We used a dialogue engine to power the chatbot, and layered encryption and secure APIs to ensure data safety. This setup allowed us to support complex financial workflows — while keeping the app agile and efficient.
Results achieved
After six months of development and design, Mudra was ready for launch. The product has been prepared for release across 12+ countries globally.
What started as a simple budget tracker transformed into a full-fledged fintech tool that combines AI, UX, and financial logic — making budgeting easier, smarter, and more accessible for users.
8 Ways to Generate Revenue From Your Fintech Super App
Fintech super apps rely on multiple income streams because users interact with a wide range of financial services. A balanced revenue mix helps the platform stay profitable while keeping most features accessible and low friction.
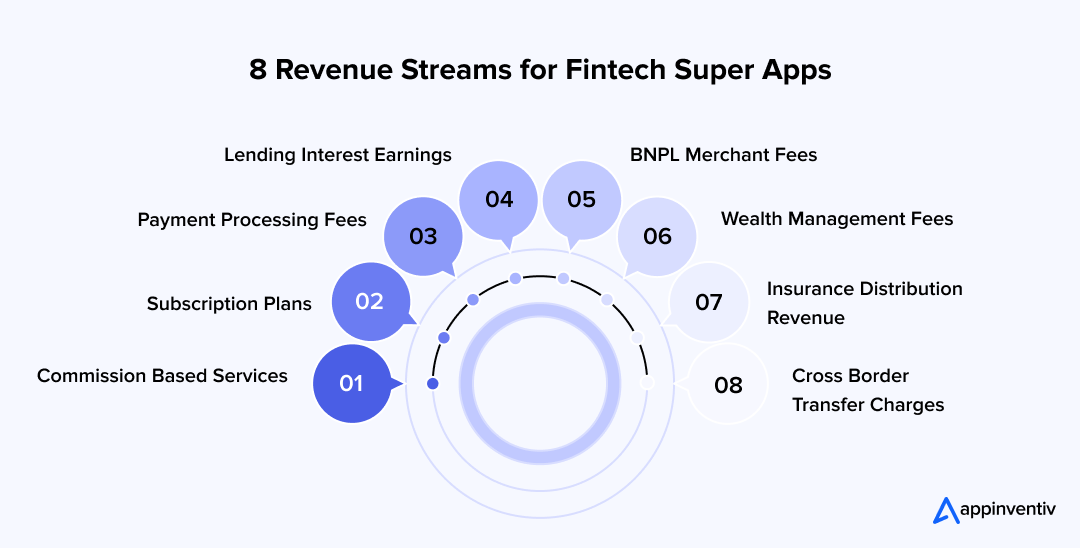
- Commission based revenue: Many services inside a super app earn small commissions for every transaction. This includes bill payments, recharges, ticketing, insurance referrals, or partner services.
- Subscription fees: Premium features such as advanced insights, faster transfers, higher limits, or priority support can be offered through monthly or annual subscription plans.
- Payment processing fees: Super apps earn a margin on each payment processed through their gateway or wallet. Even small per-transaction fees add up when the app handles large volumes.
- Lending interest: If the platform offers personal loans, micro loans, or credit lines, it earns interest on the borrowed amount. Lending becomes a major revenue driver as the user base grows.
- BNPL merchant fees: Buy now pay later generates revenue through merchant discount rates. Businesses pay a small fee for each BNPL powered purchase because it increases conversion and order value.
- Wealth management fees: Investment tools inside the app earn money through brokerage fees, advisory charges, or a percentage of assets under management. This works well for users building long term financial habits.
- Insurance distribution earnings: Super apps that partner with insurers receive payouts for every policy sold through the platform. These commissions vary based on category and coverage.
- Cross border transfer charges: International remittances generate revenue through small transfer fees or currency conversion margins. With global user bases rising, this becomes a dependable income stream.
The Future of Fintech Super Apps
The future of fintech super apps feels like it is heading toward a world where money work happens quietly in the background. People want less effort and more clarity, and these platforms are slowly moving in that direction. The same shift is shaping the broader future of financial super apps in fintech, where everything from payments to planning your month sits in one smooth flow.
- More personal guidance: Apps will start feeling a little more like a helpful companion. Small reminders, gentle nudges, and simple tips will show up right when users need them.
- AI doing the heavy lifting: A lot of behind the scenes work will get faster. Approvals, risk checks, budgeting insights, and investment suggestions will feel quicker and more natural because the app handles most of the thinking.
- Everyday tasks blending with money: People will book a ride, pay a bill, save a little, or apply for a small credit line without feeling like they are switching between separate tools.
- Simpler support across borders: As platforms grow, they will make it easier for users who move money between countries. Cross border actions will feel less like a big task and more like a normal part of using the app.
- Tighter protection: Stronger checks, quieter monitoring, and safer sign-ins will keep users comfortable as more of their financial life moves into one place.
Why Partner with Appinventiv for Your Fintech Super App
Creating a fintech super app that feels fast, secure, and reliable is never just about writing code. It demands an understanding of regulations, user psychology, financial workflows, and long term scalability. Appinventiv brings all of this together through years of focused work in the financial domain.
With 10+ years of fintech expertise and 200+ fintech products delivered, our teams have helped startups, digital banks, and global enterprises turn complex financial ideas into stable, compliant, user friendly products. This experience plays a major role in helping businesses manage their fintech super app development cost without cutting corners on quality or security.
Our approach to custom fintech app development focuses on building strong foundations. We help you validate your feature list, plan the compliance roadmap, choose the right architecture, and design financial journeys that feel simple even when the logic behind them is complex. Every step is structured to reduce rework and support long term scalability.
Whether you are planning a full scale financial ecosystem or expanding an existing product into a super app, Appinventiv can guide you through the decisions that matter and help you build a platform people trust with their money.
FAQs
Q. What tech stack is used in the finance super app development process?
A. Most teams use a mix of mobile frameworks, microservices, cloud hosting, and secure data tools. A typical stack includes a modular backend (often microservices), an API gateway, encrypted databases, and real time analytics. For the app layer, teams choose native or cross platform frameworks based on budget and scale. AI tools are added separately, and the cost to integrate AI in fintech super app features depends on how deep the intelligence layer needs to run.
Q. What are the biggest cost drivers in fintech super app development?
A. The heaviest costs usually come from backend architecture, third party APIs, compliance work, and any advanced AI features. Adding lending, investments, insurance, or cross border flows also increases the Fintech super app development cost, especially when you want the platform to perform at scale.
Q. How long does it take to build a fintech super app end to end?
A. A basic version takes around four to six months. A wider ecosystem with lending, investments, insurance, and AI driven services can take nine months to more than a year. Timelines depend on team size, number of modules, and how many features you want to add while you build fintech super app workflows.
Q. What are the examples of a super app?
A. Platforms like Alipay, WeChat, Grab, and Gojek are common examples. They bring payments, shopping, travel, and financial services into one place. These apps also show how different types of fintech super apps can grow into full ecosystems over time.
Q. How does a super app earn money?
A. Super apps earn through processing fees, lending interest, BNPL charges, subscriptions, and insurance commissions. Once the platform grows, the financial ecosystem becomes a strong revenue engine. All these models influence the overall Fintech super app development cost because each earning path requires its own tech and compliance setup.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Open Banking in Australia: A Practical Guide for Businesses
Key takeaways: Open banking-driven “Smart Data” initiatives are projected to contribute up to $10 billion annually to the Australian economy. Enterprises that follow a phased rollout covering readiness assessment, compliance alignment, API integration, cybersecurity, and scaling achieve faster deployment and lower operational risk. Constant CDR updates, accreditation complexity, and modernising legacy banking systems continue to…

Financial Wellness App Development: Process, Features and Costs
Key Takeaways Strategic ROI: Financial wellness apps are no longer "perks"; they are critical tools for reducing financial presenteeism and improving institutional retention. Technical Integrity: Successful deployment requires seamless integration with Human Capital Management (HCM) systems and secure Open Banking APIs. Compliance-First: Enterprise-grade solutions must prioritize SOC2, GDPR, and ISO 27001 standards to protect sensitive…

Money Transfer App Development: Building Secure Payment Apps in 2026
Key Takeaways Money transfer apps in 2026 succeed when compliance, security, and scalability are designed into the platform from day one, not added later. Choosing the right app type early helps avoid costly rework as transaction volumes, regions, and regulatory demands increase. Strong internal ledgers, clear settlement states, and automation are critical to preventing reconciliation…