- Key Aspects of Denial Management
- 1. Prevention Comes Before Recovery
- 2. Clear Ownership Across the Revenue Cycle
- 3. Consistent Denial Classification and Language
- 4. Visibility into Volume, Value, and Effort
- 5. Continuous Feedback into Front-End Processes
- How Does Denial Management Automation Integrate With Existing RCM Systems?
- Step-by-Step Roadmap to Implement Denial Management Automation
- Phase 0 – Readiness and Baseline Assessment
- Phase 1 – Automating Pre-Claim and Front-End Controls
- Phase 2 – Denial Intake, Classification, and Workqueue Automation
- Phase 3 – Appeals and Follow-Up Automation
- Phase 4 – Analytics-Driven Denial Prevention
- How Denial Management Automation Fits Into Existing RCM Systems and What It Costs
- How it Integrates in Practice
- How Much it Costs
- Goals and Benefits of Automated Healthcare Denials Management
- 1. Reducing Preventable Denials at the Source
- 2. Improving Speed and Consistency in Resolution
- 3. Lowering Cost and Manual Effort
- 4. Enabling Data-Driven Decision Making
- 5. Creating Predictable Revenue Outcomes
- Strategies for Effective Healthcare Denial Management
- 1. Strengthen Front-End Processes
- 2. Standardize Denial Categorization and Ownership
- 3. Use Data to Guide Priorities
- 4. Build Feedback Loops into Daily Operations
- Challenges in Implementing Automation in Denials Management and How to Overcome Them
- 1. Weak or Inconsistent Front-End Data
- 2. Trying to Automate Around Broken Processes
- 3. Too Many Interpretations of the Same Denial
- 4. Introducing Advanced Automation Too Early
- 5. Change Fatigue Among Teams
- What Compliance Considerations Apply to Denial Management Automation?
- Future of Denial Management in Healthcare
- Building Scalable Denial Management Automation With Appinventiv
- FAQs
Key Takeaways
- Denial management works best when prevention is prioritized before recovery, starting at registration, eligibility, and authorization.
- Automation delivers the most value when introduced in phases, aligned with existing revenue cycle maturity.
- Clean data, clear ownership, and consistent denial categorization matter more than tools alone.
- Analytics and AI help teams focus on high-impact denials, but human judgment remains essential.
- Organizations that automate thoughtfully gain better visibility, faster resolution, and more predictable cash flow.
In 2025, 41% of healthcare providers reported that at least one in ten claims was denied, and denial volumes continue to rise year over year, putting sustained pressure on revenue cycle teams, according to a recent study by Experian. That reality is pushing denial management automation in healthcare from a “nice improvement” into a financial necessity for any serious RCM denial management program.
For revenue cycle leaders, this isn’t a distant analytics headline. It shows up every day in denial management in healthcare and medical billing through avoidable rework, delayed cash, and escalating administrative load, often without a clear view of where the denial management process is breaking down. The result is fragmented denials management, where teams stay busy, but outcomes don’t consistently improve.
Still, simply adding denial management system won’t fix the problem on its own. To reduce denials and protect margins, organizations need an implementation approach that aligns people, data, workflows, and controls.
This blog walks through that path step by step, with practical actions leaders can apply without disrupting revenue flow.
A structured denial assessment helps identify preventable losses, ownership gaps, and automation opportunities across your revenue cycle.
Key Aspects of Denial Management
Denial management is not a back-end clean-up activity. It cuts across registration, coding, billing, and follow-up, long before a claim is submitted. When these touchpoints are misaligned, issues surface later as avoidable denials that are harder and costlier to resolve.
Understanding the key aspects of denial management helps organizations decide where to intervene within the denial management process and how to structure intelligent automation effectively.
1. Prevention Comes Before Recovery
Strong medical claims denial management starts upstream. Many denials originate during registration, eligibility checks, or authorization, well before billing teams are involved.
This typically involves:
- Accurate patient and coverage data at intake
- Clear authorization and referral workflows
- Documentation that supports denial management in medical coding and billing
When prevention is weak, medical billing denial management becomes reactive and unpredictable.
Also Read: AI in Medical Billing: Boosting Accuracy in Healthcare
2. Clear Ownership Across the Revenue Cycle
Denials rarely belong to one team. They are the outcome of actions taken across departments over time.
Effective healthcare RCM denial management depends on:
- Defined ownership for each denial category
- Clear handoffs across registration, coding, billing, and follow-up
- Accountability for both prevention and resolution
Clear ownership reduces delays and strengthens denial management workflow discipline.
3. Consistent Denial Classification and Language
In denials management, inconsistency is a major barrier. Payers use different codes, and internal teams interpret them differently.
To create alignment:
- Normalize denial reasons into a shared internal taxonomy
- Align payer codes with internal categories
- Use consistent language across reporting and denial management system
This consistency is essential for automation and meaningful analysis.
4. Visibility into Volume, Value, and Effort
Denial management improves only when leaders can see beyond denial rates.
Effective visibility includes:
- Denial volume and financial impact
- Preventable versus non-preventable denials
- Time and effort required per denial
Without this context, hospital denial management teams focus on activity instead of outcomes.
5. Continuous Feedback into Front-End Processes
Denial management should not end with resolution. Insights must flow back into earlier stages of the revenue cycle.
This feedback loop helps:
- Fix recurring registration and authorization issues
- Update claim edits and payer rules
- Reduce repeat denials over time
Organizations that close this loop move from reactive recovery to controlled, scalable denial management in rcm.
How Does Denial Management Automation Integrate With Existing RCM Systems?
Denial management automation does not replace core RCM platforms. It integrates with them.
Most healthcare organizations already operate EHRs, practice management systems, clearinghouses, and payer portals. Effective automation connects these systems rather than creating another silo.
Common integration points include:
- Eligibility and authorization data from front-end systems
- Claim submission and remittance feeds from billing platforms
- Denial reason codes from clearinghouses and payers
- Documentation repositories used for appeals
The goal is a single, consistent denial workflow that pulls data from multiple systems and presents it in a single operational view. When integration is done well, teams stop switching tools and start resolving denials faster.
Step-by-Step Roadmap to Implement Denial Management Automation
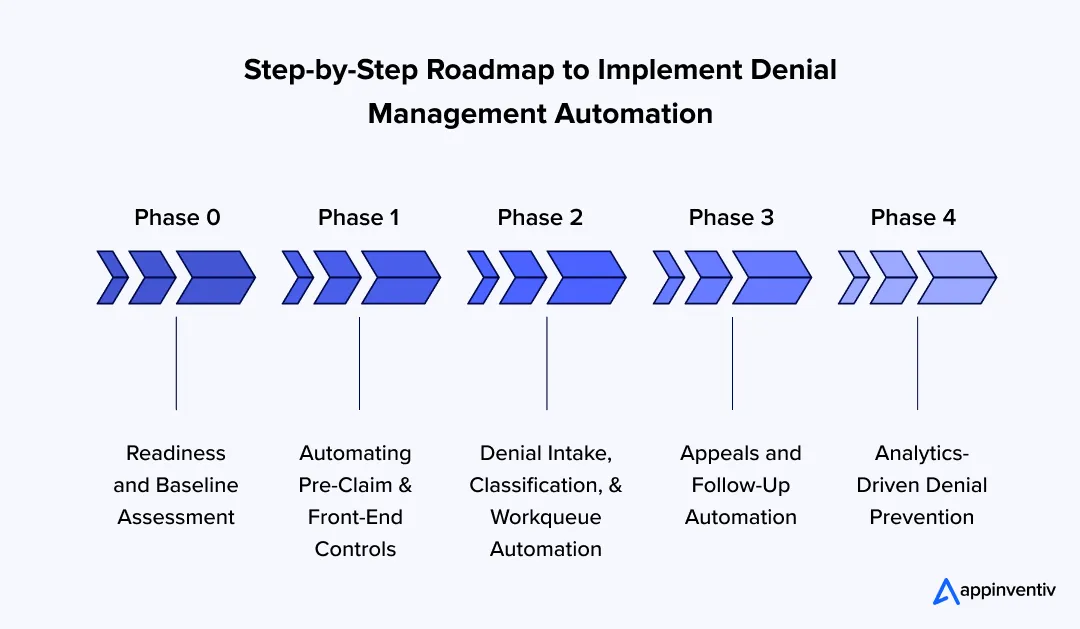
Denial automation is rarely a one-time initiative. In practice, denial management automation in healthcare unfolds in stages, shaped by the maturity of the revenue cycle. Organizations that slow down at the start and prepare properly tend to see stronger outcomes and fewer disruptions across denial management in healthcare operations once automation is introduced.
What follows is a practical roadmap for strengthening the denial management process without overwhelming teams or destabilizing revenue flow.
Phase 0 – Readiness and Baseline Assessment
Automation should not begin with tools or platforms. It should start with understanding how denial management in medical billing actually works inside the organization today.
Most healthcare providers quickly realize that medical claims denial management touches far more teams than expected. Errors introduced during registration often surface later in billing. Authorization gaps appear during follow-up. Issues in denial management in medical coding delay appeals. Mapping this end-to-end flow creates shared visibility across the entire denial management workflow.
This phase typically includes:
- Walking through the denial journey from registration to final resolution
- Identifying manual steps, handoffs, and repeated rework across RCM teams
- Noting delays or unclear ownership within denial management
Once workflows are visible, leadership can establish a baseline that reflects reality rather than assumptions.
Key baseline metrics to capture include:
- Monthly denial volume and dollar impact
- Preventable versus non-preventable denials
- Recovery rates and average effort per case in medical billing denial management
A common challenge at this stage is inconsistent denial language. Payers describe similar issues in different ways, and internal teams often interpret them differently, weakening denials management efforts.
To address this:
- Align denial reason codes across payers
- Map them to internal categories with clear ownership
- Use standardized language to support reporting and denial management platform rules
Before moving forward, data quality needs a close review. Automation will magnify existing gaps.
Final checks before progressing include:
- Accuracy of registration and eligibility data
- Completeness of authorization fields
- Consistency in coding and documentation across hospital denial management teams
Phase 1 – Automating Pre-Claim and Front-End Controls
The easiest denials to resolve are the ones that never occur. Front-end automation delivers early impact by targeting repeatable issues at the source of the denial management in RCM lifecycle.
Most organizations start here because these controls are visible, relatively low risk, and quick to stabilize.
Common focus areas include:
- Real-time eligibility checks during scheduling and registration
- Automated prompts for missing or expired authorizations
- Coverage validation tied to payer-specific rules
Claim scrubbing also becomes more effective when edits reflect real denial patterns rather than generic assumptions, strengthening denial management automation in healthcare outcomes.
What teams usually notice first:
- Fewer avoidable denials are reaching follow-up teams
- Cleaner claims moving through the system
- Less friction between registration and billing staff
These early wins build confidence in broader automated denial management solutions development efforts.
Phase 2 – Denial Intake, Classification, and Workqueue Automation
As denial volumes increase, manual sorting becomes unsustainable. This phase focuses on improving flow and consistency across medical claims denial management.
Instead of staff pulling information from multiple portals and spreadsheets, denials are captured automatically and centralized within denial management software.
Changes introduced at this stage include:
- Automated denial intake from clearing houses and payer systems
- Consistent classification using rules and assisted intelligence
- A single source of truth for denial inventory across denials management
Workqueues also become more structured.
Routing decisions are based on:
- Dollar value and likelihood of recovery
- Aging risk
- Required skill set or team ownership
The result is less time spent deciding what to work on and more time resolving denials within the denial management workflow.
Phase 3 – Appeals and Follow-Up Automation
Appeals are often where teams feel the most strain in denial management in medical billing. The work is detailed, repetitive, and time-sensitive.
Automation here is designed to support staff while preserving clinical and coding judgment.
Typical improvements include:
- Automated assembly of appeal packets and supporting documentation
- Standardized templates aligned with payer expectations
- Ongoing status checks to prevent missed deadlines
Workflows remain flexible for complex or clinical denials, while routine appeals move faster with fewer manual steps. Over time, this stabilizes hospital denial management performance metrics.
Teams typically see:
- Shorter appeal turnaround times
- More consistent follow-up
- Reduced burnout among denial staff
Phase 4 – Analytics-Driven Denial Prevention
At maturity, AI denial management healthcare capabilities help organizations move beyond recovery and toward prevention.
Instead of reviewing reports after the fact, teams use trends to guide day-to-day decisions across registration, authorization, and coding.
This phase focuses on:
- Identifying repeat denial drivers by payer and service line
- Feeding insights back into front-end workflows
- Updating rules as payer behavior evolves
Analytics become embedded into operations rather than existing only in dashboards.
The long-term outcome:
- Fewer recurring denials
- More predictable cash flow
- Denial management that feels controlled, not reactive
Also Read: Patient Waitlist Management Software Development
A phased automation approach works best when it’s mapped to your workflows, data readiness, and RCM priorities.
How Denial Management Automation Fits Into Existing RCM Systems and What It Costs
Denial management automation does not replace revenue cycle systems. In most healthcare organizations, that would be unrealistic. What it does instead is bring order to work that is already spread across too many tools.
Registration teams live in one system. Billing teams in another. Follow-up staff log into multiple payer portals. Automation sits across this setup and connects the dots.
How it Integrates in Practice
In real-world environments, integration is usually straightforward and incremental.
Automation typically:
- Pulls eligibility and authorization details from registration systems
- Reads claim and remittance responses from billing platforms and clearinghouses
- Captures denial codes directly from payer responses
- Links existing clinical and billing documents for appeal work
The biggest change is visibility. Denials arrive already grouped, routed, and prioritized. Teams stop chasing information and start working cases with context. Over time, denial management feels less like recovery work and more like routine revenue cycle control.
How Much it Costs
There is no flat price for denial management automation. Cost depends almost entirely on how disciplined the current process is.
Organizations with clean intake data and clear ownership usually spend less. Those with inconsistent workflows often need to fix basics before automation pays off.
Cost is shaped by:
- Revenue cycle complexity and payer mix
- How much of the denial lifecycle is included, prevention only or end-to-end
- Integration effort with existing RCM systems
- Whether advanced reporting or prioritization logic is added early
At the enterprise level, automation is rarely approved as a cost-cutting project. It is treated as a stable investment. Fewer preventable denials. Less manual effort per case. More predictable cash flow.
Teams that move in phases tend to see better results and fewer surprises. They automate where it helps, pause where it doesn’t, and expand only when the workflow proves itself.
That restraint is usually what makes automation stick.
Goals and Benefits of Automated Healthcare Denials Management
The goal of automation in denial management is not just to process denials faster. It’s to create a system in which fewer denials occur and the ones that do are handled with clarity and consistency. When done right, automated denials management strengthens financial performance without adding operational complexity.
For many organizations, automation serves as the bridge between reactive cleanup and controlled denial management.
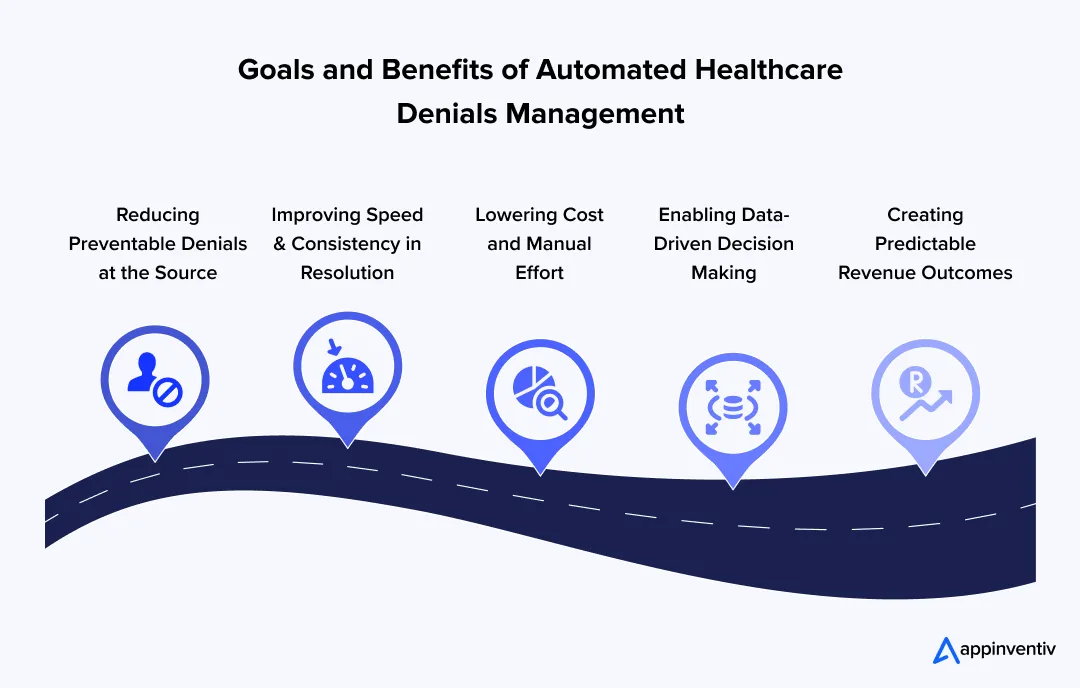
1. Reducing Preventable Denials at the Source
One of the primary goals of denial management automation in healthcare is prevention. By introducing front-end automation, organizations can catch common issues before claims are submitted.
Key benefits include:
- Fewer eligibility, authorization, and demographic errors
- Cleaner claims entering the system
- Lower dependency on manual rework in denial management in medical billing
This shift reduces noise across the entire denial management workflow.
2. Improving Speed and Consistency in Resolution
Automation also brings structure to how denials are handled once they occur. Instead of relying on individual effort, the development of automated denial management solutions creates repeatable processes.
This leads to:
- Faster denial intake and classification
- More consistent routing within denial management teams
- Reduced variability in medical claims denial management outcomes
Consistency improves both recovery rates and team productivity.
3. Lowering Cost and Manual Effort
Manual denial work is expensive and difficult to scale. Automation reduces the number of touches required per denial and allows teams to focus on higher-value tasks.
Operational benefits include:
- Lower cost per denial
- Reduced staff burnout
- Better utilization of denial management software across the revenue cycle
Over time, this creates a more sustainable approach to hospital denial management
4. Enabling Data-Driven Decision Making
Automation improves visibility, not just speed. Standardized workflows and data capture make it easier to analyze trends across healthcare denial management.
Organizations gain:
- Clear insight into repeat denial drivers
- Better prioritization within the denial management process
- Stronger feedback loops into registration, coding, and authorization
This foundation also supports more advanced AI denial management healthcare capabilities as maturity grows.
5. Creating Predictable Revenue Outcomes
Ultimately, the biggest benefit of automated denial management is predictability. Fewer surprises, clearer ownership, and faster resolution improve cash flow reliability.
When automation is aligned with people and processes, denial management shifts from reactive firefighting to a controlled approach to revenue protection.
Strategies for Effective Healthcare Denial Management
Effective healthcare denial management is less about reacting faster and more about fixing what causes denials in the first place. Organizations that see consistent improvement focus on alignment across people, processes, and data rather than isolated fixes.
The following strategies help create stability and long-term control in healthcare denial management.
1. Strengthen Front-End Processes
Most avoidable denials originate before a claim is submitted. Tightening controls at the front end reduces downstream pressure on billing teams.
Key actions include:
- Improving accuracy during patient registration and eligibility checks
- Verifying authorizations and referrals before services are delivered
- Ensuring documentation supports denial management in medical coding
Also Read: How to Build Patient Management Software: Process & Costs
2. Standardize Denial Categorization and Ownership
Denials become difficult to manage when teams speak different languages. Consistency is critical for any denial management process to work at scale.
Effective practices involve:
- Using a shared denial taxonomy across payers
- Assigning clear ownership for each denial category
- Aligning follow-up workflows within denial management
3. Use Data to Guide Priorities
Not all denials deserve the same level of attention. Data helps teams focus on where recovery and impact are highest.
This means:
- Prioritizing denials by dollar value and recoverability
- Tracking repeat denial drivers across service lines
- Using insights to refine denial management workflow decisions
4. Build Feedback Loops into Daily Operations
Resolution should inform prevention. The most effective organizations treat denial insights as input for continuous improvement.
Strong feedback loops help:
- Update front-end checks and payer rules
- Reduce repeat denials over time
- Strengthen overall medical claims denial management outcome.
Challenges in Implementing Automation in Denials Management and How to Overcome Them
Most denial automation efforts don’t fail because the technology is weak. They struggle because the underlying work is messy. Denial management touches too many teams, too much data, and too many payer rules for automation to succeed without preparation.
The challenges below are common, but they’re also manageable when addressed early.
1. Weak or Inconsistent Front-End Data
Automation depends on what it’s given. When registration details are incomplete, authorizations are missing, or coding varies by team, even the best denial management software will struggle.
How to work through it:
- Fix repeat data issues at registration and authorization
- Agree on minimum data standards across billing and coding
- Clean up common errors before expanding denial management automation in healthcare
2. Trying to Automate Around Broken Processes
Some organizations move straight to tools without first stabilizing the denial management process. The result is faster movement, but in the wrong direction.
How to work through it:
- Walk the denial journey end to end before automating
- Clarify who owns what within denial management
- Start small with clear, rule-based workflows
3. Too Many Interpretations of the Same Denial
In healthcare denials management, different teams often read the same denial differently. That inconsistency makes automation unreliable and reporting misleading.
How to work through it:
- Standardize denial categories across payers
- Use the same language in follow-up, reporting, and workflows
- Keep classification simple before adding intelligence
4. Introducing Advanced Automation Too Early
Advanced tools, including AI denial management healthcare, can help, but only after the basics are stable. When introduced too soon, they often create confusion instead of clarity.
How to work through it:
- Use automation first to reduce manual work
- Let AI in healthcare support prioritization, not replace judgment
- Expand only once teams trust the denial management workflow
5. Change Fatigue Among Teams
Automation can feel like disruption when teams don’t see immediate value. Resistance often comes from uncertainty, not unwillingness.
How to work through it:
- Focus early wins on reducing day-to-day effort
- Be clear about what’s changing and why
- Position automation as support within hospital denial management, not oversight
When automation is introduced with patience and structure, automated healthcare denials management becomes a stabilizing force. Organizations that fix fundamentals first see smoother adoption, better engagement, and more predictable revenue outcomes.
What Compliance Considerations Apply to Denial Management Automation?
Denial management automation operates on sensitive patient, billing, and clinical data. As a result, compliance must be designed into workflows from the start rather than layered on later.
Key compliance considerations include:
- Data privacy and security controls: Automation platforms must align with HIPAA and regional healthcare data protection requirements. Role-based access, audit trails, and secure integrations are essential.
- Documentation integrity: Automated workflows should preserve original clinical and billing documentation without alteration. Appeals and resubmissions must remain traceable and defensible.
- Payer rule transparency: When rules or AI-assisted classification are used, teams need clarity on how decisions are made. Black-box logic creates compliance and audit risks.
- Human oversight: Automation should support staff decisions, not replace them. Clinical judgment, coding interpretation, and appeal strategy must remain under human control.
Organizations that treat compliance as a design constraint rather than a checklist see smoother adoption and fewer downstream risks.
Future of Denial Management in Healthcare
The future of denial management is moving away from reactive recovery and toward prevention built into everyday operations. As payer rules evolve and claim complexity increases, denial management will become more proactive, data-driven, and integrated.
Key shifts shaping the future include:
- Greater focus on prevention over recovery: Front-end controls will play a larger role, reducing reliance on manual follow-up in medical billing denial management.
- Wider adoption of intelligent automation: Tools supporting AI denial management healthcare will help prioritize denials, identify patterns, and flag issues earlier in the revenue cycle.
- Closer alignment across RCM and clinical teams: Denial insights will increasingly inform registration, authorization, and denial management in medical coding decisions.
- More predictive, measurable workflows: Advanced analytics will enable faster decisions in the denial management workflow, improving cash-flow predictability.
- Denial management as a continuous improvement function: Rather than a clean-up task, denial management in RCM will become an ongoing discipline tied to operational performance and financial planning.
As denial management becomes more predictive and prevention-led, organizations that act early will gain better control and consistency.
Building Scalable Denial Management Automation With Appinventiv
Implementing denial automation takes more than tools. It requires a partner who understands healthcare workflows, compliance expectations, and the realities of the revenue cycle. As a trusted medical software development company, Appinventiv helps healthcare organizations design and implement automation that fits naturally into existing RCM and clinical systems.
Our healthcare experience spans data-driven platforms where accuracy and usability are critical. In the Soniphi Vitality Health App, we enabled personalized health insights that rely on clean data and structured workflows. At the same time, the Health-e People Health Assessment App focused on capturing accurate patient inputs upfront, a foundation, that directly supports stronger denial prevention and cleaner claims.
By combining healthcare domain knowledge with scalable engineering, Appinventiv supports organizations in building automation that reduces operational friction and improves revenue predictability. From front-end controls to analytics-driven workflows, we help turn denial management into a more controlled and sustainable process.
If you’re exploring denial automation or planning to modernize your revenue cycle workflows, our healthcare specialists can help you assess readiness and define the right implementation path. Connect with Appinventiv to discuss how automation can support your denial management goals.
FAQs
Q. What is a denial in medical billing and healthcare?
A. In simple terms, a denial happens when a payer decides not to pay a claim, either fully or partially. In day-to-day denial management, this usually stems from eligibility gaps, missing authorizations, documentation issues, or coding mismatches. Each denial adds friction, slows cash flow, and pulls teams away from higher-value work.
Q. What is denial management automation in healthcare, and how does it differ from traditional denial management?
A. Denial management automation in healthcare uses structured workflows, system integrations, and analytics to prevent avoidable claim denials and handle unavoidable ones more efficiently. Unlike traditional denial management, which is largely manual and reactive, automation embeds denial controls directly into the revenue cycle. This shift moves teams away from spreadsheets and payer portals toward standardized intake, prioritization, and prevention, reducing rework and improving visibility across the entire denial management process.
Q. How should denials be handled in medical billing?
A. Handling denials in medical billing denial management is less about speed and more about structure. Teams need to understand why the denial happened, who owns it, and whether it’s worth pursuing. When the denial management workflow is clear, follow-ups become more consistent, appeals improve, and the same mistakes stop repeating.
Q. How do healthcare organizations reduce denial rates using automation?
A. Organizations reduce denial rates by using denial management automation in healthcare to catch problems early and streamline follow-up later. Automated eligibility checks, authorization validation, and smarter routing help prevent avoidable errors. Over time, this approach strengthens medical claims denial management by reducing rework and improving consistency across teams.
Q. What are the risks of not automating denial management?
A. Without automation, denial management in healthcare quickly becomes reactive. Teams spend more time chasing denials than fixing root causes. This often leads to delayed reimbursements, rising administrative costs, staff burnout, and limited visibility into what’s actually driving denials. In the long run, manual processes weaken rcm denial management and make revenue unpredictable.
Q. How does denial management fit into revenue cycle management (RCM)?
A. Denial management sits at the center of denial management in rcm. It connects front-end activities such as registration and authorization to back-end billing and appeals. When denials management is handled well, it reinforces the entire revenue cycle. When it’s weak, inefficiencies show up everywhere else.
Q. How is AI powering denial management automation?
A. AI-powered denial management healthcare tools help teams see patterns that are easy to miss manually. They can flag repeat payer behavior, highlight high-risk claims, and support prioritization decisions. Used responsibly, AI doesn’t replace human judgment. It strengthens the denial management platform by helping teams focus their time where it matters most.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

A Practical Guide to Building Your Mental Health Chatbot - Use Cases, Cost, & ROI
Key takeaways: Mental health chatbots work when they know their limits. They’re most useful as a gentle first step, not as a stand-in for real care. Good chatbot design is more about judgment than AI. Clear boundaries, calm responses, and safety matter more than smart language models. Enterprises invest in chatbots to make support easier…

How To Hire the Right Healthcare Developers As Per Your Business Needs?
Key Takeaways The guide to the step-by-step approach to recruiting the right healthcare software developers to meet your business requirements. In-depth dissection of the major technical skills, certifications and healthcare-specific expertise required in developers. Guidelines for carrying out the evaluation of candidates using portfolios, technical interviews, and trial projects. Industry-specific ERM approaches help address regulatory,…

Healthcare 4.0: Redefining the Future of Connected Care and Clinical Intelligence
Key Takeaways Healthcare 4.0's ecosystem is autonomous and patient-centric, integrating AI, IoT, and cloud computing. AI-driven clinical intelligence enhances personalized care for healthcare professionals and improves patient outcomes through predictive analytics. IoT and AI are being implemented in smart hospitals to improve operational efficiency, resource management, and patient care. Connected care enables better patient empowerment…