- How Do Enterprises Use AI and IoT to Turn Data Into Decisions?
- What Is IoT in the Enterprise Context
- What Is AI in the Enterprise Context
- Why AI and IoT Are Stronger Together
- How Do AI and IoT Work Together Across the End-to-End Process?
- Data Capture From IoT Devices And Sensors
- Edge Vs Cloud Data Processing Considerations
- AI Model Training, Inference, And Continuous Learning
- Feedback Loops And Automated Execution
- Key Business Benefits Of AI and IoT integration
- Data-Driven Decision-Making At Scale
- Improved Customer Experience And Personalization
- Risk Reduction And Compliance Support
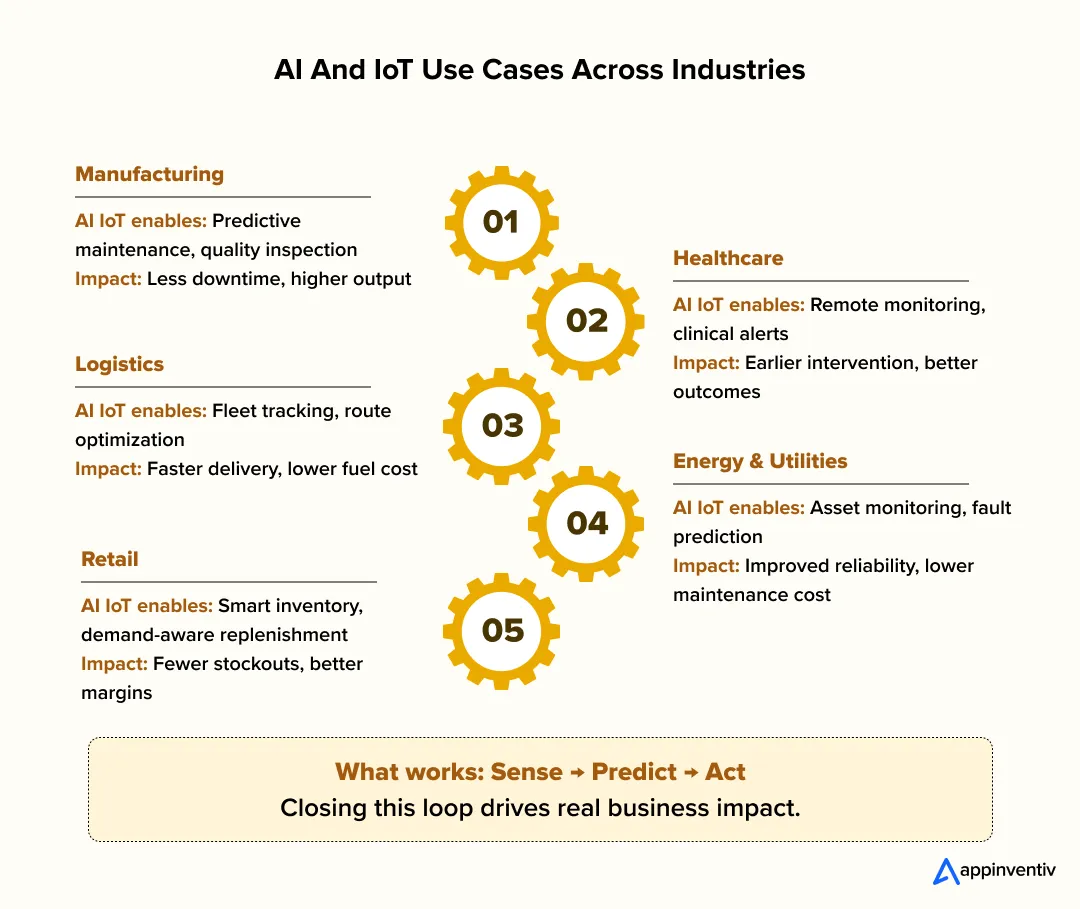
- AI and IoT Use Cases Across Industries (With Business Impact)
- Manufacturing And Industrial Operations
- Healthcare And Life Sciences
- Logistics And Supply Chain
- Retail And Consumer Commerce
- Energy, Utilities, And Smart Infrastructure
- AI and IoT integration Architecture
- Core Components Of An AI IoT Stack (Reference Architecture)
- Cloud, Edge, And Hybrid Deployment Models (Execution Architecture)
- Security And Data Governance Considerations (Control Architecture)
- AI and IoT Implementation Process For Enterprises
- Discovery And Use Case Prioritization
- Data Readiness And Infrastructure Assessment
- Model Development And System Integration
- Testing, Validation, And Phased Rollout
- Monitoring, Optimization, And Scaling
- Common Challenges In AI and IoT Adoption (And How Enterprises Work Through Them)
- Data Quality And Interoperability Issues
- Legacy System Integration
- Scalability And Latency Constraints
- Security, Privacy, And Compliance Risks
- Skills Gaps And Organizational Readiness
- Cost Of Implementing AI and IoT Solutions
- Where The Money Actually Goes
- One-Time Spend Vs Ongoing Commitment
- Why Costs Vary So Widely Across Enterprises
- How Enterprises Look At ROI Over Time
- How Appinventiv Helps Enterprises Succeed With AI and IoT
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- AI and IoT change how decisions are made, turning real-time data into actions instead of after-the-fact reports.
- Value comes from execution, not dashboards. The biggest gains appear when insights directly trigger operational responses.
- Strong architecture matters more than tools. Hybrid edge and cloud setups, clean data flows, and ownership determine success.
- ROI compounds over time. Each rollout gets faster and more valuable once the foundation is in place.
- Most failures are process-related, not technical. Clear priorities and phased execution make the difference.
Enterprises today are surrounded by data but often starved of real insight. Traditional IoT initiatives have delivered connectivity and visibility, yet many organizations still operate reactively, responding after issues occur rather than preventing them. This is where AI in IoT changes the operating model. When AI and IoT come together, connected systems can interpret data as it is generated, predict outcomes, and trigger actions automatically, shifting enterprises from monitoring assets to optimizing business performance in real time.
Looking ahead, this convergence is only gaining momentum. Industry forecasts indicate a sharp rise in connected environments, with global IoT deployments moving toward tens of billions of devices by the end of the decade. At the same time, enterprise adoption of AI continues to deepen, driven by the need to manage scale, reduce latency, and extract value from increasingly complex data streams.
This guide is written for enterprise leaders evaluating how to move IoT initiatives from visibility to autonomous, AI-driven operations without increasing risk, latency, or compliance exposure.
Without AI for IoT, many organizations face growing pain points such as data overload, slow decision cycles, higher infrastructure costs, and limited ROI from IoT investments. AI IoT architectures directly address these challenges by embedding intelligence across edge and cloud systems.
This blog will help you understand how AI in IoT internet of things solutions work in practice, where they create the strongest business impact, and what enterprises should consider when integrating and scaling them. It is designed to give decision-makers a clear, practical view of how AI and IoT together can move operations from reactive to resilient, predictive, and future-ready.
McKinsey notes that nearly 70% of AI initiatives fail to scale, allowing early movers to pull ahead while others stay stuck.
How Do Enterprises Use AI and IoT to Turn Data Into Decisions?
Before getting into use cases or architecture diagrams, it is important to be clear about what IoT and AI actually do inside real enterprise environments. Many programs fail not because of technology limits, but because these roles are misunderstood from the start.
What Is IoT in the Enterprise Context
In large organizations, IoT is less about “smart” devices and more about making operations observable. Sensors, connected machines, vehicles, medical equipment, and infrastructure continuously send signals about what is happening on the ground. Edge systems handle time-sensitive data locally, while broader streams flow into enterprise platforms.
What IoT delivers in practice:
- Ongoing visibility into assets, processes, and physical conditions
- Automated data capture across locations and systems
- Early warnings when performance starts drifting
That said, most enterprise IoT applications reach a familiar limit. They show activity, not intent. Teams can see the data, but still struggle to decide what action makes sense and how fast to respond.
What Is AI in the Enterprise Context
AI comes into play when volume and complexity make manual analysis unrealistic. In enterprises, this includes machine learning algorithms/models that learn from patterns, computer vision systems that interpret visual data, predictive analytics that anticipate outcomes, and generative AI that supports reasoning and recommendations.
Used well, AI helps organizations:
- Move beyond static rules and thresholds
- Anticipate failures, demand shifts, or quality issues
- Turn large, messy data sets into decisions that can be acted on
This is where IoT in AI starts to matter. AI becomes the thinking layer that sits on top of enterprise data and guides how systems respond.
Also Read: Harnessing AI for Business Transformation: A Comprehensive Guide
Why AI and IoT Are Stronger Together
On their own, IoT collects signals and AI analyzes information. When combined, AI in IoT connects those steps into a continuous loop. Data flows from sensors into models that interpret conditions and trigger responses, often without waiting for human intervention.
When AI and IoT are integrated properly, enterprises see:
- Systems that sense, analyze, and act as one workflow
- Fewer reactive decisions and less manual firefighting
- Intelligence pushed closer to operations, including at the edge
This is what modern AI IoT systems look like in practice. Data does not stop at dashboards. It feeds living systems that learn over time and quietly improve how the business runs every day.
How Do AI and IoT Work Together Across the End-to-End Process?
In enterprise environments, the real challenge is not connectivity. It is decision latency. AI in IoT closes the gap between what is happening in the physical world and how fast the business can respond, by linking data, intelligence, and execution into a single operational flow.
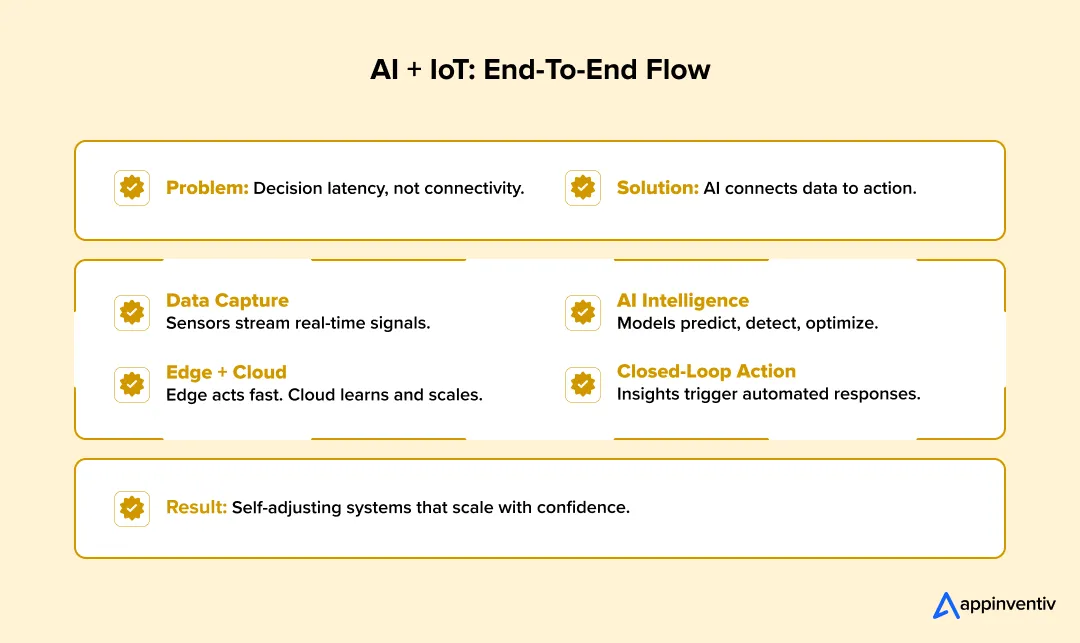
Data Capture From IoT Devices And Sensors
IoT devices continuously stream data from machines, vehicles, facilities, and infrastructure. At scale, this gives rise to common enterprise pain points: noisy data, inconsistent formats, and fragmented visibility across vendors and locations. With AI enabled IoT, teams can monitor:
- High-frequency sensor data across distributed assets
- Inconsistent data quality and context across systems
- Limited ability to prioritize signals that actually matter
Edge Vs Cloud Data Processing Considerations
Not every decision can wait for the cloud. Safety events, quality checks, and latency-sensitive operations require processing closer to the source, while deeper analysis and optimization run centrally. Many enterprises struggle to design this balance, leading to either delayed decisions or rising infrastructure costs. Adding intelligence to IoT helps in:
- Edge computing for processing real-time, mission-critical actions
- Cloud platforms for aggregation, analytics, and model management
- Ongoing complexity in synchronizing models across edge and cloud
AI Model Training, Inference, And Continuous Learning
AI models learn from historical and live IoT data to predict failures, detect anomalies, and optimize performance. The challenge is not initial training, but staying accurate over time. Asset behavior changes, environments shift, and static models quickly lose relevance.
- Model training using historical IoT data
- Real-time inference on incoming sensor streams
- Continuous retraining to manage data and model drift
Also Read: Generative AI for Business: A Practical Guide to Real-World Enterprise Adoption
Feedback Loops And Automated Execution
The final step turns insight into action. AI outputs trigger automated responses across systems, and results are fed back to improve future decisions. This is where AI and IoT move beyond monitoring into autonomy.
- Automated actions such as parameter tuning or maintenance scheduling
- Reduced manual intervention and faster response times
- Closed-loop learning that improves decisions with each cycle
This end-to-end flow is what defines scalable AI IoT systems. Data does not stop at analysis. It drives intelligent, self-adjusting operations that help enterprises respond faster, operate leaner, and scale with confidence.
AI And IoT Complexity Matrix: Where Do You Stand Today?
| Dimension | Connected Devices (Basic IoT) | Predictive Systems (AI IoT) | Autonomous Agents (Agentic IoT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Capability | Device connectivity and data collection | Pattern detection, prediction, and recommendations | Goal-driven decision-making and automated action |
| Data Usage | Raw telemetry and status data | Historical + real-time data for forecasting | Continuous learning from outcomes and feedback |
| Decision Model | Rule-based and manual | AI-assisted, human-in-the-loop | AI-driven, system-led decisions |
| Typical Use Cases | Asset tracking, monitoring, alerts | Predictive maintenance, demand forecasting | Self-optimizing operations, adaptive control |
| Level of Automation | Low | Medium | High |
| Operational Risk | Low but limited value | Moderate, depends on data quality | High if governance is weak |
| Scalability Ceiling | Reached quickly | Scales with strong data pipelines | Requires mature architecture and controls |
| Common Enterprise Pain Point | Visibility without action | Insights without full execution | Governance, trust, and oversight |
| What’s Needed Next | Intelligence layer | Execution and closed loops | Architecture, governance, and control |
| Where Appinventiv Helps | IoT foundations and integration | AI IoT architecture and deployment | Agentic design, governance, and scaling |
Key Business Benefits Of AI and IoT integration
The real value of AI in IoT does not come from isolated pilots or dashboards. It emerges when intelligence is embedded directly into operational workflows, decision paths, and control systems. At scale, AI and IoT integration changes how enterprises manage assets, make decisions, engage customers, and control risk across distributed environments.
Operational Efficiency And Cost Optimization
In traditional enterprise environments, maintenance and optimization rely heavily on schedules, averages, and manual inspections. IoT changes this by instrumenting assets with continuous telemetry. AI for IoT takes it further by learning how assets behave under real operating conditions.
At a technical level:
- IoT sensors capture vibration, temperature, pressure, energy use, and load data
- Machine learning models establish normal operating baselines
- Predictive AI analytics identify early signals of degradation or inefficiency
- Edge inference enables immediate action where latency matters
This results in:
- Predictive maintenance that prevents failures rather than reacting to them
- Dynamic asset utilization based on real demand and performance
- Reduced spare parts inventory and optimized maintenance windows
For large enterprises, especially in manufacturing, energy, and logistics, this shift can reduce downtime, extend asset life, and lower operating costs at scale.
Data-Driven Decision-Making At Scale
Many enterprises still depend on batch reports and historical dashboards, which creates decision lag. By the time insights reach leadership, conditions have already changed. AI IoT architectures replace this model with continuous intelligence.
How this works in practice:
- Helps with IoT data analytics in near real time
- AI models evaluate patterns, trends, and anomalies as data arrives
- Decisions are triggered automatically or surfaced instantly to teams
This enables enterprises to:
- Move from retrospective analysis to real-time operational control
- Apply consistent decision logic across regions and business units
- Reduce reliance on manual interpretation and subjective judgment
As data volumes grow, this becomes essential. Without IoT in AI driven decision systems, scale itself becomes a liability rather than an advantage.
Also Read: AI Analytics for Businesses – Benefits, Use Cases, and Real Examples
Improved Customer Experience And Personalization
Customer experience is increasingly shaped by context, not static profiles. AI in IoT devices allows enterprises to understand how products and services are actually used, not just how they were sold.
From a systems perspective:
- Usage data, environmental conditions, and behavioral signals are captured in real time
- AI models correlate this data to predict intent, needs, or issues
- Responses are triggered automatically across digital and physical touchpoints
This supports:
- Context-aware personalization that adapts to real-world behavior
- Proactive service interventions before customers raise issues
- More accurate recommendations based on usage, not assumptions
Across healthcare, retail, mobility, and smart services, AI in IoT applications help enterprises shift from reactive support to continuous, experience-driven engagement.
Risk Reduction And Compliance Support
As operations become more connected and distributed, traditional risk controls struggle to keep up. Point-in-time audits and manual checks are no longer sufficient. AI and IoT enable continuous oversight instead.
At a technical level:
- IoT systems monitor operational, environmental, and security conditions
- AI models detect deviations from expected patterns
- Anomalies trigger alerts, automated actions, or escalation workflows
This helps enterprises:
- Identify operational risks before they escalate into failures
- Detect security or compliance issues in near real time
- Maintain audit trails through continuous data capture and monitoring
For regulated industries, this directly addresses long-standing gaps & improvement of security in IoT & AI, reducing both regulatory exposure and operational risk without adding manual overhead.
AI and IoT Use Cases Across Industries (With Business Impact)
Enterprises get the best results from AI in IoT use cases when they focus on one thing: closing the loop between sensing, predicting, and acting. Below are high-impact applications of AI in IoT across industries, with real brand examples backed by high-authority sources.
Manufacturing And Industrial Operations
In manufacturing, industrial IoT and AI is most effective when telemetry is tied directly to maintenance and quality workflows. The pain point is familiar: too much sensor data, not enough signal, plus downtime that shows up as missed output and rushed repairs.
What’s being done in practice:
- Predictive maintenance from vibration, temperature, and load signals
- Edge AI for anomaly detection and near real-time alerts
- Computer vision quality inspection on production lines
Example: Siemens’ Senseye Predictive Maintenance is positioned to help reduce downtime by turning asset data into predictive insights across plants.
A complementary view from Arm highlights Siemens’ push toward edge AI-driven predictive maintenance to improve factory reliability.
Where this is heading: in mature deployments, AI agents in industrial IoT can recommend or trigger maintenance actions based on confidence scores, asset criticality, and production schedules, not just thresholds.
Healthcare And Life Sciences
AI and IoT in healthcare typically starts with remote monitoring, but the real enterprise value comes when streaming device data is converted into clinical signals clinicians can trust. Key pain points include alert fatigue, fragmented patient data, and delayed escalation.
High-value use cases:
- IoT powered remote patient monitoring and continuous vitals tracking
- AI-assisted detection of deterioration risk from streaming signals
- Workflow automation that routes actionable alerts to care teams
Example: Philips explains how it is using AI to transform patient monitoring data into actionable insights and streamline clinical workflows, with a focus on creating a unified real-time view for clinicians.
This is where iot and ai in healthcare becomes practical: fewer false alarms, earlier interventions, and smoother care delivery across inpatient and remote settings.
Logistics And Supply Chain
Logistics is a classic environment for IoT, AI and machine learning because conditions change constantly. Without these enterprises have to deal with delays, fuel costs, missed ETAs, and limited ability to respond to disruptions as they happen.
Common use cases:
- Fleet telematics for location, fuel, temperature, and asset health
- AI-driven route optimization and dispatch decisions
- Demand forecasting using historical + real-time operational signals
Example: DHL’s IoT trend report describes using connected devices and analytics to optimize routes and improve fleet efficiencies, including fuel economy improvements and reduced “deadhead” miles.
When implemented well, machine learning in logistics becomes an always-on decision engine: learn from every trip, adjust routing rules continuously, and reduce variability in delivery performance.
Retail And Consumer Commerce
Retailers often have the data but not the accuracy. The biggest operational pain points are inventory mismatch, stockouts, and promotions that do not match real-world demand. Here, AI in IoT devices becomes the foundation for inventory intelligence and store execution.
High-impact use cases:
- RFID and smart shelf signals for near real-time inventory visibility
- Demand-aware replenishment and shrink detection
- Context-driven promotions based on store conditions and customer patterns
Example: Forbes reported Walmart expanding RFID usage to improve store-level inventory accuracy in categories like home goods and consumer electronics.
This is where AI IoT shifts margins: fewer stockouts, better on-shelf availability, and smarter replenishment decisions.
Energy, Utilities, And Smart Infrastructure
Utilities and infrastructure operators run distributed, high-risk systems. Their pain points are outages, asset degradation, and the cost of inspecting and maintaining networks at scale. AI enabled IoT helps by continuously monitoring assets and predicting failures earlier.
Core use cases:
- Grid and asset monitoring using connected sensors and meters
- AI-based load forecasting and energy optimization
- Fault prediction and faster restoration workflows
Example: Schneider Electric’s case study with Capgemini describes an Energy Command Center built on EcoStruxure, aimed at unified and efficient energy management in buildings.
This is also where advanced analytics programs, including AI powered predictive approaches, are positioned to reduce downtime by anticipating equipment issues earlier.
Explore how structured AI IoT architectures, integration frameworks, and governance models help enterprises move from pilots to scale.
AI and IoT integration Architecture
In enterprise deployments, IoT in AI does not run on a single platform or layer. It operates across a distributed architecture where sensing, intelligence, and execution are deliberately separated but tightly coordinated. Getting this architecture right is what determines whether an AI IoT initiative scales or stalls.
Core Components Of An AI IoT Stack (Reference Architecture)
A production-grade AI IoT architecture follows a layered model, with each layer responsible for a specific function and failure domain.
- Device And Sensor Layer
This layer includes physical devices such as industrial sensors, cameras, meters, wearables, and embedded controllers.
Architecture characteristics:
- Device firmware with secure boot and identity provisioning
- Local buffering to handle network interruptions
- Standardized telemetry schemas to reduce downstream complexity
CIO risk: inconsistent device data undermines every analytics and AI initiative downstream.
- Connectivity And Messaging Layer
This layer transports data reliably and securely from devices to processing systems.Typical architecture includes:
- Lightweight messaging protocols like MQTT or AMQP
- Industrial protocols such as OPC UA for factory environments
- Message brokers or gateways for protocol translation and buffering
CTO concern: fragile networks introduce silent data loss that breaks trust in AI outputs.
- Data Ingestion And Streaming Layer
This is the backbone of AI in IoT applications. It handles scale and velocity. Architecture pattern:
- Event streaming platforms for high-throughput ingestion
- Real-time stream processors for filtering and enrichment
- Time-series databases for sensor data storage
Decision impact: without this layer, IoT programs remain trapped in pilots and dashboards.
- AI And Intelligence Layer
This layer is where AI for IoT delivers value. Architecture components include:
- Offline model training pipelines using historical IoT data
- Real-time inference services connected to streaming data
- Model monitoring and retraining workflows to manage drift
Leadership risk: models that cannot be governed or retrained become liabilities, not assets.
- Application And Control Layer
This layer translates intelligence into action. Architecture includes:
- Dashboards for human-in-the-loop decisions
- APIs that supports integration with ERP, MES, CMMS, and CRM systems
- Automated control interfaces that trigger actions directly
Board-level concern: insight without execution does not justify investment.
Cloud, Edge, And Hybrid Deployment Models (Execution Architecture)
Where AI runs is as important as how it runs. Most enterprise AI and IoT integration architectures are hybrid by design.
- Edge Architecture
Edge nodes sit close to devices and handle time-sensitive workloads. Used when:
- Latency must be under milliseconds
- Network reliability cannot be guaranteed
- Safety or quality decisions must be immediate
Architecture pattern:
- Lightweight inference engines deployed on gateways or industrial PCs
- Local rules and fallback logic if models fail
Trade-off: harder lifecycle management across thousands of nodes.
- Cloud Architecture
Cloud environments provide centralized intelligence and coordination. Used for:
- Model training at scale
- Cross-site optimization and forecasting
- Enterprise-wide visibility and governance
Architecture pattern:
- Centralized data lakes and feature stores
- Managed AI services for training and evaluation
- Unified dashboards and orchestration layers
Trade-off: higher latency and dependency on connectivity.
- Hybrid Architecture (Most Common)
This is the dominant AI IoT pattern in enterprises. How it works:
- Inference and control run at the edge
- Training, governance, and optimization run in the cloud
- Models and policies are synchronized across environments
Enterprise pain point: version control, observability, and rollback across distributed inference nodes.
Security And Data Governance Considerations (Control Architecture)
In AI ML and IoT systems, security issues rarely stop at data leaks. A single weakness can lead to unsafe machine behavior, service outages, or compliance problems that ripple across operations. As AI takes on a bigger role in automated decision-making, security and governance cannot be treated as add-ons after deployment.
Many enterprises are now building these controls directly into their architecture, aligning with Zero-Trust approaches and emerging regulations like the EU AI Act to manage risk as systems scale.
- Device And Edge Security Architecture
Includes:
- Hardware-backed identity and access management
- Secure firmware updates and remote patching
- Continuous device health monitoring
Risk if ignored: compromised devices feeding poisoned data into AI models.
- Data Integrity And Trust Architecture
AI decisions are only as reliable as their data. Key controls:
- End-to-end encryption from device to cloud
- Data validation and lineage tracking
- Tamper detection for critical telemetry
Risk if ignored: corrupted data leading to unsafe or incorrect automated actions.
- Access Control And Governance Architecture
As AI begins to automate decisions, accountability becomes critical. Architecture must define:
- Role-based access to data, models, and controls
- Audit logs for model decisions and overrides
- Policy enforcement across regions and regulatory zones
This directly addresses long-standing gaps & improvement of security in IoT & AI that surface as deployments scale.
AI And IoT architecture: what each layer must get right
| Architecture Layer | Primary Role | What Breaks If Done Poorly |
|---|---|---|
| Device & Sensor Layer | Capture reliable, secure telemetry | Inaccurate data undermines all AI decisions |
| Connectivity & Messaging | Move data safely and consistently | Silent data loss, delayed insights |
| Data Ingestion & Streaming | Handle scale and velocity | Pilots never scale beyond dashboards |
| AI & Intelligence Layer | Predict, detect, optimize | Models drift, insights lose trust |
| Application & Control Layer | Turn insight into action | Intelligence never reaches operations |
| Security & Governance Layer | Control risk and accountability | Compliance gaps, unsafe automation |
In practice, IoT in AI architecture is less about choosing a platform and more about designing for failure, scale, and change. Enterprises that succeed treat architecture as a living system, one that continuously adapts as devices increase, models evolve, and business priorities shift.
AI and IoT Implementation Process For Enterprises
Rolling out AI in IoT at enterprise scale rarely fails because of weak technology. It fails because teams move too fast, skip steps, or underestimate how tightly AI and operations are linked. The organizations that succeed treat implementation as a structured, learning-driven process rather than a one-time rollout.
Discovery And Use Case Prioritization
Most enterprises start with far more ideas than they can realistically execute. The real work here is deciding what not to build. High-value AI ML and IoT initiatives usually sit close to operational pain points where delays, downtime, or inefficiencies already cost money.
Teams typically focus on:
- Processes where real-time decisions can change outcomes
- Use cases with clear owners and measurable business impact
- Scenarios where automation reduces manual dependency, not just effort
This step sets expectations early and prevents pilots that look impressive but never reach production.
Also Read: How to Build an AI Strategy for Enterprise Applications That Actually Scales
Data Readiness And Infrastructure Assessment
Before models or platforms enter the picture, enterprises need an honest view of their data. Many IoT environments collect large volumes of signals but lack consistency, context, or reliability. That gap becomes visible the moment AI for IoT is introduced.
Key questions at this stage include:
- Is sensor data accurate, complete, and available at the right frequency?
- Can edge and cloud systems support continuous data flow?
- How well do existing systems expose data and accept AI-driven outputs?
Skipping this assessment usually leads to fragile systems and loss of confidence in AI results.
Model Development And System Integration
Once data pipelines are stable, AI development becomes practical. Models are trained on historical patterns and refined using live IoT streams. This is where IoT AI machine learning moves from theory into daily operations.
In practice, this involves:
- Aligning model outputs with how teams make decisions today
- Embedding inference into workflows rather than standalone dashboards
- Ensuring AI recommendations can be acted on without friction
The biggest risk here is misalignment. If insights do not fit operational reality, they are ignored.
Testing, Validation, And Phased Rollout
Enterprises rarely flip a switch on automation. Instead, they validate performance in controlled stages. Operators, engineers, and domain experts play a key role in testing whether AI in IoT applications behave as expected under real conditions.
This phase typically includes:
- Running models in parallel with existing processes
- Validating accuracy, timing, and reliability
- Expanding gradually across sites, assets, or regions
Phased rollout reduces disruption and builds trust across teams.
Monitoring, Optimization, And Scaling
After deployment, the real work begins. Assets age, usage patterns change, and models drift. Enterprises that treat AI IoT systems as static quickly lose value.
Ongoing focus areas include:
- Tracking model performance and decision outcomes
- Updating models as conditions evolve
- Scaling governance, security, and infrastructure alongside adoption
When handled well, implementing AI and IoT becomes repeatable. Each rollout gets faster, more predictable, and more valuable than the last.
Common Challenges In AI and IoT Adoption (And How Enterprises Work Through Them)
Most enterprises discover the real complexity of AI in IoT after the first few pilots. The technology works, but scaling it across real operations exposes issues that were easy to ignore early on. The good news is that these challenges are well understood, and experienced teams now know how to deal with them.
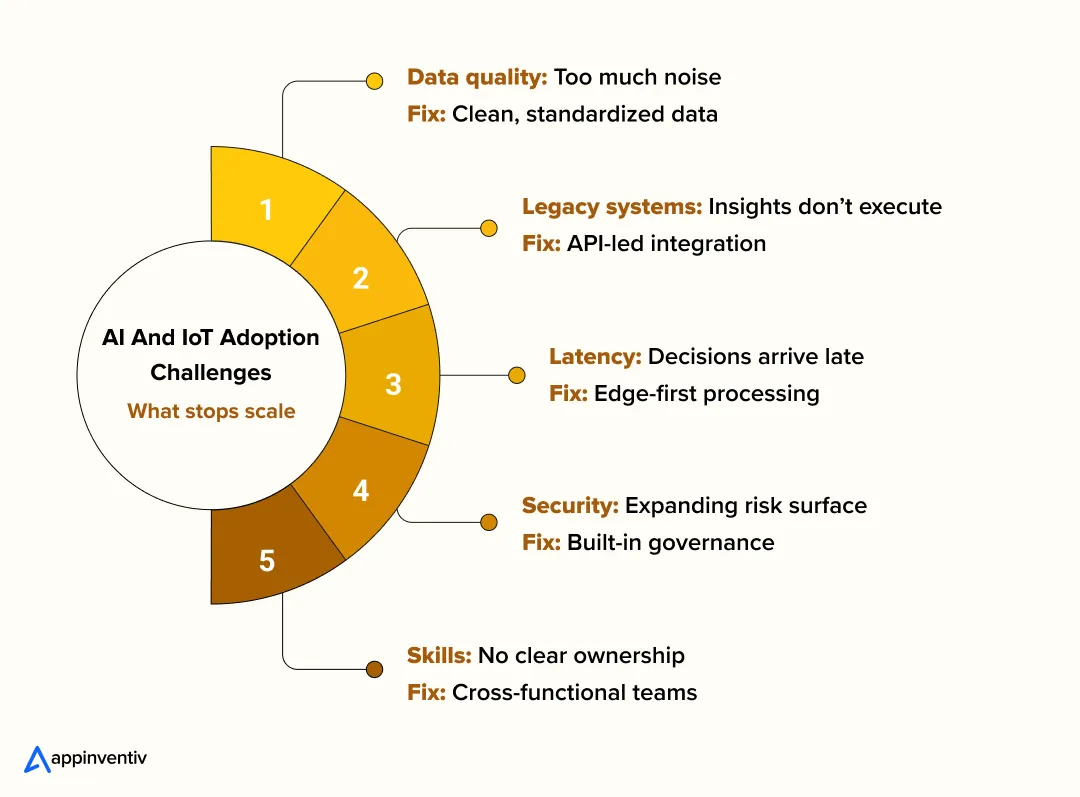
Data Quality And Interoperability Issues
IoT systems collect a lot of data, but not all of it is useful. Sensors drift, formats vary by vendor, and context is often missing. When this data feeds AI models, predictions become unreliable and confidence drops fast.
What actually works: Enterprises that succeed invest early in data discipline. They standardize device data models, clean data as it enters the system, and add lightweight validation before AI ever touches it. This ensures AI for IoT learns from signals, not noise.
Legacy System Integration
AI outputs often stop at dashboards because legacy ERP, MES, or control systems cannot consume them. Intelligence exists, but it never reaches the point where decisions are executed.
What actually works: Instead of ripping out existing systems, enterprises layer AI alongside them. APIs, event streams, and integration services allow AI, ML and IoT insights to flow into familiar workflows without disrupting core operations. Adoption improves because teams keep working the way they know.
Scalability And Latency Constraints
As device counts grow, centralized processing creates delays. Decisions arrive too late, bandwidth costs rise, and systems become fragile under load.
What actually works: Teams shift time-sensitive decisions closer to the edge while keeping training and optimization centralized. This hybrid approach keeps AI IoT systems responsive without sacrificing visibility or control as deployments expand.
Security, Privacy, And Compliance Risks
Every connected device becomes a potential entry point. If data is tampered with or access is poorly controlled, AI-driven decisions can amplify the damage.
What actually works: Enterprises design security into the system, not around it. Device identity, encrypted data paths, strict access controls, and audit logs become standard. Addressing gaps & improvement of security in IoT & AI early prevents painful retrofits later.
Skills Gaps And Organizational Readiness
AI and IoT programs stall when responsibility is unclear. Data teams build models, operations teams do not trust them, and no one owns the final decision.
What actually works: Leading organizations bring domain experts, engineers, and data teams together from day one. They start with decision support, not full automation, and build confidence gradually. Over time, AI in IoT becomes part of how the business runs, not a side project.
Cost Of Implementing AI and IoT Solutions
When enterprises talk about the cost of AI in IoT, the number itself is rarely the real concern. What leadership wants to understand is how investment translates into operational impact. In practice, most implementations fall between $40,000 and $400,000, depending on how many systems are connected, how much intelligence is required, and how deeply the solution is embedded into day-to-day operations.
Where The Money Actually Goes
AI and IoT programs are built across layers, and each layer carries its own cost profile.
- Hardware and devices
Sensors, gateways, cameras, and edge hardware form the foundation. Costs rise with scale, environmental conditions, and accuracy requirements. - Software and connectivity
Device management, data ingestion, messaging, and system integration sit here. This is where complexity often grows faster than expected. - Data platforms
Streaming pipelines, time-series storage, and analytics infrastructure are required to handle continuous IoT data. - AI development and integration
Model building, training, deployment, and integration into workflows. This is where AI for IoT creates real differentiation, but also where experience matters most.
Enterprises that plan for integration early tend to avoid expensive rework later.
One-Time Spend Vs Ongoing Commitment
AI IoT is not a “set it and forget it” initiative. Costs appear in two phases, and confusing the two often leads to budget surprises.
Upfront costs usually include architecture design, device rollout, and initial model development. Ongoing costs show up in infrastructure usage, model monitoring, retraining, and system maintenance. Over time, operational costs stabilize, while the system continues to deliver value as it learns and improves.
Why Costs Vary So Widely Across Enterprises
Not every industry spends in the same places. Manufacturing and logistics often invest more in hardware and edge systems. Healthcare environments carry higher costs around compliance and validation. Retail and infrastructure projects tend to scale device volume first, then analytics.
Smaller deployments typically stay closer to the $40K–$100K range. Multi-site or region-wide rollouts, where AI and IoT integration drives automation across core workflows, push budgets toward $250K–$400K.
How Enterprises Look At ROI Over Time
Most organizations do not justify AI IoT on experimentation alone. They link returns to concrete outcomes like reduced downtime, lower energy usage, faster decisions, or fewer manual interventions. What often becomes clear after the first rollout is that the second and third implementations cost less and deliver value faster.
For many CIOs, implementing AI and IoT becomes a capability investment. Once the foundation is in place, each new use case builds on it, improving long-term returns and making the initial spend easier to defend.
Work with a partner that designs AI IoT systems to integrate cleanly into existing platforms, processes, and compliance models.
How Appinventiv Helps Enterprises Succeed With AI and IoT
Enterprises rarely struggle with intent. They struggle with execution. AI in IoT initiatives often stalls when pilots do not scale, architectures fragments, or intelligence never reaches operational workflows. Appinventiv works at this execution layer, helping enterprises translate AI in IoT strategies into systems that run reliably inside real business environments.
Appinventiv delivers end-to-end AI and IoT consulting, development, and integration, starting with use-case discovery and moving through architecture design, model development, and production rollout. The focus stays on building systems that integrate cleanly with existing platforms and processes, not standalone proofs of concept. This is where deep experience in IoT app development becomes critical, especially when deployments span devices, edge environments, and enterprise systems.
Industry context shapes every decision. Appinventiv builds industry-specific AI IoT solutions designed for scale, governance, and regulatory realities. From mobility and logistics to healthcare and large consumer platforms, solutions are architected to meet compliance needs without slowing innovation. Our strong foundations as an Al development company ensure models remain explainable, maintainable, and aligned with operational constraints as adoption grows.
This approach is backed by experience delivering production-grade systems. One example is the work delivered for flynas, where Appinventiv engineered a large-scale digital platform capable of handling real-time data flows, complex integrations, and high transaction volumes. The same architectural discipline used in such environments applies directly to enterprise AI and IoT deployments that must perform under continuous load.
If you are planning to scale AI and IoT beyond pilots, Appinventiv can help you assess readiness, design the right architecture, and move forward with confidence, without disrupting critical operations.
FAQs
Q. How Can AI Help In Securing IoT Devices?
A. Most IoT security problems do not come from one big breach. They start small. A device behaves a little differently, sends data at odd times, or responds slower than usual. AI helps by noticing these changes early, before they turn into incidents.
In real deployments, this usually means:
- Watching device behavior continuously instead of relying on fixed rules
- Flagging unusual patterns that humans would miss
- Taking basic action automatically, like isolating a device or raising alerts
As generative AI IoT matures, teams also use it to test “what if” scenarios, stress security controls, and harden systems before attackers find the gaps.
Q. How Can AI And IoT Together Drive Enterprise Digital Transformation?
A. On their own, IoT shows what is happening. AI explains what it means. Together, they shorten the distance between events in the real world and decisions inside the business. That is where transformation actually starts.
For many organizations, AI IoT for enterprises becomes the layer that connects operations, analytics, and execution. The use of AI in IoT turns data into something teams can act on immediately, not something they review later in a report.
Q. What Business Problems Can AI IoT Solve For Large Enterprises?
A. At scale, problems tend to repeat. Assets fail unexpectedly. Decisions arrive too late. Teams spend time reacting instead of planning. AI IoT helps by shifting these patterns.
What enterprises usually see first:
- Fewer surprises from equipment and infrastructure
- Better use of resources across sites and regions
- More stable operations during demand spikes or disruptions
In more advanced setups, AI IoT robotics takes over routine inspection and handling tasks, while AI IoT business solutions bring consistency to decisions that were previously made differently in every location.
Q. How Should Enterprises Approach AI And IoT Integration?
A. The biggest mistake is starting with tools. The better starting point is the business problem that keeps showing up. Once that is clear, teams can work backward into data, architecture, and integration choices.
A phased approach tends to work best. Early stages focus on decision support. Automation comes later. This is especially important in areas like AI IoT integration in smart homes and connected facilities, where reliability and trust matter more than speed. Over time, AI IoT for enterprises becomes part of core operations, not a separate initiative.
Q. How Can Appinventiv Help Enterprises Implement AI And IoT Solutions?
A. Appinventiv works with enterprises that want to move beyond pilots. The focus is on building systems that operate reliably inside existing platforms, security models, and workflows.
That typically includes:
- Designing architectures that can scale without constant rework
- Integrating intelligence where teams already work
- Delivering AI IoT business solutions that balance innovation with control
The team also supports complex programs involving AI IoT robotics and real-time automation, where failure is not an option.
Q. What ROI Can Enterprises Expect From AI And IoT Adoption?
A. ROI usually shows up quietly at first. Less downtime. Fewer manual interventions. Faster responses when something goes wrong. Over time, these gains add up.
As systems mature, generative AI IoT opens up additional value through scenario analysis and smarter recommendations. In environments like AI IoT integration in smart homes, returns also come from better user experiences, lower support costs, and systems that are easier to manage long term.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
IoT in Wearables: An Enterprise Guide to Architecture, Integration, and Scalable Deployment
Key Takeaways IoT wearables are shifting from pilot projects to enterprise infrastructure across the healthcare, industrial, and logistics sectors. Secure integration, compliance readiness, and data architecture determine wearable success more than device hardware alone. Continuous wearable data enables predictive healthcare, workforce safety optimization, and new enterprise operational intelligence capabilities. AI-driven analytics are transforming wearable data…
IoT in Mining: Modernizing Operations for Enterprise Efficiency and Safety
Key takeaways: The Internet of Things in mining turns scattered operational signals into live, decision-ready visibility across fleets, fixed plants, people, and the environment. The biggest wins usually show up first in uptime, then in safety response, and finally in energy and process stability. “More data” does not automatically mean better performance. Value comes when…

IoT in Banking Industry: Use Cases, Examples, ROI
Key takeaways: IoT in banking creates real value only when it is treated as a software and integration problem, not a hardware initiative. Security, governance, and audit readiness determine whether IoT programs scale or quietly stall in regulated environments. IoT implementation in banking typically ranges from $40,000 to $600,000+, with cost driven more by integration…