- Why IoT Matters for Insurance
- What Are the Key Benefits of IoT in Insurance?
- 7 Key Benefits of IoT in Insurance
- 10+ High-Value IoT Use Cases in Insurance
- 1. Usage-Based Auto Insurance
- 2. Smart Home and Property Monitoring
- 3. Commercial and Industrial Asset Tracking
- 4. Faster and More Accurate Claim Settlement
- 5. Fraud Prevention and Validation
- 6. Usage-Based Pricing for Multiple Product Lines
- 7. Customer Engagement and Retention
- 8. Better Underwriting and Risk Modeling
- 9. Loss Prevention Through Early Action
- 10. Fleet and Cargo Monitoring
- 11. Embedded Insurance and Smart Device Partnerships
- How IoT Enables New Business Models for Insurers
- Business Models Gaining Traction
- Why This Matters for Insurers
- How IoT Works Behind the Scenes in Insurance
- Connected Devices and Sensors
- Gateways and Data Transmission
- Cloud Storage and Processing
- Integration Through APIs
- AI and Predictive Scoring
- Why This Matters
- Protecting Data and Staying Compliant with IoT Insurance
- What Data Responsibility Means in IoT Insurance
- Consent and Transparency
- Security and Technical Protection
- Regional Legal Requirements
- Why This Matters for Insurers
- What Are the Common Challenges and Practical Solutions for IoT in Insurance?
- Integration With Legacy Systems
- Data Accuracy and Device Reliability
- Customer Consent and Adoption
- Vendor and Platform Selection
- Scaling Beyond Pilot Programs
- Why This Matters for Insurers
- Understanding the ROI of IoT in Insurance
- Where The Cost Comes From
- Where Financial Return Appears
- What to Measure
- Why ROI Matters In IoT Decision-Making
- Real World Examples of IoT in Insurance
- IoT in Car Insurance – Progressive Snapshot
- IoT in Home Insurance – Chubb with Hartford Steam Boiler (HSB)
- IoT in Life Insurance – John Hancock Vitality (wearable driven underwriting)
- IoT in Commercial and Industrial Insurance – Munich Re IoT Cover
- What Are the Future Trends of IoT in the Insurance Industry?
- 5G Connectivity for Real-Time Insurance Decisions
- Edge Computing for Faster Local Insights
- Satellite IoT for Remote Asset and Property Coverage
- AI-powered Risk Scoring Models
- Why These Future Trends Matter
- 10 Point Checklist for Insurers Starting IoT Transformation
- How Appinventiv Supports IoT Transformation in the Insurance Industry
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- IoT in insurance moves decisions from static risk estimates to real-time insights drawn from vehicles, homes, and personal devices.
- Connected sensors help insurers lower fraud, detect issues early, and settle claims faster with clear evidence instead of guesswork.
- The biggest IoT use cases today include telematics for driving habits, smart home leak and fire alerts, wearable health tracking, and industrial equipment monitoring.
- Successful rollout depends on strong privacy controls, customer consent, secure data handling, and compliance with laws like GDPR and CCPA.
- Future growth will come from 5G connectivity, edge analytics, satellite IoT for remote assets, and AI-powered risk scoring models.
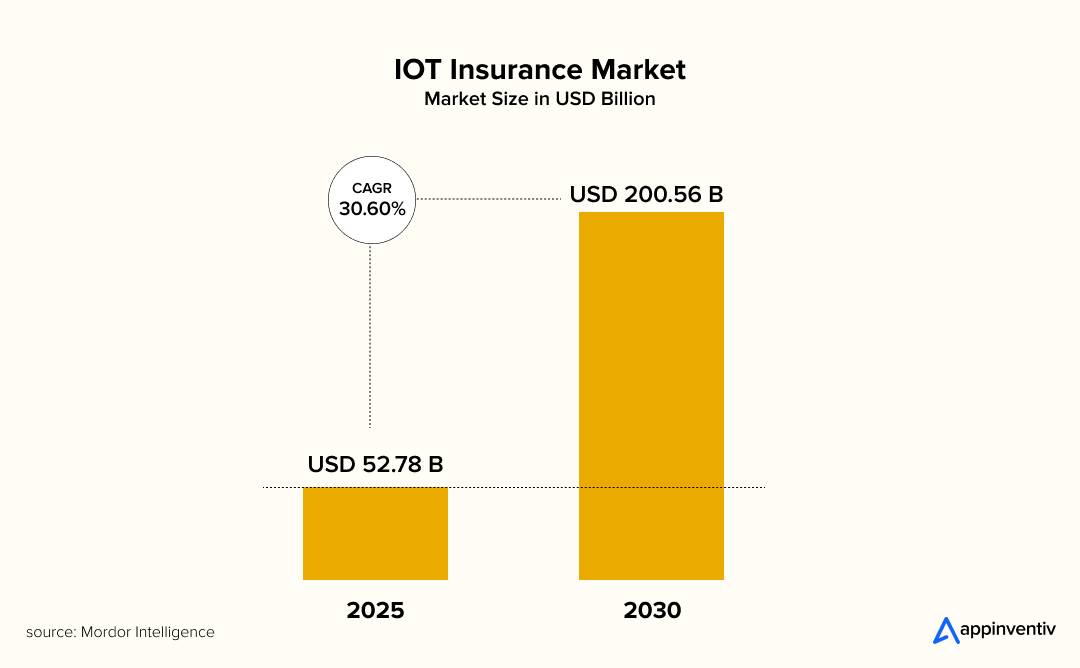
The insurance sector is shifting toward real-time risk prevention instead of waiting for losses to occur. A core driver behind this transformation is the rising adoption of IoT in the insurance industry, leveraging data from connected vehicles, homes, wearables, and other smart devices. According to a recent market analysis, the global IoT insurance market is expected to reach $200 Billion by 2030, reflecting a growing tilt toward continuous risk monitoring and prevention.
In the article that follows, we explore 10+ meaningful ways in which connected devices are reshaping insurance. From underwriting to claims, prevention to personalization, we will explore all these examples of IoT in insurance, real-world results, and a clear view of opportunities and challenges ahead.
Why IoT Matters for Insurance
Most insurance decisions still rely on old records and broad risk categories that do not change once a policy is issued. IoT introduces a smarter model built on live data from vehicles, homes, and personal devices. This steady flow of real-time information helps insurers understand what is happening now, not what happened months or years ago. It is a key reason the IoT in the insurance industry continues to grow.
How IoT creates value for insurers:
- Better accuracy in underwriting: Decisions shift from estimated risk to measured behavior through connected devices.
- Faster claim response: real-time alerts allow insurers to act before issues turn into full claims.
- Early risk detection: Common IoT use cases in insurance include spotting water leaks, unsafe driving habits, or abnormal activity in buildings.
- Personalized policy design: Coverage can match the way customers actually live, drive, and maintain their homes.
- Customer engagement and retention: Policyholders respond well to guidance and rewards instead of long paperwork and delayed payouts.
This mix of precision, prevention, and improved customer experience shows why connected insurance solutions are becoming a standard expectation rather than an experimental technology.
What Are the Key Benefits of IoT in Insurance?
One of the biggest shifts in the insurance space is the move toward direct, real-time visibility. IoT gives insurers data they never had before, collected continuously from connected vehicles, home sensors, wearable devices, industrial systems, and more.
Instead of working with outdated risk scores or broad assumptions, teams can make decisions based on what is happening in real life. This helps insurers build services that feel timely, personal, and practical for customers. IoT in health insurance also benefits from this shift since wellness data can support preventive treatment, early alerts, and lower risk exposure over time.
7 Key Benefits of IoT in Insurance
- Real-time risk evaluation
IoT data helps insurers detect patterns that signal rising risk. A temperature spike in a commercial building or an unusual vibration in a delivery truck can trigger early intervention and reduce the chance of costly claims. - Lower fraud cases
Fraud remains a major cost driver in both personal and commercial lines. Connected sensors provide event proof, time stamps, and usage records that help verify claim accuracy. This is especially useful when addressing insurance fraud issues. - Faster claim settlement
Claims often get delayed due to missing details. With connected devices supplying live data, insurers spend less time collecting documents and more time resolving cases. This reduces administration burdens and improves customer satisfaction. - Usage-based pricing
Instead of fixed annual rates, policies can mirror real behavior. Safe drivers, well-maintained buildings, and active lifestyle choices can lead to lower premiums. Risk becomes transparent on both sides of the process. - Improved customer experience
Alerts that warn of water leaks, unsafe driving, or health concerns give customers clear value before any claim occurs. People get support throughout the policy life cycle, not just when something goes wrong. - Data-driven decision-making
IoT devices create structured and unstructured data that insurers can analyze to design better products and services. Actuarial teams get access to current information rather than working with limited historical datasets. - Operational cost reduction
When claims are prevented or resolved quickly, insurers lower service costs and improve loss ratios. This makes digital transformation efforts in insurance easier to justify at the leadership level.
These benefits of IoT in insurance position carriers to shift from reactive problem-solving to ongoing risk partnership. It builds more accurate pricing models, creates stronger customer relationships, and sets a clearer path for innovation.
10+ High-Value IoT Use Cases in Insurance
Connected data systems change how insurance works at every stage. From underwriting to claims and customer engagement, IoT produces a continuous flow of information that helps insurers understand risk in real life. These IoT in insurance use cases show how connected devices improve clarity, reduce uncertainty, and support daily decision-making.
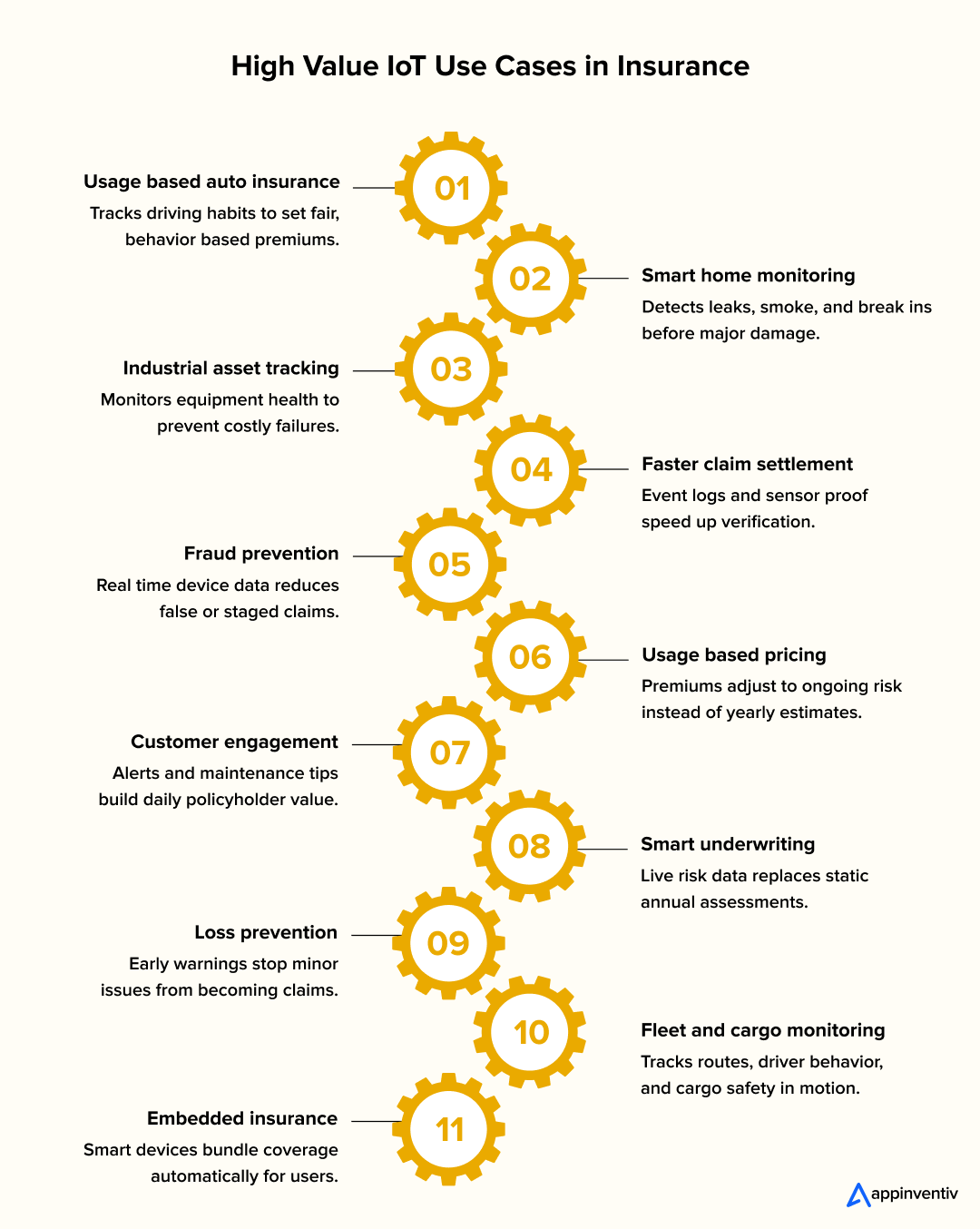
1. Usage-Based Auto Insurance
Auto risk is not the same for every driver. Traditional pricing models rely on broad groups like age or location, but these categories often fail to reflect how someone actually drives. With IoT telematics in place, insurers gain access to real behavior data taken from each trip in real-time.
What it includes
- Tracking acceleration, braking, and cornering behavior
- Recording phone interaction or distraction during driving
- Measuring mileage, rush hour exposure, and night driving habits
Impact for insurers: Premiums reflect genuine risk, supporting fairness and value in IoT in car insurance while encouraging safer driving patterns.
2. Smart Home and Property Monitoring
Homes contain multiple systems that can fail without warning. Water pipes, heating units, smoke alarms, and entry points create risk when unseen issues start small and expand over time. IoT sensors bring visibility to these moments so homeowners can respond before damage gets worse.
What it includes
- Leak sensors that detect early moisture before major flooding
- Smart alarms for smoke, carbon monoxide, and unusual heat
- Window and door sensors for break-in detection
- Temperature and humidity tracking to protect household items
Impact for insurers: Claims drop as issues are detected earlier, and underwriting improves when IoT in home insurance data shows how well a property is maintained.
3. Commercial and Industrial Asset Tracking
Large properties, such as plants, warehouses, and offices, often contain equipment that can be costly to repair or replace if a failure goes unnoticed. IoT introduces continuous monitoring that signals potential hazards long before serious damage occurs.
What it includes
- Environmental sensors to monitor temperature or humidity
- Vibration tracking to detect mechanical stress in machinery
- Electrical monitoring to predict fire or power system issues
- Moisture sensors for storage areas that protect valuable goods
Impact for insurers: Commercial risk becomes predictable and measurable, allowing deep insight rather than one-time inspections or static ratings.
4. Faster and More Accurate Claim Settlement
Claims require evidence. Before IoT, adjusters often had to investigate by asking questions and reviewing photos or documents provided by the policyholder. IoT supplies real-time records that reduce confusion and speed up verification.
What it includes
- Automatic event logging with timestamps and incident triggers
- Sensor data that shows when and how a loss happened
- Digital records that remove repetitive claim documentation
Impact for insurers: Faster claim settlement strengthens trust, reduces handling costs, and makes service smoother for policyholders.
5. Fraud Prevention and Validation
Fraudulent claims are difficult to identify using paperwork alone. IoT devices create a transparent record of physical events, which helps insurers verify details and minimize disputes. This drives more confident decision-making.
What it includes
- GPS logs that confirm location statements
- Time-based records to confirm or question reported incidents
- Device data that supports or challenges reported damages
Impact for insurers: Reduces uncertainty in disputed cases, lowers instances of IoT in insurance fraud, and improves overall profitability.
6. Usage-Based Pricing for Multiple Product Lines
Pricing based only on historical data creates inconsistencies. IoT provides continuous risk signals, allowing insurers to create policy terms that match ongoing experiences rather than relying on a single annual review.
What it includes
- Discounts for ongoing sensor use
- Real-time adjustments based on recent data patterns
- Renewal pricing that reflects current property or driving habits
Impact for insurers: Customers get clearer expectations and transparent terms, which support long-term trust and easier renewal conversations.
7. Customer Engagement and Retention
Insurance communication usually happens during claims or renewal. IoT introduces daily interactions built around prevention and safety, shifting the experience from occasional contact to regular ongoing value.
What it includes
- Alerts that warn of risks in vehicles, homes, or personal health
- Notifications for maintenance or improvement suggestions
- Reward programs that encourage safe or healthy choices
Impact for insurers: Engaged customers tend to remain long-term, file fewer claims, and view insurance as a service instead of a transactional product.
8. Better Underwriting and Risk Modeling
Underwriting based on static annual reviews can miss ongoing risk updates. IoT data turns underwriting into a continuous process, allowing teams to recalculate risk as new data is collected each week or month.
What it includes
- Real-time data feeds united with actuarial models
- Predictive analytics that score risk from sensor inputs
- Segmenting customers into precise risk cohorts
Impact for insurers: Smarter predictions create room for better planning and reduce uncertainty when designing or adjusting policies.
9. Loss Prevention Through Early Action
Insurers benefit when losses do not occur. Prevention is often cheaper than paying out claims, so IoT encourages a shift from financial recovery to proactive protection.
What it includes
- Smart systems that alert users about leaks, smoke, or unusual vibrations
- Safety notifications before damage spreads
- Simple maintenance reminders supported by sensor feedback
Impact for insurers: Lower claim frequency improves financial outcomes, and policyholders receive real practical support.
10. Fleet and Cargo Monitoring
Transport, logistics, and delivery operations expose vehicles and cargo to changing conditions. IoT tracking gives insurers detailed insight into risk along every route.
What it includes
- Real-time location updates
- Driver performance tracking throughout trips
- Temperature or shock sensors for sensitive cargo
Impact for insurers: Data transparency improves underwriting decisions and encourages safer operations in commercial fleet coverage.
11. Embedded Insurance and Smart Device Partnerships
Insurers can offer policies that operate in the background, supported by the connected devices customers already use. This creates an ongoing cycle of protection that does not require customers to think about insurance actively.
What it includes
- Bundled policy options linked to smart equipment
- Premium reduction based on ongoing device usage
- Shared value model connected to daily preventive actions
Impact for insurers: Embedded coverage strengthens loyalty and supports future growth across IoT in insurance sector offerings.
Explore our insurance software development services for IoT applications and real time risk data.
How IoT Enables New Business Models for Insurers
Most insurers start with basic IoT use cases such as tracking vehicles or monitoring leaks in homes. The next stage is discovering new ways to package insurance services that go beyond claim payments. IoT provides consistent data, visibility, and touch points that support fresh revenue opportunities and customer experiences.
Business Models Gaining Traction
- Proactive risk prevention services
Insurance shifts from financial recovery to active value delivery. Carriers can offer services like maintenance reminders, real-time hazard alerts, or condition monitoring packages as part of the policy. - Behavior-based rewards programs
Connected devices make it possible to measure safe driving, consistent exercise, or proper home care, and reward customers for positive actions. These incentives encourage preventive behavior while reducing claims. - Pay as you use coverage
Rather than fixed annual premiums, IoT supports flexible coverage that changes based on how often and how safely assets are used. This works in auto, property, fleet, and equipment insurance. - Equipment monitoring and maintenance bundles
Insurers can include access to sensor kits, monitoring platforms, or building inspection tools as a value add. Customers receive peace of mind, and insurers gain better data insight. - Shared risk partnerships with service providers
Connected home technology, vehicle platforms, or facility management tools can combine with insurance. This creates service ecosystems where prevention, data, and coverage are packaged together.
Why This Matters for Insurers
By combining sensor data with policy design, insurers build deeper relationships and unlock recurring value beyond traditional premium models. These new IoT opportunities in insurance expand how coverage is sold, delivered, and experienced, making insurance a daily service instead of a distant safety net.
How IoT Works Behind the Scenes in Insurance
Most teams see IoT through a dashboard or a claim notification, but a full chain of steps sits behind every useful alert. Understanding the flow makes planning easier and sets realistic expectations before devices go live in the field.
Connected Devices and Sensors
Sensors pick up simple physical signals: movement, temperature, pressure, vibration, location, and similar clues that something is changing in the real world. These devices sit in homes, vehicles, or equipment and usually run on low power networks such as NB IoT, Zigbee, or LTE M so they can operate for long stretches without constant attention.
Gateways and Data Transmission
Gateways act as collectors. They gather sensor activity and pass it on to cloud services. Many enterprise setups use MQTT or CoAP messaging because these protocols move telemetry with little delay. It is common to see insurers lean on AWS IoT Core or Azure IoT Hub to manage authentication, device identity, and data transfer without building everything from scratch.
Cloud Storage and Processing
After the data arrives in the cloud, it needs to be sorted and made usable. Time series databases or storage services like S3, Data Lake, or BigQuery keep the information organized. Stream tools such as Kafka or Kinesis help filter out noise so underwriting and claims teams can read signals in near real time rather than waiting for end of day reports.
Integration Through APIs
IoT data carries value only when it reaches policy systems, claims tools, or CRM platforms. That connection usually happens through APIs. REST or GraphQL endpoints let insurers bring new data streams into existing systems without rewriting legacy software. It is often a gradual process rather than a full system overhaul.
AI and Predictive Scoring
AI-powered risk scoring models look for patterns in this steady flow of information. They can flag unusual driving behavior, identify a leak risk from humidity changes, or send a warning after repeated vibration spikes in machinery. Popular cloud platforms include SageMaker and Azure Machine Learning, but the key result is the same: decisions based on current conditions instead of general assumptions.
Why This Matters
A clear view of the technical flow makes it easier to budget, plan, and choose vendors. Instead of treating IoT like a single product purchase, leaders see how devices, messaging, storage, and analytics fit together. This helps avoid common surprises and gives teams a roadmap they can follow at their own pace.
Protecting Data and Staying Compliant with IoT Insurance
IoT brings a steady stream of personal and behavioral data into insurance systems. Managing that information responsibly is essential. Privacy controls, clear consent, and alignment with local laws protect customers and reduce the risk of regulatory issues for insurers.
| Category | What It Covers | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Who controls IoT data from devices | Define ownership clearly in policy terms and IoT device agreements |
| User Consent | Permission to collect and use data | Use clear opt-in steps and simple language for disclosure |
| Data Collection Limits | What data is gathered through sensors | Only collect data required for underwriting, claims, or risk prevention |
| Storage and Retention | Where data is stored and for how long | Plan retention periods that support customer rights and compliance rules |
| Security Controls | Protecting data from unauthorized access | Use encryption, access controls, and regular security reviews |
| Customer Rights | Access, update, or deletion of personal data | Support easy requests and transparent procedures |
| Regulatory Compliance | Alignment with local privacy laws | Track changes to CCPA, GDPR, UAE PDPL, DPDP Act, and similar rules |
| Third Party Handling | Data shared with external vendors or platforms | Create vendor agreements with clear privacy and risk controls |
| Breach Response | Steps if unauthorized access occurs | Prepare incident response plans and notification processes |
What Data Responsibility Means in IoT Insurance
Connected devices record more than simple status updates. They capture location, movement patterns, maintenance history, environmental conditions, and sometimes personal health information. Each data type requires careful consideration.
Insurers need to decide:
- Which data is necessary
- How long data remains in storage
- Who can access it across internal teams
- When and how customers may request removal
Consent and Transparency
Transparency supports trust. Customers should know why their data is being collected and how it supports their policy or claim. Consent must be simple to grant and simple to withdraw.
Important actions include:
- Clear opt-in choices before device activation
- Privacy notifications in plain language
- Easy access to personal data records
Security and Technical Protection
Personal data must remain protected from unauthorized access. Security planning starts at the device level and continues through data transmission and storage.
Areas to address:
- Encryption during data transfer
- Strong authentication for device access
- Regular reviews for potential vulnerabilities
Regional Legal Requirements
Compliance varies globally. Insurers deploying systems across international markets should understand local rules around data use.
Examples include:
- The California Consumer Privacy Act in the United States
- The General Data Protection Regulation in the European Union
- New data laws under the UAE and Saudi Arabia personal data standards
- India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act policies
Why This Matters for Insurers
Strong privacy practices create confidence and reduce the likelihood of complaints or legal disputes. IoT solutions scale more smoothly when built around secure data design that supports customer rights from the beginning. This approach also sets a stable base for future innovation in IoT in insurance industry applications.
What Are the Common Challenges and Practical Solutions for IoT in Insurance?
Adopting IoT gives insurers real-time insight, better underwriting models, and stronger customer engagement. At the same time, IoT introduces operational, technical, and regulatory hurdles. Planning ahead with clear solutions helps insurers reduce risk and move from pilot projects to successful deployment.
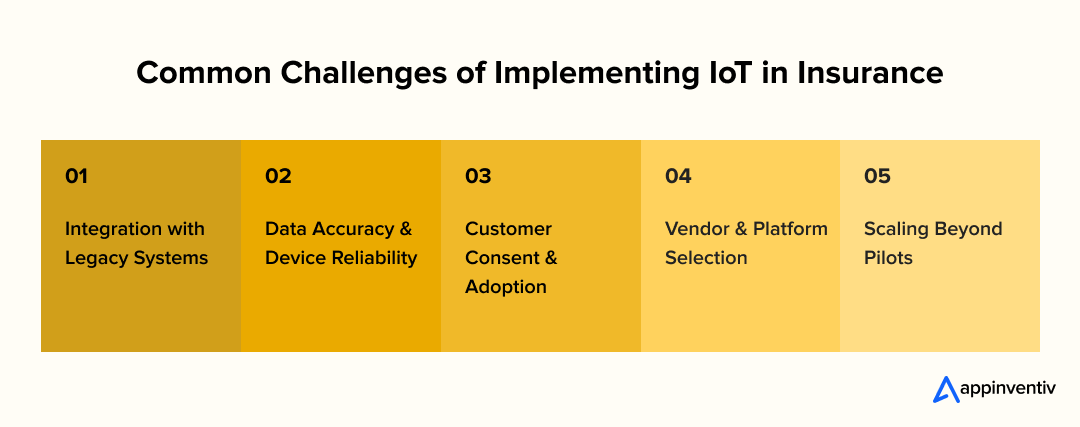
Integration With Legacy Systems
Existing policy and claim systems were built to manage static records rather than continuous sensor streams. This creates bottlenecks during large scale data ingestion.
Key issues
- Legacy databases struggle with high frequency IoT data
- real-time alerts do not fit traditional workflows
- Batch processing delays decision-making
Practical solutions
- Introduce a middleware layer to translate sensor data into policy systems
- Use scalable cloud storage instead of legacy servers
- Deploy message queues to handle real-time alerts smoothly
Data Accuracy and Device Reliability
Sensor readings need to be consistent. Faulty devices, poor installation, or signal interruptions can lead to incomplete or incorrect data sets.
Key issues
- Incorrect readings reduce trust in IoT systems
- Environmental conditions can distort data
- Inconsistent device performance requires ongoing checks
Practical solutions
- Set calibration schedules for sensors at installation and regular intervals
- Test devices under real conditions before rollout
- Use IoT platforms that can flag unusual or missing data patterns
Customer Consent and Adoption
Customers may hesitate to install devices or share personal data unless benefits are clear. Strong communication and ease of use influence adoption rates.
Key issues
- Concerns related to privacy and tracking
- Installation effort may discourage participation
- Misunderstanding about what data is collected
Practical solutions
- Provide simple onboarding instructions and self setup options
- Use short, clear value statements explaining what customers gain
- Include incentives such as premium discounts or rewards for device usage
Vendor and Platform Selection
The IoT marketplace is fragmented. Insurers may need multiple vendors for devices, connectivity, analytics, and integration which increases complexity.
Key issues
- Compatibility concerns across device types
- Varying support levels and update timelines
- Contract challenges around data ownership and handling
Practical solutions
- Choose vendors based on open standards and API availability
- Include data governance requirements in vendor contracts
- Consider a unified IoT management platform to reduce fragmentation
Scaling Beyond Pilot Programs
Small scale tests are manageable, but growth introduces new responsibilities in support, logistics, and monitoring.
Key issues
- Managing thousands of devices and firmware updates
- Training staff to handle real-time data streams
- Customer service volume increases as adoption grows
Practical solutions
- Develop a long-term device lifecycle management plan
- Prepare internal training programs for claims and underwriting teams
- Start with limited product lines and expand based on measured success
Why This Matters for Insurers
Addressing these IoT challenges in insurance early can reduce delays, improve return on investment, and support long-term success. A solution driven approach turns common obstacles into manageable planning steps rather than barriers to innovation.
Understanding the ROI of IoT in Insurance
Insurance companies need a clear view of cost and value to adopt IoT confidently. Return on investment depends on how well sensors, platforms, and data processes reduce losses and improve customer experience. The goal is to make IoT a predictable business decision rather than a technology experiment.
| Category | What It Includes | How It Creates Value | Key KPIs to Track |
|---|---|---|---|
| Device and Sensor Costs | Leak detectors, telematics, wearables, industrial monitors | Enables real-time data capture and preventive action | Number of devices deployed, device uptime |
| Connectivity & Data Flow | Network fees, gateways, data transmission services | Supports rapid alert delivery and continuous monitoring | Data latency, connection reliability |
| Cloud Storage & Processing | Data cleaning, analytics, and storage platforms | Improves decision accuracy for underwriting and claims | Time to analyze data, data completeness |
| Integration & Software Development | Linking IoT data with policy and claim systems | Removes manual work and accelerates automation | Claim processing time, workflow efficiency |
| Maintenance & Support | Firmware updates, quality checks, device support | Preserves long-term data reliability and system accuracy | Device error rate, data quality score |
| Claim Reduction | Early detection and fewer events turning into claims | Lowers operational and payout cost | Claim frequency, average claim value |
| Faster Claim Settlement | Automated validation and incident records | Reduces manual investigation effort | Claim cycle duration |
| Customer Retention | Alerts, guidance, and incentive programs | Encourages loyalty and renewals | Renewal rate, NPS or satisfaction |
| Accurate Pricing | real-time Behavior-based risk scoring | Reduces mispricing and exposure to high risk policies | Loss ratio, pricing accuracy score |
Where The Cost Comes From
IoT requires several types of investment. Devices are the most visible expense, but supporting systems also require planning.
- Device installation: Physical sensors such as leak detectors, telematics modules, wearables, or commercial monitor units.
- Connectivity and data transmission: Network fees for moving data from sensors to cloud systems.
- Platform and storage requirements: Systems needed to store, clean, filter, and analyze continuous device data.
- Integration and customization: Work required to connect IoT information with existing underwriting and claims tools.
- Ongoing support: Regular device maintenance, updates, and quality checks.
Where Financial Return Appears
ROI develops over time as real data improves visibility and decision-making. The greatest returns often appear in claims management and customer engagement.
- Lower loss frequency: Early alerts and preventive action reduce the number of claims submitted.
- Lower loss severity: Small issues get fixed earlier, keeping repair or replacement costs down.
- Faster claim handling: Sensor records shorten claim assessment cycles and reduce case management time.
- Better retention and renewals: Customers stay longer when insurance feels useful before an incident occurs.
- More accurate pricing: real-time data supports precise risk scores, reducing mispricing and reducing exposure.
What to Measure
A simple way to measure ROI is to compare improvement in key insurance metrics after IoT deployment.
Track changes in:
- Loss ratio
- Claim cycle time
- Average claim size
- Policy retention rate
- Customer satisfaction
Why ROI Matters In IoT Decision-Making
Clear ROI planning helps insurers choose the right place to begin, whether it is auto telematics, property monitoring, or health risk scoring. It supports realistic budgeting and backs long-term vision for the future of IoT in insurance solutions that scale with confidence.
Real World Examples of IoT in Insurance
Insurers around the world have shifted from theoretical IoT pilots to active, large scale deployments. These examples show how connected devices are shaping pricing, claims, engagement, and prevention in everyday insurance operations.
IoT in Car Insurance – Progressive Snapshot
Progressive uses telematics insurance through its Snapshot program to record real driving behaviors such as braking, acceleration, mileage, and phone distraction. Drivers who show consistent safe habits may qualify for lower premiums. The program demonstrates how real driving data creates fairer pricing and encourages safety.
IoT in Home Insurance – Chubb with Hartford Steam Boiler (HSB)
Chubb partnered with Hartford Steam Boiler (HSB, part of Munich Re group) to install IoT sensors in select homes and businesses. The sensors detect water leaks, humidity and temperature fluctuations, vibration or pressure changes to warn users before damage escalates. This marks a shift from “repair and replace” to “predict and prevent.
IoT in Life Insurance – John Hancock Vitality (wearable driven underwriting)
John Hancock uses wearable data through its Vitality program to encourage healthier lifestyles. Policyholders track activity using Fitbit, Garmin, and Apple Health devices. Healthier behavior contributes to rewards, lower premiums, and better long-term life insurance outcomes. This shows how IoT in life insurance supports continuous risk scoring beyond medical records.
IoT in Commercial and Industrial Insurance – Munich Re IoT Cover
Munich Re’s IoT Cover program offers insurance “backed by smart IoT components,” covering industrial IoT, connected buildings and services, infrastructure, and machinery. Their offerings help clients detect malfunctions or hazards early (temperature, humidity, vibration, structural stress), helping avoid breakdowns, reduce losses, and offer a new kind of coverage tied to IoT performance guarantees
These examples show that IoT use cases in insurance are not limited to pilots or test environments. Large brands deploy connected systems to improve underwriting, lower claim frequency, and support customers before problems occur. The approach is becoming standard practice for insurers focused on future growth and customer experience.
What Are the Future Trends of IoT in the Insurance Industry?
As IoT in insurance matures, the technology behind connected data is evolving fast. The next wave of innovation will be driven by faster networks, distributed analytics, global device coverage, and intelligent risk scoring. These developments will make IoT more reliable and useful for underwriting, claims, and customer support.
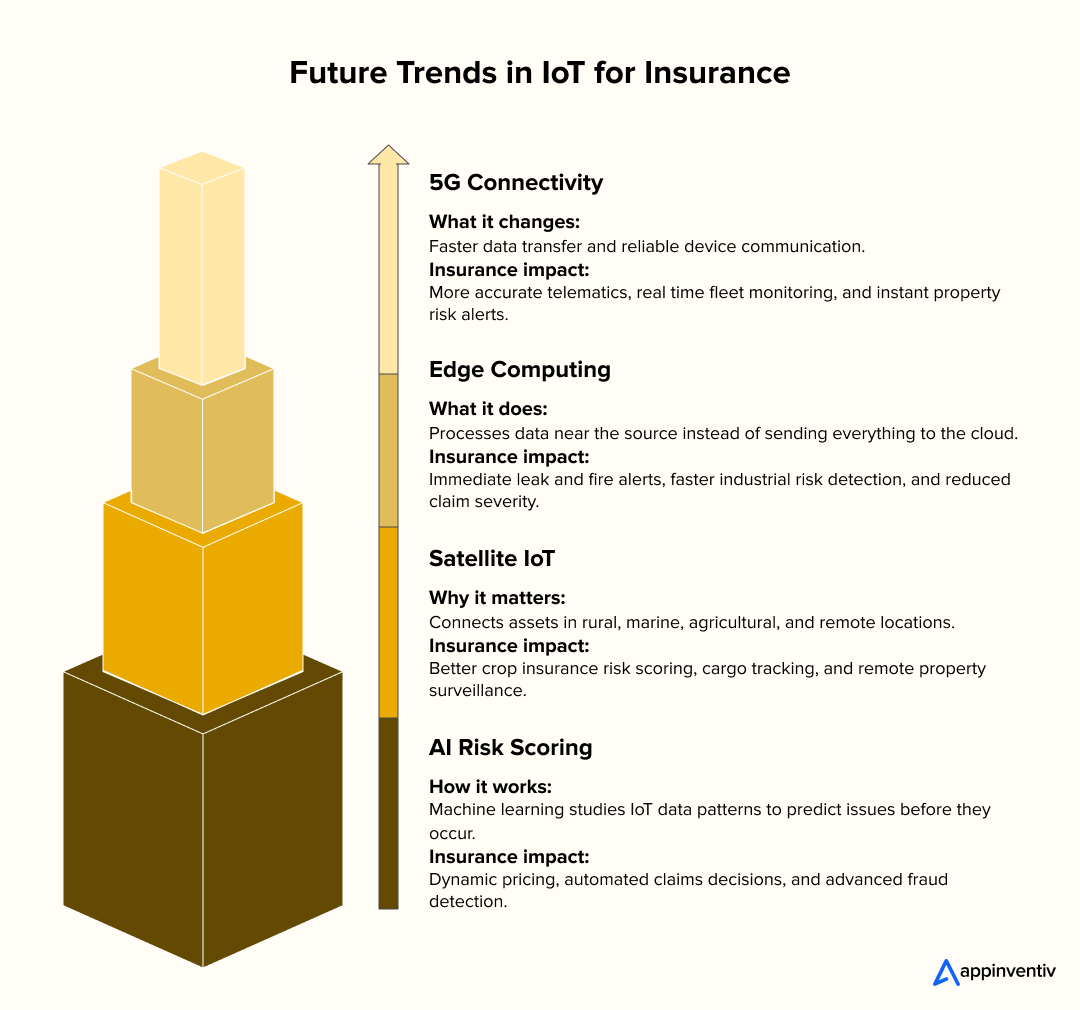
5G Connectivity for Real-Time Insurance Decisions
5G networks provide faster data transmission and more reliable device connectivity. For insurers, this allows sensors to send high frequency updates without delays, especially in areas where response time matters.
What changes in insurance:
- Improved telematics accuracy for driving analytics
- real-time monitoring for logistics and fleet insurance
- Live property risk alerts during storms or environmental events
5G and IoT supports policy decisions that reflect immediate conditions instead of historical averages.
Edge Computing for Faster Local Insights
Edge computing in IoT processes data closer to where it is generated instead of sending everything to centralized servers. This reduces latency and improves performance for IoT systems.
How insurers can benefit:
- Instant alerts from leak sensors or temperature monitors
- Faster damage detection in industrial locations
- Local risk assessment without waiting for cloud processing
Edge computing supports a preventive approach where action happens faster and claim severity decreases.
Satellite IoT for Remote Asset and Property Coverage
Satellite connected devices allow insurers to monitor remote regions where typical broadband or cellular networks do not reach. This opens new opportunities for agricultural, marine, rural, and infrastructure insurance.
Where it makes an impact:
- Farm equipment monitoring and crop insurance risk assessment
- Marine cargo tracking across international shipping routes
- Remote property surveillance in wildfire, flood, or desert areas
Satellite IoT expands coverage possibilities and supports new insurance product lines.
AI-powered Risk Scoring Models
Artificial intelligence uses IoT data patterns to score risk in ways that manual underwriting cannot. Models learn from large datasets, identify unusual behavior, and improve pricing accuracy over time.
Applications for insurers:
- Behavior-based risk scores for auto, home, and health insurance
- Automated decision support for claims assessment
- AI-powered fraud detection based on abnormal sensor patterns
AI models help insurers move from static risk profiles to adaptive scoring driven by real world conditions.
Why These Future Trends Matter
These technologies establish the foundation for scalable, intelligent, and global IoT in insurance industry solutions. Insurers that invest early in connectivity, analytics, and automation in insurance will be able to deliver faster service, fairer pricing, and stronger prevention tools across personal, commercial, and specialty insurance lines.
10 Point Checklist for Insurers Starting IoT Transformation
Insurers succeed with IoT when they treat it like a business program instead of a technology experiment. The checklist below helps teams make disciplined decisions that support security, value, and long-term adoption.
- Pick one high impact line of business: Choose a single domain where IoT can show fast results such as auto telematics, home leak detection, or commercial temperature monitoring.
- Start with device partners instead of building hardware: Work with established IoT vendors to reduce engineering overhead and avoid delays in procurement, testing, and certification.
- Get legal and compliance teams involved early: Data consent, privacy disclosures, and retention rules shape every IoT deployment. Bring legal teams in before your first device ships.
- Focus on alert automation rather than dashboards: Human attention is limited. Automated alerts triggered by threshold conditions provide more value than dashboards people forget to check.
- Include customer incentive design from the beginning: IoT success depends on user participation. Plan rewards, discounts, or premium benefits to encourage customers to install and maintain devices.
- Require integration planning before rollout: Decide where IoT data goes in underwriting, claims, or CRM systems. Integration matters more than device features.
- Define data security rules and exception handling: Set standards for missing, corrupt, or late data. Clear data security and safety rules improve users’ trust in IoT metrics and reduce confusion internally.
- Track a limited set of performance metrics: Focus on three to five KPIs such as claim frequency, claim severity, loss ratio, and average claim cycle time.
- Prepare device lifecycle support: Plan for replacement schedules, firmware updates, connectivity trouble, and customer support related to physical devices.
- Create a cross functional IoT task group: Include people from underwriting, claims, IT, compliance, operations, and customer service. IoT will touch all of them.
This checklist gives insurers a straightforward way to begin planning IoT in insurance industry transformation with clarity and control. Let me know if you want this formatted as a visual graphic or quick reference card.
Talk to our experts about deploying scalable IoT solutions for underwriting, claims, and prevention.
How Appinventiv Supports IoT Transformation in the Insurance Industry
Insurers entering IoT need a partner with technical depth and a history of building Data-driven products at scale. Appinventiv has delivered more than 200 FinTech solutions over the past 10 years, and this experience gives our teams a practical understanding of sensitive data handling, real-time event processing, and regulated product environments. These strengths transfer directly into projects involving IoT in the insurance industry where risk data, device outputs, and customer experience must align with compliance and speed.
Our insurance software development services include device integration, policy data automation, cloud migration, analytics dashboards, and alert engines built around real-time triggers. A good example of our IoT capability is the ActiDrive driver assistant application. This solution captures live driver behavior data, identifies unsafe actions, and supports immediate response through mobile alerts. While not an insurance platform, it shows how our IoT application development services turn physical world signals into meaningful digital decisions.
Appinventiv helps insurers plan IoT rollouts without complexity by building systems that work with existing platforms rather than replacing them. We support integration with third party devices, design scalable data pipelines, and set up workflows that convert raw sensor information into practical business outcomes. The result is a clear path from IoT vision to live deployment with measurable results in prevention, pricing, and service quality.
If you want to explore IoT in the insurance industry with a reliable technology partner, our team is ready to help you get started.
FAQs
Q. How does IoT reduce insurance fraud?
A. IoT devices create time stamped, verifiable data that shows when and where an event occurred. This helps insurers confirm whether a loss is genuine and detect unusual patterns such as staged accidents or exaggerated damage. Sensor logs, telematics data, and environmental readings provide objective evidence that reduces dispute risk and lowers the cost of fraud in the IoT in the health insurance industry.
Q. What role does AI play in IoT based insurance?
A. AI analyzes large volumes of IoT data to identify trends, detect anomalies, and score risk. It can recommend pricing adjustments, automate claim validation, and alert teams to potential fraud. In practice, AI turns raw sensor information into decision support for underwriting, claims, and customer engagement.
Q. What are the data privacy concerns in IoT insurance solutions?
A. Privacy issues revolve around how personal data is collected, stored, shared, and retained. IoT devices can gather location, behavior patterns, and real-time activity data, so insurers must ensure clear consent, minimal data collection, encryption, and transparency around sharing information with third parties.
Q. How does IoT in insurance comply with data privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA?
A. Compliance requires obtaining explicit user consent, defining data usage clearly, and providing customer rights such as access, correction, and deletion. Insurers working with the iot in the insurance industry must implement secure storage, data minimization, audit trails, and region-specific policies that align with GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and HIPAA for health-related information in the United States.
Q. Are there certified IoT security standards insurers should follow?
A. Yes. Common frameworks include ISO/IEC 27001 for information security management, NIST guidelines for cybersecurity, and OWASP recommendations for IoT device protection. Following these standards helps insurers establish strong security baselines for connected devices, data networks, and cloud systems.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.
IoT in Wearables: An Enterprise Guide to Architecture, Integration, and Scalable Deployment
Key Takeaways IoT wearables are shifting from pilot projects to enterprise infrastructure across the healthcare, industrial, and logistics sectors. Secure integration, compliance readiness, and data architecture determine wearable success more than device hardware alone. Continuous wearable data enables predictive healthcare, workforce safety optimization, and new enterprise operational intelligence capabilities. AI-driven analytics are transforming wearable data…
IoT in Mining: Modernizing Operations for Enterprise Efficiency and Safety
Key takeaways: The Internet of Things in mining turns scattered operational signals into live, decision-ready visibility across fleets, fixed plants, people, and the environment. The biggest wins usually show up first in uptime, then in safety response, and finally in energy and process stability. “More data” does not automatically mean better performance. Value comes when…

IoT in Banking Industry: Use Cases, Examples, ROI
Key takeaways: IoT in banking creates real value only when it is treated as a software and integration problem, not a hardware initiative. Security, governance, and audit readiness determine whether IoT programs scale or quietly stall in regulated environments. IoT implementation in banking typically ranges from $40,000 to $600,000+, with cost driven more by integration…





































