- What AI Governance Means in 2026?
- Why Guidelines Are No Longer Enough
- Understanding AI Guardrails for Enterprise Use
- Guardrails vs Policies vs Constraints
- Why This Matters for Leaders:
- Building Production-Grade Guardrails for LLMs
- Input Validation And Prompt Filtering
- Output Filtering And Toxicity Detection
- Detecting Hallucinations
- Preventing Prompt Injection
- Data Leakage Prevention
- Guardrails For RAG Systems
- Guardrails For Agentic AI Systems
- Designing Enterprise-Grade AI Observability for Governance
- What Enterprises Need Visibility Into
- Telemetry, Logging, and Lineage
- Dashboards and Real-Time Alerting
- Why This Matters for the Board & CRO:
- Inside the Structure of a Responsible and Governed AI Pipeline
- 1. Data Layer
- 2. Training and Fine-Tuning
- 3. Model Registry
- 4. Deployment Layer
- 5. Observability
- 6. Feedback and Retraining
- Why This Matters for Enterprise Scale:
- How Enterprises Govern Modern AI Systems Like Generative AI, LLMs, RAG, and Agentic AI
- LLM-Specific Risks and the Fix
- RAG-Specific Risks and the Fix
- Multimodal Risks and the Fix
- Agentic AI Risks and the Fix
- Preventing Hallucinations in LLMs
- How Enterprises Detect, Route, and Block Hallucinations
- Guardrail Patterns That Reduce Incorrect Outputs
- Where Observability Supports Hallucination Control
- Ensuring Data Privacy and Compliance in LLM Workflows
- Regulatory Landscape Executives Need to Understand
- GDPR (European Union)
- EU AI Act
- HIPAA (United States)
- CCPA (California)
- PDPL (UAE)
- Compliance Mapping Table for AI Systems
- Documentation, Explainability, Lineage, and Audit Trails
- Lineage Tracking That Works for Enterprises
- Risk Scoring for Governance Reviews
- Model Card Template for Transparency
- ROI of Investing in AI Governance
- Cost of Failure
- Cost of Compliance Failures
- Efficiency Gains From Automation
- Scalable and Safe Innovation
- How Enterprises Measure AI Governance Effectiveness
- How AI Governance Consulting Helps Enterprises Mature Faster?
- How to Find the Right AI Governance Consulting Partner
- How Appinventiv Builds Governed, Compliant, Enterprise-Ready AI Systems
- FAQs
- Enterprises can no longer rely on principles alone; AI governance must be built into pipelines, model workflows, and decision systems from day one.
- Strong guardrails across training, inference, retrieval, and agentic actions reduce risks like hallucinations, data leakage, and prompt injection.
- AI observability is central to governance, giving leaders real-time visibility into drift, bias, safety issues, and compliance signals.
- Responsible AI pipelines help standardize development, deployment, monitoring, and documentation, ensuring every model follows the same rules.
- Governance consulting accelerates enterprise maturity by bringing structure, templates, and proven operational patterns that scale safely.
Most enterprises are now using AI — but far too few have the guardrails needed to manage risks. According to the 2025 McKinsey & Company “State of AI” report, 88% of organizations say they use AI in at least one business function.
What stands out is how uneven the maturity levels are. Teams are launching copilots, experimenting with LLMs, and automating decisions, yet the supporting AI compliance and governance layers often lag behind. AuditBoard’s survey shows that only 25% of companies have a fully implemented governance program, which means many are deploying advanced systems without a strong enterprise AI governance framework or clear oversight for data usage, model behavior, and compliance obligations.
For executives, this gap introduces avoidable operational, financial, and reputational exposure. It’s why building AI guardrails for enterprises and working with partners who understand Responsible AI strategy consulting are now becoming foundational to enterprise transformation rather than a late-stage maturity add-on. These governance foundations also create room for responsible AI development and governance, helping organizations scale AI without overextending risk.
In this blog, we’ll explore how enterprises can strengthen trust in their systems, adopt AI governance best practices, and move toward responsible adoption with confidence. Each section builds toward a practical view of what strong guardrails, monitoring, and responsible AI pipelines consulting can look like inside real enterprise environments.
Is your AI governance ready?
What AI Governance Means in 2026?
AI governance in 2026 is much more practical than the early “principles and promises” stage. For enterprises, it refers to the rules, workflows, and technical controls that guide how AI gets built, tested, deployed, and watched over. When people search “What is AI governance?” They want to know how an organization keeps their models reliable, compliant, and accountable as they scale through a more mature AI governance framework consulting approach.
How governance differs for ML and LLMs
- Traditional ML still depends on strong data quality checks, drift monitoring, and clear performance thresholds, which remain central to governance in machine learning models.
- LLMs, and especially generative models, introduce a different mix of challenges. They can leak information, invent facts, accept harmful prompts, or produce outputs no one expects.
- Because of this, enterprises now need governance that covers both predictable statistical models and far less predictable language models — a shift that requires stronger AI risk governance and security measures than in previous years.
Why Guidelines Are No Longer Enough
Most companies already have Responsible AI principles written down somewhere. The real shift in 2026 is turning those ideas into controls inside the pipeline, not just statements in a document. This is where implementing AI compliance and governance becomes essential, since governance has become operational, not theoretical.
Why C-level leaders care
Executives want to move quickly with AI, but they also worry about compliance gaps, bias, and unpredictable model behavior. Good governance helps them move forward without slowing teams down, giving the business a way to innovate with fewer surprises. This is also why many leaders now prioritize Responsible AI guardrails for enterprises as part of their long-term AI roadmap.
Next, we’ll step into how enterprises approach guardrails that make this possible.
Understanding AI Guardrails for Enterprise Use
AI guardrails are the practical controls that keep models safe, predictable, and aligned with business rules. When people search “What are AI guardrails?” or “How do you make LLMs safe?” They’re really asking how enterprises prevent harmful or unreliable behavior in production systems, which is a core part of modern AI Guardrails and Observability practices.
Where enterprise should implement guardrails:
- Training: Filtering datasets, removing sensitive information, checking and reducing AI bias before a model ever learns from the data.
- Inference: validating inputs, blocking unsafe prompts, scanning outputs for toxicity or leakage, and stopping responses that fall outside accepted boundaries.
- Retrieval: making sure LLMs only pull from authorized sources, use fresh content, and avoid exposing internal documents.
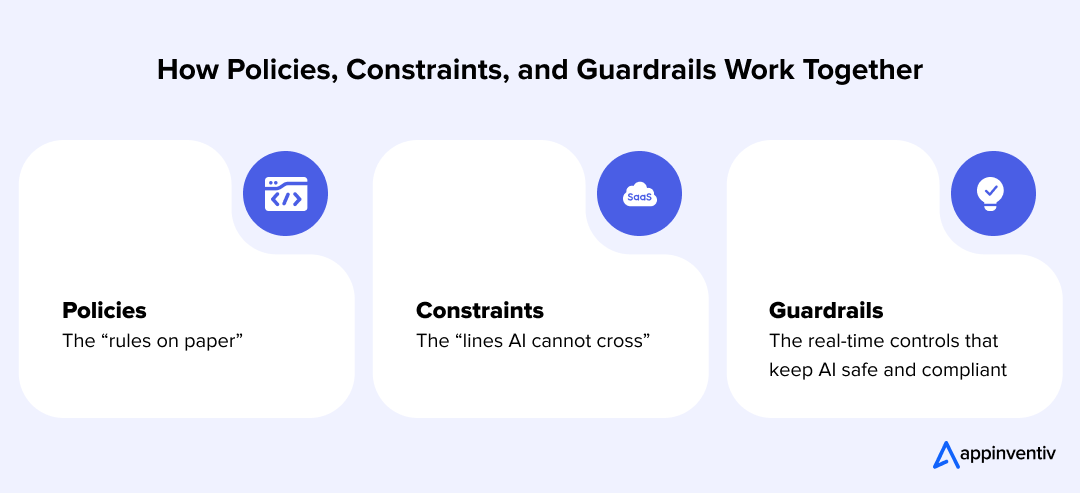
Guardrails vs Policies vs Constraints
Enterprises often use these terms interchangeably, but they serve different purposes.
- Policies describe the principles the organization wants to follow. They explain what “responsible” or “safe” AI should look like, but they don’t enforce anything on their own.
- Constraints define the limits a system must operate within, such as blocked data types, restricted actions, or boundaries for acceptable outputs.
- Guardrails bring both together in a practical way. They sit inside the pipeline and actively shape model behavior, whether that means rejecting an unsafe prompt, filtering a toxic response, or preventing an LLM from accessing restricted documents.
In other words, policies tell teams what to aim for, constraints set the boundaries, and guardrails make sure those boundaries are followed every time the model runs. Understanding this distinction is important for enterprises investing in ethical AI systems for businesses that need predictable and accountable outputs.
Why This Matters for Leaders:
- Enables board-defensible AI decisions, not just technically safe outputs.
- Reduces regulatory exposure by enforcing controls at runtime, not post-incident.
- Prevents uncontrolled LLM or agent behavior before it impacts customers or compliance.
- Shifts AI risk from reactive firefighting to predictable, governed execution.
Building Production-Grade Guardrails for LLMs
Enterprises deploying LLMs quickly realize that these systems behave very differently from traditional models. They generate text, follow prompts, and draw inferences in ways that aren’t always predictable. According to a NIST research brief, large language models remain highly vulnerable to prompt injection, data leakage, and fabricated outputs, even when deployed in controlled settings.
This is why building AI guardrails for enterprises has become a core requirement for any production LLM and why so many teams now rely on stronger AI risk management frameworks to keep failures contained.
Below are the layers that make these guardrails both effective and scalable.
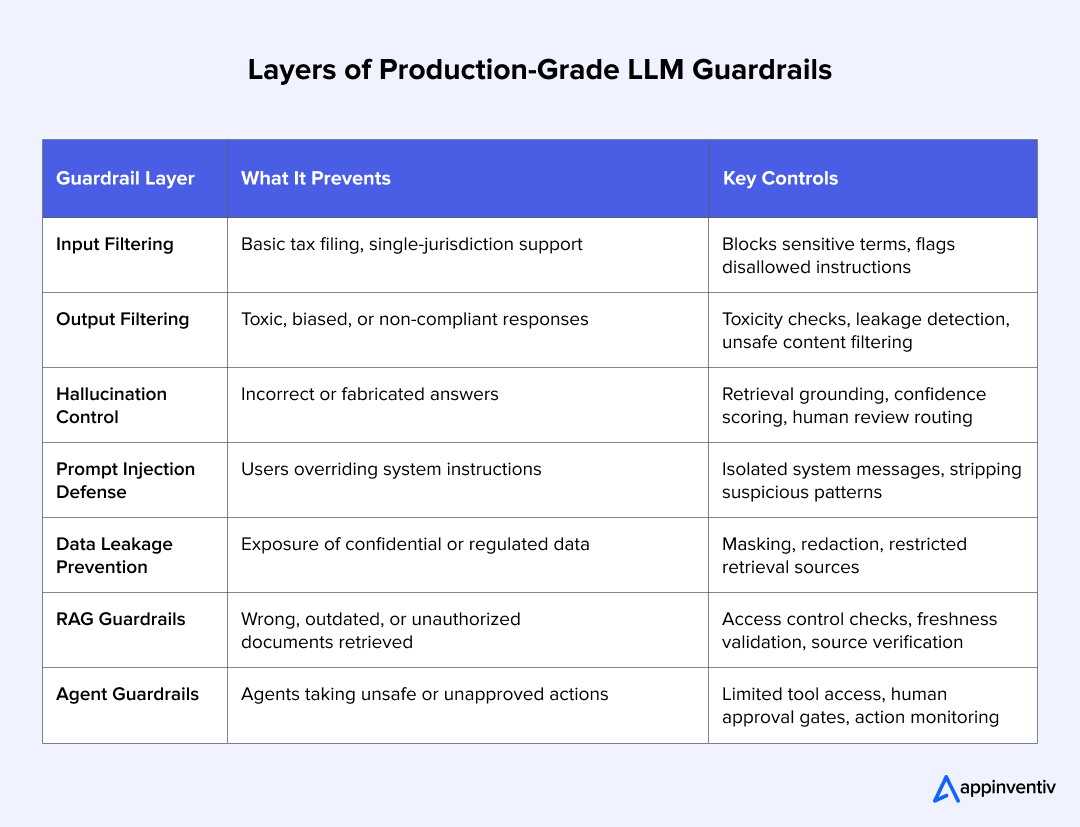
Input Validation And Prompt Filtering
Before an LLM processes anything, the system should check:
- whether the prompt is allowed
- whether sensitive terms or disallowed instructions appear
- whether the request falls outside policy or risk thresholds
Example: An internal finance chatbot should reject prompts asking for employee salaries or customer account details. These early checks help with AI bias detection and mitigation, especially when prompts may expose inequities in responses.
Output Filtering And Toxicity Detection
LLMs can produce harmful, biased, or inappropriate text. Output filters act as the final checkpoint before content reaches a user or downstream system.
What this layer usually checks:
- toxicity or abusive language
- personal data leakage
- policy violations
- harmful instructions or unsafe recommendations
Example: A healthcare assistant LLM must block outputs that resemble clinical diagnosis unless approved workflows are followed.
Detecting Hallucinations
Hallucinations are one of the most common issues executives ask about: “How do we stop LLM hallucinations?”
Guardrails for hallucination management often include:
- grounding responses through retrieval instead of free generation
- adding confidence scoring to highlight uncertain outputs
- routing risky queries to a human reviewer
- enforcing source linking so the LLM can only answer using verified documents
Example: A customer service LLM must cite the internal knowledge base or return “I don’t have that information” instead of inventing policies.
Preventing Prompt Injection
Prompt injection allows users to override system instructions. NIST highlights this as one of the most active attack vectors against enterprise LLMs.
Effective defenses include:
- isolating system messages so users cannot modify them
- stripping or flagging suspicious patterns (“ignore previous instructions”)
- sandboxing external content before it’s fed into the prompt
- enforcing role-based access control in LLM chains
Example: An employee-facing HR bot should not reveal internal policy drafts through a cleverly constructed prompt. Many enterprises bring in ethical AI consulting for enterprises here to validate safety assumptions.
Data Leakage Prevention
Data leakage is the question C-suite leaders ask the most: “How do we ensure LLMs don’t leak data?”
Guardrails here include:
- strict filters for names, IDs, financial fields, medical terms
- on-the-fly masking or redaction
- restricting retrieval sources and excluding high-risk documents
- banning the model from training on user queries
Example: A banking LLM must mask account numbers in every answer, even if the user typed them in the prompt.
Guardrails For RAG Systems
Retrieval-Augmented Generation solves many hallucination problems but introduces new risks.
RAG guardrails typically cover:
- validating document access rights
- filtering outdated or expired content
- ensuring the retrieval step returns only trusted sources
- adding guardrails between retrieval and the LLM to prevent unauthorized data flow
Example: A legal research assistant must only pull from approved contracts, not old drafts in shared folders.
Guardrails For Agentic AI Systems
Agentic systems can perform tasks on their own, increasing both value and risk.
Guardrails here include:
- limiting the actions an agent can take
- requiring human approval for high-risk steps
- restricting which tools or APIs the agent can access
- monitoring action sequences for unusual patterns
Example: A procurement agent may draft vendor emails automatically but must get approval before sending them. Strong boundaries here become part of an organization’s broader AI risk governance and security program.
Designing Enterprise-Grade AI Observability for Governance
As AI becomes embedded in core business workflows, observability is no longer optional. C-level leaders searching for “What is AI observability?” or “How do you monitor LLMs?” want a clear view into how models behave in production and why they behave that way. Observability sits at the center of AI governance best practices, helping enterprises move from reactive oversight to proactive risk management.
It goes beyond basic monitoring by tying model behavior to root-cause signals, and it supports auditability by preserving a complete record of how decisions were generated. Together, these capabilities strengthen AI compliance and governance for both traditional ML systems and modern LLMs. This helps in forming a foundation for mature AI observability solutions across the enterprise.
What Enterprises Need Visibility Into
A strong observability layer acts as a real-time safety net. The most important signals for C-level teams include:
- Drift detection to identify whether model predictions begin deviating from expected patterns
- Bias indicators supporting AI bias detection and mitigation
- Data quality shifts that impact downstream accuracy
- Latency and reliability metrics for production workloads
- Security anomalies, such as unusual prompt structures or repeated access attempts
- Toxicity and safety signals that highlight harmful or non-compliant outputs
- Usage analytics required for audits and observability and accountability in AI governance
These metrics form the backbone of modern AI observability solutions, allowing enterprises to detect failures long before they affect customers or compliance obligations.
Telemetry, Logging, and Lineage
To make observability actionable, organizations rely on a consistent telemetry schema. Effective AI pipeline observability solutions typically capture:
- Inputs and outputs, with masking for regulated fields
- Confidence scores, retrieval sources, and reasoning traces
- System prompts and role-based instructions
- Error logs, drift events, and rejected responses
- Policy-violation markers generated by guardrails
This level of logging supports investigations, compliance reviews, and model explainability efforts. It also strengthens responsible AI technology integration, since development teams can trace issues back to specific events or model states.
Dashboards and Real-Time Alerting
Data is only useful if teams can interpret and act on it. Enterprise dashboards often track safety, performance, fairness, and reliability in one place, giving leaders a complete view of model health. Effective alerting systems include:
- Threshold alerts when drift, bias, or safety scores cross defined limits
- Auto-escalation for high-risk or repeated violations
- Human approval triggers for sensitive or low-confidence outputs
With these controls in place, enterprises gain a stronger foundation for AI risk governance and security while still enabling teams to deliver AI features quickly and confidently.
Why This Matters for the Board & CRO:
- Provides real-time visibility into model risk, drift, bias, and safety violations.
- Creates audit-ready evidence for regulators, internal risk committees, and legal reviews.
- Transforms AI oversight from periodic reviews to continuous governance assurance.
- Allows executives to intervene before AI issues escalate into incidents.
Inside the Structure of a Responsible and Governed AI Pipeline
A responsible AI pipeline is where governance actually takes shape. It brings consistency to how models are built, reviewed, deployed, and monitored. Instead of depending on scattered processes, enterprises use this pipeline to make sure every model follows the same checks and safeguards, no matter who built it or where it runs.
This is the layer where responsible AI pipelines consulting becomes practical, turning policies into technical controls. Below is how a mature enterprise AI governance framework usually comes together.
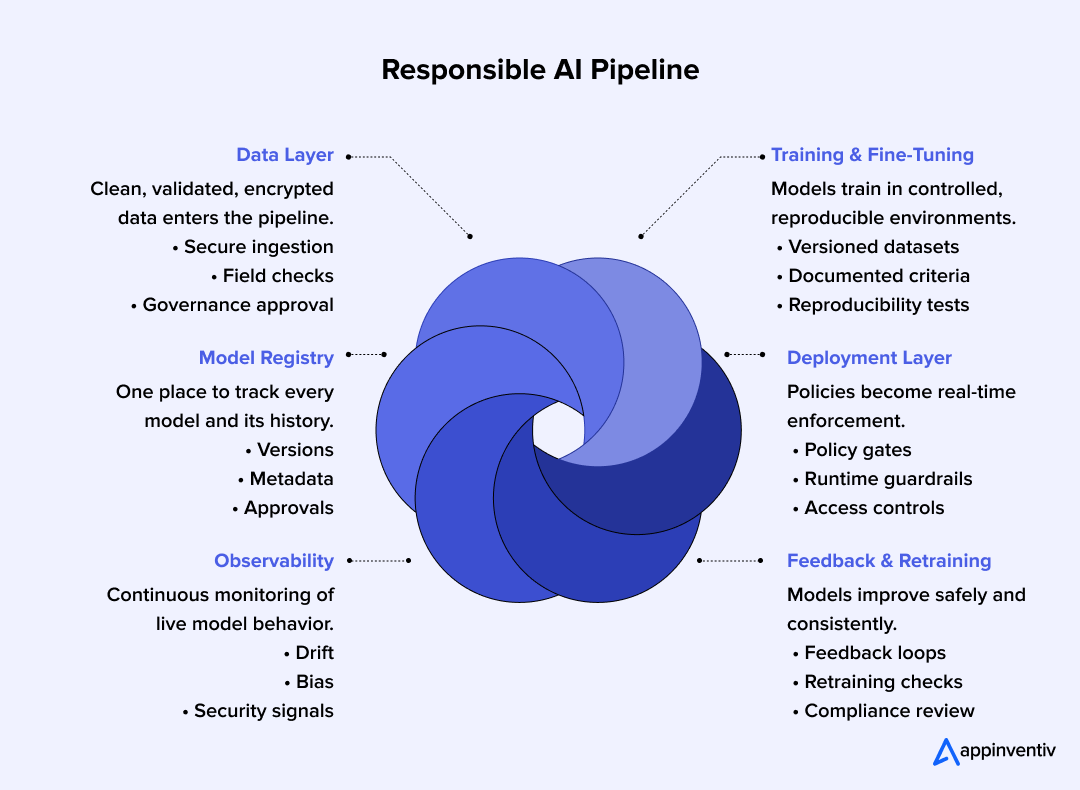
1. Data Layer
This stage focuses on getting the data right before anything reaches the model. Strong controls here prevent many of the issues that later show up as bias, drift, or compliance violations, aligning directly with AI governance best practices.
Key elements include:
- Secure data ingestion
- Field-level validation rules
- Encryption for sensitive attributes
- Dataset governance reviews to approve training inputs
2. Training and Fine-Tuning
Models are trained in environments where every step can be reproduced. This matters for audits, troubleshooting, and making sure the model behaves the same way across environments.
Typical practices:
- Isolated training environments
- Versioned datasets and scripts
- Documented LLM fine-tuning criteria
- Reproducibility tests before approval
3. Model Registry
The registry serves as the control room of the entire ecosystem. It records every model version and tracks its lineage. A governed registry prevents accidental deployment of outdated or unapproved models and supports governance in machine learning models.
The registry usually stores:
- Version history
- Training metadata and signatures
- “Golden model” designation vs. experimental versions
- Approval status and evaluation results
4. Deployment Layer
This is where enforcement becomes real. Before a model goes live, it passes through policy checks and guardrails that ensure it behaves within acceptable boundaries.
Deployment safeguards often include:
- Policy enforcement gates
- Runtime guardrails for inputs and outputs
- Access controls for sensitive operations
- Automatic rejection of unsafe or non-compliant requests
5. Observability
Once deployed, the model needs constant visibility. Observability helps teams catch early warnings and understand why the model is behaving a certain way. This forms a core part of Observability in AI governance.
What enterprises monitor:
- Drift signals
- Bias and safety indicators
- Reliability and latency trends
- Security anomalies or misuse attempts
6. Feedback and Retraining
Models evolve as data changes. This stage helps teams decide when updates are needed and ensures every change is documented for compliance and future reference.
Key steps in this stage:
- Collecting user and system feedback
- Retraining based on performance drops
- Recording updates in documentation templates
- Verifying compliance before redeployment
Together, these steps form a pipeline that allows enterprises to scale AI with confidence instead of guesswork. It provides structure, reduces risk, and helps teams maintain control even as their AI footprint grows under a more mature AI compliance and governance discipline.
Why This Matters for Enterprise Scale:
- Standardizes governance so every model follows the same approval and risk rules.
- Eliminates shadow AI deployments across teams and vendors.
- Makes accountability clear across data, model, deployment, and monitoring stages.
- Enables faster AI scaling without multiplying compliance and operational risk.
How Enterprises Govern Modern AI Systems Like Generative AI, LLMs, RAG, and Agentic AI
As enterprises scale, generative AI security and governance challenges shift from controlling simple predictions to managing far more flexible and context-dependent behavior. Each system type introduces its own set of risks, and each requires targeted fixes to keep outputs reliable, compliant, and safe.
This is where a structured enterprise AI governance framework becomes essential for operationalizing controls across different model classes.
LLM-Specific Risks and the Fix
LLMs can produce hallucinated facts, leak sensitive information, or respond differently depending on how a prompt is structured. They are also more exposed to manipulation attempts like prompt injection, making them a central focus in modern AI governance for LLMs.
Fix:
- Ground responses in approved internal knowledge sources
- Add output filtering and safety classifiers
- Apply masking to sensitive fields
- Enforce strict system-role separation to block injection attempts
- Route low-confidence answers to human review
RAG-Specific Risks and the Fix
RAG pipelines improve accuracy but can pull the wrong documents, outdated information, or content the user should not have access to. These challenges highlight why enterprises need strong governance in machine learning models that extend into retrieval workflows.
Fix:
- Apply document-level access controls before retrieval
- Enforce freshness checks and timestamp validation
- Add retrieval validation layers that reject unverified sources
- Log retrieval paths to support audits and explainability
Multimodal Risks and the Fix
Multimodal AI models process images, text, audio, and other inputs. Each modality brings different vulnerabilities. An image might contain sensitive details, while audio might capture unintended background information, requiring robust AI governance best practices to handle modality-specific risks.
Fix:
- Use modality-specific sanitization (blur, mask, redact)
- Apply safety checks on all input types before they reach the model
- Restrict output channels based on compliance requirements
- Store separate audit logs for each modality to trace decisions
Agentic AI Risks and the Fix
Agentic systems can execute tasks autonomously, chain actions together, and operate across tools or APIs. Without boundaries, an agent may perform steps that should require human approval. Mature enterprises often rely on Responsible AI pipelines consulting to define these operational limits.
Fix:
- Define clear autonomy limits
- Restrict tool and API access by role
- Add human approval gates for financial, legal, or high-impact actions
- Monitor agent activity with action-level logs and escalation rules
Preventing Hallucinations in LLMs
Hallucinations remain one of the biggest concerns for leaders deploying LLMs inside critical workflows. They happen because the model predicts text based on patterns rather than verified truth, which means it may “fill gaps” with confident but inaccurate information. Hallucinations increase when prompts lack context, training data is incomplete, or the model is allowed to answer freely without grounding.
This is why enterprises now treat hallucination control as a core part of AI governance best practices rather than a post-launch fix.
How Enterprises Detect, Route, and Block Hallucinations
A mature hallucination-prevention setup rarely relies on one control. Teams combine several checks to keep risky outputs from reaching users. This approach forms an essential layer of Responsible AI development and governance.
Common techniques include:
- Confidence scoring to flag low-certainty responses
- Requiring source citations from approved documents
- Routing uncertain outputs to a human reviewer
- Blocking responses when the model cannot find verified information
- Using fallback responses (“I don’t have enough information to answer that”) instead of forcing an answer
Guardrail Patterns That Reduce Incorrect Outputs
Enterprises rely on guardrails that sit between the model and the user. These patterns shape predictable behavior and support broader AI risk management frameworks.
They typically include:
- Restricting open-ended generation unless retrieval data is available
- Enforcing answer templates that limit the model’s freedom
- Preventing the model from generating information outside its allowed domain
- Adding logic that forces the model to check retrieval results before responding
These patterns guide the model toward safe, factual answers.
Where Observability Supports Hallucination Control
Observability helps teams track when hallucinations are happening and why. The most valuable signals include drift, low-confidence patterns, and policy violations, which together strengthen AI pipeline observability solutions.
Signals teams monitor include:
- Frequent low-confidence responses
- Responses that bypass retrieval steps
- Outputs that fail validation or violate policy rules
- Drift indicators that show the model’s reasoning is changing
- Repeated correction events from human reviewers
With the right observability layer, hallucinations become visible trends rather than isolated surprises, allowing teams to adjust guardrails, prompts, or retrieval sources before issues escalate. This visibility also supports more effective AI observability solutions as models grow more complex.
Ensuring Data Privacy and Compliance in LLM Workflows
Data privacy becomes a real challenge when LLMs interact with sensitive information. These models don’t naturally distinguish between public and confidential data, which is why enterprises need controls that prevent accidental exposure.
As part of broader AI compliance and governance, organizations now treat privacy safeguards as mandatory, not optional.
Masking, redaction, and access control: Before any prompt or dataset reaches the model, sensitive fields should be masked or redacted. Access control layers make sure only authorized users or systems can send high-risk inputs.
These steps reduce the chance of the model learning from or repeating confidential details while supporting stronger AI risk governance and security across workflows.
Authorization-aware retrieval: For LLMs connected to internal knowledge sources, retrieval must respect user permissions. Authorization-aware retrieval ensures the model only pulls documents the user is allowed to see, preventing hidden data from appearing in generated responses.
It also aligns with ethical AI systems for businesses that handle regulated information.
Together, these safeguards help enterprises keep LLM workflows compliant and prevent the kinds of data leaks leaders worry about most.
Regulatory Landscape Executives Need to Understand
As more companies weave AI into daily operations, leaders keep circling back to the same question: “Which rules actually apply to the models we’re building?” There isn’t one universal answer, but a few major frameworks show up again and again when enterprises handle personal or sensitive data.
Understanding these frameworks is now a core part of any AI governance framework for ethical decision making, especially as systems scale across functions.
GDPR (European Union)
GDPR sets the tone for most privacy discussions. For AI teams, it means being careful about what data they collect, how long they keep it, and whether the model might reveal something users never agreed to share.
It also pushes companies to explain how automated decisions come together, not just what the model produced.
EU AI Act
The EU AI Act brings a different kind of pressure. It labels certain AI systems as “high-risk,” which covers things like hiring tools, healthcare apps, lending models, and public-sector systems.
Once you fall into that group, you’re expected to show documentation, keep close watch on the system, and make sure a human can step in when needed. For most enterprises, this is where AI governance framework consulting becomes crucial.
HIPAA (United States)
In the US, HIPAA decides what happens when AI and healthcare meet. If an LLM ever touches medical records, even indirectly, teams have to control how prompts are cleaned, how logs are stored, and who has access to what.
A small slip can become a major compliance issue and may require help from AI compliance and ethics consulting partners.
CCPA (California)
CCPA gives California residents more control over their personal information. For AI, this often means tracing where data came from, how it moves through the pipeline, and making sure a person can ask to have their information removed without breaking the model.
These obligations tie directly into implementing AI compliance and governance practices inside enterprise pipelines.
PDPL (UAE)
PDPL in the UAE is becoming a common requirement for businesses working in or within the region. It covers consent, data transfers, and privacy expectations for any system that uses personal data.
AI teams in finance, telecom, and government-facing industries feel this most directly.
These rules shape the environment AI systems operate in. Leaders don’t need to memorize every clause, but they do need a clear view of which regulations touch their models and what must be built into the workflow from day one.
Compliance Mapping Table for AI Systems
Executives often struggle to see how different compliance requirements apply across ML models, LLMs, and RAG applications. A simple mapping helps teams understand what must be logged, who signs off, and how compliance should be documented. No single regulation covers everything, so clarity at this level keeps projects from stalling later.
Below is a practical table enterprises can use as a baseline.
| Obligation | ML | LLM | RAG | What Needs to Be Logged | Who Approves It | How to Document Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Privacy Requirements | Yes | Yes | Yes | Data sources, masking steps, retention rules | Data Privacy Officer | Data-flow diagrams, DPIA notes, masking logs |
| Bias and Fairness Checks | Yes | Yes | Partial (depends on retrieval docs) | Bias test results, dataset composition | AI Governance Lead | Model cards, fairness reports |
| Model Explainability | Moderate | Harder | Moderate | Explanation attempts, feature summaries, retrieval trace | Risk/Compliance Team | Explainability reports, trace logs |
| Access Control & Authorization | Yes | Yes | High | User access logs, permission checks | Security Lead | Access-control matrix, IAM records |
| Content Safety & Output Controls | Low | High | High | Output filters, rejection events, toxicity scores | AI Safety Lead | Safety evaluations, guardrail configs |
| Retrieval Source Governance | No | No | Yes | Source lists, document timestamps, access rights | Knowledge Management / Compliance | Retrieval audit logs, freshness reports |
| Model Versioning & Approval | Yes | Yes | Yes | Version history, evaluation metrics | Technical Reviewer / Product Owner | Model registry notes, approval signatures |
| Monitoring & Drift Detection | Yes | Yes | Yes | Drift signals, alert events, performance changes | MLOps Lead | Monitoring dashboards, incident logs |
| Incident Reporting & Escalation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Error events, safety violations | Compliance + Engineering | Incident reports, corrective-action notes |
Documentation, Explainability, Lineage, and Audit Trails
CNA, CTO, and CDO teams often look for practical answers to questions like “How do you document AI models for compliance?” or “What does AI auditability really mean?” At an enterprise level, documentation isn’t a formality. It’s the record that explains how a model was built, how it changed over time, and whether its behavior can be justified during an audit.
This layer has become a core part of AI governance best practices, especially as enterprises move toward more structured, accountable workflows.
Lineage Tracking That Works for Enterprises
Lineage shows the full story of a model:
- where the data came from,
- how it was cleaned,
- which training runs were used,
- which version made it to production, and
- who approved each step.
A common lineage entry looks like this:
Lineage Format Example
- Model ID
- Dataset versions used
- Training environment and parameters
- Fine-tuning notes
- Evaluation results
- Deployment date and owner
- Change history with timestamps
This level of detail helps leaders explain decisions when regulators or risk committees ask for proof. It also strengthens governance in machine learning models, since lineage provides the traceability required for assessments and audits.
Risk Scoring for Governance Reviews
Enterprises often use a simple scoring method to decide how much oversight a model needs. A lightweight template keeps the process consistent and supports broader AI risk governance and security decisions.
Risk Scoring Template
- Data sensitivity: Low / Medium / High
- Model impact: Informational / Operational / High-impact
- User group: Internal / External / Regulated
- Failure consequences: Minimal / Moderate / Severe
- Required oversight level: 1 / 2 / 3
This helps governance teams decide when to involve legal, privacy, or domain experts as part of a more formal Responsible AI development and governance workflow.
Model Card Template for Transparency
Model cards summarize the most important details in a single page. They help teams understand what a model can and cannot do.
Model Card Template
- Purpose and intended use
- Out-of-scope or disallowed use cases
- Training data overview
- Known limitations and bias considerations
- Evaluation metrics
- Safety constraints and guardrails applied
- Contact for approvals or escalation
A consistent model card makes internal reviews faster, improves transparency, and creates a clear paper trail for audits, aligning closely with modern AI ethics and governance consulting standards inside enterprises.
ROI of Investing in AI Governance
Executives want clarity on whether the cost and effort of implementing AI governance guardrails actually pay off. In reality, the returns appear fast because strong governance reduces avoidable mistakes and gives teams a safer runway for scale and growth.
This is where a structured AI governance framework consulting approach helps leaders see the connection between safeguards and measurable business outcomes.
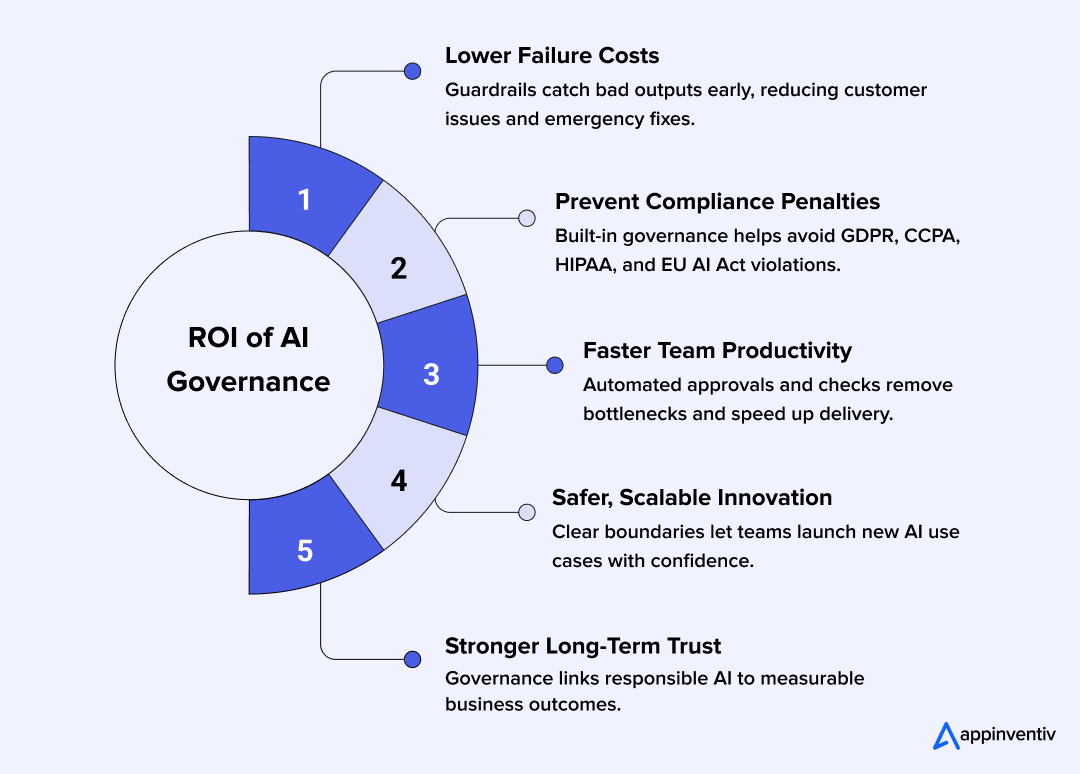
Cost of Failure
AI mistakes aren’t theoretical. A wrong answer, a misrouted prediction, or a model that behaves unpredictably can lead to customer complaints, financial exposure, or hours of emergency engineering work. Strong oversight and AI risk management frameworks lower the odds of those moments and keep the organization out of fire-drill mode.
Cost of Compliance Failures
Privacy and AI regulations are tightening everywhere. A slip involving GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, or the EU AI Act can bring fines, audits, and a level of scrutiny no team wants. When governance is built into the workflow offers clear approvals, better documentation, traceable decisions. This also strengthens long-term AI compliance and governance readiness.
Efficiency Gains From Automation
Teams move faster when the guardrails are already in place. Instead of debating who approves what or chasing down old model versions, they work inside a process that handles the routine checks automatically. It saves time, reduces back-and-forth, and keeps projects from stalling during handoffs.
Mature enterprises often see this as part of Responsible AI strategy consulting because it ties governance directly to operational efficiency.
Scalable and Safe Innovation
Strong governance gives leaders confidence to expand AI into more parts of the business. With boundaries and controls already defined, new use cases don’t feel risky. Teams can experiment without worrying that a small oversight will turn into a major incident later.
For most companies, governance ends up being less about slowing things down and more about creating the conditions that let AI scale safely.
How Enterprises Measure AI Governance Effectiveness
- % of models with full lineage and approval history
→ Measures audit readiness and traceability - Mean time to detect drift, bias, or safety violations
→ Indicates observability and risk responsiveness - Reduction in audit preparation time
→ Shows operational maturity of governance processes - Number of AI incidents blocked pre-production
→ Demonstrates effectiveness of guardrails and policy gates - Ratio of autonomous actions requiring human approval
→ Tracks controlled autonomy in agentic AI systems
How AI Governance Consulting Helps Enterprises Mature Faster?
Enterprises that adopt AI often move quickly on experimentation but slowly on structure. Governance consulting helps close that gap by bringing the clarity and consistency most teams lack. Strong partners begin with a maturity assessment, then guide the roadmap, upgrade the AI pipeline, deploy a monitoring stack, and refine documentation for audits and executive reviews.
This upfront work often includes early support in AI compliance and ethics consulting to establish the safeguards needed for scale.
Most companies don’t struggle with ideas; they struggle with consistency. A consulting partner introduces patterns, templates, and guardrails that already work in other enterprises, helping teams mature faster. Many leaders see this as an extension of Responsible AI strategy consulting, allowing them to move from early pilots to governed, enterprise-grade systems with far fewer risks.
How to Find the Right AI Governance Consulting Partner
Choosing the right partner matters as much as the governance framework itself. Leaders should look for consultants who:
- Assess before advising: They begin with a clear maturity review rather than jumping into tools. This aligns with best practices in AI governance framework consulting.
- Build roadmaps tied to business goals: Not generic slides — real timelines, responsibilities, and measurable checkpoints.
- Understand enterprise pipelines: They know how data moves, how models are deployed, and where governance controls must exist within governance in machine learning models and LLM workflows.
- Implement monitoring and observability: They help set up the stack that tracks drift, bias, safety signals, and compliance alerts through strong AI observability solutions.
- Strengthen documentation and audit trails: They provide templates for lineage, model cards, change logs, and approval workflows.
- Bring real transformation examples: They show how similar organizations moved from experimentation to controlled, scalable AI.
The right partner doesn’t replace internal teams. They accelerate them, giving the organization a faster and safer path toward enterprise-grade AI maturity and stronger Responsible AI development and governance.
How Appinventiv Builds Governed, Compliant, Enterprise-Ready AI Systems
Enterprises adopting AI today need systems that behave predictably, meet compliance standards, and maintain trust at scale. Appinventiv follows a governance-first approach focused on building AI guardrails for enterprises, ensuring safety and reliability from the start. With 300+ AI solutions delivered and 200+ engineers, we help organizations design transparent and accountable AI ecosystems.
A strong example is MyExec, an AI-powered business consultant that needed accurate insights without risking data exposure or model drift. Our team implemented a controlled RAG pipeline that restricted retrieval to authorized sources, filtered sensitive content, and grounded outputs in verified information. This governed setup was strengthened with access controls, evaluation checkpoints, and observability, forming a complete suite of AI governance services.
Across industries, Appinventiv supports enterprises as a trusted AI consulting company, helping them build secure architectures, align with global regulations, and operationalize responsible pipelines. We also deploy continuous monitoring frameworks that keep models accountable long after launch. If your organization is preparing to scale AI safely, our team can guide you from early assessment to full implementation.
Looking to strengthen your AI governance strategy? Our team can support you from assessment to full-scale implementation.
FAQs
Q. How can AI governance consulting improve business outcomes?
A. AI governance consulting helps organizations reduce operational risks, enhance model reliability, and accelerate safe adoption of AI. Clear workflows, approval paths, and compliance checks allow teams to innovate without unintended consequences. It also supports long-term scalability by ensuring systems remain transparent and auditable as they grow.
Q. What are the benefits of responsible AI pipelines for enterprises?
A. Responsible AI pipelines bring consistency to how models are trained, deployed, and monitored. They reduce compliance gaps, prevent unverified outputs from reaching users, and ensure every update is reviewed and documented. For organizations scaling AI across teams, responsible AI pipelines consulting provides the structure needed to operate safely at enterprise level.
Q. How to build AI governance frameworks for enterprises?
A. A strong AI governance framework defines roles, controls, documentation standards, and technical safeguards across the entire lifecycle. It typically includes data oversight, model validation, risk scoring, observability, and audit-ready documentation. Enterprises benefit most when these elements are built directly into the development and deployment workflow, not managed as separate processes.
Q. What are the best practices for implementing AI guardrails in my company?
A. Start by identifying where risks can occur across training, inference, and retrieval. Add controls that filter unsafe prompts, block harmful outputs, prevent unauthorized data access, and detect anomalies. Many organizations begin with building AI guardrails for enterprises that align with internal policies, security standards, and regulatory expectations.
Q. How can Appinventiv help with AI governance and compliance?
A. Appinventiv supports enterprises with governance-first architecture design, model validation workflows, observability setups, regulatory alignment, and responsible deployment practices. Our teams help integrate guardrails, documentation templates, and monitoring tools so organizations can scale AI confidently while maintaining compliance across regions and industries.
Q. What should be included in an enterprise AI observability strategy?
A. An effective observability strategy tracks model drift, bias indicators, safety violations, data quality issues, latency trends, and anomalous behaviors. It should combine real-time dashboards with automated alerts, audit logs, and retrieval traces. Together, these tools give leaders the visibility they need to ensure systems remain reliable, compliant, and aligned with business risk thresholds.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

AI-Powered Booking Optimization for Beauty Salons in Dubai: Costs, ROI & App Development
Key Highlights AI booking optimization improves utilization, reduces no-shows, and stabilizes predictable salon revenue streams. Enterprise salon platforms enable centralized scheduling, customer insights, and scalable multi-location operational control. AI-enabled booking platforms can be designed to align with UAE data protection regulations and secure payment standards. Predictive scheduling and personalization increase customer retention while significantly reducing…

Data Mesh vs Data Fabric: Which Architecture Actually Scales With Business Growth?
Key takeaways: Data Mesh supports decentralized scaling, while Data Fabric improves integration efficiency across growing business environments. Hybrid architectures often deliver flexibility, governance, and scalability without forcing premature enterprise-level complexity decisions. Early architecture choices directly influence reporting accuracy, experimentation speed, and future AI readiness across teams. Phased adoption reduces risk, controls costs, and allows architecture…
Governance vs. Speed: Designing a Scalable RPA CoE for Enterprise Automation
Key takeaways: Enterprise RPA fails at scale due to operating model gaps, not automation technology limitations. A federated RPA CoE balances delivery speed with governance, avoiding bottlenecks and audit exposure. Governance embedded into execution enables faster automation without introducing enterprise risk. Scalable RPA requires clear ownership, defined escalation paths, and production-grade operational controls. Measuring RPA…