- Understanding Private Blockchain for Businesses
- Key Components of a Private Blockchain
- Key Features to Create a Private Blockchain
- 1. Permissioned Network Participation
- 2. Selective Data Visibility
- 3. Configurable Smart Contracts
- 4. Real-Time Transaction Finality
- 5. High Throughput Performance
- 6. Private Transaction Channels
- 7. Governance Flexibility
- 8. Role-Based Identity Management
- 9. Modular Network Customization
- 10. Native Multi-Layer Privacy Support
- 11. Audit-Ready Logging and Monitoring
- 12. Cross-Platform Interoperability
- How to Build a Private Blockchain Platform?
- 1. Define the Purpose
- 2. Select the Consensus Algorithm
- 3. Set Up the Network
- 4. Choose the Blockchain Platform
- 5. Design the Smart Contracts
- 6. Implement Data Encryption and Test the Blockchain
- 7. Deploy and Maintain the Network
- How Does a Private Blockchain Work?
- Advantages of Private Blockchain Development for Businesses
- Enhanced Security
- Cost Savings and Boosted Efficiency
- Increased Transparency
- Enhanced Data Privacy
- Streamlined Collaboration
- Scalability and Customization
- Examples of Private Blockchain: Real-World Platforms that Businesses Can Leverage
- Hyperledger Fabric
- Corda
- Quorum
- IBM Food Trust
- Multiple Use Cases of Private Blockchain
- Best Practices for Using a Private Blockchain
- Choose a Consensus Algorithm
- Use a Permissioned Network
- Use Strong Encryption
- Ensure Network Resilience
- Use Smart Contracts
- Ensure Compliance
- Regularly Test and Audit
- Private vs. Public Blockchains: A Comparative Analysis
- Why is Private Blockchain the Best Option?
- How Can Appinventiv Help You Build a Private Blockchain Network?
- FAQs
Key takeaways:
- Private blockchain addresses growing concerns around data security and breaches.
- It lowers compliance costs and improves operational efficiency across business processes.
- These blockchains provide secure, scalable, real-time ecosystems for enterprise use.
- Top companies like Walmart and J.P. Morgan have already implemented private blockchain solutions.
- Successful adoption requires clear goals, robust encryption, and experienced support.
- Private blockchain is becoming a strategic edge, not just an optional upgrade.
Every day in 2025, financial and healthcare companies through logistics and all sectors in between inject trillions of sensitive data into centralized repositories—repositories still costing an organization an average of $4.9 million per breach and undermining confidence by the day. The harsh truth is that conventional stopgaps that band-aid around access control gaps and data leaks just aren’t good enough. Businesses demand solutions engineered on a foundation of confidence and not as an afterthought.
That’s where private blockchain enters. Just think about having protected infrastructure: every transaction indelibly recorded, cryptographically verified and only accessible by approved participants. While public blockchains don’t offer enterprise teams even any level of control—over read/write/validation authorizations—private networks offer complete control—over who can read/write/validate—yet offer traceability that’s tamper-proof. This alters everything in industries where governance and compliance aren’t negotiable.
Now as business is driven further by regulation and cyber threats are increasing faster still, secure, permissioned ecosystems are becoming increasingly necessary. Gartner predicts blockchain will unlock $176 billion of business value by 2025 and jump to $3.1 trillion by 2030 and much of that will be driven by private, permissioned use cases where data security and access controls come first.
Thus, businesses everywhere can witness business uptake of secure networked systems spike and can note that private blockchain infrastructure is no longer a niche investment—it’s an industry-wide strategic imperative. The savings aren’t theoretical. Companies using private blockchain networks are realizing cost reductions on compliance and operational levels because of decentralized and reduced record-keeping, automated verification, and real-time traceability.
This blog will help you understand the nitty-gritty of how to create a private blockchain, its benefits for the business, and its multiple use cases. So, let’s explore the world of private blockchain in detail and discover what advantages it can bring to your business.
But before diving into all the details, let us shed a brief light on what exactly is a private blockchain and how it works.
Discover how a custom-built private blockchain can give your business the security, control, and scalability it actually needs.
Understanding Private Blockchain for Businesses
A private blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that operates within a restricted ecosystem, accessible only to trusted participants. Unlike public blockchains, private blockchains offer a more exclusive and secure environment, ideal for businesses and organizations seeking confidentiality and control over their data.
In a private blockchain for businesses, access to the network is confidential, and all the participants must be granted explicit authorization to contribute to it. This access control safeguards sensitive information from unauthorized access and manipulation from external malware practices and thefts.
Private blockchains are widely used in industries prioritizing data privacy and security, including finance, healthcare, supply chain management, and government sectors. For instance, financial institutions employ private blockchains to enable secure and efficient cross-border transactions among authorized parties, improving operational efficiency while complying with regulations.
To further help you understand the underlying structure of private blockchains, let’s take a look at the key components that make them so secure and efficient for business use.
Key Components of a Private Blockchain
A private blockchain isn’t just about restricted access—it’s built on a foundation of tightly controlled, business-critical components. Let’s break down the core elements that make private blockchains secure, efficient, and enterprise-ready.
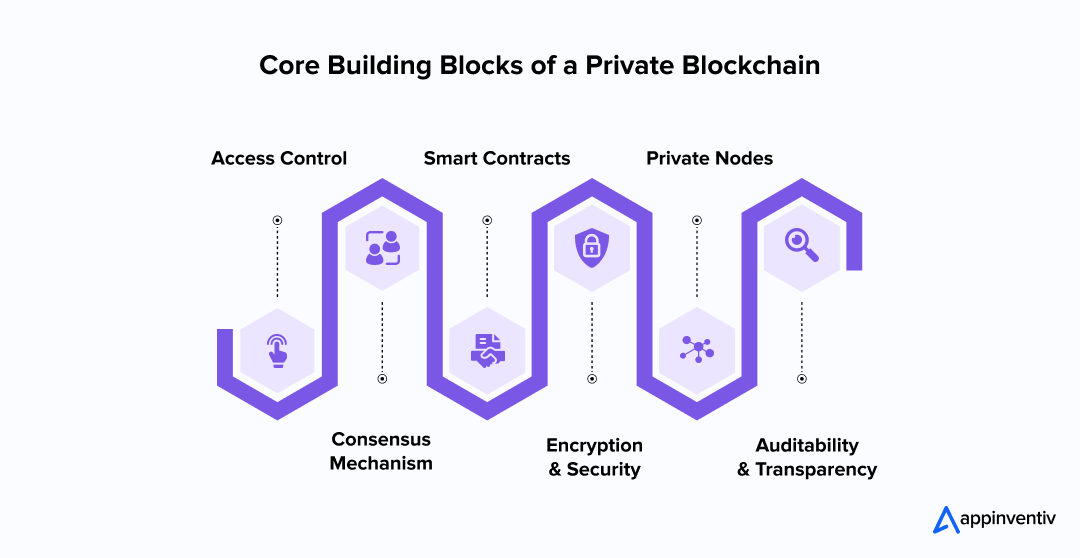
- Access Control
Private blockchains are defined by strict access control mechanisms. Unlike public blockchains, where anyone can participate, private blockchains require authorization for network access. This ensures that only trusted participants are able to contribute to the blockchain, offering a higher level of confidentiality and control over who has the right to validate transactions. - Consensus Mechanism
The consensus mechanism in a private blockchain governs how participants agree on the validity of transactions. While public blockchains may use Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, private blockchains often use more efficient consensus algorithms, such as Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), where participants agree on transactions through a smaller, pre-approved group. - Smart Contracts
Private blockchains often utilize smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute actions once predefined conditions are met, allowing for more streamlined and secure business transactions without the need for intermediaries. - Encryption and Security
The security of private blockchains relies heavily on encryption techniques, such as public-key cryptography, to ensure that data is protected. Encryption technology is used not only to protect the information during transmission but also to verify the identity of participants, adding an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access or tampering. - Private Nodes
A private blockchain typically consists of a set of private nodes that are run by authorized entities. These nodes store the blockchain’s data, validate transactions, and participate in consensus activities. The nodes’ privacy and their centralized management within a controlled environment are essential to maintaining the integrity of the blockchain. - Auditability and Transparency
While the data on a private blockchain is accessible only to authorized participants, it remains auditable. This means that authorized users can view transaction histories and ensure transparency and compliance, which is especially critical in regulated industries like finance and healthcare.
Key Features to Create a Private Blockchain
When you create a private blockchain, it’s the system’s features that define what it can do — not just how it’s built. Below are the true functional features of a private blockchain, combining both core and advanced elements, aligned with real-world business needs and private blockchain development services.
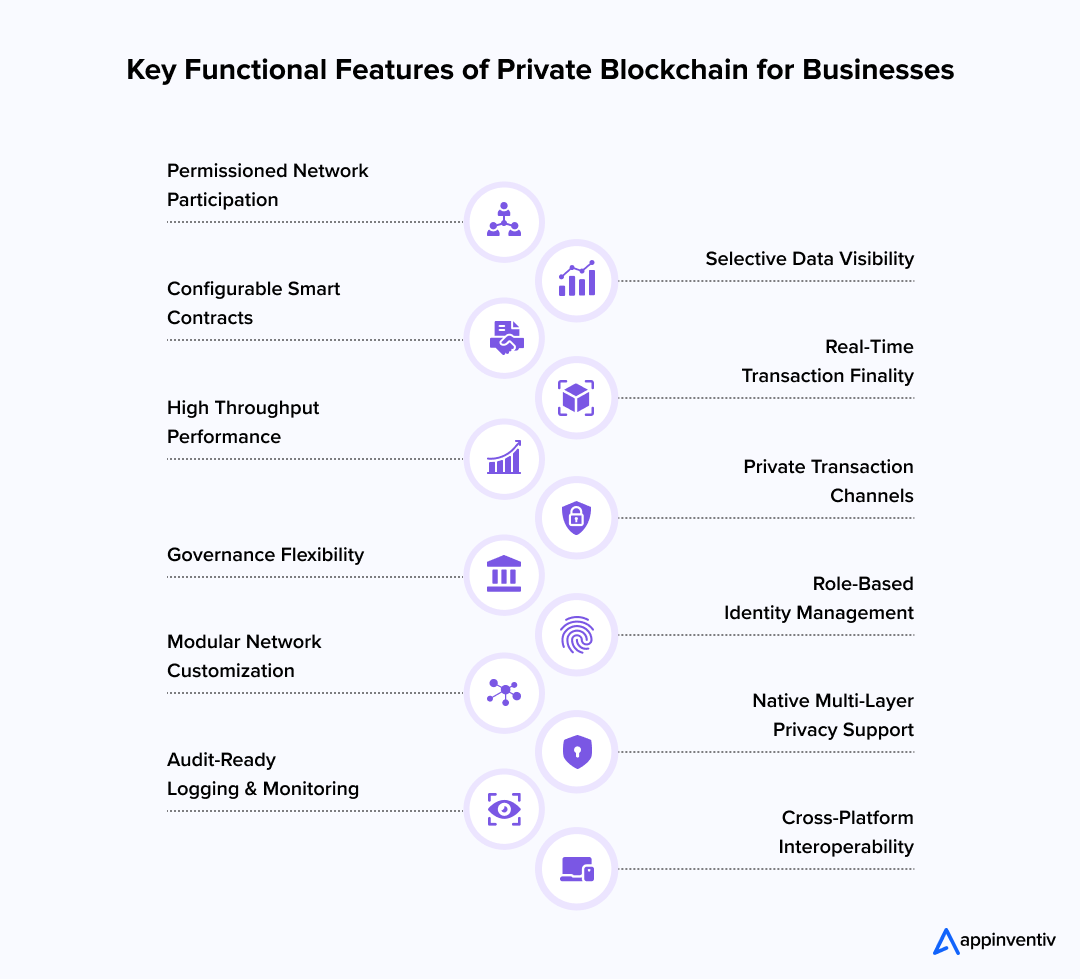
1. Permissioned Network Participation
Private blockchains operate on a permissioned model where only verified participants can join the network. This feature enables enterprises to fully control membership and transaction validation, a cornerstone of most private blockchain applications in finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
2. Selective Data Visibility
Unlike public blockchains, private blockchains offer granular control over who can see which transactions. This selective data visibility feature supports enterprise private blockchain needs where confidentiality between internal teams, departments, or partner organizations is critical.
3. Configurable Smart Contracts
Private blockchains feature smart contracts that can be configured, paused, or upgraded based on governance rules. This flexibility is essential in private blockchain development where businesses require adjustable automation without losing network integrity.
4. Real-Time Transaction Finality
Transactions on private blockchains reach finality almost instantly. This feature is vital for enterprise operations where quick transaction settlement is non-negotiable, such as in cross-border payments, supply chains, and internal fund transfers.
5. High Throughput Performance
Private blockchains are designed for high transaction throughput thanks to their controlled validator environments. This native speed feature supports use cases that demand bulk processing, like payment hubs and digital asset exchanges.
6. Private Transaction Channels
Many private blockchain platforms offer the feature of creating private sub-channels or transaction layers within the main network. This enables confidential exchanges between specific parties without exposing details to the broader network.
7. Governance Flexibility
Unlike public blockchains with rigid governance, private blockchain solutions offer fully customizable governance models. Enterprises can define voting rights, upgrade procedures, and validation roles to match their internal policies and compliance standards.
8. Role-Based Identity Management
Role-based identity management is a native feature of private blockchain technology that controls access to data and transaction rights based on organizational hierarchies or user roles. This aligns perfectly with enterprise-grade security and privacy requirements.
9. Modular Network Customization
Private blockchains can be configured to easily add or remove nodes, participants, or functionalities without disrupting the system. This feature supports enterprise scalability, making it easier to evolve as your business or network partners grow.
10. Native Multi-Layer Privacy Support
Private blockchains support multi-layered privacy, allowing the creation of different permission levels for transactions, smart contracts, and node operations. This feature is critical for regulated industries that must balance collaboration with strict confidentiality.
11. Audit-Ready Logging and Monitoring
A built-in feature of most private blockchain development platforms is detailed transaction logging and monitoring. This allows businesses to quickly track and audit activities across the network to support regulatory compliance and internal reporting.
12. Cross-Platform Interoperability
Many private blockchain development services now offer cross-platform interoperability features, allowing seamless integration with other blockchains, databases, or legacy systems. This is especially important for businesses with hybrid infrastructures.
How to Build a Private Blockchain Platform?
Creating a private blockchain is a strategic approach for businesses and organizations looking for a secure and efficient way to manage their private data and transactions. By building a private blockchain, enterprises can gain more control over their network, ensuring privacy, security, and faster processing speeds.
Businesses must understand that partnering with a private blockchain development company can ensure you have the expertise needed to optimize your resources and get the most out of your investment. Let’s look into the steps to create a private blockchain in detail:
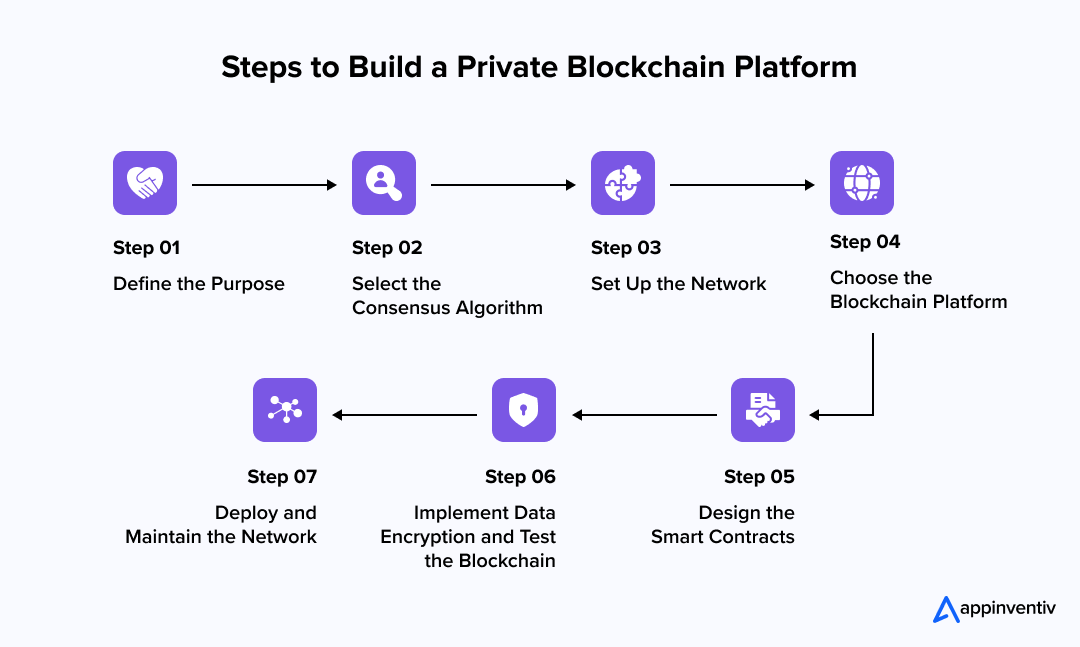
1. Define the Purpose
The first step in private blockchain development is to define the purpose of the blockchain. Understanding the specific use case and goals is essential, as it helps tailor the blockchain solution to meet your unique business requirements. Whether you’re looking to improve supply chain transparency, enhance data privacy in finance, or streamline healthcare records, private blockchain applications can solve these challenges effectively.
Identifying your business goals ensures that the private blockchain platform will deliver the advantages of private blockchain, such as secure data management and efficient transaction handling. This stage also involves assessing any legal or regulatory considerations for private blockchain for businesses in your industry.
2. Select the Consensus Algorithm
Once the purpose is defined, the next step is selecting a consensus algorithm that will best suit your business’s needs. The consensus algorithm ensures that all participants on the network agree on the validity of transactions. For private blockchain solutions, you can choose from a variety of algorithms, such as Proof of Authority (PoA), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), or Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
These algorithms ensure faster transaction validation, energy efficiency, and a trusted validation process. Choosing the right consensus algorithm will help address the specific challenges of your private blockchain use cases, ensuring optimized performance and scalability for your enterprise.
3. Set Up the Network
In this phase, a permissioned network is established, meaning that only authorized participants will be able to join the blockchain and participate in validating transactions. Setting up this network involves configuring nodes that will serve as the validators in your private blockchain platform. These nodes must be pre-approved, ensuring that no unauthorized parties can access or alter sensitive data.
This step also involves deciding how the blockchain will handle permissions and access control, ensuring that only those with the proper credentials can interact with the blockchain. Private blockchain for businesses ensures that the network remains secure, reliable, and operates within the boundaries set by your organization’s policies.
4. Choose the Blockchain Platform
Choosing the right blockchain platform is one of the most critical steps that businesses undertake when they create a private blockchain. The platform must align with your business’s technical and operational requirements. Options like Hyperledger Fabric, Corda, and Quorum are popular choices for creating enterprise private blockchain solutions. Each platform offers unique features suited for different business needs.
For instance, Hyperledger Fabric is great for businesses requiring modularity, while Corda focuses on providing privacy for financial transactions. The choice of platform should be driven by the private blockchain use cases you aim to address and the scalability and performance demands of your business.
5. Design the Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into code. After selecting the blockchain platform, the next step is to design the smart contracts that will automate processes and agreements within the network. Smart contracts reduce the need for intermediaries, cut down on transaction times, and ensure the smooth execution of business operations.
In private blockchain development, these contracts can be tailored to suit the specific needs of your industry, whether it’s automating payments in finance or enforcing compliance in healthcare. Creating and deploying smart contracts is vital to ensuring your private blockchain solution operates seamlessly and efficiently.
6. Implement Data Encryption and Test the Blockchain
Data privacy and security are paramount in private blockchain applications. In this phase, strong encryption methods are implemented to protect data both in transit and at rest. By using encryption protocols, businesses can ensure that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized parties. After encryption, it’s crucial to test the blockchain for vulnerabilities. This step involves conducting thorough audits to identify any security risks or flaws in functionality.
Private blockchain development services will typically run several rounds of testing to ensure that the blockchain is secure, operational, and compliant with industry standards. The goal here is to guarantee the integrity of the blockchain and ensure it meets business requirements.
7. Deploy and Maintain the Network
The final phase involves deploying the private blockchain network. Once the network is set up and thoroughly tested, it’s time to roll it out across the business. This phase also includes setting up protocols for ongoing maintenance, including regular updates, security patches, and backups to ensure the blockchain’s smooth operation over time.
Private blockchain development companies usually provide post-deployment support to handle any issues that arise and ensure the network continues to perform optimally. By implementing regular updates and maintaining the network, you can create a private blockchain that remains secure, scalable, and adaptable to any future changes in your business’s needs.
Leverage our experience in developing high-performance, tamper-proof blockchain networks tailored to your unique business needs.
How Does a Private Blockchain Work?
A private blockchain works by allowing only authorized participants to access, validate, and record transactions within a decentralized system. Unlike public blockchains, which are open to anyone, private blockchains provide businesses with a controlled, permissioned environment where data can be securely shared and managed.
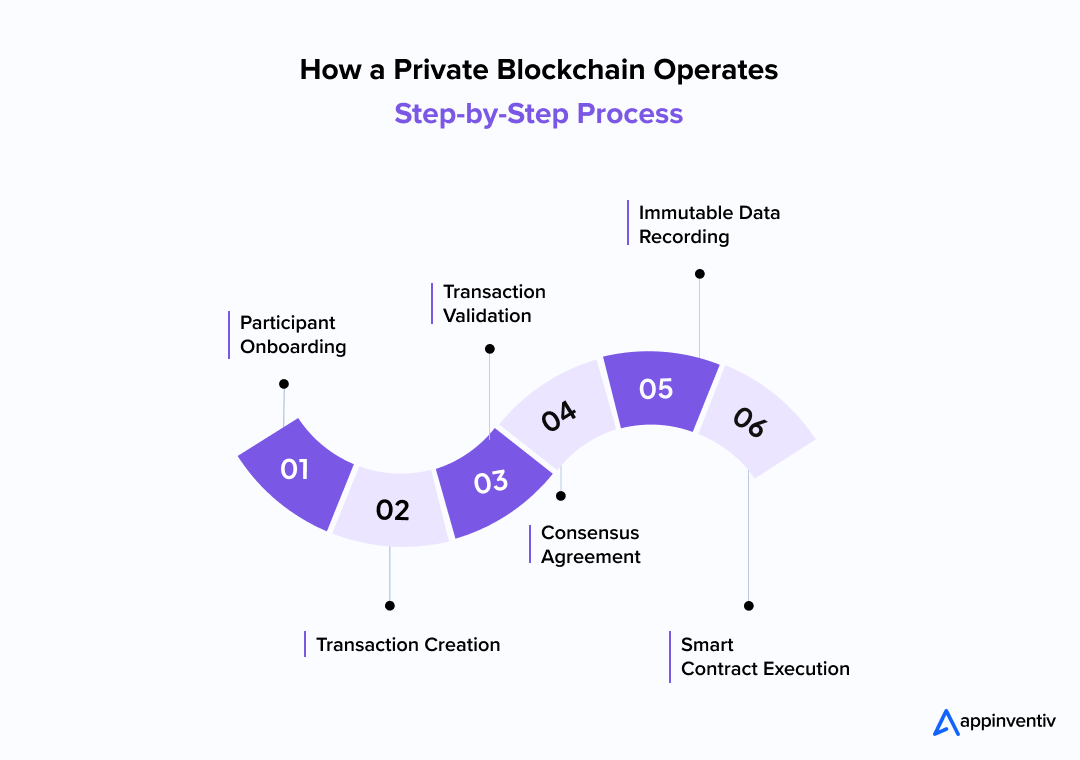
- Participants Join the Network: Only trusted entities or organizations are given access to the private blockchain platform. These participants can be internal or external businesses, and their activities on the network are closely monitored and controlled.
- Transaction Creation: When a transaction occurs (e.g., transferring data or assets), the involved participants create the transaction request and broadcast it to the network. These transactions can include business agreements, payments, or data exchanges.
- Transaction Validation: Instead of relying on an open network of miners like in public blockchains, private blockchain developers set up a set of authorized validators or nodes that verify the transactions. The consensus process ensures that only legitimate transactions are added to the blockchain.
- Consensus Mechanism: The network uses a consensus algorithm to agree on the validity of transactions. In private blockchains, this can be more efficient than in public blockchains, with algorithms like Proof of Authority (PoA) or Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) used to reach consensus quickly and securely.
- Data Recording: Once the transaction is validated, it is added to the blockchain as a new block. This block is time-stamped and linked to the previous block, forming an immutable record of all transactions. This ensures transparency, traceability, and data integrity.
- Smart Contracts Execution: Many private blockchains also leverage smart contracts—automated, self-executing agreements that enforce business rules. These contracts are triggered when predefined conditions are met, making processes more efficient and reducing the need for intermediaries.
Advantages of Private Blockchain Development for Businesses
By leveraging private blockchain technology, businesses can enhance data security, privacy, and collaboration while facilitating scalability. Let us look at the multiple benefits offered by private blockchain development for businesses:
Enhanced Security
Private blockchains provide enhanced security compared to public blockchains by limiting participation to authorized entities, thereby minimizing the risk of unauthorized access, data tampering, and malicious activities. These blockchains use permissioned networks that make the participants undergo verification and validation, thereby establishing high trust within the network. Private blockchains are ideal solutions for safeguarding sensitive information considering their use of various cryptographic techniques like digital signatures, capable of ensuring data integrity.
Cost Savings and Boosted Efficiency
One of the most sought-after advantages of private blockchain is cost savings. Private blockchains simplify business operations by removing intermediaries and automating trust. This makes transactions faster, reduces mistakes, and minimizes delays. It also helps optimize cost by cutting out intermediary fees and time-consuming processes. These benefits are especially important in industries like supply chain management and finance, where accuracy and speed are paramount.
Increased Transparency
A shared ledger is created by private blockchains that cannot be tampered with. Furthermore, the transactions are time-stamped and linked to create an unchangeable record. This transparency ensures that everyone on the network has the same information, reducing the chance of disagreements. In industries like healthcare and finance, private blockchains make it easier to follow regulations and undergo audits, which builds trust and ensures compliance.
Enhanced Data Privacy
One of the most sought-after benefits of private blockchain development is enhanced data privacy. Enterprise Private blockchains offer selective disclosure, allowing blockchain development companies and other companies to choose what information to share with specific participants while maintaining confidentiality. This level of privacy ensures that sensitive information is only shared with authorized parties, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. This allows organizations to mitigate concerns about data misuse and ensure compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
[Also Read: How to Develop a GDPR-Compliant Software for Your Business?]
Streamlined Collaboration
Private blockchains facilitate secure and efficient collaboration by offering organizations a trusted and shared infrastructure for data exchange. They allow businesses to create a secure network of trusted participants that removes the need for intermediaries. Furthermore, real-time tracking of transactions builds trust among stakeholders and improves collaboration.
Scalability and Customization
Private blockchains provide scalability and flexibility to meet the expanding requirements of businesses. These blockchains are optimized for handling high transaction volumes, ensuring business performance is not compromised. Companies can customize and implement smart contracts tailored to their operations, improving operational efficiency. Furthermore, the seamless integration with existing systems facilitates a smooth transition to blockchain technology without disrupting ongoing operations.
Examples of Private Blockchain: Real-World Platforms that Businesses Can Leverage
Private blockchains have become essential in various industries, offering secure, permissioned environments that allow businesses to manage data efficiently, streamline operations, and enhance trust among stakeholders. Below are a few prominent private blockchain examples that showcase how different sectors are harnessing blockchain technology to improve efficiency, privacy, and security.
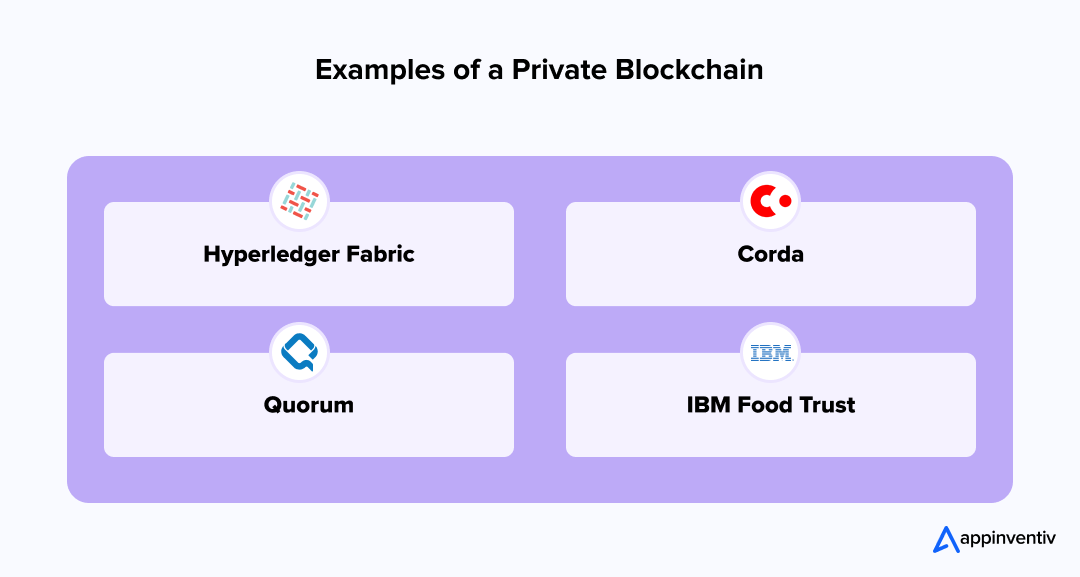
Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Fabric is a highly flexible private blockchain platform, widely used for supply chain management and other enterprise solutions. It provides a permissioned network where only authorized participants can access the data, ensuring greater security and confidentiality.
Example: Walmart uses Hyperledger Fabric to enhance transparency in its food supply chain. By implementing a private blockchain, Walmart enabled real-time tracking of food items from farm to shelf. The network ensures that only authorized participants, such as suppliers and distributors, can access sensitive information. This implementation significantly reduced tracking time from days to seconds, improved food safety, and helped quickly identify contamination sources, leading to better supply chain management and increased consumer trust.
Corda
Corda, developed by R3, is a private blockchain designed specifically for the financial services industry. It allows financial institutions to securely and efficiently exchange transactions and sensitive data while maintaining privacy.
Example: Large financial institutions such as J.P. Morgan use Corda for sharing financial data in a highly secure manner. Corda’s permissioned network enables banks to exchange transaction details and trade information without compromising confidentiality, making it an ideal choice for private blockchain solutions in the BFSI sector. It has simplified cross-border payments, securities trading, and regulatory compliance for many financial organizations.
Quorum
Quorum, is one of the major private blockchain examples that was developed by JPMorgan Chase. The permissioned private blockchain is designed specifically to address the security and privacy concerns of financial institutions. It is built on Ethereum but modified to provide higher throughput and enhanced privacy features, making it suitable for sensitive financial transactions.
Example: Quorum is used by multiple banks and financial organizations, including J.P. Morgan, to manage private transactions more securely. The private blockchain platform ensures that only the relevant parties can access transaction details, ensuring privacy and confidentiality in operations like interbank payments, lending, and trading. It’s particularly useful in managing large-scale financial applications, where transparency and privacy are critical.
IBM Food Trust
IBM’s Food Trust network is an example of a private blockchain in the food industry. It uses a permissioned blockchain to track the journey of food products from farm to table. The platform ensures transparency and accountability across the entire supply chain, from growers to retailers.
Example: Nestlé and Dole are two prominent companies that have partnered with IBM to use its private blockchain solution to track and trace food products. By having a secure, immutable ledger, these companies can ensure the safety and quality of their products, verify sources of contamination, and improve operational efficiency.
Multiple Use Cases of Private Blockchain
Enterprise private blockchains have proven to be a powerful solution for businesses looking to manage data securely and efficiently. Private blockchain development allows for customized solutions that meet specific business needs, enabling companies to innovate and streamline operations. Below are some prominent private blockchain use cases that showcase how blockchain technology is being leveraged across industries:
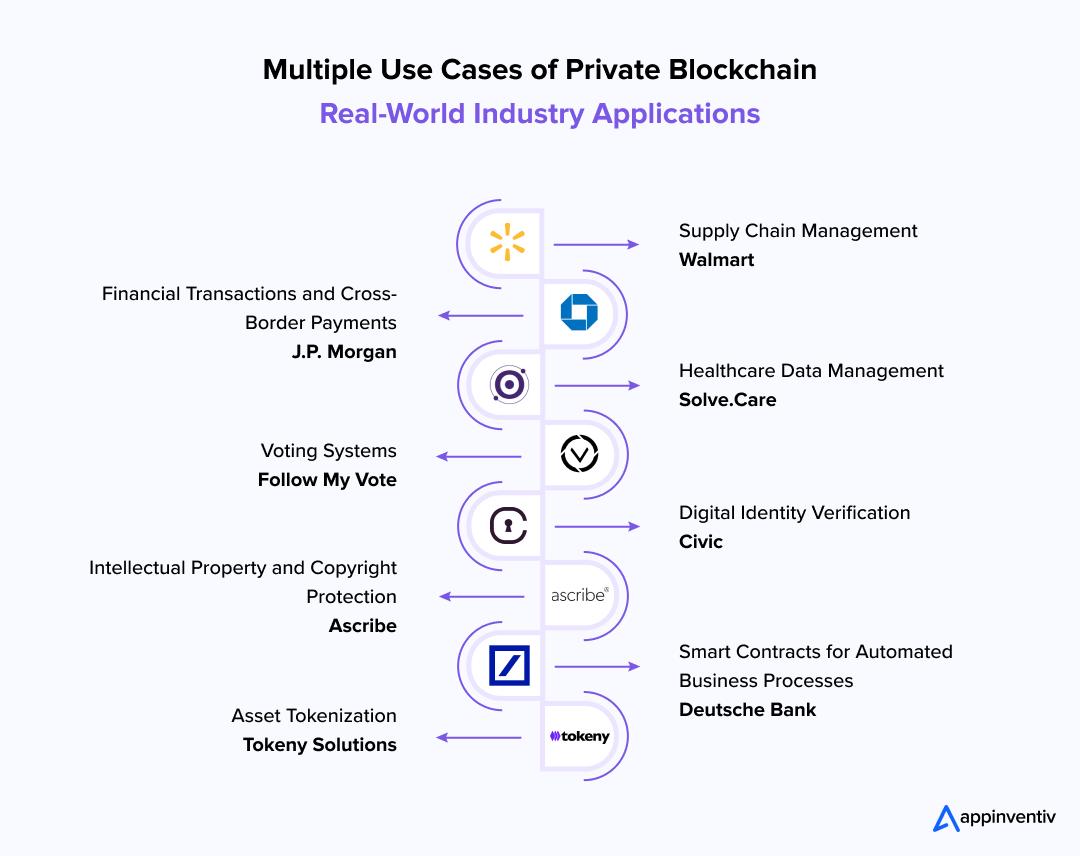
1. Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is one of the most impactful private blockchain applications. By providing a transparent, immutable ledger, private blockchains ensure that all transactions within the supply chain are secure, traceable, and verified. Businesses can monitor the movement of goods, verify the origin of products, and identify bottlenecks in real-time, resulting in enhanced efficiency, reduced fraud, and improved accountability.
- Real-world Example: Walmart uses Hyperledger Fabric in its private blockchain solution for supply chain management. It has drastically reduced the time it takes to trace food products, from days to mere seconds. With the blockchain, Walmart and its suppliers can track the origin and status of goods, enabling better inventory management and faster response to issues like contamination or product recalls.
2. Financial Transactions and Cross-Border Payments
Private blockchain technology has revolutionized the financial sector, particularly in managing cross-border payments and enabling secure financial transactions. It allows faster, more transparent, and cost-effective transactions by eliminating intermediaries and providing a secure environment for sensitive financial data.
Real-world Example: J.P. Morgan uses Quorum, a private blockchain built on Ethereum, for secure and efficient cross-border payments. The bank has leveraged Quorum’s enhanced privacy features to improve payment processing speeds and reduce transaction costs. Quorum’s private network allows multiple financial institutions to exchange payments securely, helping streamline financial operations and improve cross-border collaborations.
3. Healthcare Data Management
The healthcare industry is increasingly turning to private blockchain solutions for managing sensitive patient data. By using a permissioned blockchain, healthcare providers can share medical records securely, ensuring privacy and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA. Blockchain also streamlines healthcare administrative processes, such as billing, insurance claims, and patient care coordination.
Real-world Example: Solve.Care, a private blockchain solution, is used in healthcare to manage patient care and medical administration. Solve.Care provides a secure platform where patient data is only accessible to authorized healthcare providers and insurance companies. This improves data integrity, ensures compliance with regulations, and enhances patient care by enabling quicker access to records and reducing administrative overhead.
4. Voting Systems
Private blockchains are increasingly being used in digital voting systems. These systems leverage blockchain’s immutability and transparency to ensure the accuracy and security of votes. Blockchain-based voting systems help eliminate fraud, reduce human error, and enhance the overall reliability of elections.
Real-world Example: Follow My Vote is a company that has implemented a private blockchain for secure online voting. Using private blockchain technology, the platform ensures that votes are tamper-proof, traceable, and auditable, offering greater transparency and security for both the voters and election authorities.
5. Digital Identity Verification
Private blockchains are an excellent solution for managing digital identities securely. Blockchain provides a decentralized and tamper-proof way to verify individuals’ identities online. By utilizing private blockchain technology, businesses can streamline customer onboarding processes, reduce identity theft, and improve overall security.
Real-world Example: Civic, a blockchain-based identity verification service, uses a private blockchain to enable users to control their personal information securely. Civic’s solution allows users to authenticate their identity without sharing sensitive data, which is especially useful for sectors like banking and healthcare, where secure identity management is critical.
6. Intellectual Property and Copyright Protection
Intellectual property (IP) management is an increasingly vital area where private blockchains are used to protect copyrights, patents, and trademarks. A blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures that creators and organizations can securely track ownership and rights to their intellectual property, reducing the risk of infringement and ensuring fair distribution of royalties.
Real-world Example: Ascribe, a platform for artists and content creators, uses private blockchain technology to help individuals secure ownership of their digital creations. By recording the details of a work (such as images, songs, and software code) on the blockchain, Ascribe ensures that artists and creators maintain control over their intellectual property and can easily prove ownership.
7. Smart Contracts for Automated Business Processes
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts where the terms are written into code and automatically enforced when conditions are met. Private blockchain solutions allow businesses to automate processes, such as payments, supply chain coordination, and compliance management, without the need for intermediaries. This reduces operational costs and improves efficiency.
Real-world Example: Deutsche Bank is exploring the use of smart contracts in private blockchain platforms to automate financial transactions and legal agreements. By implementing blockchain technology for smart contracts, Deutsche Bank can automate payment processing, trade execution, and settlement, improving efficiency and minimizing errors in financial operations.
8. Asset Tokenization
Private blockchains also enable the tokenization of physical and digital assets, turning them into digital tokens that can be traded, sold, or used within a blockchain-based system. This enables more efficient asset management, transparent ownership tracking, and better liquidity for previously illiquid assets.
Real-world Example: Tokeny Solutions uses private blockchain technology to enable asset tokenization. The platform allows businesses to tokenize real estate, fine art, and other physical assets, giving investors the ability to trade fractional ownership in high-value assets. This innovation is transforming asset management and investment practices, providing a more inclusive and efficient marketplace.
Best Practices for Using a Private Blockchain
To ensure the successful implementation and operation of private blockchains, many industry best practices are vital to implement. Let us look at them in detail:
Choose a Consensus Algorithm
When choosing an algorithm for nodes agreement, it is important to select the one as per your business requirements carefully. Some options to consider are Proof of Authority (PoA), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
Use a Permissioned Network
One of the most sought-after practices to create a private blockchain is to use a permissioned network. To enhance security and scalability, ensuring that only authorized people with proper credentials can participate in the network is crucial.
Use Strong Encryption
To safeguard your blockchain against attackers, employ strong encryption techniques for data in transit and at rest. Additionally, adhere to secure key management protocols.
Ensure Network Resilience
We need to establish a strong network infrastructure that can handle potential disruptions. This includes implementing a well-defined disaster recovery plan, conducting regular backups, and having protocols to address possible attacks.
Use Smart Contracts
Self-executing smart contracts can be implemented to automate the execution of agreements, providing security and integrity for transactions.
Ensure Compliance
To maintain legal compliance in order to create a private blockchain, it is vital to adhere to associated laws and regulations, including anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements.
Regularly Test and Audit
Frequent testing and audits are essential to ensure the proper functioning and security of the blockchain. It is recommended to conduct penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code audits before implementation.
Private vs. Public Blockchains: A Comparative Analysis
Private and public blockchains both serve as decentralized ledger systems, but they cater to different needs and industries. Understanding the key differences between them can help businesses choose the right type of blockchain for their use cases.
| Feature | Private Blockchain | Public Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control | Permissioned; access is restricted to authorized participants. | Open; anyone can join and participate in the network. |
| Consensus Mechanism | Typically uses consensus algorithms like Proof of Authority (PoA) or Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT). | Typically uses Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), which requires mining or staking. |
| Transparency | Limited transparency; only authorized users can view and validate transactions. | Full transparency; anyone can view and validate transactions. |
| Security | Highly secure due to restricted access and use of encryption. | High security but potentially vulnerable to attacks like 51% attacks due to open access. |
| Scalability | More scalable due to fewer participants and controlled consensus. | Less scalable; as the number of participants increases, so does the processing time and transaction fees. |
| Speed | Faster transactions because fewer nodes are involved in validating transactions. | Slower due to the large number of participants and consensus mechanisms. |
| Cost | Generally lower transaction costs as it requires fewer computational resources. | Higher transaction fees due to the need for mining or staking, and network congestion. |
| Data Privacy | Offers greater privacy as data is accessible only to trusted participants. | Less privacy as all transactions are visible to everyone on the network. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for businesses needing confidentiality, such as financial institutions, healthcare, and supply chain management. | Suited for applications requiring full decentralization and transparency, like cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum). |
| Control | Greater control; organizations can manage who participates in the network. | No central control; the network is governed by consensus among all participants. |
| Example | Hyperledger Fabric, Corda, Quorum used in industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain. | Bitcoin, Ethereum are prime examples for decentralized applications (dApps) and cryptocurrency transactions. |
Why is Private Blockchain the Best Option?
While both private and public blockchains offer unique benefits, private blockchains are often the best choice for businesses seeking control, security, and efficiency. Here’s why:
- Control: Businesses can dictate who participates, ensuring only trusted entities have access to sensitive data.
- Performance: Private blockchains offer faster transactions and greater scalability due to fewer participants and streamlined consensus mechanisms.
- Privacy: Unlike public blockchains, private ones ensure data is visible only to authorized participants, offering enhanced confidentiality.
- Cost-Efficiency: Without the need for mining or heavy computational power, private blockchains have lower transaction costs.
How Can Appinventiv Help You Build a Private Blockchain Network?
Private blockchain development offers a myriad of advantages to businesses. They enhance the overall security, efficiency, and privacy of data while facilitating collaboration and scalability. From protecting sensitive information to increasing transparency, private blockchain are the entities that can help you thrive in the digital age. Thus, evaluating your business needs and deciding if a private blockchain is the right solution to meet your goals and stay ahead of the competition is advisable.
Appinventiv is a dedicated private blockchain development company with years of expertise in the field. Our skilled blockchain developers can guide businesses through the entire process of creating a private blockchain, all the way from defining the purpose and use case to implementing and deploying the platform.
Our customer-centric approach for blockchain development services ensures that the solution is tailored to meet each business’s specific needs and objectives. By prioritizing security and efficiency, we strive to utilize cutting-edge encryption techniques and consensus algorithms to create a robust and scalable network.
We recently collaborated on the blockchain-based Empire App, a mobile platform that offered guests a seamless and transparent hotel-booking experience. The immutability and transparency of the blockchain solved the double booking issue and eliminated third parties from the transactions.
Get in touch with our experts to create a private blockchain for your business venture now!
FAQs
Q. What is the difference between a private blockchain and a public blockchain?
A. Private blockchains are the digital ledgers that are restricted to a specific group of participants who have access to the network, providing businesses with more privacy and control. They are often used for internal purposes where sensitive data must be protected from public view, so they are more suitable for industries such as finance, healthcare and supply chain management.
On the other hand, public blockchains are open to everyone, allowing anyone to participate, view and verify transactions, but with reduced privacy and control, making them suitable for decentralized applications and publicly available cryptocurrencies.
Q. How much does it cost to build an app on a private blockchain network?
A. The overall cost to create a private blockchain-based app can vary from $50,000 to $300,000. There are further several factors that can impact the overall cost of development such as the location of the hired app development firm, the overall complexity of the app, the consensus algorithm used, customization and security requirements, etc. Get in touch with blockchain developers to get cost estimates based on your custom business requirements.
Q. How can you secure your private blockchain?
A. Securing a private blockchain is essential to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of transactions. To achieve this, access control can be implemented to restrict the participation to a few limited participants, creating a permissioned network. Strong encryption techniques can be used to safeguard data during transmission and while stored on the blockchain. A robust consensus mechanism is chosen to ensure all authorized nodes agree on the validity of transactions.
In addition to these, regular security audits and vulnerability testing can be conducted to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in the network. Additionally, smart contracts that can automate agreements should be carefully designed and audited for potential weaknesses.
Q. What team is required to build and maintain a private blockchain?
A. To build a private blockchain, you need a well-rounded team with expertise across multiple domains. Typically, this includes blockchain developers who design and deploy smart contracts and customize the private blockchain platform to suit your business needs. You’ll also need backend engineers to manage system integrations, databases, and APIs that connect your blockchain to other applications.
A strong DevOps team is essential to handle infrastructure setup, cloud management, and smooth deployment processes. QA testers and security experts ensure the system is robust, compliant, and protected against vulnerabilities. Additionally, a business analyst helps align blockchain capabilities with real-world use cases to maximize impact. Many companies choose to partner with a private blockchain development company to access this complete skill set, along with post-launch support, updates, and governance.


How Much Does it Cost to Build a Blockchain App in the UAE?
Key takeaways: The UAE blockchain market is rapidly expanding, with the BFSI sector capturing over 50% of the market share. As blockchain adoption accelerates, development costs in the UAE range from AED 55,000 to AED 1.85 million, depending on app complexity and features. Factors such as platform selection, security measures, and third-party integrations directly impact…

How Blockchain Integration Is Optimizing Business Processes in Dubai
Key takeaways: Blockchain is a strategic enabler in Dubai, transforming traditional business workflows by enhancing efficiency, transparency, and automation beyond cryptocurrency applications. Dubai’s supportive regulatory environment and government initiatives (e.g., VARA, Dubai Blockchain Strategy) create a clear, innovation-friendly framework, accelerating blockchain adoption. Integration with legacy systems through modular blockchain solutions enables enterprises to modernize operations…

OTC Crypto Exchange Development - Benefits, Features, Process, Costs
As the world of cryptocurrency continues to evolve, the demand for Over-the-Counter (OTC) crypto exchanges has surged. Unlike traditional exchanges that are open to all traders and often suffer from market slippage when large trades are executed, OTC exchanges cater specifically to institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, and corporate traders who need to make large transactions…