- Importance of agricultural technology
- The impact of technology on agriculture
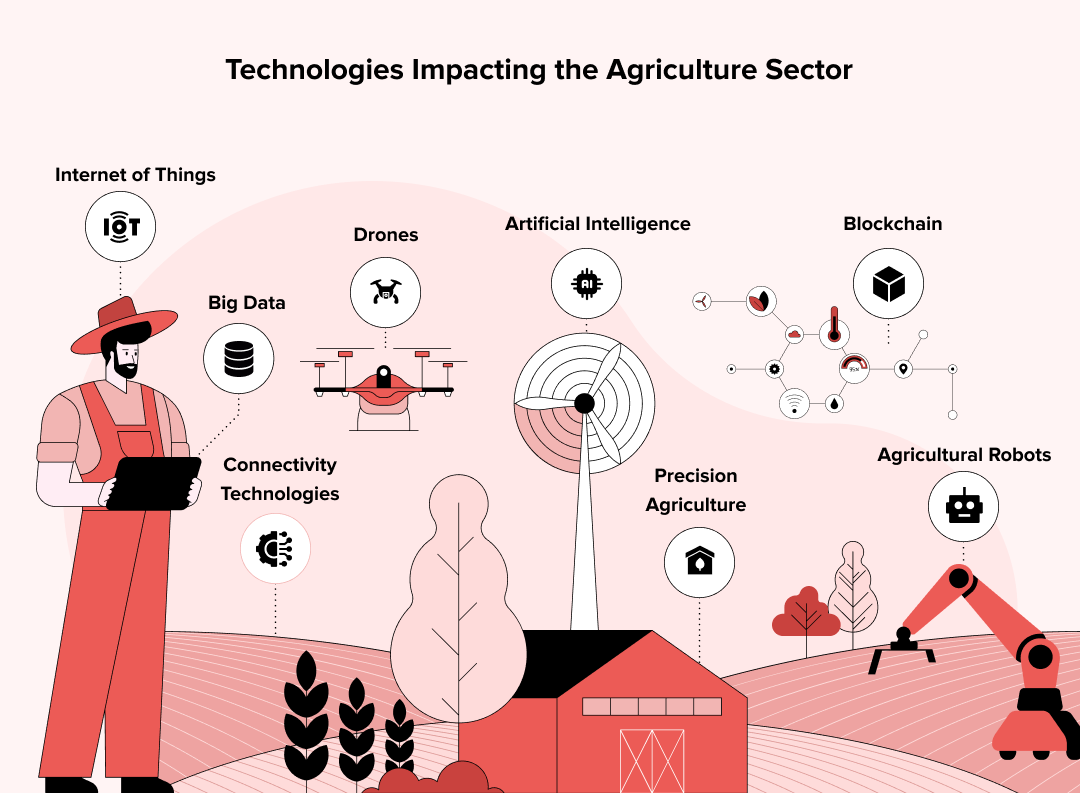
- Internet of Things
- Agricultural robots
- Artificial Intelligence
- Drones
- Precision agriculture
- Big data
- Connectivity technologies
- Blockchain
- The current state of connectivity in agriculture and the impact it can create
- FAQs
- Q. What kind of agricultural software solutions can I use for my business?
- Q. How technology in agriculture is reforming the industry?
- Q. What are the top 5 emerging technologies in agriculture?
The agriculture industry has seen multiple revolutions over the last 50 years.
The advancements in agriculture, specially in machinery has, over time, expanded the speed, scale, and farm equipment productivity – leading to better land cultivation.
Today, in the 21st century, agriculture has found itself in the center of yet another revolution. An agricultural technology revolution where emerging technologies like robotics, artificial intelligence, IoT, etc. are increasing yields, bettering water efficiency, and creating resilience and sustainability across crop cultivation, animal husbandry.
The true essence of this digitalization-led agricultural movement lies in understanding the role of technology in it. Let us briefly look into the importance of agricultural technology before we delve deeper into the different technologies making the space better.
Importance of agricultural technology

The modern-day agricultural operations and farms work drastically different from what they used to a few decades ago. At the back of the new technology in agriculture with elements like sensors, GPS, intelligence-powered devices, etc. the space is able to redefine its list of importance of agricultural technology.
- Greater crop productivity
- Lesser use of pesticide, water, and fertilizer – thus lowering the food prices
- Reduced impact on natural ecosystems
- Lesser runoff of chemicals in the ground waters and rivers
- Better worker safety
- Robotic technologies offering reliable management of natural resources
But how is technology able to change how we do agricultural activities on a ground level? So much so that its inclusion is promising positive economics and ecological impact? Let’s find out in the next section where we look into how technology has changed farming.
The impact of technology on agriculture
The technological advancements in the agriculture space holds the ability to meet the increasing demand for digitalization, farm automation, and sustainability. How has technology changed farming is a question that the space is answering by marking a shift towards effective use of resources and time, while lowering the crop losses.
There are multiple technologies that have come on the forefront to change how we approach digitalization of the sector. Let us look at a few of those which are changing the future of agriculture.
Internet of Things
Monitoring crop fields in conventional farming required physical equipment, intensive labor, time and effort.
IoT in agriculture provides an alternative to this. An IoT device consists of sensors which collect farm’s data and give real-time, precise information through apps or other means. These IoT sensors help perform agricultural activities like –
- soil temperature and humidity sensing
- plant and livestock tracking
- remote monitoring of farms
- automate water delivery to crops
In addition to these, several startups are building innovative connected sensors that connect IoT devices with robots, drones, and computer imaging to better the accuracy, agility in the farming process.
Agricultural robots
Lack of labor is a crucial problem that farmers face, especially in the large sized operations. The advanced technology in agriculture that is solving this issue is agricultural robots.
Several startups have started manufacturing robots to assist the farmers in manual-intensive tasks like harvesting, fruit-picking, planting, spraying, and weeding. Multiple farmers, across the globe, have already started relying on agricultural technology to automate repetitive field tasks.
Some of the robots they are investing in to see the impact of technology in agriculture include –
- smart agricultural machines, like autonomous and semi-autonomous tractors for harvesting
- robots for livestock management activities like – incubators, automated weighing scales, auto feeders, and milking machines
Artificial Intelligence
The importance of technology in agriculture can be witnessed through the incorporation of AI-backed tools and data into the field operations. Artificial Intelligence offers farmers data into weather, crop yield, and even the best crop prices they should keep, thereby helping farmers in making sound decisions.
Another element of AI agricultural technology is smart chatbots that offer recommendations and suggestions to the farmers. However, while chatbots work on a more micro level, on a more widespread level AI and ML algorithms can help identify and monitor anomalies and diseases in plants and livestock.
Drones
Increasing the farm’s productivity while saving on the operational costs is a difficult balance to make. But, there is one advanced technology in agriculture that is helping farmers overcome this challenge – drones. The machines collect raw data which is then converted into useful information for farm monitoring.
Equipped with camera for surveying and aerial imaging, drones help with –
- data related to optimizing fertilizers, seeds, water, pesticides
- livestock tracking, grazing, geofencing monitoring
There are several drone-based agricultural technology examples where startups are working on drones with the ability to measure chlorophyll level and soil mineral chemical composition.
Precision agriculture
Different parts of a farm field have different soil properties, get different sunlight levels, and have multiple slopes. Thus, treating the entire farm in the same way can lead to inefficiency and a greater wastage of time and resources.
To solve this issue, the industry has come up with precision-based use of technology in agriculture. The concept, popularly known as precision agriculture, is where the farmers are using exact amounts of inputs like pesticide, water, fertilizers, etc. in a particular area of their field. Information they are gathering through drones and AI-backed analysis.
Big data
Big data techniques are transforming the restricted technological advancements in agriculture by converting all the farm data into actionable insights.
Some of the ways the agricultural technology is working is –
- Laying the base of next season’s farming through studying the statistics of crop area, production, land use, irrigation, agricultural prices, weather forecasts, and crop diseases
- Using data around weather events, water cycles, farm equipment, and quantity, quality of crops to extract information related to farm’s everyday operations.
Big data-backed use of technology in agriculture enables growers in identifying the relationships and patterns which might remain hidden in plain sight.
Connectivity technologies
Smart farming cannot happen in the absence of smart connectivity technologies like 5G, LPWAN, or satellite-based communication. These connectivity technological advancements in agriculture powers the adoption of devices which need to communicate at high speed in real-time like robots, IoT devices, sensors, etc.
For example, if you wish to develop an AI-powered dating app, integrating advanced capabilities like behavioral matchmaking and enhanced security protocols.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology is emerging as a powerful tool for revolutionizing agricultural supply chains. By securely recording every transaction along the food production and distribution process, blockchain enhances traceability and transparency.
Blockchain in agriculture further allows farmers, distributors, and retailers to verify information about crop origins, production methods, and storage conditions, which in turn helps reduce fraud and ensure the quality of products. Additionally, smart contracts powered by blockchain can automate payments and quality checks, streamlining the entire process and fostering trust among stakeholders.
At the center of these technologies’ adoption in the agriculture domain there lies connectivity. An ecosystem which is able to connect all these technologies together is able to take the space towards a new developed realm.
The current state of connectivity in agriculture and the impact it can create
In recent years, even though the agriculture space has been witnessing digitalization, very limited nations have access to digital tools which would help convert data into insights. Even in the United States, only one-quarter of the total farm area uses connected devices for accessing data.
However, a ray of hope can be seen in the fact that earlier cost of connected hardware used to be expensive, which is now coming down at a substantial rate, thus increasing the scope of agricultural investment in them. All this has led to a scope where by the time this decade ends, connectivity in agriculture would add up to $500 billion in the global gross domestic product!
Here are some of the use cases of connectivity in the agricultural domain –
- Crop monitoring – Connectivity provides multiple ways to improve crops care. By adding in data like weather, nutrient, and irrigation, the use of resources can be improved and the yields can be boosted by accurately finding deficiencies.
The crop monitoring tools also have far-reaching implications on soil-monitoring. For example, the machines which collect soil samples are generally guided by GPS and are coded for pulling out samples on specific frequencies and collecting data while harvesting. - Livestock monitoring – The prevention of diseases among farm animals remains a global challenge. Using high-end technologies like body sensors that measure pulse, temperature, and blood pressure can help identify illnesses, prevent herd infection, and better the food technology. Likewise, environment sensors like the one that tracks barn ventilation and heating improves the farm animals’ living conditions.
- Equipment and building management – The sensors used for monitoring and measuring the warehouse production levels can push automated reordering and reduce the inventory costs. These chips and sensors can also help better the inputs shelf life and lower the post-harvest losses by keeping a tab on the optimized storage conditions. Another talked about use case of this lies in using the predictive-maintenance systems technology for lowering the repair charges and extending the equipment life.
So here were the many ways connected technological advancements in agriculture are shaping the industry’s future. As we continue to enter a phase where the demand for food is going to surpass the supply, now is the time to lay the groundwork for a sustainable future.
As businesses looking to enter the Agritech space, this would require you to partner with agriculture IT consulting firm that knows the nitty-gritties of adding new technology in agriculture.
We can help. At Appinventiv, we carry an expertise in building technological solutions that bring the production costs of farming down, while increasing its yield quality. For example, we recently helped IFOAM build an interactive educational app for the NMA nations’ farmers to get expert advice on crop planning.
Get in touch with us today to become a part of the future of agriculture.
FAQs
Q. What kind of agricultural software solutions can I use for my business?
A. The best agriculture software companies, like Appinventiv, offer various kinds of agriculture software solutions depending on your business requirements:
- Livestock management software solution– This kind of agriculture consulting software solution offers advanced suggestions and analytics for breeding, herd management, and finance management.
- Precision agriculture software solution- This kind of software solution helps you to analyze and manage your agricultural land with precision land management, soil sensors, and smart farming apps.
- Aquaculture software solution- This kind of software solution can easily track the population of your harvesting and breeding. This includes ERP integrations and aquaculture workflow, sensor technology, data analysis, fish farm management systems, and more.
- Agriculture farm management software– Farm management software solutions can help you in crop planning, reporting, inventory, accounting, and equipment maintenance.
Q. How technology in agriculture is reforming the industry?
A. By boosting agricultural productivity and establishing connections between farmers, technology in agriculture can assist in resolving this problem. Farmers can connect with other farmers to share best practices and obtain the tools and information they need to boost yields by utilizing the power of mobile apps. Farmers are increasingly using mobile applications to manage their farms more successfully and efficiently. Here’s how technology reformed the agriculture industry:
- Crop Management
- Irrigation Management
- Livestock Management
- Market Information
- Farm Accounting
Q. What are the top 5 emerging technologies in agriculture?
A. Here is the list of the top 5 advanced technologies utilized in agriculture:
- Soil and Water Sensors
- Weather Tracking
- Satellite Imaging
- Pervasive Automation
- Minichromosomal Technology



How is Digital Technology Transforming Agri-food Systems?
Over the past fifty years, the agricultural sector has undergone a significant shift. Farm machinery has become vast, better, and more productive because of technological advances, enabling the more efficient cultivation of wider areas. Furthermore, vastly improved crops, irrigation, and chemicals have helped farmers raise yields. The next wave of digital transformation in agriculture technology…

AI in Agriculture: Benefits, Applications, Challenges, and Innovations
Agriculture has always been the backbone of the economy, providing essential food and resources. However, as the global demand for food rises, agricultural businesses face the challenge of scaling operations efficiently while minimizing environmental impact. Thanks to tech innovations like Artificial Intelligence that facilitate industry with high-end functionalities like demand forecasting and predictive analytics to…

Breaking the Digital Frontier with Mobile Apps for Agriculture
There was a time when technology and agriculture were at opposite ends of the value chain spectrum. Not anymore! Today, we have ample evidence to substantiate the role of a mobile application for agriculture and multiple reasons to prove its irrevocable dependency in farming operations. According to Statista, smart agriculture is expected to grow from…

















