In a planet ravaged by the COVID-19 epidemic, demand for safe and healthy food is now on the rise, making it an ideal time to seize a win-win scenario for farmers, buyers, and the environment.
Changes have also occurred in the local food chain. Despite the fact that many farmers have faced hardships as a result of restaurant and market shutdown or prohibitions, there is undeniably an increasing demand for fresh items from local sources. Consider developing a buying or selling organic food ecommerce marketplace for farmers and suppliers to enable local producers interact directly with customers or restaurants (B2B agriculture marketplace).
During the epidemic, many farmers chose to go digital to overcome challenges and improve their businesses using ecommerce app development companies. This article is created for the producers who have decided to go online in order to increase sales volume. This blog covers everything an entrepreneur (who may or may not be a farmer) needs to know about creating an online producers’ marketplace, from the business concept to the must-have elements.
But before starting to know how to sell organic products online, let’s have a look at the stats and numbers:
- According to Statista, in 2020, retail e-commerce sales worldwide amounted to 4.28 trillion US dollars and e-retail revenues are projected to grow to 5.4 trillion US dollars in 2022.
- As per Grand View Research, the global Business-to-Business e-commerce market size was valued at USD 6.64 trillion in 2020 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 18.7% from 2021 to 2028. North America captured around 14% of the overall B2B agriculture marketplace e-commerce revenue in 2020.
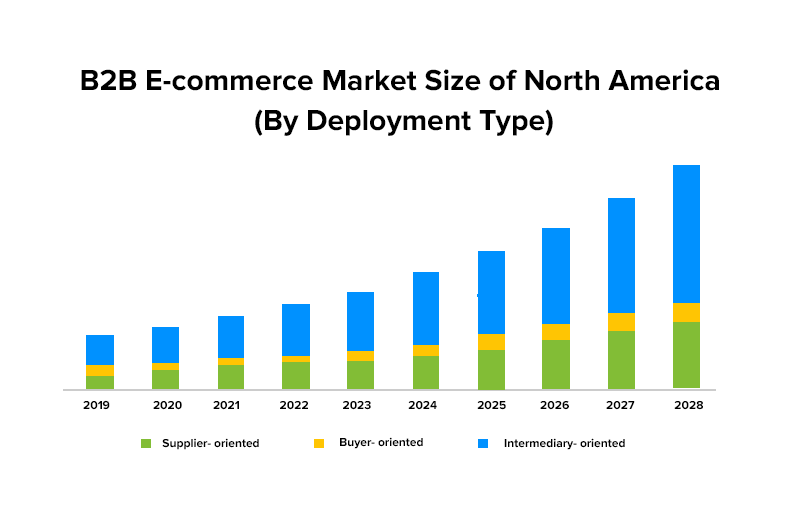
- Revenue from the e-commerce food and beverage industry in the United States stood at 18.7 billion U.S dollars in 2020. The Statista Digital Market Outlook estimates that by 2025, this figure will rise to 25.7 billion dollars.
What Can Farmers Sell Online?
Below mentioned are some generally consumed food products that farmers can sell by developing an organic products ecommerce platform:
Fruits and Vegetables
Dairy Products
Meat & Seafood
Bakery Products
Organic Food Products
Business Model of an Online Farmers Marketplace
In this model if you are the business personnel and want to form partnerships with farmers from various parts of the country who will set up shop on the market and sell their fresh produce. Farmers can use an internet agricultural e commerce platform to manage inventory, sales data, and product deliveries, among other things.

Buyers will create an account on the organic ecommerce platform, add food products to the cart, then make payment for their order. Buyers can simply order fresh, healthy, locally sourced products from the comfort of their homes using this method or they can also buy direct from farmers online. The merchandise will be delivered to the customer’s location by delivery personnel. Product shipment can be handled by either the operator or a third-party logistic provider.
Components Of The Model
Many buyers are making use of technology to improve market linkages by utilizing technology to satisfy the increased demand for fresh farm produce from by consumers. It is better to create web-based and mobile-based platforms to sell fresh agricultural items to consumers directly.
If you are thinking about how to buy organic produce wholesale, then here is the answer where customers place orders through digital platforms, and the firms gather the goods from farmers for distribution. While this strategy is mostly centered on fresh produce, it can also be used for other items (like grains, spices, tea, coffee, and so on) that links producers directly to markets or the buyers.

Collection
In emerging economies, systems that use the internet to connect farmers and buyers are quickly gaining traction, and a handful of have developed online platforms to sell organic ecommerce store market directly to consumers. By eliminating middlemen from the distribution network and obtaining greater prices for the farmers, these approaches are opening the way for efficient market linkages for farmers.
Produce is procured at farm gates and weighed, graded, and packaged on the farm. Then these businesses pay farmers immediately after they purchase the product.
For example, Agruppa, gives orders to farmers a day prior to collecting it from their farms; it also joins with local transporters to collect the produce from farms.
Marketing
Farmers and purchasers have been connected because of the widespread use of mobile phones. For example, Eatfromfarms provides an innovative e commerce platform wherein buyers can place orders for goods easily. This solution enables direct communication between customers and sellers, as well as simple and quick purchase and delivery processes. Though not all farmers and purchasers have access to the internet, the majority of them have a phone, and the platform is trying to ease out the communication process using mobile phones.
Distribution
Several businesses utilize algorithms to connect farmers with buyers depending on their needs and the pricing at which they are prepared to sell. Farmers either send the produce straight to buyers after a sale or seek assistance from businesses to carry the ecommerce organic products online from farm to the final buyer.
A platform for producers may be helpful if they can deliver ecommerce organic products marketplace produce to consumers using their own transportation or pay a modest price to have the produce transported to the consumers. For example, In Indonesia, Kecipir works with local hosts to run centrally situated delivery centers where customers can pick up their orders or have products brought to their doorstep.
[Also Read: How is Digital Technology Transforming Agri-food Systems?]
Features of an Online Agricultural E-commerce Platform
We can emphasize the vital aspects necessary for a good farmers’ e commerce mobile app development services after seeing some of the most popular organic products online store marketplaces for farmers, buyers, and customers.
If it’s a buy direct from farmers online marketplace for organic products, then the features for both roles must be carefully considered for easy use and checkout of the process.
Features for Sellers
- Vendors can sign up quickly and easily
Simplify the onboarding process for your clients to save them time.
- Product management that is effective
Farmers should be able to quickly add or remove any items they possess, set prices, and supply other pertinent information
- Order processing is simple and convenient
Vendors need to know exactly how to buy organic products online store, what was ordered, how much it cost, and when it was delivered, as well as be notified of any changes in the delivery process.
- Tools for communication
To rapidly fix any issues, sellers and buyers must interact with one another.
- System of evaluation or rating
Buyers want to know that they can trust the seller at all times.
- Rating and evaluation of system
Buyers want to know that they can trust the seller at all times. Farmers can develop confidence with future customers by allowing comments from prior buyers.
- Promotion of goods
The buy and sell organic food ecommerce marketplace should include tools for farmers and suppliers to promote their products, such as featured products or discount promotions, so that they may sell more.
Parting Thoughts
Most farmers around the world are trapped in a vicious cycle marked by low risk-taking ability, lack of investment, reduced productivity, poor market orientation, little value addition, and low profits. A severe lack of market linkages, which denies them efficient market access, is one of the major hurdles to breaking this vicious cycle.
Farmers are left with very little as middlemen bridge the gap between farms and markets, earning margins at every point of the distribution chain.
Understanding this market vacuum, social enterprises are looking into how they may use the internet’s power and the growing availability of mobile phones to establish direct market connections between farmers and purchasers.
These businesses assist farmers in obtaining greater prices for their produce by eliminating middlemen from the distribution chain. They also help farmers save money by securing purchases and payments at the farm gate.


- In just 2 mins you will get a response
- Your idea is 100% protected by our Non Disclosure Agreement.

Key takeaways: Outdated systems cause inefficiencies, poor customer experiences, and missed opportunities. Appinventiv helped a US retailer achieve a 25% sales increase and 15% growth in AOV post-transition. Real-time data enhances customer experiences and reduces the cart abandonment rate The new platform handled 3x traffic during peak periods, supporting future growth. Ever noticed how fast…

How Much Does It Cost to Build an E-commerce App Like Noon?
Key takeaways: Noon’s success highlights the rising demand for mobile-first eCommerce in the UAE. Building a similar app can cost anywhere between $ 30,000 and $200,000+, depending on the scope. The blog covers all key user and admin features needed to build a Noon-like app. Identify key cost drivers, including feature complexity, scalability, platform, and…

How to Build a Quick Commerce App? Features, Process, Costs
Key Takeaways Quick commerce is a rapidly growing market driven by consumer demand for ultra-fast delivery and seamless convenience, projected to reach 900 million users by 2029. Quick commerce app development costs vary widely based on features and scale, ranging from $40,000 for an MVP to $400,000+ for a fully featured app. Core features, such…
















